f011d220af424969a11cab4a9983befb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Jasig - Spring 2010 Wednesday, March 10, 2010 8: 30 am Kuali Identity Management: Introduction and Implementation Options
Jasig - Spring 2010 Wednesday, March 10, 2010 8: 30 am Kuali Identity Management: Introduction and Implementation Options
 Kuali Identity Management: Introduction and Implementation Options Eric Westfall Indiana University ewestfal@indiana. edu Dan Seibert University of California, San Diego dseibert@ucsd. edu 2
Kuali Identity Management: Introduction and Implementation Options Eric Westfall Indiana University ewestfal@indiana. edu Dan Seibert University of California, San Diego dseibert@ucsd. edu 2
 Implementing Kuali Identity Management at your Institution KIM Introduction
Implementing Kuali Identity Management at your Institution KIM Introduction
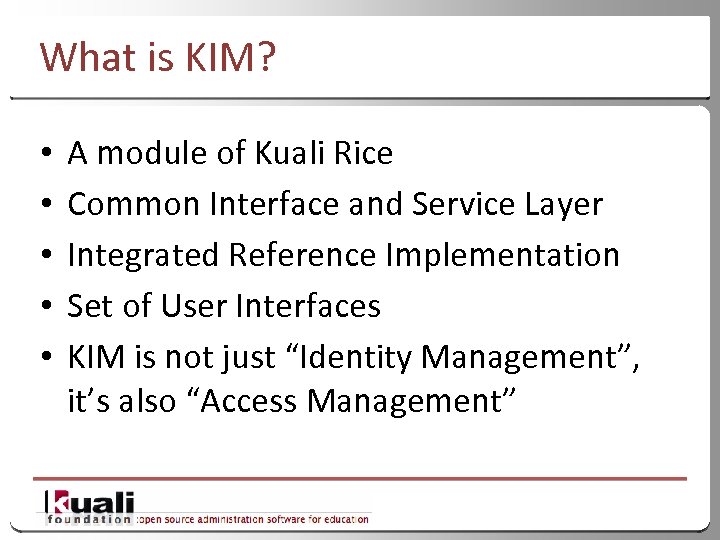 What is KIM? • • • A module of Kuali Rice Common Interface and Service Layer Integrated Reference Implementation Set of User Interfaces KIM is not just “Identity Management”, it’s also “Access Management” 4
What is KIM? • • • A module of Kuali Rice Common Interface and Service Layer Integrated Reference Implementation Set of User Interfaces KIM is not just “Identity Management”, it’s also “Access Management” 4
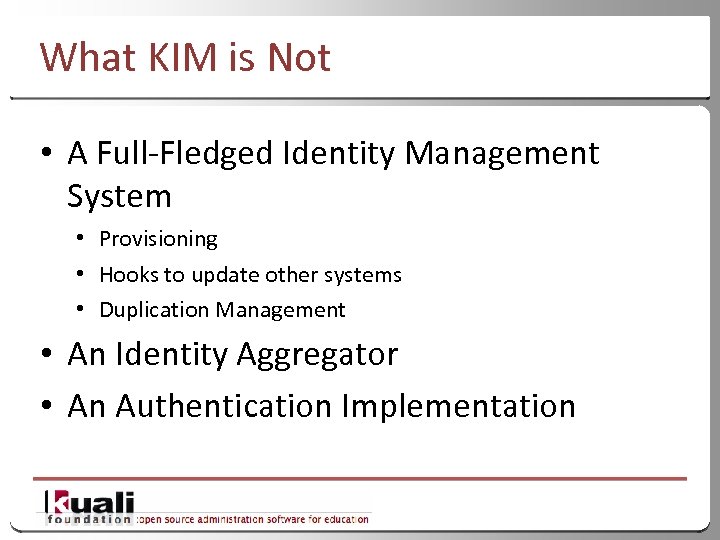 What KIM is Not • A Full-Fledged Identity Management System • Provisioning • Hooks to update other systems • Duplication Management • An Identity Aggregator • An Authentication Implementation 5
What KIM is Not • A Full-Fledged Identity Management System • Provisioning • Hooks to update other systems • Duplication Management • An Identity Aggregator • An Authentication Implementation 5
 Why Did We Create KIM?
Why Did We Create KIM?
 Motivations • Expansion of Kuali • Common Identity Management API • Consistent Authorization Implementation 7
Motivations • Expansion of Kuali • Common Identity Management API • Consistent Authorization Implementation 7
 What we did not want KFS IDM KC IDM KS 8
What we did not want KFS IDM KC IDM KS 8
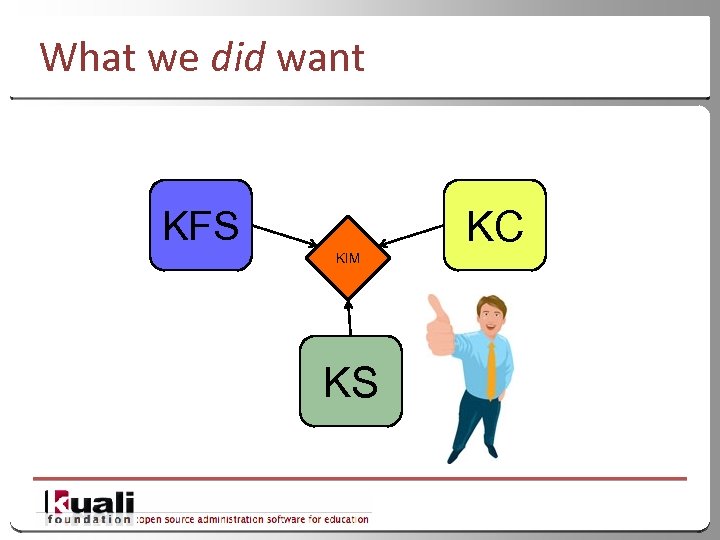 What we did want KC KFS KIM KS 9
What we did want KC KFS KIM KS 9
 Design Considerations • • • Existence of Other Id. M Solutions Legacy/Existing Implementations Replaceable Services Separation of Concerns Service Bus Maintenance GUIs 10
Design Considerations • • • Existence of Other Id. M Solutions Legacy/Existing Implementations Replaceable Services Separation of Concerns Service Bus Maintenance GUIs 10
 KIM Terminology
KIM Terminology
 KIM Terminology • Namespace • Entity • Principal ID • Principal Name • Person • Entity Type 12
KIM Terminology • Namespace • Entity • Principal ID • Principal Name • Person • Entity Type 12
 KIM Terminology • Group • Role • Qualifier • Permission / Permission Template • Responsibility / Responsibility Template 13
KIM Terminology • Group • Role • Qualifier • Permission / Permission Template • Responsibility / Responsibility Template 13
 KIM Services
KIM Services
 Components • Service Interface API • Reference Implementation • Functional Maintenance User Interfaces 15
Components • Service Interface API • Reference Implementation • Functional Maintenance User Interfaces 15
 KIM Core Services • • • Identity Service Group Service Role Service Permission Service Responsibility Service “Authentication” Service 16
KIM Core Services • • • Identity Service Group Service Role Service Permission Service Responsibility Service “Authentication” Service 16
 Other KIM Services • • • Identity Management Service Role Management Service Person Service Identity Archive Service “Update” Services 17
Other KIM Services • • • Identity Management Service Role Management Service Person Service Identity Archive Service “Update” Services 17
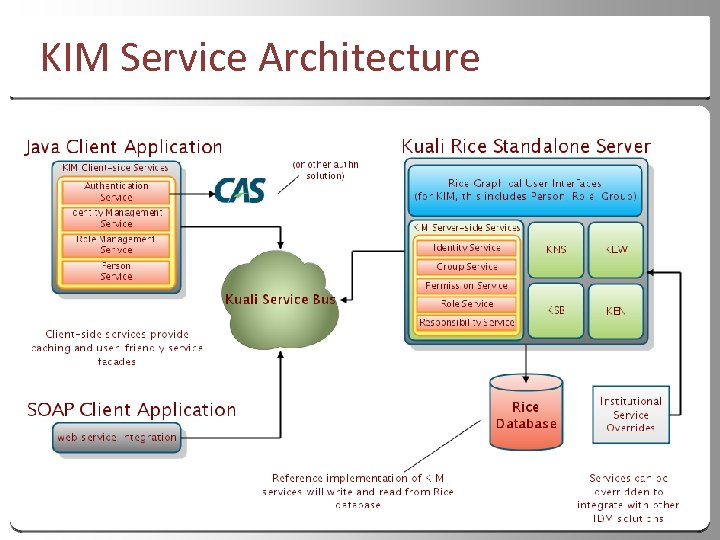 KIM Service Architecture 18
KIM Service Architecture 18
 Remember… • The primary goal of KIM was to build a service-oriented abstraction layer for Identity and Access Management • Integration with other IDM services was acknowledged, expected, and designed for! 19
Remember… • The primary goal of KIM was to build a service-oriented abstraction layer for Identity and Access Management • Integration with other IDM services was acknowledged, expected, and designed for! 19
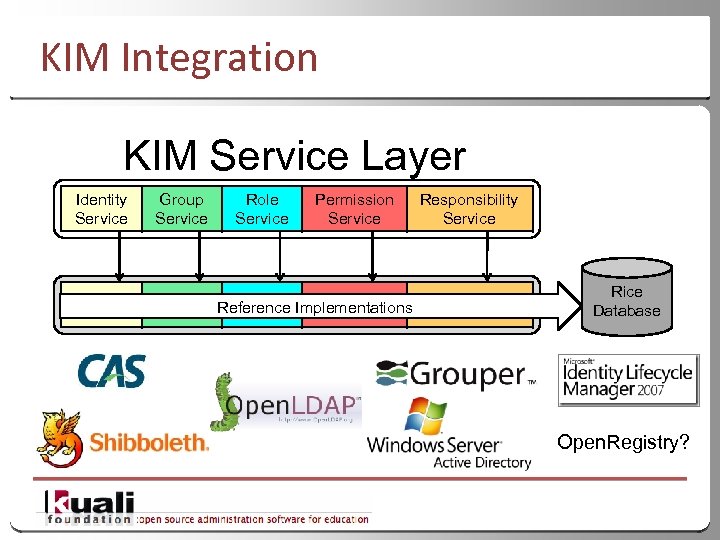 KIM Integration KIM Service Layer Identity Service Group Service Role Service Permission Service Reference Implementations Responsibility Service Rice Database Open. Registry? 20
KIM Integration KIM Service Layer Identity Service Group Service Role Service Permission Service Reference Implementations Responsibility Service Rice Database Open. Registry? 20
 Implementing Kuali Identity Management at your Institution Integrating KIM with other Id. M products
Implementing Kuali Identity Management at your Institution Integrating KIM with other Id. M products
 KIM Integration with various Identity Management Systems 22
KIM Integration with various Identity Management Systems 22
 with • CAS – Authentication system for Single Sign On (SSO) • Two ways to integrate: 1. CAS Server 2. Rice Client Application • Integration with Rice Client application will be the most likely integration scenario 23
with • CAS – Authentication system for Single Sign On (SSO) • Two ways to integrate: 1. CAS Server 2. Rice Client Application • Integration with Rice Client application will be the most likely integration scenario 23
 CAS – Server Integration • Implement a custom CAS Authentication. Handler which interfaces with the KIM services or database • Kuali already provides such an implementation in it’s Subversion repository • kuali-cas project 24
CAS – Server Integration • Implement a custom CAS Authentication. Handler which interfaces with the KIM services or database • Kuali already provides such an implementation in it’s Subversion repository • kuali-cas project 24
 CAS – Rice Client Integration • Integrate the CAS client with: 1. Kuali Rice Standalone Server 2. A Kuali Rice client application • KIM provides an “Authentication. Service” which is used to inform the Rice framework about the authenticated principal • Default implementation simply reads REMOTE_USER • Sufficient for CAS integration 25
CAS – Rice Client Integration • Integrate the CAS client with: 1. Kuali Rice Standalone Server 2. A Kuali Rice client application • KIM provides an “Authentication. Service” which is used to inform the Rice framework about the authenticated principal • Default implementation simply reads REMOTE_USER • Sufficient for CAS integration 25
 CAS – Setup • Simply configure the standard CAS servlet filters in your web. xml as you would normally • Authentication. Filter • Cas 20 Proxy. Receiving. Ticket. Validation. Filter • Http. Servlet. Request. Wrapper. Filter • The usernames entered into the CAS login must match the principal names in your KIM implementation 26
CAS – Setup • Simply configure the standard CAS servlet filters in your web. xml as you would normally • Authentication. Filter • Cas 20 Proxy. Receiving. Ticket. Validation. Filter • Http. Servlet. Request. Wrapper. Filter • The usernames entered into the CAS login must match the principal names in your KIM implementation 26
 with • Microsoft Active Directory provides “LDAP-like” directory services among other network services • We will concentrate on groups defined in ADS and how they can be integrated with the KIM Group. Service • This particular usage has been implemented at Indiana University 27
with • Microsoft Active Directory provides “LDAP-like” directory services among other network services • We will concentrate on groups defined in ADS and how they can be integrated with the KIM Group. Service • This particular usage has been implemented at Indiana University 27
 ADS – KIM Group Requirements • Should be able to use ADS groups in addition to the out-of-the-box KIM group store • Groups must have a unique ID • Groups are also uniquely identified by a combination of Namespace and Name • Group membership can be nested 28
ADS – KIM Group Requirements • Should be able to use ADS groups in addition to the out-of-the-box KIM group store • Groups must have a unique ID • Groups are also uniquely identified by a combination of Namespace and Name • Group membership can be nested 28
 ADS Group Integration – Implementation • ADS groups are assigned a namespace of “ADS” which allows the Group. Service to determine how to load the Group • ADS groups have an ID assigned to them consisting of “ADS” and the group name • i. e. ADS: My. Ads. Group. Name 29
ADS Group Integration – Implementation • ADS groups are assigned a namespace of “ADS” which allows the Group. Service to determine how to load the Group • ADS groups have an ID assigned to them consisting of “ADS” and the group name • i. e. ADS: My. Ads. Group. Name 29
 ADS Group Integration – Group. Service • Override the Group. Service so that it loads groups from both ADS (via LDAP) and the KIM database • IF - id starts with “ADS” or namespace equals “ADS”, query ADS • ELSE - delegate to reference implementation • Various operations need to be customized including operations to load Group. Info objects as well as checking Group membership • Also customize the Group Lookup screen so that it can search for Groups in ADS 30
ADS Group Integration – Group. Service • Override the Group. Service so that it loads groups from both ADS (via LDAP) and the KIM database • IF - id starts with “ADS” or namespace equals “ADS”, query ADS • ELSE - delegate to reference implementation • Various operations need to be customized including operations to load Group. Info objects as well as checking Group membership • Also customize the Group Lookup screen so that it can search for Groups in ADS 30
 Integrating KIM with LDAP • LDAP Integration Efforts • University of Arizona • San Joaquin Delta College • UC Davis • Using CAS to connect to LDAP 31
Integrating KIM with LDAP • LDAP Integration Efforts • University of Arizona • San Joaquin Delta College • UC Davis • Using CAS to connect to LDAP 31
 KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Identity information is available in UA’s Enterprise Directory Service (EDS) • Uses Spring LDAP as an adapter layer between Spring and LDAP datasource • Uses KIM Parameter. Service to map between KIM and LDAP attributes • Implement / Override KIM Identity. Service • In order to use the KIM GUI’s properly, the UIDocument. Service is also overridden 32
KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Identity information is available in UA’s Enterprise Directory Service (EDS) • Uses Spring LDAP as an adapter layer between Spring and LDAP datasource • Uses KIM Parameter. Service to map between KIM and LDAP attributes • Implement / Override KIM Identity. Service • In order to use the KIM GUI’s properly, the UIDocument. Service is also overridden 32
 KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Setup Spring LDAP module • •
KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Setup Spring LDAP module • •
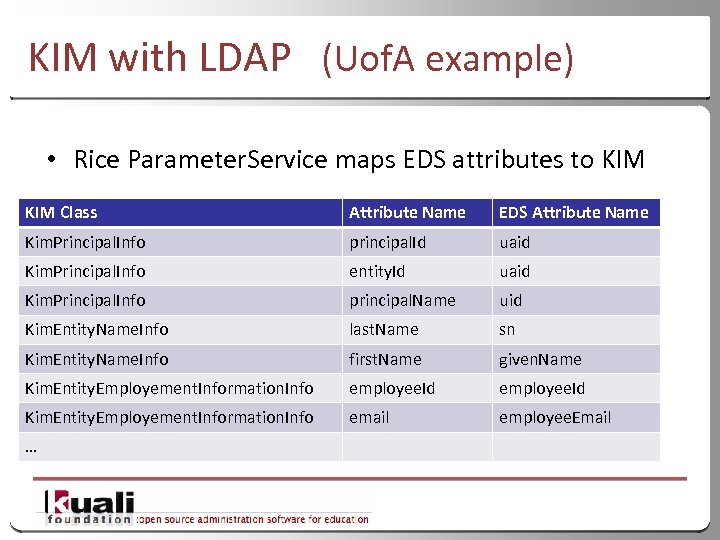 KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Rice Parameter. Service maps EDS attributes to KIM Class Attribute Name EDS Attribute Name Kim. Principal. Info principal. Id uaid Kim. Principal. Info entity. Id uaid Kim. Principal. Info principal. Name uid Kim. Entity. Name. Info last. Name sn Kim. Entity. Name. Info first. Name given. Name Kim. Entity. Employement. Information. Info employee. Id Kim. Entity. Employement. Information. Info email employee. Email … 34
KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) • Rice Parameter. Service maps EDS attributes to KIM Class Attribute Name EDS Attribute Name Kim. Principal. Info principal. Id uaid Kim. Principal. Info entity. Id uaid Kim. Principal. Info principal. Name uid Kim. Entity. Name. Info last. Name sn Kim. Entity. Name. Info first. Name given. Name Kim. Entity. Employement. Information. Info employee. Id Kim. Entity. Employement. Information. Info email employee. Email … 34
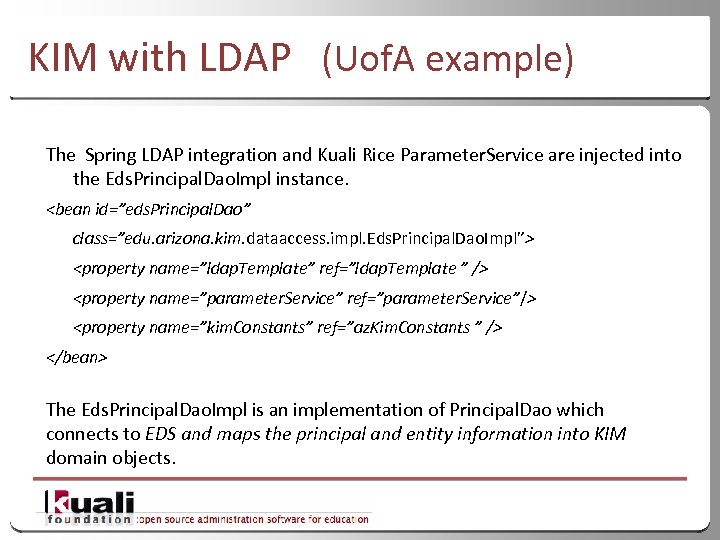 KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) The Spring LDAP integration and Kuali Rice Parameter. Service are injected into the Eds. Principal. Dao. Impl instance.
KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) The Spring LDAP integration and Kuali Rice Parameter. Service are injected into the Eds. Principal. Dao. Impl instance.
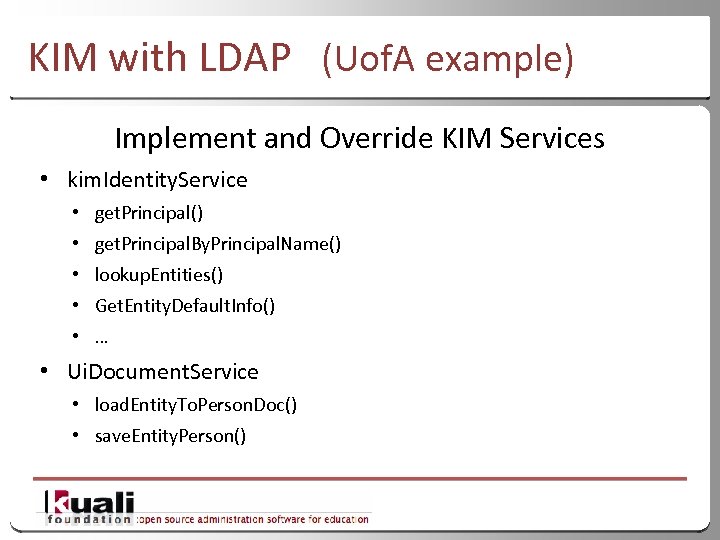 KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) Implement and Override KIM Services • kim. Identity. Service • get. Principal() • get. Principal. By. Principal. Name() • lookup. Entities() • Get. Entity. Default. Info() • … • Ui. Document. Service • load. Entity. To. Person. Doc() • save. Entity. Person() 36
KIM with LDAP (Uof. A example) Implement and Override KIM Services • kim. Identity. Service • get. Principal() • get. Principal. By. Principal. Name() • lookup. Entities() • Get. Entity. Default. Info() • … • Ui. Document. Service • load. Entity. To. Person. Doc() • save. Entity. Person() 36
 with • • Intra-campus Web SSO Federated Access to a Rice application KIM as an Identity Provider (Id. P) Using Shibboleth Attributes for KIM authorization 37
with • • Intra-campus Web SSO Federated Access to a Rice application KIM as an Identity Provider (Id. P) Using Shibboleth Attributes for KIM authorization 37
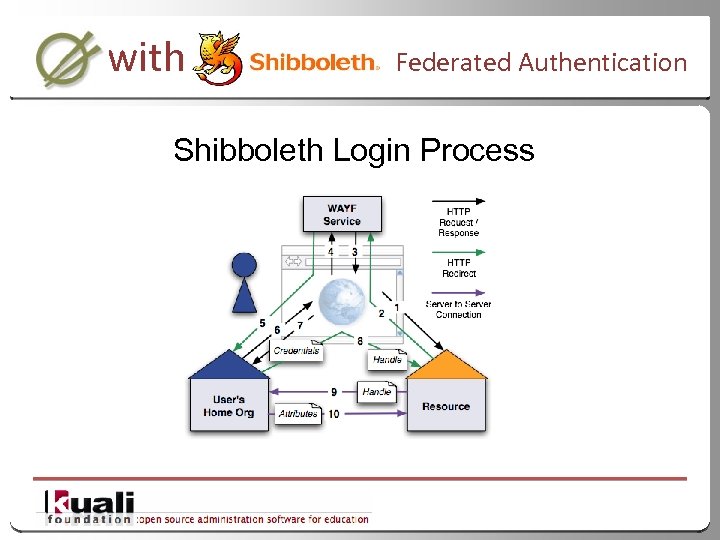 with Federated Authentication Shibboleth Login Process 38
with Federated Authentication Shibboleth Login Process 38
 with Federated Authentication Protecting a Rice application as a Service Provider (SP) • A web server and openssl must be available first • Add Shibboleth filters to the web server. • Metadata defines the attributes to be passed between the Identity Provider and Service Provider. • Override KIM Authentication Service 39
with Federated Authentication Protecting a Rice application as a Service Provider (SP) • A web server and openssl must be available first • Add Shibboleth filters to the web server. • Metadata defines the attributes to be passed between the Identity Provider and Service Provider. • Override KIM Authentication Service 39
 with Federated Authentication Metadata Example:
with Federated Authentication Metadata Example:
 with KIM as an Identity Provider • Prerequisites: SSL certificate, source of SAML Metadata • Install Shibboleth Id. P • Load SAML Metadata • Configure KIM as the User Authentication Mechanism • Implement kim. Authentication. Service to authenticate the user and provide the appropriate attributes. 41
with KIM as an Identity Provider • Prerequisites: SSL certificate, source of SAML Metadata • Install Shibboleth Id. P • Load SAML Metadata • Configure KIM as the User Authentication Mechanism • Implement kim. Authentication. Service to authenticate the user and provide the appropriate attributes. 41
 with • • Authorization Attributes Using Shibboleth Attributes for KIM Authorization Entity Attributes Group Roles Permissions / Responsibilities 42
with • • Authorization Attributes Using Shibboleth Attributes for KIM Authorization Entity Attributes Group Roles Permissions / Responsibilities 42
 with KIM / Grouper Collaboration 43
with KIM / Grouper Collaboration 43
 with Adapter Overview Custom Implementation of KIM Services using Grouper Client API • Group. Service • Group. Update. Service • Identity. Service 44
with Adapter Overview Custom Implementation of KIM Services using Grouper Client API • Group. Service • Group. Update. Service • Identity. Service 44
 with • • Installation grouper. Client. jar grouper. Kim. Connector. jar grouper. client. properties Override kim. Group. Service and kim. Identity. Service 45
with • • Installation grouper. Client. jar grouper. Kim. Connector. jar grouper. client. properties Override kim. Group. Service and kim. Identity. Service 45
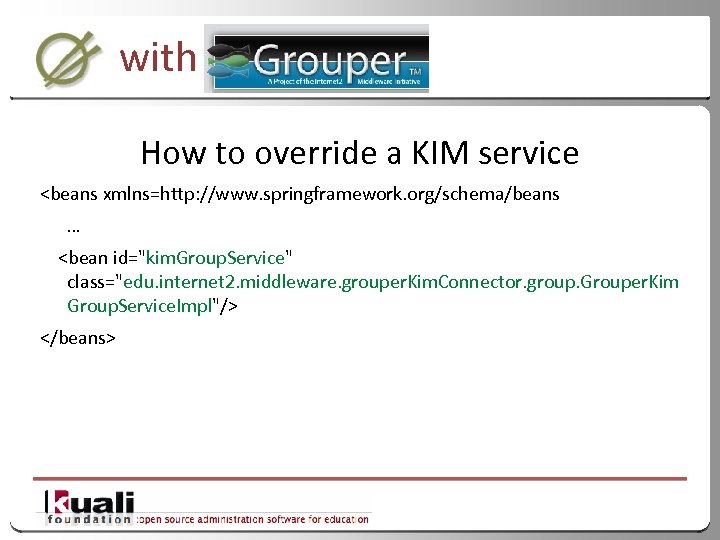 with How to override a KIM service
with How to override a KIM service
 with • Recall… • Earlier we stated that KIM is NOT an identity aggregator • Well, Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Manager (ILM) is! • Current branding of this tool is Forefront Identity Manager • Indiana University has used this tool as part of our Kuali Identity Management implementation • Essentially synchronizes identities from multiple sources into our KIM database 47
with • Recall… • Earlier we stated that KIM is NOT an identity aggregator • Well, Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Manager (ILM) is! • Current branding of this tool is Forefront Identity Manager • Indiana University has used this tool as part of our Kuali Identity Management implementation • Essentially synchronizes identities from multiple sources into our KIM database 47
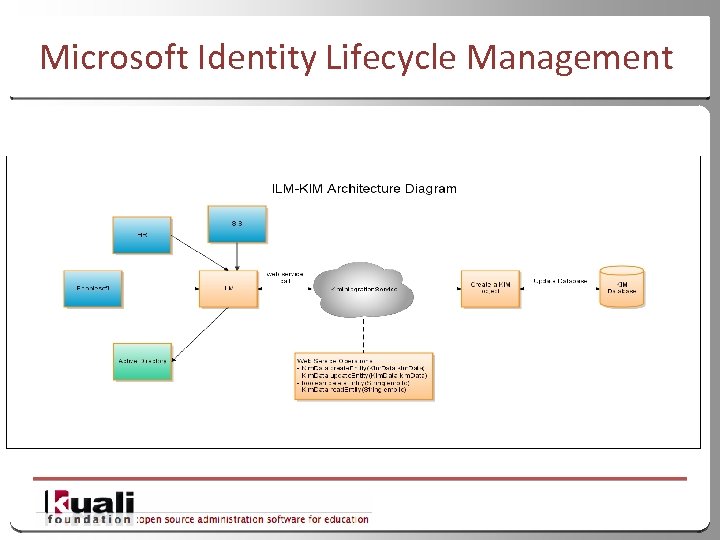 Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Management 48
Microsoft Identity Lifecycle Management 48



