778a7743681e7cedd71b205e73dafa26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 JEMS Today 2004 Saturday March 6, 2004 Data and Network Security: Guarding Your Data William E. Ott, MS, Paramedic CPCS Technologies www. cpcstech. com
JEMS Today 2004 Saturday March 6, 2004 Data and Network Security: Guarding Your Data William E. Ott, MS, Paramedic CPCS Technologies www. cpcstech. com
 Today’s Data Security Environments Can Be Scary Hackers & Extremists on Lond of yd’s 2001 Llo rces e – Jan r fo acke web sit H ose to cl TRUST Securit yl Barclay apse closes s’ August online bank – 2000 Changing Technologies Loss of Competitive Advantage On a ve have rage, 60 % s the la uffered a of organ is secu st two rity b ations years - 200 reach in 1 ent perc 90 that ad d foun sses h ches e Opportunities for a rvey e su ed busin uter bre om 62 n O FRAUD fr pl mp f sam nced co riod – up ar o e e ie xper month p revious y e p 12 Viruses & Worms in a nt in the e “Free” Access for per c 2001 h Employees New IT Projects Marc g tainin on ails c ding f em a ber o d by a le ove the m nu Outsourcing The s detecte rose ab 001 Malicio 2 e e u virus ing servic - August bn. ec s code attac onomi nn ark c impa ks had $13. 2 2002 IT System Crashes sca in 400 m ct in 2 001 - J one an
Today’s Data Security Environments Can Be Scary Hackers & Extremists on Lond of yd’s 2001 Llo rces e – Jan r fo acke web sit H ose to cl TRUST Securit yl Barclay apse closes s’ August online bank – 2000 Changing Technologies Loss of Competitive Advantage On a ve have rage, 60 % s the la uffered a of organ is secu st two rity b ations years - 200 reach in 1 ent perc 90 that ad d foun sses h ches e Opportunities for a rvey e su ed busin uter bre om 62 n O FRAUD fr pl mp f sam nced co riod – up ar o e e ie xper month p revious y e p 12 Viruses & Worms in a nt in the e “Free” Access for per c 2001 h Employees New IT Projects Marc g tainin on ails c ding f em a ber o d by a le ove the m nu Outsourcing The s detecte rose ab 001 Malicio 2 e e u virus ing servic - August bn. ec s code attac onomi nn ark c impa ks had $13. 2 2002 IT System Crashes sca in 400 m ct in 2 001 - J one an
 Specific Items to Address • EMS as Information Workers • Information security risks – Network – Wireless – Voice – Social engineering • Information security measures – Firewall – IDS – Antivirus • Business continuity planning • Data backup and restoration
Specific Items to Address • EMS as Information Workers • Information security risks – Network – Wireless – Voice – Social engineering • Information security measures – Firewall – IDS – Antivirus • Business continuity planning • Data backup and restoration
 EMS following the Fed. Ex lead? • EMS is following the IT example of Fed. Ex, transitioning from package delivery with associated information to an information management company with the end result of package delivery • EMS is, and should follow this model, from being a emergency response, patient care service with associated information to one of being an information management agency with the end result being quality patient care.
EMS following the Fed. Ex lead? • EMS is following the IT example of Fed. Ex, transitioning from package delivery with associated information to an information management company with the end result of package delivery • EMS is, and should follow this model, from being a emergency response, patient care service with associated information to one of being an information management agency with the end result being quality patient care.
 EMS as Information Workers • What is involved? – Electronic patient records – CAD data pre and post response – GIS data pre and post response – System performance data – Application of performance data to the continuing education program – Personnel data – System / Vehicle data – Facility/Event preplan data
EMS as Information Workers • What is involved? – Electronic patient records – CAD data pre and post response – GIS data pre and post response – System performance data – Application of performance data to the continuing education program – Personnel data – System / Vehicle data – Facility/Event preplan data
 Threats to Information Systems • • Malicious abuse Denial of Service and related attacks Virus, Worm, and Trojan attacks Outside Hacker attacks Theft of service Theft of information Poorly trained IT staff Not staying current with system patches, antivirus definitions, etc. . • Not performing proper system maintenance • Poor or no backup and contingency plans
Threats to Information Systems • • Malicious abuse Denial of Service and related attacks Virus, Worm, and Trojan attacks Outside Hacker attacks Theft of service Theft of information Poorly trained IT staff Not staying current with system patches, antivirus definitions, etc. . • Not performing proper system maintenance • Poor or no backup and contingency plans
 Do you have an IT Security Plan? • Harden and Secure for known issues • Prepare with policies and education • Detect intrusions and threats • Respond to intrusions and threats • Improve IT security measures and policies
Do you have an IT Security Plan? • Harden and Secure for known issues • Prepare with policies and education • Detect intrusions and threats • Respond to intrusions and threats • Improve IT security measures and policies
 What can happen to my data? • Lost data or missing data is inaccessible • Stolen data has been accessed or copied without authorization • Inaccurate data was entered incorrectly, deliberately or accidentally altered, or not updated
What can happen to my data? • Lost data or missing data is inaccessible • Stolen data has been accessed or copied without authorization • Inaccurate data was entered incorrectly, deliberately or accidentally altered, or not updated
 Causes for Concern • 94%+ of corrupt, compromised, or deleted data is because of user error, mistake, hardware failure, or deliberate misuse • 78%+ of malicious damage to data is attributed to ‘trusted’ personnel according to FBI/CERT statistics for 2002
Causes for Concern • 94%+ of corrupt, compromised, or deleted data is because of user error, mistake, hardware failure, or deliberate misuse • 78%+ of malicious damage to data is attributed to ‘trusted’ personnel according to FBI/CERT statistics for 2002
 Threats to Productivity • Spam – wastes resources – wastes time – offensive, dangerous • Popup ads – wastes resources – annoying • Malicious use of resources – wastes bandwidth, storage – violates law and privacy
Threats to Productivity • Spam – wastes resources – wastes time – offensive, dangerous • Popup ads – wastes resources – annoying • Malicious use of resources – wastes bandwidth, storage – violates law and privacy
 Threats to Privacy / Confidentiality • • • No security plan No security training or awareness Smart or Meta Tags in shared documents Social Engineering Unencrypted network Unencrypted e-mail No firewall No antivirus system Rogue wireless PDAs connecting to network and servers
Threats to Privacy / Confidentiality • • • No security plan No security training or awareness Smart or Meta Tags in shared documents Social Engineering Unencrypted network Unencrypted e-mail No firewall No antivirus system Rogue wireless PDAs connecting to network and servers

 What is driving improved Security? • Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) • Maturation of existing data systems • Inexpensive to implement security on new data systems • It’s the right thing to do
What is driving improved Security? • Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) • Maturation of existing data systems • Inexpensive to implement security on new data systems • It’s the right thing to do
 Data Security Issues • • • Development of user levels Education of users Proper use policies Improper info via unsecured e-mail Intrusion detection systems / scans Antivirus protections
Data Security Issues • • • Development of user levels Education of users Proper use policies Improper info via unsecured e-mail Intrusion detection systems / scans Antivirus protections
 Some Security Options • • • Virtual Private Networking (VPN) Active Anti. Virus Screening Stateful packet inspection Firewalling Proxy servers Opt-in e-mail Database encryption E-mail encryption Network / PC security policies Two Factor User Authentication Aggressive Audit logging and review
Some Security Options • • • Virtual Private Networking (VPN) Active Anti. Virus Screening Stateful packet inspection Firewalling Proxy servers Opt-in e-mail Database encryption E-mail encryption Network / PC security policies Two Factor User Authentication Aggressive Audit logging and review
 Virtual Private Network • A VPN is defined as a system in which two or more networks are connected through a third, untrusted, network. • The two networks are usually a main office and a satellite office, and the third network is usually the Internet.
Virtual Private Network • A VPN is defined as a system in which two or more networks are connected through a third, untrusted, network. • The two networks are usually a main office and a satellite office, and the third network is usually the Internet.
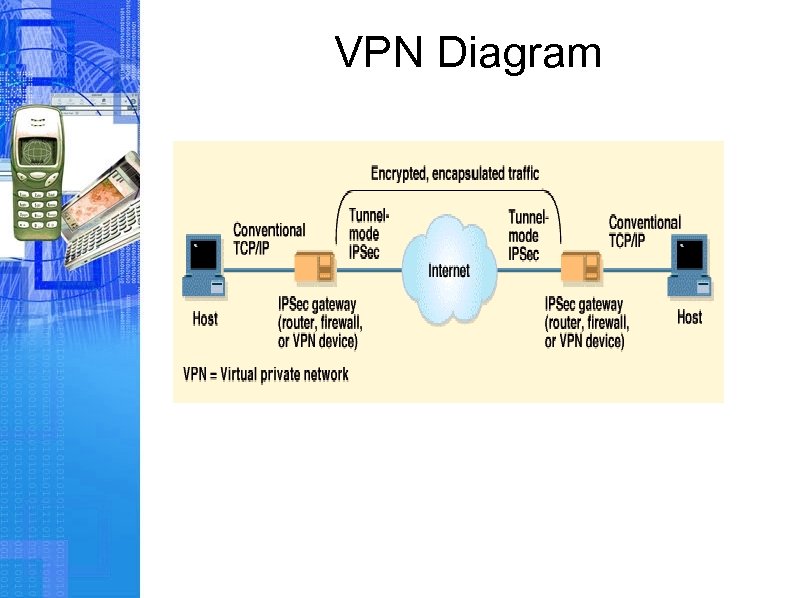 VPN Diagram
VPN Diagram
 E-mail Security • • E-mail is the most used network application Very insecure as Internet developed Security has been a low priority for all but a few Phil Zimmerman – Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) Digital Certificates Symmetric or Asymmetric encryption Think about opt-in or digital certificates to control spam
E-mail Security • • E-mail is the most used network application Very insecure as Internet developed Security has been a low priority for all but a few Phil Zimmerman – Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) Digital Certificates Symmetric or Asymmetric encryption Think about opt-in or digital certificates to control spam
 Ultimate Goal: Information Control • Easy to use – Simple model – Native environment • Dependable Security • Dependable Authentication • Persistent and Dynamic Control when applicable • Use control (copy and print) • Comprehensive Auditing • Supports breadth of content types • Scalable and deployable
Ultimate Goal: Information Control • Easy to use – Simple model – Native environment • Dependable Security • Dependable Authentication • Persistent and Dynamic Control when applicable • Use control (copy and print) • Comprehensive Auditing • Supports breadth of content types • Scalable and deployable
 Solutions & Suggestions • Tie security to ROI – what is the competition doing, positive PR, etc. (at minimum tie it to loss mitigation costs ) • Remind Privacy Rule & statute mandate sound security practices • Educate, educate • Use horror stories judiciously
Solutions & Suggestions • Tie security to ROI – what is the competition doing, positive PR, etc. (at minimum tie it to loss mitigation costs ) • Remind Privacy Rule & statute mandate sound security practices • Educate, educate • Use horror stories judiciously
 Solutions & Suggestions • Present options, accept risk and remain flexible • Remember brevity with top executives – make your point quickly and avoid fluff • Cultivate security advocates within and outside the organization • Incorporate a bottom up approach (I. e. , train end users, period security announcements to staff, etc. )
Solutions & Suggestions • Present options, accept risk and remain flexible • Remember brevity with top executives – make your point quickly and avoid fluff • Cultivate security advocates within and outside the organization • Incorporate a bottom up approach (I. e. , train end users, period security announcements to staff, etc. )
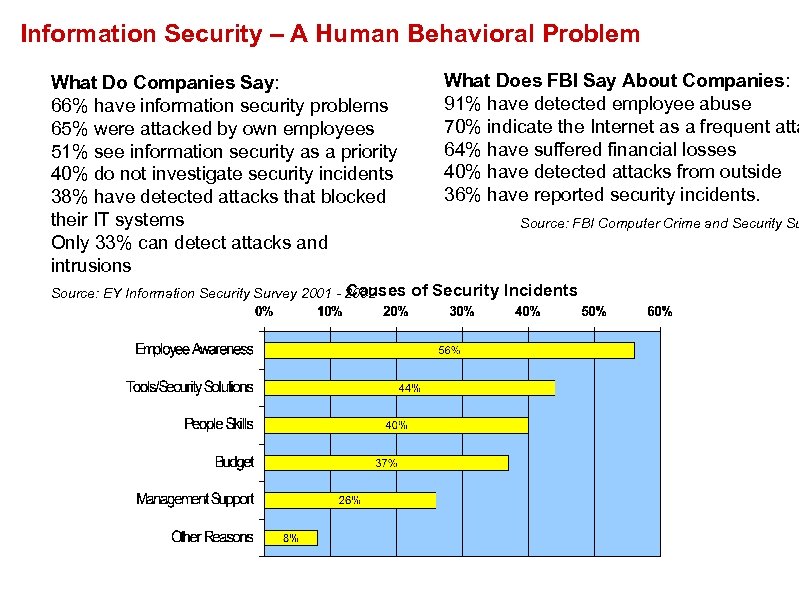 Information Security – A Human Behavioral Problem What Do Companies Say: 66% have information security problems 65% were attacked by own employees 51% see information security as a priority 40% do not investigate security incidents 38% have detected attacks that blocked their IT systems Only 33% can detect attacks and intrusions Causes Source: EY Information Security Survey 2001 - 2002 What Does FBI Say About Companies: 91% have detected employee abuse 70% indicate the Internet as a frequent atta 64% have suffered financial losses 40% have detected attacks from outside 36% have reported security incidents. Source: FBI Computer Crime and Security Su of Security Incidents Source: EY Information Security Survey 2001
Information Security – A Human Behavioral Problem What Do Companies Say: 66% have information security problems 65% were attacked by own employees 51% see information security as a priority 40% do not investigate security incidents 38% have detected attacks that blocked their IT systems Only 33% can detect attacks and intrusions Causes Source: EY Information Security Survey 2001 - 2002 What Does FBI Say About Companies: 91% have detected employee abuse 70% indicate the Internet as a frequent atta 64% have suffered financial losses 40% have detected attacks from outside 36% have reported security incidents. Source: FBI Computer Crime and Security Su of Security Incidents Source: EY Information Security Survey 2001
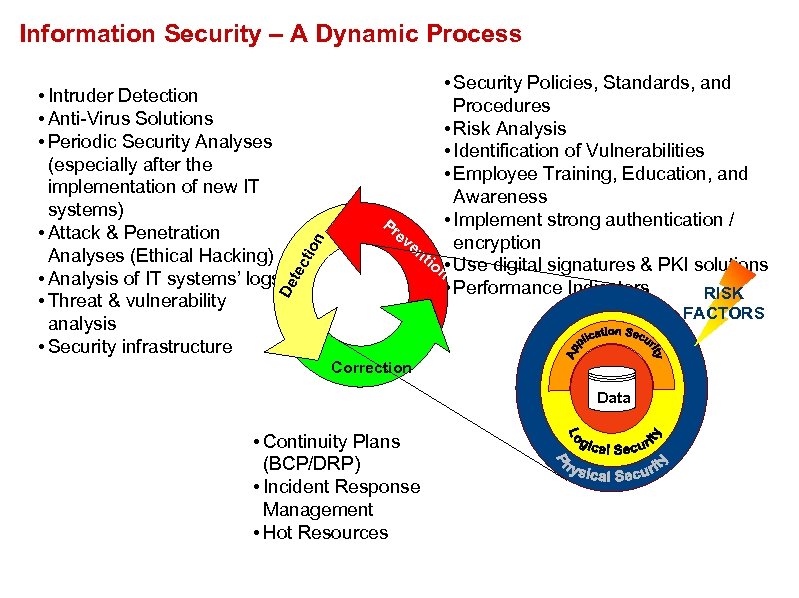 tec De • Intruder Detection • Anti-Virus Solutions • Periodic Security Analyses (especially after the implementation of new IT systems) • Attack & Penetration Analyses (Ethical Hacking) • Analysis of IT systems’ logs • Threat & vulnerability analysis • Security infrastructure tio n Information Security – A Dynamic Process • Security Policies, Standards, and Procedures • Risk Analysis • Identification of Vulnerabilities • Employee Training, Education, and Awareness • Implement strong authentication / Pr ev encryption en tio n • Use digital signatures & PKI solutions • Performance Indicators RISK FACTORS Correction Data • Continuity Plans (BCP/DRP) • Incident Response Management • Hot Resources
tec De • Intruder Detection • Anti-Virus Solutions • Periodic Security Analyses (especially after the implementation of new IT systems) • Attack & Penetration Analyses (Ethical Hacking) • Analysis of IT systems’ logs • Threat & vulnerability analysis • Security infrastructure tio n Information Security – A Dynamic Process • Security Policies, Standards, and Procedures • Risk Analysis • Identification of Vulnerabilities • Employee Training, Education, and Awareness • Implement strong authentication / Pr ev encryption en tio n • Use digital signatures & PKI solutions • Performance Indicators RISK FACTORS Correction Data • Continuity Plans (BCP/DRP) • Incident Response Management • Hot Resources
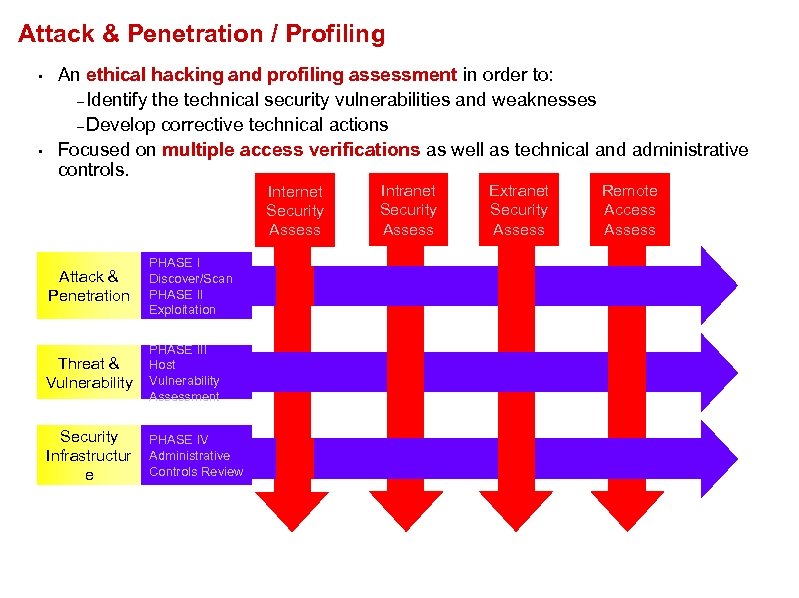 Attack & Penetration / Profiling • • An ethical hacking and profiling assessment in order to: – Identify the technical security vulnerabilities and weaknesses – Develop corrective technical actions Focused on multiple access verifications as well as technical and administrative controls. Internet Security Assess Attack & Penetration PHASE I Discover/Scan PHASE II Exploitation Threat & Vulnerability PHASE III Host Vulnerability Assessment Security Infrastructur e PHASE IV Administrative Controls Review Intranet Security Assess Extranet Security Assess Remote Access Assess
Attack & Penetration / Profiling • • An ethical hacking and profiling assessment in order to: – Identify the technical security vulnerabilities and weaknesses – Develop corrective technical actions Focused on multiple access verifications as well as technical and administrative controls. Internet Security Assess Attack & Penetration PHASE I Discover/Scan PHASE II Exploitation Threat & Vulnerability PHASE III Host Vulnerability Assessment Security Infrastructur e PHASE IV Administrative Controls Review Intranet Security Assess Extranet Security Assess Remote Access Assess
 What Are Potential Disasters? q External • Storms (hurricanes, tornados, floods, hail…) • Accidents (planes, trains, automobiles, hazardous mat. ) • Regional Outages (power, communications…) • Violence (civil unrest, terrorist acts, bioterrorism…) q Internal • Hardware Failures (servers, data stores, cyber attacks. . ) • Accidents (fires, water leaks, electrical…) • Violence (disgruntled employee, corp. sabotage…)
What Are Potential Disasters? q External • Storms (hurricanes, tornados, floods, hail…) • Accidents (planes, trains, automobiles, hazardous mat. ) • Regional Outages (power, communications…) • Violence (civil unrest, terrorist acts, bioterrorism…) q Internal • Hardware Failures (servers, data stores, cyber attacks. . ) • Accidents (fires, water leaks, electrical…) • Violence (disgruntled employee, corp. sabotage…)
 What Are The Chances? q Computing Probability of Occurrence • Trying to construct a probabilistic model by type of exposure reaches diminishing returns very quickly. • Should a low probability of occurrence in a given area alter the scope of a BCP Plan? q Responsible BCP Planning • Assesses the environment and mitigates the obvious risks. (servers in a basement in a flood plane area) • Hopes for the best, but must plan for the worst.
What Are The Chances? q Computing Probability of Occurrence • Trying to construct a probabilistic model by type of exposure reaches diminishing returns very quickly. • Should a low probability of occurrence in a given area alter the scope of a BCP Plan? q Responsible BCP Planning • Assesses the environment and mitigates the obvious risks. (servers in a basement in a flood plane area) • Hopes for the best, but must plan for the worst.
 Data Disaster Facts • Disaster Recovery Journal reports two in five companies are not able to reopen after a disaster • Gartner Group Information loss is more critical than hardware failure or loss • Ontrack Data research indicates that 80% of its data loss customers regularly back up their data, only to find them less than adequate at the critical moment they need to restore. Despite technological advances in the reliability of magnetic storage media, data loss continues to rise, making data recovery more important than ever
Data Disaster Facts • Disaster Recovery Journal reports two in five companies are not able to reopen after a disaster • Gartner Group Information loss is more critical than hardware failure or loss • Ontrack Data research indicates that 80% of its data loss customers regularly back up their data, only to find them less than adequate at the critical moment they need to restore. Despite technological advances in the reliability of magnetic storage media, data loss continues to rise, making data recovery more important than ever
 Why Does This Happen • • • Systems becoming more complex Focus on Backup Not Recovery Shrinking Backup Window Write-Verify Function Turned Off Application/Data Available 24 x 7
Why Does This Happen • • • Systems becoming more complex Focus on Backup Not Recovery Shrinking Backup Window Write-Verify Function Turned Off Application/Data Available 24 x 7
 Gartner Group: Key trends • By year-end 2003, 80 percent of mobile workers will have at least two computing devices, and 40 percent will have three. • Windows CE (Pocket. PC) will dominate in the industrial handheld market space. • Web-enabled phones are widely available; first-generation content was a curiosity, second-generation useful • Software complexity will remain the biggest barrier to mobile productivity. • Widespread embedded Bluetooth is 2004 phenomenon. • Mobile network bandwidth will not be a barrier to compelling applications. • Spending on network capabilities will provide more productivity than spending on processors.
Gartner Group: Key trends • By year-end 2003, 80 percent of mobile workers will have at least two computing devices, and 40 percent will have three. • Windows CE (Pocket. PC) will dominate in the industrial handheld market space. • Web-enabled phones are widely available; first-generation content was a curiosity, second-generation useful • Software complexity will remain the biggest barrier to mobile productivity. • Widespread embedded Bluetooth is 2004 phenomenon. • Mobile network bandwidth will not be a barrier to compelling applications. • Spending on network capabilities will provide more productivity than spending on processors.
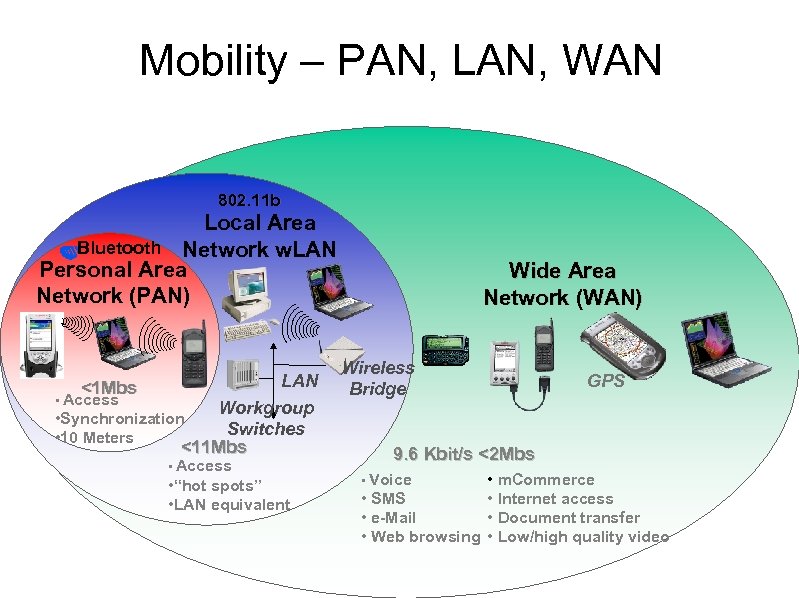 Mobility – PAN, LAN, WAN 802. 11 b Local Area Bluetooth Network w. LAN Personal Area Network (PAN) LAN <1 Mbs • Access Workgroup • Synchronization Switches • 10 Meters <11 Mbs • Access • “hot spots” • LAN equivalent Wide Area Network (WAN) Wireless Bridge GPS 9. 6 Kbit/s <2 Mbs • m. Commerce • SMS • Internet access • e-Mail • Document transfer • Web browsing • Low/high quality video • Voice
Mobility – PAN, LAN, WAN 802. 11 b Local Area Bluetooth Network w. LAN Personal Area Network (PAN) LAN <1 Mbs • Access Workgroup • Synchronization Switches • 10 Meters <11 Mbs • Access • “hot spots” • LAN equivalent Wide Area Network (WAN) Wireless Bridge GPS 9. 6 Kbit/s <2 Mbs • m. Commerce • SMS • Internet access • e-Mail • Document transfer • Web browsing • Low/high quality video • Voice
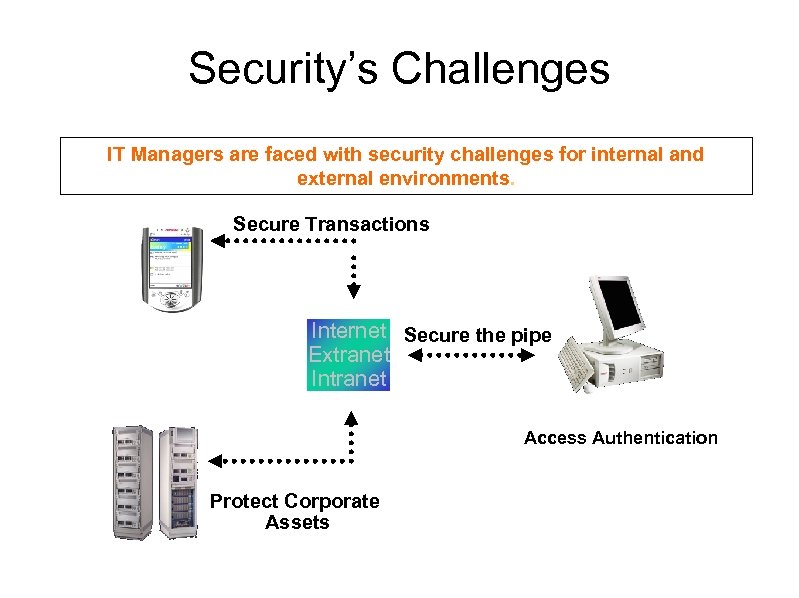 Security’s Challenges IT Managers are faced with security challenges for internal and external environments. Secure Transactions Internet Secure the pipe Extranet Intranet Access Authentication Protect Corporate Assets
Security’s Challenges IT Managers are faced with security challenges for internal and external environments. Secure Transactions Internet Secure the pipe Extranet Intranet Access Authentication Protect Corporate Assets
 Friend or Foe?
Friend or Foe?

 Technology Introduction – Extensions and sub-standards • 802. 11 a – 5 Ghz band, 6 - 54 Mbit/sec (“Wi. Fi 5”) • 802. 11 b – 2. 4 Ghz band, 1 - 11 Mbit/sec (“Wi. Fi”) • 802. 11 c – Bridge Operation Procedures • 802. 11 d – Global Harmonization • 802. 11 e – MAC Enhancements for Qo. S • 802. 11 f – Inter Access Point Protocol (roaming) • 802. 11 g – 2. 4 Ghz band, “ 20+ Mbit/sec” • 802. 11 h – Spectrum Managed 802. 11 a (European) • 802. 11 i - MAC Enhancements for Enhanced Security
Technology Introduction – Extensions and sub-standards • 802. 11 a – 5 Ghz band, 6 - 54 Mbit/sec (“Wi. Fi 5”) • 802. 11 b – 2. 4 Ghz band, 1 - 11 Mbit/sec (“Wi. Fi”) • 802. 11 c – Bridge Operation Procedures • 802. 11 d – Global Harmonization • 802. 11 e – MAC Enhancements for Qo. S • 802. 11 f – Inter Access Point Protocol (roaming) • 802. 11 g – 2. 4 Ghz band, “ 20+ Mbit/sec” • 802. 11 h – Spectrum Managed 802. 11 a (European) • 802. 11 i - MAC Enhancements for Enhanced Security
 Technology Introduction • What is 802. 11? – 802. 11 b and 802. 11 g interoperate – There are devices that implement 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b/g
Technology Introduction • What is 802. 11? – 802. 11 b and 802. 11 g interoperate – There are devices that implement 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b/g
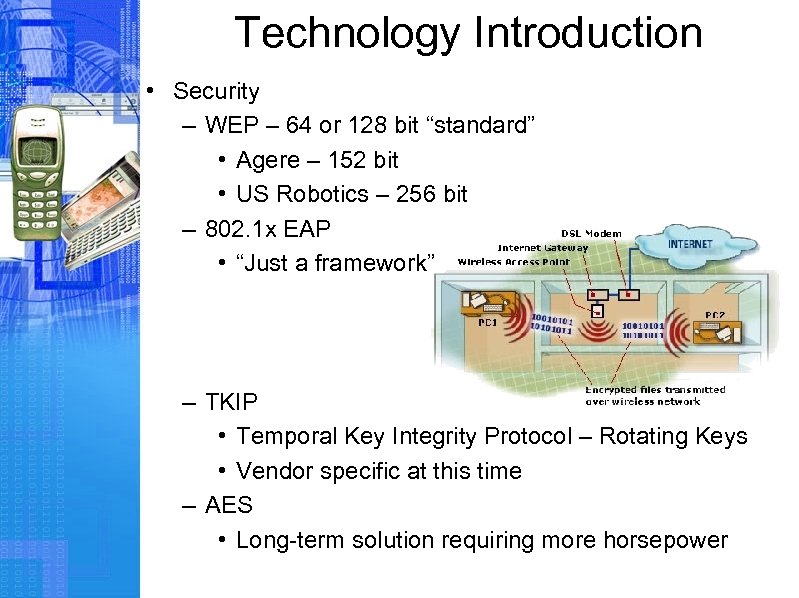 Technology Introduction • Security – WEP – 64 or 128 bit “standard” • Agere – 152 bit • US Robotics – 256 bit – 802. 1 x EAP • “Just a framework” – TKIP • Temporal Key Integrity Protocol – Rotating Keys • Vendor specific at this time – AES • Long-term solution requiring more horsepower
Technology Introduction • Security – WEP – 64 or 128 bit “standard” • Agere – 152 bit • US Robotics – 256 bit – 802. 1 x EAP • “Just a framework” – TKIP • Temporal Key Integrity Protocol – Rotating Keys • Vendor specific at this time – AES • Long-term solution requiring more horsepower
 802. 11 a/b/g weakness Rogue AP Compromise of encryption key Hardware theft is equivalent to key theft Packet spoofing, disassociation attack Known plain-text attack Brute force attack Passive monitoring
802. 11 a/b/g weakness Rogue AP Compromise of encryption key Hardware theft is equivalent to key theft Packet spoofing, disassociation attack Known plain-text attack Brute force attack Passive monitoring
 Hardware Changes • Commercial Products – Many consumer products are being used in the “commercial” arena
Hardware Changes • Commercial Products – Many consumer products are being used in the “commercial” arena
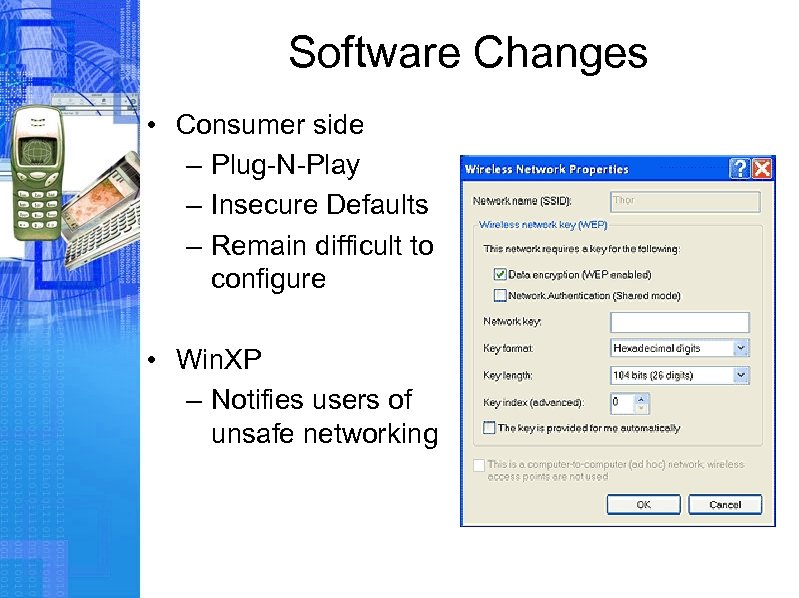 Software Changes • Consumer side – Plug-N-Play – Insecure Defaults – Remain difficult to configure • Win. XP – Notifies users of unsafe networking
Software Changes • Consumer side – Plug-N-Play – Insecure Defaults – Remain difficult to configure • Win. XP – Notifies users of unsafe networking
 Attitude Changes • Widespread Acceptance – Trains, Planes, Automobiles and phone booths – Mc. Donalds in San Francisco • $4. 95 for 2 hours, or free with food purchase Public WLAN Hot Spots Worldwide 2002 2003* Retail outlets 11, 109 50, 287 Hotels 2, 274 11, 687 Others 1, 369 9, 105 Total 14, 752 71, 079 *Projected Source: Dataquest Inc. , San Jose
Attitude Changes • Widespread Acceptance – Trains, Planes, Automobiles and phone booths – Mc. Donalds in San Francisco • $4. 95 for 2 hours, or free with food purchase Public WLAN Hot Spots Worldwide 2002 2003* Retail outlets 11, 109 50, 287 Hotels 2, 274 11, 687 Others 1, 369 9, 105 Total 14, 752 71, 079 *Projected Source: Dataquest Inc. , San Jose
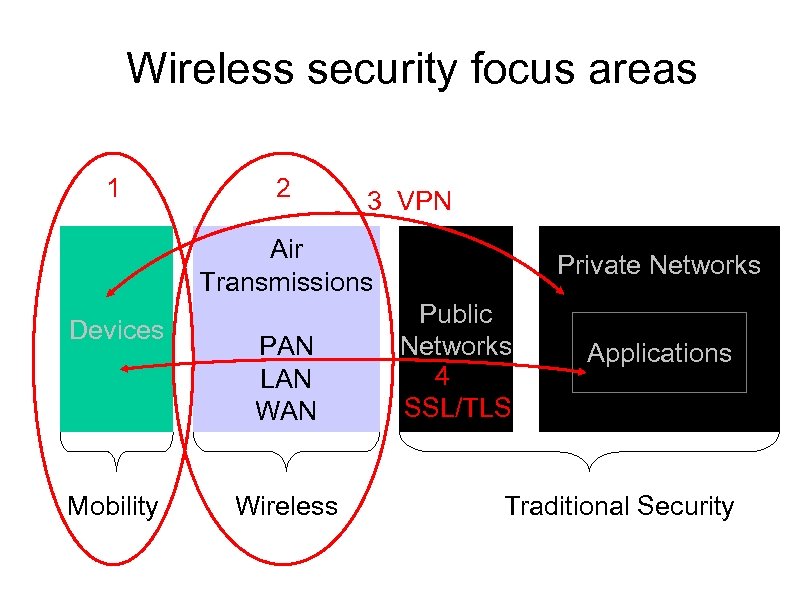 Wireless security focus areas 1 2 3 VPN Air Transmissions Devices Mobility PAN LAN Wireless Private Networks Public Networks 4 SSL/TLS Applications Traditional Security
Wireless security focus areas 1 2 3 VPN Air Transmissions Devices Mobility PAN LAN Wireless Private Networks Public Networks 4 SSL/TLS Applications Traditional Security




