ba67cb53b50d3375b3a8f194387f0283.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
Jakob Noah Jorge Elizabeth Vanessa Aliza Sydney L Catalina Teacher’s Desk Gabriella Alexis Andres 1 Desiree Sydney P Steven Mariyah Tomas Estrella Anna Kyle B Quintan Grayson Sydney K Jaylen st 1 DOOR Hour Karina Manuel Jax Armando Natalie Jose Jordan Sean Jared Alan
nd 2 Hour Lorenzo Alexis Shayna Matt Dominique Jared Logan Daniel Alejandro Taylor Anthony C Kayla Chris Kelechi Dante Jonathan River Mei Adrian Josslan Michael Teacher’s Desk Briseida Joseph A DOOR Sam Anthony O Jackson Ian Maleek Marcel Anthony L Brooke
Andrew A. Castillo Austin Caitlin Jessica G Asiano Gerardo Eunice Halle Kiana Liliana Edgar Eunice Jose Diana Mauricio Osceola Jaren Sarah Alejandra Aisake A. Cristan Roberto Jessica M Kassandra Luis Daniel Juliana Mario Eduardo Jessica Carolina Charles Gianni 3 rd DOOR Teacher’s Desk
5 th Hour Teacher’s Desk Adriana William Elmer Jasmine. Marco Isaiha Lauren Andrew Josh Edward Odalis Serina Alexis W Adrian Ivanna Ty Rosalia Destinee Taylor Yakia Nick Kohl Juan Bryan Hubble Adi Andrea Sonia Michael Harrison Marcos DOOR Brian Kura Alexis M
6 th Hour Joshua Ruben Teacher’s Desk Janette Antonio Giovany Juedial Raul B. Lloyd Frederico B. Leach Ingrid Claudia Travys Conrad Sid Denise Diego Jackie Haley Shannon Alex Jeremiah Audrey Carmen DOOR Kyejah Audrey Taylor Nicholas Ricardo Cody Andrew Moses Anthony Richard Fernando

This and next week… • Wednesday/Thursday: ▫ Discuss Feudalism ▫ Group Activity • Friday ▫ Chivalry • Next Week: AIMS testing (Go to CCA on block days T-TR) ▫ ▫ ▫ Monday: 1 -6 Tuesday: 1 -3 -5 Wednesday: 2 -4 -6 Thursday: 1 -3 -5 Friday: 2 -4 -6

Welcome Back! • Going over syllabus • Rules • Expectations • Pass back test Friday ▫ Those who need to take the test- Next Monday or Tuesday after school in Mr. Martinez’s room

Warm-Up: • Use this for today, Friday, and Monday ▫ If you lived in a time of CONSTANT threat of murderers and thieves (like the mob), would you give up your freedom for protection? Why/Why not? ▫ Please respond in 3 sentences.

Learning Goals 1. Explore how feudalism helped shape political & social development in Europe during the Middle Ages 2. Identify the ways in which the manorial system influenced economic growth in Europe during the Middle Ages

Why is this important? ? ? • The rights and duties of a feudal relationships helped shaped today’s forms of representative government.

13. 2 Feudalism in Europe Feudalism, a political and economic system based on land-holding and protective alliances, emerges in Europe.

Vikings, Magyars, and Moors…Oh My! • After the breakup of Charlemagne’s empire, invaders attacked Europe ▫ Vikings attacked from the North Viking ships could navigate upriver and raid inland towns ▫ Magyars swept in from the east (from present day Hungary) ▫ Muslims came from the south
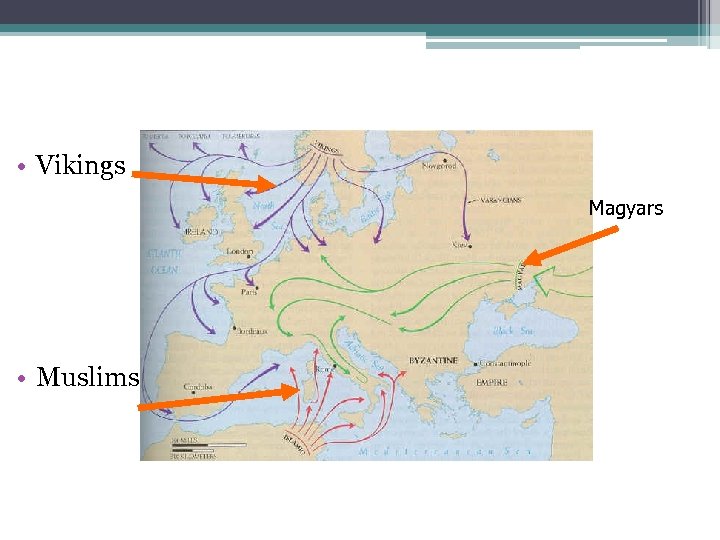
• Vikings Magyars • Muslims
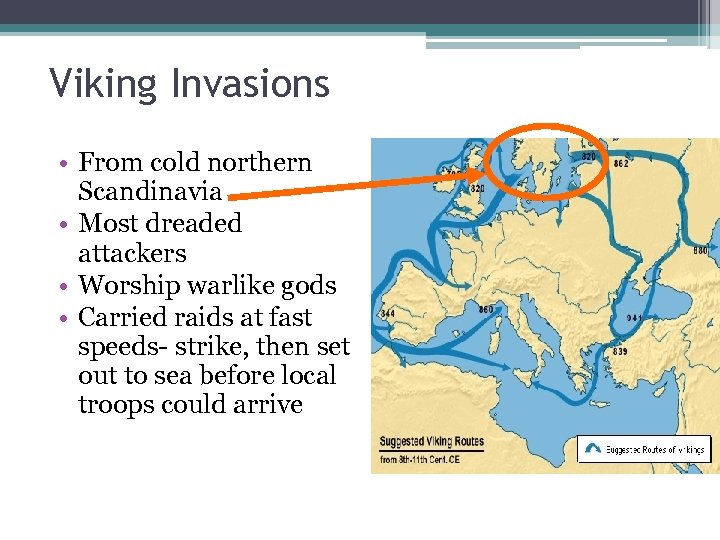
Viking Invasions • From cold northern Scandinavia • Most dreaded attackers • Worship warlike gods • Carried raids at fast speeds- strike, then set out to sea before local troops could arrive

Vikings • Used swords and heavy wooden shields • Built amazing boats • Boats could carry 300 men, 72 oars, weigh 20 tons and sail in 3 ft of water • Would use shallow streams to loot villages and monasteries • Were not just warriors, also were traders, farmers and explorers

Viking Boats

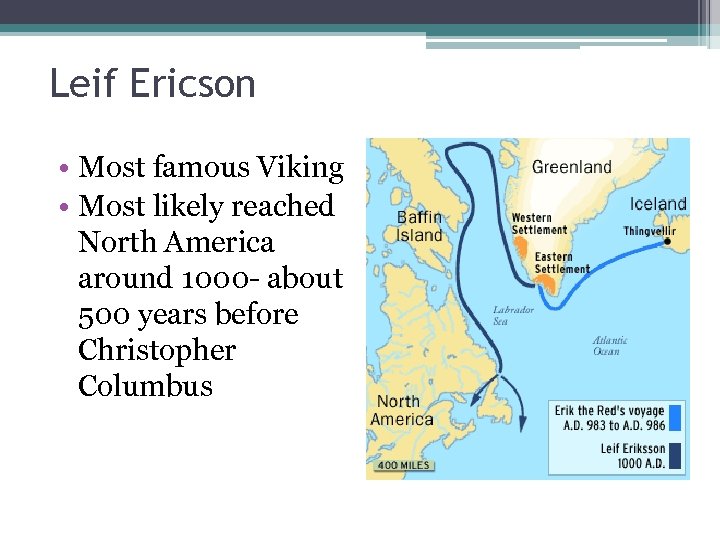
Leif Ericson • Most famous Viking • Most likely reached North America around 1000 - about 500 years before Christopher Columbus

Viking Invasions End • Around the same time Leif Ericson reached the America’s Viking terror faded • Vikings gradually accepted Christianity and stopped raising monasteries • A warming trend in Europe made farming easier in Scandinavia, so many didn’t adopt the Viking seafaring way of life
A sketch of a Viking longboat
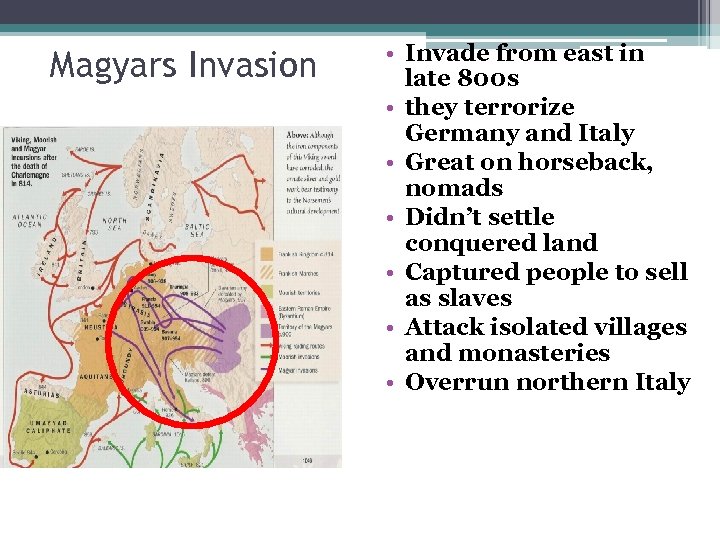
Magyars Invasion • Invade from east in late 800 s • they terrorize Germany and Italy • Great on horseback, nomads • Didn’t settle conquered land • Captured people to sell as slaves • Attack isolated villages and monasteries • Overrun northern Italy
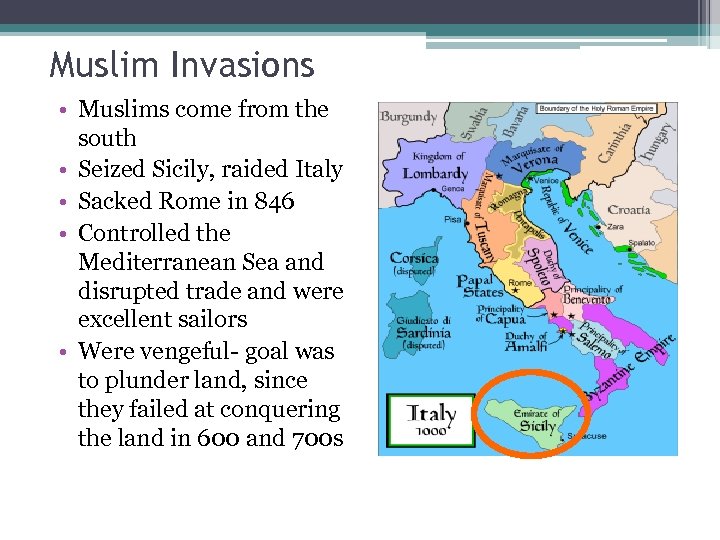
Muslim Invasions • Muslims come from the south • Seized Sicily, raided Italy • Sacked Rome in 846 • Controlled the Mediterranean Sea and disrupted trade and were excellent sailors • Were vengeful- goal was to plunder land, since they failed at conquering the land in 600 and 700 s

Living in Fear • Invasions of Vikings, Magyars and Muslims caused disorder and suffering • Europeans lived in fear and constant danger • Central authority proved powerless • Many turned to local leaders with their own armies

Feudalism

Feudalism: Weak Kings, Strong Nobles

A New Social Order • Worst years of invaders attacks were 850 -950. • During this time, rulers and warriors made similar agreements in many parts of Europe • The system of governing and landholding called feudalism had emerged in Europe

Feudal System • Based on mutual obligations • A lord (landowner) granted land called a fief in exchange for military protection and other services • Person receiving the fief was a vassal • So, Charles the Simple was the lord, and Rollo would have been the vassal
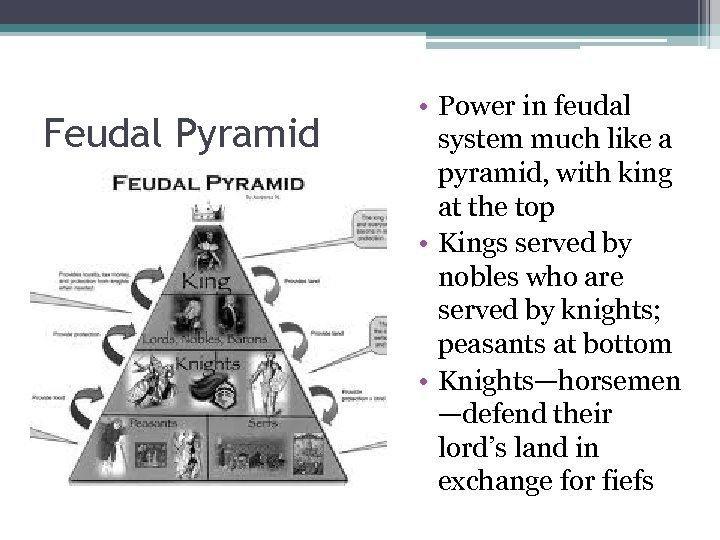
Feudal Pyramid • Power in feudal system much like a pyramid, with king at the top • Kings served by nobles who are served by knights; peasants at bottom • Knights—horsemen —defend their lord’s land in exchange for fiefs

Social Hierarchy

It’s a Pyramid Scheme • At the top is the king (the lord) • The vassals to the king are wealthy nobles • Below the wealthy nobles, are knights ▫ A knight would then be a vassal to a wealthy nobleman ▫ The knight would pledge his support to his lord (the wealthy nobleman) • At the bottom of the pyramid were the landless peasants referred to as serfs • A serf could not legally leave his lord’s estate • Even though they were bound to the land serfs were not slaves


Social Classes • Status determined a person’s prestige and power • People were placed into 3 groups: 1) Those who foughtnobles and knights 2) Those who prayedmen and women of church 3) Those who workedthe peasants • Social class was usually inherited

Serfs • Majority of people in Europe were peasants • Most peasants were serfs • Serfs were people who couldn’t lawfully leave the place where they were born • Even though they were bound to the land, they were not slaves • Lords could not buy or sell them

Feudalism: Life in a Castle

Manor • The manor was the lords estate • The manor system was the basic economic arrangement • Lord provided the serfs and peasants with housing, strips of farmland protection from bandits

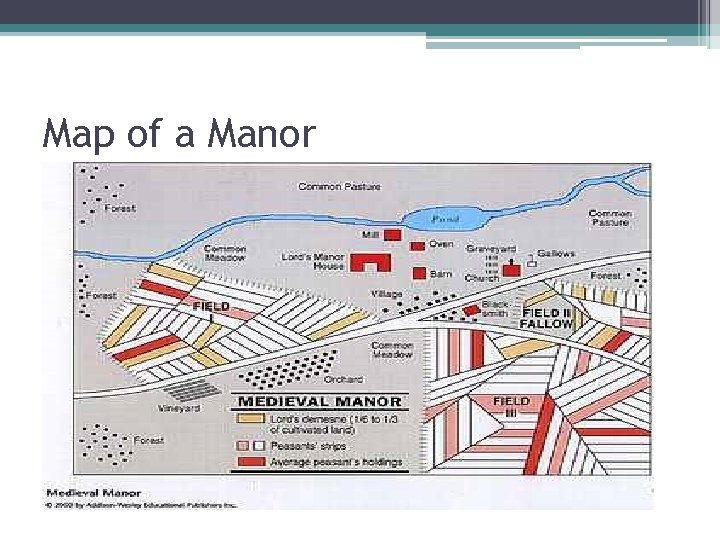
Map of a Manor

Self Sufficient Manor • Everything needed for daily life was produced on the manor: *crops *fuel *cloth *leather goods *lumber

• The only outside purchases were salt, iron and a few unusual objects like millstones- stones used to grind flour
Feudalism: Relationships

Peasant Life on the Manor • Since it was considered a privilege to live on the manor, peasants paid a high price • Paid a tax on all grain ground on the lord’s mill • Was considered a crime to avoid paying taxes • Paid a tax on marriage- weddings could only take place with the lord’s consent • All peasant families had to pay a tithe (church tax) to the village priest (10% of income)

• Serfs and peasants lived in cottages with only 1 or 2 rooms • Would warm their dirt floor by bringing pigs inside • Families would huddle together on pile of straw crawling with insects to stay warm

Simple Diet • Peasant diets consisted of: *vegetables *coarse brown bread *grain *cheese *soup

• Serfs accepted their way of life, and viewed it as part of church teachings • Believed God determined a person’s place in society

Vocab Activity • Write the definition of each vocabulary word in FULL sentences. You can find the definitions in your book starting on page 303. • Next, use the word in a full sentence that YOU created, not taken out of the book or from a partner. • Must be done at the end of class • NO PARTNERS!!!!
ba67cb53b50d3375b3a8f194387f0283.ppt