c988b1040905071f91ac99fa53eab460.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Joint Research Activity JRA 4 Multi-coincidence detectors for low-energy particles Coordinators: Joachim Ullrich, Alexander Dorn Max Planck Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Participating countries France, Germany, Israel Tasks A) Multi-pixel detectors for low-energy particles B) CCD-camera based multifragment-detector development C) Optimization of the delay line technique D) Crossed wire detector
Joint Research Activity JRA 4 Multi-coincidence detectors for low-energy particles Coordinators: Joachim Ullrich, Alexander Dorn Max Planck Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Participating countries France, Germany, Israel Tasks A) Multi-pixel detectors for low-energy particles B) CCD-camera based multifragment-detector development C) Optimization of the delay line technique D) Crossed wire detector
 Interaction of energetic ions with matter: • At least a few but usually many tens of electrons and ions are freed on a fs-time scale. • Many-particle imaging and detection systems become indispensable. • Present day detectors in many aspects do not fulfill the required specifications. Joint Research Activity JRA 4: Optimize the most promising and complementary concepts on the market Develop new, more risky technologies Well-adapted selection of solutions
Interaction of energetic ions with matter: • At least a few but usually many tens of electrons and ions are freed on a fs-time scale. • Many-particle imaging and detection systems become indispensable. • Present day detectors in many aspects do not fulfill the required specifications. Joint Research Activity JRA 4: Optimize the most promising and complementary concepts on the market Develop new, more risky technologies Well-adapted selection of solutions
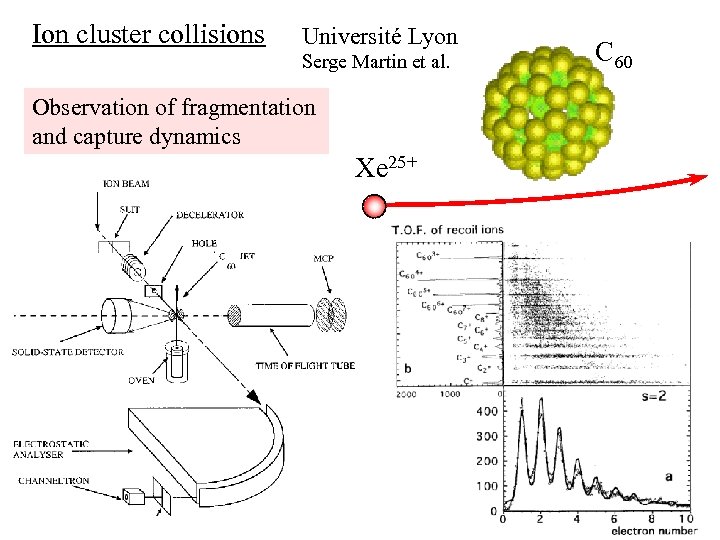 Ion cluster collisions Université Lyon Serge Martin et al. Observation of fragmentation and capture dynamics Xe 25+ C 60
Ion cluster collisions Université Lyon Serge Martin et al. Observation of fragmentation and capture dynamics Xe 25+ C 60
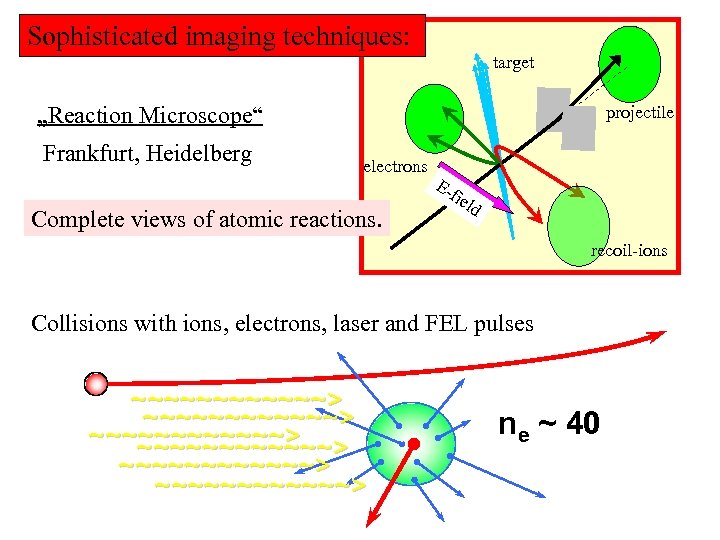 Sophisticated imaging techniques: target „Reaction Microscope“ Frankfurt, Heidelberg projectile electrons Complete views of atomic reactions. Efie ld recoil-ions Collisions with ions, electrons, laser and FEL pulses ~~~~~~~~~~~~> ~~~~~~~~~~~~> ne ~ 40
Sophisticated imaging techniques: target „Reaction Microscope“ Frankfurt, Heidelberg projectile electrons Complete views of atomic reactions. Efie ld recoil-ions Collisions with ions, electrons, laser and FEL pulses ~~~~~~~~~~~~> ~~~~~~~~~~~~> ne ~ 40
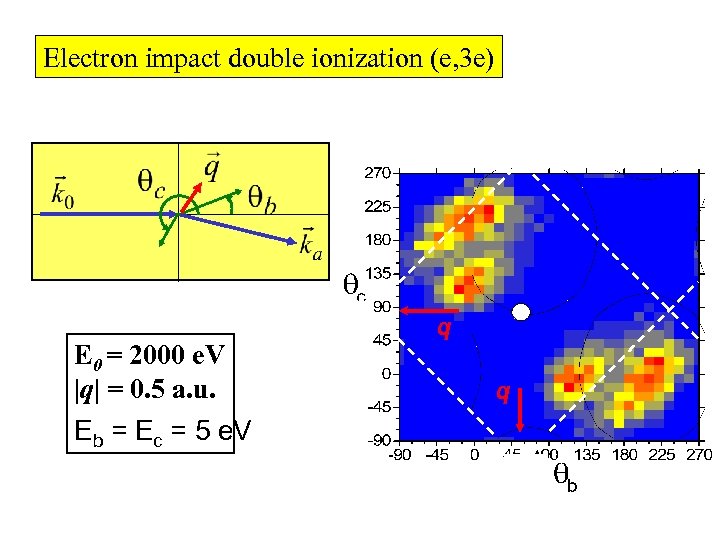 Electron impact double ionization (e, 3 e) q E 0 = 2000 e. V |q| = 0. 5 a. u. Eb = Ec = 5 e. V 59 53 48 43 37 32 27 21 16 10 5 0 q E q q
Electron impact double ionization (e, 3 e) q E 0 = 2000 e. V |q| = 0. 5 a. u. Eb = Ec = 5 e. V 59 53 48 43 37 32 27 21 16 10 5 0 q E q q
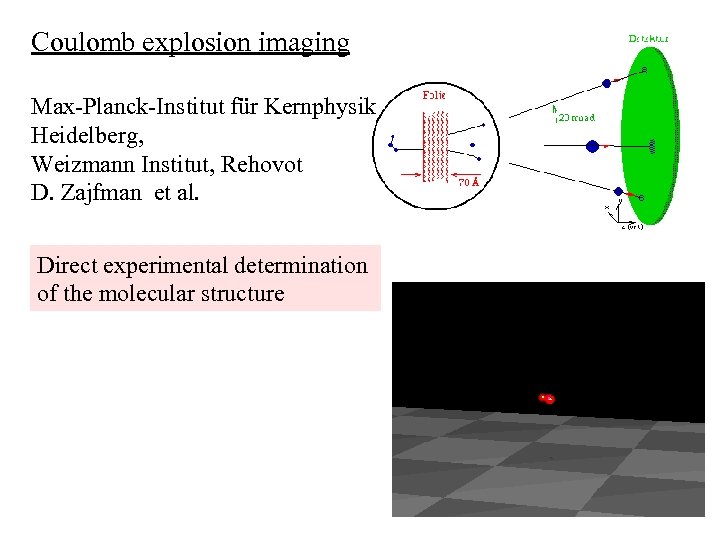 Coulomb explosion imaging Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Weizmann Institut, Rehovot D. Zajfman et al. Direct experimental determination of the molecular structure
Coulomb explosion imaging Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Weizmann Institut, Rehovot D. Zajfman et al. Direct experimental determination of the molecular structure
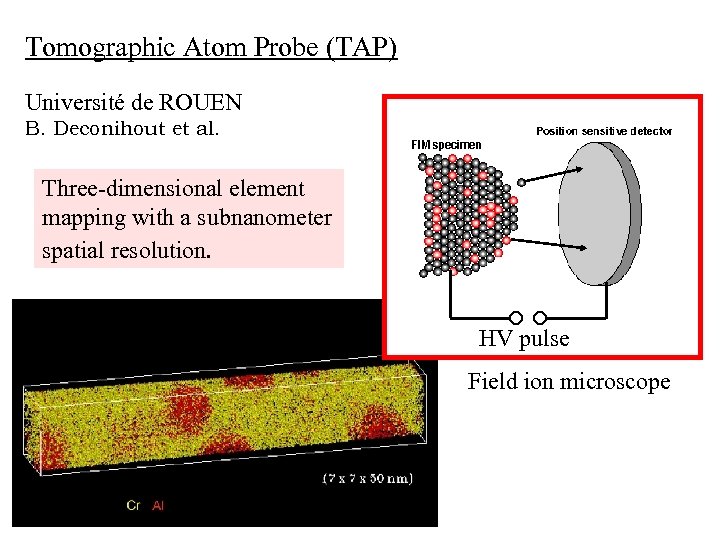 Tomographic Atom Probe (TAP) Université de ROUEN B. Deconihout et al. Three-dimensional element mapping with a subnanometer spatial resolution. HV pulse Field ion microscope
Tomographic Atom Probe (TAP) Université de ROUEN B. Deconihout et al. Three-dimensional element mapping with a subnanometer spatial resolution. HV pulse Field ion microscope
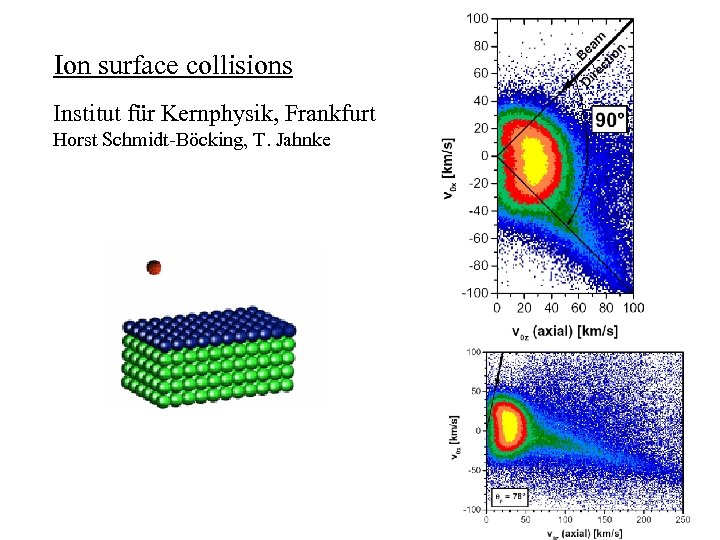 Ion surface collisions Institut für Kernphysik, Frankfurt Horst Schmidt-Böcking, T. Jahnke
Ion surface collisions Institut für Kernphysik, Frankfurt Horst Schmidt-Böcking, T. Jahnke
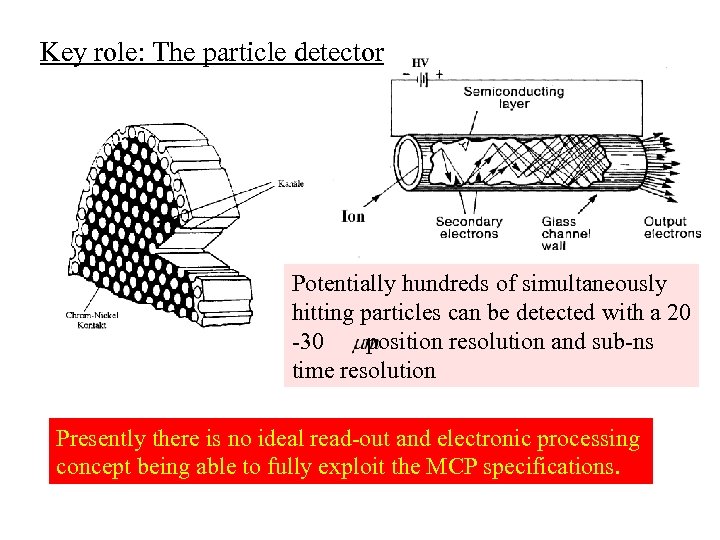 Key role: The particle detector Potentially hundreds of simultaneously hitting particles can be detected with a 20 -30 position resolution and sub-ns time resolution Presently there is no ideal read-out and electronic processing concept being able to fully exploit the MCP specifications.
Key role: The particle detector Potentially hundreds of simultaneously hitting particles can be detected with a 20 -30 position resolution and sub-ns time resolution Presently there is no ideal read-out and electronic processing concept being able to fully exploit the MCP specifications.
 Task A Multi-pixel detectors A. Dorn, MPIK, Heidelberg Task B CCD-camera based detectors D. Zajfmann, WIS, Rehovot Task C Optimization of the delay line technique O. Jagutzki, ROE, Kelkheim Task D Crossed wire detector H. Rothard, CEA, CIRIL/Caen
Task A Multi-pixel detectors A. Dorn, MPIK, Heidelberg Task B CCD-camera based detectors D. Zajfmann, WIS, Rehovot Task C Optimization of the delay line technique O. Jagutzki, ROE, Kelkheim Task D Crossed wire detector H. Rothard, CEA, CIRIL/Caen
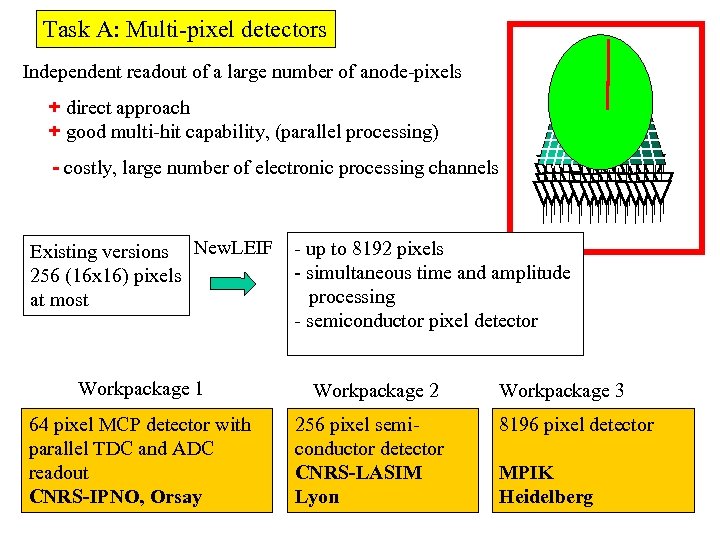 Task A: Multi-pixel detectors Independent readout of a large number of anode-pixels + direct approach + good multi-hit capability, (parallel processing) - costly, large number of electronic processing channels Existing versions New. LEIF 256 (16 x 16) pixels at most Workpackage 1 64 pixel MCP detector with parallel TDC and ADC readout CNRS-IPNO, Orsay - up to 8192 pixels - simultaneous time and amplitude processing - semiconductor pixel detector Workpackage 2 256 pixel semiconductor detector CNRS-LASIM Lyon Workpackage 3 8196 pixel detector MPIK Heidelberg
Task A: Multi-pixel detectors Independent readout of a large number of anode-pixels + direct approach + good multi-hit capability, (parallel processing) - costly, large number of electronic processing channels Existing versions New. LEIF 256 (16 x 16) pixels at most Workpackage 1 64 pixel MCP detector with parallel TDC and ADC readout CNRS-IPNO, Orsay - up to 8192 pixels - simultaneous time and amplitude processing - semiconductor pixel detector Workpackage 2 256 pixel semiconductor detector CNRS-LASIM Lyon Workpackage 3 8196 pixel detector MPIK Heidelberg
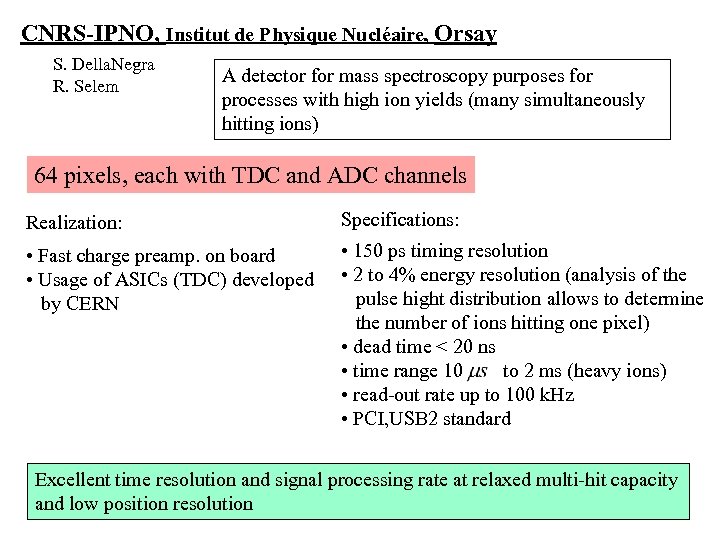 CNRS-IPNO, Institut de Physique Nucléaire, Orsay S. Della. Negra R. Selem A detector for mass spectroscopy purposes for processes with high ion yields (many simultaneously hitting ions) 64 pixels, each with TDC and ADC channels Realization: Specifications: • Fast charge preamp. on board • Usage of ASICs (TDC) developed by CERN • 150 ps timing resolution • 2 to 4% energy resolution (analysis of the pulse hight distribution allows to determine the number of ions hitting one pixel) • dead time < 20 ns • time range 10 to 2 ms (heavy ions) • read-out rate up to 100 k. Hz • PCI, USB 2 standard Excellent time resolution and signal processing rate at relaxed multi-hit capacity and low position resolution
CNRS-IPNO, Institut de Physique Nucléaire, Orsay S. Della. Negra R. Selem A detector for mass spectroscopy purposes for processes with high ion yields (many simultaneously hitting ions) 64 pixels, each with TDC and ADC channels Realization: Specifications: • Fast charge preamp. on board • Usage of ASICs (TDC) developed by CERN • 150 ps timing resolution • 2 to 4% energy resolution (analysis of the pulse hight distribution allows to determine the number of ions hitting one pixel) • dead time < 20 ns • time range 10 to 2 ms (heavy ions) • read-out rate up to 100 k. Hz • PCI, USB 2 standard Excellent time resolution and signal processing rate at relaxed multi-hit capacity and low position resolution
 CNRS-LASIM, University Lyon surface barrier silicon detector Serge Martin et al. Passivated Implanted Planar Silicon (PIPS) Detector Canberra Inc. ? Heigh threshold: tens of ke. V ? Large integration time: microssec. ? Low position resolution • Detection of electrons accellerated to 20 ke. V • Signal amplification and serial data transfer with ASICs • Up to 256 individual elements Specifications: • ns timing resolution • Position resolution few 100 • Energy resolution sufficient to identify the number of electrons impinging on one pixel • 16 hits per pixel in a 100 ns time window • Relaxed vacuum requirements compared to MCP Multi-pixel semiconductor detector with moderate position and good time-resolution at potentially high data-processing rates
CNRS-LASIM, University Lyon surface barrier silicon detector Serge Martin et al. Passivated Implanted Planar Silicon (PIPS) Detector Canberra Inc. ? Heigh threshold: tens of ke. V ? Large integration time: microssec. ? Low position resolution • Detection of electrons accellerated to 20 ke. V • Signal amplification and serial data transfer with ASICs • Up to 256 individual elements Specifications: • ns timing resolution • Position resolution few 100 • Energy resolution sufficient to identify the number of electrons impinging on one pixel • 16 hits per pixel in a 100 ns time window • Relaxed vacuum requirements compared to MCP Multi-pixel semiconductor detector with moderate position and good time-resolution at potentially high data-processing rates
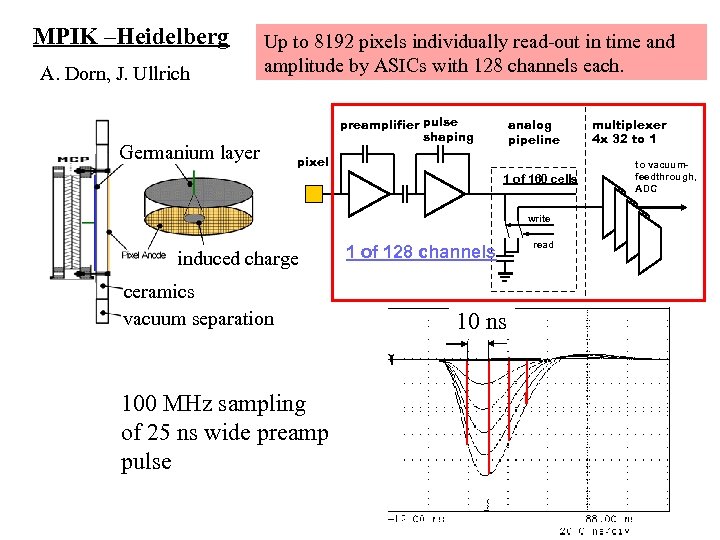 MPIK –Heidelberg A. Dorn, J. Ullrich Up to 8192 pixels individually read-out in time and amplitude by ASICs with 128 channels each. Germanium layer preamplifier pulse shaping analog pipeline pixel 1 of 160 cells write induced charge ceramics vacuum separation 100 MHz sampling of 25 ns wide preamp pulse 1 of 128 channels 10 ns read multiplexer 4 x 32 to 1 to vacuumfeedthrough, ADC
MPIK –Heidelberg A. Dorn, J. Ullrich Up to 8192 pixels individually read-out in time and amplitude by ASICs with 128 channels each. Germanium layer preamplifier pulse shaping analog pipeline pixel 1 of 160 cells write induced charge ceramics vacuum separation 100 MHz sampling of 25 ns wide preamp pulse 1 of 128 channels 10 ns read multiplexer 4 x 32 to 1 to vacuumfeedthrough, ADC
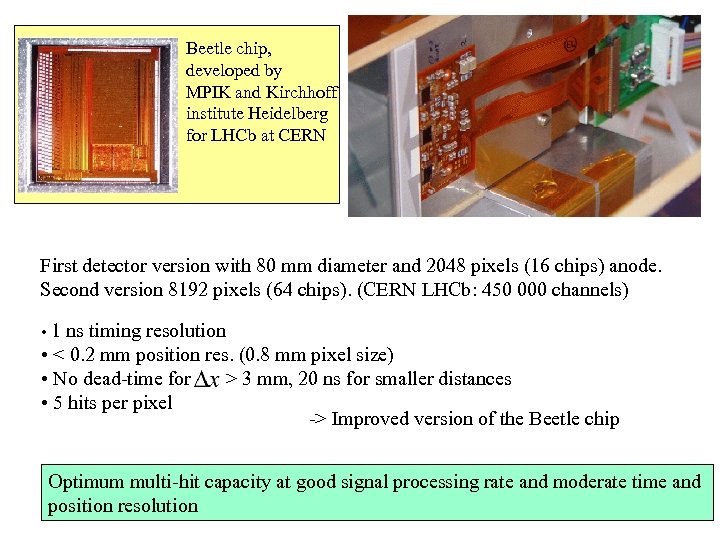 Beetle chip, developed by MPIK and Kirchhoff institute Heidelberg for LHCb at CERN First detector version with 80 mm diameter and 2048 pixels (16 chips) anode. Second version 8192 pixels (64 chips). (CERN LHCb: 450 000 channels) • 1 ns timing resolution • < 0. 2 mm position res. (0. 8 mm pixel size) • No dead-time for > 3 mm, 20 ns for smaller distances • 5 hits per pixel -> Improved version of the Beetle chip Optimum multi-hit capacity at good signal processing rate and moderate time and position resolution
Beetle chip, developed by MPIK and Kirchhoff institute Heidelberg for LHCb at CERN First detector version with 80 mm diameter and 2048 pixels (16 chips) anode. Second version 8192 pixels (64 chips). (CERN LHCb: 450 000 channels) • 1 ns timing resolution • < 0. 2 mm position res. (0. 8 mm pixel size) • No dead-time for > 3 mm, 20 ns for smaller distances • 5 hits per pixel -> Improved version of the Beetle chip Optimum multi-hit capacity at good signal processing rate and moderate time and position resolution
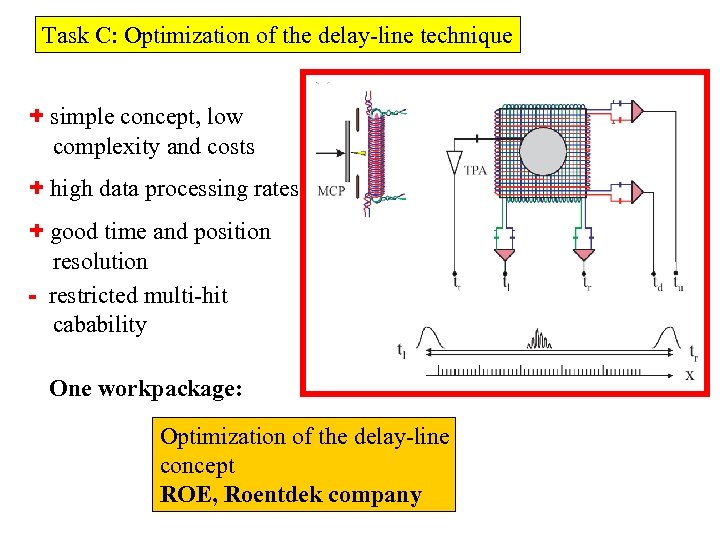 Task C: Optimization of the delay-line technique + simple concept, low complexity and costs + high data processing rates + good time and position resolution - restricted multi-hit cabability One workpackage: Optimization of the delay-line concept ROE, Roentdek company
Task C: Optimization of the delay-line technique + simple concept, low complexity and costs + high data processing rates + good time and position resolution - restricted multi-hit cabability One workpackage: Optimization of the delay-line concept ROE, Roentdek company
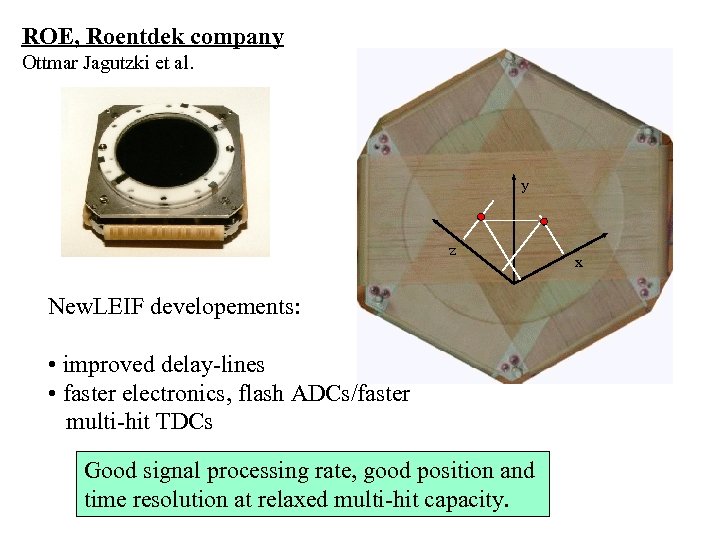 ROE, Roentdek company Ottmar Jagutzki et al. y z New. LEIF developements: • improved delay-lines • faster electronics, flash ADCs/faster multi-hit TDCs Good signal processing rate, good position and time resolution at relaxed multi-hit capacity. x
ROE, Roentdek company Ottmar Jagutzki et al. y z New. LEIF developements: • improved delay-lines • faster electronics, flash ADCs/faster multi-hit TDCs Good signal processing rate, good position and time resolution at relaxed multi-hit capacity. x
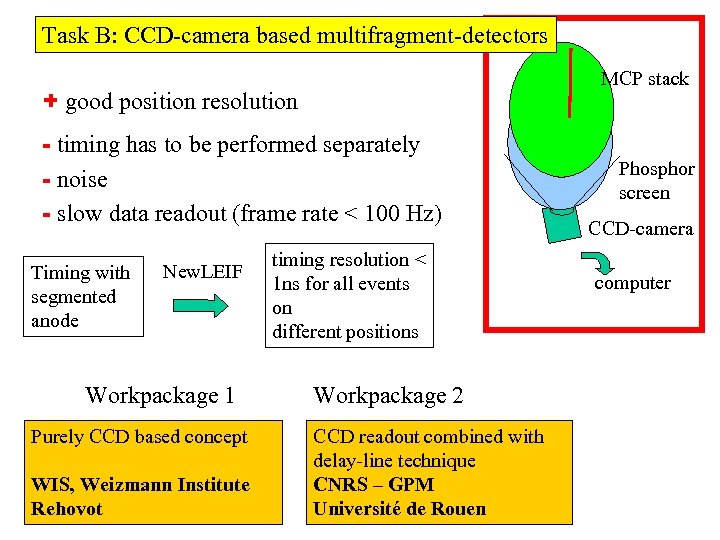 Task B: CCD-camera based multifragment-detectors MCP stack + good position resolution - timing has to be performed separately - noise - slow data readout (frame rate < 100 Hz) Timing with segmented anode New. LEIF Workpackage 1 Purely CCD based concept WIS, Weizmann Institute Rehovot timing resolution < 1 ns for all events on different positions Workpackage 2 CCD readout combined with delay-line technique CNRS – GPM Université de Rouen Phosphor screen CCD-camera computer
Task B: CCD-camera based multifragment-detectors MCP stack + good position resolution - timing has to be performed separately - noise - slow data readout (frame rate < 100 Hz) Timing with segmented anode New. LEIF Workpackage 1 Purely CCD based concept WIS, Weizmann Institute Rehovot timing resolution < 1 ns for all events on different positions Workpackage 2 CCD readout combined with delay-line technique CNRS – GPM Université de Rouen Phosphor screen CCD-camera computer
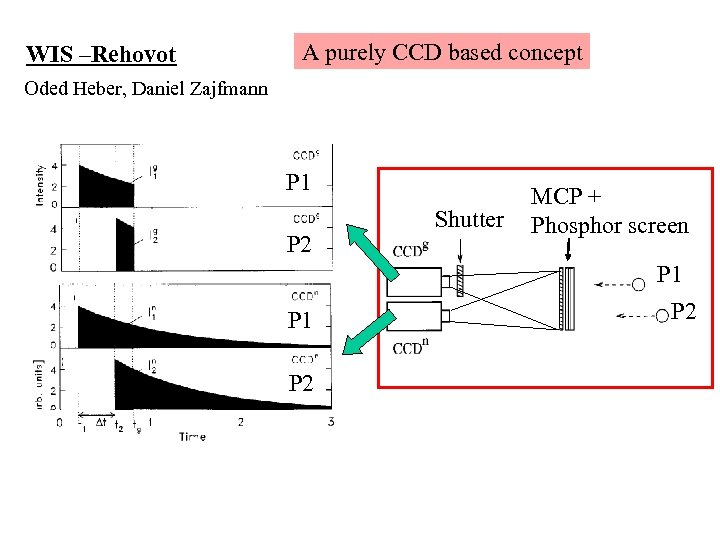 A purely CCD based concept WIS –Rehovot Oded Heber, Daniel Zajfmann P 1 P 2 Shutter MCP + Phosphor screen P 1 P 1 P 2 P 2
A purely CCD based concept WIS –Rehovot Oded Heber, Daniel Zajfmann P 1 P 2 Shutter MCP + Phosphor screen P 1 P 1 P 2 P 2
 Example: Letters illuminated by a single ns laser pulse Envisaged specifications: + timing resolution down to 0. 2 ns + position resolution down to < 0. 05 mm + no dead time for different positions far close - no multi hit detection for the same position - low signal processing rate < 100 1/s Optimum time-, position and multi-hit capacity at low signal processing rates
Example: Letters illuminated by a single ns laser pulse Envisaged specifications: + timing resolution down to 0. 2 ns + position resolution down to < 0. 05 mm + no dead time for different positions far close - no multi hit detection for the same position - low signal processing rate < 100 1/s Optimum time-, position and multi-hit capacity at low signal processing rates
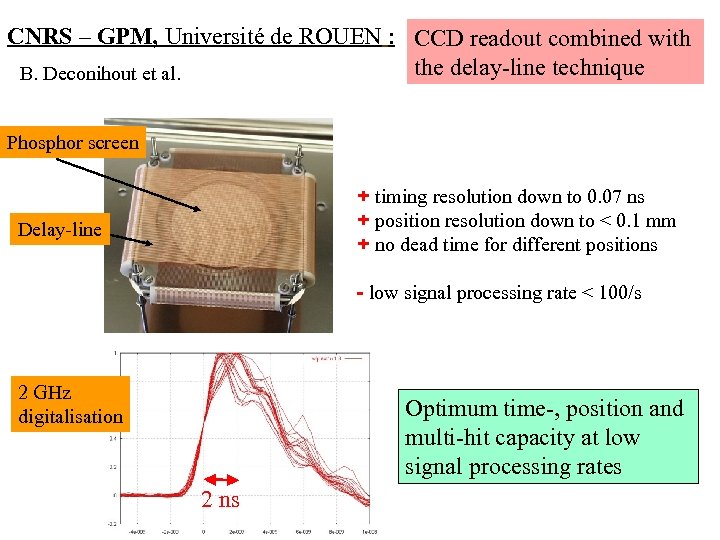 CNRS – GPM, Université de ROUEN : CCD readout combined with the delay-line technique B. Deconihout et al. Phosphor screen + timing resolution down to 0. 07 ns + position resolution down to < 0. 1 mm + no dead time for different positions Delay-line - low signal processing rate < 100/s 2 GHz digitalisation Optimum time-, position and multi-hit capacity at low signal processing rates 2 ns
CNRS – GPM, Université de ROUEN : CCD readout combined with the delay-line technique B. Deconihout et al. Phosphor screen + timing resolution down to 0. 07 ns + position resolution down to < 0. 1 mm + no dead time for different positions Delay-line - low signal processing rate < 100/s 2 GHz digitalisation Optimum time-, position and multi-hit capacity at low signal processing rates 2 ns
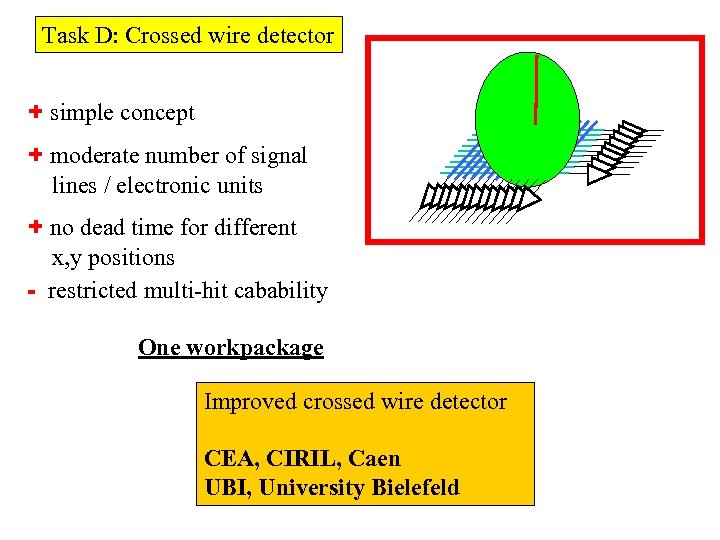 Task D: Crossed wire detector + simple concept + moderate number of signal lines / electronic units + no dead time for different x, y positions - restricted multi-hit cabability One workpackage Improved crossed wire detector CEA, CIRIL, Caen UBI, University Bielefeld
Task D: Crossed wire detector + simple concept + moderate number of signal lines / electronic units + no dead time for different x, y positions - restricted multi-hit cabability One workpackage Improved crossed wire detector CEA, CIRIL, Caen UBI, University Bielefeld
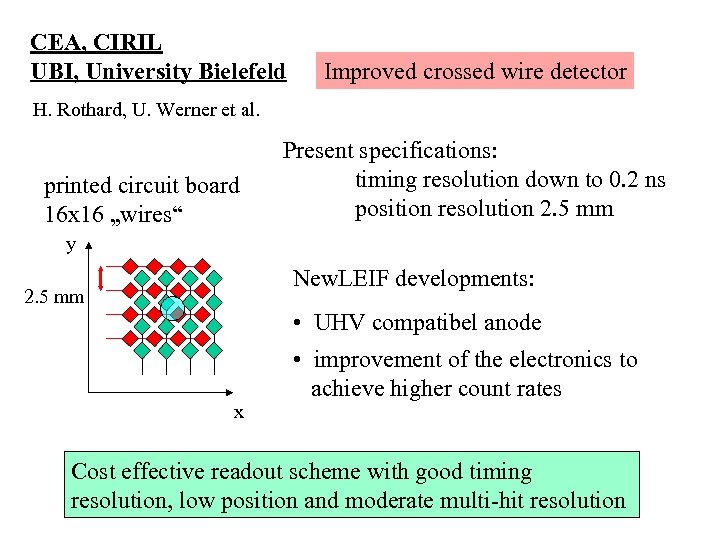 CEA, CIRIL UBI, University Bielefeld Improved crossed wire detector H. Rothard, U. Werner et al. printed circuit board 16 x 16 „wires“ Present specifications: timing resolution down to 0. 2 ns position resolution 2. 5 mm y New. LEIF developments: 2. 5 mm • UHV compatibel anode x • improvement of the electronics to achieve higher count rates Cost effective readout scheme with good timing resolution, low position and moderate multi-hit resolution
CEA, CIRIL UBI, University Bielefeld Improved crossed wire detector H. Rothard, U. Werner et al. printed circuit board 16 x 16 „wires“ Present specifications: timing resolution down to 0. 2 ns position resolution 2. 5 mm y New. LEIF developments: 2. 5 mm • UHV compatibel anode x • improvement of the electronics to achieve higher count rates Cost effective readout scheme with good timing resolution, low position and moderate multi-hit resolution
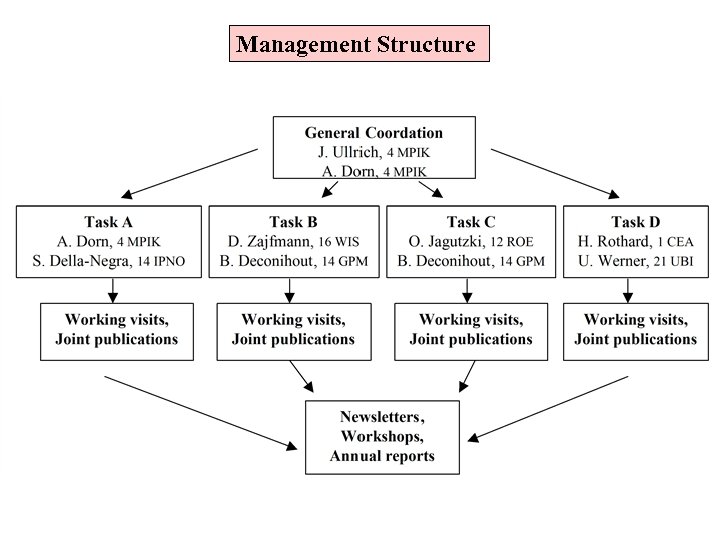 Management Structure
Management Structure
 Communication • Two JRA 4 meetings will be held per annum as part of a larger I 3 meeting • Progress reports • Working visits • Website as a subsection of the proposed I 3 website Monitoring and reporting progress • Annual progress reports are given by the task managers • Monitoring of delivery of milestones • Evaluation after 18 month • New. LEIF newsletter • Monthly updates of the JRA 4 part of the New. LEIF homepage
Communication • Two JRA 4 meetings will be held per annum as part of a larger I 3 meeting • Progress reports • Working visits • Website as a subsection of the proposed I 3 website Monitoring and reporting progress • Annual progress reports are given by the task managers • Monitoring of delivery of milestones • Evaluation after 18 month • New. LEIF newsletter • Monthly updates of the JRA 4 part of the New. LEIF homepage


