7e2d2d51a3c1bab70e6dab1d40c1fe9f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Java. Script is an object-based scripting language that is lightweight and cross-platform. 18 -Mar-18

About Java. Script is not Java, or even related to Java The original name for Java. Script was “Live. Script” The name was changed when Java became popular Now that Microsoft no longer likes Java, its name for their Java. Script dialect is “Active Script” Statements in Java. Script resemble statements in Java, because both languages borrowed heavily from the C language Java. Script should be fairly easy for Java programmers to learn However, Java. Script is a complete, full-featured, complex language Java. Script is seldom used to write complete “programs” Instead, small bits of Java. Script are used to add functionality to HTML pages Java. Script is often used in conjunction with HTML “forms” Java. Script is reasonably platform-independent 2

Java. Script is used to create interactive websites Client-side validation Dynamic drop-down menus Displaying data and time Displaying popup windows and dialog boxes (like alert dialog box, confirm dialog box and prompt dialog box) Displaying clocks etc. 3

Referring to external java script file <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" src="message. js"></script> </head> <body> <p>Welcome to Java. Script</p> <form> <input type="button" value="click" onclick="msg()"/> </form> </body> </html> external Java. Script file that prints Hello in a alert dialog box. message. js function msg(){ alert("Hello"); 4 }

Using Java. Script in a browser Java. Script code is included within <script> tags inside a HTML page or we can create a seperate java script file ending with js extension and keep our code there: <script type="text/javascript"> ……………. </script> Notes: The type attribute is to allow you to use other scripting languages (but Java. Script is the default) This simple code does the same thing as just putting <h 1>Hello World!</h 1> in the same place in the HTML document The semicolon at the end of the Java. Script statement is optional You need semicolons if you put two or more statements on the same line 5 It’s probably a good idea to keep using semicolons

Java. Script isn’t always available Some old browsers do not recognize script tags as browser need a java script engine to execute java script. These browsers will ignore the script tags but will display the included Java. Script To get old browsers to ignore the whole thing, use: <script type="text/javascript"> <!-document. write("Hello World!") --> </script> <!-- This is treated as a one-line JS comment Some users turn off Java. Script Use the <noscript>message</noscript> to display a message in place of whatever the Java. Script would put there 6

Where to put Java. Script can be put in the <head> or in the <body> of an HTML document Java. Script functions should be defined in the <head> This ensures that the function is loaded before it is needed Java. Script in the <body> will be executed as the page loads Java. Script can be put in a separate. js file <script src="my. Java. Script. File. js"></script> Put this HTML wherever you would put the actual Java. Script code An external. js file lets you use the same Java. Script on multiple HTML pages The external. js file cannot itself contain a <script> tag Java. Script can be put in an HTML form object, such as a button This Java. Script will be executed when the form object is used 7
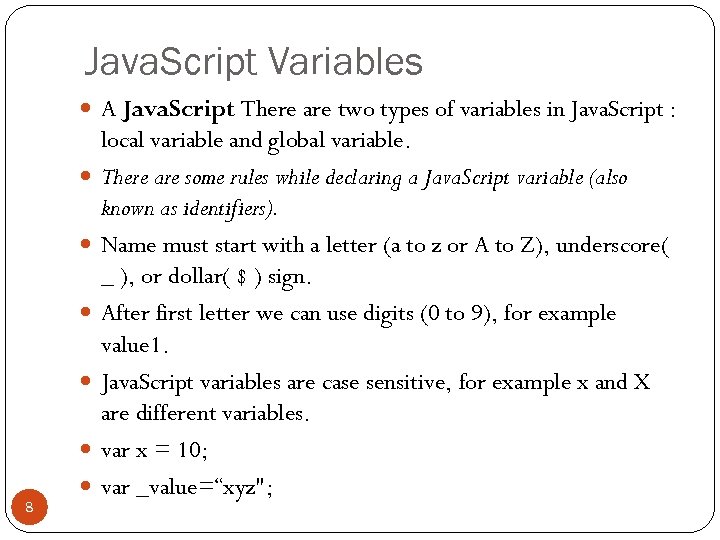
Java. Script Variables A Java. Script There are two types of variables in Java. Script : 8 local variable and global variable. There are some rules while declaring a Java. Script variable (also known as identifiers). Name must start with a letter (a to z or A to Z), underscore( _ ), or dollar( $ ) sign. After first letter we can use digits (0 to 9), for example value 1. Java. Script variables are case sensitive, for example x and X are different variables. var x = 10; var _value=“xyz";
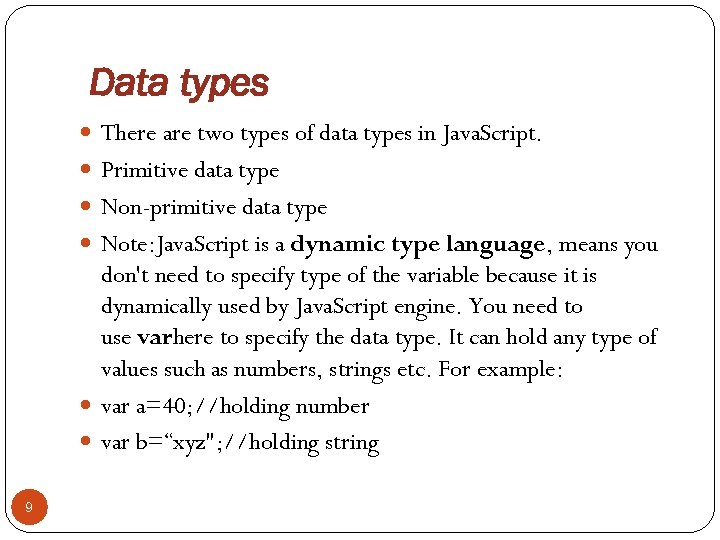
Data types There are two types of data types in Java. Script. Primitive data type Non-primitive data type Note: Java. Script is a dynamic type language, means you don't need to specify type of the variable because it is dynamically used by Java. Script engine. You need to use varhere to specify the data type. It can hold any type of values such as numbers, strings etc. For example: var a=40; //holding number var b=“xyz"; //holding string 9
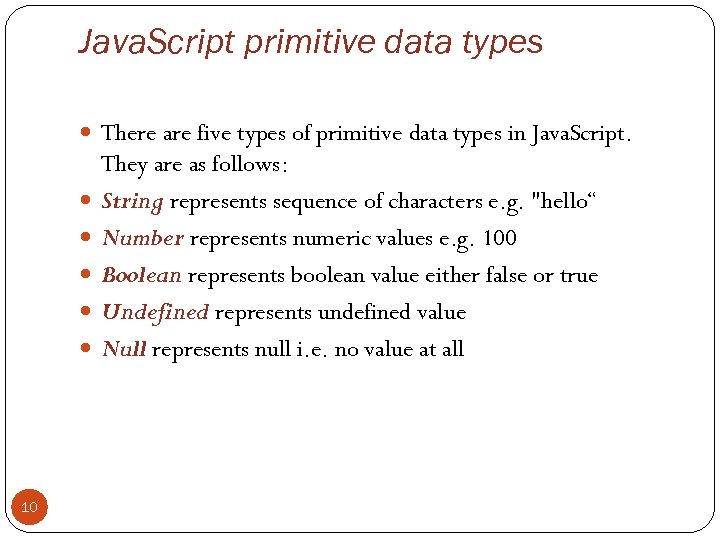
Java. Script primitive data types There are five types of primitive data types in Java. Script. 10 They are as follows: String represents sequence of characters e. g. "hello“ Number represents numeric values e. g. 100 Boolean represents boolean value either false or true Undefined represents undefined value Null represents null i. e. no value at all

The non-primitive data types are as follows Object represents instance through which we can access members Array represents group of similar values Reg. Exp represents regular expression 11

Variables are declared with a var statement: variable is simply a name of storage location. var pi = 3. 1416, x, y, name = "Dr. Dave" ; Variables names must begin with a letter or underscore Variable names are case-sensitive Variables are untyped (they can hold values of any type) The word var is optional (but it’s good style to use it) Variables declared within a function are local to that function 12 (accessible only within that function) Variables declared outside a function are global (accessible from anywhere on the page)

Operators in Java. Script . Arithmetic Operators Comparison (Relational) Operators Bitwise Operators Logical Operators Assignment Operators Special Operators 13
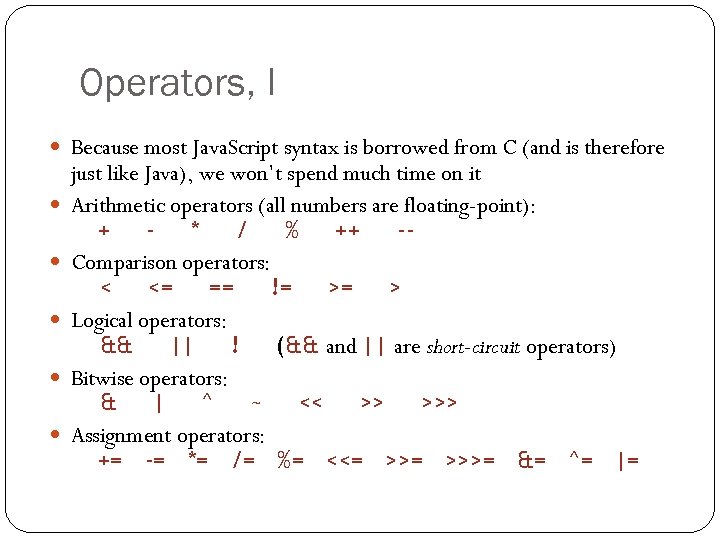
Operators, I Because most Java. Script syntax is borrowed from C (and is therefore 14 just like Java), we won’t spend much time on it Arithmetic operators (all numbers are floating-point): + * / % ++ -Comparison operators: < <= == != >= > Logical operators: && || ! (&& and || are short-circuit operators) Bitwise operators: & | ^ ~ << >> >>> Assignment operators: += -= *= /= %= <<= >>>= &= ^= |=

Operators, II String operator: + The conditional operator: condition ? value_if_true : value_if_false Special equality tests: == and != try to convert their operands to the same type before performing the test === and !== consider their operands unequal if they are of different types Additional operators (to be discussed): new 15 typeof void delete

Comments are as in C or Java: Between // and the end of the line Between /* and */ Java’s javadoc comments, /**. . . */, are treated just the same as /*. . . */ comments; they have no special meaning in Java. Script 16

Function We can call function by passing arguments. Let’s see the example 17 of function that has one argument. <script> function getcube(number){ alert(number*number); } </script> <form> <input type="button" value="click" onclick="getcube(4)"/> </form>

Function with Return Value We can call function that returns a value and use it in our program. 18 Let’s see the example of function that returns value. <script> function get. Info(){ return "hello javatpoint! How r u? "; } </script> <script> document. write(get. Info()); </script>
Java. Script if-else statement The Java. Script if-else statement is used to execute the code 19 whether condition is true or false. There are three forms of if statement in Java. Script. If Statement If else statement if else if statement

Statements, I Most Java. Script statements are also borrowed from C Assignment: greeting = "Hello, " + name; Compound statement: { statement; . . . ; statement } If statements: if (condition) statement; else statement; Familiar loop statements: while (condition) statement; do statement while (condition); for (initialization; condition; increment) statement; 20
Statements, II The switch statement: switch (expression) { case label : statement; break; . . . default : statement; } Other familiar statements: break; continue; The empty statement, as in ; ; or { } 21

Java. Script Objects • A java. Script object is an entity having state and behavior (properties and method). • For example: car, pen, bike, chair, glass, keyboard, monitor etc. • Java. Script is an object-based language. Everything is an object in Java. Script. • Java. Script is template based not class based. Here, we don't create class to get the object. But, we direct create objects. 22

Creating Objects in Java. Script • There are 3 ways to create objects. • By object literal • By creating instance of Object directly (using new keyword) • By using an object constructor (using new keyword) 23
using an Object constructor Here, you need to create function with arguments. Each argument 24 value can be assigned in the current object by using this keyword. The this keyword refers to the current object. <script> function emp(id, name, salary){ this. id=id; this. name=name; this. salary=salary; } e=new emp(103, "Vimal Jaiswal", 30000); </script>

The syntax of creating object using object literal object={property 1: value 1, property 2: value 2. . . property. N: val ue. N} <script> emp={id: 102, name: "Shyam Kumar", salary: 40000} document. write(emp. id+" "+emp. name+" "+emp. salary); </script> 25

By creating instance of Object 26 The syntax of creating object directly is given below: var objectname=new Object(); Here, new keyword is used to create object. Let’s see the example of creating object directly. <script> var emp=new Object(); emp. id=101; emp. name="Ravi Malik"; emp. salary=50000; document. write(emp. id+" "+emp. name+" "+emp. salary);

Objects in javascript Java. Script array is an object that represents a collection of similar type of elements. The Java. Script date object can be used to get year, month and day. You can display a timer on the webpage by the help of Java. Script date object. 27

Creating instance of Object The syntax of creating object directly is given below: var objectname=new Object(); Here, new keyword is used to create object. Let’s see the example of creating object directly. <script> var emp=new Object(); emp. id=101; emp. name="Ravi Malik"; emp. salary=50000; document. write(emp. id+" "+emp. name+" "+emp. salary); </sc ript> 28
Java. Script Array Java. Script array is an object that represents a collection of 29 similar type of elements. Java. Script array literal The syntax of creating array using array literal is given below: var arrayname=[value 1, value 2. . . value. N]; As you can see, values are contained inside [ ] and separated by , (comma). Let’s see the simple example of creating and using array in Java. Script.
![Example <script> var emp=["Sonoo", "Vimal", "Ratan"]; for (i=0; i<emp. length; i++){ document. write(emp[i] + Example <script> var emp=["Sonoo", "Vimal", "Ratan"]; for (i=0; i<emp. length; i++){ document. write(emp[i] +](https://present5.com/presentation/7e2d2d51a3c1bab70e6dab1d40c1fe9f/image-30.jpg)
Example <script> var emp=["Sonoo", "Vimal", "Ratan"]; for (i=0; i<emp. length; i++){ document. write(emp[i] + "<br/>"); } </script> 30
Java. Script String The Java. Script string is an object that represents a 31 sequence of characters. There are 2 ways to create string in Java. Script First way by string literal The string literal is created using double quotes. The syntax of creating string using string literal is given below: var stringname="string value";

Second way to create string object (using new keyword) The syntax of creating string object using new keyword is given below: var stringname=new String("string literal"); 32
Java. Script Math Object The Java. Script math object provides several constants and 33 methods to perform mathematical operation. Unlike date object, it doesn't have constructors. Math. sqrt(n) The Java. Script math. sqrt(n) method returns the square root of the given number. Math. random() The Java. Script math. random() method returns the random number between 0 to 1.
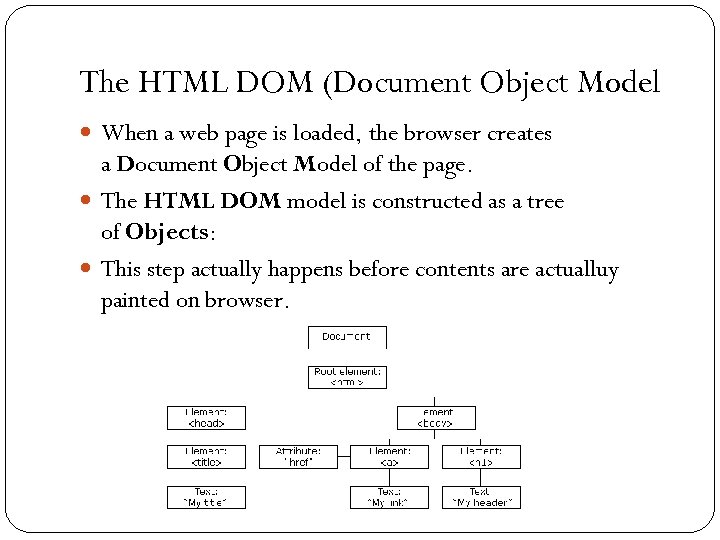
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page. The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects: This step actually happens before contents are actualluy painted on browser. 34
Continued DOM is a standard defined by w 3 c API are defined by w 3 c. And implemented by different browser vendors We can use different methods to manipuate DOM objects. Since different html elements are represented as objects of DOM. 35
What is the DOM? The DOM is a W 3 C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard. The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents: "The W 3 C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language- 36 neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document. " The W 3 C DOM standard is separated into 3 different parts: Core DOM - standard model for all document types XML DOM - standard model for XML documents HTML DOM - standard model for HTML documents
What is the HTML DOM? The HTML DOM is a standard object model 37 and programming interface for HTML. It defines: The HTML elements as objects The properties of all HTML elements The methods to access all HTML elements The events for all HTML elements In other words: The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.
In the HTML DOM object model, the document object represents your web page. Dom API is implemented by different browser vendors. The document object is the owner of all other objects in your web page. If you want to access objects in an HTML page, you always start with accessing the document object. 38
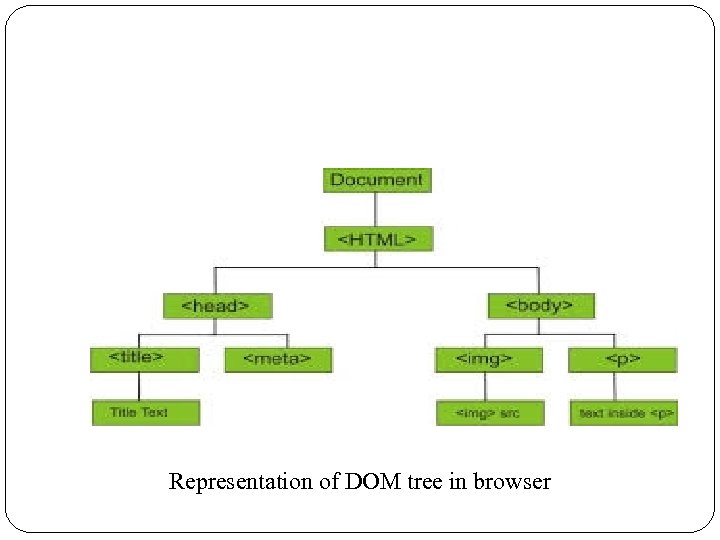
Representation of DOM tree in browser 39

Real power of javascript With the object model, Java. Script gets all the power it needs to 40 create dynamic HTML: Java. Script can change all the HTML elements in the page Java. Script can change all the CSS styles in the page Java. Script can remove existing HTML elements and attributes Java. Script can react to all existing HTML events in the page

Java. Script - HTML DOM Methods HTML DOM methods are actions you can perform (on HTML Elements) HTML DOM properties are values (of HTML Elements) that you can set or change 41
The DOM Programming Interface The HTML DOM can be accessed with Java. Script (and with other programming languages). In the DOM, all HTML elements are defined as objects. The programming interface is the properties and methods of each object. 42

Manipulating contents The get. Element. By. Id Method The most common way to access an HTML element is to use 43 the id of the element. In the example above the get. Element. By. Id method used id="demo" to find the element. The inner. HTML Property The easiest way to get the content of an element is by using the inner. HTML property. The inner. HTML property is useful for getting or replacing the content of HTML elements.
Finding HTML Elements Often, with Java. Script, you want to manipulate HTML 44 elements. To do so, you have to find the elements first. There a couple of ways to do this: Finding HTML elements by id Finding HTML elements by tag name Finding HTML elements by class name Finding HTML elements by CSS selectors Finding HTML elements by HTML object collections
7e2d2d51a3c1bab70e6dab1d40c1fe9f.ppt