2fec861cd8b407a2f95e9d28d5d47dfa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Joint ITU-WHO Workshop on e-Health Standards and Interoperability (Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012) Remote Healthcare ICT and Mobile Healthcare ICT -Model Project in Japan by Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Shigeru Tomita Head of Strategy Planning Office NTTDATA CORPORATION tomitasg@nttdata. co. jp Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012

Agenda Introduction 3 cases of Remote Healthcare ICT and Mobile Healthcare ICT Conclusion and Recommendation Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 2
Introduction Current Healthcare status in Japan Super aging society 23. 1% is over 65 years old 20% of households are elderly only Increasing of medical expenditure 36. 6 Trillion Yen (2011 FY Approximation) http: //www. mhlw. go. jp/topics/medias/year/10/ With the advancing aging society Increasing of life style related diseases Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 3
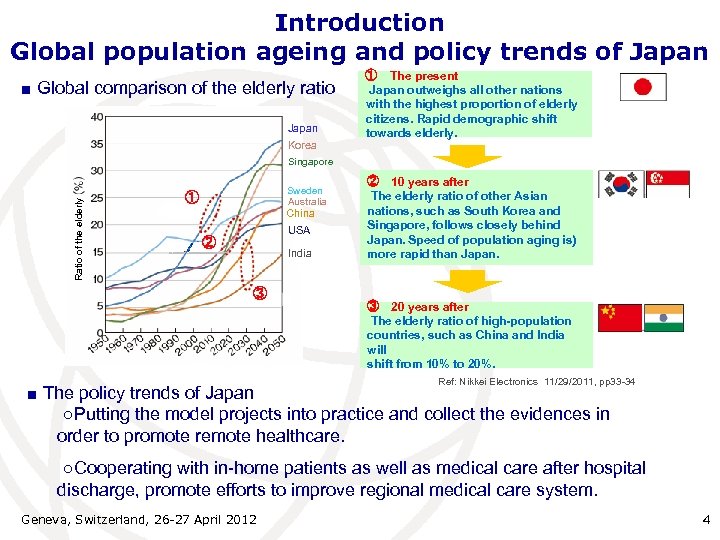
Introduction Global population ageing and policy trends of Japan ■ Global comparison of the elderly ratio Japan Korea ① The present Japan outweighs all other nations with the highest proportion of elderly citizens. Rapid demographic shift towards elderly. Ratio of the elderly Singapore Sweden Australia ① China USA ② India ③ ② 10 years after The elderly ratio of other Asian nations, such as South Korea and Singapore, follows closely behind Japan. Speed of population aging is) more rapid than Japan. ③ 20 years after The elderly ratio of high-population countries, such as China and India will shift from 10% to 20%. Ref: Nikkei Electronics 11/29/2011, pp 33 -34 ■ The policy trends of Japan ○Putting the model projects into practice and collect the evidences in order to promote remote healthcare. ○Cooperating with in-home patients as well as medical care after hospital discharge, promote efforts to improve regional medical care system. Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 4
3 cases 1. Remote Healthcare for Monitoring after discharging (for “cure” and “care”) -MIC Project 2. Remote Health promotion for elderly( for “prevention” ) -MIC Project 3. Mobile Healthcare for Post Disaster Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 5

1. Remote Healthcare for Monitoring after discharging -MIC Project Purpose: cure & care Provide Healthcare service for Homecare Patients after their discharges Service: Remote data monitoring using vital sensors Remote consultations over video phone Technology Authentication by PKI for Healthcare Continua Health Alliance based video phone Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 6
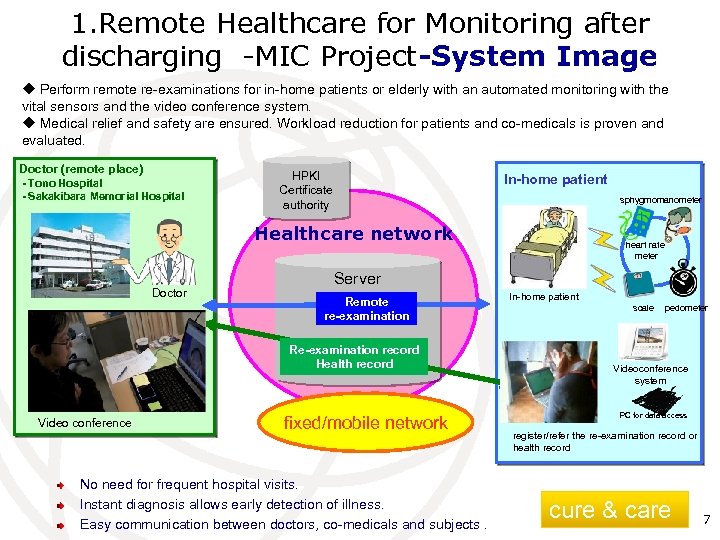
1. Remote Healthcare for Monitoring after discharging -MIC Project-System Image u Perform remote re-examinations for in-home patients or elderly with an automated monitoring with the vital sensors and the video conference system. u Medical relief and safety are ensured. Workload reduction for patients and co-medicals is proven and evaluated. Doctor (remote place) - Tono Hospital - Sakakibara Memorial Hospital HPKI Certificate authority In-home patient sphygmomanometer Healthcare network Doctor Server Remote re-examination Re-examination record Health record Video conference heart rate meter fixed/mobile network No need for frequent hospital visits. Instant diagnosis allows early detection of illness. Easy communication between doctors, co-medicals and subjects. In-home patient scale pedometer Videoconference system PC for data access register/refer the re-examination record or health record cure & care 7

2. Remote Health promotion for elderly -MIC Project prevention Purpose: Health Promotion for elderly in Rural area Service: Sharing vital data and consultation with health professionals Technology: Authentication by PKI for Healthcare Continua Health Alliance based video phone Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 8
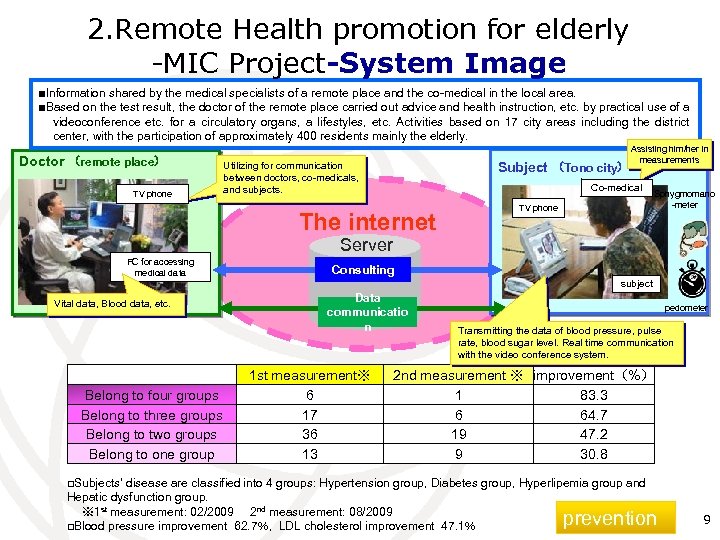
2. Remote Health promotion for elderly -MIC Project-System Image ■Information shared by the medical specialists of a remote place and the co-medical in the local area. ■Based on the test result, the doctor of the remote place carried out advice and health instruction, etc. by practical use of a videoconference etc. for a circulatory organs, a lifestyles, etc. Activities based on 17 city areas including the district center, with the participation of approximately 400 residents mainly the elderly. Doctor (remote place) TV phone Subject (Tono city) Utilizing for communication between doctors, co-medicals, and subjects. Assisting him/her in measurements Co-medical The internet TV phone コメディカル Sphygmomano -meter Server PC for accessing medical data Consulting subject Vital data, Blood data, etc. Belong to four groups Belong to three groups Belong to two groups Belong to one group Data communicatio n 1 st measurement※ 6 17 36 13 pedometer Transmitting the data of blood pressure, pulse rate, blood sugar level. Real time communication with the video conference system. 2 nd measurement ※ improvement(%) 1 83. 3 6 64. 7 19 47. 2 9 30. 8 □Subjects’ disease are classified into 4 groups: Hypertension group, Diabetes group, Hyperlipemia group and Hepatic dysfunction group. ※ 1 st measurement: 02/2009 2 nd measurement: 08/2009 □Blood pressure improvement 62. 7%, LDL cholesterol improvement 47. 1% prevention 9

3. Mobile Healthcare for post disaster Purpose: Provide better healthcare service at the shelters after the earthquake Service: Sharing medical records with doctors in some Medical Service Teams Technology: On. Demand VPN IPSec + IKE HL 7 Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 10
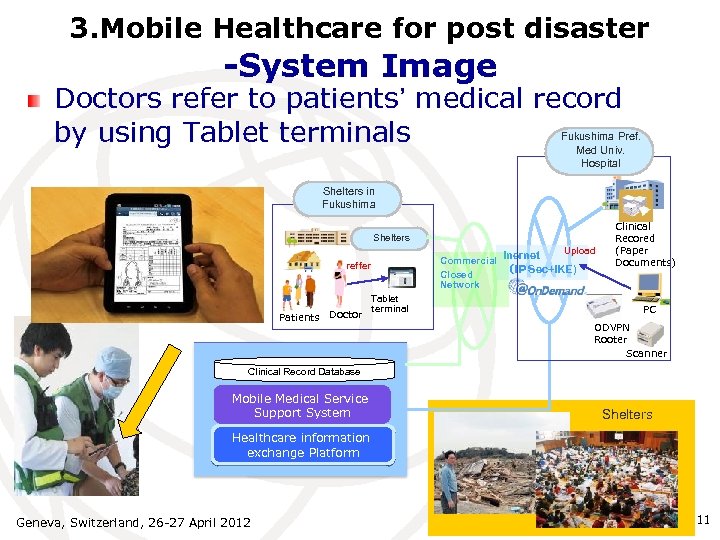
3. Mobile Healthcare for post disaster -System Image Doctors refer to patients’ medical record by using Tablet terminals Fukushima Pref. Med Univ. Hospital Shelters in Fukushima Shelters Inernet reffer Patients Doctor Upload Commercial (IPSec+IKE) Closed Network Tablet terminal Clinical Recored (Paper Documents) PC ODVPN Rooter Scanner Clinical Record Database Mobile Medical Service Support System Shelters Healthcare information exchange Platform Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 11
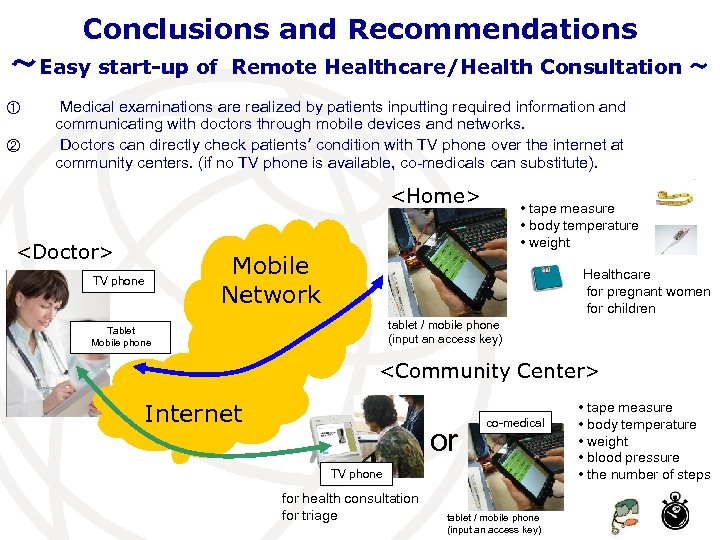
Conclusions and Recommendations ~Easy start-up of Remote Healthcare/Health Consultation ~ ① ② Medical examinations are realized by patients inputting required information and communicating with doctors through mobile devices and networks. Doctors can directly check patients’ condition with TV phone over the internet at community centers. (if no TV phone is available, co-medicals can substitute). <Home> <Doctor> TV phone • tape measure • body temperature • weight Mobile Network Healthcare for pregnant women for children tablet / mobile phone (input an access key) Tablet Mobile phone <Community Center> Internet or co-medical TV phone for health consultation for triage tablet / mobile phone (input an access key) • tape measure • body temperature • weight • blood pressure • the number of steps

Conclusions and Recommendations Remote/Mobile Healthcare by using ICT is effective Issues to be discussed Security Interoperability Recommendations: We need to discuss the standardization in ITU workshops (considering of unique colors and real-time capability in medical services) On demand VPN Continua Health Alliance Geneva, Switzerland, 26 -27 April 2012 13
2fec861cd8b407a2f95e9d28d5d47dfa.ppt