545a098b244e8c2f5d7bf48a86ce1213.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Jerry Stevens STSM, AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 1: Overview) Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team 1 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
Jerry Stevens STSM, AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 1: Overview) Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team 1 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Trademarks The following are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. IBM* IBM Logo* AIX* Blade. Center* Data. Power* POWER 7* z/OS* System z* PR/SM z/VM* System z 10 RACF* z/VSE z 10 Redbooks* z. Enterprise System p* System x* * Registered trademarks of IBM Corporation The following are trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies. Adobe, the Adobe logo, Post. Script, and the Post. Script logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States, and/or other countries. Cell Broadband Engine is a trademark of Sony Computer Entertainment, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both and is used under license therefrom. Java and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both. Microsoft, Windows NT, and the Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. INFINIBAND, Infini. Band Trade Association and the INFINIBAND design marks are trademarks and/or service marks of the INFINIBAND Trade Association. Intel, Intel logo, Intel Inside logo, Intel Centrino logo, Celeron, Intel Xeon, Intel Speed. Step, Itanium, and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both. ITIL is a registered trademark, and a registered community trademark of the Office of Government Commerce, and is registered in the U. S. Patent and Trademark Office. IT Infrastructure Library is a registered trademark of the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, which is now part of the Office of Government Commerce. * All other products may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. Notes: Performance is in Internal Throughput Rate (ITR) ratio based on measurements and projections using standard IBM benchmarks in a controlled environment. The actual throughput that any user will experience will vary depending upon considerations such as the amount of multiprogramming in the user's job stream, the I/O configuration, the storage configuration, and the workload processed. Therefore, no assurance can be given that an individual user will achieve throughput improvements equivalent to the performance ratios stated here. IBM hardware products are manufactured from new parts, or new and serviceable used parts. Regardless, our warranty terms apply. All customer examples cited or described in this presentation are presented as illustrations of the manner in which some customers have used IBM products and the results they may have achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics will vary depending on individual customer configurations and conditions. This publication was produced in the United States. IBM may not offer the products, services or features discussed in this document in other countries, and the information may be subject to change without notice. Consult your local IBM business contact for information on the product or services available in your area. All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. Information about non-IBM products is obtained from the manufacturers of those products or their published announcements. IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the performance, compatibility, or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of those products. Prices subject to change without notice. Contact your IBM representative or Business Partner for the most current pricing in your geography. 2 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Trademarks The following are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. IBM* IBM Logo* AIX* Blade. Center* Data. Power* POWER 7* z/OS* System z* PR/SM z/VM* System z 10 RACF* z/VSE z 10 Redbooks* z. Enterprise System p* System x* * Registered trademarks of IBM Corporation The following are trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies. Adobe, the Adobe logo, Post. Script, and the Post. Script logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States, and/or other countries. Cell Broadband Engine is a trademark of Sony Computer Entertainment, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both and is used under license therefrom. Java and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both. Microsoft, Windows NT, and the Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. INFINIBAND, Infini. Band Trade Association and the INFINIBAND design marks are trademarks and/or service marks of the INFINIBAND Trade Association. Intel, Intel logo, Intel Inside logo, Intel Centrino logo, Celeron, Intel Xeon, Intel Speed. Step, Itanium, and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both. ITIL is a registered trademark, and a registered community trademark of the Office of Government Commerce, and is registered in the U. S. Patent and Trademark Office. IT Infrastructure Library is a registered trademark of the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, which is now part of the Office of Government Commerce. * All other products may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. Notes: Performance is in Internal Throughput Rate (ITR) ratio based on measurements and projections using standard IBM benchmarks in a controlled environment. The actual throughput that any user will experience will vary depending upon considerations such as the amount of multiprogramming in the user's job stream, the I/O configuration, the storage configuration, and the workload processed. Therefore, no assurance can be given that an individual user will achieve throughput improvements equivalent to the performance ratios stated here. IBM hardware products are manufactured from new parts, or new and serviceable used parts. Regardless, our warranty terms apply. All customer examples cited or described in this presentation are presented as illustrations of the manner in which some customers have used IBM products and the results they may have achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics will vary depending on individual customer configurations and conditions. This publication was produced in the United States. IBM may not offer the products, services or features discussed in this document in other countries, and the information may be subject to change without notice. Consult your local IBM business contact for information on the product or services available in your area. All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. Information about non-IBM products is obtained from the manufacturers of those products or their published announcements. IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the performance, compatibility, or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of those products. Prices subject to change without notice. Contact your IBM representative or Business Partner for the most current pricing in your geography. 2 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Abstract § You've heard a lot about the IBM z. Enterprise™ System. The new machines are faster, more powerful and more energy efficient. But the most significant change is that other kinds of computers can now be “plugged into” the mainframe to create an “Ensemble Network” where security exposures are minimized and the data center can be managed as if it were a single computer. Many questions about speeds, feeds, feature codes, operating system levels have been answered, but many more questions have been raised about network design and network security. Attend the sessions in a two-part series to hear the answers to questions about Ensemble networking: questions on the underlying architecture, on the routing and security structures, and on the software definitions. § The first session in the series, “IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 1: Overview), ” presents a high-level overview of the networking topics surrounding the new architecture. Part 1 is suitable for both an executive and a technical audience with both architects and implementers represented. § The second session, “IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 2: Detail), ” presents a more detailed view of the underlying architecture, its routing and security structures, and some of its software definitions. Part 2 is suitable for a technical audience that wants to understand more about the design, positioning, and implementation of the new architecture. § Both documents are available at: w 3. ibm. com/support/techdocs 3 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Abstract § You've heard a lot about the IBM z. Enterprise™ System. The new machines are faster, more powerful and more energy efficient. But the most significant change is that other kinds of computers can now be “plugged into” the mainframe to create an “Ensemble Network” where security exposures are minimized and the data center can be managed as if it were a single computer. Many questions about speeds, feeds, feature codes, operating system levels have been answered, but many more questions have been raised about network design and network security. Attend the sessions in a two-part series to hear the answers to questions about Ensemble networking: questions on the underlying architecture, on the routing and security structures, and on the software definitions. § The first session in the series, “IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 1: Overview), ” presents a high-level overview of the networking topics surrounding the new architecture. Part 1 is suitable for both an executive and a technical audience with both architects and implementers represented. § The second session, “IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Part 2: Detail), ” presents a more detailed view of the underlying architecture, its routing and security structures, and some of its software definitions. Part 2 is suitable for a technical audience that wants to understand more about the design, positioning, and implementation of the new architecture. § Both documents are available at: w 3. ibm. com/support/techdocs 3 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Agenda – IBM z. Enterprise System Networking Overview § z. Enterprise and IBM z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager (z. Manager) - Overview § z. Enterprise Node Physical Infrastructure § Communications within the Ensemble § Network and OSA Types and Attributes § External Network Access § Network Virtualization Management § Provisioning Virtual Networks § Network Access Control and Security Notices: 1. All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. 2. The z. Enterprise internal networks are provided with redundant hardware – redundancy is NOT shown in this presentation 4 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Agenda – IBM z. Enterprise System Networking Overview § z. Enterprise and IBM z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager (z. Manager) - Overview § z. Enterprise Node Physical Infrastructure § Communications within the Ensemble § Network and OSA Types and Attributes § External Network Access § Network Virtualization Management § Provisioning Virtual Networks § Network Access Control and Security Notices: 1. All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. 2. The z. Enterprise internal networks are provided with redundant hardware – redundancy is NOT shown in this presentation 4 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
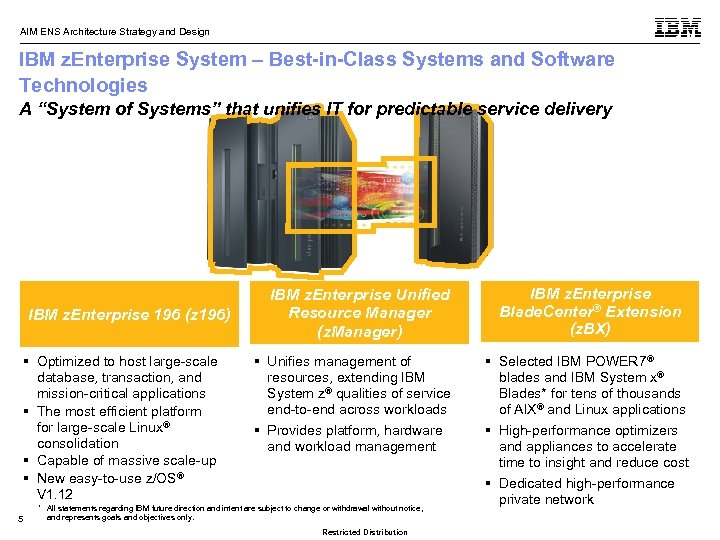 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System – Best-in-Class Systems and Software Technologies A “System of Systems” that unifies IT for predictable service delivery IBM z. Enterprise 196 (z 196) § Optimized to host large-scale database, transaction, and mission-critical applications § The most efficient platform for large-scale Linux® consolidation § Capable of massive scale-up § New easy-to-use z/OS® V 1. 12 5 IBM z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager (z. Manager) § Unifies management of resources, extending IBM System z® qualities of service end-to-end across workloads § Provides platform, hardware and workload management * All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Restricted Distribution IBM z. Enterprise Blade. Center® Extension (z. BX) § Selected IBM POWER 7® blades and IBM System x® Blades* for tens of thousands of AIX® and Linux applications § High-performance optimizers and appliances to accelerate time to insight and reduce cost § Dedicated high-performance private network © 2010 IBM Corporation
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System – Best-in-Class Systems and Software Technologies A “System of Systems” that unifies IT for predictable service delivery IBM z. Enterprise 196 (z 196) § Optimized to host large-scale database, transaction, and mission-critical applications § The most efficient platform for large-scale Linux® consolidation § Capable of massive scale-up § New easy-to-use z/OS® V 1. 12 5 IBM z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager (z. Manager) § Unifies management of resources, extending IBM System z® qualities of service end-to-end across workloads § Provides platform, hardware and workload management * All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Restricted Distribution IBM z. Enterprise Blade. Center® Extension (z. BX) § Selected IBM POWER 7® blades and IBM System x® Blades* for tens of thousands of AIX® and Linux applications § High-performance optimizers and appliances to accelerate time to insight and reduce cost § Dedicated high-performance private network © 2010 IBM Corporation
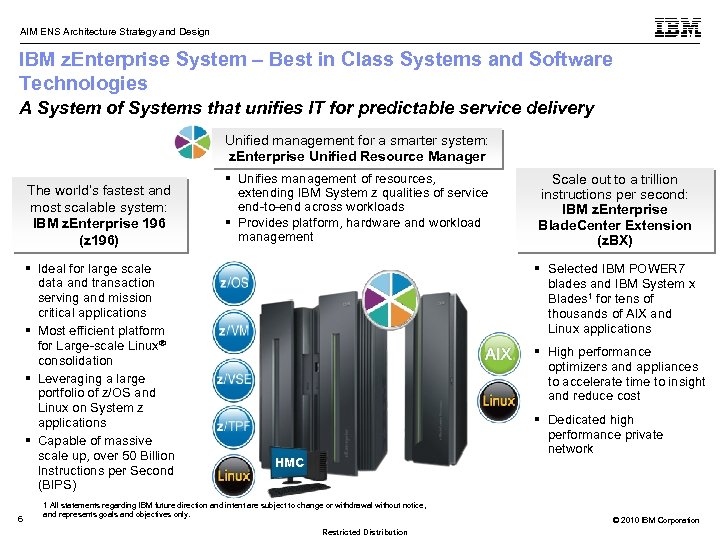 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System – Best in Class Systems and Software Technologies A System of Systems that unifies IT for predictable service delivery Unified management for a smarter system: z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager The world’s fastest and most scalable system: IBM z. Enterprise 196 (z 196) § Ideal for large scale data and transaction serving and mission critical applications § Most efficient platform for Large-scale Linux ® consolidation § Leveraging a large portfolio of z/OS and Linux on System z applications § Capable of massive scale up, over 50 Billion Instructions per Second (BIPS) 6 § Unifies management of resources, extending IBM System z qualities of service end-to-end across workloads § Provides platform, hardware and workload management Scale out to a trillion instructions per second: IBM z. Enterprise Blade. Center Extension (z. BX) § Selected IBM POWER 7 blades and IBM System x Blades 1 for tens of thousands of AIX and Linux applications § High performance optimizers and appliances to accelerate time to insight and reduce cost § Dedicated high performance private network HMC 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System – Best in Class Systems and Software Technologies A System of Systems that unifies IT for predictable service delivery Unified management for a smarter system: z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager The world’s fastest and most scalable system: IBM z. Enterprise 196 (z 196) § Ideal for large scale data and transaction serving and mission critical applications § Most efficient platform for Large-scale Linux ® consolidation § Leveraging a large portfolio of z/OS and Linux on System z applications § Capable of massive scale up, over 50 Billion Instructions per Second (BIPS) 6 § Unifies management of resources, extending IBM System z qualities of service end-to-end across workloads § Provides platform, hardware and workload management Scale out to a trillion instructions per second: IBM z. Enterprise Blade. Center Extension (z. BX) § Selected IBM POWER 7 blades and IBM System x Blades 1 for tens of thousands of AIX and Linux applications § High performance optimizers and appliances to accelerate time to insight and reduce cost § Dedicated high performance private network HMC 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
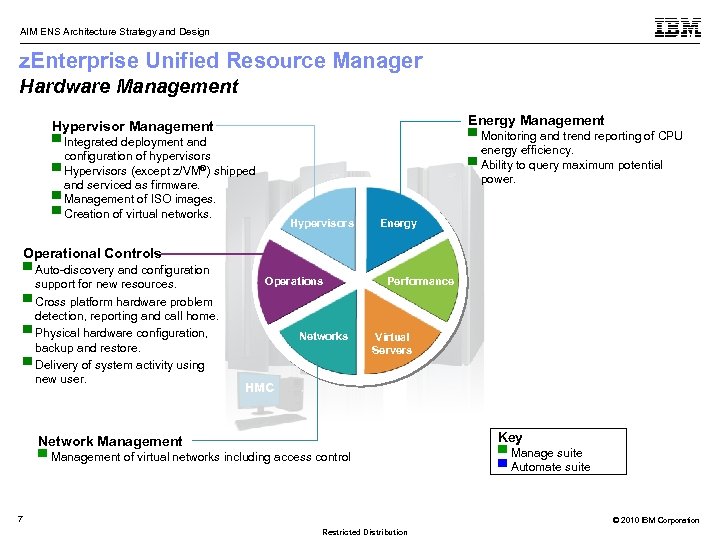 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager Hardware Management Energy Management Hypervisor Management ▀ Monitoring and trend reporting of CPU energy efficiency. ▀ Ability to query maximum potential power. ▀ Integrated deployment and configuration of hypervisors ▀ Hypervisors (except z/VM®) shipped and serviced as firmware. ▀ Management of ISO images. ▀ Creation of virtual networks. Hypervisors Energy Operational Controls ▀ Auto-discovery and configuration support for new resources. ▀ Cross platform hardware problem detection, reporting and call home. ▀ Physical hardware configuration, backup and restore. ▀ Delivery of system activity using new user. Operations Networks Performance Virtual Servers HMC Key Network Management ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control 7 ▀ Manage suite ▀ Automate suite © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager Hardware Management Energy Management Hypervisor Management ▀ Monitoring and trend reporting of CPU energy efficiency. ▀ Ability to query maximum potential power. ▀ Integrated deployment and configuration of hypervisors ▀ Hypervisors (except z/VM®) shipped and serviced as firmware. ▀ Management of ISO images. ▀ Creation of virtual networks. Hypervisors Energy Operational Controls ▀ Auto-discovery and configuration support for new resources. ▀ Cross platform hardware problem detection, reporting and call home. ▀ Physical hardware configuration, backup and restore. ▀ Delivery of system activity using new user. Operations Networks Performance Virtual Servers HMC Key Network Management ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control 7 ▀ Manage suite ▀ Automate suite © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
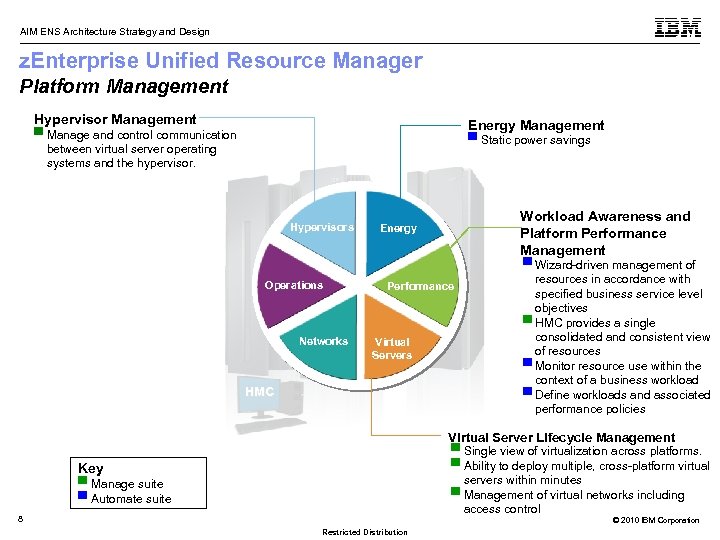 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager Platform Management Hypervisor Management Energy Management ▀ Manage and control communication between virtual server operating systems and the hypervisor. ▀ Static power savings Hypervisors Operations Networks Workload Awareness and Platform Performance Management Energy Performance Virtual Servers HMC ▀ Wizard-driven management of resources in accordance with specified business service level objectives ▀ HMC provides a single consolidated and consistent view of resources ▀ Monitor resource use within the context of a business workload ▀ Define workloads and associated performance policies Virtual Server Lifecycle Management ▀ Single view of virtualization across platforms. ▀ Ability to deploy multiple, cross-platform virtual Key servers within minutes ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control ▀ Manage suite ▀ Automate suite 8 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Unified Resource Manager Platform Management Hypervisor Management Energy Management ▀ Manage and control communication between virtual server operating systems and the hypervisor. ▀ Static power savings Hypervisors Operations Networks Workload Awareness and Platform Performance Management Energy Performance Virtual Servers HMC ▀ Wizard-driven management of resources in accordance with specified business service level objectives ▀ HMC provides a single consolidated and consistent view of resources ▀ Monitor resource use within the context of a business workload ▀ Define workloads and associated performance policies Virtual Server Lifecycle Management ▀ Single view of virtualization across platforms. ▀ Ability to deploy multiple, cross-platform virtual Key servers within minutes ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control ▀ Manage suite ▀ Automate suite 8 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
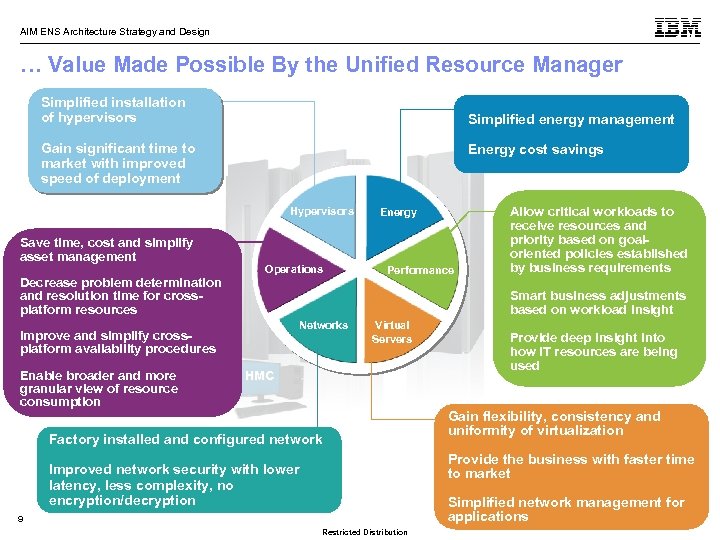 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise hardware management and platform management … … Value Made Possible By the Unified Resource Manager Simplified installation of hypervisors Energy Management Simplified energy management ▀ Monitoring and trend reporting of CPU energy efficiency. ▀ Ability to query maximum potential power. Energy cost savings ▀ Static power savings. Gain significant time to market with improved speed of deployment Hypervisors Operational Controls Save time, cost and simplify ▀ Auto-discovery and configuration asset management support for new resources. Decrease problem determination ▀ Cross platform hardware problem and resolution time for crossdetection, reporting and call home. platform resources ▀ Physical hardware configuration, Operations Energy Performance Smart business adjustments based on workload insight Networks backup and restore. Improve and simplify cross▀ Delivery of system activity using new platform availability procedures Virtual Servers user. Enable broader and more granular view of resource consumption Allow critical workloads to receive resources and priority based on goaloriented policies established by business requirements HMC Network Management configured network Factory installed and ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control Improved network security with lower latency, less complexity, no encryption/decryption Provide deep insight into how IT resources are being used Gain flexibility, consistency and Virtual Server Lifecycle Management uniformity of virtualization ▀ Single view of virtualization across platforms. ▀ Ability to deploy multiple, cross-platform virtual Provide the business with faster time to servers within minutes market ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control Simplified network management for applications © 2010 IBM Corporation 9 Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise hardware management and platform management … … Value Made Possible By the Unified Resource Manager Simplified installation of hypervisors Energy Management Simplified energy management ▀ Monitoring and trend reporting of CPU energy efficiency. ▀ Ability to query maximum potential power. Energy cost savings ▀ Static power savings. Gain significant time to market with improved speed of deployment Hypervisors Operational Controls Save time, cost and simplify ▀ Auto-discovery and configuration asset management support for new resources. Decrease problem determination ▀ Cross platform hardware problem and resolution time for crossdetection, reporting and call home. platform resources ▀ Physical hardware configuration, Operations Energy Performance Smart business adjustments based on workload insight Networks backup and restore. Improve and simplify cross▀ Delivery of system activity using new platform availability procedures Virtual Servers user. Enable broader and more granular view of resource consumption Allow critical workloads to receive resources and priority based on goaloriented policies established by business requirements HMC Network Management configured network Factory installed and ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control Improved network security with lower latency, less complexity, no encryption/decryption Provide deep insight into how IT resources are being used Gain flexibility, consistency and Virtual Server Lifecycle Management uniformity of virtualization ▀ Single view of virtualization across platforms. ▀ Ability to deploy multiple, cross-platform virtual Provide the business with faster time to servers within minutes market ▀ Management of virtual networks including access control Simplified network management for applications © 2010 IBM Corporation 9 Restricted Distribution
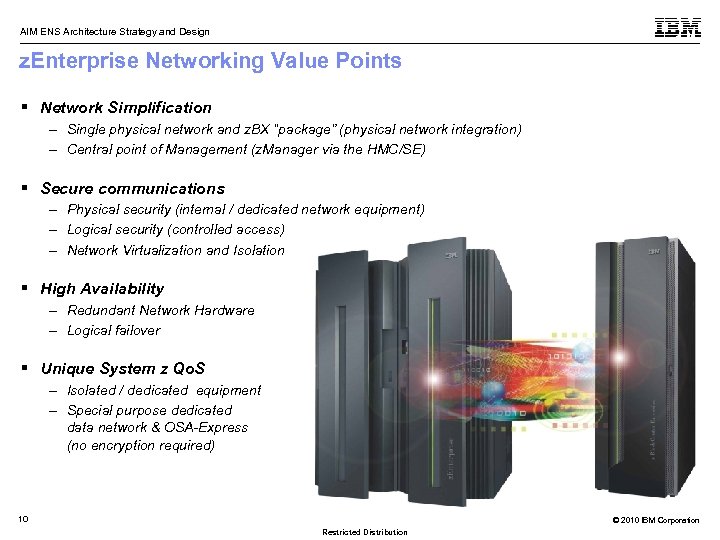 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Networking Value Points § Network Simplification – Single physical network and z. BX “package” (physical network integration) – Central point of Management (z. Manager via the HMC/SE) § Secure communications – Physical security (internal / dedicated network equipment) – Logical security (controlled access) – Network Virtualization and Isolation § High Availability – Redundant Network Hardware – Logical failover § Unique System z Qo. S – Isolated / dedicated equipment – Special purpose dedicated data network & OSA-Express (no encryption required) 10 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Networking Value Points § Network Simplification – Single physical network and z. BX “package” (physical network integration) – Central point of Management (z. Manager via the HMC/SE) § Secure communications – Physical security (internal / dedicated network equipment) – Logical security (controlled access) – Network Virtualization and Isolation § High Availability – Redundant Network Hardware – Logical failover § Unique System z Qo. S – Isolated / dedicated equipment – Special purpose dedicated data network & OSA-Express (no encryption required) 10 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
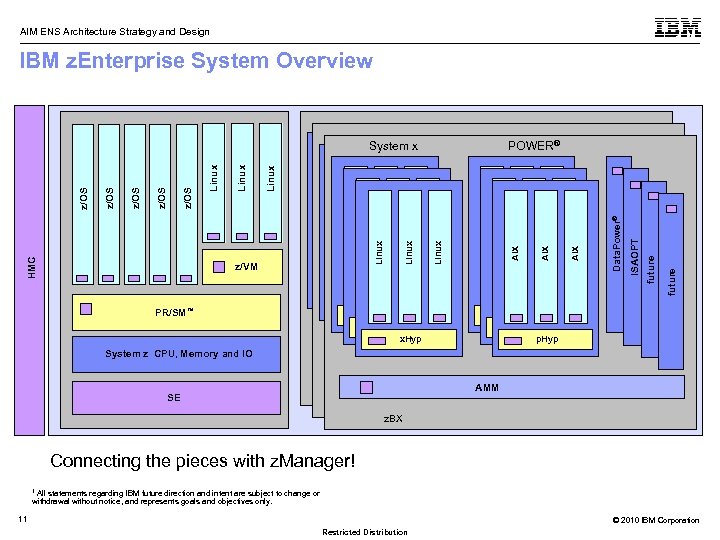 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System Overview POWER® PR/SM™ PR/SM AIX AIX AIX AIX x. Hyp z/VM p. Hyp System z CPU, Memory and IO Z CPU, Memory and IO SE SE z Blade Extension z. BX ISS DP Data. Power® DP Cell ISAOPT Cell DWA future Linux Linux Linux Linux Linux Virtual Machine z/OS HMC Virtual Machine z/OS System x AMM AMM Connecting the pieces with z. Manager! 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. 11 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise System Overview POWER® PR/SM™ PR/SM AIX AIX AIX AIX x. Hyp z/VM p. Hyp System z CPU, Memory and IO Z CPU, Memory and IO SE SE z Blade Extension z. BX ISS DP Data. Power® DP Cell ISAOPT Cell DWA future Linux Linux Linux Linux Linux Virtual Machine z/OS HMC Virtual Machine z/OS System x AMM AMM Connecting the pieces with z. Manager! 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. 11 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
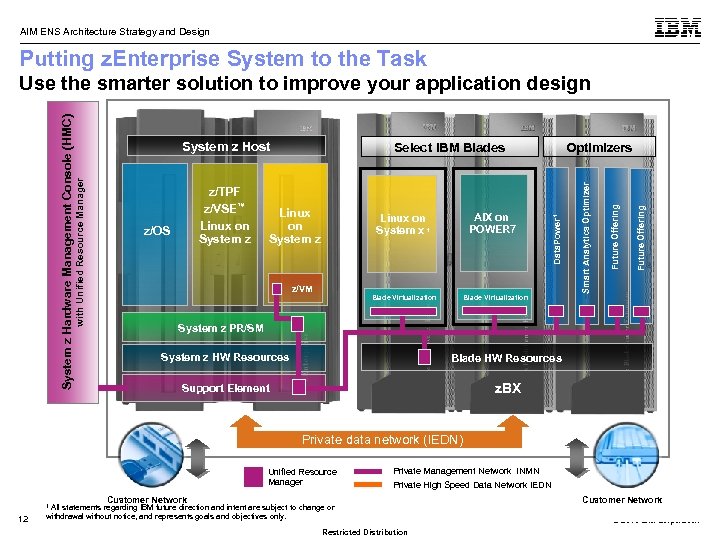 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Putting z. Enterprise System to the Task z/VM Blade Virtualization Future Offering AIX on POWER 7 Linux on System x 1 Future Offering z/OS Linux on System z Optimizers Data. Power 1 z/TPF z/VSE™ Linux on System z Select IBM Blades Smart Analytics Optimizer System z Host with Unified Resource Manager System z Hardware Management Console (HMC) Use the smarter solution to improve your application design System z PR/SM System z HW Resources Blade HW Resources Support Element z. BX Private data network (IEDN) Unified Resource Manager Private Management Network INMN Private High Speed Data Network IEDN Customer Network 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or 12 withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Customer Network © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Putting z. Enterprise System to the Task z/VM Blade Virtualization Future Offering AIX on POWER 7 Linux on System x 1 Future Offering z/OS Linux on System z Optimizers Data. Power 1 z/TPF z/VSE™ Linux on System z Select IBM Blades Smart Analytics Optimizer System z Host with Unified Resource Manager System z Hardware Management Console (HMC) Use the smarter solution to improve your application design System z PR/SM System z HW Resources Blade HW Resources Support Element z. BX Private data network (IEDN) Unified Resource Manager Private Management Network INMN Private High Speed Data Network IEDN Customer Network 1 All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or 12 withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. Customer Network © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
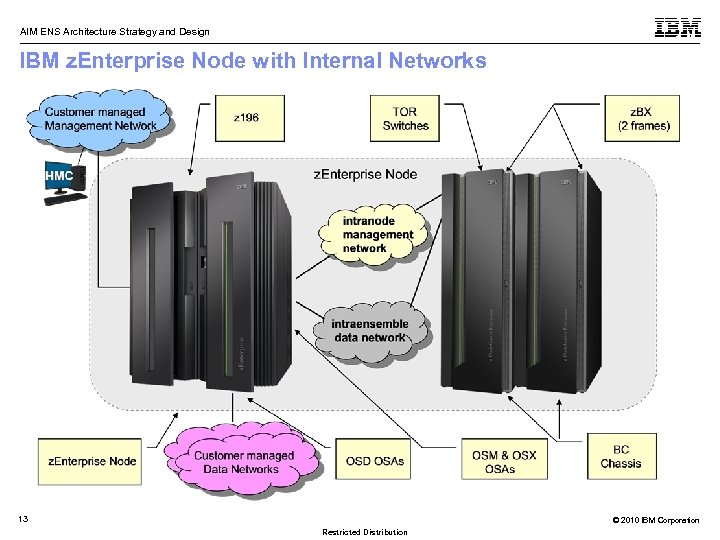 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise Node with Internal Networks 13 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise Node with Internal Networks 13 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
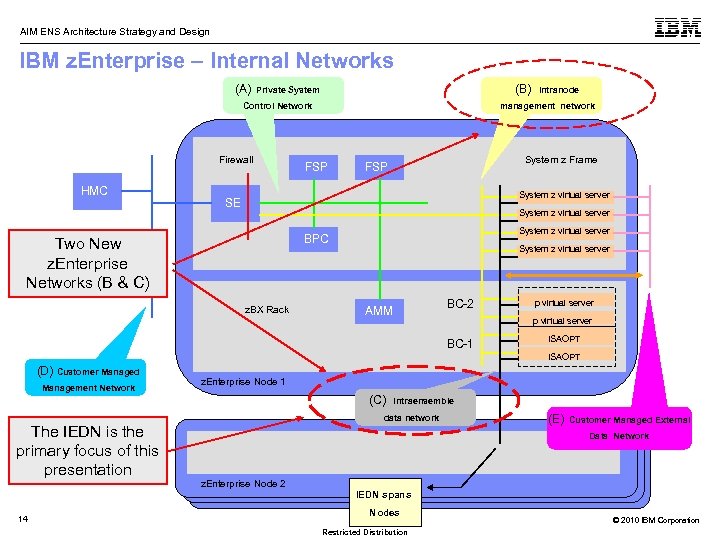 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – Internal Networks (A) Private System (B) intranode Control Network management network Firewall HMC FSP System z Frame FSP System z virtual server SE System z virtual server BPC Two New z. Enterprise Networks (B & C) z. BX Rack System z virtual server AMM BC-2 p virtual server BC-1 ISAOPT (D) Customer Managed Management Network The IEDN is the primary focus of this presentation z. Enterprise Node 1 (C) intraensemble data network (E) Customer Managed External Data Network z. Enterprise Node 2 IEDN spans 14 Nodes Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – Internal Networks (A) Private System (B) intranode Control Network management network Firewall HMC FSP System z Frame FSP System z virtual server SE System z virtual server BPC Two New z. Enterprise Networks (B & C) z. BX Rack System z virtual server AMM BC-2 p virtual server BC-1 ISAOPT (D) Customer Managed Management Network The IEDN is the primary focus of this presentation z. Enterprise Node 1 (C) intraensemble data network (E) Customer Managed External Data Network z. Enterprise Node 2 IEDN spans 14 Nodes Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
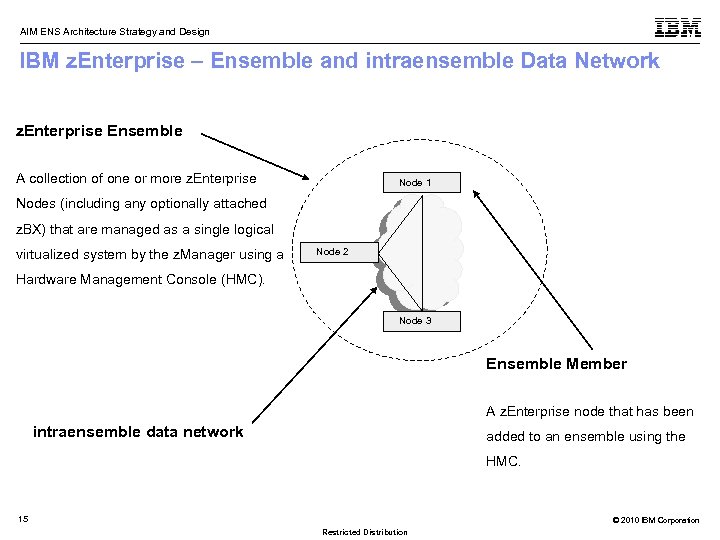 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – Ensemble and intraensemble Data Network z. Enterprise Ensemble A collection of one or more z. Enterprise Node 1 Nodes (including any optionally attached z. BX) that are managed as a single logical virtualized system by the z. Manager using a Node 2 Hardware Management Console (HMC). Node 3 Ensemble Member A z. Enterprise node that has been intraensemble data network added to an ensemble using the HMC. 15 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – Ensemble and intraensemble Data Network z. Enterprise Ensemble A collection of one or more z. Enterprise Node 1 Nodes (including any optionally attached z. BX) that are managed as a single logical virtualized system by the z. Manager using a Node 2 Hardware Management Console (HMC). Node 3 Ensemble Member A z. Enterprise node that has been intraensemble data network added to an ensemble using the HMC. 15 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
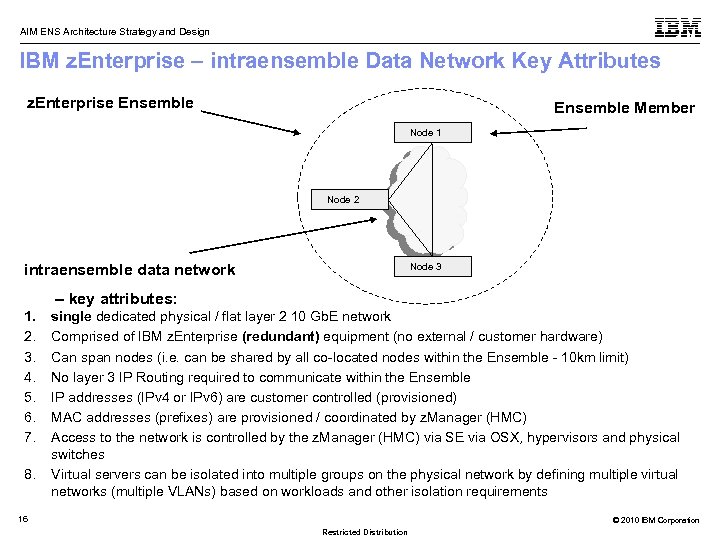 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – intraensemble Data Network Key Attributes z. Enterprise Ensemble Member Node 1 Node 2 intraensemble data network Node 3 – key attributes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. single dedicated physical / flat layer 2 10 Gb. E network Comprised of IBM z. Enterprise (redundant) equipment (no external / customer hardware) Can span nodes (i. e. can be shared by all co-located nodes within the Ensemble - 10 km limit) No layer 3 IP Routing required to communicate within the Ensemble IP addresses (IPv 4 or IPv 6) are customer controlled (provisioned) MAC addresses (prefixes) are provisioned / coordinated by z. Manager (HMC) Access to the network is controlled by the z. Manager (HMC) via SE via OSX, hypervisors and physical switches Virtual servers can be isolated into multiple groups on the physical network by defining multiple virtual networks (multiple VLANs) based on workloads and other isolation requirements 16 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – intraensemble Data Network Key Attributes z. Enterprise Ensemble Member Node 1 Node 2 intraensemble data network Node 3 – key attributes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. single dedicated physical / flat layer 2 10 Gb. E network Comprised of IBM z. Enterprise (redundant) equipment (no external / customer hardware) Can span nodes (i. e. can be shared by all co-located nodes within the Ensemble - 10 km limit) No layer 3 IP Routing required to communicate within the Ensemble IP addresses (IPv 4 or IPv 6) are customer controlled (provisioned) MAC addresses (prefixes) are provisioned / coordinated by z. Manager (HMC) Access to the network is controlled by the z. Manager (HMC) via SE via OSX, hypervisors and physical switches Virtual servers can be isolated into multiple groups on the physical network by defining multiple virtual networks (multiple VLANs) based on workloads and other isolation requirements 16 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
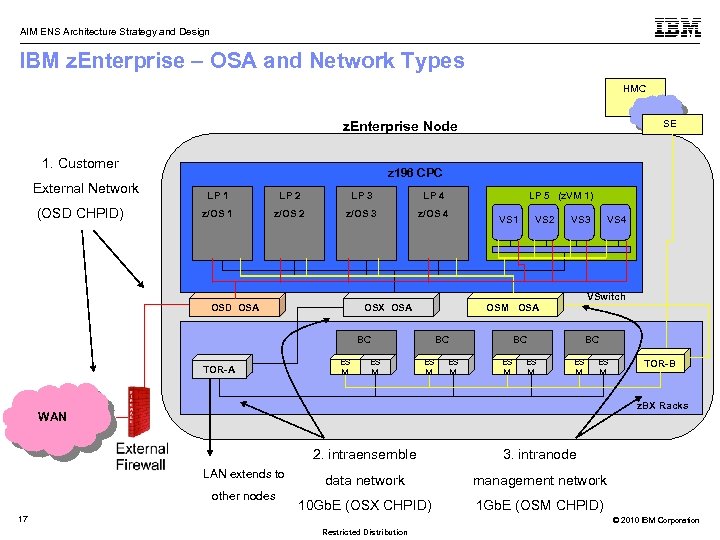 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – OSA and Network Types HMC SE z. Enterprise Node 1. Customer External Network z 196 CPC LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 (OSD CHPID) OSD OSA OSX OSA BC TOR-A LP 5 (z. VM 1) ES M VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VSwitch OSM OSA BC ES M VS 4 BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN 2. intraensemble LAN extends to other nodes 3. intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 17 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design IBM z. Enterprise – OSA and Network Types HMC SE z. Enterprise Node 1. Customer External Network z 196 CPC LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 (OSD CHPID) OSD OSA OSX OSA BC TOR-A LP 5 (z. VM 1) ES M VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VSwitch OSM OSA BC ES M VS 4 BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN 2. intraensemble LAN extends to other nodes 3. intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 17 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
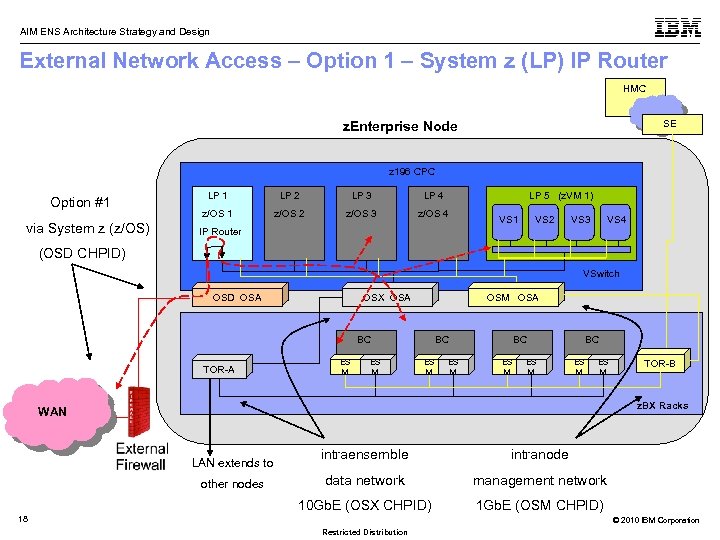 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design External Network Access – Option 1 – System z (LP) IP Router HMC SE z. Enterprise Node z 196 CPC Option #1 via System z (z/OS) (OSD CHPID) LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 LP 5 (z. VM 1) z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VS 4 IP Router VSwitch OSD OSA OSX OSA BC TOR-A ES M OSM OSA BC ES M BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN other nodes intraensemble intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) LAN extends to 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 18 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design External Network Access – Option 1 – System z (LP) IP Router HMC SE z. Enterprise Node z 196 CPC Option #1 via System z (z/OS) (OSD CHPID) LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 LP 5 (z. VM 1) z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VS 4 IP Router VSwitch OSD OSA OSX OSA BC TOR-A ES M OSM OSA BC ES M BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN other nodes intraensemble intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) LAN extends to 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 18 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
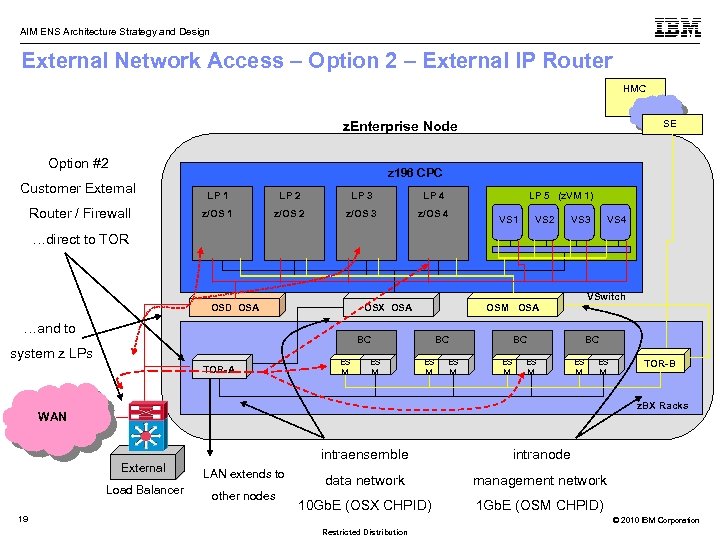 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design External Network Access – Option 2 – External IP Router HMC SE z. Enterprise Node Option #2 z 196 Customer External LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 Router / Firewall …direct to TOR CPC OSD OSA …and to OSX OSA BC system z LPs TOR-A LP 5 (z. VM 1) ES M VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VSwitch OSM OSA BC ES M VS 4 BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN intraensemble External LAN extends to Load Balancer other nodes intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 19 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design External Network Access – Option 2 – External IP Router HMC SE z. Enterprise Node Option #2 z 196 Customer External LP 1 LP 2 LP 3 LP 4 z/OS 1 z/OS 2 z/OS 3 z/OS 4 Router / Firewall …direct to TOR CPC OSD OSA …and to OSX OSA BC system z LPs TOR-A LP 5 (z. VM 1) ES M VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 VSwitch OSM OSA BC ES M VS 4 BC ES M TOR-B z. BX Racks WAN intraensemble External LAN extends to Load Balancer other nodes intranode data network management network 10 Gb. E (OSX CHPID) 1 Gb. E (OSM CHPID) 19 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
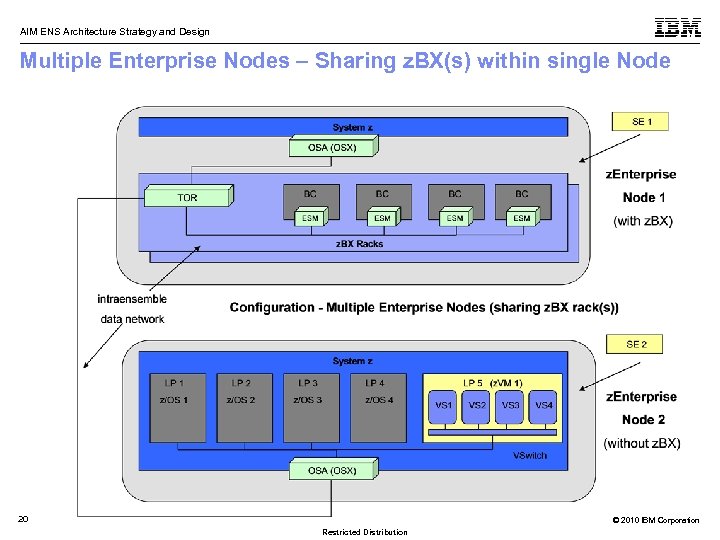 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Multiple Enterprise Nodes – Sharing z. BX(s) within single Node 20 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Multiple Enterprise Nodes – Sharing z. BX(s) within single Node 20 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
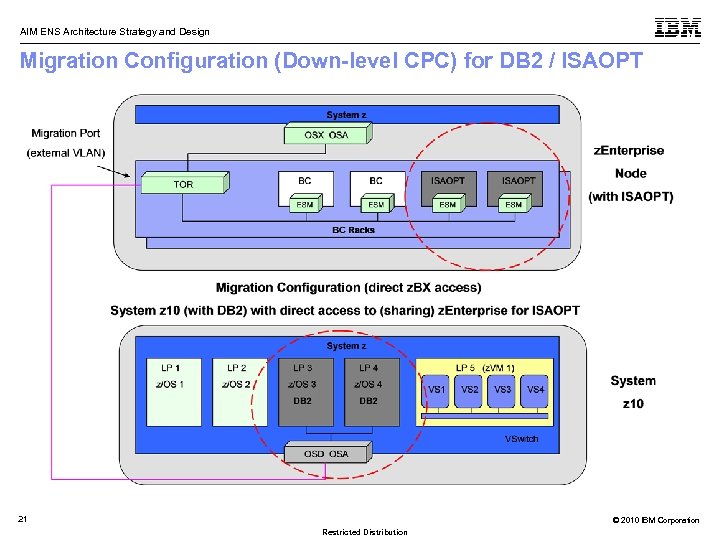 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Migration Configuration (Down-level CPC) for DB 2 / ISAOPT 21 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Migration Configuration (Down-level CPC) for DB 2 / ISAOPT 21 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
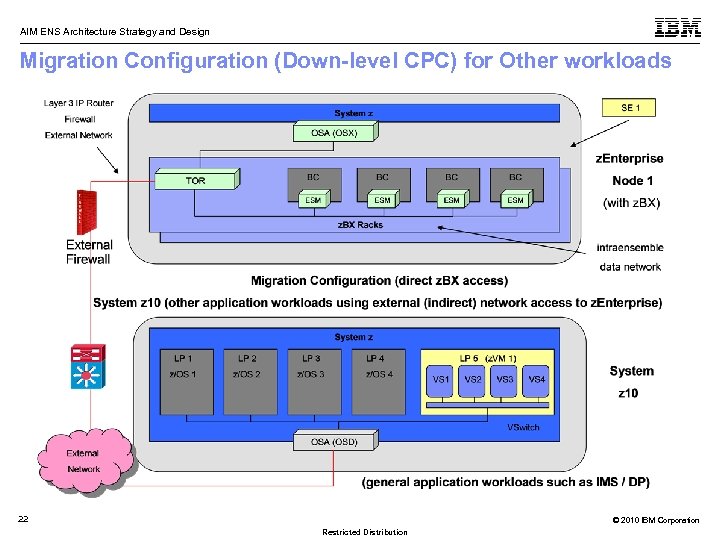 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Migration Configuration (Down-level CPC) for Other workloads 22 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Migration Configuration (Down-level CPC) for Other workloads 22 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
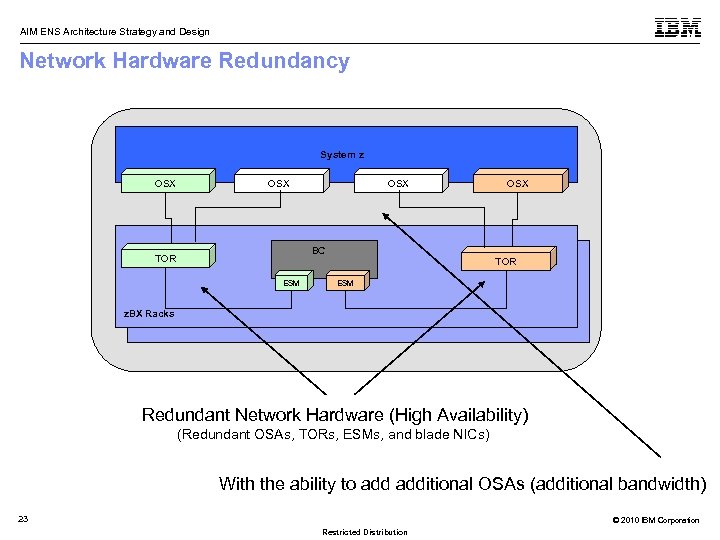 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Network Hardware Redundancy System z OSX TOR OSX BC ESM OSX TOR ESM z. BX Racks Redundant Network Hardware (High Availability) (Redundant OSAs, TORs, ESMs, and blade NICs) With the ability to additional OSAs (additional bandwidth) 23 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Network Hardware Redundancy System z OSX TOR OSX BC ESM OSX TOR ESM z. BX Racks Redundant Network Hardware (High Availability) (Redundant OSAs, TORs, ESMs, and blade NICs) With the ability to additional OSAs (additional bandwidth) 23 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
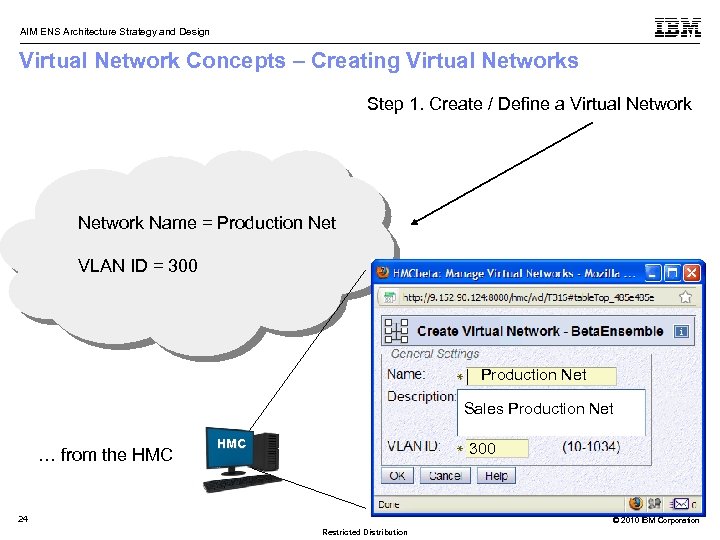 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Virtual Network Concepts – Creating Virtual Networks Step 1. Create / Define a Virtual Network Name = Production Net VLAN ID = 300 Production Net Sales Production Net … from the HMC 300 24 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Virtual Network Concepts – Creating Virtual Networks Step 1. Create / Define a Virtual Network Name = Production Net VLAN ID = 300 Production Net Sales Production Net … from the HMC 300 24 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
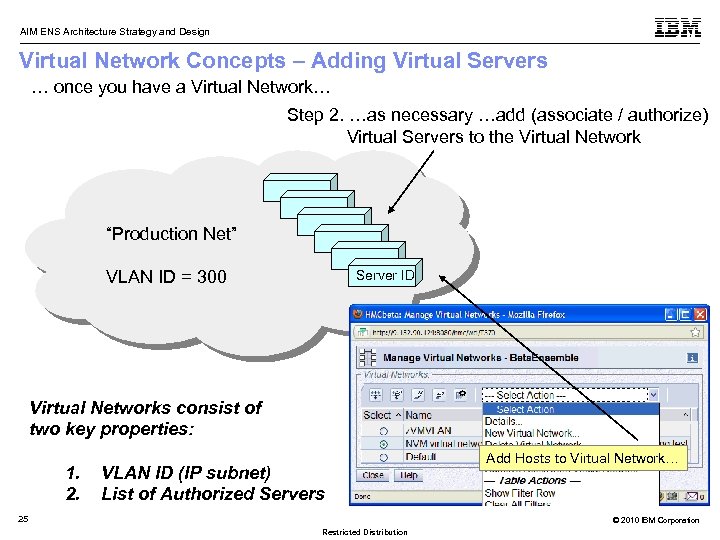 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Virtual Network Concepts – Adding Virtual Servers … once you have a Virtual Network… Step 2. …as necessary …add (associate / authorize) Virtual Servers to the Virtual Network “Production Net” Server ID VLAN ID = 300 Virtual Networks consist of two key properties: 1. 2. VLAN ID (IP subnet) List of Authorized Servers 25 Add Hosts to Virtual Network… © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Virtual Network Concepts – Adding Virtual Servers … once you have a Virtual Network… Step 2. …as necessary …add (associate / authorize) Virtual Servers to the Virtual Network “Production Net” Server ID VLAN ID = 300 Virtual Networks consist of two key properties: 1. 2. VLAN ID (IP subnet) List of Authorized Servers 25 Add Hosts to Virtual Network… © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
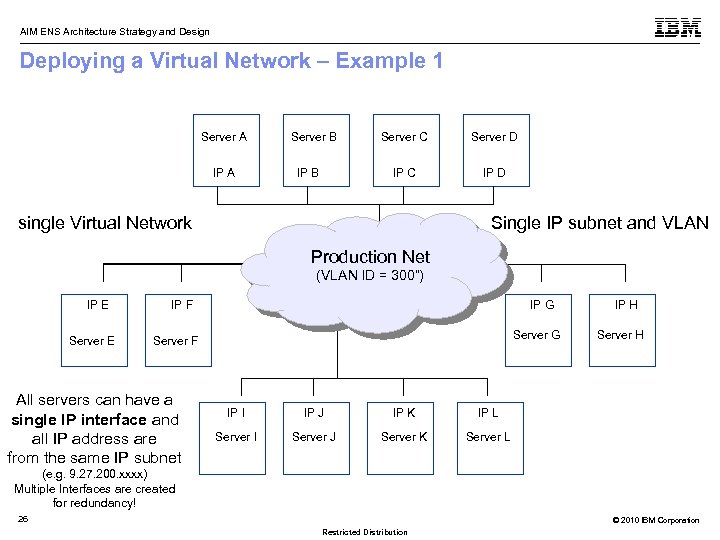 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying a Virtual Network – Example 1 Server A IP A Server B Server D IP C IP B Server C IP D single Virtual Network Single IP subnet and VLAN ID Production Net TOR Switch (VLAN ID = 300”) IP E Server E IP F IP G Server F All servers can have a single IP interface and all IP address are from the same IP subnet IP I IP J IP K Server J Server K Server H IP L Server I IP H Server L (e. g. 9. 27. 200. xxxx) Multiple Interfaces are created for redundancy! 26 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying a Virtual Network – Example 1 Server A IP A Server B Server D IP C IP B Server C IP D single Virtual Network Single IP subnet and VLAN ID Production Net TOR Switch (VLAN ID = 300”) IP E Server E IP F IP G Server F All servers can have a single IP interface and all IP address are from the same IP subnet IP I IP J IP K Server J Server K Server H IP L Server I IP H Server L (e. g. 9. 27. 200. xxxx) Multiple Interfaces are created for redundancy! 26 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
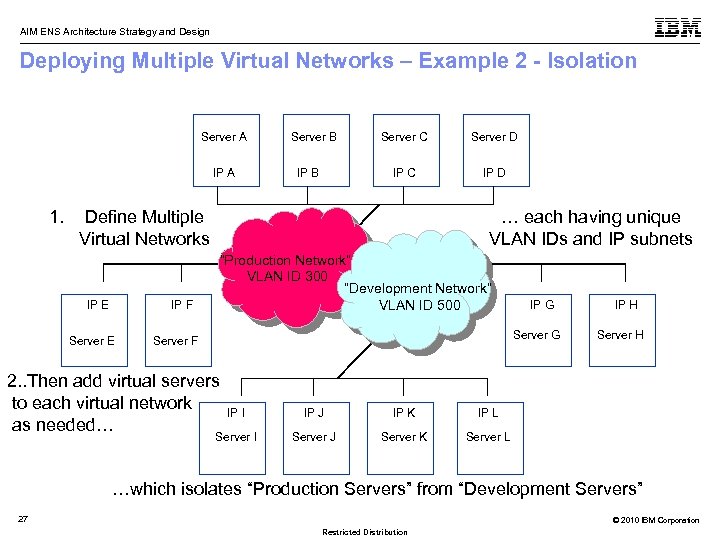 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying Multiple Virtual Networks – Example 2 - Isolation Server A IP A 1. Server B Server D IP C IP B Server C IP D Define Multiple Virtual Networks IP E IP F Server E … each having unique VLAN IDs and IP subnets “Production Network” VLAN ID 300 TOR Switch “Development Network” VLAN ID 500 IP G Server F 2. . Then add virtual servers to each virtual network as needed… IP I IP J IP K Server J Server K Server H IP L Server I IP H Server L …which isolates “Production Servers” from “Development Servers” 27 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying Multiple Virtual Networks – Example 2 - Isolation Server A IP A 1. Server B Server D IP C IP B Server C IP D Define Multiple Virtual Networks IP E IP F Server E … each having unique VLAN IDs and IP subnets “Production Network” VLAN ID 300 TOR Switch “Development Network” VLAN ID 500 IP G Server F 2. . Then add virtual servers to each virtual network as needed… IP I IP J IP K Server J Server K Server H IP L Server I IP H Server L …which isolates “Production Servers” from “Development Servers” 27 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
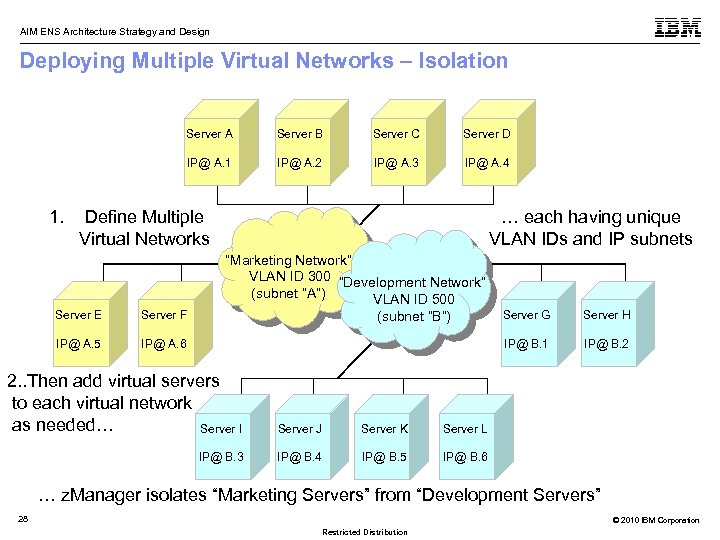 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying Multiple Virtual Networks – Isolation Server A Server C Server D IP@ A. 1 1. Server B IP@ A. 2 IP@ A. 3 IP@ A. 4 Define Multiple Virtual Networks … each having unique VLAN IDs and IP subnets “Marketing Network” VLAN ID 300 TOR Switch “Development Network” (subnet “A”) VLAN ID 500 Server E IP@ A. 5 (subnet “B”) Server F IP@ A. 6 Server J Server K IP@ B. 4 IP@ B. 5 IP@ B. 2 Server L IP@ B. 3 Server H IP@ B. 1 2. . Then add virtual servers to each virtual network as needed… Server I Server G IP@ B. 6 … z. Manager isolates “Marketing Servers” from “Development Servers” 28 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Deploying Multiple Virtual Networks – Isolation Server A Server C Server D IP@ A. 1 1. Server B IP@ A. 2 IP@ A. 3 IP@ A. 4 Define Multiple Virtual Networks … each having unique VLAN IDs and IP subnets “Marketing Network” VLAN ID 300 TOR Switch “Development Network” (subnet “A”) VLAN ID 500 Server E IP@ A. 5 (subnet “B”) Server F IP@ A. 6 Server J Server K IP@ B. 4 IP@ B. 5 IP@ B. 2 Server L IP@ B. 3 Server H IP@ B. 1 2. . Then add virtual servers to each virtual network as needed… Server I Server G IP@ B. 6 … z. Manager isolates “Marketing Servers” from “Development Servers” 28 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
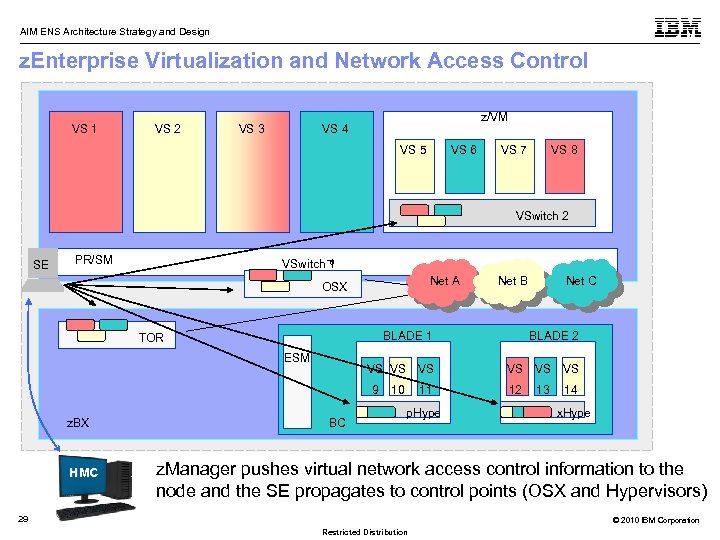 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Virtualization and Network Access Control VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 z/VM VS 4 VS 5 VS 6 VS 7 VS 8 VSwitch 2 PR/SM VSwitch 1 P SE Net A OSX BLADE 2 VS VS VS ESM VS VS VS 9 HMC Net C BLADE 1 TOR z. BX Net B BC 10 11 p. Hype 12 13 14 x. Hype z. Manager pushes virtual network access control information to the node and the SE propagates to control points (OSX and Hypervisors) 29 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design z. Enterprise Virtualization and Network Access Control VS 1 VS 2 VS 3 z/VM VS 4 VS 5 VS 6 VS 7 VS 8 VSwitch 2 PR/SM VSwitch 1 P SE Net A OSX BLADE 2 VS VS VS ESM VS VS VS 9 HMC Net C BLADE 1 TOR z. BX Net B BC 10 11 p. Hype 12 13 14 x. Hype z. Manager pushes virtual network access control information to the node and the SE propagates to control points (OSX and Hypervisors) 29 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
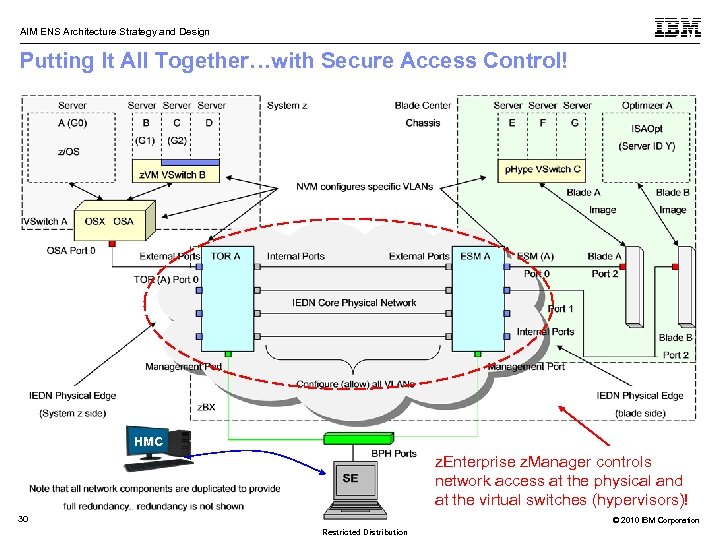 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Putting It All Together…with Secure Access Control! HMC z. Enterprise z. Manager controls network access at the physical and at the virtual switches (hypervisors)! 30 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Putting It All Together…with Secure Access Control! HMC z. Enterprise z. Manager controls network access at the physical and at the virtual switches (hypervisors)! 30 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
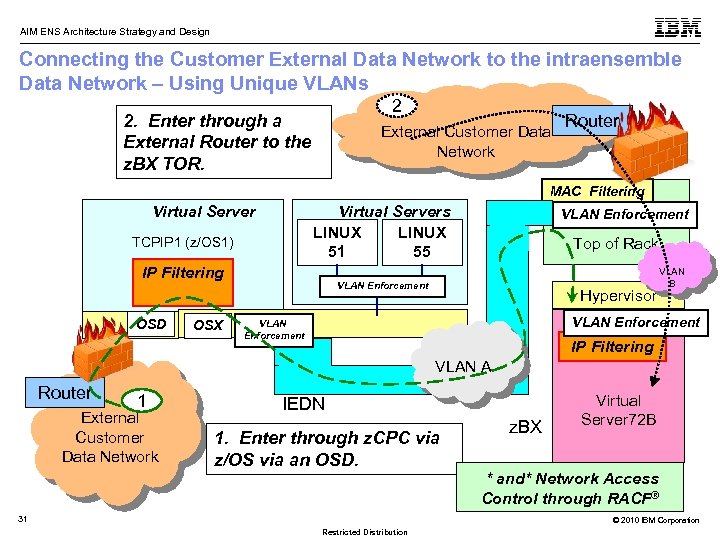 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Connecting the Customer External Data Network to the intraensemble Data Network – Using Unique VLANs 2 2. Enter through a External Router to the z. BX TOR. External Customer Data Network Router MAC Filtering Virtual Servers LINUX 51 55 TCPIP 1 (z/OS 1) IP Filtering OSD OSX VLAN Enforcement Top of Rack VLAN Enforcement Hypervisor VLAN B VLAN Enforcement IP Filtering VLAN A Router 1 External Customer Data Network IEDN 1. Enter through z. CPC via z/OS via an OSD. z. BX Virtual Server 72 B * and* Network Access Control through RACF® 31 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Connecting the Customer External Data Network to the intraensemble Data Network – Using Unique VLANs 2 2. Enter through a External Router to the z. BX TOR. External Customer Data Network Router MAC Filtering Virtual Servers LINUX 51 55 TCPIP 1 (z/OS 1) IP Filtering OSD OSX VLAN Enforcement Top of Rack VLAN Enforcement Hypervisor VLAN B VLAN Enforcement IP Filtering VLAN A Router 1 External Customer Data Network IEDN 1. Enter through z. CPC via z/OS via an OSD. z. BX Virtual Server 72 B * and* Network Access Control through RACF® 31 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
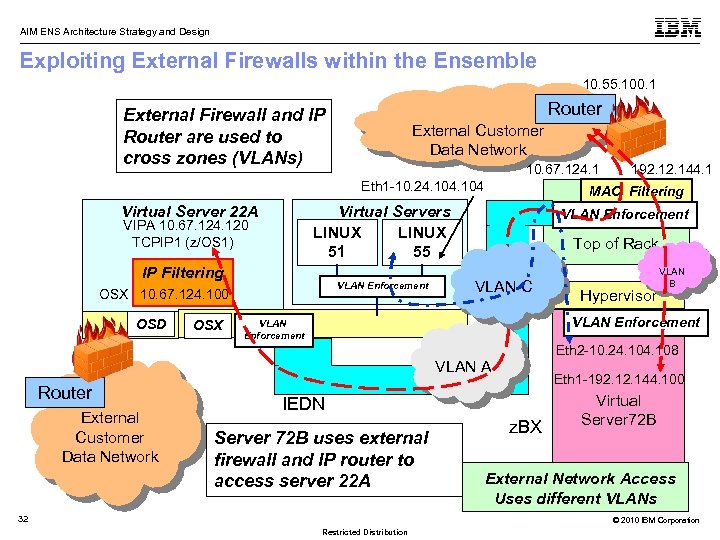 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Exploiting External Firewalls within the Ensemble 10. 55. 100. 1 Router External Firewall and IP Router are used to cross zones (VLANs) External Customer Data Network 10. 67. 124. 1 Eth 1 -10. 24. 104 Virtual Server 22 A IP Filtering VLAN Enforcement OSX 10. 67. 124. 100 OSD OSX MAC Filtering Virtual Servers LINUX 51 55 VIPA 10. 67. 124. 120 TCPIP 1 (z/OS 1) VLAN Enforcement Top of Rack VLAN C External Customer Data Network Hypervisor VLAN B VLAN Enforcement Eth 2 -10. 24. 108 VLAN A Router 192. 144. 1 Eth 1 -192. 144. 100 IEDN Server 72 B uses external firewall and IP router to access server 22 A 32 z. BX Virtual Server 72 B External Network Access Uses different VLANs © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Exploiting External Firewalls within the Ensemble 10. 55. 100. 1 Router External Firewall and IP Router are used to cross zones (VLANs) External Customer Data Network 10. 67. 124. 1 Eth 1 -10. 24. 104 Virtual Server 22 A IP Filtering VLAN Enforcement OSX 10. 67. 124. 100 OSD OSX MAC Filtering Virtual Servers LINUX 51 55 VIPA 10. 67. 124. 120 TCPIP 1 (z/OS 1) VLAN Enforcement Top of Rack VLAN C External Customer Data Network Hypervisor VLAN B VLAN Enforcement Eth 2 -10. 24. 108 VLAN A Router 192. 144. 1 Eth 1 -192. 144. 100 IEDN Server 72 B uses external firewall and IP router to access server 22 A 32 z. BX Virtual Server 72 B External Network Access Uses different VLANs © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
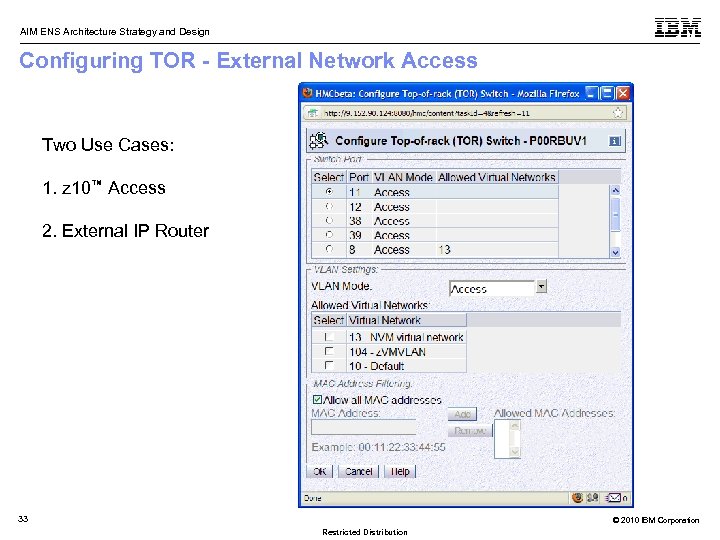 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Configuring TOR - External Network Access Two Use Cases: 1. z 10™ Access 2. External IP Router 33 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Configuring TOR - External Network Access Two Use Cases: 1. z 10™ Access 2. External IP Router 33 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
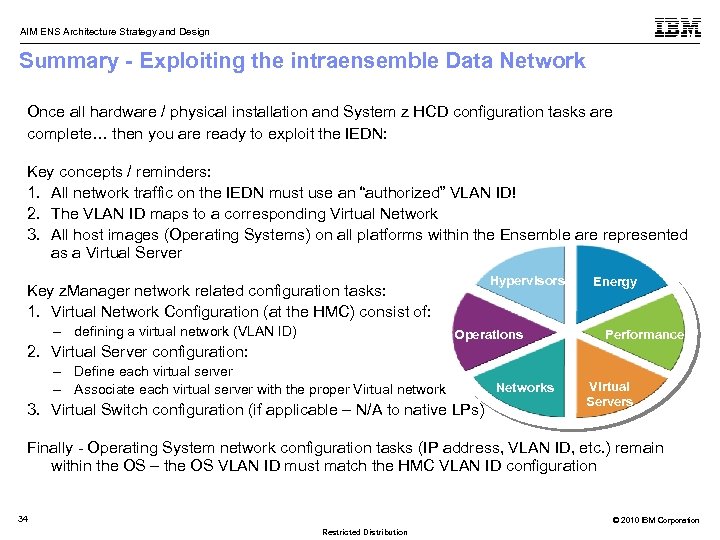 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Summary - Exploiting the intraensemble Data Network Once all hardware / physical installation and System z HCD configuration tasks are complete… then you are ready to exploit the IEDN: Key concepts / reminders: 1. All network traffic on the IEDN must use an “authorized” VLAN ID! 2. The VLAN ID maps to a corresponding Virtual Network 3. All host images (Operating Systems) on all platforms within the Ensemble are represented as a Virtual Server Hypervisors Energy Key z. Manager network related configuration tasks: 1. Virtual Network Configuration (at the HMC) consist of: – defining a virtual network (VLAN ID) Operations 2. Virtual Server configuration: – Define each virtual server – Associate each virtual server with the proper Virtual network 3. Virtual Switch configuration (if applicable – N/A to native LPs) Networks Performance Virtual Servers Finally - Operating System network configuration tasks (IP address, VLAN ID, etc. ) remain within the OS – the OS VLAN ID must match the HMC VLAN ID configuration 34 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Summary - Exploiting the intraensemble Data Network Once all hardware / physical installation and System z HCD configuration tasks are complete… then you are ready to exploit the IEDN: Key concepts / reminders: 1. All network traffic on the IEDN must use an “authorized” VLAN ID! 2. The VLAN ID maps to a corresponding Virtual Network 3. All host images (Operating Systems) on all platforms within the Ensemble are represented as a Virtual Server Hypervisors Energy Key z. Manager network related configuration tasks: 1. Virtual Network Configuration (at the HMC) consist of: – defining a virtual network (VLAN ID) Operations 2. Virtual Server configuration: – Define each virtual server – Associate each virtual server with the proper Virtual network 3. Virtual Switch configuration (if applicable – N/A to native LPs) Networks Performance Virtual Servers Finally - Operating System network configuration tasks (IP address, VLAN ID, etc. ) remain within the OS – the OS VLAN ID must match the HMC VLAN ID configuration 34 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References 35 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References 35 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (White Papers, FAQs, Presentations) § z. Enterprise System Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – www. ibm. com/systems/z/faq § z. Enterprise Network Security White Paper (ZSW 03167 -USEN-00) and Other Resources – www. ibm. com/systems/z/resources (Select “Literature” Entries) – http: //www. ibm. com/common/ssi/cgibin/ssialias? infotype=SA&subtype=WH&appname=STGE_ZS_ZS_USEN&htmlfid=ZSW 03167 USEN &attachment=ZSW 03167 USEN. PDF § IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Parts 1 and 2: Overview and Detail) – w 3. ibm. com/support/techdocs § IBM System z Hardware Management Console Security White Paper – Author Kurt Schroeder (schroedk@us. ibm. com), Sept. 2008 – http: //nascpok. ibm. com/rsf/z. HMCSecurity. Whitepaper. pdf 36 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (White Papers, FAQs, Presentations) § z. Enterprise System Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – www. ibm. com/systems/z/faq § z. Enterprise Network Security White Paper (ZSW 03167 -USEN-00) and Other Resources – www. ibm. com/systems/z/resources (Select “Literature” Entries) – http: //www. ibm. com/common/ssi/cgibin/ssialias? infotype=SA&subtype=WH&appname=STGE_ZS_ZS_USEN&htmlfid=ZSW 03167 USEN &attachment=ZSW 03167 USEN. PDF § IBM z. Enterprise System Network Virtualization, Management, and Security (Parts 1 and 2: Overview and Detail) – w 3. ibm. com/support/techdocs § IBM System z Hardware Management Console Security White Paper – Author Kurt Schroeder (schroedk@us. ibm. com), Sept. 2008 – http: //nascpok. ibm. com/rsf/z. HMCSecurity. Whitepaper. pdf 36 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (Hardware) § z. BX Publications – – – – z. BX Service Guide GC 28 -6884 -01 z. BX Installation Manual (2458 -002) GC 27 -2610 -00 z. BX IMPP (2458 -002) GC 27 -2611 -00 z. BX Service Education SE 245800 z. BX Safety Inspection (for mod 1 and 2) GC 28 -6889 -00 IBM License Agreement for Machine Code SC 28 -6872 -00 Systems Environmental Notices and User Guide Z 125 -5823 -02 Systems Safety Notices G 229 -9054 -02 § Redbooks (www. redbooks. ibm. com) – – – IBM z. Enterprise Technical Introduction, SG 24 -7832 IBM z. Enterprise Technical Guide, SG 24 -7833 IBM z. Enterprise Configuration Setup, SG 24 -7834 IBM z. Enterprise Platform Management, SG 24 -7835 IBM System p® Advanced POWER Virtualizaiton Best Practices, redp 4194 IBM Blade. Center JS 12 and JS 22 Implementation Guide, SG 24 -7655) § z. BX 2458 -002 SAPR Guide – SA 10 -006 2458 TDA Confirmation Form § System z and z. Enterprise – Input/Output Configuration Program User's Guide for ICP IOCP, SB 10 -7037 -08 37 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (Hardware) § z. BX Publications – – – – z. BX Service Guide GC 28 -6884 -01 z. BX Installation Manual (2458 -002) GC 27 -2610 -00 z. BX IMPP (2458 -002) GC 27 -2611 -00 z. BX Service Education SE 245800 z. BX Safety Inspection (for mod 1 and 2) GC 28 -6889 -00 IBM License Agreement for Machine Code SC 28 -6872 -00 Systems Environmental Notices and User Guide Z 125 -5823 -02 Systems Safety Notices G 229 -9054 -02 § Redbooks (www. redbooks. ibm. com) – – – IBM z. Enterprise Technical Introduction, SG 24 -7832 IBM z. Enterprise Technical Guide, SG 24 -7833 IBM z. Enterprise Configuration Setup, SG 24 -7834 IBM z. Enterprise Platform Management, SG 24 -7835 IBM System p® Advanced POWER Virtualizaiton Best Practices, redp 4194 IBM Blade. Center JS 12 and JS 22 Implementation Guide, SG 24 -7655) § z. BX 2458 -002 SAPR Guide – SA 10 -006 2458 TDA Confirmation Form § System z and z. Enterprise – Input/Output Configuration Program User's Guide for ICP IOCP, SB 10 -7037 -08 37 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (Software and Security) § z/OS Ensemble Implementation – – z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 SNA Network Implementation Guide (SC 31 -8777) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 SNA Network Definition Reference (SC 31 -8778) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IP Configuration Guide (SC 31 -8775) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IP Configuration Reference (SC 31 -8776) § IPv 6 Information – z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IPv 6 Network and Application Design Guide (SC 31 -8885) § z/VM Ensemble Implementation • z/VM 6. 1 with Small Programming Enhancement (SPE): CP Planning and Configuration (SC 24 -6083) § Introducing the IBM Security Framework and IBM Security Blueprint to Realize Business-Driven Security; IBM Red. Guide REDP-4528 -00, July 2009 – www. redbooks. ibm. com § Security on the IBM Mainframe, SG 24 -7803 -00 Redbooks®, published 30 April 2010 – www. redbooks. ibm. com § Introduction to the New Mainframe: Security, SG 24 -6776 -00 Redbooks, published 3 April 2007, last updated 26 April 2007 – www. redbooks. ibm. com 38 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design References (Software and Security) § z/OS Ensemble Implementation – – z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 SNA Network Implementation Guide (SC 31 -8777) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 SNA Network Definition Reference (SC 31 -8778) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IP Configuration Guide (SC 31 -8775) z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IP Configuration Reference (SC 31 -8776) § IPv 6 Information – z/OS Communications Server V 1 R 12 IPv 6 Network and Application Design Guide (SC 31 -8885) § z/VM Ensemble Implementation • z/VM 6. 1 with Small Programming Enhancement (SPE): CP Planning and Configuration (SC 24 -6083) § Introducing the IBM Security Framework and IBM Security Blueprint to Realize Business-Driven Security; IBM Red. Guide REDP-4528 -00, July 2009 – www. redbooks. ibm. com § Security on the IBM Mainframe, SG 24 -7803 -00 Redbooks®, published 30 April 2010 – www. redbooks. ibm. com § Introduction to the New Mainframe: Security, SG 24 -6776 -00 Redbooks, published 3 April 2007, last updated 26 April 2007 – www. redbooks. ibm. com 38 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Questions ? ? Thank You! gdente@us. ibm. com ZSP 03433 -USEN-01 39 Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Questions ? ? Thank You! gdente@us. ibm. com ZSP 03433 -USEN-01 39 Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team Restricted Distribution © 2010 IBM Corporation
 AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Questions? - Thank You! sjerry@us. ibm. com Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team 40 ZSP 03439 -USEN-00 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution
AIM ENS Architecture Strategy and Design Questions? - Thank You! sjerry@us. ibm. com Available in Hard Copy Once Presented by the IBM Account Team 40 ZSP 03439 -USEN-00 © 2010 IBM Corporation Restricted Distribution


