468cc414de384c2519e82843138ed74d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Jayne Bernardini Peter Schunk Jan Vanecek

Presentation Outline Evolution of Security Software Company Profiles Compare System


Security Defined Ensure data stored in a computer cannot be read without authorization Data encryption and passwords Encryption-translation of document into unintelligible language Source: http: //www. cert. org/encyc_article/tocencyc. html#Impr. Sec

History of Internet Security Incidents 1969 ARPANET begins 1986 First well-publicized security incident 1988 First automated network security incident “the Morris Worm” 1989 ARPANET officially becomes the Internet WANK/OILZ worm 1994 Tools “sniff” packets from the network 1995 Attacks on computers that have trust relationships Source: http: //www. cert. org/encyc_article/tocencyc. html#Impr. Sec

Security Technology Operational Technology Passwords Firewalls Monitoring Tools Security Analysis Tools Antivirus Crytography Level 1 • Internet • ISP Level 2 • WAN, MAN • Server Level 3 • LAN • PC Source: http: //www. cert. org/encyc_article/tocencyc. html#Impr. Sec
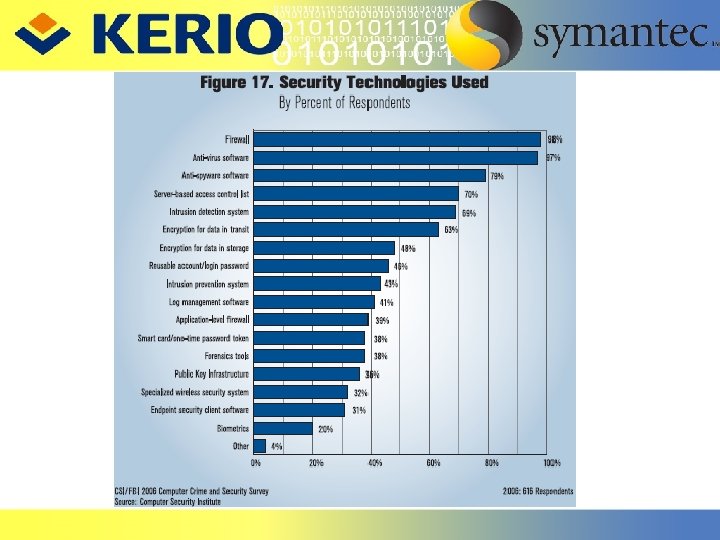


Future of Security Technology Internetworking Protocols Cope with vastly increased routing needs Intrusion Detection Anomaly detection and pattern recognition Software Engineering and System Survivability No single point of failure Web-Related Programming and Scripting Languages Inform users Intelligent Autonomous Agents Performs computation or gathers info and presents a result Source: http: //www. cert. org/encyc_article/tocencyc. html#Impr. Sec


Kerio Entered market in 1997 2005 revenue – $20, 253 Customers in 70 countries Offices in U. S. , Great Britain, and Czech Republic Services Communication Security Software Products Internet Messaging and Firewall products Kerio Mail Server Kerio Win. Route Firewall Kerio Web. STAR Source: Kerio s. r. o. Symantec Founded in April 1982 2005 revenue – $2, 583 million IPO on June 23, 1989 More than 17, 500 employees Operations in 40 countries securing sensitive online consumer interactions financial transactions instant messaging preventing malicious threats and crime ware Source: Symantec

Kerio Mail Server – Release history January 17, 2002 * SSL now works from browsers supporting 40 -bit enryption March 25, 2003 + Spam. Assassin spam filter * improved spam header filter April 2, 2003 + spam filter can change message subject September 26, 2003 + fax plugin July 18, 2005 + Web. Mail mini + support for Mac. OS X Tiger (10. 4) + Kerio Synchronization Plug-in for Outlook (synchronization of contacts and calendars in Outlook e-mail profile) Source: http: //www. kerio. com

Kerio Mail Server – Release history + ability to use two antiviruses simultaneously (Mc. Afee + one external plugin) + support for PDA in Web. Mail (http: //server/pda) October 26, 2005 * Enhanced backup options: added support for differential backup, backup scheduler is more flexible July 18, 2006 + Added two-level spam rating. Spam messages could be tagged or blocked depending on spam score. + New SURBL (Spam URI Realtime Blocklist) anti-spam check significantly increases Spam Filter efficiency. December 13, 2006 + Over-the-air synchronization with Microsoft mobile devices via Microsoft Active. Sync® protocol. Source: http: //www. kerio. com
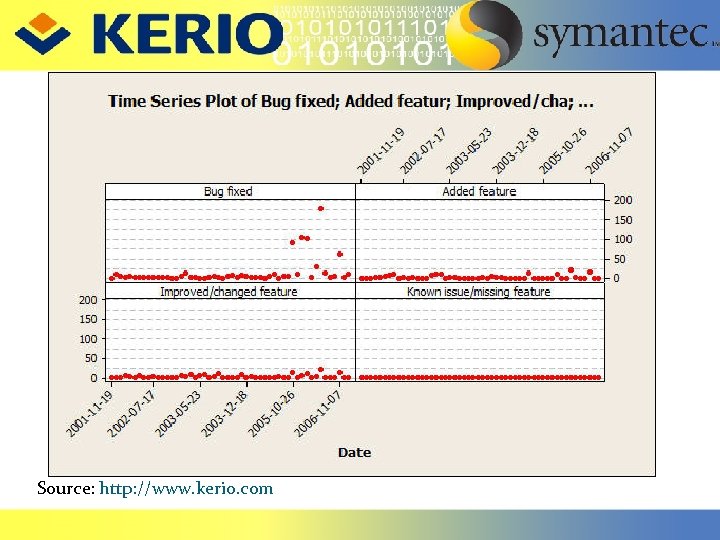
Source: http: //www. kerio. com
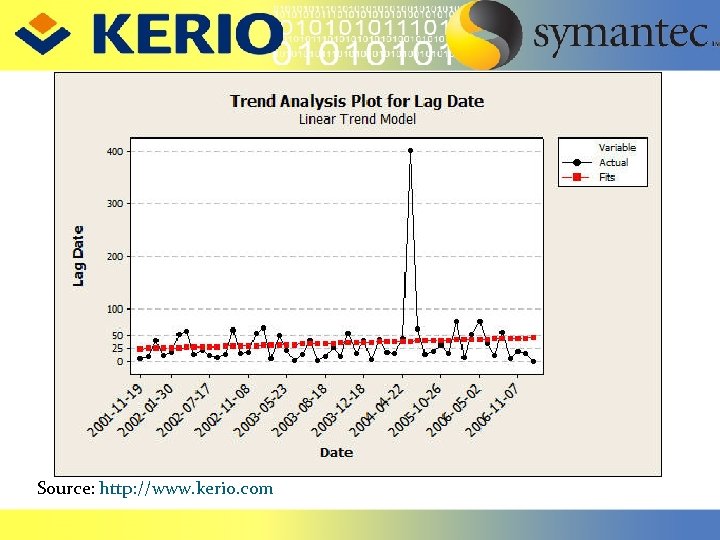
Source: http: //www. kerio. com
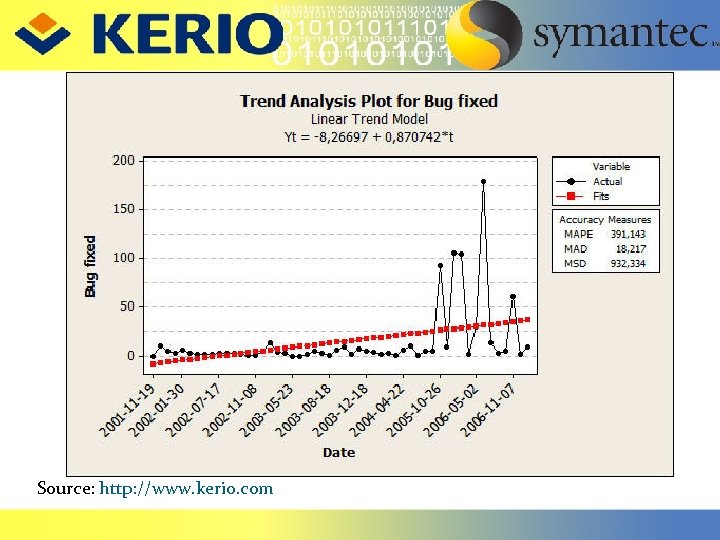
Source: http: //www. kerio. com
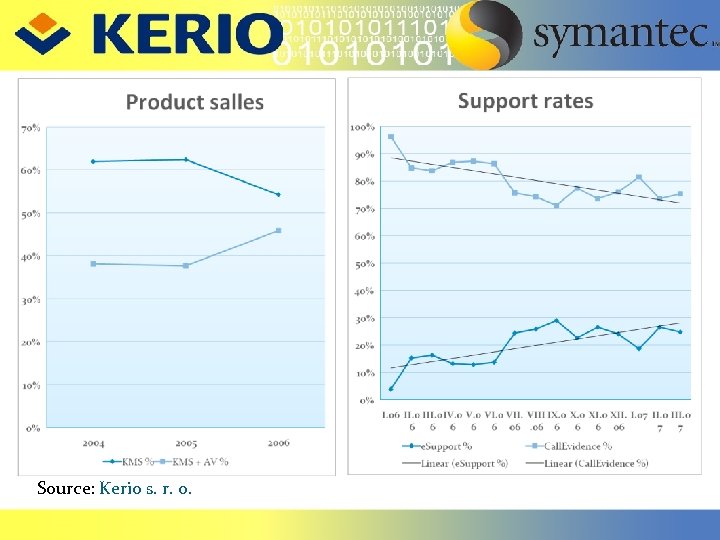
Source: Kerio s. r. o.

Compare Systems

What is mail security software? Includes: Integrated virus scanning Antispam Content filtering controls Flexibility to choose between multi-platform softwarebased Appliance-based and hosted service solutions

System Requirements • Symantec Mail Security for Microsoft Exchange: Microsoft Exchange Symantec Server 2000/2003 Exchange Intel Server-class 32 -bit processor, 1 GB of RAM • Kerio Mail Server CPU 500 MHz, 256 MB RAM Microsoft Windows, Linux Kerio OS OS

Business Requirements United States: B&B Electronics Long-Term plans Often renew licenses with same vendor Price User-friendly Czech Republic: IIB s. r. o. Short-Term plans Shorter licenses Price sensitive User-friendliness only a “plus”
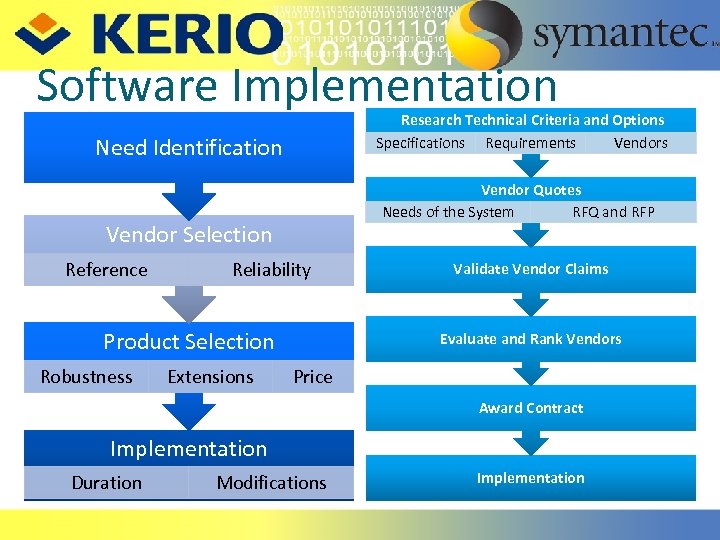
Software Implementation Research Technical Criteria and Options Specifications Requirements Vendors Need Identification Vendor Quotes Needs of the System RFQ and RFP Vendor Selection Reference Reliability Product Selection Robustness Extensions Validate Vendor Claims Evaluate and Rank Vendors Price Award Contract Implementation Duration Modifications Implementation

Common Elements Management commitment Tech support Communication of the policy Security awareness of all users

Questions? Thank you for your attention.
468cc414de384c2519e82843138ed74d.ppt