e905b46c7cd999ba4018a50621434dc7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop August 28 -29, 2012 Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects Karol Furdik karol. furdik@tuke. sk, karol. furdik@fintersoft. sk • Technical University of Kosice, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Kosice, Slovakia, www. fei. tuke. sk • Inter. Soft, a. s. , Kosice, Slovakia, www. intersoft. sk 1
IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop August 28 -29, 2012 Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects Karol Furdik karol. furdik@tuke. sk, karol. furdik@fintersoft. sk • Technical University of Kosice, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Kosice, Slovakia, www. fei. tuke. sk • Inter. Soft, a. s. , Kosice, Slovakia, www. intersoft. sk 1
 Contents Internet of Things • basic concepts, definitions • objectives, applications, R&D challenges, • Io. T research in Europe, FP 7 priorities and projects ebbits project • basic facts, concepts, technology • pilot applications: automotive manufacturing, food traceability • achievements, activities, future work ELLIOT project • basic facts, concepts, technology • the Smart Office pilot application • results, future work Conclusions • general observations on Io. T research • challenges, possible R&D directions in future K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 2
Contents Internet of Things • basic concepts, definitions • objectives, applications, R&D challenges, • Io. T research in Europe, FP 7 priorities and projects ebbits project • basic facts, concepts, technology • pilot applications: automotive manufacturing, food traceability • achievements, activities, future work ELLIOT project • basic facts, concepts, technology • the Smart Office pilot application • results, future work Conclusions • general observations on Io. T research • challenges, possible R&D directions in future K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 2
 Internet of Things Definitions: • a dynamic global network infrastructure of adaptable and interoperable devices integrated in a common information and communication network (CERP-Io. T - IERC, http: //www. rfidin-action. eu/cerp/) • a collection of technologies that make it possible to connect things like sensors and actuators to the Internet, thereby allowing the physical world to be accessed through software (Contiki project, http: //www. contiki-os. org) • a layer of digital connectivity on top of existing infrastructure and things (Io. T Council, http: //www. theinternetofthings. eu) • a vision of employing the networked devices and applications in business, information, and social processes Characteristics, features: • well established and continuously expanding research domain • significant outcomes for many sectors of industry already available • enabling technologies: sensor networks, RFID, multi-agent systems, event-driven architectures, service-oriented architectures, web services K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 3
Internet of Things Definitions: • a dynamic global network infrastructure of adaptable and interoperable devices integrated in a common information and communication network (CERP-Io. T - IERC, http: //www. rfidin-action. eu/cerp/) • a collection of technologies that make it possible to connect things like sensors and actuators to the Internet, thereby allowing the physical world to be accessed through software (Contiki project, http: //www. contiki-os. org) • a layer of digital connectivity on top of existing infrastructure and things (Io. T Council, http: //www. theinternetofthings. eu) • a vision of employing the networked devices and applications in business, information, and social processes Characteristics, features: • well established and continuously expanding research domain • significant outcomes for many sectors of industry already available • enabling technologies: sensor networks, RFID, multi-agent systems, event-driven architectures, service-oriented architectures, web services K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 3
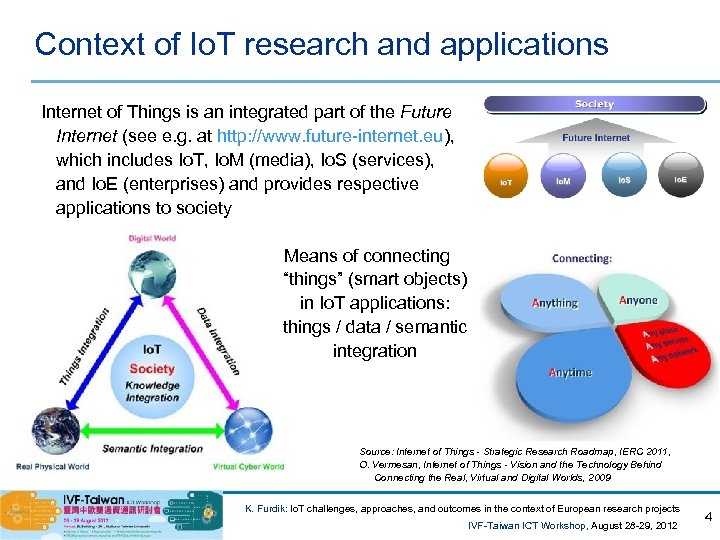 Context of Io. T research and applications Internet of Things is an integrated part of the Future Internet (see e. g. at http: //www. future-internet. eu), which includes Io. T, Io. M (media), Io. S (services), and Io. E (enterprises) and provides respective applications to society Means of connecting “things” (smart objects) in Io. T applications: things / data / semantic integration Source: Internet of Things - Strategic Research Roadmap, IERC 2011, O. Vermesan, Internet of Things - Vision and the Technology Behind Connecting the Real, Virtual and Digital Worlds, 2009 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 4
Context of Io. T research and applications Internet of Things is an integrated part of the Future Internet (see e. g. at http: //www. future-internet. eu), which includes Io. T, Io. M (media), Io. S (services), and Io. E (enterprises) and provides respective applications to society Means of connecting “things” (smart objects) in Io. T applications: things / data / semantic integration Source: Internet of Things - Strategic Research Roadmap, IERC 2011, O. Vermesan, Internet of Things - Vision and the Technology Behind Connecting the Real, Virtual and Digital Worlds, 2009 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 4
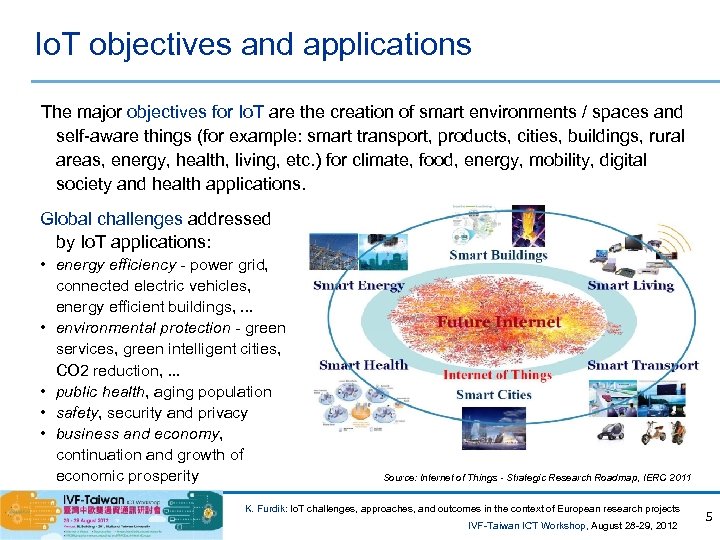 Io. T objectives and applications The major objectives for Io. T are the creation of smart environments / spaces and self-aware things (for example: smart transport, products, cities, buildings, rural areas, energy, health, living, etc. ) for climate, food, energy, mobility, digital society and health applications. Global challenges addressed by Io. T applications: • energy efficiency - power grid, connected electric vehicles, energy efficient buildings, . . . • environmental protection - green services, green intelligent cities, CO 2 reduction, . . . • public health, aging population • safety, security and privacy • business and economy, continuation and growth of economic prosperity Source: Internet of Things - Strategic Research Roadmap, IERC 2011 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 5
Io. T objectives and applications The major objectives for Io. T are the creation of smart environments / spaces and self-aware things (for example: smart transport, products, cities, buildings, rural areas, energy, health, living, etc. ) for climate, food, energy, mobility, digital society and health applications. Global challenges addressed by Io. T applications: • energy efficiency - power grid, connected electric vehicles, energy efficient buildings, . . . • environmental protection - green services, green intelligent cities, CO 2 reduction, . . . • public health, aging population • safety, security and privacy • business and economy, continuation and growth of economic prosperity Source: Internet of Things - Strategic Research Roadmap, IERC 2011 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 5
 Challenges on application level • Network management – network technologies should be reliable, intelligent, selfmanaged, context aware and adaptable • Interfaces – to refine interaction between HW, SW, algorithms, devices, . . . ; smart human / machine interfaces, enabling mobile SW • Embedded smart functionality – further development of sensors, actuators, storage, energy sources, middleware, sensor networks, etc. • Multi-domain communications – to enhance information and signal processing, identification technology, discovery and search engine technologies • Security, privacy, business safety – improvements needed by developing novel security techniques and concepts • Standardisation, interoperability, validation and modularization of the Io. T technologies needs enhancements • New governance principles should be defined – free access to knowledge for further technology and business development (while maintaining respect for privacy, security and safety) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 6
Challenges on application level • Network management – network technologies should be reliable, intelligent, selfmanaged, context aware and adaptable • Interfaces – to refine interaction between HW, SW, algorithms, devices, . . . ; smart human / machine interfaces, enabling mobile SW • Embedded smart functionality – further development of sensors, actuators, storage, energy sources, middleware, sensor networks, etc. • Multi-domain communications – to enhance information and signal processing, identification technology, discovery and search engine technologies • Security, privacy, business safety – improvements needed by developing novel security techniques and concepts • Standardisation, interoperability, validation and modularization of the Io. T technologies needs enhancements • New governance principles should be defined – free access to knowledge for further technology and business development (while maintaining respect for privacy, security and safety) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 6
 Challenges on technology enablers • Energy – ultra low power devices needed • Intelligence – capabilities of self-awareness, adaptability, inter-machine communication, knowledge discovery, etc. • Communication – new smart antennas, protocols, APIs, together with network management and visualization techniques need to be developed • Integration – wireless ID technologies (RFID) should be integrated to devices • Dependability – individual authentication of billions of heterogeneous devices • Semantic technologies – large scale distributed ontologies, semantic discovery of devices, semantic web services, rule engines, . . . • Real world Io. T scenarios – to evaluate Io. T solutions in real large-scale industrial applications; to illustrate business-based scenarios • Modeling and design – innovative M-D frameworks needed for large scale Io. T systems • Interoperability, standards – ensure interoperability of devices by integrating different standardized architectures, protocols, etc. ; define open standards and reference models • Manufacturing – to lower costs of key technologies (e. g. , RFID) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 7
Challenges on technology enablers • Energy – ultra low power devices needed • Intelligence – capabilities of self-awareness, adaptability, inter-machine communication, knowledge discovery, etc. • Communication – new smart antennas, protocols, APIs, together with network management and visualization techniques need to be developed • Integration – wireless ID technologies (RFID) should be integrated to devices • Dependability – individual authentication of billions of heterogeneous devices • Semantic technologies – large scale distributed ontologies, semantic discovery of devices, semantic web services, rule engines, . . . • Real world Io. T scenarios – to evaluate Io. T solutions in real large-scale industrial applications; to illustrate business-based scenarios • Modeling and design – innovative M-D frameworks needed for large scale Io. T systems • Interoperability, standards – ensure interoperability of devices by integrating different standardized architectures, protocols, etc. ; define open standards and reference models • Manufacturing – to lower costs of key technologies (e. g. , RFID) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 7
 Io. T research in Europe 7 th Framework Programme of EC: • Io. T research is included into priorities of ICT • Call 5, 2009 -2010, Objective 1. 3 : Internet of Things and Enterprise environments • Call 7, 2011, Objectives 1. 3: Internet-connected objects, 1. 6: Future Internet Research and Experimentation • Call 8, 2011, Objectives 1. 1: Future Networks • Currently, in the last FP 7 call – Io. T-related areas: • Smart Cities • Secure clean and efficient energy • Improving delivery of Public Sector Services Io. T-related EU research communities: • Io. T European Research Cluster (IERC), http: //www. internet-of-things-research. eu • Io. T Council, http: //www. theinternetofthings. eu • Io. T Hub Europe, http: //www. internet-of-things. eu • Internet of Things Expert Group (Io. T-EG) (E 02514) • FIn. ES Cluster (Future Internet Enterprise Systems), http: //www. fines-cluster. eu • Internet of Things group on Linked. In, http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? home=&gid=73311 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 8
Io. T research in Europe 7 th Framework Programme of EC: • Io. T research is included into priorities of ICT • Call 5, 2009 -2010, Objective 1. 3 : Internet of Things and Enterprise environments • Call 7, 2011, Objectives 1. 3: Internet-connected objects, 1. 6: Future Internet Research and Experimentation • Call 8, 2011, Objectives 1. 1: Future Networks • Currently, in the last FP 7 call – Io. T-related areas: • Smart Cities • Secure clean and efficient energy • Improving delivery of Public Sector Services Io. T-related EU research communities: • Io. T European Research Cluster (IERC), http: //www. internet-of-things-research. eu • Io. T Council, http: //www. theinternetofthings. eu • Io. T Hub Europe, http: //www. internet-of-things. eu • Internet of Things Expert Group (Io. T-EG) (E 02514) • FIn. ES Cluster (Future Internet Enterprise Systems), http: //www. fines-cluster. eu • Internet of Things group on Linked. In, http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? home=&gid=73311 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 8
 Io. T-related FP 7 projects IERC Members: http: //www. internet-of-things-research. eu/partners. htm • CASAGRAS 2, Coordination and Support Action for Global RFID-related Activities and Standardisation – 2, www. iot-casagras. org • Io. T-I, Internet Of Things Initiative, www. iot-i. eu • Io. T-A, Internet Of Things Architecture, www. iot-a. eu • SPRINT, Software Platform For Integration Of Engineering And Things, www. sprint-iot. eu • Smart. Agri. Food, Smart Food and Agribusiness, www. smartagrifood. eu • i. Core, Internet Connected Objects for Reconfigurable Ecosystems, www. iot-icore. eu • Io. T@Work, Internet of Things at Work, www. iot-at-work. eu • Hydra, FP 6 project on semantic Io. T middleware, www. hydramiddleware. eu • . . . • ebbits & ELLIOT K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 9
Io. T-related FP 7 projects IERC Members: http: //www. internet-of-things-research. eu/partners. htm • CASAGRAS 2, Coordination and Support Action for Global RFID-related Activities and Standardisation – 2, www. iot-casagras. org • Io. T-I, Internet Of Things Initiative, www. iot-i. eu • Io. T-A, Internet Of Things Architecture, www. iot-a. eu • SPRINT, Software Platform For Integration Of Engineering And Things, www. sprint-iot. eu • Smart. Agri. Food, Smart Food and Agribusiness, www. smartagrifood. eu • i. Core, Internet Connected Objects for Reconfigurable Ecosystems, www. iot-icore. eu • Io. T@Work, Internet of Things at Work, www. iot-at-work. eu • Hydra, FP 6 project on semantic Io. T middleware, www. hydramiddleware. eu • . . . • ebbits & ELLIOT K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 9
 EBBITS project – basic facts ebbits: Enabling Business-Based Internet of Things and Services • Integrated EU project, FP 7 ICT, Activity ICT-2009. 1. 3 “Internet of Things and Enterprise environments”, Contract no. : 257852 • Duration: 09/2010 – 08/2014 (48 months) • Web: www. ebbits-project. eu • Coordinator: Fraunhofer Institute, Germany • Project consortium: 9 partners (universities, research institutes, private companies) from 5 countries (GE, SWE, DEN, IT, SK) • 2 pilot applications - Italy and Denmark Main project objective: • To develop architecture, technologies and processes, which allow businesses to semantically integrate the Internet of Things into mainstream enterprise systems and support interoperable real-world, on-line end-to-end business applications K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 10
EBBITS project – basic facts ebbits: Enabling Business-Based Internet of Things and Services • Integrated EU project, FP 7 ICT, Activity ICT-2009. 1. 3 “Internet of Things and Enterprise environments”, Contract no. : 257852 • Duration: 09/2010 – 08/2014 (48 months) • Web: www. ebbits-project. eu • Coordinator: Fraunhofer Institute, Germany • Project consortium: 9 partners (universities, research institutes, private companies) from 5 countries (GE, SWE, DEN, IT, SK) • 2 pilot applications - Italy and Denmark Main project objective: • To develop architecture, technologies and processes, which allow businesses to semantically integrate the Internet of Things into mainstream enterprise systems and support interoperable real-world, on-line end-to-end business applications K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 10
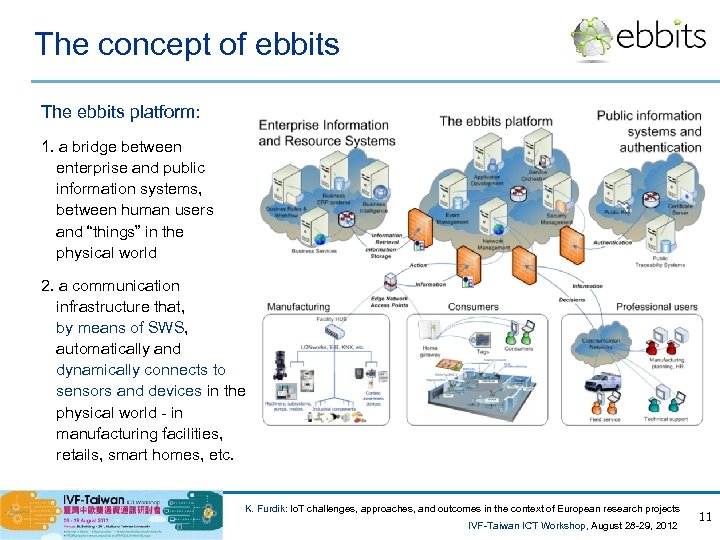 The concept of ebbits The ebbits platform: 1. a bridge between enterprise and public information systems, between human users and “things” in the physical world 2. a communication infrastructure that, by means of SWS, automatically and dynamically connects to sensors and devices in the physical world - in manufacturing facilities, retails, smart homes, etc. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 11
The concept of ebbits The ebbits platform: 1. a bridge between enterprise and public information systems, between human users and “things” in the physical world 2. a communication infrastructure that, by means of SWS, automatically and dynamically connects to sensors and devices in the physical world - in manufacturing facilities, retails, smart homes, etc. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 11
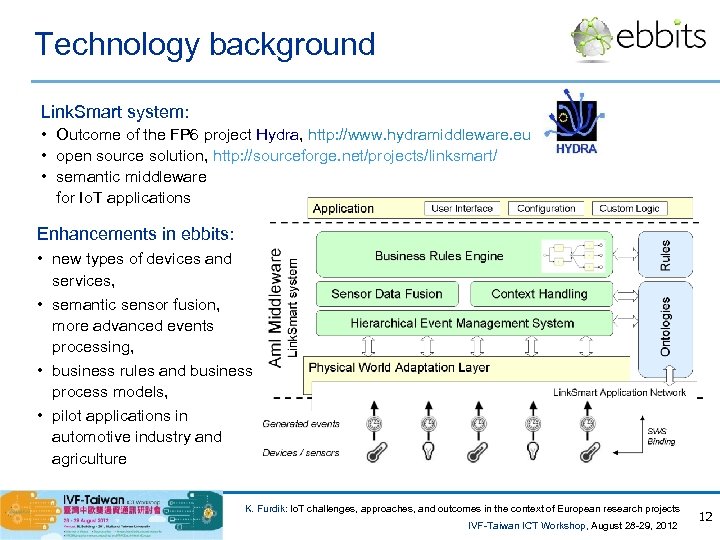 Technology background Link. Smart system: • Outcome of the FP 6 project Hydra, http: //www. hydramiddleware. eu • open source solution, http: //sourceforge. net/projects/linksmart/ • semantic middleware for Io. T applications Enhancements in ebbits: • new types of devices and services, • semantic sensor fusion, more advanced events processing, • business rules and business process models, • pilot applications in automotive industry and agriculture K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 12
Technology background Link. Smart system: • Outcome of the FP 6 project Hydra, http: //www. hydramiddleware. eu • open source solution, http: //sourceforge. net/projects/linksmart/ • semantic middleware for Io. T applications Enhancements in ebbits: • new types of devices and services, • semantic sensor fusion, more advanced events processing, • business rules and business process models, • pilot applications in automotive industry and agriculture K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 12
 Outcomes and pilot applications • Expected project outcomes: • enhanced Link. Smart semantic middleware, optimized for real-world business applications • toolset for development of semantic models and semantically annotated business rules / processes • interfaces to new types of devices • methodology for building a Link. Smart-based Io. T solution • Pilot #1: Deployment in the manufacturing stage: • to manage production optimization with special emphasis on energy savings and CO 2 reduction; • automotive industry, assembly processes; • data collected from sensors in the assembly line, semantically annotated and processed towards the optimization criteria. • Pilot #2: Deployment in the consumption stage: • traceability throughout the food chain, from “farm to fork”, across the lifecycle history of the food; • collecting data automatically from various actors, sensors and systems, indexing and intelligently registering it in public databases. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 13
Outcomes and pilot applications • Expected project outcomes: • enhanced Link. Smart semantic middleware, optimized for real-world business applications • toolset for development of semantic models and semantically annotated business rules / processes • interfaces to new types of devices • methodology for building a Link. Smart-based Io. T solution • Pilot #1: Deployment in the manufacturing stage: • to manage production optimization with special emphasis on energy savings and CO 2 reduction; • automotive industry, assembly processes; • data collected from sensors in the assembly line, semantically annotated and processed towards the optimization criteria. • Pilot #2: Deployment in the consumption stage: • traceability throughout the food chain, from “farm to fork”, across the lifecycle history of the food; • collecting data automatically from various actors, sensors and systems, indexing and intelligently registering it in public databases. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 13
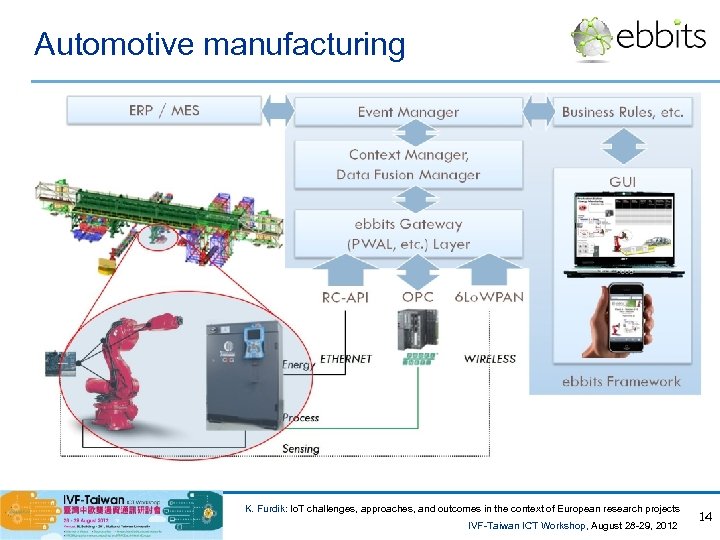 Automotive manufacturing K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 14
Automotive manufacturing K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 14
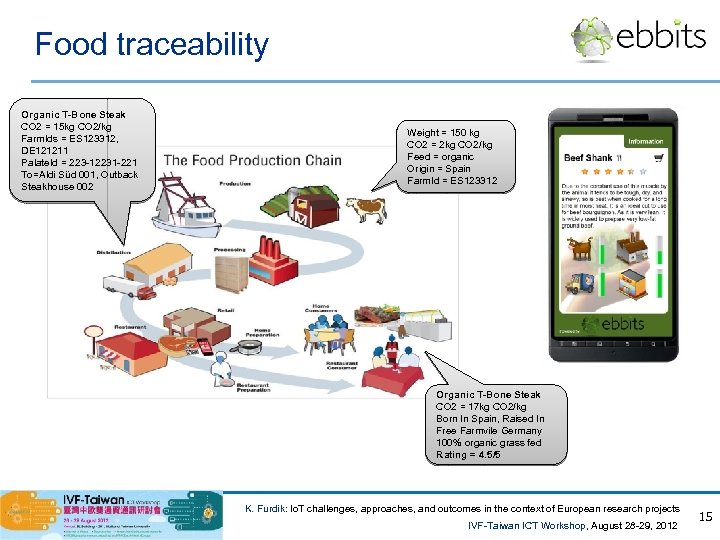 Food traceability Organic T-Bone Steak CO 2 = 15 kg CO 2/kg Farm. Ids = ES 123312, DE 121211 Palate. Id = 223 -12231 -221 To=Aldi Süd 001, Outback Steakhouse 002 Weight = 150 kg CO 2 = 2 kg CO 2/kg Feed = organic Origin = Spain Farm. Id = ES 123312 Organic T-Bone Steak CO 2 = 17 kg CO 2/kg Born In Spain, Raised In Free Farmvile Germany 100% organic grass fed Rating = 4. 5/5 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 15
Food traceability Organic T-Bone Steak CO 2 = 15 kg CO 2/kg Farm. Ids = ES 123312, DE 121211 Palate. Id = 223 -12231 -221 To=Aldi Süd 001, Outback Steakhouse 002 Weight = 150 kg CO 2 = 2 kg CO 2/kg Feed = organic Origin = Spain Farm. Id = ES 123312 Organic T-Bone Steak CO 2 = 17 kg CO 2/kg Born In Spain, Raised In Free Farmvile Germany 100% organic grass fed Rating = 4. 5/5 K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 15
 Achievements, future work • Work done so far: • • architecture of updated Link. Smart specified, implementation is ongoing OWLIM ontology infrastructure employed for semantics and context awareness j. Boss / Drools framework for business rules processing M 24 demo prepared, focus on the automotive manufacturing scenario • Next steps: • project review in October 2012 • further development, focus on the food traceability scenario • Other activities: • workshops and activities within the FIn. ES Cluster (Future Internet Week, Io. T Week) • Ce. BIT 2012 – ebbits co-exhibited with Action. Plan. T project at the stand: ICT for the Factories of the Future K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 16
Achievements, future work • Work done so far: • • architecture of updated Link. Smart specified, implementation is ongoing OWLIM ontology infrastructure employed for semantics and context awareness j. Boss / Drools framework for business rules processing M 24 demo prepared, focus on the automotive manufacturing scenario • Next steps: • project review in October 2012 • further development, focus on the food traceability scenario • Other activities: • workshops and activities within the FIn. ES Cluster (Future Internet Week, Io. T Week) • Ce. BIT 2012 – ebbits co-exhibited with Action. Plan. T project at the stand: ICT for the Factories of the Future K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 16
 ELLIOT project - basic facts ELLIOT: Experiential Living Lab for the Internet Of Things Framework Programme 7, ICT Call 5 : FP 7 -ICT-2009 -5 Objective ICT-2009. 1. 3: Internet of Things and Enterprise environments Project type: STREP / Collaborative research, Project No: 287560 Duration: 30 months (September 2010 - February 2013) Web: www. elliot-project. eu Coordinator: TXT Polymedia S. p. A. , Italy Partners: 9 + 3 (Italy, Germany, France, UK, Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia) Aims of the project: • the development of an Internet of Things experiential platform, • to directly involve users (customers, citizens) in co-creating, exploring and experimenting new ideas, concepts and technological artefacts, • to study a potential impact of Io. T and the Future Internet in the context of the Open User-Centred Innovation paradigm and of the Living Lab approach. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 17
ELLIOT project - basic facts ELLIOT: Experiential Living Lab for the Internet Of Things Framework Programme 7, ICT Call 5 : FP 7 -ICT-2009 -5 Objective ICT-2009. 1. 3: Internet of Things and Enterprise environments Project type: STREP / Collaborative research, Project No: 287560 Duration: 30 months (September 2010 - February 2013) Web: www. elliot-project. eu Coordinator: TXT Polymedia S. p. A. , Italy Partners: 9 + 3 (Italy, Germany, France, UK, Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia) Aims of the project: • the development of an Internet of Things experiential platform, • to directly involve users (customers, citizens) in co-creating, exploring and experimenting new ideas, concepts and technological artefacts, • to study a potential impact of Io. T and the Future Internet in the context of the Open User-Centred Innovation paradigm and of the Living Lab approach. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 17
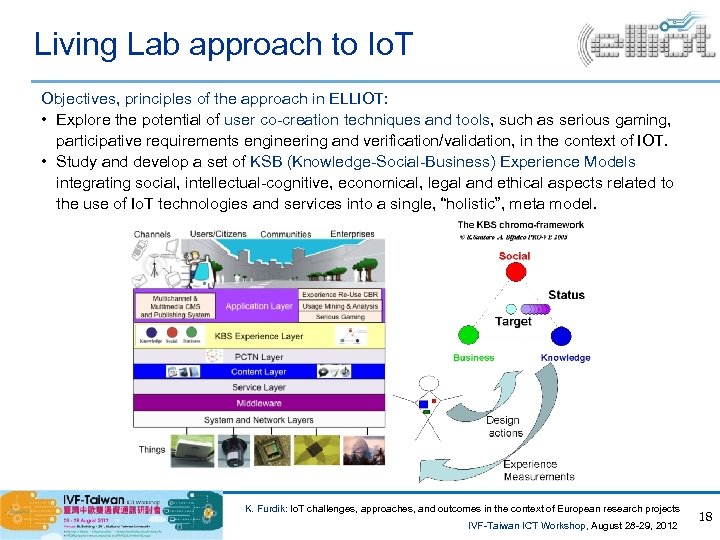 Living Lab approach to Io. T Objectives, principles of the approach in ELLIOT: • Explore the potential of user co-creation techniques and tools, such as serious gaming, participative requirements engineering and verification/validation, in the context of IOT. • Study and develop a set of KSB (Knowledge-Social-Business) Experience Models integrating social, intellectual-cognitive, economical, legal and ethical aspects related to the use of Io. T technologies and services into a single, “holistic”, meta model. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 18
Living Lab approach to Io. T Objectives, principles of the approach in ELLIOT: • Explore the potential of user co-creation techniques and tools, such as serious gaming, participative requirements engineering and verification/validation, in the context of IOT. • Study and develop a set of KSB (Knowledge-Social-Business) Experience Models integrating social, intellectual-cognitive, economical, legal and ethical aspects related to the use of Io. T technologies and services into a single, “holistic”, meta model. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 18
 ELLIOT-EEU extension Extension to the Enlarged European Union (EEU): • Duration: 18 months (September 2011 - February 2013) • 3 new use cases - pilot applications: Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia, as complements to former ELLIOT pilots Focus of pilots: • Logistics PLM: Logistics Product Life-cycle Management (PLM) supported by Io. T and RFID technologies • BIBA Log. Dynamics Lab, Bremen, Germany • Safe. Pay Systems Ltd. , Hungary • Extended concept of “Well Being” in a hospital environment • San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy • Virtech Ltd. , Bulgaria • Green Services @ ICT Usage Lab • INRIA (Sophia Antipolis), France • Inter. Soft, a. s. , Kosice, Slovakia K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 19
ELLIOT-EEU extension Extension to the Enlarged European Union (EEU): • Duration: 18 months (September 2011 - February 2013) • 3 new use cases - pilot applications: Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia, as complements to former ELLIOT pilots Focus of pilots: • Logistics PLM: Logistics Product Life-cycle Management (PLM) supported by Io. T and RFID technologies • BIBA Log. Dynamics Lab, Bremen, Germany • Safe. Pay Systems Ltd. , Hungary • Extended concept of “Well Being” in a hospital environment • San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy • Virtech Ltd. , Bulgaria • Green Services @ ICT Usage Lab • INRIA (Sophia Antipolis), France • Inter. Soft, a. s. , Kosice, Slovakia K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 19
 ELLIOT Living Lab in Slovakia Pilot name: ECOffices - Ambient Intelligence in energy saving • The Smart Office use case: • Integrates Am. I-Io. T & semantic technologies, with respect to the KSB (knowledge-social-business) aspects of user interactions • Targets the optimization of energy consumption in offices • Focus, goals: • experiment the ELLIOT outcomes and the new semantically enhanced Am. I technology in the Energy test case in Slovakia • demonstrate the platform capabilities towards a positive impact on environment (energy consumption, CO 2 footprint) • Technology: • Am. I-Io. T: based on Link. Smart middleware, using outcomes of the FP 7 project ebbits. • Semantics: device ontology, fusion of generated events, business rules • Devices: energy consumption, environment conditions, and occupancy sensors - Plugwise, Arduino, … K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 20
ELLIOT Living Lab in Slovakia Pilot name: ECOffices - Ambient Intelligence in energy saving • The Smart Office use case: • Integrates Am. I-Io. T & semantic technologies, with respect to the KSB (knowledge-social-business) aspects of user interactions • Targets the optimization of energy consumption in offices • Focus, goals: • experiment the ELLIOT outcomes and the new semantically enhanced Am. I technology in the Energy test case in Slovakia • demonstrate the platform capabilities towards a positive impact on environment (energy consumption, CO 2 footprint) • Technology: • Am. I-Io. T: based on Link. Smart middleware, using outcomes of the FP 7 project ebbits. • Semantics: device ontology, fusion of generated events, business rules • Devices: energy consumption, environment conditions, and occupancy sensors - Plugwise, Arduino, … K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 20
 The Smart Office concept From “Smart Houses” to “Smart Offices” Smart House: • a house that has advanced automatic systems for lighting, heating, air-conditioning, window and door operations, security etc. • many solutions, both commercial and research Smart Office: • • • to employ the paradigm of the smart house in a business environment, inclusion of / integration with business processes, optimization of existing processes in an organization (or office), ability to implement new and more efficient business processes, expected benefits on the user level regarding to more organized and coordinated social interactions. Challenges: • correspondence of Am. I-Io. T with business processes, • acceptance and support from the side of employees (and management), • possible solution: Am. I-enhanced services and processes should follow the recommendations of IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL, http: //www. itil-officialsite. com) and the related standard ISO/IEC 20000: 1 -5. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 21
The Smart Office concept From “Smart Houses” to “Smart Offices” Smart House: • a house that has advanced automatic systems for lighting, heating, air-conditioning, window and door operations, security etc. • many solutions, both commercial and research Smart Office: • • • to employ the paradigm of the smart house in a business environment, inclusion of / integration with business processes, optimization of existing processes in an organization (or office), ability to implement new and more efficient business processes, expected benefits on the user level regarding to more organized and coordinated social interactions. Challenges: • correspondence of Am. I-Io. T with business processes, • acceptance and support from the side of employees (and management), • possible solution: Am. I-enhanced services and processes should follow the recommendations of IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL, http: //www. itil-officialsite. com) and the related standard ISO/IEC 20000: 1 -5. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 21
 Application partner : RWE IT Slovakia, http: //www. rweit-slovakia. com • belongs to RWE group, leading energy (gas, electricity) distributor in Eastern Slovakia • daughter company of RWE IT Gmb. H, IT services provider for RWE ECOffices pilot is implemented in the premises of RWE IT: • office type: open space room • 8 employees in the office (administration department) • central heating, air conditioning individually controlled within the office • equipment: computers, monitors, phones, 2 x printers, 1 x scanner / copier K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 22
Application partner : RWE IT Slovakia, http: //www. rweit-slovakia. com • belongs to RWE group, leading energy (gas, electricity) distributor in Eastern Slovakia • daughter company of RWE IT Gmb. H, IT services provider for RWE ECOffices pilot is implemented in the premises of RWE IT: • office type: open space room • 8 employees in the office (administration department) • central heating, air conditioning individually controlled within the office • equipment: computers, monitors, phones, 2 x printers, 1 x scanner / copier K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 22
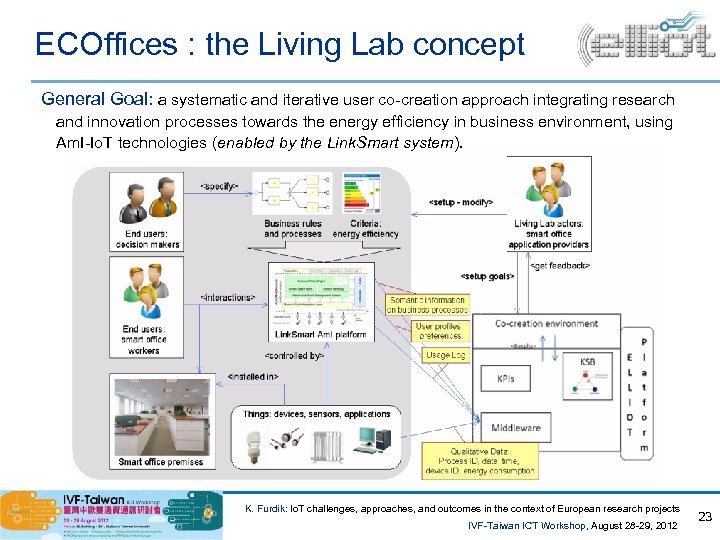 ECOffices : the Living Lab concept General Goal: a systematic and iterative user co-creation approach integrating research and innovation processes towards the energy efficiency in business environment, using Am. I-Io. T technologies (enabled by the Link. Smart system). K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 23
ECOffices : the Living Lab concept General Goal: a systematic and iterative user co-creation approach integrating research and innovation processes towards the energy efficiency in business environment, using Am. I-Io. T technologies (enabled by the Link. Smart system). K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 23
 Living Lab scenarios Scenario #1: Exploration of a suitable occupancy sensing device • 4 different types of occupancy sensors identified by Io. T experts • Goal: Users exploring, experiments and evaluation; Focus: to find a balance between: • Comfortable environment • Amount of saved energy / CO 2 emissions • Privacy loss Scenario #2: Process-based adaptation of the working environment • Uses occupancy sensor as an output of scenario #1. • Template process model given, e. g. predefined work hours, seasonal settings of environment • Adaptation of working environment according to user preferences • Goal: Adapted process model as an explicit representation of the working environment settings in a given time scale Scenario #3: Exploration of a suitable occupancy sensing device • Users playing a “game” saving real energy • A visualization showing actual consumption and CO 2 footprint data, overall ranking given • Ranking provided to decision makers -> e. g. awarding of winners? K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 24
Living Lab scenarios Scenario #1: Exploration of a suitable occupancy sensing device • 4 different types of occupancy sensors identified by Io. T experts • Goal: Users exploring, experiments and evaluation; Focus: to find a balance between: • Comfortable environment • Amount of saved energy / CO 2 emissions • Privacy loss Scenario #2: Process-based adaptation of the working environment • Uses occupancy sensor as an output of scenario #1. • Template process model given, e. g. predefined work hours, seasonal settings of environment • Adaptation of working environment according to user preferences • Goal: Adapted process model as an explicit representation of the working environment settings in a given time scale Scenario #3: Exploration of a suitable occupancy sensing device • Users playing a “game” saving real energy • A visualization showing actual consumption and CO 2 footprint data, overall ranking given • Ranking provided to decision makers -> e. g. awarding of winners? K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 24
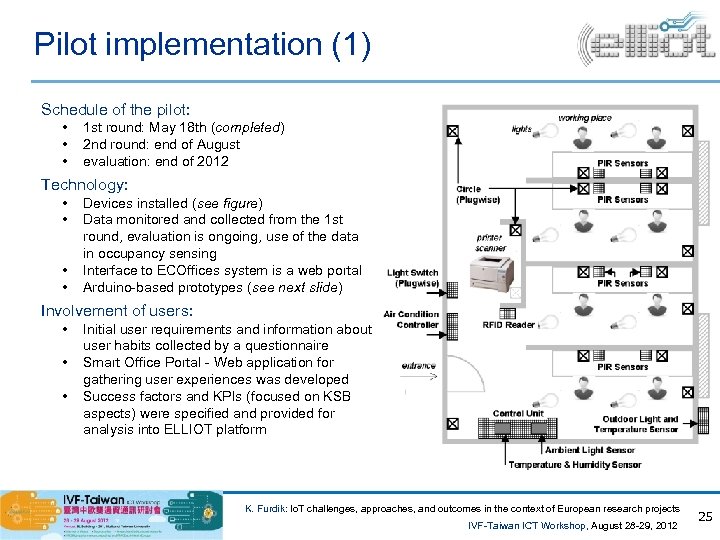 Pilot implementation (1) Schedule of the pilot: • • • 1 st round: May 18 th (completed) 2 nd round: end of August evaluation: end of 2012 Technology: • • Devices installed (see figure) Data monitored and collected from the 1 st round, evaluation is ongoing, use of the data in occupancy sensing Interface to ECOffices system is a web portal Arduino-based prototypes (see next slide) Involvement of users: • • • Initial user requirements and information about user habits collected by a questionnaire Smart Office Portal - Web application for gathering user experiences was developed Success factors and KPIs (focused on KSB aspects) were specified and provided for analysis into ELLIOT platform K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 25
Pilot implementation (1) Schedule of the pilot: • • • 1 st round: May 18 th (completed) 2 nd round: end of August evaluation: end of 2012 Technology: • • Devices installed (see figure) Data monitored and collected from the 1 st round, evaluation is ongoing, use of the data in occupancy sensing Interface to ECOffices system is a web portal Arduino-based prototypes (see next slide) Involvement of users: • • • Initial user requirements and information about user habits collected by a questionnaire Smart Office Portal - Web application for gathering user experiences was developed Success factors and KPIs (focused on KSB aspects) were specified and provided for analysis into ELLIOT platform K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 25
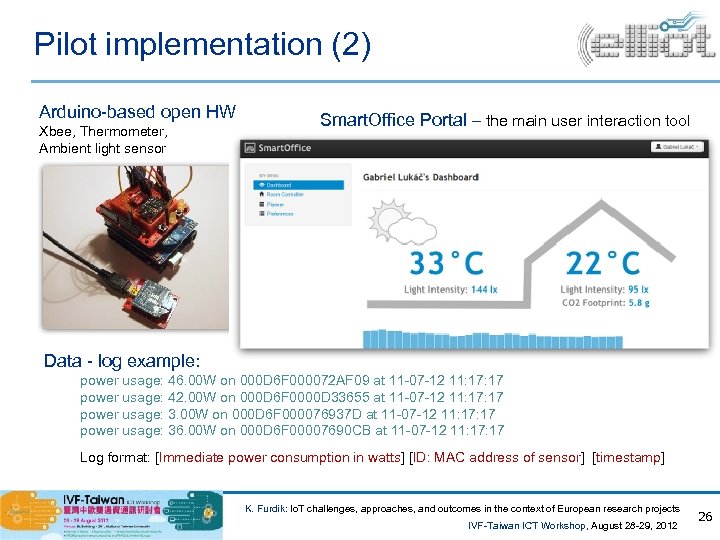 Pilot implementation (2) Arduino-based open HW Xbee, Thermometer, Ambient light sensor Smart. Office Portal – the main user interaction tool Data - log example: power usage: 46. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 000072 AF 09 at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 42. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 0000 D 33655 at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 3. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 000076937 D at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 36. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 00007690 CB at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 Log format: [Immediate power consumption in watts] [ID: MAC address of sensor] [timestamp] K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 26
Pilot implementation (2) Arduino-based open HW Xbee, Thermometer, Ambient light sensor Smart. Office Portal – the main user interaction tool Data - log example: power usage: 46. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 000072 AF 09 at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 42. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 0000 D 33655 at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 3. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 000076937 D at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 power usage: 36. 00 W on 000 D 6 F 00007690 CB at 11 -07 -12 11: 17 Log format: [Immediate power consumption in watts] [ID: MAC address of sensor] [timestamp] K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 26
 Summary, future steps Work done so far: • • Link. Smart middleware adapted for the ECOffices Living Lab pilot prototype implemented 1 st round of experiments on Scenario #1 accomplished data from sensors collected and provided to the ELLIOT platform for KSB analysis Next steps: • new types of devices - actuators: air conditioning control, light switches • business rule / process engine, based on Drools framework, www. drools. org • template process model for Scenario #2 will be developed • Scenario #2 experiments, evaluation • the Smart Office portal will be enhanced to enable the “game” on energy savings • Scenario #3 experiments, evaluation • ECOffices Living Lab has an ambition to join the European Network of Living Labs (ENo. LL, www. openlivinglabs. eu) in its next wave. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 27
Summary, future steps Work done so far: • • Link. Smart middleware adapted for the ECOffices Living Lab pilot prototype implemented 1 st round of experiments on Scenario #1 accomplished data from sensors collected and provided to the ELLIOT platform for KSB analysis Next steps: • new types of devices - actuators: air conditioning control, light switches • business rule / process engine, based on Drools framework, www. drools. org • template process model for Scenario #2 will be developed • Scenario #2 experiments, evaluation • the Smart Office portal will be enhanced to enable the “game” on energy savings • Scenario #3 experiments, evaluation • ECOffices Living Lab has an ambition to join the European Network of Living Labs (ENo. LL, www. openlivinglabs. eu) in its next wave. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 27
 Conclusions General observations: • Innovative applications addressing global challenges needed • Focus on practical applicability of Io. T solutions in a real world business environment • Advanced technologies (e. g. , semantics, Am. I, web services, clouds, . . . ) could be applied, but a shift from research to real business is necessary • Wider involvement of users, e. g by means of Living Lab approach, is needed Challenges, future R&D directions: • Living Lab, as a co-creative environment for design, development, and testing of Io. T solutions, seems to be very promising approach • Semantics, if applied in Io. T, should be improved in terms of powerful intelligent reasoning, retrieval, matching, etc. (i. e. , use relational DBs instead of ontologies, if appropriate) • Business processes and rules are capable to control the interactions between devices • A framework for managing provided Io. T solutions as IT services – candidate: IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL, http: //www. itil-officialsite. com) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 28
Conclusions General observations: • Innovative applications addressing global challenges needed • Focus on practical applicability of Io. T solutions in a real world business environment • Advanced technologies (e. g. , semantics, Am. I, web services, clouds, . . . ) could be applied, but a shift from research to real business is necessary • Wider involvement of users, e. g by means of Living Lab approach, is needed Challenges, future R&D directions: • Living Lab, as a co-creative environment for design, development, and testing of Io. T solutions, seems to be very promising approach • Semantics, if applied in Io. T, should be improved in terms of powerful intelligent reasoning, retrieval, matching, etc. (i. e. , use relational DBs instead of ontologies, if appropriate) • Business processes and rules are capable to control the interactions between devices • A framework for managing provided Io. T solutions as IT services – candidate: IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL, http: //www. itil-officialsite. com) K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 28
 Proposal for cooperation Other Io. T-related projects: • VENIS, Virtual Enterprises enabled by Networked Interoperability Services, www. venis-project. eu • Adapt 4 EE, www. adapt 4 ee. eu Technical University • a holistic approach to the planning, design & evaluation of energy performance of construction of Kosice products at an early design phase and prior to their realization www. tuke. sk • occupancy behavior , business processes and assets, semantic models of enterprises • INERTIA, Maximizing Response Capacity and Surplus of House. Hold and Tertiary Prosumers • starting in October 1 st, 2012 • goal: to develop a framework addressing a) energy efficiency (for steady state load minimization); b) peak load management (for daily operations); and c) dynamic demand (for event driven dynamic peak load reduction) • . . . R&D in areas of Smart City, energy efficiency, Io. T-supported manufacturing, . . . Opportunities: Inter. Soft, a. s. www. intersoft. sk • Smart Cities and Communities EIP (European Innovation Partnership), released by EC in July 2012 • areas of energy, mobility & transport, ICT in urban context (Smart Cities) • international cooperation is encouraged – possibility of a joint project? K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 29
Proposal for cooperation Other Io. T-related projects: • VENIS, Virtual Enterprises enabled by Networked Interoperability Services, www. venis-project. eu • Adapt 4 EE, www. adapt 4 ee. eu Technical University • a holistic approach to the planning, design & evaluation of energy performance of construction of Kosice products at an early design phase and prior to their realization www. tuke. sk • occupancy behavior , business processes and assets, semantic models of enterprises • INERTIA, Maximizing Response Capacity and Surplus of House. Hold and Tertiary Prosumers • starting in October 1 st, 2012 • goal: to develop a framework addressing a) energy efficiency (for steady state load minimization); b) peak load management (for daily operations); and c) dynamic demand (for event driven dynamic peak load reduction) • . . . R&D in areas of Smart City, energy efficiency, Io. T-supported manufacturing, . . . Opportunities: Inter. Soft, a. s. www. intersoft. sk • Smart Cities and Communities EIP (European Innovation Partnership), released by EC in July 2012 • areas of energy, mobility & transport, ICT in urban context (Smart Cities) • international cooperation is encouraged – possibility of a joint project? K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 29
 Thank you for your attention! Questions, suggestions, . . . ? Contact: • e-mail: Karol. Furdik@tuke. sk, Karol. Furdik@intersoft. sk • web: http: //web. tuke. sk/fei-cit/furdik/index-a. html Acknowledgements: The presented work was supported by the ELLIOT project (http: //www. elliotproject. eu) and the EBBITS project (http: //www. ebbits-project. eu), co-founded by the European Commission within the contracts No. 287560 and No. 257852, respectively. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 30
Thank you for your attention! Questions, suggestions, . . . ? Contact: • e-mail: Karol. Furdik@tuke. sk, Karol. Furdik@intersoft. sk • web: http: //web. tuke. sk/fei-cit/furdik/index-a. html Acknowledgements: The presented work was supported by the ELLIOT project (http: //www. elliotproject. eu) and the EBBITS project (http: //www. ebbits-project. eu), co-founded by the European Commission within the contracts No. 287560 and No. 257852, respectively. K. Furdik: Io. T challenges, approaches, and outcomes in the context of European research projects IVF-Taiwan ICT Workshop, August 28 -29, 2012 30


