e6ba81a758a6dbedfb5580a26f83aa6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Jan Roscoe Publications OCR Examinations AS and A Level Physical Education AS / A year 1 (A 1) AS H 155 / A Component 01 Physiological factors affecting performance 2. 3 Sport and society 21 st century sport globalisation of sport
2. 3 Sport and society INDEX 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 13 14 15 index OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education GLOBALISATION OF SPORT THE IMPACT OF THE MEDIA ON INDIVIDUAL PERFORMERS PROS & CONS OF MEDIA-BASED SPONSORSHIP GOVERNMENT OF SPORT BY MEDIA-BASED SPONSORSHIP THE EFFECT OF INCREASED MEDIA ATTENTION ON SPECTATORS ENJOYMENT THE MEDIA GOLDEN TRIANGLE MEDIA AND THE GLOBAL MARKET MEDIA AND THE GENDER BIAS MARKETING THE WORLD CUP (MEN) MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 2

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education GLOBALISATION OF SPORT • globalisation refers to the spread of sport across the world • this has taken place gradually over the past 150 years • and describes the importance of sport in most societies across the world: – the infrastructure (sports stadia, indoor and outdoor facilities) – the involvement of people in sports activities – the commercialism and money involved – the media (print and electronic), and so on – industry (clothing, footwear and equipment) index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 3
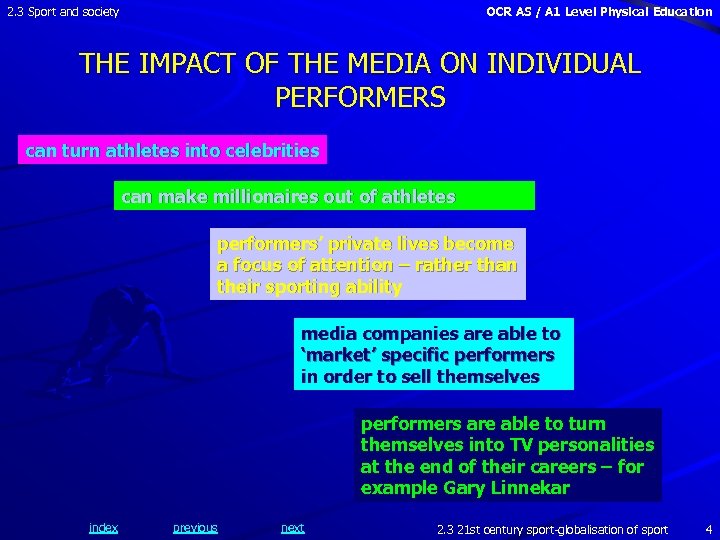
2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education THE IMPACT OF THE MEDIA ON INDIVIDUAL PERFORMERS can turn athletes into celebrities can make millionaires out of athletes performers’ private lives become a focus of attention – rather than their sporting ability media companies are able to ‘market’ specific performers in order to sell themselves performers are able to turn themselves into TV personalities at the end of their careers – for example Gary Linnekar index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 4
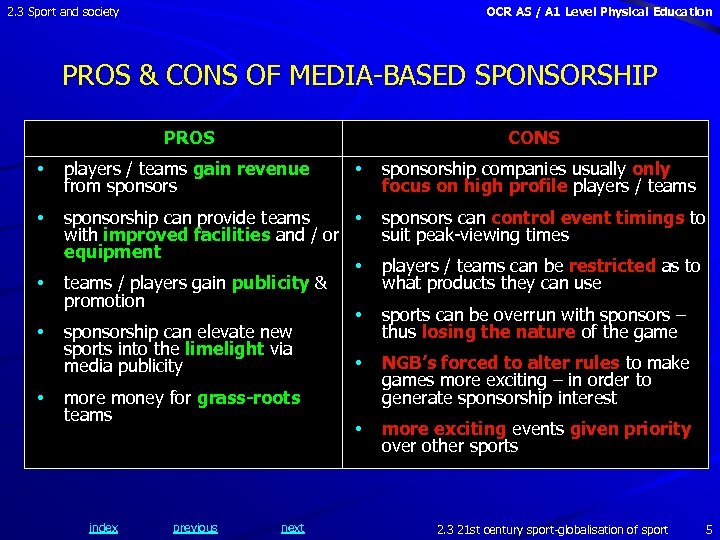
2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education PROS & CONS OF MEDIA-BASED SPONSORSHIP PROS CONS • players / teams gain revenue from sponsors • sponsorship can provide teams • with improved facilities and / or equipment • teams / players gain publicity & promotion • sponsorship can elevate new sports into the limelight via • media publicity • • • more money for grass-roots teams index previous next • • sponsorship companies usually only focus on high profile players / teams sponsors can control event timings to suit peak-viewing times players / teams can be restricted as to what products they can use sports can be overrun with sponsors – thus losing the nature of the game NGB’s forced to alter rules to make games more exciting – in order to generate sponsorship interest more exciting events given priority over other sports 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 5
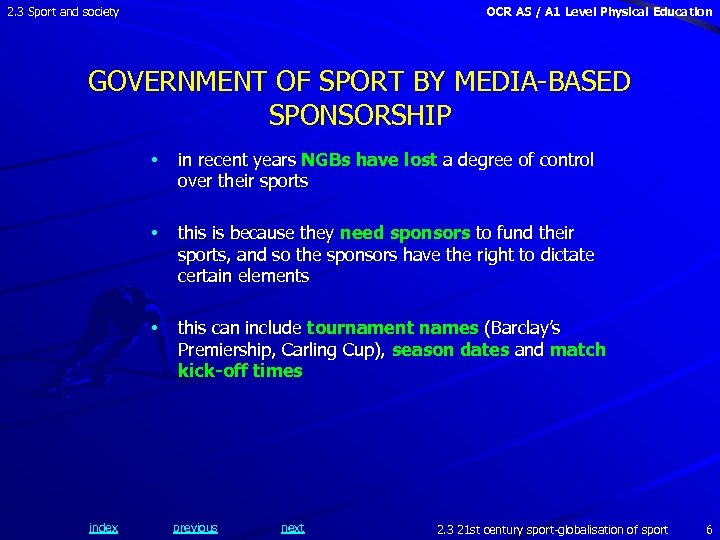
2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education GOVERNMENT OF SPORT BY MEDIA-BASED SPONSORSHIP • • this is because they need sponsors to fund their sports, and so the sponsors have the right to dictate certain elements • index in recent years NGBs have lost a degree of control over their sports this can include tournament names (Barclay’s Premiership, Carling Cup), season dates and match kick-off times previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 6

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education THE EFFECT OF INCREASED MEDIA ATTENTION ON SPECTATORS ENJOYMENT • there is a very close-knit relationship between the spectator, the media and sponsors • without one, the other two cannot survive • however, increased media attention has led to sports becoming more exciting • thus it is likely that spectators enjoy watching their favourite games more index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 7

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education buy sponsors’ products if they are popular & marketed well buy merchandise from media company eg sky subscriptions rely on subscriptions bought by fans to cover transmission costs rely on fans buying their products attract sponsors as spectators watch / read their coverage index previous next need media to promote products demand media space (adverts) for marketing 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 8

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MEDIA AND THE GLOBAL MARKET • • changes in contemporary technologies and the economics of the broadcast and print media have contributed significantly to an expansion of the media globalisation of sport the new media global explosion makes “any sport, any event, any time, any device” a viable reality for fans • • the Internet is now a significant medium for sport coverage allowing fans from all over the World to access the latest news about their favourite team, sport or event • by engaging fans via social media, sports rights holders can open new communication channels with their audience that can be measured and valued as a new commercial opportunity with sponsors • the list of possible outlets for sport is endless: high definition and 3 D television, IPTV, mobile phones, You. Tube, web streaming, digital radio, i. Player, games consoles, and social networking sites index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 9

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MEDIA AND THE GLOBAL MARKET index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 10

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MEDIA AND THE GLOBAL MARKET • complex business relationships have grown up around television, sponsors and sport • meanwhile commercial advertising benefits from increased brand affinity and loyalty • mobile phones and tablets have allowed social media to flourish • now football stadiums such as Liverpool’s Anfield and the Etihad Stadium, home of Manchester City, offer fans Wi-Fi enabling not only more interactions at live events but more commercial activity, too spectators now have the ability to make additional purchases or seat upgrades, for example, from the venue • • index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 11

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MEDIA AND THE GLOBAL MARKET • the monies involved are staggering • • sponsors such as Mc. Donalds, Adidas, Nike have got involved in January 2016, Adidas withdrew their sponsorship of the IAAF (Athletics international governing body) following their recent involvement in drugs and corruption controversies • • • major professional teams become global institutions for example, Manchester United has 5 million fans in the USA alone a following enhanced through Rupert Murdoch's marketing of his Fox Sports World TV. . . to promote the sport throughout the USA • • and attract large and predictable audiences for advertisers with global investments and partnerships index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 12

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MEDIA AND THE GENDER BIAS • • UKs women won one third of the medals in the 2012 Olympic games Jessica Ennis-Hill and Nicola Adams became household names and hoped that the nation's newspapers would reflect coverage of women's sports in this sort of ratio research from Birmingham University revealed that six of our national newspapers reduced coverage of women sports people to one twentieth compared to before the Olympics the arguments usually put forward for the lack of coverage is that no one is interested in women's sport yet the interest shown on social media and among TV viewers suggests otherwise women's football got its own series on BBC 2 for a bit, while the women's football World Cup final of 2011 was at the time the most tweeted event in the history of Twitter perhaps the main reason for the imbalance in media coverage of women’s events is due to the fact that the media industry is dominated by males index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 13

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MARKETING THE WORLD CUP (MEN) • massive TV audiences watch the matches, as well as thousands of live spectators • FIFA has made the game globally available through selling TV rights for the games the revenue generated from these rights form a major part of the finances for host countries • • • index in order to improve marketing of the World Cup, FIFA enlisted the help of ISL Worldwide are responsible for organising and coordinating the multi-national businesses who lend their financial and organisational support to the World Cup previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 14

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 15

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR • • • index athletes are on the move in some sports this involves sport labour movement from one country to another within or between continents in other sports athletes assume an almost nomadic migratory lifestyle, constantly on the move from one sport festival to another migration patterns of sporting labour have developed globally since the 1990’s particularly since the introduction of the club’s licence to contract players and with the professionalism and organisation in male professional team sports previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 16
2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 17

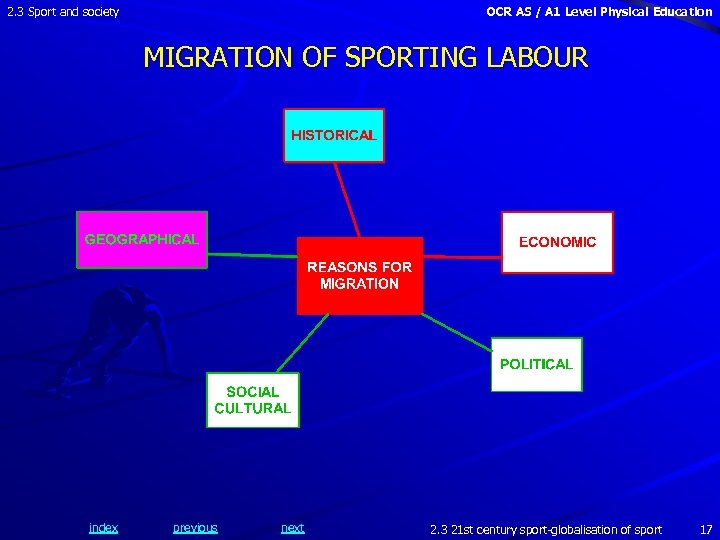
2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR HISTORICAL • migration was local within the boundaries of a country • • resulting in increased labour mobility – for example, within the EU there is greater european integration and so easier to move location and work • index but with the increased role of the media, such as TV contracts, sponsorship and overseas investors, professional football clubs have increased their wealth and status recent indication that elite female football players are becoming part of the network of global migration previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 18

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR ECONOMIC • huge transfer fees are paid for elite global male football players to the extent that many of the UK ‘s premier league clubs • such as Manchester United and Arsenal, are predominantly made up of overseas players • index more than half of the English Premier Leagues are owned by foreign businessmen and are perceived as non-profit making, but highly valued as ‘global investors’ of multi-national enterprises previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 19

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR ECONOMY - FACILITY INVESTMENT • is also partly responsible for player/coach migration – for example, NBA which has built state-of-the art basketball arenas in China and is attracting global talent • • index the entire revenue of the US Big Four sports of football, baseball, basketball and ice hockey represents only a small percentage of the US economy, but is perceived as a very important part of cultural lifestyle global sport stars, such as Usain Bolt, Andy Murray, obtain sponsorship, advertise products, and are exposed to extensive media hype, which enhances their financial worth to a sponsor previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 20

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR SOCIAL/CULTURAL • new global migration and mobility have altered cultural composition to create cosmopolitan communities and intercultural acceptance within communities, teams and clubs GEOGRAPHICAL • many of these transfers are close to home and so the cultural/social transitions for both players and family are not too drastic • index during the 2014 -15 season Canada attracted 31 international players to its NBA league previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 21

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR • Talent pipelines - Case study – The demands of global rugby are having an impact: (include photo of player who has migrated to Japan) • since the 1990 s several Fijians and Kiwi rugby players have received lucrative contracts to play in professional club rugby in Japan where rugby is a minor team sport players/coaches are attracted by secure contracts offering multi-year secure deals, new cars and free or subsidised apartments and full-time sporting careers that are sponsored by large corporations who dominate Japanese rugby far better financial and long-term contracts that NZ offer this sometimes creates a player drain which depletes the country of its talent pool • • index some of these elite sports performers become full-time residents and represent their adopted country at International global events previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 22

2. 3 Sport and society OCR AS / A 1 Level Physical Education MIGRATION OF SPORTING LABOUR Media • sports events have become global spectacles and are far and away the most watched television programmes in the world • for example, 30 billion viewers watched the 2006 Soccer world cup, 4. 7 billion viewers watched the 2008 Beijing Olympics • super bowl reaches around 160 million viewers across the globe • this global following attracts publicity and sponsorship and networks that encourage global migration • along with sporting icons such as David Beckham, Ronaldino, , Michael Jordan who are recognised and admired world over as stereotypes, with their skilful performances and ability to enhance the reputation ( shop window effect) and desirability for other sports performers to migrate to their sporting locations/clubs index previous next 2. 3 21 st century sport-globalisation of sport 23
e6ba81a758a6dbedfb5580a26f83aa6c.ppt