stomach ulcer.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35
 JSC “Medical University of Astana” Department of the general surgery Stomach ulcer Report by: Assem Baltabayeva. , 443 GM.
JSC “Medical University of Astana” Department of the general surgery Stomach ulcer Report by: Assem Baltabayeva. , 443 GM.
 What is a stomach ulcer? O Stomach ulcers are painful sores that can be found in the stomach lining or small intestine. Stomach ulcers are the most visible sign of peptic ulcer disease. They occur when the thick layer of mucus that protects your stomach from digestive juices is reduced, thus enabling the digestive acids to eat away at the lining tissues of the stomach.
What is a stomach ulcer? O Stomach ulcers are painful sores that can be found in the stomach lining or small intestine. Stomach ulcers are the most visible sign of peptic ulcer disease. They occur when the thick layer of mucus that protects your stomach from digestive juices is reduced, thus enabling the digestive acids to eat away at the lining tissues of the stomach.
 What causes stomach ulcers? O Stomach ulcers aren’t necessarily caused by one single factor. The decrease in the stomach’s mucus lining that leads to an ulcer is usually caused by one of the following:
What causes stomach ulcers? O Stomach ulcers aren’t necessarily caused by one single factor. The decrease in the stomach’s mucus lining that leads to an ulcer is usually caused by one of the following:
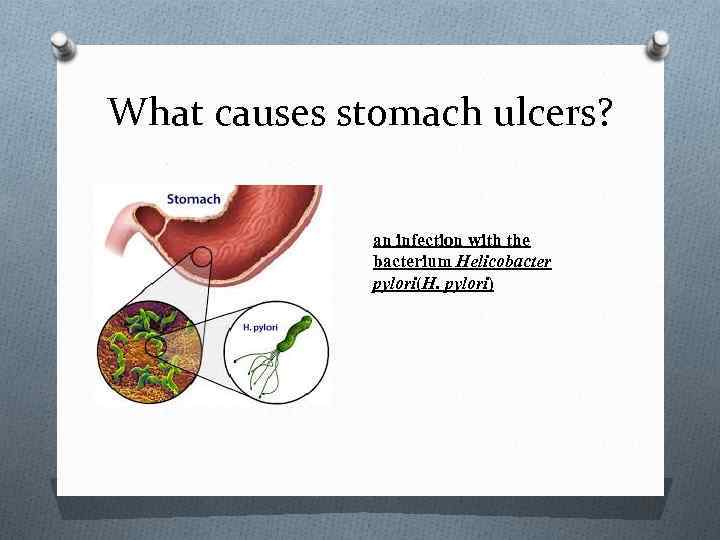 What causes stomach ulcers? an infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori(H. pylori)
What causes stomach ulcers? an infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori(H. pylori)
 What causes stomach ulcers? long-term use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen
What causes stomach ulcers? long-term use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen
 What causes stomach ulcers? excess acid (hyperacidity) in the stomach, which may be related to genetics, lifestyle (stress, smoking),
What causes stomach ulcers? excess acid (hyperacidity) in the stomach, which may be related to genetics, lifestyle (stress, smoking),
 Did you know?
Did you know?
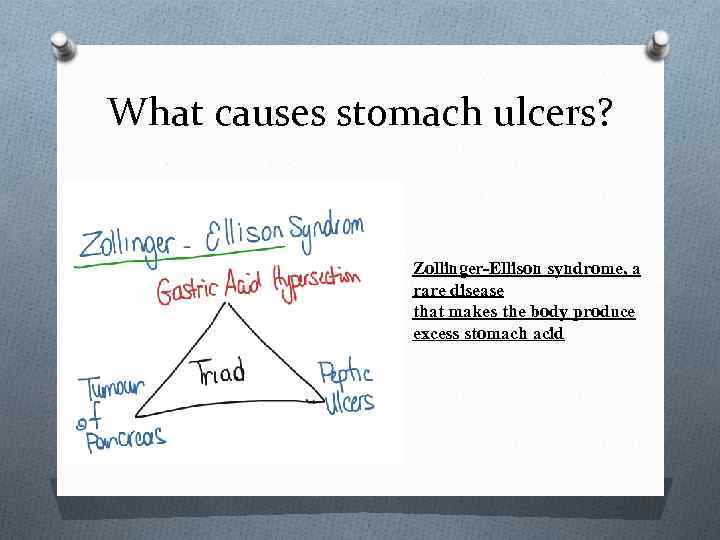 What causes stomach ulcers? Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare disease that makes the body produce excess stomach acid
What causes stomach ulcers? Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare disease that makes the body produce excess stomach acid
 Certain factors and behaviors can put you at higher risk for developing stomach ulcers: O smoking O frequent use of steroids (such as those for treating O O asthma) hypercalcemia (overproduction of calcium) family history of stomach ulcers being over 50 years old excessive consumption of alcohol
Certain factors and behaviors can put you at higher risk for developing stomach ulcers: O smoking O frequent use of steroids (such as those for treating O O asthma) hypercalcemia (overproduction of calcium) family history of stomach ulcers being over 50 years old excessive consumption of alcohol
 Symptoms of stomach ulcers O The most common symptom is a burning sensation or pain in the area between your chest and belly button. Normally, the pain will be more intense when your stomach is empty and it can last for a few minutes or several hours.
Symptoms of stomach ulcers O The most common symptom is a burning sensation or pain in the area between your chest and belly button. Normally, the pain will be more intense when your stomach is empty and it can last for a few minutes or several hours.
 Other common symptoms include: O dull pain in the stomach O weight loss O not wanting to eat because of pain O nausea or vomiting O bloating O burping or acid reflux O heartburn (burning sensation in the chest) O pain improves when you eat, drink, or take antacids
Other common symptoms include: O dull pain in the stomach O weight loss O not wanting to eat because of pain O nausea or vomiting O bloating O burping or acid reflux O heartburn (burning sensation in the chest) O pain improves when you eat, drink, or take antacids
 Did you know? O Stomach ulcers are common. According to the American Gastroenterological Association, an estimated 4 million Americans have peptic ulcer disease, which includes duodenal ulcers.
Did you know? O Stomach ulcers are common. According to the American Gastroenterological Association, an estimated 4 million Americans have peptic ulcer disease, which includes duodenal ulcers.
 How Are Stomach Ulcers Diagnosed? O Diagnosis and treatment will depend on your symptoms and the severity of your ulcer. To diagnose a stomach ulcer, your doctor will review your medical history along with your symptoms and any prescription or over-thecounter medications you’re taking. O To rule out H. pylori infection, a blood, stool, or breath test may be ordered. In a breath test, you’ll be instructed to drink a clear liquid and breathe into a bag, which is then sealed. If H. pylori is present, the breath sample will contain higher-than-normal levels of carbon dioxide.
How Are Stomach Ulcers Diagnosed? O Diagnosis and treatment will depend on your symptoms and the severity of your ulcer. To diagnose a stomach ulcer, your doctor will review your medical history along with your symptoms and any prescription or over-thecounter medications you’re taking. O To rule out H. pylori infection, a blood, stool, or breath test may be ordered. In a breath test, you’ll be instructed to drink a clear liquid and breathe into a bag, which is then sealed. If H. pylori is present, the breath sample will contain higher-than-normal levels of carbon dioxide.
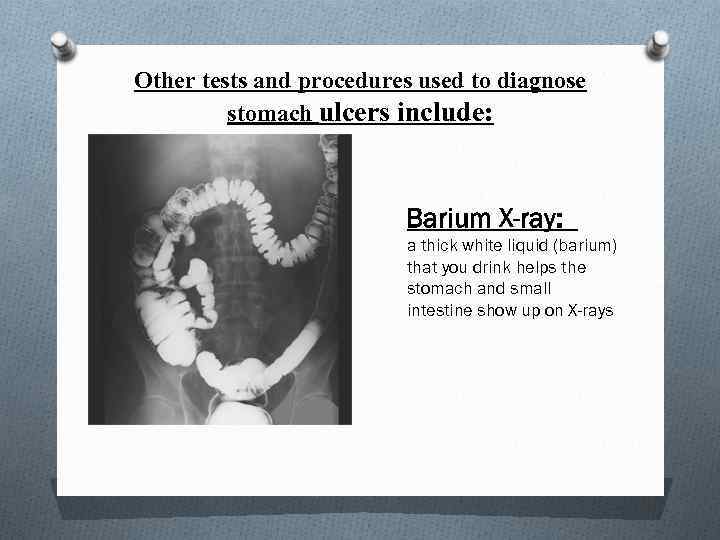 Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Barium X-ray: a thick white liquid (barium) that you drink helps the stomach and small intestine show up on X-rays
Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Barium X-ray: a thick white liquid (barium) that you drink helps the stomach and small intestine show up on X-rays
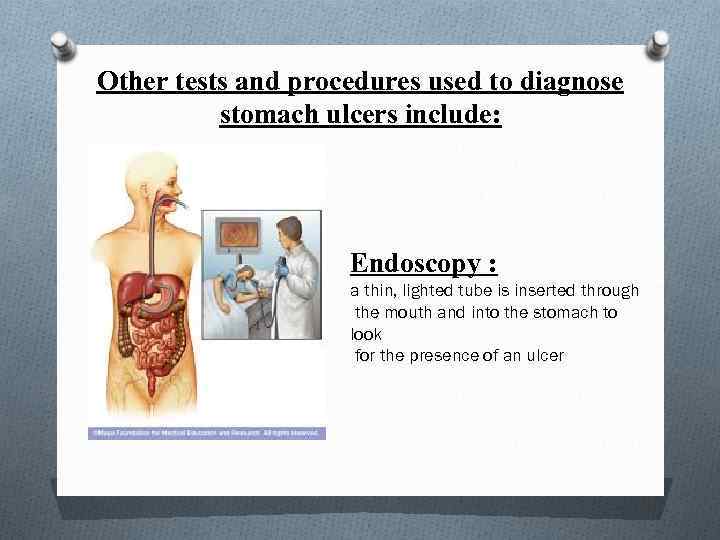 Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Endoscopy : a thin, lighted tube is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach to look for the presence of an ulcer
Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Endoscopy : a thin, lighted tube is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach to look for the presence of an ulcer
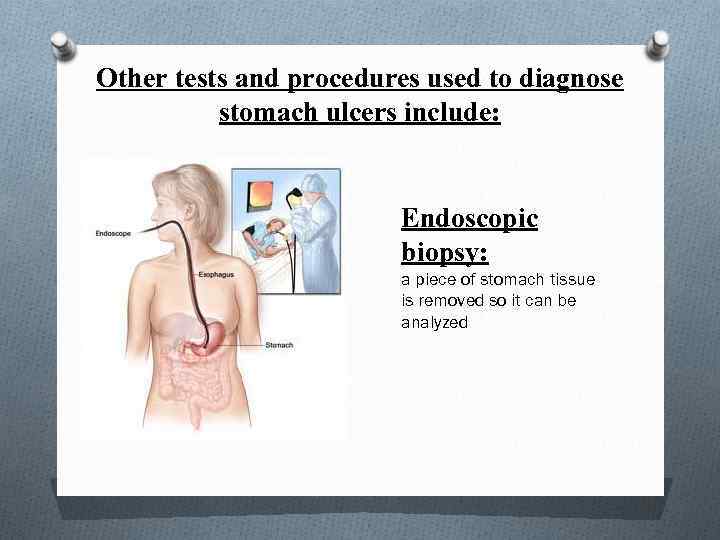 Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Endoscopic biopsy: a piece of stomach tissue is removed so it can be analyzed
Other tests and procedures used to diagnose stomach ulcers include: Endoscopic biopsy: a piece of stomach tissue is removed so it can be analyzed
 Treating Stomach Ulcers Nonsurgical treatment O If your stomach ulcer is the result of H. pylori, you’ll need antibiotics. For mild to moderate stomach ulcers, your doctor will usually prescribe the following medications:
Treating Stomach Ulcers Nonsurgical treatment O If your stomach ulcer is the result of H. pylori, you’ll need antibiotics. For mild to moderate stomach ulcers, your doctor will usually prescribe the following medications:
 H 2 blockers: to prevent your stomach from making too much acid
H 2 blockers: to prevent your stomach from making too much acid
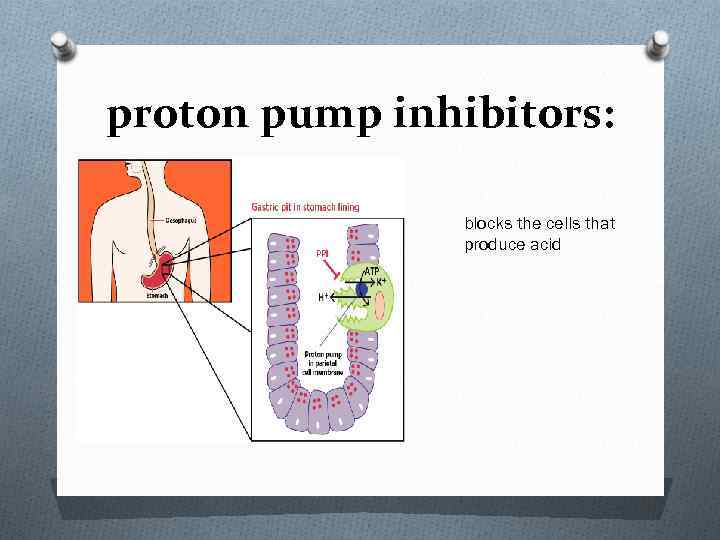 proton pump inhibitors: blocks the cells that produce acid
proton pump inhibitors: blocks the cells that produce acid
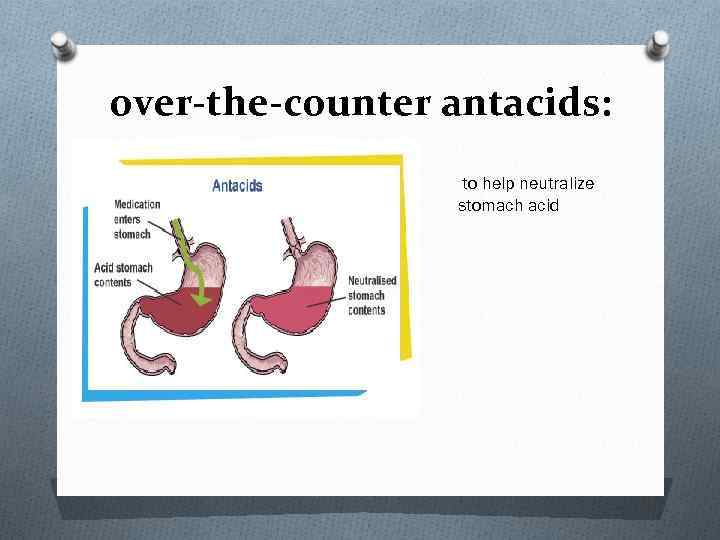 over-the-counter antacids: to help neutralize stomach acid
over-the-counter antacids: to help neutralize stomach acid
 cytoprotective agents: to protect the lining of the stomach and small intestine, such as Pepto-Bismol
cytoprotective agents: to protect the lining of the stomach and small intestine, such as Pepto-Bismol
 Important! ! ! O Symptoms of an ulcer may subside quickly with treatment. Even if your symptoms disappear, you should continue to take medicine prescribed by your doctor. This is especially important for H. pylori infections to ensure that all bacteria are destroyed. Doctors will also suggest that you avoid smoking, alcohol, and any medications or foods that can trigger symptoms.
Important! ! ! O Symptoms of an ulcer may subside quickly with treatment. Even if your symptoms disappear, you should continue to take medicine prescribed by your doctor. This is especially important for H. pylori infections to ensure that all bacteria are destroyed. Doctors will also suggest that you avoid smoking, alcohol, and any medications or foods that can trigger symptoms.
 Treating Stomach Ulcers Nonsurgical treatment O Certain side effects associated with stomach ulcer O O O treatment include: nausea dizziness headaches diarrhea These side effects are temporary. Talk to your doctor about changing your medication if you experience extreme discomfort as a result of these side effects.
Treating Stomach Ulcers Nonsurgical treatment O Certain side effects associated with stomach ulcer O O O treatment include: nausea dizziness headaches diarrhea These side effects are temporary. Talk to your doctor about changing your medication if you experience extreme discomfort as a result of these side effects.
 Surgical Treatment O In very rare cases, a complicated stomach ulcer will O O O require surgery. These include ulcers that: continue to return don’t heal bleed tear the stomach or small intestine keep food from flowing out of the stomach into the small intestine
Surgical Treatment O In very rare cases, a complicated stomach ulcer will O O O require surgery. These include ulcers that: continue to return don’t heal bleed tear the stomach or small intestine keep food from flowing out of the stomach into the small intestine
 Surgery may include: O removal of the entire ulcer O taking tissue from another part of the intestines and sewing it over the ulcer site O tying off a bleeding artery O cutting off nerve supply to the stomach to reduce the production of stomach acid
Surgery may include: O removal of the entire ulcer O taking tissue from another part of the intestines and sewing it over the ulcer site O tying off a bleeding artery O cutting off nerve supply to the stomach to reduce the production of stomach acid
 Surgical Treatment O Indications for surgical treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer are absolute and relative.
Surgical Treatment O Indications for surgical treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer are absolute and relative.
 Surgical Treatment O Absolute indications for surgical treatment of ulcers occur in perforation, penetration, pyloric stenosis and uncontrolled bleeding. Relative indications arise after failure of conservative treatment with frequent recurrences of ulcer. At length yavzy stomach up to 1 year
Surgical Treatment O Absolute indications for surgical treatment of ulcers occur in perforation, penetration, pyloric stenosis and uncontrolled bleeding. Relative indications arise after failure of conservative treatment with frequent recurrences of ulcer. At length yavzy stomach up to 1 year
 Surgical Treatment O Types of surgical interventions in gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer:
Surgical Treatment O Types of surgical interventions in gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer:
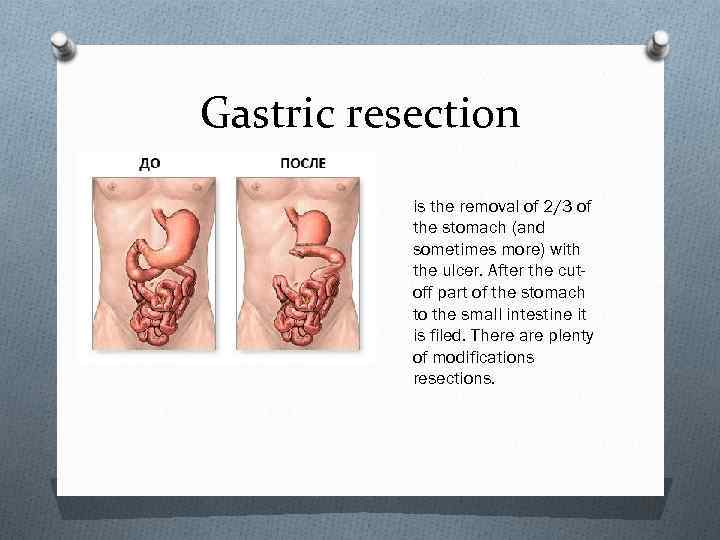 Gastric resection is the removal of 2/3 of the stomach (and sometimes more) with the ulcer. After the cutoff part of the stomach to the small intestine it is filed. There are plenty of modifications resections.
Gastric resection is the removal of 2/3 of the stomach (and sometimes more) with the ulcer. After the cutoff part of the stomach to the small intestine it is filed. There are plenty of modifications resections.
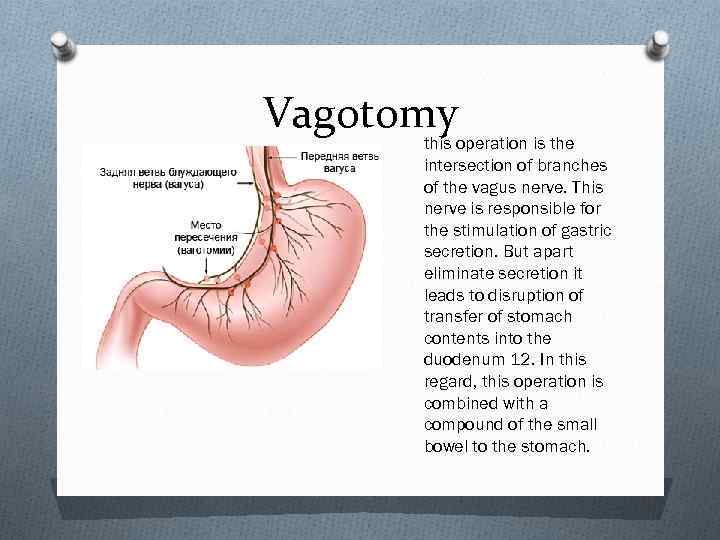 Vagotomy this operation is the intersection of branches of the vagus nerve. This nerve is responsible for the stimulation of gastric secretion. But apart eliminate secretion it leads to disruption of transfer of stomach contents into the duodenum 12. In this regard, this operation is combined with a compound of the small bowel to the stomach.
Vagotomy this operation is the intersection of branches of the vagus nerve. This nerve is responsible for the stimulation of gastric secretion. But apart eliminate secretion it leads to disruption of transfer of stomach contents into the duodenum 12. In this regard, this operation is combined with a compound of the small bowel to the stomach.
 Surgical Treatment O The disadvantage of surgical treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer - is the probability of complications after surgery. They can occur in the early postoperative period, and late. Briefly list them.
Surgical Treatment O The disadvantage of surgical treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer - is the probability of complications after surgery. They can occur in the early postoperative period, and late. Briefly list them.
 Complications O Early complications: - bleeding divergence (insolvency) seams places the stomach and small intestine connection (anastomosis) inflammation place anastomosis (anastomosis)
Complications O Early complications: - bleeding divergence (insolvency) seams places the stomach and small intestine connection (anastomosis) inflammation place anastomosis (anastomosis)
 Complications O Late complications: O dumping syndrome - is the rapid dropping of the ingested food from the stomach into the intestine. O syndrome resulting ulcer - is that the food from the stomach enters the blindly ending intestine. Once the bowel section accumulates a certain amount of food mass, all this is released into the stomach. O alkaline reflux gastritis - the most common complication is the fact that there is a throw alkali content of 12 duodenal ulcer in the stomach, resulting in an irritation and damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach - gastritis.
Complications O Late complications: O dumping syndrome - is the rapid dropping of the ingested food from the stomach into the intestine. O syndrome resulting ulcer - is that the food from the stomach enters the blindly ending intestine. Once the bowel section accumulates a certain amount of food mass, all this is released into the stomach. O alkaline reflux gastritis - the most common complication is the fact that there is a throw alkali content of 12 duodenal ulcer in the stomach, resulting in an irritation and damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach - gastritis.
 Prevention of Stomach Ulcers O To prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce risk of bacterial infection, wash your hands with soap and water on a regular basis. Make sure all food is properly cleaned and cooked thoroughly. O Certain lifestyle changes can also help prevent ulcers from forming. Limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding tobacco products, and properly managing stress can all contribute to a healthy stomach lining.
Prevention of Stomach Ulcers O To prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce risk of bacterial infection, wash your hands with soap and water on a regular basis. Make sure all food is properly cleaned and cooked thoroughly. O Certain lifestyle changes can also help prevent ulcers from forming. Limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding tobacco products, and properly managing stress can all contribute to a healthy stomach lining.
 Thanks for Attention ! ! !
Thanks for Attention ! ! !


