363f573d9049495019f00ac85434b648.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 143
 Jeopardy Rules Teams: You may play individually or with your seat partner. Both people should be actively engaged in figuring out and reviewing the answers. Keep your study guide handy so that you can highlight/circle the topics you need to review. Keep your own score. 1
Jeopardy Rules Teams: You may play individually or with your seat partner. Both people should be actively engaged in figuring out and reviewing the answers. Keep your study guide handy so that you can highlight/circle the topics you need to review. Keep your own score. 1
 2
2
 Ecology 3
Ecology 3
 Populations 4
Populations 4
 Global Warming 5
Global Warming 5
 Soil 6
Soil 6
 Parks, Agriculture, Fishery, Forest 7
Parks, Agriculture, Fishery, Forest 7
 Human Interactions 8
Human Interactions 8
 $100 $200 $200 $100 $200 $300 $300 $400 $400 $500 $500 9
$100 $200 $200 $100 $200 $300 $300 $400 $400 $500 $500 9
 Living & nonliving components of an ecosystem. 10
Living & nonliving components of an ecosystem. 10
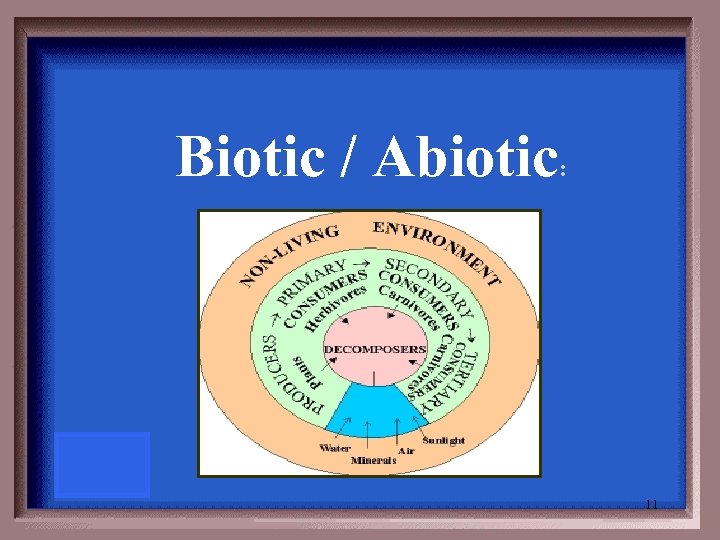 Biotic / Abiotic : 11
Biotic / Abiotic : 11
 Only 10% of the usable energy is transferred because usable energy lost as heat (2 nd law), not all biomass is digested & absorbed, predators expend energy to catch prey. 12
Only 10% of the usable energy is transferred because usable energy lost as heat (2 nd law), not all biomass is digested & absorbed, predators expend energy to catch prey. 12
 Energy flow in food webs: Trophic levels • Keystone Species • Indicator Species 13
Energy flow in food webs: Trophic levels • Keystone Species • Indicator Species 13
 A large distinct terrestrial region having similar climate, soil, plants & animals. Name 4 out of the 8 terrestrial ones. 14
A large distinct terrestrial region having similar climate, soil, plants & animals. Name 4 out of the 8 terrestrial ones. 14
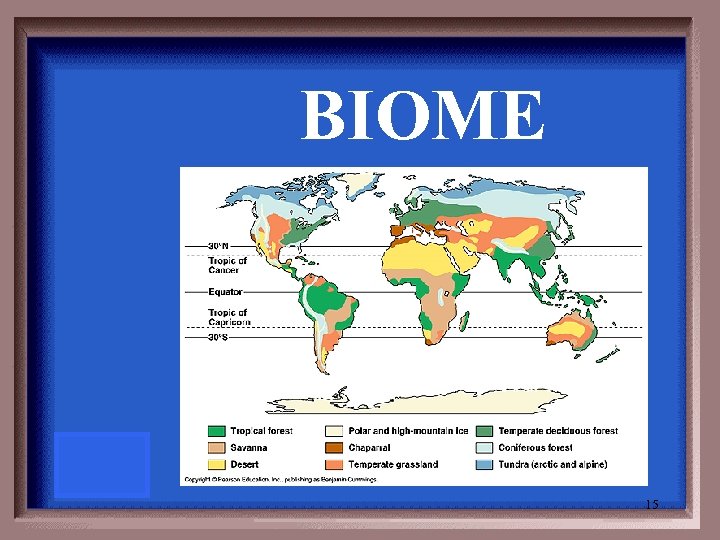 BIOME 15
BIOME 15
 Three Forms of Symbiosis and the form shown below 16
Three Forms of Symbiosis and the form shown below 16
 Mutualism , Commensalism, Parasitism 17
Mutualism , Commensalism, Parasitism 17
 Development of communities in a lifeless area not previously inhabited by life (lava) & Life progresses where soil remains (clear cut forest, fire) 18
Development of communities in a lifeless area not previously inhabited by life (lava) & Life progresses where soil remains (clear cut forest, fire) 18
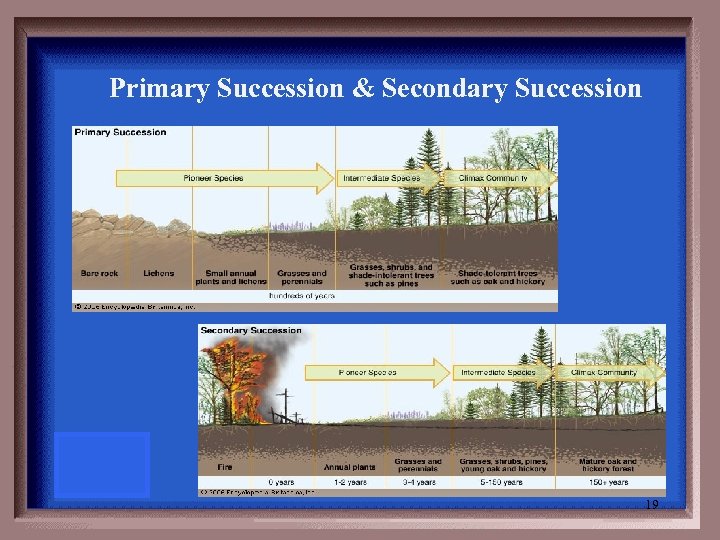 Primary Succession & Secondary Succession 19
Primary Succession & Secondary Succession 19
 The number of individuals that can be sustained in an area. 20
The number of individuals that can be sustained in an area. 20
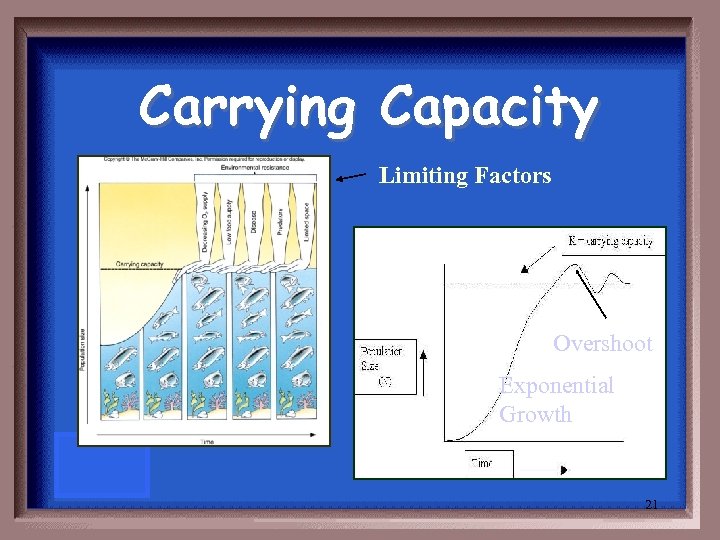 Carrying Capacity Limiting Factors Overshoot Exponential Growth 21
Carrying Capacity Limiting Factors Overshoot Exponential Growth 21
 Strategist: that reproduce early, many small unprotected offspring. 22
Strategist: that reproduce early, many small unprotected offspring. 22
 R strategist: Insects, fish, frogs Short lives High bio potential High reproductive rate Rely on instinct K strategist: Elephants, humans, cougar Low biotic potential Rely on learning Long gestation Lower population growth 23
R strategist: Insects, fish, frogs Short lives High bio potential High reproductive rate Rely on instinct K strategist: Elephants, humans, cougar Low biotic potential Rely on learning Long gestation Lower population growth 23
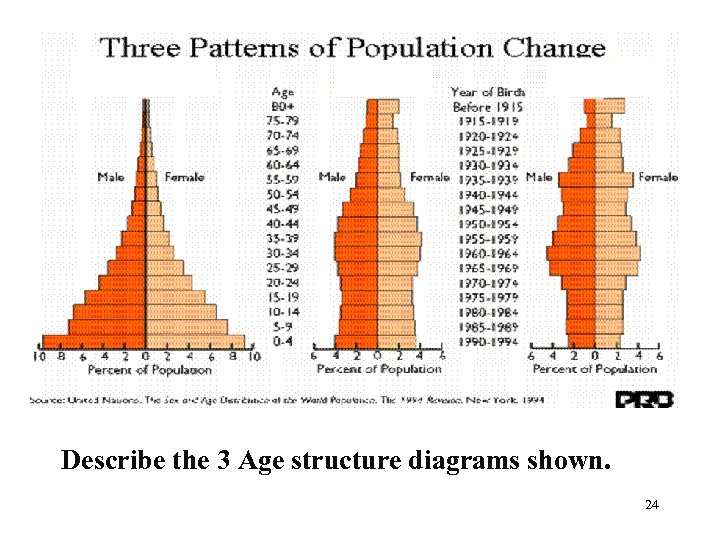 Describe the 3 Age structure diagrams shown. 24
Describe the 3 Age structure diagrams shown. 24
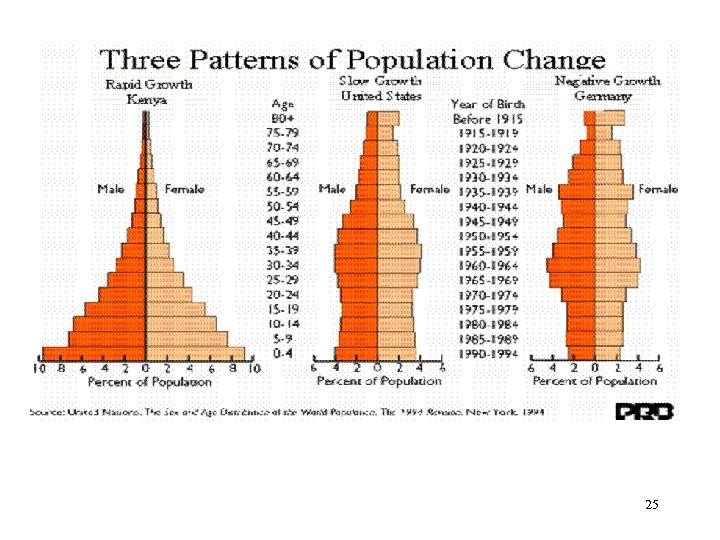 25
25
 1. 1 st & 2 nd most populated countries: 2. World Population: 3. US Population: 4. Most important thing affecting population growth. Answer any 3 of the 4 above. 26
1. 1 st & 2 nd most populated countries: 2. World Population: 3. US Population: 4. Most important thing affecting population growth. Answer any 3 of the 4 above. 26
 1. China & India 2. 7 Billion 3. 350 Million 4. education of woman * Rule of 70 70 divided by the percent growth rate gives you the time to doubling Ex: 70/2%=35 years 27
1. China & India 2. 7 Billion 3. 350 Million 4. education of woman * Rule of 70 70 divided by the percent growth rate gives you the time to doubling Ex: 70/2%=35 years 27
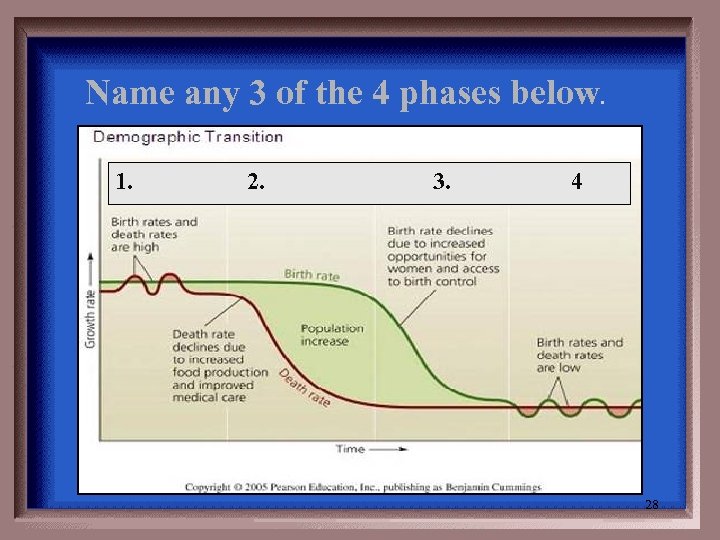 Name any 3 of the 4 phases below. 1. 2. 3. 4 28
Name any 3 of the 4 phases below. 1. 2. 3. 4 28
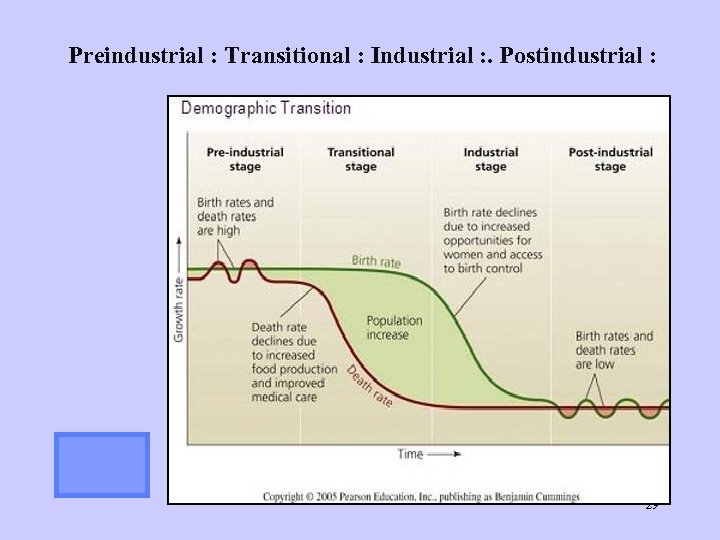 Preindustrial : Transitional : Industrial : . Postindustrial : 29
Preindustrial : Transitional : Industrial : . Postindustrial : 29
 Greenhouse gases: Name 3 of the 6 30
Greenhouse gases: Name 3 of the 6 30
 Examples: H 2 O, CO 2, O 3, methane (CH 4), Nitous oxide (NO 2) & CFCs EFFECT: they trap outgoing infrared (heat) energy causing earth to warm 31
Examples: H 2 O, CO 2, O 3, methane (CH 4), Nitous oxide (NO 2) & CFCs EFFECT: they trap outgoing infrared (heat) energy causing earth to warm 31
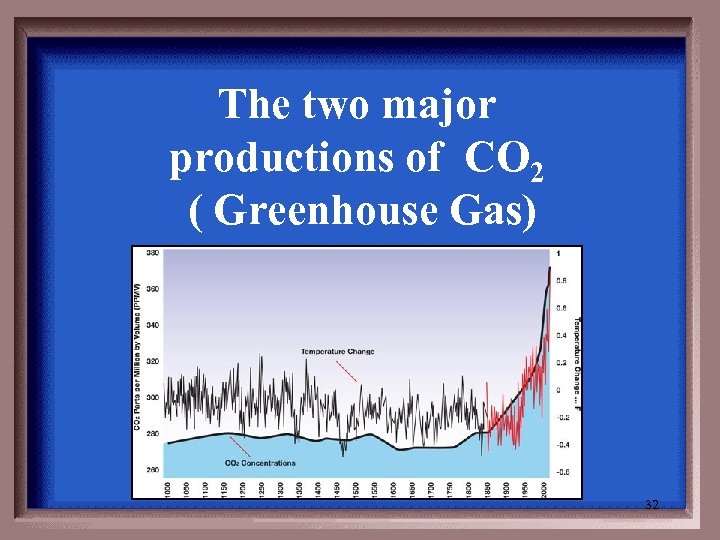 The two major productions of CO 2 ( Greenhouse Gas) 32
The two major productions of CO 2 ( Greenhouse Gas) 32
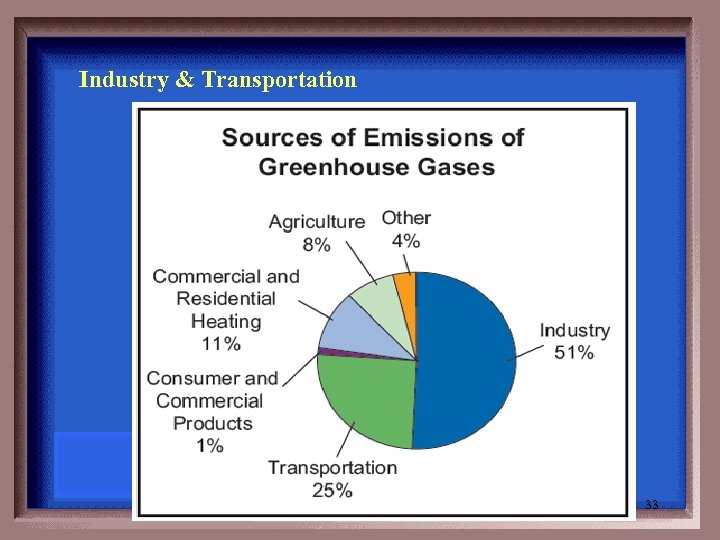 Industry & Transportation 33
Industry & Transportation 33
 Three effects of global warming are: 34
Three effects of global warming are: 34
 Rising sea level (thermal expansion), extreme weather, droughts (famine), extinctions, melting of the polar ice caps. 35
Rising sea level (thermal expansion), extreme weather, droughts (famine), extinctions, melting of the polar ice caps. 35
 36
36
 Name two carbon sinks or ways to sequester CO 2. 37
Name two carbon sinks or ways to sequester CO 2. 37
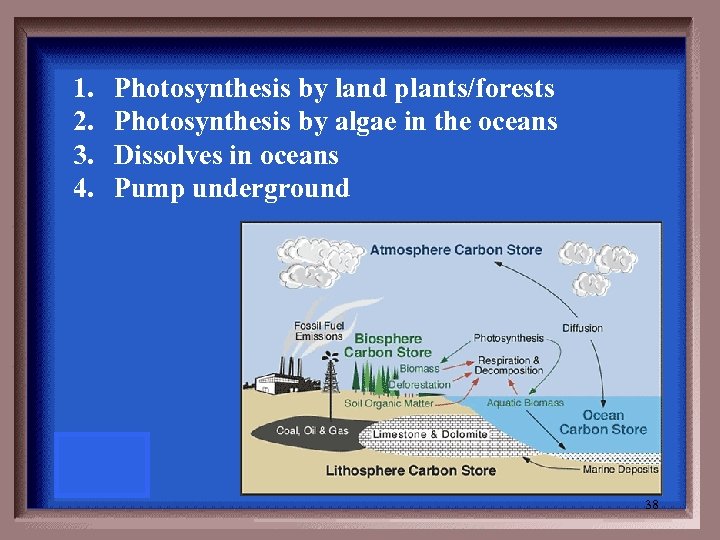 1. 2. 3. 4. Photosynthesis by land plants/forests Photosynthesis by algae in the oceans Dissolves in oceans Pump underground 38
1. 2. 3. 4. Photosynthesis by land plants/forests Photosynthesis by algae in the oceans Dissolves in oceans Pump underground 38
 Protocals: 1. Controlling global warming by setting greenhouse gas emissions targets for developed countries 2. Phase out of ozone deleting substances 39
Protocals: 1. Controlling global warming by setting greenhouse gas emissions targets for developed countries 2. Phase out of ozone deleting substances 39
 Kyoto , Japan & Global Warming CFC”S Montreal, Canada 40
Kyoto , Japan & Global Warming CFC”S Montreal, Canada 40
 The Best Soil Type – 40% silt, 40 % sand & 20 % clay. 41
The Best Soil Type – 40% silt, 40 % sand & 20 % clay. 41
 LOAM By particle size- smallest to largest. (Clay-Silt-Sand) 42
LOAM By particle size- smallest to largest. (Clay-Silt-Sand) 42
 In arid regions, water evaporates leaving salts behind. & Degradation of land in arid and dry subhumid areas, resulting primarily from anthropogenic , natural activities and influenced by climatic variations. 43
In arid regions, water evaporates leaving salts behind. & Degradation of land in arid and dry subhumid areas, resulting primarily from anthropogenic , natural activities and influenced by climatic variations. 43
 Salinization Water logging Desertification 44
Salinization Water logging Desertification 44
 Name 3 things that help fix/prevent soil degradation. 45
Name 3 things that help fix/prevent soil degradation. 45
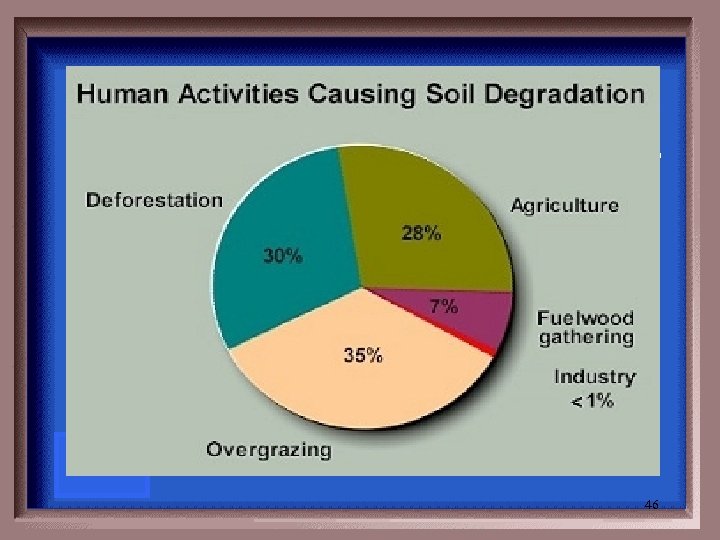 Conservation tillage, Crop rotation, Cover Crops Contour plowing, Terracing, Wind Breaks, Alley Cropping , Organic fertilizers 46
Conservation tillage, Crop rotation, Cover Crops Contour plowing, Terracing, Wind Breaks, Alley Cropping , Organic fertilizers 46
 Soil Profile Name the profile layers below. 47
Soil Profile Name the profile layers below. 47
 Leaf Litter Top Soil / Humus Subsoil Bedrock/ Parent Material 48
Leaf Litter Top Soil / Humus Subsoil Bedrock/ Parent Material 48
 TWO- Parts Part 1 - ______ Revolution usually refers to the transformation of agriculture that began in 1945. Part 2. One of the two acts created to prevent soil degradation. 49
TWO- Parts Part 1 - ______ Revolution usually refers to the transformation of agriculture that began in 1945. Part 2. One of the two acts created to prevent soil degradation. 49
 Green Revolution 1935 Soil Erosion Act 1977 Soil & Water Conservation Act 50
Green Revolution 1935 Soil Erosion Act 1977 Soil & Water Conservation Act 50
 The logging and burning of trees in a forested area. List two reasons for doing so: 51
The logging and burning of trees in a forested area. List two reasons for doing so: 51
 Deforestation Charcoal Lumber Pastures Plantations- Cash Crops Human Settlement. Loss of carbon dioxide (CO 2) up take and when tree rot they produce CO 2 * Soil erosion * Silting of water courses, lakes and dams. * Extinction of species 52 * Desertification
Deforestation Charcoal Lumber Pastures Plantations- Cash Crops Human Settlement. Loss of carbon dioxide (CO 2) up take and when tree rot they produce CO 2 * Soil erosion * Silting of water courses, lakes and dams. * Extinction of species 52 * Desertification
 Mining Describe two methods of surface mining. 53
Mining Describe two methods of surface mining. 53
 Placer Strip mining Mountain top removal Open pit Hydraulic fracturing (Fracking) 54
Placer Strip mining Mountain top removal Open pit Hydraulic fracturing (Fracking) 54
 Which act instigated the need for Environmental Impact Statements to be done before any project affecting federal lands can be started (1970)? 55
Which act instigated the need for Environmental Impact Statements to be done before any project affecting federal lands can be started (1970)? 55
 National Environmental Policy Act: Multiple uses US public land: National Forest & National Resource lands Moderately restricted use land: National Wildlife Refuges Restricted Use lands: National Parks, National Wilderness Preservation System (Sanctuaries) 56
National Environmental Policy Act: Multiple uses US public land: National Forest & National Resource lands Moderately restricted use land: National Wildlife Refuges Restricted Use lands: National Parks, National Wilderness Preservation System (Sanctuaries) 56
 As lakes become more nutrient rich from run off of fertilizers and detergents which add nitrogen and phosphorus to the lakes a process called _______ may occur. 57
As lakes become more nutrient rich from run off of fertilizers and detergents which add nitrogen and phosphorus to the lakes a process called _______ may occur. 57
 Eutrophication 58
Eutrophication 58
 59
59
 FISHERY - The BLUE REVOLUTION 1. What are three forms of large-scale fishing? 2. What is the term for any creatures, such as dolphins and turtles, that are caught unintentionally? 3. List one law that protects some sort of marine life. 60
FISHERY - The BLUE REVOLUTION 1. What are three forms of large-scale fishing? 2. What is the term for any creatures, such as dolphins and turtles, that are caught unintentionally? 3. List one law that protects some sort of marine life. 60
 1. Long line, Drift “gill” net, Sonar, Trawlers, Purse seine. 2. By Catch 3. Magnuson Fishery Act- Over fishiing, ESA, CITES, Marine Mammal Protection Act. 61
1. Long line, Drift “gill” net, Sonar, Trawlers, Purse seine. 2. By Catch 3. Magnuson Fishery Act- Over fishiing, ESA, CITES, Marine Mammal Protection Act. 61
 Which term describes having an abundance of resources and property? Communities that are ______ typically contribute to environmental destruction disproportionally? 62
Which term describes having an abundance of resources and property? Communities that are ______ typically contribute to environmental destruction disproportionally? 62
 Affluence 63
Affluence 63
 The meaning of the following two acronyms in reference to land development. NIMBY & BANANA 64
The meaning of the following two acronyms in reference to land development. NIMBY & BANANA 64
 NIMBY (not in my backyard) BANANA Build Absolutely Nothing Anywhere Near Anything (or Anyone) 65
NIMBY (not in my backyard) BANANA Build Absolutely Nothing Anywhere Near Anything (or Anyone) 65
 Environmental World Views Which world view is represented by this view? “Humans are the most important species but should care for the rest of nature. ” Planetary Management Stewardship Environmental Wisdom 66
Environmental World Views Which world view is represented by this view? “Humans are the most important species but should care for the rest of nature. ” Planetary Management Stewardship Environmental Wisdom 66
 Planetary Management- we are in charge of nature. Stewardship- care for nature. Environmental Wisdom – nature exist for all species. 67
Planetary Management- we are in charge of nature. Stewardship- care for nature. Environmental Wisdom – nature exist for all species. 67
 ___________ Ecology is the science of inventing, establishing and maintaining new habitats to conserve species diversity in places where people live, work or play. * changing for the better a relationship 68
___________ Ecology is the science of inventing, establishing and maintaining new habitats to conserve species diversity in places where people live, work or play. * changing for the better a relationship 68
 Reconciliation Ecology Conservation: allows the use of resources in a responsible manner. Preservation: setting aside areas & protecting them from human activities. Utilitarianism is the belief that something is right if it produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people for the longest time. 69
Reconciliation Ecology Conservation: allows the use of resources in a responsible manner. Preservation: setting aside areas & protecting them from human activities. Utilitarianism is the belief that something is right if it produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people for the longest time. 69
 A dilemma in which multiple individuals acting independently in their own self-interest can ultimately destroy a shared limited resource even when it is clear that it is not in anyone's long term interest for this to happen. * Give two examples of a “Global Common”. 70
A dilemma in which multiple individuals acting independently in their own self-interest can ultimately destroy a shared limited resource even when it is clear that it is not in anyone's long term interest for this to happen. * Give two examples of a “Global Common”. 70
 The Tragedy of the Commons Garret Hardin Atmosphere & Oceans are used by all and owned by none. 71
The Tragedy of the Commons Garret Hardin Atmosphere & Oceans are used by all and owned by none. 71
 72
72
 73
73
 Mining 74
Mining 74
 Water/Treatment 75
Water/Treatment 75
 Energy 76
Energy 76
 Toxins 77
Toxins 77
 Pollution 78
Pollution 78
 MISCELLANEOUS 79
MISCELLANEOUS 79
 $200 $400 $400 $200 $400 $600 $600 $800 $800 $1000 $1000 80
$200 $400 $400 $200 $400 $600 $600 $800 $800 $1000 $1000 80
 ACT /LAW -requires coal strip mines to reclaim the land. (SMCRA) 81
ACT /LAW -requires coal strip mines to reclaim the land. (SMCRA) 81
 Surface Mining Control & Reclamation Act: 82
Surface Mining Control & Reclamation Act: 82
 1. Type of mining that is cheaper & can remove more minerals, less hazardous to workers. 2. Give 2 examples 83
1. Type of mining that is cheaper & can remove more minerals, less hazardous to workers. 2. Give 2 examples 83
 Surface Mining Examples. Strip Contour Strip Open pit Mountain top removal 84
Surface Mining Examples. Strip Contour Strip Open pit Mountain top removal 84
 Steps in coal formation: a. b. c. d. anthracite, peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite peat, , peat, bituminous. lignite, , anthracite peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite 85
Steps in coal formation: a. b. c. d. anthracite, peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite peat, , peat, bituminous. lignite, , anthracite peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite 85
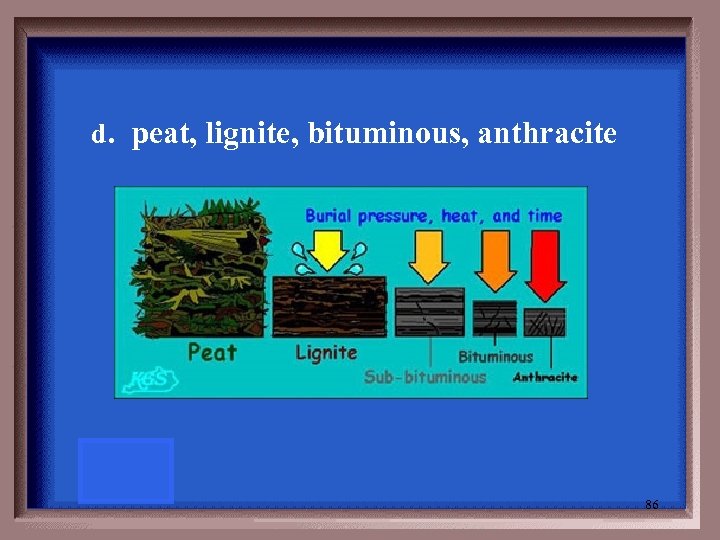 d. peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite 86
d. peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite 86
 ROCK CYCLE The three major types of rocks are 87
ROCK CYCLE The three major types of rocks are 87
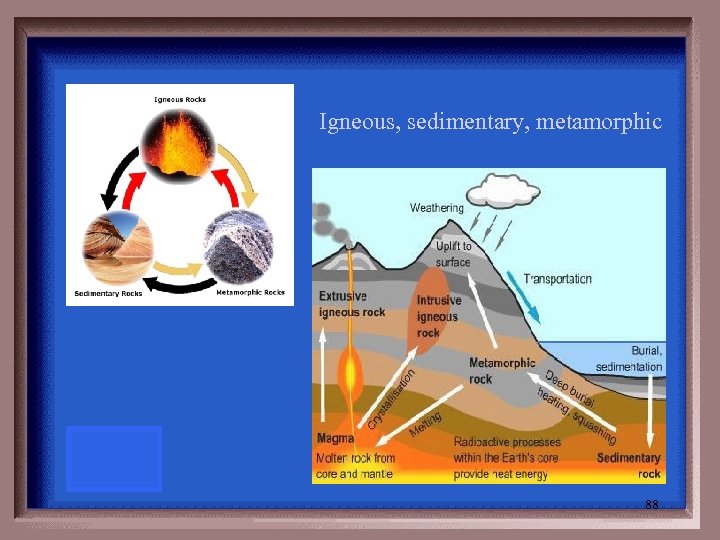 Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic 88
Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic 88
 After ore is mined , the unusable part ( ______ ) that remains is placed in piles called _____. A. B. C. D. Waste , Overburden Spoil, Seam Waste Leachate , Tailings Spoil , Tailings
After ore is mined , the unusable part ( ______ ) that remains is placed in piles called _____. A. B. C. D. Waste , Overburden Spoil, Seam Waste Leachate , Tailings Spoil , Tailings
 D. Spoil , Tailings Mine tailings often include sulfide compounds. ACID DRAINAGE 90
D. Spoil , Tailings Mine tailings often include sulfide compounds. ACID DRAINAGE 90
 _______ % of water pollution in the US come from soil erosion, atmospheric deposition and * surface run off. 25 % , 33 % 55% , 75 % 91
_______ % of water pollution in the US come from soil erosion, atmospheric deposition and * surface run off. 25 % , 33 % 55% , 75 % 91
 75% 95% of water pollution in developing countries come from raw sewage. (high population growth without the money for treatment plants) 92
75% 95% of water pollution in developing countries come from raw sewage. (high population growth without the money for treatment plants) 92
 __________ Act : set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways. . aim to make surface waters swimmable and fishable. 93
__________ Act : set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways. . aim to make surface waters swimmable and fishable. 93
 Clean Water Act 1. 5 billion people lack access to clean drinking water and 3 billion people lack good sanitation need to prevent communicable diseases from spreading. 94
Clean Water Act 1. 5 billion people lack access to clean drinking water and 3 billion people lack good sanitation need to prevent communicable diseases from spreading. 94
 Sources of Pollution • ________ pollution sources (e. g. , factories, sewage treatment plants, mines, oil wells, oil tankers) (* Identifiable) 95
Sources of Pollution • ________ pollution sources (e. g. , factories, sewage treatment plants, mines, oil wells, oil tankers) (* Identifiable) 95
 Point Sources • Nonpoint sources (e. g. , acid deposition, substances picked up in runoff, seepage into groundwater) • Agriculture is largest source of water pollution in the U. S. (64% of pollutants into streams and 57% of pollutants entering lakes 96
Point Sources • Nonpoint sources (e. g. , acid deposition, substances picked up in runoff, seepage into groundwater) • Agriculture is largest source of water pollution in the U. S. (64% of pollutants into streams and 57% of pollutants entering lakes 96
 GROUND WATER Define the terms for: 1. Any water-bearing layer in the ground. 2. Near the coast, over pumping of groundwater causes saltwater to move into the well. 97
GROUND WATER Define the terms for: 1. Any water-bearing layer in the ground. 2. Near the coast, over pumping of groundwater causes saltwater to move into the well. 97
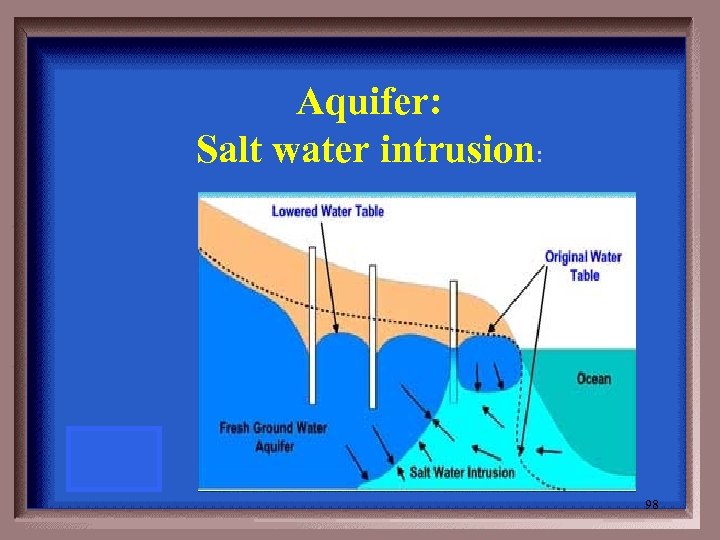 Aquifer: Salt water intrusion: 98
Aquifer: Salt water intrusion: 98
 The 3 major stages of Water Treatment Stage and Primary action. 99
The 3 major stages of Water Treatment Stage and Primary action. 99
 Primary (mechanical process) – filters out debris through screens and by allowing it to settle out in a settling tank Secondary (biological process) – uses aerobic and anaerobic bacteria to remove organic wastes, includes: trickling filters, activated sludge process (where bacteria degrades wastes) Combined w/primary, get out: most suspended particles, oxygen demanding wastes, toxic metal compounds, and SOME phosphates and nitrates… Tertiary (chemical process) – very costly, uses membranes for: reverse osmosis, microfiltration, ultrafiltration After the last process, water is bleached w/chlorine to disinfect and then released… 100
Primary (mechanical process) – filters out debris through screens and by allowing it to settle out in a settling tank Secondary (biological process) – uses aerobic and anaerobic bacteria to remove organic wastes, includes: trickling filters, activated sludge process (where bacteria degrades wastes) Combined w/primary, get out: most suspended particles, oxygen demanding wastes, toxic metal compounds, and SOME phosphates and nitrates… Tertiary (chemical process) – very costly, uses membranes for: reverse osmosis, microfiltration, ultrafiltration After the last process, water is bleached w/chlorine to disinfect and then released… 100
 An appliance operates at 120 volts and 10. 0 amps for 1 hour. How many kilowatt hours does it use in that hour? ( Watt-hours = volts x amps x time ) (A) 1. 2 kilowatt hours (B) 12 kilowatt hours (C) 1. 2 watt hours (D) 120 watt hours (E). 1200 watt hours 101
An appliance operates at 120 volts and 10. 0 amps for 1 hour. How many kilowatt hours does it use in that hour? ( Watt-hours = volts x amps x time ) (A) 1. 2 kilowatt hours (B) 12 kilowatt hours (C) 1. 2 watt hours (D) 120 watt hours (E). 1200 watt hours 101
 1. 2 kilowatt-hours 1 Watt = 1 J / sec (Watts = Joules/time) Watts (x) Time= k. Wh kilo=1000 If you see Kw-hr, that is a measure of ENERGY (if you want to convert JOULES to WATTS, you need to divide it by TIME) 102
1. 2 kilowatt-hours 1 Watt = 1 J / sec (Watts = Joules/time) Watts (x) Time= k. Wh kilo=1000 If you see Kw-hr, that is a measure of ENERGY (if you want to convert JOULES to WATTS, you need to divide it by TIME) 102
 1. A Car that runs on gas and electricity. 2. The meaning of CAFE. 103
1. A Car that runs on gas and electricity. 2. The meaning of CAFE. 103
 HYBRID Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards 104
HYBRID Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards 104
 Three Forms of Non-renewable energy sources. (Fossil Fuels) In order of World Wide consumption. 105
Three Forms of Non-renewable energy sources. (Fossil Fuels) In order of World Wide consumption. 105
 OIL-World reserves and global demand Saudi Arabia – 26% - MOST, then Iraq, Kuwait, Iran… 13 countries w/the most reserves make up OPEC – set prices (many are located in unstable areas of the world US uses the most – 26%, then Japan, then China. COAL- World reserves – US (biggest, 66%), then Russia, China have largest supply Global demand – world’s most abundant fossil fuel – 225 y at current rate. NATURAL GAS- “cleanest” World reserves – 42% in Russia and Kazakhstan, then Iran, Qatar. Global demand – 125 y of potential reserves 106
OIL-World reserves and global demand Saudi Arabia – 26% - MOST, then Iraq, Kuwait, Iran… 13 countries w/the most reserves make up OPEC – set prices (many are located in unstable areas of the world US uses the most – 26%, then Japan, then China. COAL- World reserves – US (biggest, 66%), then Russia, China have largest supply Global demand – world’s most abundant fossil fuel – 225 y at current rate. NATURAL GAS- “cleanest” World reserves – 42% in Russia and Kazakhstan, then Iran, Qatar. Global demand – 125 y of potential reserves 106
 List 4 forms of Renewable Energy Sources. 107
List 4 forms of Renewable Energy Sources. 107
 Wind- fastest growing source of energy. Wind- Solar- Heat & Photovoltaic Geothermal- Heat from the earth. Hydroelectric-Dams, Tides, Waves Biofuels- Corn , Soy beans. Hydrogen Fuel Cells- “future” 108
Wind- fastest growing source of energy. Wind- Solar- Heat & Photovoltaic Geothermal- Heat from the earth. Hydroelectric-Dams, Tides, Waves Biofuels- Corn , Soy beans. Hydrogen Fuel Cells- “future” 108
 In addition to CO 2, these are two of the main emissions from coalfired power plants. 109
In addition to CO 2, these are two of the main emissions from coalfired power plants. 109
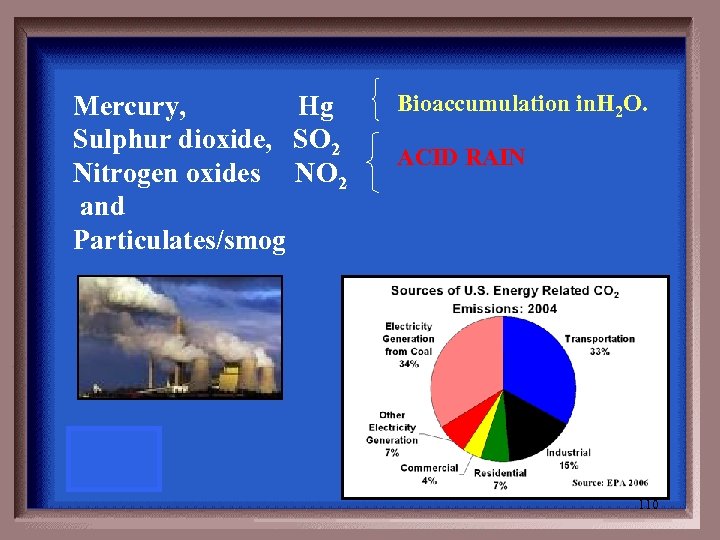 Mercury, Hg Sulphur dioxide, SO 2 Nitrogen oxides NO 2 and Particulates/smog Bioaccumulation in. H 2 O. ACID RAIN 110
Mercury, Hg Sulphur dioxide, SO 2 Nitrogen oxides NO 2 and Particulates/smog Bioaccumulation in. H 2 O. ACID RAIN 110
 LD 50 111
LD 50 111
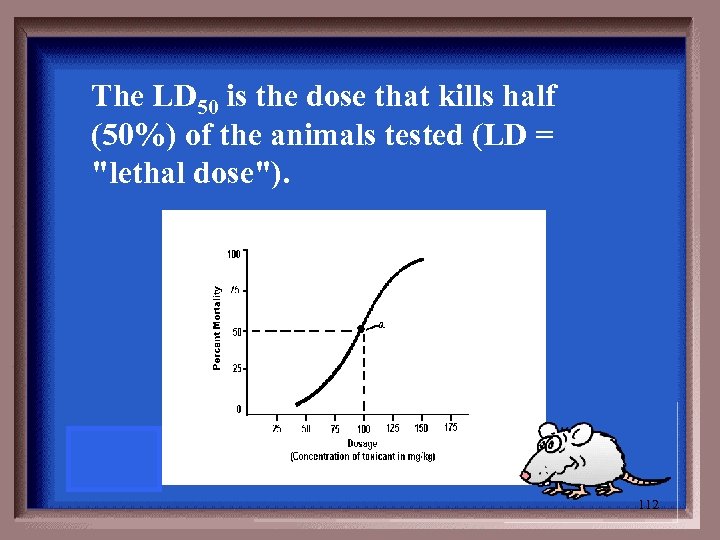 The LD 50 is the dose that kills half (50%) of the animals tested (LD = "lethal dose"). 112
The LD 50 is the dose that kills half (50%) of the animals tested (LD = "lethal dose"). 112
 Name two alternatives / solutions other than pesticides to Control Pests 113
Name two alternatives / solutions other than pesticides to Control Pests 113
 1. Crop rotation 2. Poly culture. 3. Planting trap crops 4. Genetically Resistant Plants 5. Using Natural Enemies to Help Control Pests: 6. Using Biopesticides to Control Pests 7. Insect Birth Control, Sex Attractants, and Hormones 8. Hot Water: The ‘Aqua Heat’ 9. Radiation: 10. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): 114
1. Crop rotation 2. Poly culture. 3. Planting trap crops 4. Genetically Resistant Plants 5. Using Natural Enemies to Help Control Pests: 6. Using Biopesticides to Control Pests 7. Insect Birth Control, Sex Attractants, and Hormones 8. Hot Water: The ‘Aqua Heat’ 9. Radiation: 10. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): 114
 The name of the book and author written about DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane ) in 1962. 115
The name of the book and author written about DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane ) in 1962. 115
 In 1962, Silent Spring by American biologist Rachel Carson * Cats in Borneo & DDT 116
In 1962, Silent Spring by American biologist Rachel Carson * Cats in Borneo & DDT 116
 What is one benefit and one risk of using pesticides. (+) (-) 117
What is one benefit and one risk of using pesticides. (+) (-) 117
 Benefits: 1. Save human lives 2. Increase profits for farmers 3. Increase food supplies/lower cost 4. work faster/better than alternatives 5. when used properly/risks are less than benefits Risks: 1. Genetic resistance to pesticides **BIGGEST 2. Broad-spectrum insecticides also kill natural predators/parasites. 3. Pesticides don’t stay put. 4. Can threaten human health 118
Benefits: 1. Save human lives 2. Increase profits for farmers 3. Increase food supplies/lower cost 4. work faster/better than alternatives 5. when used properly/risks are less than benefits Risks: 1. Genetic resistance to pesticides **BIGGEST 2. Broad-spectrum insecticides also kill natural predators/parasites. 3. Pesticides don’t stay put. 4. Can threaten human health 118
 What is FIFRA? 119
What is FIFRA? 119
 Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act – requires EPA approval for use of all commercial pesticides EPA sets tolerance level specifying amount of toxic pesticide that can remain on crops that people eat Banned: most chlorinated hydrocarbons, several carbamates /organophosphates 120
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act – requires EPA approval for use of all commercial pesticides EPA sets tolerance level specifying amount of toxic pesticide that can remain on crops that people eat Banned: most chlorinated hydrocarbons, several carbamates /organophosphates 120
 Term used to describe the following condition (s)- cities are warmer, rainier, foggier, cloudier than suburbs and rural areas b/c of heat generated by multiple pollutants (cars, factories, …) in the area. 121
Term used to describe the following condition (s)- cities are warmer, rainier, foggier, cloudier than suburbs and rural areas b/c of heat generated by multiple pollutants (cars, factories, …) in the area. 121
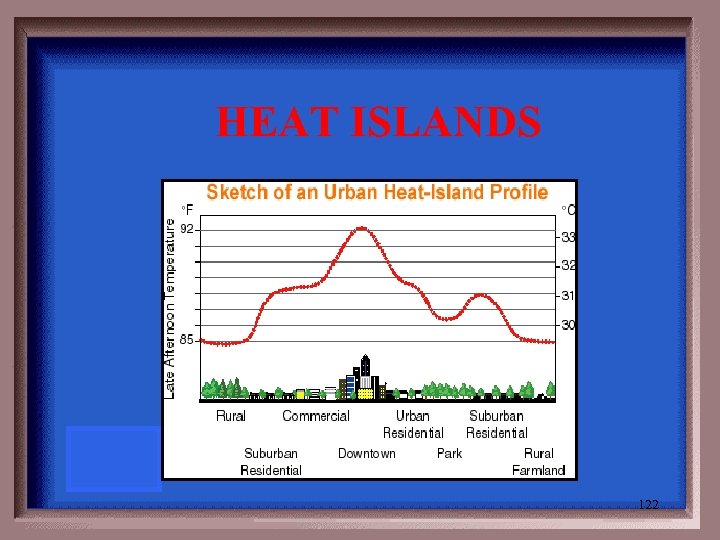 HEAT ISLANDS 122
HEAT ISLANDS 122
 Which of the following is not a form of indoor air pollution? A) Asbestos B) Tobacco smoke C) Formaldehyde D) Radon E) Brown Air Smog 123
Which of the following is not a form of indoor air pollution? A) Asbestos B) Tobacco smoke C) Formaldehyde D) Radon E) Brown Air Smog 123
 Many pollutant level are 2 -5 x higher inside than outside, leads to higher risk of cancer and costs $$ b/c of absenteeism, some main ones: -Asbestos (from pipe insulation, floor tiles) – can cause lung cancer -# 1 Tobacco smoke (from cigarettes) – can cause lung cancer -Formaldehyde (from furniture stuffing, insulation) – throat/lung irritation -Radon (from radioactive soil near foundation) – causes lung cancer -New Building syndrome – being in new buildings causes sickness b/c of reduced air exchange, chemicals from new carpets/furniture. 124
Many pollutant level are 2 -5 x higher inside than outside, leads to higher risk of cancer and costs $$ b/c of absenteeism, some main ones: -Asbestos (from pipe insulation, floor tiles) – can cause lung cancer -# 1 Tobacco smoke (from cigarettes) – can cause lung cancer -Formaldehyde (from furniture stuffing, insulation) – throat/lung irritation -Radon (from radioactive soil near foundation) – causes lung cancer -New Building syndrome – being in new buildings causes sickness b/c of reduced air exchange, chemicals from new carpets/furniture. 124
 The 5 R’s of waste reduction. 125
The 5 R’s of waste reduction. 125
 Reduce Reuse Recycle Repurpose Refuse * Re-buy ? 126
Reduce Reuse Recycle Repurpose Refuse * Re-buy ? 126
 Is the increase in concentration of a substance, such as the pesticide DDT, that occurs in a food chain as a consequence of eating at a higher trophic layer. Occurs within a trophic level, and is the increase in concentration of a substance in an individuals' tissues due to uptake from food and sediments in an aquatic milieu. FOOD 127
Is the increase in concentration of a substance, such as the pesticide DDT, that occurs in a food chain as a consequence of eating at a higher trophic layer. Occurs within a trophic level, and is the increase in concentration of a substance in an individuals' tissues due to uptake from food and sediments in an aquatic milieu. FOOD 127
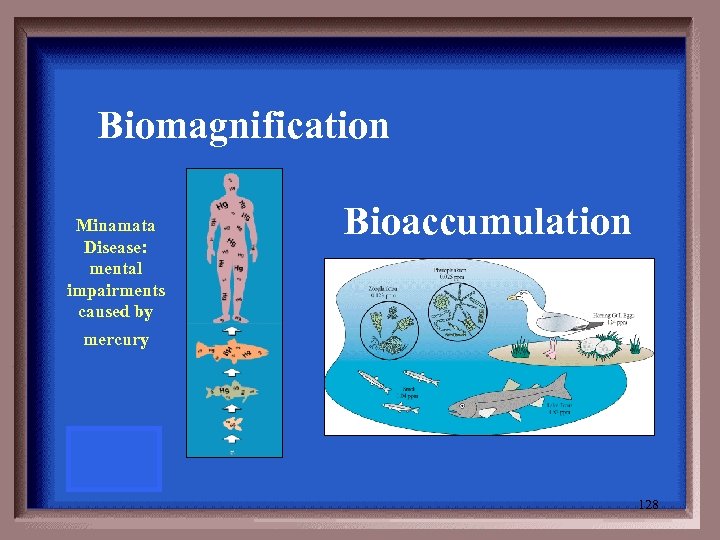 Biomagnification Minamata Disease: mental impairments caused by Bioaccumulation mercury 128
Biomagnification Minamata Disease: mental impairments caused by Bioaccumulation mercury 128
 129
129
 3 ways to dispose of MSW (municipal solid waste) 130
3 ways to dispose of MSW (municipal solid waste) 130
 Incineration Landfills Recycle Compost Exporting waste • The “TRASH NO ONE WANTED” from The Islip, L. I. 131
Incineration Landfills Recycle Compost Exporting waste • The “TRASH NO ONE WANTED” from The Islip, L. I. 131
 The name given to the environmental program established to address abandoned hazardous waste sites. 132
The name given to the environmental program established to address abandoned hazardous waste sites. 132
 SUPERFUND CERCLA– Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act The Love Canal, New York 133
SUPERFUND CERCLA– Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act The Love Canal, New York 133
 Which of the following means “trade off” – _______ banking is when destruction of existing wetland/land is allowed as long as an equal area of the same type of wetland/land is created or restored A) Preservation B) Restoration C) Remediation D) Mitigation 134
Which of the following means “trade off” – _______ banking is when destruction of existing wetland/land is allowed as long as an equal area of the same type of wetland/land is created or restored A) Preservation B) Restoration C) Remediation D) Mitigation 134
 Mitigation Preservation – set aside land for protection – John Muir was an early leader of the preservationist movement he also founded the Sierra Club Remediation – similar to decontamination - removal or neutralization of chemical substances from a site to prevent any adverse effects Mitigation – (not always successful – but better than nothing) Restoration – trying to restore a degraded habitat or ecosystem to a condition as close as possible to the predegraded state. 135
Mitigation Preservation – set aside land for protection – John Muir was an early leader of the preservationist movement he also founded the Sierra Club Remediation – similar to decontamination - removal or neutralization of chemical substances from a site to prevent any adverse effects Mitigation – (not always successful – but better than nothing) Restoration – trying to restore a degraded habitat or ecosystem to a condition as close as possible to the predegraded state. 135
 How many children should each woman have, to do no more than replace herself and her mate (assuming one mate)? What is the term for this? 136
How many children should each woman have, to do no more than replace herself and her mate (assuming one mate)? What is the term for this? 136
 Replacement fertility level (RFL) As a global average, she should have about 2. 1 children. Developing countries it is higher. The number is slightly higher than two to account for infant mortality. Reproduction at this level is called- (RFL) ______________ * Total fertility rate (TFR) 137
Replacement fertility level (RFL) As a global average, she should have about 2. 1 children. Developing countries it is higher. The number is slightly higher than two to account for infant mortality. Reproduction at this level is called- (RFL) ______________ * Total fertility rate (TFR) 137
 An abnormal warming of surface ocean waters in the eastern tropical Pacific, is one part of what's called the Southern Oscillation. 138
An abnormal warming of surface ocean waters in the eastern tropical Pacific, is one part of what's called the Southern Oscillation. 138
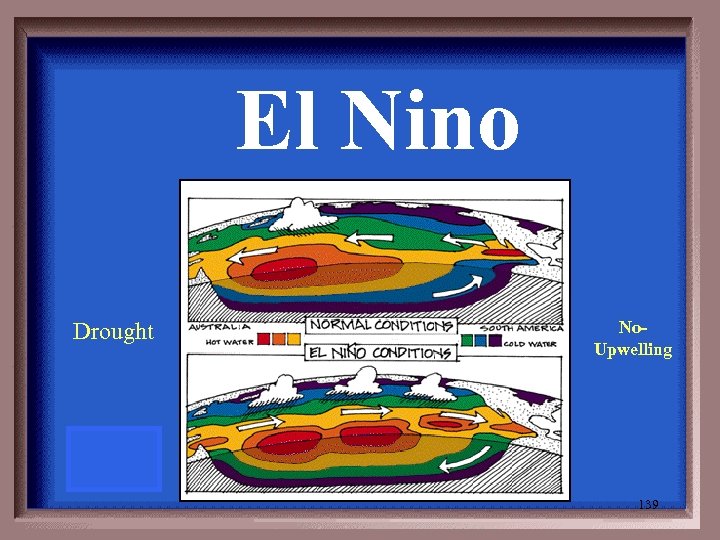 El Nino Drought No- Upwelling 139
El Nino Drought No- Upwelling 139
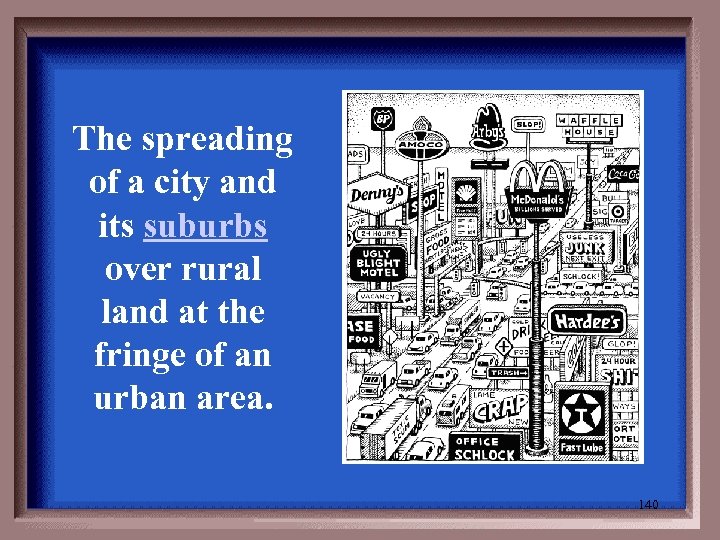 The spreading of a city and its suburbs over rural land at the fringe of an urban area. 140
The spreading of a city and its suburbs over rural land at the fringe of an urban area. 140
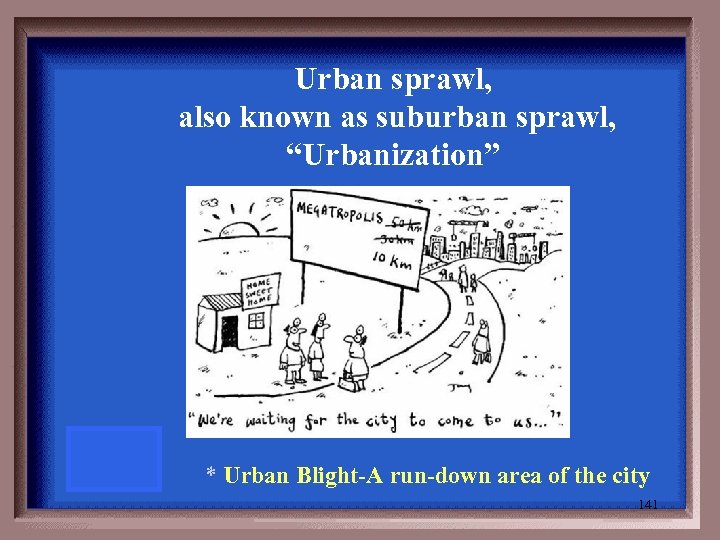 Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, “Urbanization” * Urban Blight-A run-down area of the city 141
Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, “Urbanization” * Urban Blight-A run-down area of the city 141
 FINAL JEOPARDY Founder of the 142
FINAL JEOPARDY Founder of the 142
 John Muir 143
John Muir 143


