10.Journalism in Germany.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23

Journalism in Germany Foreign Journalism Berdak Bayimbetov
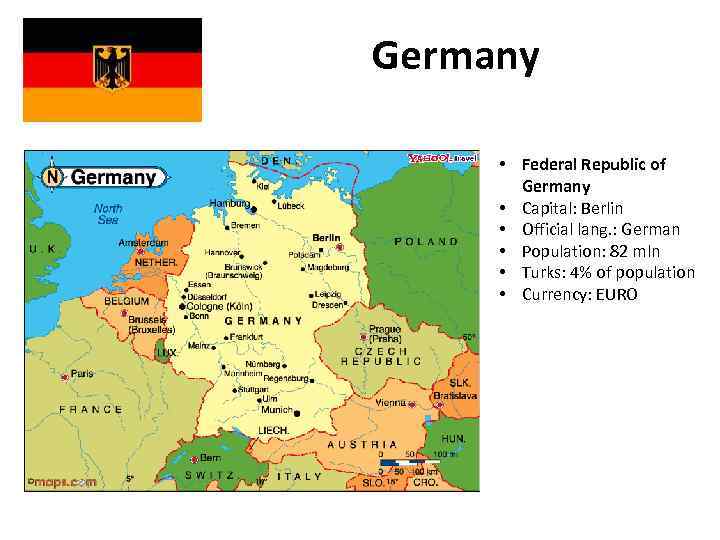
Germany • Federal Republic of Germany • Capital: Berlin • Official lang. : German • Population: 82 mln • Turks: 4% of population • Currency: EURO

Johannes Gutenberg invented movable type printing machine in 1439 This invention caused to a revolutionary flourish of print and journalism

The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog….

World’s oldest newspaper (1609) The date of birth of European newspaper is in Germany, 1609, “Relation: Aller Furnemmen”, contained news from Cologne, Antwerp, Rome, Venice, Vienna and Prague.

First newspapers • The first newspapers did not have an exact names. Dates and editor names were not shown either. • In 1609, in Augsburg, another weekly newspapers was published “Avisa Relation oder Zeitung” • Afterwards, starting from 1609 periodical press started being common in Europe. • There were periodical in 30 European cities by 1630

Die Zeit • Founded in Feb. 21, 1946 • ("Times“ in English) • German national weekly newspaper • Regarded as a qualitative paper • Circulation of 488, 036 • Estimated readership of slightly above 2 million • The most widely read German weekly newspaper.

Süddeutsche Zeitung • Often abbreviated SZ • Literally translates as "South German Newspaper“ • The largest German national subscription daily newspaper. • 1. 1 million readers daily • Functions since 1949

The Radio • From late 1933, government makes cheap radios available to the masses • Listening to the radio the duty of every citizen

The Radio • Hitler could “reach” to almost every ordinary citizen • 1939 - 70% of Germans owned a radio—highest percentage in the world at that time • Radios designed for short range, therefore could not pick up foreign stations, only Nazi views • People who did listen to foreign radio could be executed

Types of media • During the 1940’s the only way to find out what was going on was by listening to the radio; So that’s how Hitler gave his live influential speeches. • Even today, many years after TV’s invention people still use radios to learn about the news. • There are over 500 radio stations in Germany at present. Old Fashion Radios

• It has broadcast regularly since 1953 • Germany's international broadcaster • Broadcasts news and information on shortwave, Internet and satellite radio • Radio works in 30 languages • TV works in 4 languages • Offers information regarding Germany and German language courses • Very similar to BBC World Service, Voice of America, Radio Free Europe, and others

Relay stations leasing transmitter time to DW DW leases time on the following relay stations • • • Novosibirsk, Russia Irkutsk, Russia Almaty, Kazakhstan Skelton, United Kingdom Woofferton, United Kingdom Kranji, Singapore (BBC Far Eastern Relay Station) Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles (Radio Netherlands) Talata Volonondry, Madagascar (Radio Netherlands) Dhabayya, United Arab Emirates

• German public broadcasting radio station, broadcasting national news and current affairs • Functions since January 1, 1962 • Radio offers news and documentaries, covering politics, economics and science. • Very limited music output.

Television • The first public showing of television: University of Leipzig, 1929 • The first broadcast of TV pictures began in Germany in 1935, broadcasting for 90 minutes three times a week • An early highlight: 1936 Olympic Games broadcast to 150. 000 people in public assembly halls in Germany • All the main German TV channels are free-to-air

Television and Movies • There was a limited amount of citizens who actually owned their own televisions. • Most people relied on movie theaters for entertainment and war movies gave the people at home an idea of what it was really like out there. • This encouraged them to stand behind their country. Old Fashion TV

Television 365 TV channels licensed in Germany As of 2012, all channels are provided in digital format in HD
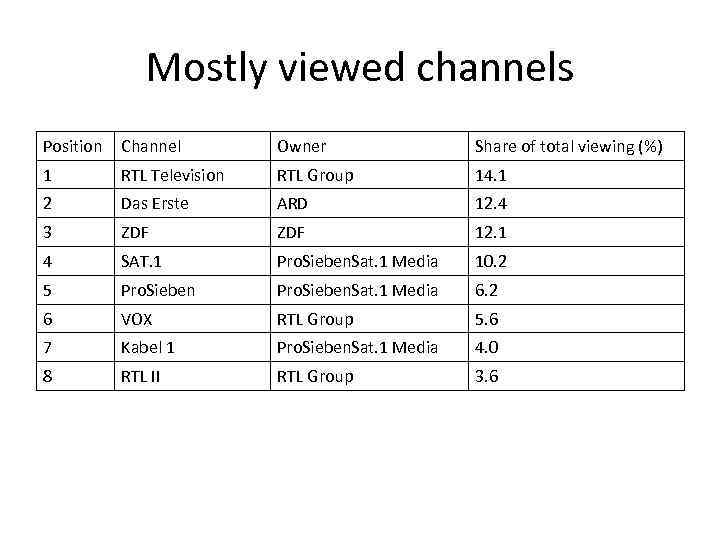
Mostly viewed channels Position Channel Owner Share of total viewing (%) 1 RTL Television RTL Group 14. 1 2 Das Erste ARD 12. 4 3 ZDF 12. 1 4 SAT. 1 Pro. Sieben. Sat. 1 Media 10. 2 5 Pro. Sieben. Sat. 1 Media 6. 2 6 VOX RTL Group 5. 6 7 Kabel 1 Pro. Sieben. Sat. 1 Media 4. 0 8 RTL II RTL Group 3. 6

• Launched in January 2, 1984 • German commercial television station distributed via cable and satellite, as well as via digital terrestrial • Also distributed in several countries: Austria, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Belgium, Netherlands, France, Poland, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Romania, Croatia, Italy, Turkey • Various content: News/news magazines, Drama, Entertainment, Comedy, Soap operas, and etc.

• Translated “as” Erstes Deutsches Fernsehen (“First German Television“) • The regular television service started on 25 December 1952 • Also distributed in: Austria, Luxembourg, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Belgium, Italy, Netherlands, Denmark, and Kosovo • Mainly news, plus mixed programmes

• Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen (English: "Second German Television") • Established in April 1, 1963 • Financed by television licence fees and advertising revenues • Well known for its famous newscast and entertainment shows.
TV licensing • As of 1 January 2013, the license fee in Germany is € 17. 98 per month (€ 215. 76 per annum) for all households and is payable regardless of equipment or television/radio usage. • Prior to 2013, only households and businesses with at least one television were required to pay. • Households with no televisions but with a radio or an internet-capable device were subject to a reduced radio-only fee. • The license fee is used to fund the public broadcasters: ZDF, Deutschlandradio and 9 regional broadcasters of the ARD network (who altogether run 22 television channels and 61 radio stations).

Freedom of the Press in Germany • In Germany, freedom of the press is not so much under threat from the state; if security forces violate the right of editors not to disclose their sources of information, the Federal Constitutional Court intervenes and teaches the state authorities the value of press freedom for democracy.
10.Journalism in Germany.pptx