742b17f0c312c4d790a67a5adcd1e020.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Java AP Computer Science (Design Patterns) Owen Astrachan Department of Computer Science, Duke University Workshop sponsored by NCSSM/Project NOW and NSF (CCR-9702550) APCS Workshop 1
Java AP Computer Science (Design Patterns) Owen Astrachan Department of Computer Science, Duke University Workshop sponsored by NCSSM/Project NOW and NSF (CCR-9702550) APCS Workshop 1
 Top ten reasons Java is better than C++ 10. main still exists, but it really is a void function 9. No = and == confusion, but instead equals and == 8. Built-in graphics API, don't need CMU, Draw. Box, … 7. Write once/run everywhere, write once/debug everywhere 6. Libraries, libraries 5. Applets make it easier to show others how clever you are APCS Workshop 2
Top ten reasons Java is better than C++ 10. main still exists, but it really is a void function 9. No = and == confusion, but instead equals and == 8. Built-in graphics API, don't need CMU, Draw. Box, … 7. Write once/run everywhere, write once/debug everywhere 6. Libraries, libraries 5. Applets make it easier to show others how clever you are APCS Workshop 2
 Top ten reasons continued 4. java. math. Big. Integer has no overloaded operators Big. Integer count = Big. Integer. ZERO; count = count. add(Big. Integer. ONE); 3. Type safety means Scheme folk won't yell as loudly 2. Don't have to understand what J# and C# are. APCS Workshop 3
Top ten reasons continued 4. java. math. Big. Integer has no overloaded operators Big. Integer count = Big. Integer. ZERO; count = count. add(Big. Integer. ONE); 3. Type safety means Scheme folk won't yell as loudly 2. Don't have to understand what J# and C# are. APCS Workshop 3
 #1 Reason Java is better than C++ James Gosling Bjarne Stroustrup APCS Workshop 4
#1 Reason Java is better than C++ James Gosling Bjarne Stroustrup APCS Workshop 4
 James Gosling l l “Invented” Java Ø First developer, originator, Impetus for GPL, free software? Ø Stallman writes emacs, gosling writes C version, shares it, sells it, oops trouble with shared Stallman: “Then he stabbed everyone in the back by putting copyrights on it, making people promise not to redistribute it and then selling it to a software-house. My later dealings with him personally showed that he was every bit as cowardly and despicable as you would expect from that history. “ APCS Workshop 5
James Gosling l l “Invented” Java Ø First developer, originator, Impetus for GPL, free software? Ø Stallman writes emacs, gosling writes C version, shares it, sells it, oops trouble with shared Stallman: “Then he stabbed everyone in the back by putting copyrights on it, making people promise not to redistribute it and then selling it to a software-house. My later dealings with him personally showed that he was every bit as cowardly and despicable as you would expect from that history. “ APCS Workshop 5
![Bjarne Stroustrup l “When I was tempted to outlaw a feature [of C++] I Bjarne Stroustrup l “When I was tempted to outlaw a feature [of C++] I](https://present5.com/presentation/742b17f0c312c4d790a67a5adcd1e020/image-6.jpg) Bjarne Stroustrup l “When I was tempted to outlaw a feature [of C++] I personally disliked, I refrained from doing so because I did not think I had the right to force my views on others” l 1994 Ø Grace Murray Hopper Award 2002 Ø From AT&T to Texas A&M l APCS Workshop 6
Bjarne Stroustrup l “When I was tempted to outlaw a feature [of C++] I personally disliked, I refrained from doing so because I did not think I had the right to force my views on others” l 1994 Ø Grace Murray Hopper Award 2002 Ø From AT&T to Texas A&M l APCS Workshop 6
 Some Java Features l l l Platform independence Ø Source and byte code are the same across platforms Ø Windows, Linux, Mac not all created equal Security Ø Designed into the language/runtime for code that “travels” Automatic garbage collection Ø Cannot free storage, cannot control when collection occurs Safety Ø e. g. , error to index past the end of an array, cannot cast objects improperly Simplicity and complexity Ø Syntactically simple with enormous libraries APCS Workshop 7
Some Java Features l l l Platform independence Ø Source and byte code are the same across platforms Ø Windows, Linux, Mac not all created equal Security Ø Designed into the language/runtime for code that “travels” Automatic garbage collection Ø Cannot free storage, cannot control when collection occurs Safety Ø e. g. , error to index past the end of an array, cannot cast objects improperly Simplicity and complexity Ø Syntactically simple with enormous libraries APCS Workshop 7
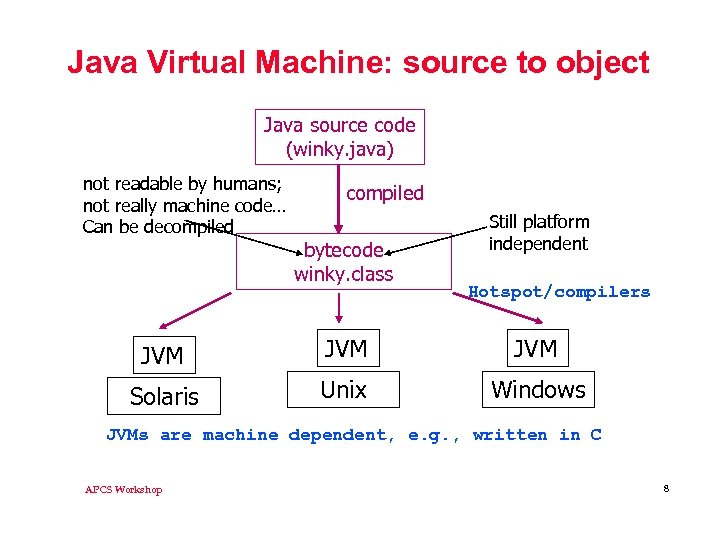 Java Virtual Machine: source to object Java source code (winky. java) not readable by humans; not really machine code… Can be decompiled bytecode winky. class Still platform independent Hotspot/compilers JVM JVM Solaris Unix Windows JVMs are machine dependent, e. g. , written in C APCS Workshop 8
Java Virtual Machine: source to object Java source code (winky. java) not readable by humans; not really machine code… Can be decompiled bytecode winky. class Still platform independent Hotspot/compilers JVM JVM Solaris Unix Windows JVMs are machine dependent, e. g. , written in C APCS Workshop 8
 Garbage Collection l Allocated memory does not need to be deallocated (delete). Ø For most programmers, who knows best? Ø Cannot prevent, cannot invoke garbage collection Ø Can take steps to free resources, e. g. , close files, dispose of Graphics contexts. l Garbage Collection Ø Concurrent/system thread tracks memory allocation Ø Checks and frees memory no longer needed/accessible Ø Designed to have minimal impact, implementation varies across platforms and JVM implementations APCS Workshop 9
Garbage Collection l Allocated memory does not need to be deallocated (delete). Ø For most programmers, who knows best? Ø Cannot prevent, cannot invoke garbage collection Ø Can take steps to free resources, e. g. , close files, dispose of Graphics contexts. l Garbage Collection Ø Concurrent/system thread tracks memory allocation Ø Checks and frees memory no longer needed/accessible Ø Designed to have minimal impact, implementation varies across platforms and JVM implementations APCS Workshop 9
 Java Object Basics l Class is an object factory Ø Class can have (static) methods Ø Defines interface programmers depend on Ø Part of inheritance hierarchy (every class is-an Object) Ø May define getter and setter methods for accessing state Ø Usually defines methods for behavior l An object is an instance of a class Ø Attributes aka state, usually private, sometimes accessible Ø Behavior invoked by calling methods Ø Allocated by calling new APCS Workshop 10
Java Object Basics l Class is an object factory Ø Class can have (static) methods Ø Defines interface programmers depend on Ø Part of inheritance hierarchy (every class is-an Object) Ø May define getter and setter methods for accessing state Ø Usually defines methods for behavior l An object is an instance of a class Ø Attributes aka state, usually private, sometimes accessible Ø Behavior invoked by calling methods Ø Allocated by calling new APCS Workshop 10
 Java primitives (not objects) l l Logical : boolean Ø No boolean/int conversion or cast while(list) {…} Text: char Ø Unicode, not part of AP subset l Integral: byte, short, int, long Ø By definition: 8, 16, 32, 64 bits long l Floating point: double, float Ø Use double, float not in the subset APCS Workshop 11
Java primitives (not objects) l l Logical : boolean Ø No boolean/int conversion or cast while(list) {…} Text: char Ø Unicode, not part of AP subset l Integral: byte, short, int, long Ø By definition: 8, 16, 32, 64 bits long l Floating point: double, float Ø Use double, float not in the subset APCS Workshop 11
 Top 10 reasons for moving AB to Java 10. Things are simpler when everything is a pointer 9. More material to cover with Map and Set, helps use up abundance of free time available in AB courses 8. Just when you thought it was safe to go back in the water, the fish become unbounded 7. ap. exam. Quilt. Problem throws Story. Too. Long Exception 6. I never understood how templates worked anyway 5. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Array. List v. apvector; String v string; Array. Stack v. apstack APCS Workshop 12
Top 10 reasons for moving AB to Java 10. Things are simpler when everything is a pointer 9. More material to cover with Map and Set, helps use up abundance of free time available in AB courses 8. Just when you thought it was safe to go back in the water, the fish become unbounded 7. ap. exam. Quilt. Problem throws Story. Too. Long Exception 6. I never understood how templates worked anyway 5. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Array. List v. apvector; String v string; Array. Stack v. apstack APCS Workshop 12
 Reason # 4 foo. cpp: In function `void print(const map
Reason # 4 foo. cpp: In function `void print(const map
 Top 10 reasons continued 3. In grading AP exams, we can have a usage error for capitalization problems, e. g. , the real-estate error public class Fish { public Location location() { return my. Loc; } } Array. List list = new Array. List(); Iterator it = list. iterator(); // code from Array. List class follows // public Iterator iterator() {…} APCS Workshop 14
Top 10 reasons continued 3. In grading AP exams, we can have a usage error for capitalization problems, e. g. , the real-estate error public class Fish { public Location location() { return my. Loc; } } Array. List list = new Array. List(); Iterator it = list. iterator(); // code from Array. List class follows // public Iterator iterator() {…} APCS Workshop 14
 #2 Reason to switch AB to Java 1. Source code: java. util. Hash. Map and stl_hashtable. h public boolean contains. Key(Object key) { Entry tab[] = table; if (key != null) { int hash = key. hash. Code(); int index = (hash & 0 x 7 FFFFFFF) % tab. length; for (Entry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e. next) if (e. hash==hash && key. equals(e. key)) return true; } return false; } size_type count(const key_type& __key) const { const size_type __n = _M_ bkt_num_key(__key); size_type __result = 0; for (const Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__n]; __cur = __cur->_M_next) if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_ val), __key)) ++__result; } return __result; APCS Workshop 15
#2 Reason to switch AB to Java 1. Source code: java. util. Hash. Map and stl_hashtable. h public boolean contains. Key(Object key) { Entry tab[] = table; if (key != null) { int hash = key. hash. Code(); int index = (hash & 0 x 7 FFFFFFF) % tab. length; for (Entry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e. next) if (e. hash==hash && key. equals(e. key)) return true; } return false; } size_type count(const key_type& __key) const { const size_type __n = _M_ bkt_num_key(__key); size_type __result = 0; for (const Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__n]; __cur = __cur->_M_next) if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_ val), __key)) ++__result; } return __result; APCS Workshop 15
 #1 Reason for using Java in AB 1. No friends, but there is free garbage collection APCS Workshop 16
#1 Reason for using Java in AB 1. No friends, but there is free garbage collection APCS Workshop 16
 java. util. Collection l Interface for collections of objects Ø See API for details, AP subset requires only a few of the methods for subinterfaces List and Set, and for separate interface Map l Which interface and class should be used? Tradeoffs. Ø Why choose Array. List vs Linked. List? Ø Why choose Hash. Set vs Tree. Set? l What about classes, interfaces, and methods not in the subset? Ø Collection interface compared to Collections class Collection. add. All(Collection); // object method Collections. sort(Collection); // static method APCS Workshop 17
java. util. Collection l Interface for collections of objects Ø See API for details, AP subset requires only a few of the methods for subinterfaces List and Set, and for separate interface Map l Which interface and class should be used? Tradeoffs. Ø Why choose Array. List vs Linked. List? Ø Why choose Hash. Set vs Tree. Set? l What about classes, interfaces, and methods not in the subset? Ø Collection interface compared to Collections class Collection. add. All(Collection); // object method Collections. sort(Collection); // static method APCS Workshop 17
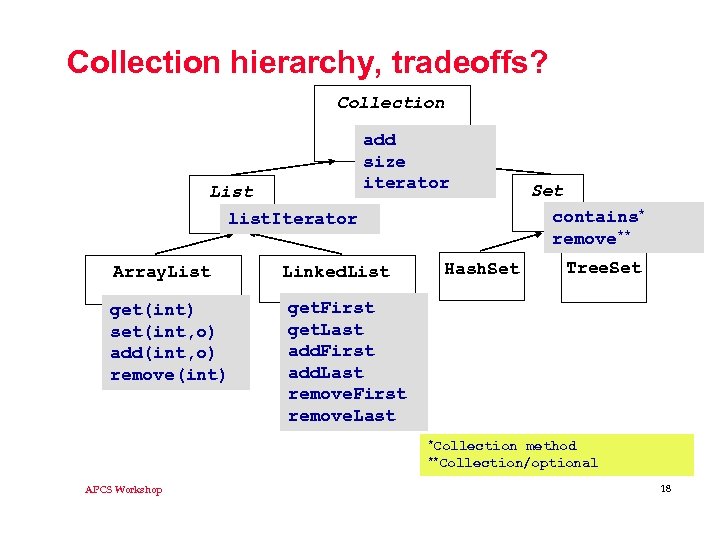 Collection hierarchy, tradeoffs? Collection List list. Iterator Array. List get(int) set(int, o) add(int, o) remove(int) add size iterator Linked. List Hash. Set contains* remove** Tree. Set get. First get. Last add. First add. Last remove. First remove. Last *Collection method **Collection/optional APCS Workshop 18
Collection hierarchy, tradeoffs? Collection List list. Iterator Array. List get(int) set(int, o) add(int, o) remove(int) add size iterator Linked. List Hash. Set contains* remove** Tree. Set get. First get. Last add. First add. Last remove. First remove. Last *Collection method **Collection/optional APCS Workshop 18
 Searching, Maps, Tables l Searching is a fundamentally important operation Ø We want to search quickly, very quickly Ø Consider searching using google. com or whitepages. com? Ø In general we want to search in a collection for a key l Finding unique words in a file (or webpage or disk or …) Ø Add words to Array. List, search before adding • Is it worth it keep the list sorted? • Add all words then remove duplicates, faster? Use java. util. Set implementations Tree. Set or Hash. Set What are the tradeoffs in these choices? Ø Algorithmic/theory, programming/engineering Ø l APCS Workshop 19
Searching, Maps, Tables l Searching is a fundamentally important operation Ø We want to search quickly, very quickly Ø Consider searching using google. com or whitepages. com? Ø In general we want to search in a collection for a key l Finding unique words in a file (or webpage or disk or …) Ø Add words to Array. List, search before adding • Is it worth it keep the list sorted? • Add all words then remove duplicates, faster? Use java. util. Set implementations Tree. Set or Hash. Set What are the tradeoffs in these choices? Ø Algorithmic/theory, programming/engineering Ø l APCS Workshop 19
 From Google to Maps l If we wanted to write a search engine we’d need to access lots of pages and keep lots of data Ø Given a word, on what pages does it appear? Ø This is a map of words->web pages l In general a map associates a key with a value Ø Look up the key in the map, get the value Ø Google: key is word/words, value is list of web pages Ø Anagram: key is string, value is words that are anagrams l Interface issues Ø Lookup a key, return boolean: in map or value: associated with the key (what if key not in map? ) Ø Insert a key/value pair into the map APCS Workshop 20
From Google to Maps l If we wanted to write a search engine we’d need to access lots of pages and keep lots of data Ø Given a word, on what pages does it appear? Ø This is a map of words->web pages l In general a map associates a key with a value Ø Look up the key in the map, get the value Ø Google: key is word/words, value is list of web pages Ø Anagram: key is string, value is words that are anagrams l Interface issues Ø Lookup a key, return boolean: in map or value: associated with the key (what if key not in map? ) Ø Insert a key/value pair into the map APCS Workshop 20
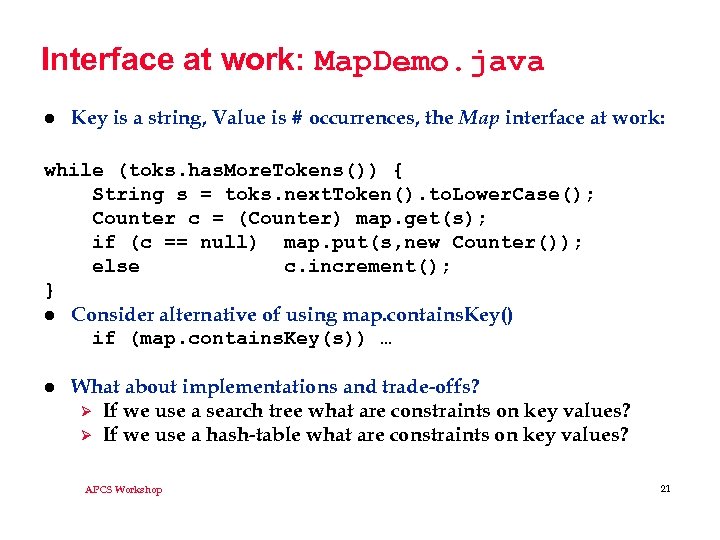 Interface at work: Map. Demo. java l Key is a string, Value is # occurrences, the Map interface at work: while (toks. has. More. Tokens()) { String s = toks. next. Token(). to. Lower. Case(); Counter c = (Counter) map. get(s); if (c == null) map. put(s, new Counter()); else c. increment(); } l Consider alternative of using map. contains. Key() if (map. contains. Key(s)) … l What about implementations and trade-offs? Ø If we use a search tree what are constraints on key values? Ø If we use a hash-table what are constraints on key values? APCS Workshop 21
Interface at work: Map. Demo. java l Key is a string, Value is # occurrences, the Map interface at work: while (toks. has. More. Tokens()) { String s = toks. next. Token(). to. Lower. Case(); Counter c = (Counter) map. get(s); if (c == null) map. put(s, new Counter()); else c. increment(); } l Consider alternative of using map. contains. Key() if (map. contains. Key(s)) … l What about implementations and trade-offs? Ø If we use a search tree what are constraints on key values? Ø If we use a hash-table what are constraints on key values? APCS Workshop 21
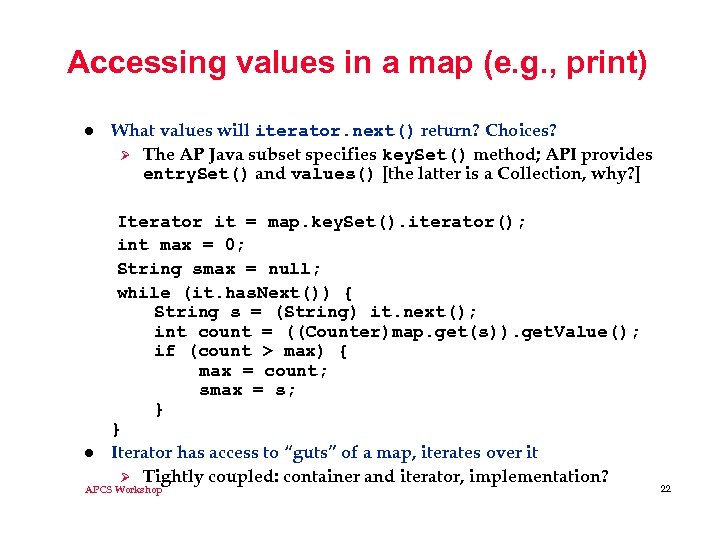 Accessing values in a map (e. g. , print) l l What values will iterator. next() return? Choices? Ø The AP Java subset specifies key. Set() method; API provides entry. Set() and values() [the latter is a Collection, why? ] Iterator it = map. key. Set(). iterator(); int max = 0; String smax = null; while (it. has. Next()) { String s = (String) it. next(); int count = ((Counter)map. get(s)). get. Value(); if (count > max) { max = count; smax = s; } } Iterator has access to “guts” of a map, iterates over it Ø Tightly coupled: container and iterator, implementation? APCS Workshop 22
Accessing values in a map (e. g. , print) l l What values will iterator. next() return? Choices? Ø The AP Java subset specifies key. Set() method; API provides entry. Set() and values() [the latter is a Collection, why? ] Iterator it = map. key. Set(). iterator(); int max = 0; String smax = null; while (it. has. Next()) { String s = (String) it. next(); int count = ((Counter)map. get(s)). get. Value(); if (count > max) { max = count; smax = s; } } Iterator has access to “guts” of a map, iterates over it Ø Tightly coupled: container and iterator, implementation? APCS Workshop 22
 Iterators and the Map. iterator() method l We ask a map/container to provide us with an iterator Ø We don't know how the map is implemented, just want an iterator Ø Map object is an iterator factory: makes/creates iterator l Typically the iterator is a nested or inner class Ø Not part of the AP Java subset, useful to know about Ø Inner class is an object that has access to enclosing object Ø Static inner class has no associated object, like nested Node class in C++ APCS Workshop 23
Iterators and the Map. iterator() method l We ask a map/container to provide us with an iterator Ø We don't know how the map is implemented, just want an iterator Ø Map object is an iterator factory: makes/creates iterator l Typically the iterator is a nested or inner class Ø Not part of the AP Java subset, useful to know about Ø Inner class is an object that has access to enclosing object Ø Static inner class has no associated object, like nested Node class in C++ APCS Workshop 23
 Map example: finding anagrams l Anagram. Finder: alternative to finding anagrams Ø Maps string (normalized): key to Array. List of Strings value Ø Look up normalized string, associate all "equal" strings with normalized form Ø To print, loop over all keys, grab Array. List, print if ? ? ? l Each value in the map is list/collection of anagrams Ø How do we look up this value? Ø How do we create initial list to store (first time) l See also mapanagram. cpp for standard C++ using STL Ø The STL code is very similar to Java! (if you can read it) APCS Workshop 24
Map example: finding anagrams l Anagram. Finder: alternative to finding anagrams Ø Maps string (normalized): key to Array. List of Strings value Ø Look up normalized string, associate all "equal" strings with normalized form Ø To print, loop over all keys, grab Array. List, print if ? ? ? l Each value in the map is list/collection of anagrams Ø How do we look up this value? Ø How do we create initial list to store (first time) l See also mapanagram. cpp for standard C++ using STL Ø The STL code is very similar to Java! (if you can read it) APCS Workshop 24
 Eric Raymond Open source evangelist Ø The Cathedral and the Bazaar http: //tuxedo. org/~esr/writings/cathedralbazaar/ Ø How to construct software “Good programmers know what to write. Great ones know what to rewrite (and reuse). ” l How to convince someone that guns are a good idea? Put this sign up: l l THIS HOME IS A GUN-FREE ZONE APCS Workshop 25
Eric Raymond Open source evangelist Ø The Cathedral and the Bazaar http: //tuxedo. org/~esr/writings/cathedralbazaar/ Ø How to construct software “Good programmers know what to write. Great ones know what to rewrite (and reuse). ” l How to convince someone that guns are a good idea? Put this sign up: l l THIS HOME IS A GUN-FREE ZONE APCS Workshop 25


