dab8a5d7c68b39d4c79d6716ea024342.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Joining it up making our cultural heritage visible online Paul Miller Interoperability Focus UK Office for Library & Information Networking (UKOLN) P. Miller@ukoln. ac. uk http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/ UKOLN is funded by Resource: the Council for Museums, Archives and Libraries, the Joint Information Systems Committee (JISC) of the Further and Higher Education Funding Councils, as well as by project funding from JISC and the EU. UKOLN also receives support from the Universities of Bath and Hull where staff are based. 1

“No man island” Donne, John, 1572– 1631 2

SCRAN e–Government strategy Community Information Services (CIS) ukonline. gov. Images of England “No citizen is an island” NGDF Metadata Project/ UKSGB The National Grid for Learning The People’s Network 100% of Government services available by 200 X ARCHSearch 3 A Netful of Jewels NOF–Digitise HEIRNET

Standard solutions The nice thing about standards… …is that there are so many to choose from! 4

Standard solutions 5

So… why use standards? • Benefit from the expertise of others • Enforce rigour in internal practices • Facilitate interoperability (and access) – Archives and monuments are held ‘in trust’ – Considered deployment of standard solutions makes access to those resources feasible for many – An enhanced Excavation Index, linking to the distributed excavation archives and the site report? . 6

What do standards do? • Help identify what’s important – CIMI’s “Access Points” – Mandatory fields • Allow for consistent use of terminology – Name Authority Files – Thesauri – Look–up tables • Enable internal and external data exchange or access • Reduce duplication of effort • Minimise (hopefully!) wasted effort • Reflect consensus. 7

What types of standard are there? • Terminology – ‘Roma’, not ‘Rome’ – ‘Roma’ is preferred to ‘Rome’ • Format – ‘Miller, A. P. 1971–’, not ‘Paul Miller’ • ‘Semantics’ – A gross simplification, and a very big bucket – ‘Creator’, ‘Subject’, ‘Title’, ‘Description’… • Syntax – <RDF xmlns = “http: //www. w 3. org/TR/WD-rdf-syntax#”> • Transfer – ftp: //ftp. niso. org/…. 8

What is ‘Interoperability’? “to be interoperable, one should actively be engaged in the ongoing process of ensuring that the systems, procedures and culture of an organisation are managed in such a way as to maximise opportunities for exchange and re-use of information, whether internally or externally. ” See http: //www. ariadne. ac. uk/issue 24/interoperability/ 9

What is ‘Metadata’? 10 – meaningless jargon – or a fashionable, and terribly misused, term for what we’ve always done – or “a means of turning data into information” – and “data about data” – and the name of a monument (‘South Cadbury’) – and the title of a book (‘Principles of Archaeological Excavation’).

Metadata Standards “Paul Miller gave a really interesting talk about Dublin Core at the National Monuments Record in Swindon” • In Swindon, or in Dublin? • About monuments and about milling? • But what was it? 11

Metadata Standards <speaker>“Paul Miller</speaker> gave a <value judgement>really interesting</value judgement> talk about <subject>Dublin Core</subject> at the <location>National Monuments Record in Swindon”</location>. 12
Opportunities Challenges Ø Many flavours of metadata Ø which one do I use? Ø Managing change Ø new varieties, and evolution of existing forms Ø Tension between functionality and simplicity, extensibility and interoperability 13 Functions, features, and cool stuff Simplicity and interoperability

Introducing the Dublin Core • An attempt to improve resource discovery on the Web – now adopted more broadly • Building an interdisciplinary consensus about a core element set for resource discovery – simple and intuitive – cross–disciplinary — not just libraries!! – international – open and consensual – flexible. 14 See http: //purl. org/dc/

Introducing the Dublin Core • • 15 elements of descriptive metadata All elements optional All elements repeatable The whole is extensible – offers a starting point for semantically richer descriptions • Interdisciplinary – libraries, government, museums, archives… • International 15 – available in more than 20 languages, with more on the way. . .
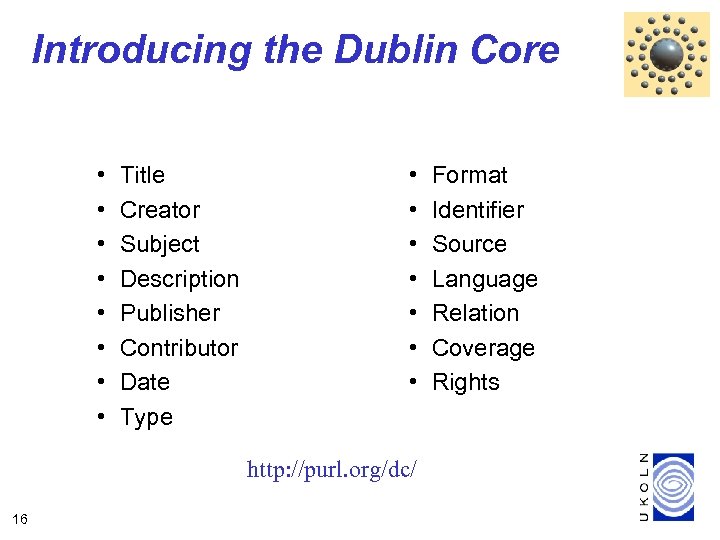
Introducing the Dublin Core • • Title Creator Subject Description Publisher Contributor Date Type • • http: //purl. org/dc/ 16 Format Identifier Source Language Relation Coverage Rights

Introducing XML • e. Xtensible Markup Language • World Wide Web Consortium recommendation • Simplified subset of SGML for use on Web • Addresses HTML’s lack of evolvability • Easily extended • Supported by major vendors • Increasingly used as a transfer syntax, but capable of far more…. 17 See http: //www. w 3. org/XML/
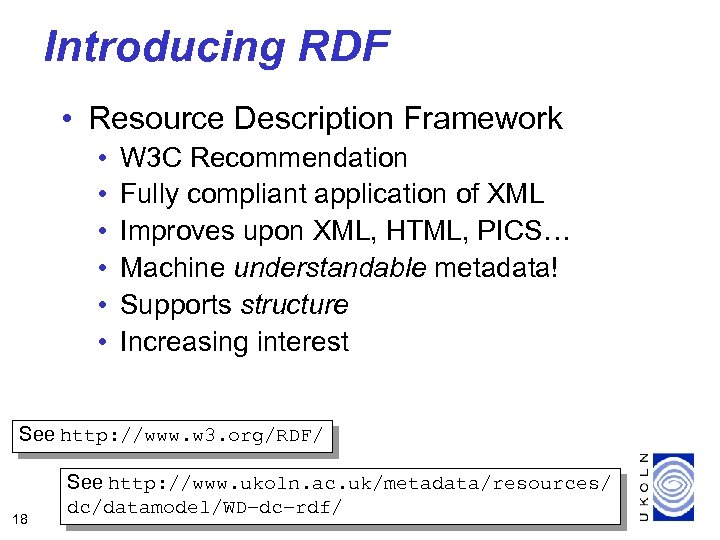
Introducing RDF • Resource Description Framework • • • W 3 C Recommendation Fully compliant application of XML Improves upon XML, HTML, PICS… Machine understandable metadata! Supports structure Increasing interest See http: //www. w 3. org/RDF/ 18 See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/metadata/resources/ dc/datamodel/WD–dc–rdf/

Introducing Z 39. 50 • North American Standard (ANSI/NISO Z 39. 50– 1995 [version 3]) • International Standard (ISO 23950) • Originally library–centric • Permits remote searching of databases • Access via Z client or over web • Relies upon ‘Profiles’ • CIMI profile for cultural heritage • GEO profile for Geospatial data. 19 See http: //www. ariadne. ac. uk/issue 21/z 3950/

Z 39. 50 Challenges • Profiles for each discipline • Defeats interoperability? • • • 20 Vendor interpretation of the standard Bib– 1 bloat Largely invisible to the user Seen as complicated and expensive Seen as old–fashioned Surely no match for XML/RDF/ whatever. See http: //www. ariadne. ac. uk/issue 21/z 3950/

Some Joined up working: The Bath Profile • Vendors and systems implement areas of the Z 39. 50 standard differently • Regional, National, and disciplinary Profiles have appeared over previous years, many of which have basic functions in common • Users wish to search across national/regional boundaries, and between vendors. See http: //www. ariadne. ac. uk/issue 21/z 3950/ 21
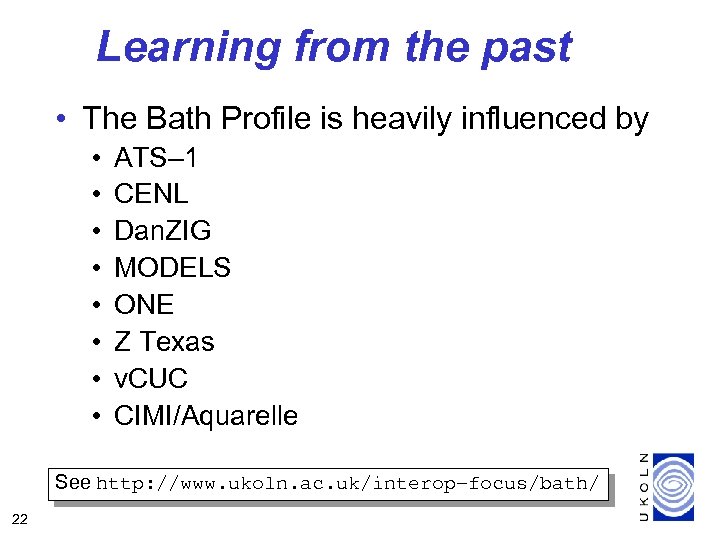
Learning from the past • The Bath Profile is heavily influenced by • • ATS– 1 CENL Dan. ZIG MODELS ONE Z Texas v. CUC CIMI/Aquarelle See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 22

Learning from the past 23 See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/

Doing the work • ZIP–PIZ–L mailing list, hosted by National Library of Canada • Meeting face–to–face • JISC supported a face–to–face meeting in Bath (UK) over the summer of 1999 • A draft was widely circulated for comment • Discussion and feedback world–wide • Profile presented at DC 7 in Frankfurt • Open Concertation day in the UK • etc. 24 See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/

Doing the work Makx Dekkers Pricewaterhouse. Coopers/ EC Janifer Gatenby GEAC Juha Hakala National Library of Finland Poul Henrik Joergensen Danish Library Centre Carrol Lunau National Library of Canada Paul Miller UKOLN Slavko Manojlovich SIRSI/ Memorial University of Newfoundland Bill Moen University of North Texas Judith Pearce National Library of Australia Joe Zeeman CGI. See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 25

What we proposed • Minimisation of ‘defaults’ • Where possible, every attribute is defined in the Profile (Use, Relation, Position, Structure, Truncation, Completeness) • Three Functional Areas • Basic Bibliographic Search & Retrieval • Bibliographic Holdings Search & Retrieval • Cross–Domain Search & Retrieval • Three Levels of Conformance in each Area. See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 26

What we proposed • SUTRS or XML and UNIMARC or MARC 21 for Bibliographic Search results • SUTRS and Dublin Core (in XML) for Cross –Domain results • Other record syntaxes also permitted, but conformant tools must support at least these. See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 27

Finishing it off… • Bath Profile 1. 1 accredited as ISO Internationally Registered Profile (IRP) • National Library of Canada as Maintenance Agency • Direct approaches to international vendors • Already begun in North America. Europe still to do. • User testing in Europe and North America • Does the Profile do what it’s meant to? • Revision of CIMI Profile and others to include Bath as a core subset. See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 28

Finishing it off… • Inclusion of explicit Bath Profile requirements in RFPs across North America and Europe already. • Bath Editorial Group working on stock text • Addition of Functional Areas and Levels of Conformance as required • Community Information? • Next open meeting in Newfoundland, 24– 25 September. See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop–focus/bath/ 29

Relevance to EH…? • Users want content • Good, quality controlled content, but not only from EH • EH sits on a wealth of information • But how much of it is really accessible to the world? • Joined–up everything • HEIRNET • Government agendas • ADS… • Portalitis. 30

Users want content… “Gimme stuff!” • Welcome to the information economy… • But if you’re ‘selling’, then they’re ‘customers’ • People only ‘buy’ what they can see • Educational agendas • Every school online by 2002, but where’s the stuff? – National Grid for Learning – Learning for Life/ Social Inclusion – e–University – 24 Hour Museum. 31 See http: //www. ukoln. ac. uk/metadata/education/

Joined–up everything… • Modernising Government/ Best Value • Government metadata/ interoperability rules • Digital Scotland • The shape of things to come? • • DNER Regional Broadband Consortia HEIRNET/ ADS Gateway NOF–DIGI • 2 EH bids through to second stage? • SOCITM. 32

Portalitis • Making your stuff portable and visible, makes it reusable and valuable. • • • 33 ukonline. gov/ Ask Giraffe DNER People’s Network/ NOF–DIGI A(H)DS Heritage Gateway? 24 Hour Museum National Grid for Learning Paul’s portal etc.

See www. ukoln. ac. uk/interop-focus/ Mail P. Miller@ukoln. ac. uk Join www. mailbase. ac. uk/lists/interoperability/ 34
dab8a5d7c68b39d4c79d6716ea024342.ppt