565f9e05dca9e3c36aa8cf6fe53bf48a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Japan’s FTAs/EPAs with APEC Economies Nobuhiko Sasaki Deputy Director-General APEC Senior Official METI Japan March 2006
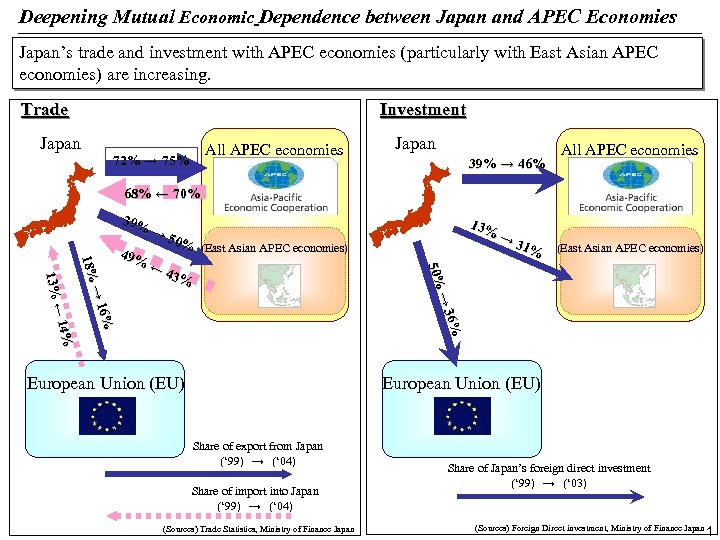
Deepening Mutual Economic Dependence between Japan and APEC Economies Japan’s trade and investment with APEC economies (particularly with East Asian APEC economies) are increasing. Trade Investment Japan All APEC economies 72% → 75% Japan 39% → 46% All APEC economies 68% ← 70% 39% → 50% (East Asian APEC economies) → → 50% → 18% 43% 36% 14% 1 % 16% ← ← 13% 1 % 49% ← 13% → 31% European Union (EU) Share of export from Japan (‘ 99) → (‘ 04) Share of import into Japan (‘ 99) → (‘ 04) (Sources) Trade Statistics, Ministry of Finance Japan Share of Japan’s foreign direct investment (‘ 99) → (‘ 03) (Sources) Foreign Direct investment, Ministry of Finance Japan 1
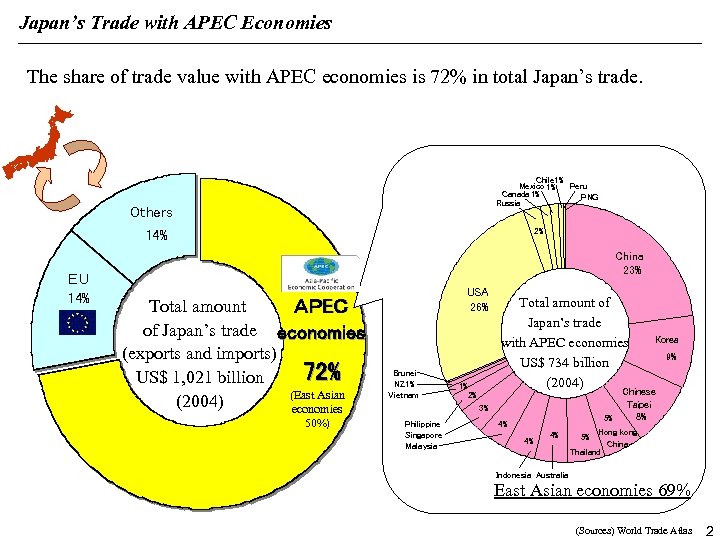
Japan’s Trade with APEC Economies The share of trade value with APEC economies is 72% in total Japan’s trade. Chile 1% Mexico 1% Peru Canada 1% PNG Russia Others 2% 14% EU 14% China 23% Total amount APEC of Japan’s trade economies (exports and imports) 72% US$ 1, 021 billion (East Asian (2004) economies 50%) USA 26% Brunei NZ 1% Vietnam 1% Total amount of Japan’s trade with APEC economies US$ 734 billion (2004) 9% Chinese Taipei 8% 5% 2% 3% Philippine Singapore Malaysia Korea 4% 4% 4% Hong kong China Thailand 5% Indonesia Australia East Asian economies 69% (Sources) World Trade Atlas 2
![Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (1) [Approach ~ 3 STEP APPROACH] 1. Institutionalization Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (1) [Approach ~ 3 STEP APPROACH] 1. Institutionalization](https://present5.com/presentation/565f9e05dca9e3c36aa8cf6fe53bf48a/image-4.jpg)
Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (1) [Approach ~ 3 STEP APPROACH] 1. Institutionalization of the de facto based regional economic linkage in the APEC region, particularly in East Asia The regional economic linkage in APEC region, particularly in East Asia, is being strengthened through the networked business operation of the private sector. Japan is institutionalizing the de facto based regional economic linkage in the area. 2. Further trade and investment liberalization, and improvement of investment climate from various aspects Japan is trying further trade and investment liberalization and facilitation in the APEC region. Japan includes many kinds of chapters, contributing to this purpose, in its FTAs/EPAs. 3. Effort toward convergence and coherence of FTAs/EPAs in the APEC region Japan is making efforts to bring convergence and coherence to FTAs/EPAs in the APEC region in collaboration with other APEC economies. 3
![Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (2) [CONCRETE ACTIONS] 1. Individual actions Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (2) [CONCRETE ACTIONS] 1. Individual actions](https://present5.com/presentation/565f9e05dca9e3c36aa8cf6fe53bf48a/image-5.jpg)
Japan’s Contribution to Bogor Goals through FTAs/EPAs Policy (2) [CONCRETE ACTIONS] 1. Individual actions under the FTAs/EPAs negotitation • Intensive negotiation for tariff-elimination, particularly on parts and components tariffs • Challenges toward an improvement of investment-climate of East Asian economies through establishment of i) investment-rule (including that for service investment), and ii) framework for consultation among both governments and investors • Inclusion of chapters on intellectual property protection, competition, and government procurement 2. Collective actions under APEC with other APEC economies • Positively participating in the discussions on creating APEC FTAs/RTAs Best Practice(2004), APEC Model Measures on Trade Facilitation(2005), and other Model Measures(2006 -) under the framework of APEC • Tackling new issues such as e-commerce, structural reform that are not easy for WTO to address, considering the nature of APEC (non-binding, voluntary) 4
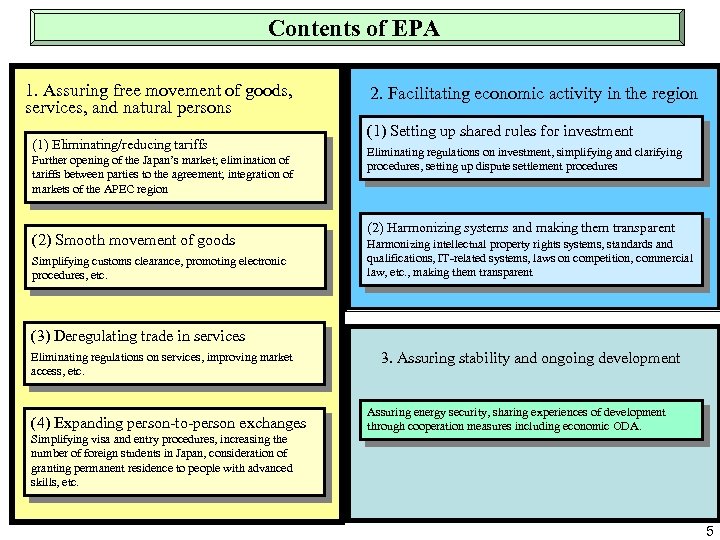
Contents of EPA 1. Assuring free movement of goods, services, and natural persons (1) Eliminating/reducing tariffs Further opening of the Japan’s market; elimination of tariffs between parties to the agreement; integration of markets of the APEC region (2) Smooth movement of goods Simplifying customs clearance, promoting electronic procedures, etc. 2. Facilitating economic activity in the region (1) Setting up shared rules for investment Eliminating regulations on investment, simplifying and clarifying procedures, setting up dispute settlement procedures (2) Harmonizing systems and making them transparent Harmonizing intellectual property rights systems, standards and qualifications, IT-related systems, laws on competition, commercial law, etc. , making them transparent (3) Deregulating trade in services Eliminating regulations on services, improving market access, etc. (4) Expanding person-to-person exchanges Simplifying visa and entry procedures, increasing the number of foreign students in Japan, consideration of granting permanent residence to people with advanced skills, etc. 3. Assuring stability and ongoing development Assuring energy security, sharing experiences of development through cooperation measures including economic ODA. 5

Chapters and elements of “WTO Plus” in EPAs (Examples) 1. Chapters • Investment • Improvement of business environment • Competition • Bilateral cooperation 2. Elements • Tariff elimination, in particular, nearly all (100% on trade volume) tariff elimination of industrial goods within 10 years • Various elements to improve investment climate -> Securing given conditions on each investment activity by manufacturing sector as what were allowed -> Establishing investor-state dispute settlement system -> Establishing one-stop service window and dialogue mechanism for solving various investment-related problems 6
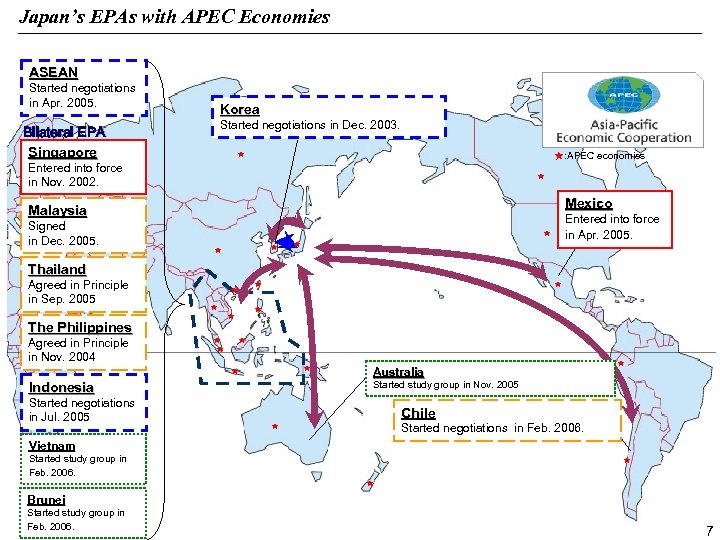
Japan’s EPAs with APEC Economies ASEAN Started negotiations in Apr. 2005. Korea Started negotiations in Dec. 2003. Bilateral EPA Singapore ★: APEC economies ★ Entered into force in Nov. 2002. ★ Mexico Malaysia Signed in Dec. 2005. Entered into force in Apr. 2005. ★ ★ Thailand Agreed in Principle in Sep. 2005 ★ ★ Agreed in Principle in Nov. 2004 ★ ★ ★ The Philippines ★ ★ Indonesia Started negotiations in Jul. 2005 Australia ★ Started study group in Nov. 2005 Chile Started negotiations in Feb. 2006. ★ Vietnam Started study group in Feb. 2006. ★ ★ Brunei Started study group in Feb. 2006. 7
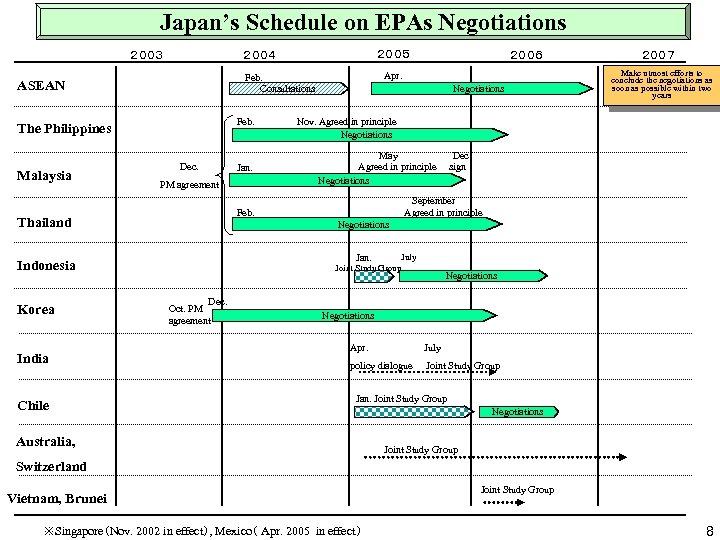
Japan’s Schedule on EPAs Negotiations 2003 Feb. The Philippines Dec. PM agreement Chile 2007 Make utmost efforts to conclude the negotiations as soon as possible within two years Nov. Agreed in principle Negotiations May Agreed in principle Negotiations Dec. sign September Agreed in principle Negotiations July Jan. Joint Study Group Indonesia India Negotiations Feb. Thailand Korea Jan. 2006 Apr. Feb. Consultations ASEAN Malaysia 2005 2004 Dec. Oct. PM agreement Negotiations Apr. July policy dialogue Joint Study Group Jan. Joint Study Group Australia, Negotiations Joint Study Group Switzerland Vietnam, Brunei ※Singapore(Nov. 2002 in effect), Mexico( Apr. 2005 in effect) Joint Study Group 8
565f9e05dca9e3c36aa8cf6fe53bf48a.ppt