f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99

Jacksonian Democracy • Bookends: – The Corrupt Bargain Election, 1824, to the end of the Mexican American War, 1848 • Theme: Growth in the power of the “Common Man” & westward expansion- Manifest Destiny • Events: – Nullification Crisis, Indian Removal, National Bank closing, Polk’s Election, Oregon Issue, Texas Independence…
What is democracy?

• democracy: Greek Origins: demos- the people + kratos- authority • government ruled directly by a majority of the people • belief in, or practice of, social equality: absence of snobbery or social exclusiveness, characterized as from the common people Versus: • republic, elect most talented people to govern, indirect government through a system of representation • More elite rule, snobbery

Matching: -ocracy, rule by… • • Monarchy Theocracy Plutocracy Meritocracy Kleptocracy Mobocracy Aristocracy • • • Rich One person Thieves Nobility Disorganized bunch of people • Church leaders • People most capable

Is it democracy? • • • Voting rights for all adults Uniforms in public schools Majority rules Equal income for all people High school slavery

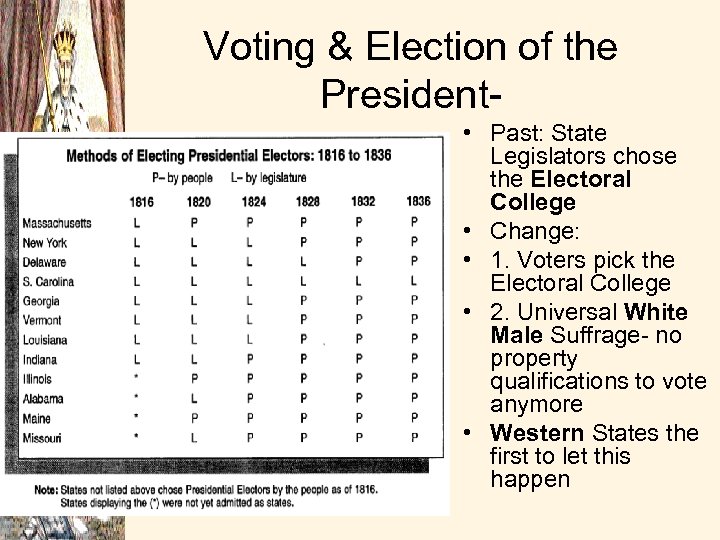
Voting & Election of the President • Past: State Legislators chose the Electoral College • Change: • 1. Voters pick the Electoral College • 2. Universal White Male Suffrage- no property qualifications to vote anymore • Western States the first to let this happen
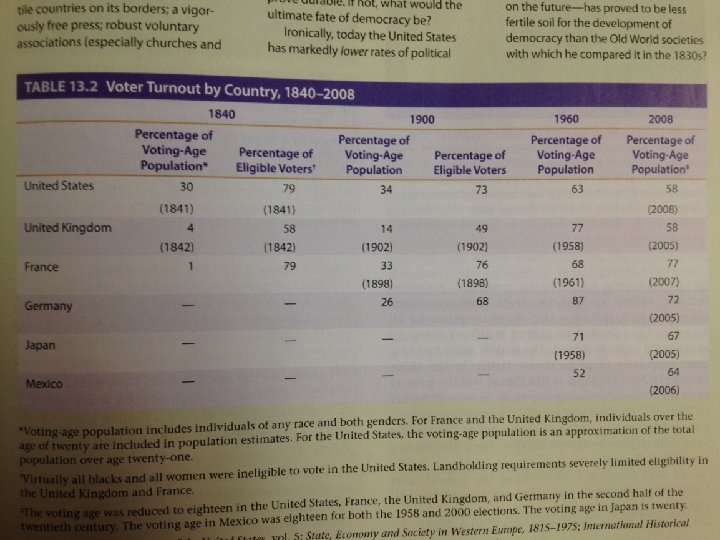
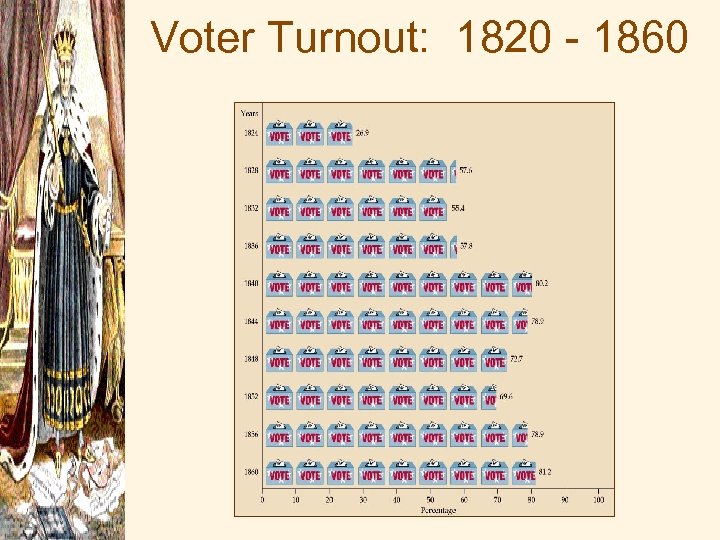
Voter Turnout: 1820 - 1860

Public Campaigns for Office • Politicians have to convince people to vote for them (running versus standing for office) • More democratic because more responsive to the public • Downgrades discussion of issues, focus on trivial matters instead of the issues (LCD) • Presidential Election of 1840 best example of this! (*Remember this*)


Rise of Political Parties • Past: “Era of Good Feelings”- only one political party in power, the Jeffersonian-Republicans • Change: New political parties form: Democrats, Whigs, Anti-Masons, and Workingmen’s Parties • More democratic because more ideas in government

Rotation in Office • Andrew Jackson gave government jobs to people for just a few years to get more common people working in government • Jackson believed that all common people were capable of holding a government job • Spoils System-Government jobs should go to loyal political party members



Why Increased Democratization? 3 White male suffrage increased 3 Party nominating committees. 3 Voters chose their state’s slate of Presidential electors. 3 Spoils system. 3 Rise of Third Parties. 3 3 Popular campaigning (parades, rallies, floats, etc. ) Two-party system returned in the 1832 election: § Dem-Reps Natl. Reps. (1828) Whigs (1832) Republicans (1854) § Democrats (1828)


Essential Question: Champion of the “Common Man”? OR “King” Andrew?


Andrew Jackson

The “Common Man’s” Presidential Candidate
![Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford](https://present5.com/presentation/f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22/image-22.jpg)
Jackson’s Opponents in 1824 Henry Clay [KY] John Quincy Adams [MA] William H. Crawford [GA] John C. Calhoun [SC]

“Corrupt Bargain” Jackson had the most votes and electoral votes but lost b/c the House of Representatives decided the election and the Speaker of the House, Henry Clay, gave all his votes to Adams in exchange for the position of Secretary of State Concept: Majority vs. Plurality Jackson said of Clay that "the Judas of the West has closed the contract and will receive thirty pieces of silver!"
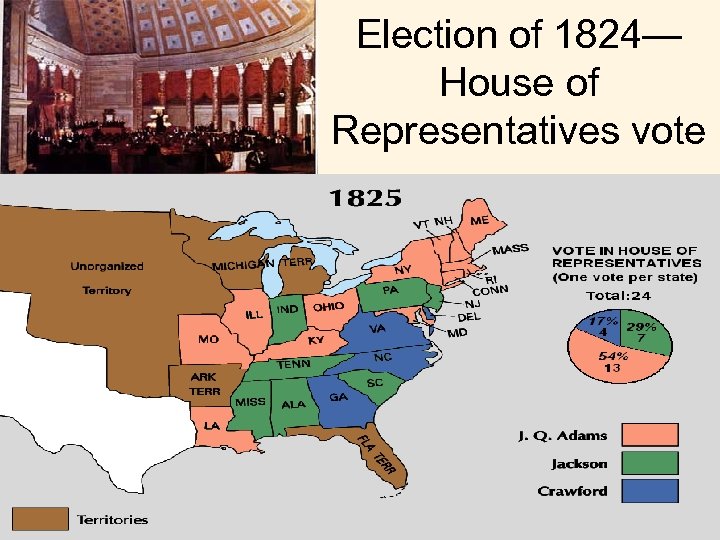
Election of 1824— House of Representatives vote


Rachel Jackson Final Divorce Decree

Coffin handbill: “Listed 14 fights, duels, brawls, shooting and cutting affairs in which Jackson killed, slashed, and clawed various American citizens”


Jackson in Mourning for His Wife
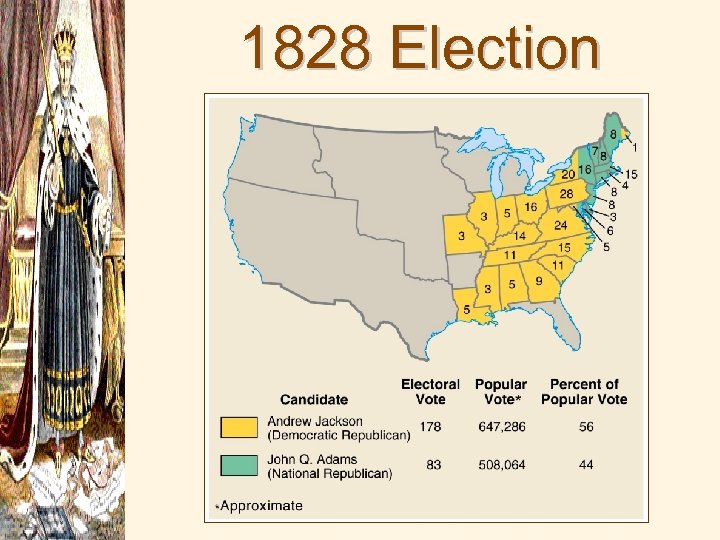
1828 Election Results

The Reign of “King Mob” 1 st Westerner, common person elected to the Presidency, Revolution?

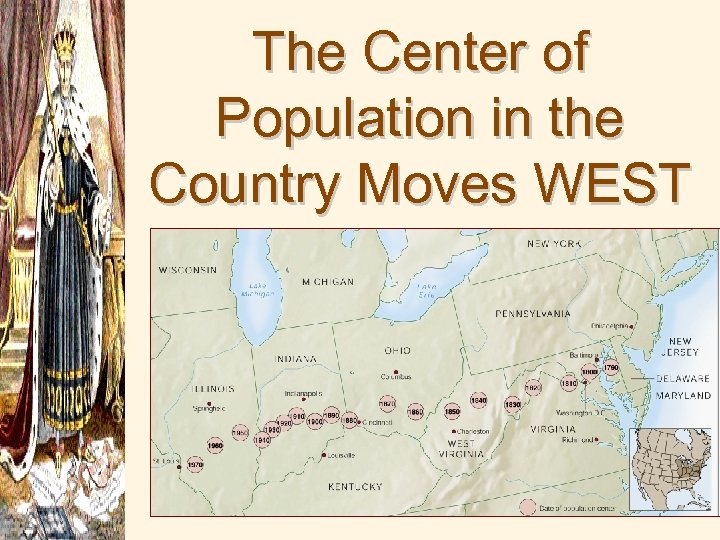
The Center of Population in the Country Moves WEST


• The Federal Gov. started to pass tariffs after the War of 1812 (American System) to protect the newly forming manufacturing in the country as opposed to the previous revenue based tariffs (Hamilton) • Tariffs of 1816 -23%, 1824 -37%, 1828 -45%, & 1832 -35% • Tariffs hurt Southern States because they bought a lot of foreign manufactured goods from their income earned from cotton • Southern politicians started to loudly complain about tariffs and named the Tariff of 1828 the Tariff of Abominations, which raised duties to 45% • Political ploy to make J. Q. Adams look bad

John Calhoun *Halloween costume suggestion, you will be the scariest person in the room!

The South Carolina Exposition and Protest 1828 • Secretly authored by VP John C. Calhoun • Way to protect minority rights in a political system of majority rule • Nullification – each state had the power to decide whether to obey a federal law that exceeded the power granted to Congress in the Constitution and null and void it – Congress could then repeal it or pass a Constitutional Amendment
![The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC] The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC]](https://present5.com/presentation/f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22/image-38.jpg)
The Webster-Hayne Debate Sen. Daniel Webster [MA] Sen. Robert Hayne [SC]

Webster-Hayne Debate, 1830 Senator Robert Hayne, S. C. • Elaborated on the Nullification theory • Stated that the federal government could not be trusted to limit its own power • Believed that the states came together to make the Union Senator Daniel Webster, Massachusetts • Nationalist Theory of the Union – “We the people” came together to make the nation, not the states – Idea of perpetual Union • Endorsed Judicial Review • “Liberty and Union, now and forever, one and inseparable”

Read pages 5 -6, the Hayne -Webster Debate • Hayne – What is the Republican doctrine of 1798? – Why does he bring up the Hartford Convention? – Why can neither Congress or the Supreme Court fix this issue? – Notice taxation issue, Revolution, Whiskey Rebellion, Tariffs, it did not end… – What does paying this tax turn him into? • Webster – According to Webster, why is he afraid “to look beyond the Union to see what might lie hidden in the dark recess behind? – What is the significance in the ordering of Liberty and Union at the end of Webster’s speech?

Jefferson Day Toast, 1830, symbolic split Jackson : Our Federal Union—it must be preserved. Calhoun : The Union, next to our liberty, most dear.

Calhoun resigned from VP in 1832 • Peggy Eaton Affair • Kitchen Cabinet • Tariffs the real issue • Calhoun, once a nationalist, became a fierce sectionalist and state’s rights advocate in the Senate.

Nullification Crisis • S. C. nullified the Tariff of 1832 • Jackson issued an order to prepare for war • Force Bill (“The Bloody Bill”) passed Congress • The South backed down • Henry Clay brokered the Tariff of 1833 Compromise, reduced tariff levels by 10% in 10 years • Closest the nation came to Civil War before it happened • South began to abandon the idea of nullification for secession after this

“… when Congress exceeded these powers … that each state could nullify, and refuse to enforce, any act of Congress found to be in violation of its delegated authority. ” “The best way to guard the South from the tyranny of the north, I maintain, is through the structure of states rights. ” Calhoun


Was Andrew Jackson democratic in dealing with the tariff controversy?

What do you think this guy does for a living?

• “Five Civilized Tribes” – called this because they adopted white cultural practices, even owned slaves Cherokee, Choctaw, Creek, Chickasaw, and Seminole Tribes

![“Treaties with the Indians [are] an absurdity. ” -- Andrew Jackson, 1817 “Treaties with the Indians [are] an absurdity. ” -- Andrew Jackson, 1817](https://present5.com/presentation/f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22/image-50.jpg)
“Treaties with the Indians [are] an absurdity. ” -- Andrew Jackson, 1817

Indian Removal • Indian Removal Act of 1830 forced the Native American tribes of the southeast to leave their homeland • Cherokee Indians fight this process, led by John Ross • Worcester v. Georgia (1832) - Supreme Court ruled that the state of Georgia’s laws had no force in Cherokee territory • Jackson said, “Marshall has made his decision, now let him enforce it. ” • Treaty of New Echota, 1835
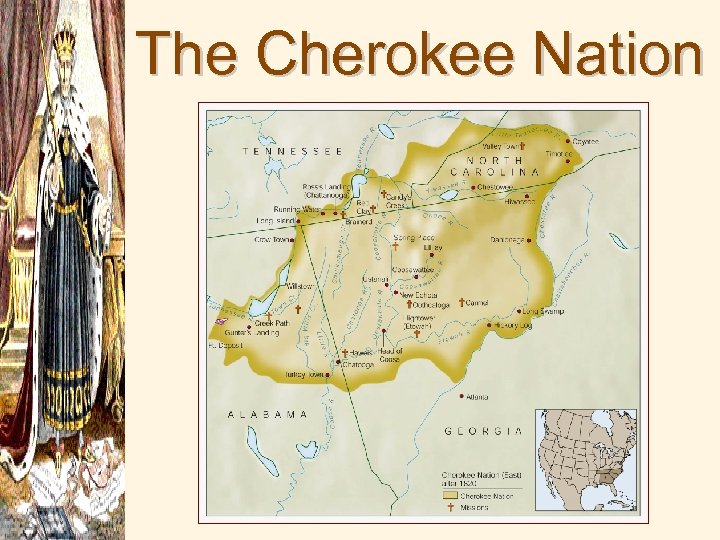
The Cherokee Nation After 1820
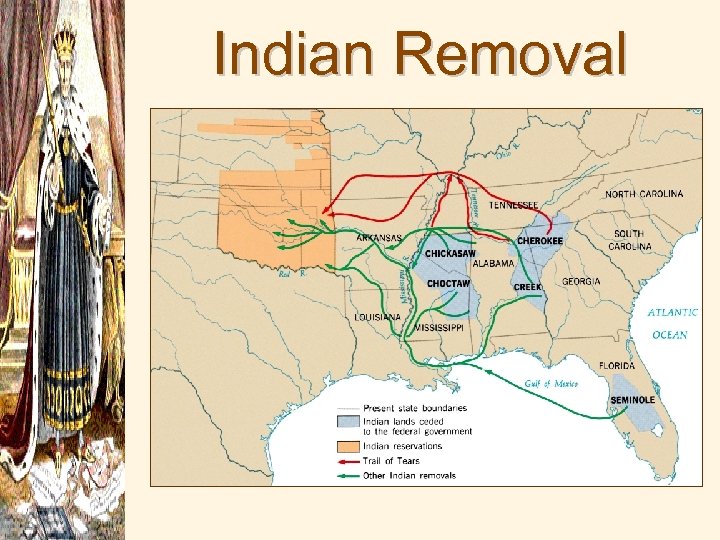
Indian Removal

• Trail of Tears refers to the forced removal of 15, 000 Native Americans from their homeland by the US Army to Indian Territory in which 4, 000 Indians die • Jackson believed that his policy was humane because if he did not remove them, then frontier settlers would massacre them. Plus, they would have land to call their own.

Trail of Tears (1838 -1839) (Van Buren was President then)


Jackson’s Professed “Love” for Native Americans

Was Andrew Jackson democratic in dealing with Native Americans?


The National Bank Debate Nicholas Biddle President Jackson

nd 2 National Bank • National Bank- more powerful than the Federal Government • Issued 1/3 of the US’s paper money, ¼ loans, and held 1/3 of the gold • People hated the National Bank because of the Panic 1819 • Bank Charter to expire in 1836 and Congress passed a bill to re-charter the bank • Jackson vetoed the bill • Whigs called Jackson King Andrew because they felt he was too powerful


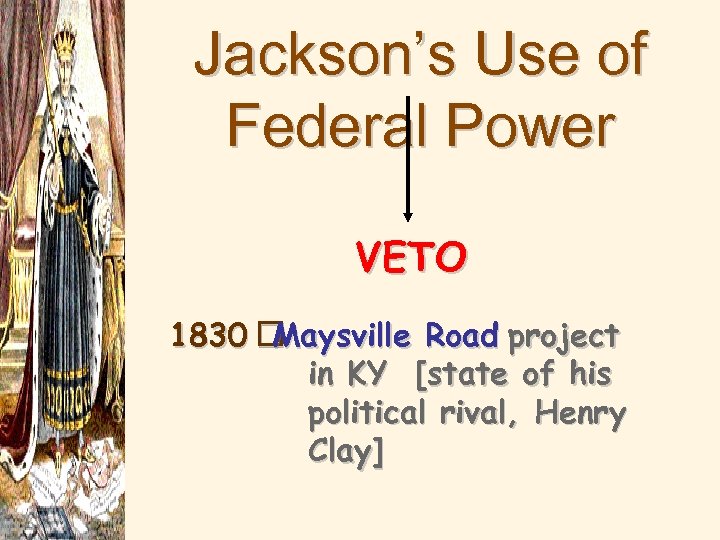
Jackson’s Use of Federal Power VETO 1830 Maysville Road project in KY [state of his political rival, Henry Clay]

• The previous 6 Presidents only used vetoes (9 in all ) when they thought a law was unconstitutional • Now Jackson began to use vetoes (12 in all ) when he thought a law was not in the best interest of the common person, expand powers of the Presidency • Jackson began to deposit federal funds in pet state banks; bank dies b/c no money was put into it • Bad Policy, caused the Panic of 1837

The Downfall of “Mother Bank”
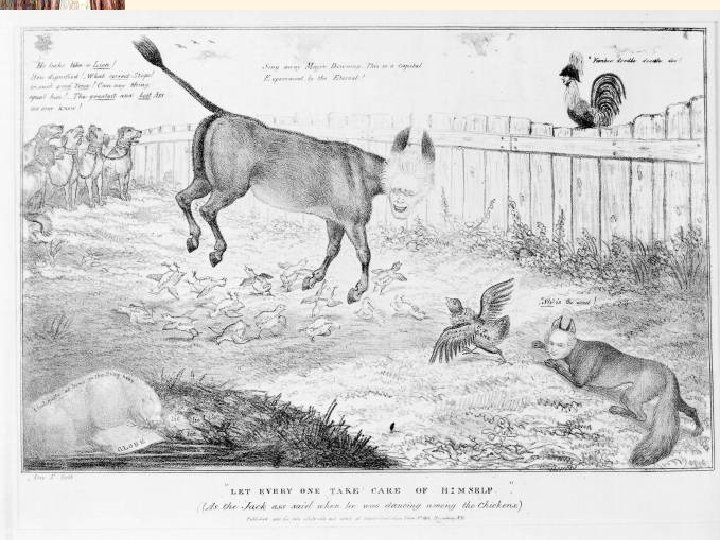



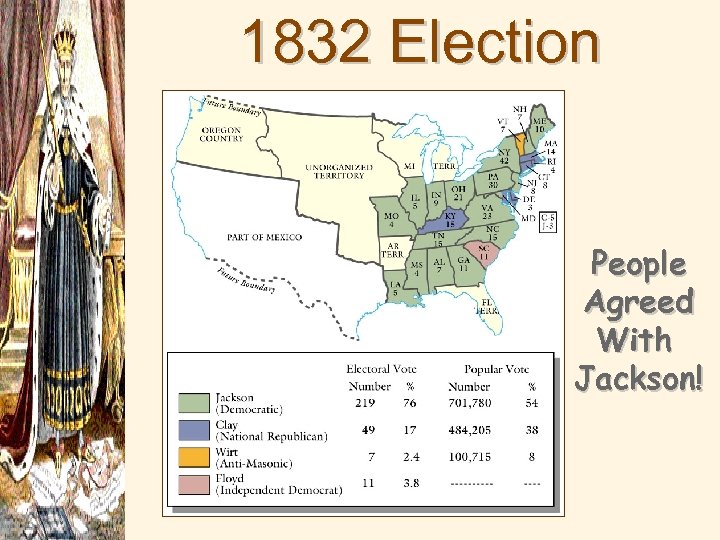
1832 Election Results People Agreed With Jackson!

The Specie Circular (1836) 3 buy future federal land only with gold or silver to stop speculation on Western Lands

BUS Banknote Specie—Gold or silver

Campaign to remove Jackson from the 20$ bill
![The 1836 Election Results Martin Van Buren “Old Kinderhook” [O. K. ] The 1836 Election Results Martin Van Buren “Old Kinderhook” [O. K. ]](https://present5.com/presentation/f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22/image-75.jpg)
The 1836 Election Results Martin Van Buren “Old Kinderhook” [O. K. ]
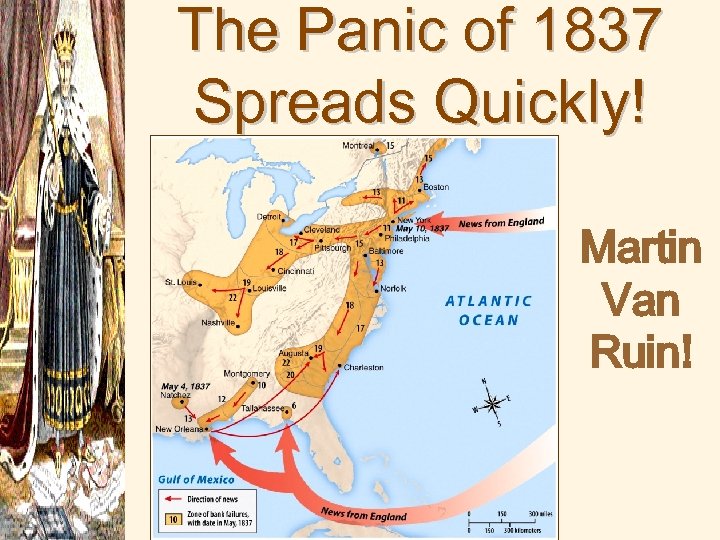
The Panic of 1837 Spreads Quickly! Martin Van Ruin!

Was Andrew Jackson democratic in dealing with the Bank of the United States (BUS)?

Andrew Jackson in Retirement • Ask slave if in heaven? • Funeral and Parrot Photo of Andrew Jackson in 1844, one year before his death • Votes for President after death

Was the Age of Jackson democratic? Consider: universal white male suffrage, voters selecting the Electoral College, campaigns, political parties, spoils system, slavery, Indian removal, BUS, Nullification Crisis, Andrew Jackson’s presidency, reform movements and the Second Great Awakening 1 3 7 9 5 ____________________ I I I Revisionists Moderates (radicals & liberals) NO Inbetween Traditional (Conservatives) YES

• Read pages 7 -8 on the bank and do the 3 multiple choice questions on a separate sheet of paper • Look at the Specie Circular Handout on page 9 • Read Jackson’s Bank Veto message and find 3 + reasons why he said the bank was undemocratic on pages 11 -12

Photo of Andrew Jackson in 1844 (one year before his death) 1767 - 1845


Make your own political cartoon, 15 pts • Make a political cartoon on Andrew Jackson on one of his controversial issues, like the Bank, nullification, Indian Removal, or the Corrupt Bargain, 8 pts • On the back of the paper write 5 sentences on what the issue is about, if you are for or against for Jackson, and explain the symbolism in your cartoon. (7 points)

Andrew Jackson traditionally is associated with the rise of democracy in America. Evaluate how democratic Andrew Jackson's presidential policies were on THREE of the following issues. -Economics -Native Americans -Nullification Crisis -Rotation of political office

• Jackson’s economic policies on the bank were democratic because he fought for the common man against the forces of the elite rich. – Henry Clay & Nicholas Biddle – Veto – Removed deposits • Jackson’s policies dealing with Native Americans were undemocratic because he ignored the democratic checks and balances processes of the Constitution. – Indian Removal Act, 1830 – John Marshall – Worcester v. Georgia • Jackson’s policies on the Nullification crisis were democratic because he enforced majority rules and preserved the Union (The institution of democracy). – John C. Calhoun – Tariff of Abominations, 1828 – Force Bill, 1832

• What caused the rise second party system in America?

How did TWO of the following contribute to the re-emergence of a two party system in the period from 1820 to 1840 n. Major political personalities/ elections n. State’s rights n. Economic issues

Read handout on page 13

Second Party System 1824 -1852: • The Whigs proposed a society that would be economically diverse but culturally uniform; the Democrats preferred a society that would be economically uniform, but were more tolerant of cultural and moral diversity.

MAJOR PARTY ISSUES • Jacksonian Democrats • A) Corrupt Bargain Need for national reform • B) Support Jeffersonian (small gov. ) • C) Support majoritarian rule • D) Support power of the Executive • E) Concerned about the "market revolution" • F) Limit the "American System“ (Banks, tariffs, internal improvements) • G) Support broad territorial expansion • H) Support Indian Removal • I) Ignore slavery as a national issue • J) Generally supportive of new immigrants National Republicans/ Whigs • • • Jackson unqualified for office Support Hamilton proactive gov. Concerned about the masses Support power of the Congress to endorse the "market revolution“ Promote the "American System“ Support restricted territorial expansion Generally opposed Indian removal Concern for morality of slavery Concerned about cultural impact of Immigrants

Major Political Personalities • ANDREW JACKSON!!!!!! • • – Spoils system Whigs- Clay, Webster, Calhoun switched, William Henry Harrison Democrats- Martin Van Buren John Quincy Adams- before parties Elections: – 1820 swept by Monroe – 1824 Corrupt Bargain- rise of political parties – 1828 Jackson elected- West Rev? – 1832 Jackson re-elected despite bank issue – 1836 Van Buren succeeded AJ – 1840 - Tippecanoe and Tyler Too!- Log Cabin Hard Cider Campaign

Economics • American System, BIT, – Bank- Jackson Veto, Specie Circular – Internal improvements- Maysville Road Veto, – Tariffs- Nullification crisis • Charles River Bridge Case • Whigs for the New Economy- Democrats against it

State’s Rights • Nullification Crisis • Indian Removal

The Jacksonian Period (1824 - 1848) has been celebrated as the era of the “Common Man. ” To what extent did the period live up to its characterization? Consider TWO of the following in your response? -Economic development -Politics -Reform movements
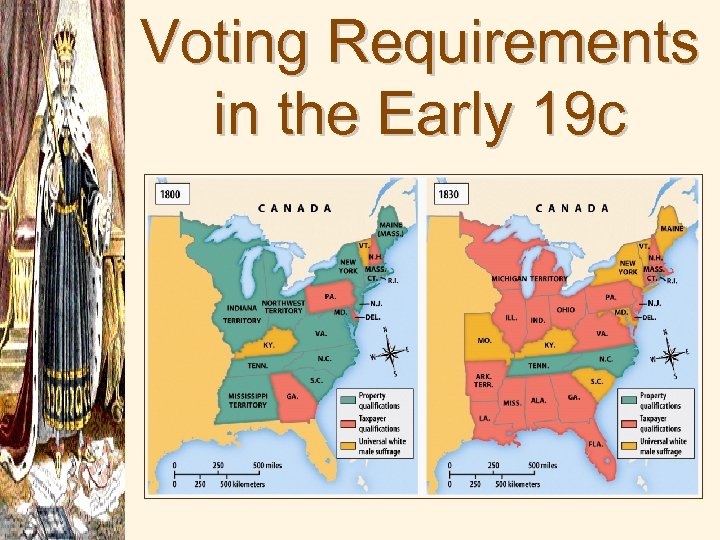
Voting Requirements in the Early 19 c



f80c9a2c28f87f783dc24c70b089fb22.ppt