c8b66e61ae0ab5380fdf6f346aba021d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Jefferson Lab Presentation to Teacher Education Program November 8, 2006 Subatomic Particles: What do we study at Jefferson Lab? Dr. Allison Lung 12 Ge. V Upgrade Project Director & Senior Staff Physicist

Nuclear Physics: All About Atoms nucleons education. jlab. org/atomtour

Building atoms……

The tiniest particles……or are they?

Just how big are they? What about all that empty space?

Even tinier particles!
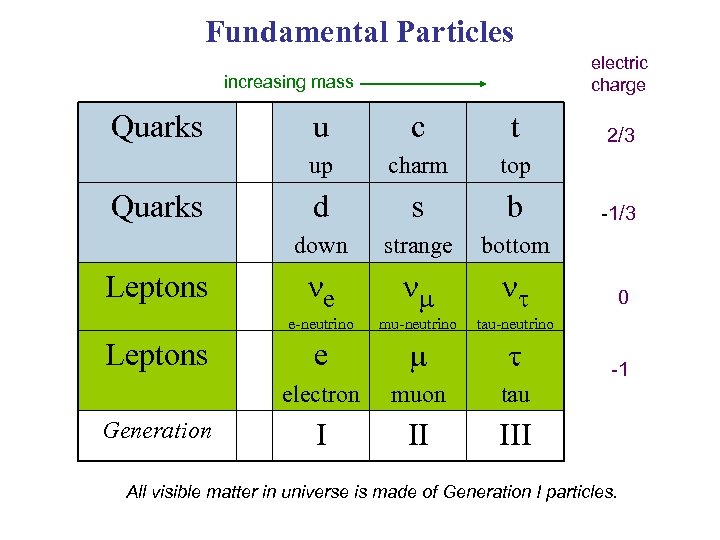
Fundamental Particles electric charge increasing mass Quarks top d s b strange bottom ne nm nt mu-neutrino tau-neutrino e m t electron Generation charm e-neutrino Leptons t down Leptons c up Quarks u muon tau I II III 2/3 -1/3 0 -1 All visible matter in universe is made of Generation I particles.

Held together by a powerful force: STRONG FORCE
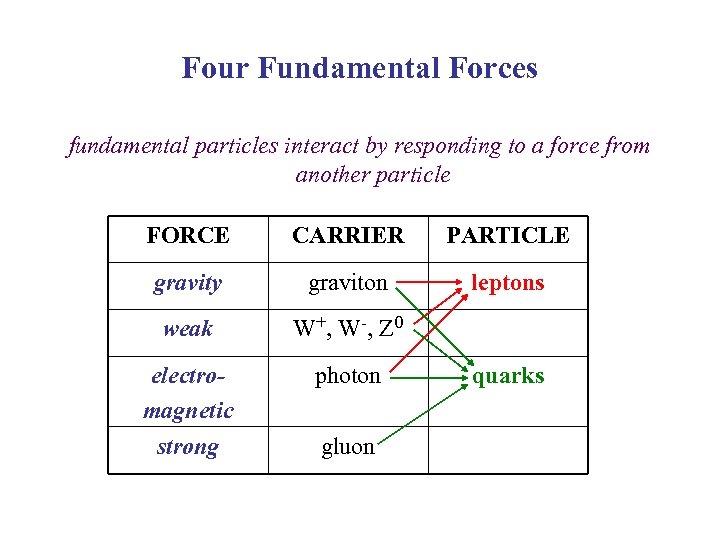
Four Fundamental Forces fundamental particles interact by responding to a force from another particle FORCE CARRIER PARTICLE gravity graviton leptons weak W + , W -, Z 0 electromagnetic strong photon gluon quarks

And still more empty space…. filled with force fields Atoms are 99. 999999% empty space !!

World of Atoms – a little background education Atom: nucleus of neutrons & protons with orbiting electrons go down one layer Electron: very light particle with negative charge Proton: weight equals ~2000 electrons, positive charge Neutron: weight almost equal to proton, no net charge go down one layer Quarks: fundamental particles, 6 types, up/down/strange are the lightest and most common Forces: strong, electromagnetic, weak, gravity; strong force holds quarks together go down one layer ? ? ? is there another layer ? ? ?
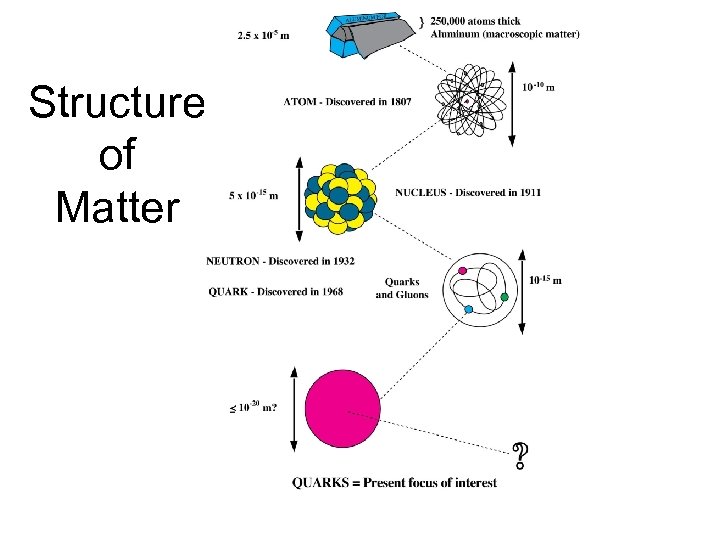
Structure of Matter
World of Atoms – a little background education we are more “empty space” than matter, “empty space” is filled with carefully balanced forces, get students to expand on the solar system model of atoms great Web pages for students: http: //www. particleadventure. org http: //education. jlab. org http: //www 2. slac. stanford. edu/vvc great Web pages for teachers: http: //www. colorado. edu/physics/2000 http: //www. fnal. gov/pub/education/k-12_programs. html http: //csee. lbl. gov http: //www. nsta. org

What really cool, tiny stuff do we study? What forces hold the neutrons and protons together in an atom? What forces hold the quarks inside a proton together? How is electric charge distributed within a neutron or proton? How is magnetic field distributed within a neutron or proton? Does a “free” quark behave the same as a quark bound inside a heavy atom?
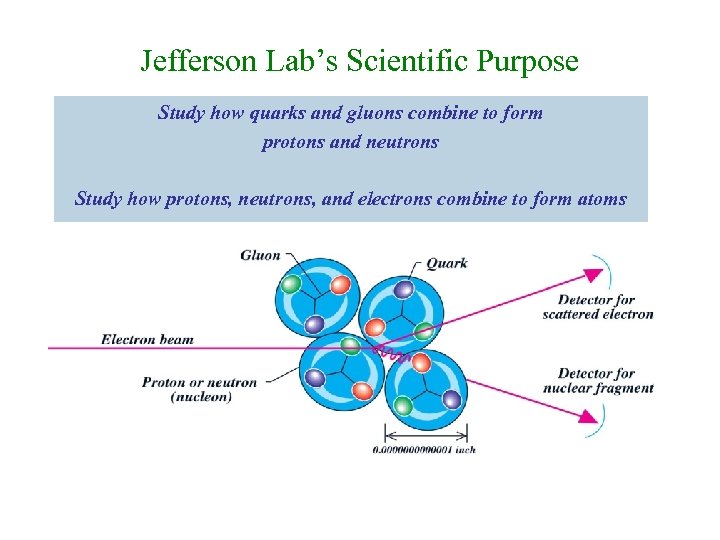
Jefferson Lab’s Scientific Purpose Study how quarks and gluons combine to form protons and neutrons Study how protons, neutrons, and electrons combine to form atoms
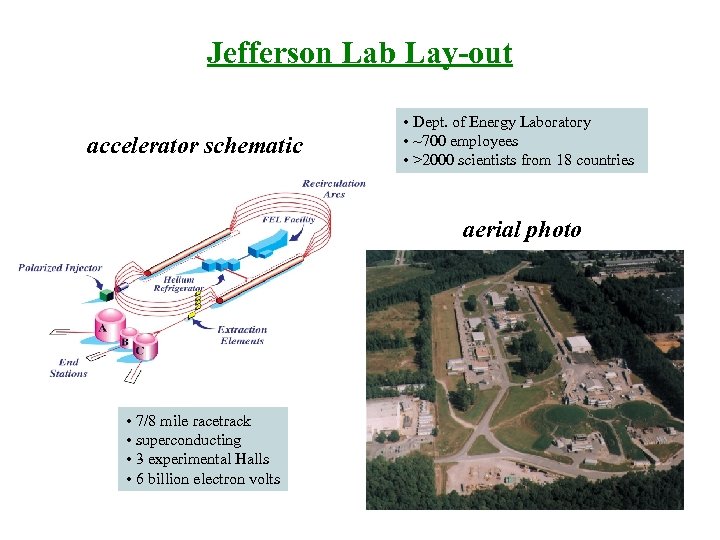
Jefferson Lab Lay-out accelerator schematic • Dept. of Energy Laboratory • ~700 employees • >2000 scientists from 18 countries aerial photo • 7/8 mile racetrack • superconducting • 3 experimental Halls • 6 billion electron volts

South Linac Cryomodules

Recirculation Arc Configuration • Arc 10
Hall C

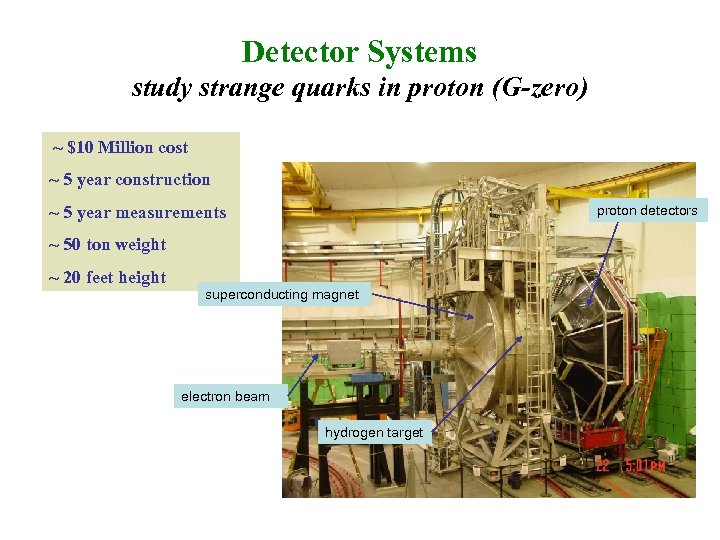
Detector Systems study strange quarks in proton (G-zero) ~ $10 Million cost ~ 5 year construction ~ 5 year measurements proton detectors ~ 50 ton weight ~ 20 feet height superconducting magnet electron beam hydrogen target

What are we studying right now ? How do strange quarks contribute to the properties of the proton? Do they contribute to the spin? Are the strange quark’s electric interactions different from their magnetic interactions?

What have we learned lately ? proton can take many shapes…… Pentaquark – 5 quark combinations may exist? quark’s spin doesn’t match neutron’s spin
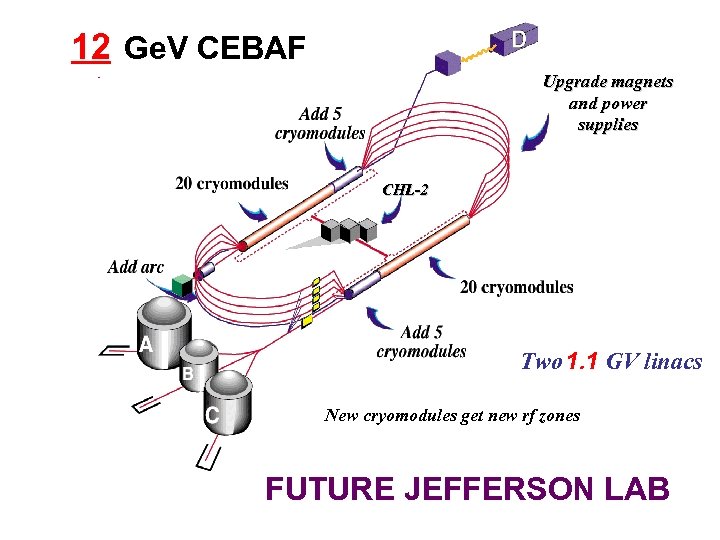
6 11 Ge. V CEBAF 12 Upgrade magnets and power supplies CHL-2 Two 1. 1 GV linacs 0. 6 New cryomodules get new rf zones FUTURE JEFFERSON LAB
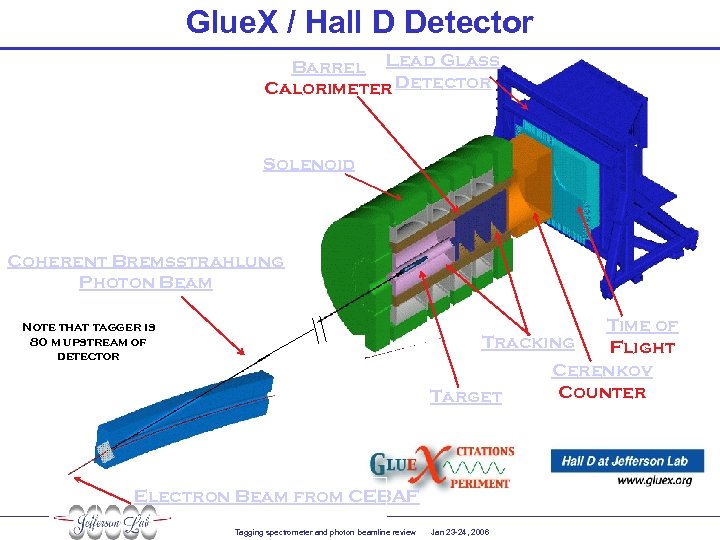
Glue. X / Hall D Detector Barrel Lead Glass Calorimeter Detector Solenoid Coherent Bremsstrahlung Photon Beam Time of Tracking Flight Cerenkov Counter Target Note that tagger is 80 m upstream of detector Electron Beam from CEBAF Tagging spectrometer and photon beamline review Jan 23 -24, 2006
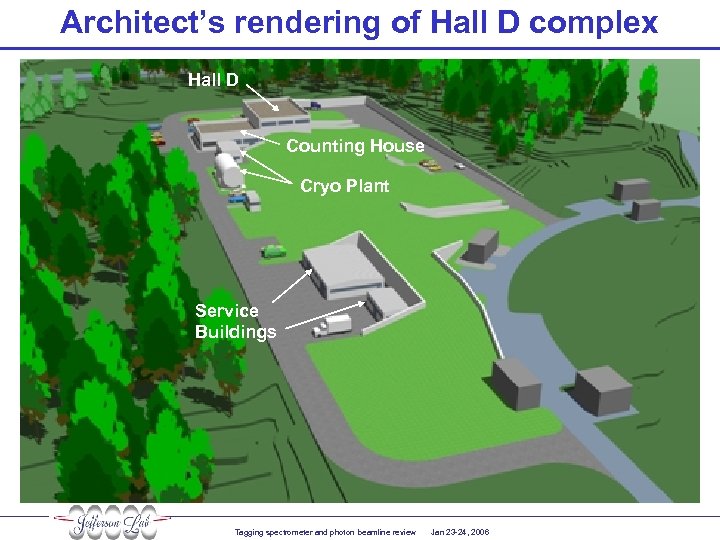
Architect’s rendering of Hall D complex Hall D Counting House Cryo Plant Service Buildings Tagging spectrometer and photon beamline review Jan 23 -24, 2006

SUMMARY Jefferson Lab: • studies how protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of atoms • studies how quarks and gluons make up neutrons and protons • collides electrons with atomic targets and measures the energy, speed, and trajectory of scattered particles for your students • introduce the solar system model of the atom • go further. . . introduce forces (gravity, weak, electromagnetic, strong) • gee whiz factor! – we are more “empty space” than matter – there are incredible forces acting in that “empty space” physics is a great career !


Nuclear Physics as a Career • college degree(s) required in physics, math, or computer science • possible career paths: – – – government laboratory scientist university professor & researcher computer firms modeling economic trends on Wall Street start-up technology companies (medical imaging, cryogenic helium…. . ) • salary range at Jefferson Lab (comparable to university professors): – Staff Scientist I (approx. $48, 000 to $75, 000) – Staff Scientist II (approx. $60, 000 to $95, 000) – Staff Scientist III (approx $75, 000 to $120, 000)
c8b66e61ae0ab5380fdf6f346aba021d.ppt