045ad3698b5f6ec3b79cdfc22fd12c64.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

JEITA’s Activities on Environmental Issues September 2004 Japan Electronics & Information Technology Industries Association 1

JEITA’s Activities on Environmental Issues ◆Measures to prevent Global Warming ‐"The New Climate Change Policy Program“ ‐The Voluntary Action Plan by Electronics Sector ◆Recycling ‐Legislative system for recycling ‐Measures for Industrial Waste ‐ 3 R ◆Chemical substances control ‐Air pollution control law ‐PRTR law ‐Soil pollution prevention law ◆Environmental Issues related to products ‐Control on the hazardous chemical substances ‐Design for environmentally conscious products ‐Design for energy conserving products ◆Green Procurement ‐Law on Green Purchasing ‐Green procurement survey standardization 2
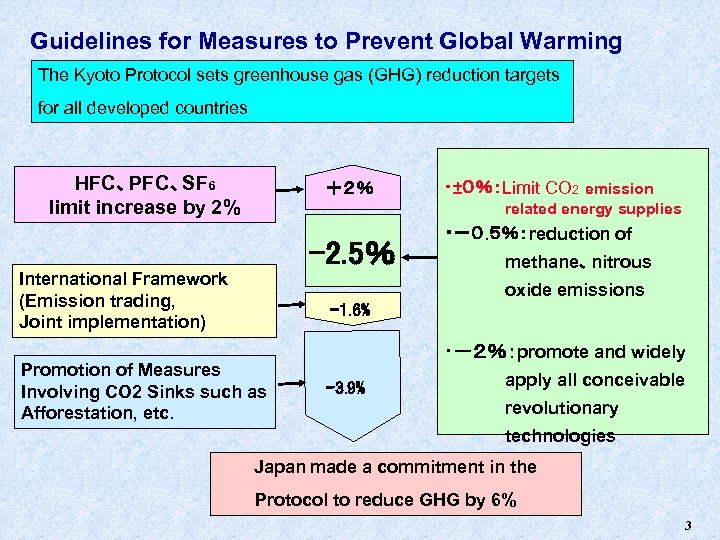
Guidelines for Measures to Prevent Global Warming The Kyoto Protocol sets greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction targets for all developed countries HFC、PFC、SF 6 limit increase by 2% +2% ・±0%:Limit CO 2 emission related energy supplies -2. 5% International Framework (Emission trading, Joint implementation) ・-0. 5%:reduction of methane、nitrous oxide emissions -1. 6% Promotion of Measures Involving CO 2 Sinks such as Afforestation, etc. ・-2%:promote and widely -3. 9% apply all conceivable revolutionary technologies Japan made a commitment in the Protocol to reduce GHG by 6% 3
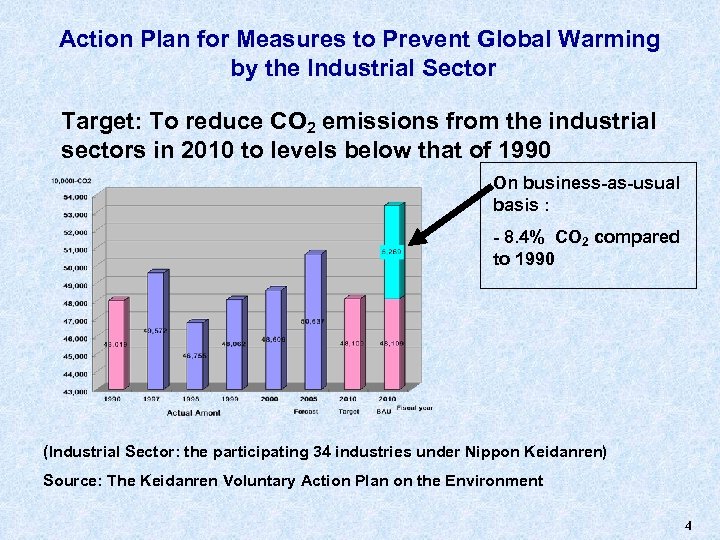
Action Plan for Measures to Prevent Global Warming by the Industrial Sector Target: To reduce CO 2 emissions from the industrial sectors in 2010 to levels below that of 1990 On business-as-usual basis : - 8. 4% CO 2 compared to 1990 (Industrial Sector: the participating 34 industries under Nippon Keidanren) Source: The Keidanren Voluntary Action Plan on the Environment 4
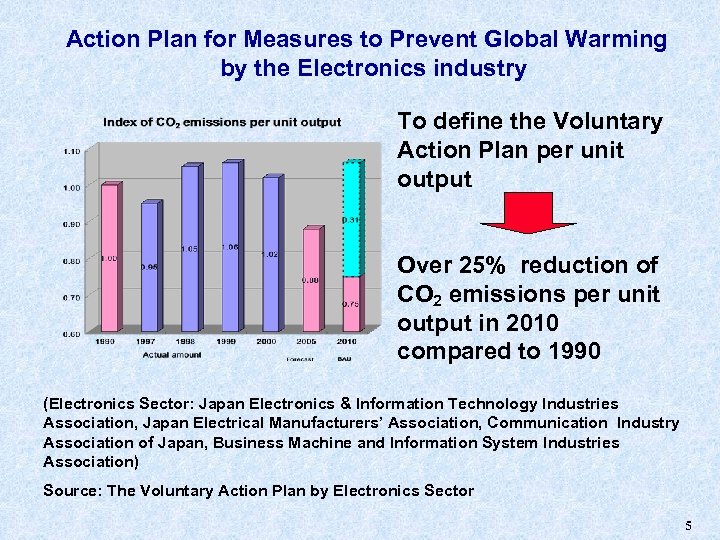
Action Plan for Measures to Prevent Global Warming by the Electronics industry To define the Voluntary Action Plan per unit output Over 25% reduction of CO 2 emissions per unit output in 2010 compared to 1990 (Electronics Sector: Japan Electronics & Information Technology Industries Association, Japan Electrical Manufacturers’ Association, Communication Industry Association of Japan, Business Machine and Information System Industries Association) Source: The Voluntary Action Plan by Electronics Sector 5
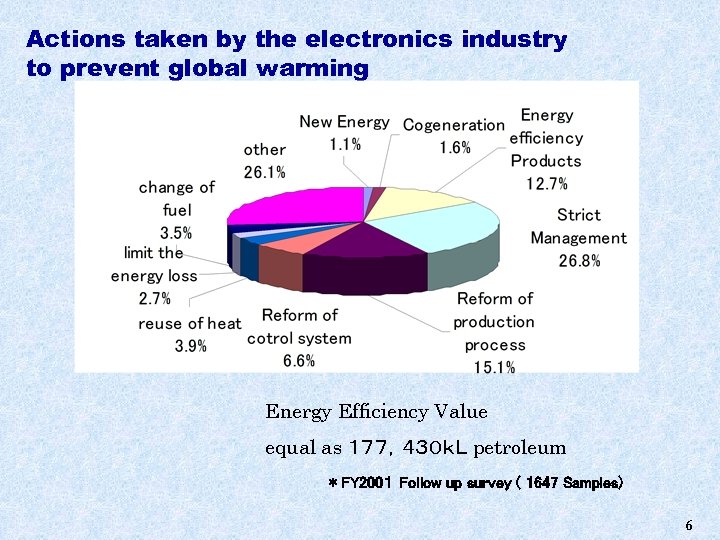
Actions taken by the electronics industry to prevent global warming Energy Efficiency Value equal as 177,430kL petroleum *FY 2001 Follow up survey ( 1647 Samples) 6
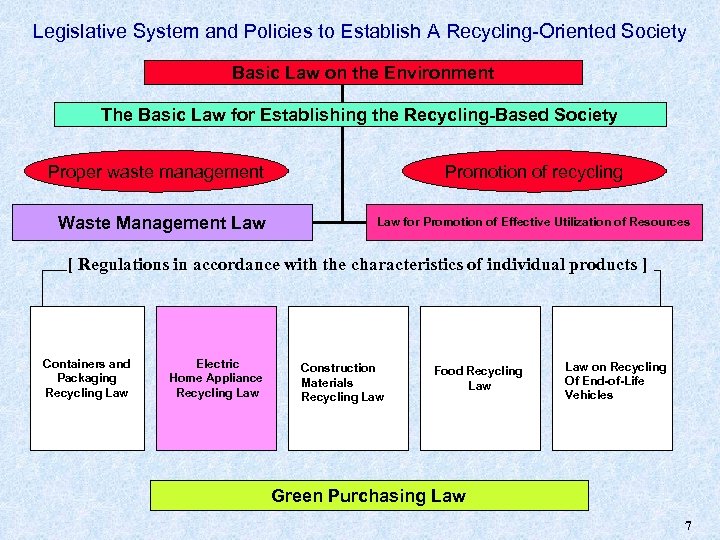
Legislative System and Policies to Establish A Recycling-Oriented Society Basic Law on the Environment The Basic Law for Establishing the Recycling-Based Society Proper waste management Waste Management Law Promotion of recycling Law for Promotion of Effective Utilization of Resources [ Regulations in accordance with the characteristics of individual products ] Containers and Packaging Recycling Law Electric Home Appliance Recycling Law Construction Materials Recycling Law Food Recycling Law on Recycling Of End-of-Life Vehicles Green Purchasing Law 7
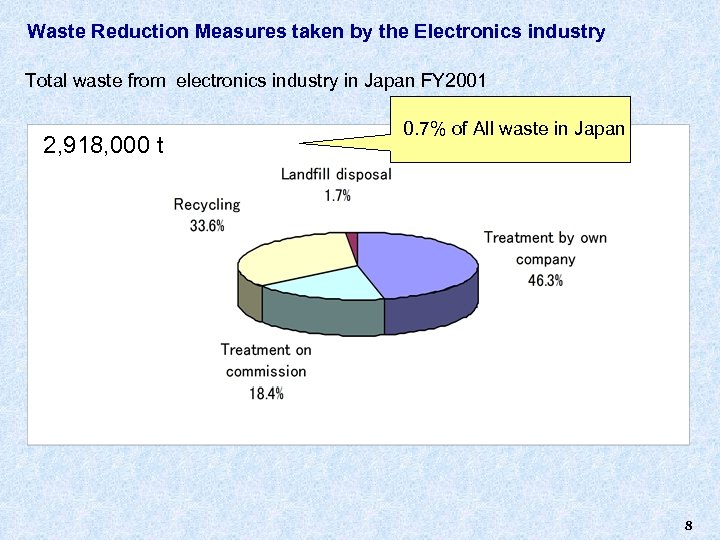
Waste Reduction Measures taken by the Electronics industry Total waste from electronics industry in Japan FY 2001 2, 918, 000 t 0. 7% of All waste in Japan 8

Electric Home Appliances Collection/ Recycling System Electric Home Appliances Recycling Law < April 2001> Products Fees Paid by Consumer Air conditioner $32 CRT TV $25 Refrigerator $42 Washing machine $22 9
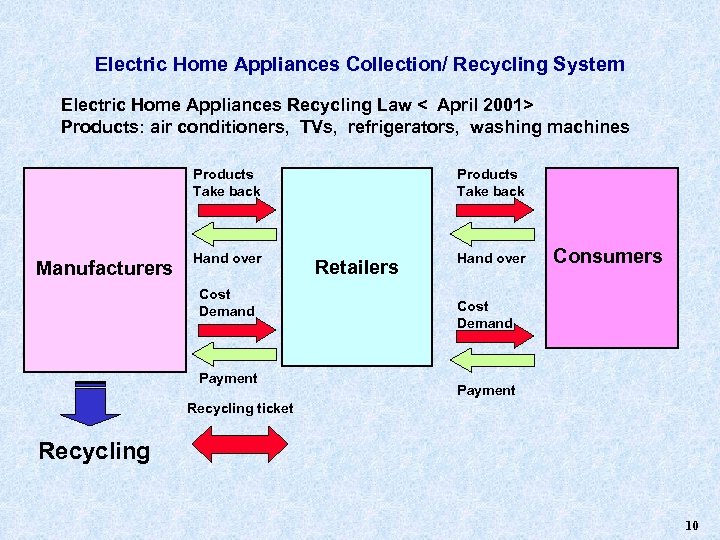
Electric Home Appliances Collection/ Recycling System Electric Home Appliances Recycling Law < April 2001> Products: air conditioners, TVs, refrigerators, washing machines Products Take back Manufacturers Hand over Cost Demand Payment Products Take back Retailers Hand over Consumers Cost Demand Payment Recycling ticket Recycling 10
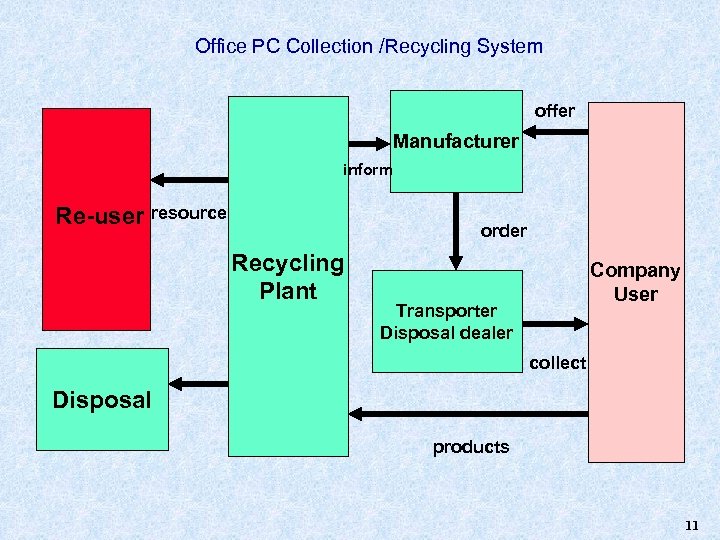
Office PC Collection /Recycling System offer Manufacturer inform Re-user resource order Recycling Plant Company User Transporter Disposal dealer collect Disposal products 11
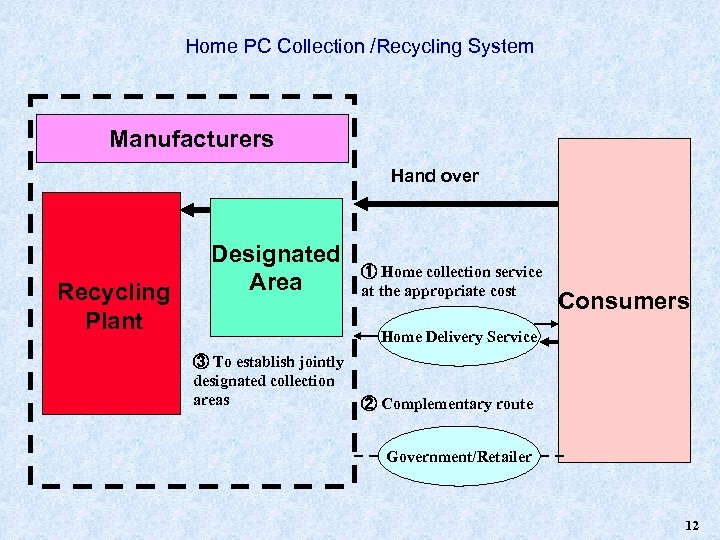
Home PC Collection /Recycling System Manufacturers Hand over Recycling Plant Designated Area ① Home collection service at the appropriate cost ③ To establish jointly designated collection areas Consumers Home Delivery Service ② Complementary route Government/Retailer 12
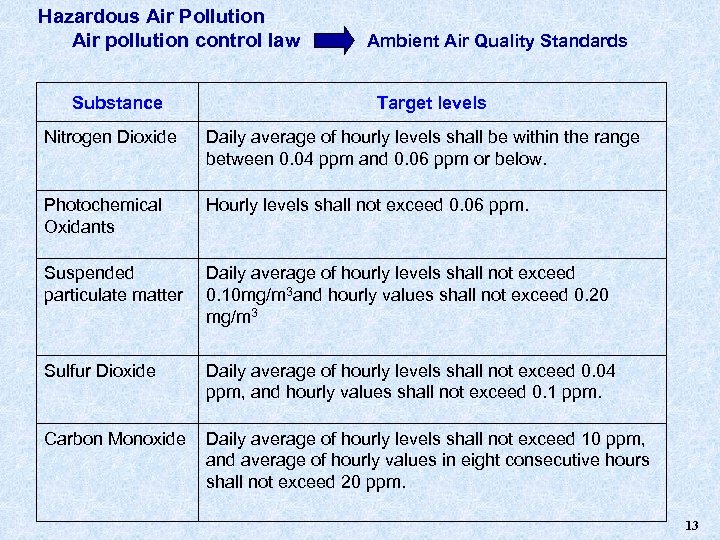
Hazardous Air Pollution Air pollution control law Ambient Air Quality Standards Substance Target levels Nitrogen Dioxide Daily average of hourly levels shall be within the range between 0. 04 ppm and 0. 06 ppm or below. Photochemical Oxidants Hourly levels shall not exceed 0. 06 ppm. Suspended particulate matter Daily average of hourly levels shall not exceed 0. 10 mg/m 3 and hourly values shall not exceed 0. 20 mg/m 3 Sulfur Dioxide Daily average of hourly levels shall not exceed 0. 04 ppm, and hourly values shall not exceed 0. 1 ppm. Carbon Monoxide Daily average of hourly levels shall not exceed 10 ppm, and average of hourly values in eight consecutive hours shall not exceed 20 ppm. 13
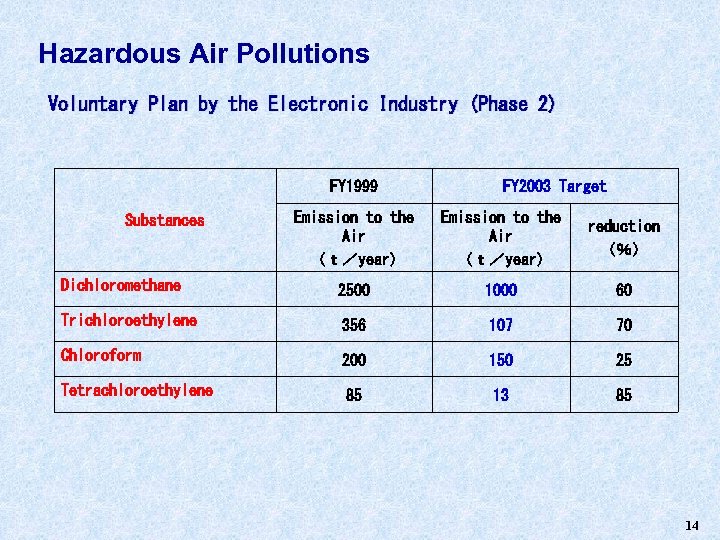
Hazardous Air Pollutions Voluntary Plan by the Electronic Industry (Phase 2) FY 1999 FY 2003 Target Emission to the Air (t/year) reduction (%) Dichloromethane 2500 1000 60 Trichloroethylene 356 107 70 Chloroform 200 150 25 Tetrachloroethylene 85 13 85 Substances 14

PRTR System Businesses are obligated to report the government annually on the release and the transfer of pollutants (345 chemical substances are designated). 15

Urban Soil Pollution Control Measures Ø“Urban" (non-agricultural) soil pollution cases increased mainly due to urban redevelopment. ØThe chemical and electroplating industries are major causes for soil pollutions. Primal soil contaminants are lead, hexavalent chromium, and trichloroethylene. ØIn August 1991 Environmental Quality Standards (EQS) for soil pollution was established to deal with soil problem issues. The EQS currently regulates 25 substances after some additions made in 1994. ØIn November 1994, the “Guidelines for Investigation and Countermeasures for Soil and Groundwater Pollution” was established. ØAdministrative guidance is provided to industries to promote voluntary clean up of polluted soil. 16
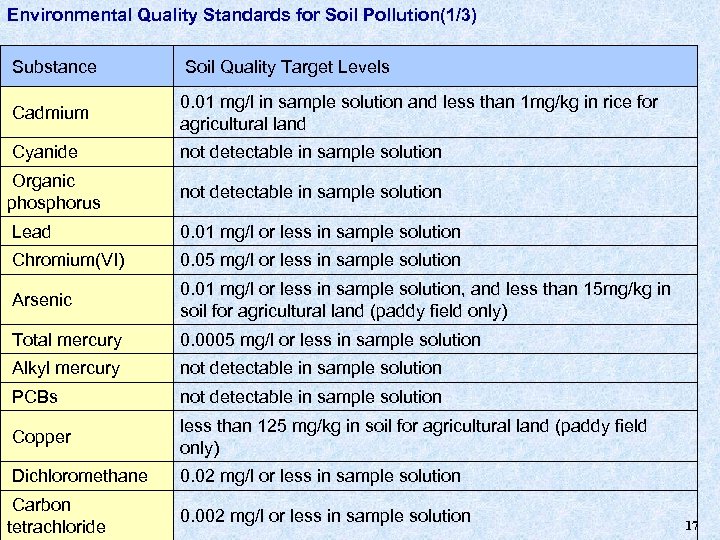
Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution(1/3) Substance Soil Quality Target Levels Cadmium 0. 01 mg/l in sample solution and less than 1 mg/kg in rice for agricultural land Cyanide not detectable in sample solution Organic phosphorus not detectable in sample solution Lead 0. 01 mg/l or less in sample solution Chromium(VI) 0. 05 mg/l or less in sample solution Arsenic 0. 01 mg/l or less in sample solution, and less than 15 mg/kg in soil for agricultural land (paddy field only) Total mercury 0. 0005 mg/l or less in sample solution Alkyl mercury not detectable in sample solution PCBs not detectable in sample solution Copper less than 125 mg/kg in soil for agricultural land (paddy field only) Dichloromethane 0. 02 mg/l or less in sample solution Carbon tetrachloride 0. 002 mg/l or less in sample solution 17
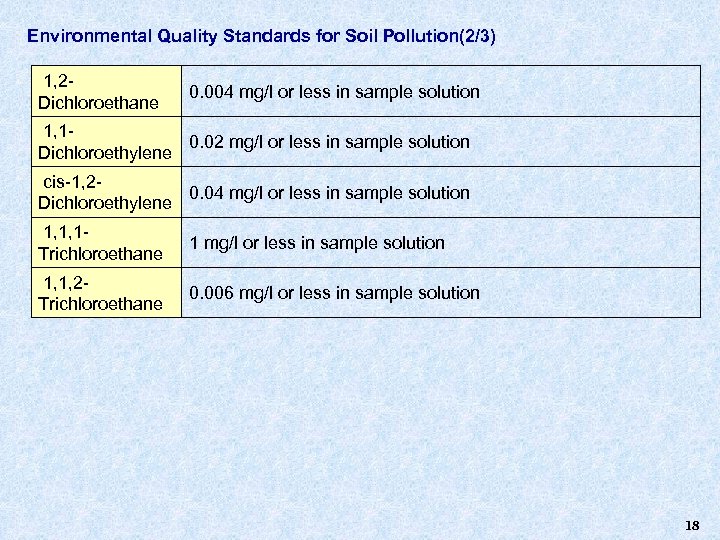
Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution(2/3) 1, 2 Dichloroethane 0. 004 mg/l or less in sample solution 1, 10. 02 mg/l or less in sample solution Dichloroethylene cis-1, 20. 04 mg/l or less in sample solution Dichloroethylene 1, 1, 1 Trichloroethane 1 mg/l or less in sample solution 1, 1, 2 Trichloroethane 0. 006 mg/l or less in sample solution 18
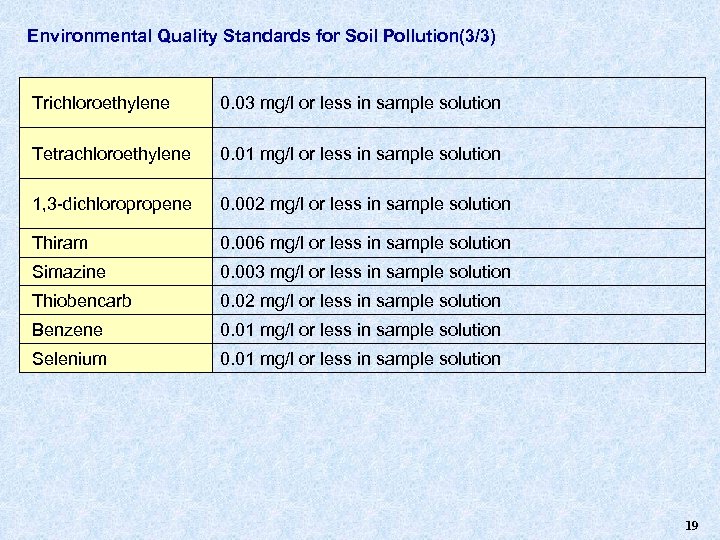
Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution(3/3) Trichloroethylene 0. 03 mg/l or less in sample solution Tetrachloroethylene 0. 01 mg/l or less in sample solution 1, 3 -dichloropropene 0. 002 mg/l or less in sample solution Thiram 0. 006 mg/l or less in sample solution Simazine 0. 003 mg/l or less in sample solution Thiobencarb 0. 02 mg/l or less in sample solution Benzene 0. 01 mg/l or less in sample solution Selenium 0. 01 mg/l or less in sample solution 19

Environmental Issues For Products - Control of the hazardous chemical substances - Design of environmentally conscious products - Design for energy conserving products Ø Top Runner Program 20

Green Procurement(1/2) Ø Meet the Hazardous Chemical Substances Regulations ØRo. HS (Restriction of the use of Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic equipment) Ø Conduct the chemical substances survey ØManufacturers must survey the chemical substances contained in the parts and materials to meet the Green Procurement standards. 21

Green Procurement(2/2) Ø Standardization of chemical substance surveys ØStandardization will improve the accuracy and effectiveness of the surveys while reducing the burden placed on the suppliers involved in the green procurement surveys. Ø Establishment of the JGPSSI (Japan Green Procurement Survey Standardization Initiative) ØTo develop the guidelines of standardized green procurement survey, JGPSSI was established by the business voluntary group in 2001. JEITA was engaged in the secretariat functions since February 2002 22
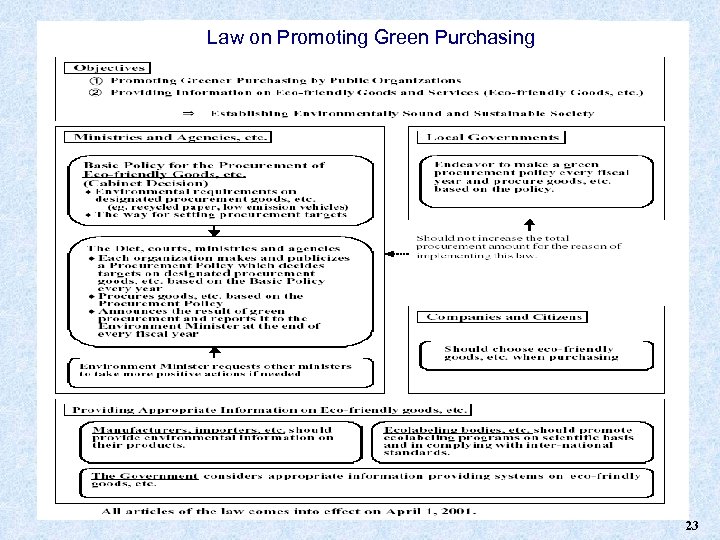
Law on Promoting Green Purchasing 23
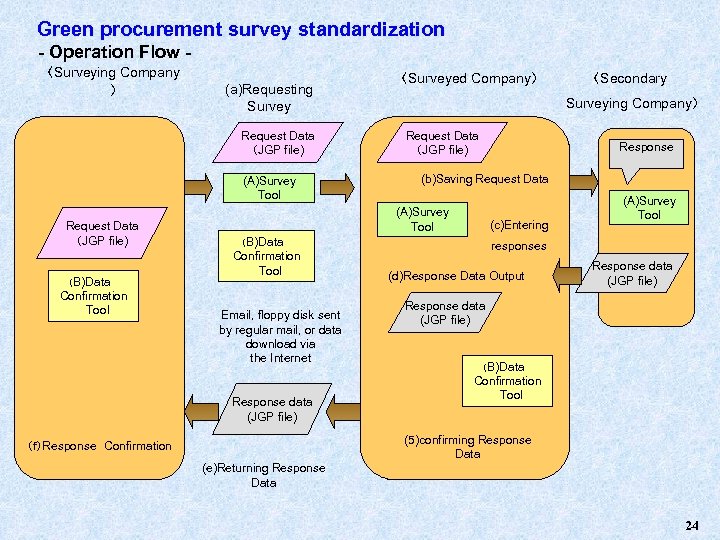
Green procurement survey standardization - Operation Flow 〈Surveying Company 〉 (a)Requesting Survey Request Data (JGP file) (A)Survey Tool Request Data (JGP file) (B)Data Confirmation Tool 〈Surveyed Company〉 Surveying Company〉 Request Data (JGP file) Response (b)Saving Request Data (A)Survey Tool (c)Entering (B)Data Confirmation Tool Email, floppy disk sent by regular mail, or data download via the Internet Response data (JGP file) 〈Secondary (A)Survey Tool responses (d)Response Data Output Response data (JGP file) (B)Data Confirmation Tool (5)confirming Response Data (f)Response Confirmation (e)Returning Response Data 24
045ad3698b5f6ec3b79cdfc22fd12c64.ppt