6658db61e4b1dcfdc327ce76d25155a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Johnson & Johnson: Use of Public Key Technology Rich Guida Rajesh Shah Director, Information Security Sr. Consultant, Information Security 1

Johnson & Johnson • The world’s largest and most comprehensive manufacturer of health care products • Founded in 1886 • Headquartered in New Brunswick, NJ • Sales of $36. 3 billion in 2002 • Over 198 operating companies in 54 countries • Over 110, 000 employees worldwide • Customers in over 175 countries 2
Statistics • 400+ UNIX servers; 1900+ Win. NT/2000 servers • 96, 000+ desktops/laptops (Win 2 K) • 60, 000+ remote users – Employ two-factor authentication (currently Secur. ID, migrating to PKI) • 50 M+ e-mails/month; 50+ TB of storage • 530+ internet and intranet servers, 3. 3 M+ website hits/day 3

Information Security Objectives • Improve enterprise security posture • Reduce costs and complexity of business processes • Interoperate with partners, customers • Comply efficiently with regulatory requirements Common thread to meet goals: Johnson & Johnson Enterprise Directory and PKI 4
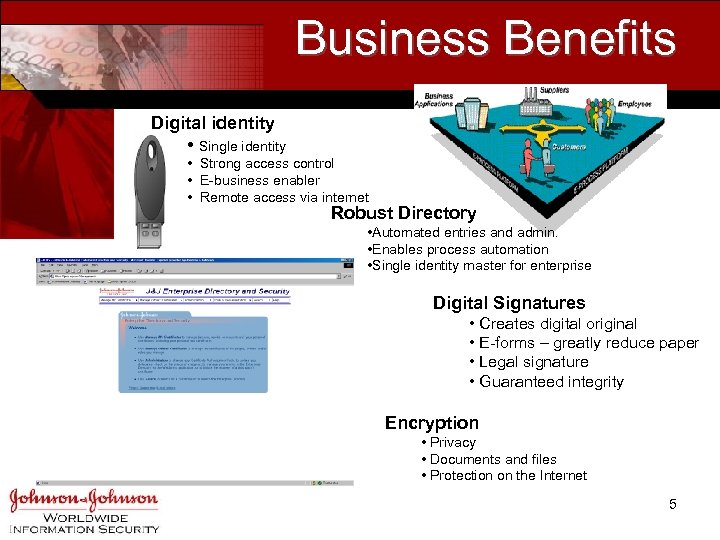
Business Benefits Digital identity • Single identity • Strong access control • E-business enabler • Remote access via internet Robust Directory • Automated entries and admin. • Enables process automation • Single identity master for enterprise Digital Signatures • Creates digital original • E-forms – greatly reduce paper • Legal signature • Guaranteed integrity Encryption • Privacy • Documents and files • Protection on the Internet 5

Enterprise Directory • Uses Active Directory forest – Separate from Win 2 K OS AD but some contents replicated • Populated by authoritative sources only • Uses World Wide Identifiers (WWIDs) as index • Supports entire security framework – Source of all information put into certificates • 250 K+ entries (employees, partners, retirees, former) • LDAP accessible 6

J&J PKI • Directory centric – certificate subscriber must be in Enterprise Directory • Certificates issued with supervisor ID proofing or through “group” registration process • Simple hierarchy – root CA and subordinate online CA; FDA validated • Standard form factor: hardware tokens (USB) • Production deployment began mid-2003 – Total of over 12, 000 certificates issued to date – Expect to issue > 100 K certificates in 2003 • Most important initial applications: – Remote authentication – Secure e-mail – Some enterprise applications 7
PKI-Enablement - Three Levels • Authentication only (usually with transmission encryption) – Example is SSLv 3 • Persistent digital signature – Usually through digitally signed hash of document or file, or portion thereof • Persistent encryption – Usually in conjunction with symmetric encryption – Public key used to encrypt symmetric key 8
PKI-Enablement • Windows applications PKI-ready – Outlook 2000 “out of the box” under any version of Windows; MS Office XP; Internet Explorer • Internal (home-grown) applications – Do it ourselves but with expert contractor help – Use FIPS validated libraries – MSCAPI and RSA BSafe preferred • External software and service suppliers - e. g. , Oracle, SAP, JDEdwards, Siebel, Documentum – Initial focus is authentication using SSLv 3 (also get transmission encryption) – Successfully done with SAP already (digital signature work continuing) and with Oracle – Siebel/JDEdwards/Documentum also underway 9

Observations • Get identity infrastructure in place first – and ensure it is well-defined • Prefer to have supervisors act as “local registration authorities” for subordinates • Hard to do ROI calculation – just like email • Many enterprise applications are PKIaware – and more are coming • Good CP/CPS critical to success and discipline 10

Challenges • Getting people familiar with the token form factor (“plug it in”) • Recovery from lost/locked token • USB port congestion/power • PDAs (CSP/PKCS 11 support) • Any problem becomes “PKI did it” • Engineers being asked for legal advice (“when to dig sig e-mail”) • Interoperability 11

Oracle Advanced Security Option Certificate based authentication 12

Business Drivers • Secure communication with database from the middle tier • Eliminate embedded passwords • Reduce & simplify maintenance 13
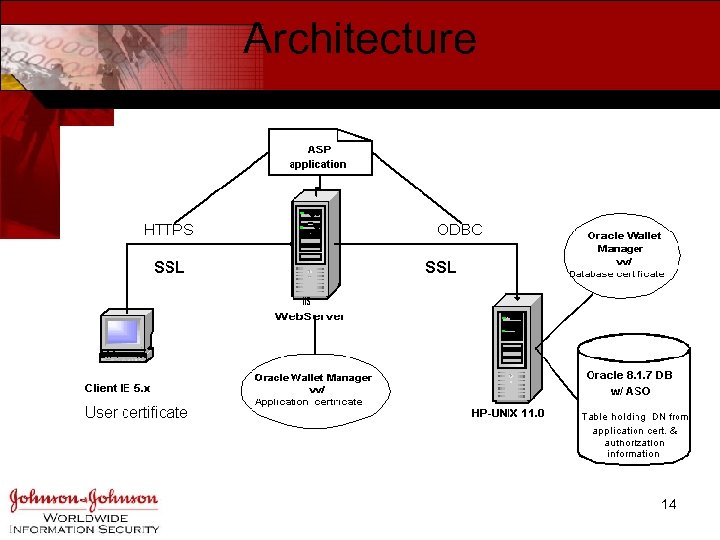
Architecture 14

Test Environment • Backend – HP-UX 11. 0 – Oracle 8. 1. 7 • Middle tier – MS W 2 K – MS IIS • Client – MS IE 5. 5 15

Next Steps/Enhancements • Certificate Revocation List (CRL) checking • Support within the Oracle tools allowing for Smartcard based logon (ex: SQLPlus connection using Smartcard) • Ability to import externally generated certificates • Ability to use of multiple wallets co-currently • PKI based authentication within the EBusiness suite • Performance benchmarks • Integration w/OS Certificate store instead of 16 Oracle wallet manager

Thank you Questions… 17
6658db61e4b1dcfdc327ce76d25155a1.ppt