1de570fcad856aef31d66f79629e3af2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 ITU Workshop on “Service Delivery Platforms (SDP) for Telecommunication Ecosystems: from today’s realities to requirements and challenges of the future” (Geneva, Switzerland, 17 October 2011 ) Future platform technologies and architectures Roberto Minerva, Manager of IC Scenarios Telecom Italia – Future Centre
ITU Workshop on “Service Delivery Platforms (SDP) for Telecommunication Ecosystems: from today’s realities to requirements and challenges of the future” (Geneva, Switzerland, 17 October 2011 ) Future platform technologies and architectures Roberto Minerva, Manager of IC Scenarios Telecom Italia – Future Centre
 Agenda A New Context for Telecomms Many paradoxes … The Rising Importance of Data Io. T and Data Personal Data = Data + Identity Deriving some requirements for Operators’ Platforms R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Agenda A New Context for Telecomms Many paradoxes … The Rising Importance of Data Io. T and Data Personal Data = Data + Identity Deriving some requirements for Operators’ Platforms R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
 A New Context for Telecomms R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
A New Context for Telecomms R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
 Towards 2020: the future of networks • Fiber reaches a large part of homes and enterprises, it guarantees: – – • Identity Management and their association to Biometric techniques Different roles and identities per user Diminishing role of SIMs Unlimited bandwidth Low cost per bit Everywhere connectivity flat rate also for mobile Fundamental Role of Terminals Abundance of Storage (1 TB in the terminal, toward infinite in the network? ) High processing Capabilities in the terminals (context controlled locally by the terminal) Capability to interoperate will be embedded in terminals and will be downloadable OTA Software embedded in the terminal makes the device more a personal service platform than a product. They will be personalized according to the specific user needs User is ABC (Always Best Connected) – – – • Services strongly related to users and their social relationships Transparent Connectivity (user always connected at the lower prices and best bandwidth) Strong Integration (at the terminal level) between mobile and fixed networks Cognitive Radio (terminals adapt to the available networks) Rapid change of Providers Dynamic Business Models Users connected to smaller, more efficient and cheaper cell Importance of Data – – – Seamless access to personal data Capability to dynamically create, aggregate and update personal data New data type and data sets Integration between real and virtual related data User controlled access to data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Pervasive Communication • • • Ubiquitous connectivity Broad classes of communicating objects (smart object, beacons, smart materials, sensors, micromachinery, . . . ) Explosion of Augmented Reality and Internet of Things applications Connectivity is a commodity Terminals are flexible and personal service platforms Data center larger and larger
Towards 2020: the future of networks • Fiber reaches a large part of homes and enterprises, it guarantees: – – • Identity Management and their association to Biometric techniques Different roles and identities per user Diminishing role of SIMs Unlimited bandwidth Low cost per bit Everywhere connectivity flat rate also for mobile Fundamental Role of Terminals Abundance of Storage (1 TB in the terminal, toward infinite in the network? ) High processing Capabilities in the terminals (context controlled locally by the terminal) Capability to interoperate will be embedded in terminals and will be downloadable OTA Software embedded in the terminal makes the device more a personal service platform than a product. They will be personalized according to the specific user needs User is ABC (Always Best Connected) – – – • Services strongly related to users and their social relationships Transparent Connectivity (user always connected at the lower prices and best bandwidth) Strong Integration (at the terminal level) between mobile and fixed networks Cognitive Radio (terminals adapt to the available networks) Rapid change of Providers Dynamic Business Models Users connected to smaller, more efficient and cheaper cell Importance of Data – – – Seamless access to personal data Capability to dynamically create, aggregate and update personal data New data type and data sets Integration between real and virtual related data User controlled access to data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Pervasive Communication • • • Ubiquitous connectivity Broad classes of communicating objects (smart object, beacons, smart materials, sensors, micromachinery, . . . ) Explosion of Augmented Reality and Internet of Things applications Connectivity is a commodity Terminals are flexible and personal service platforms Data center larger and larger
 Difference on Services Web. Cos work on DATA Telecoms work on BITS R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Difference on Services Web. Cos work on DATA Telecoms work on BITS R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
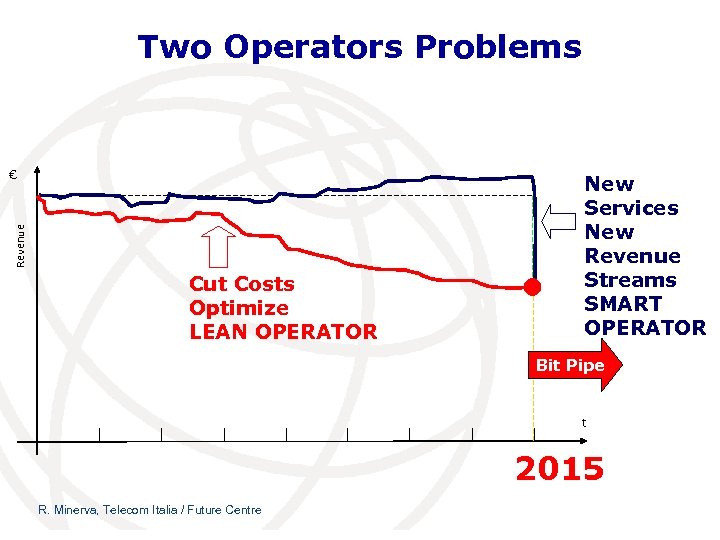 Two Operators Problems Revenue € Cut Costs Optimize LEAN OPERATOR New Services New Revenue Streams SMART OPERATOR Bit Pipe t 2015 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Two Operators Problems Revenue € Cut Costs Optimize LEAN OPERATOR New Services New Revenue Streams SMART OPERATOR Bit Pipe t 2015 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
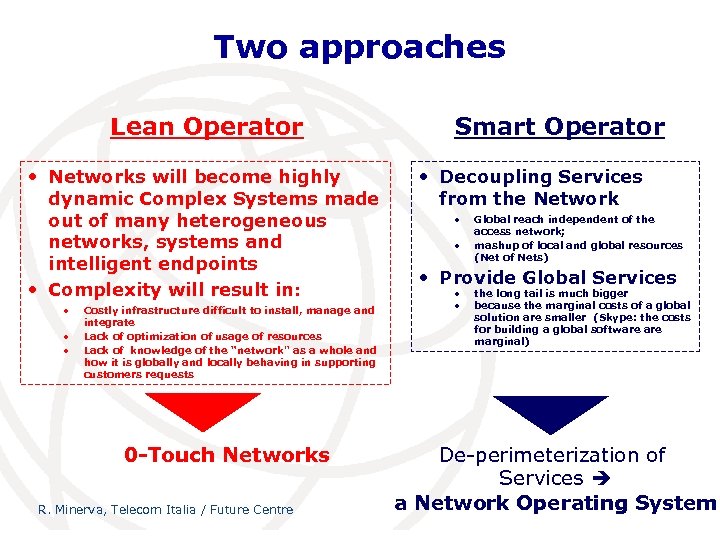 Two approaches Lean Operator • Networks will become highly dynamic Complex Systems made out of many heterogeneous networks, systems and intelligent endpoints • Complexity will result in: • • • Costly infrastructure difficult to install, manage and integrate Lack of optimization of usage of resources Lack of knowledge of the “network" as a whole and how it is globally and locally behaving in supporting customers requests 0 -Touch Networks R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Smart Operator • Decoupling Services from the Network • • Global reach independent of the access network; mashup of local and global resources (Net of Nets) • Provide Global Services • • the long tail is much bigger because the marginal costs of a global solution are smaller (Skype: the costs for building a global software marginal) De-perimeterization of Services a Network Operating System
Two approaches Lean Operator • Networks will become highly dynamic Complex Systems made out of many heterogeneous networks, systems and intelligent endpoints • Complexity will result in: • • • Costly infrastructure difficult to install, manage and integrate Lack of optimization of usage of resources Lack of knowledge of the “network" as a whole and how it is globally and locally behaving in supporting customers requests 0 -Touch Networks R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Smart Operator • Decoupling Services from the Network • • Global reach independent of the access network; mashup of local and global resources (Net of Nets) • Provide Global Services • • the long tail is much bigger because the marginal costs of a global solution are smaller (Skype: the costs for building a global software marginal) De-perimeterization of Services a Network Operating System
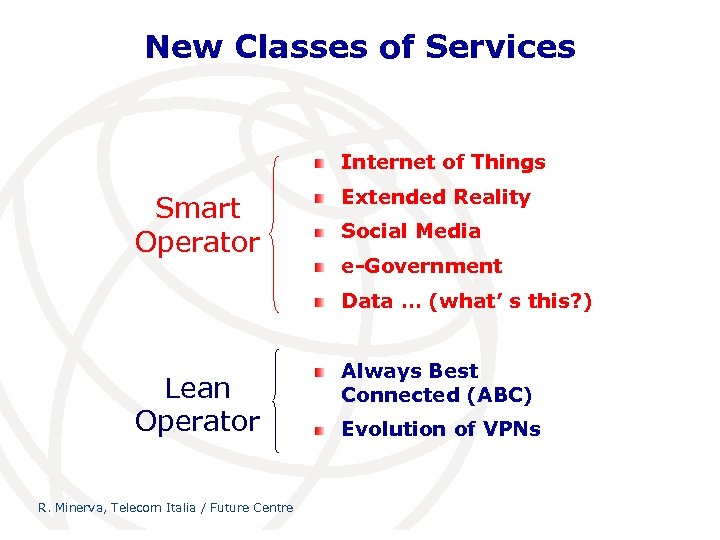 New Classes of Services Internet of Things Smart Operator Extended Reality Social Media e-Government Data … (what’ s this? ) Lean Operator R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Always Best Connected (ABC) Evolution of VPNs
New Classes of Services Internet of Things Smart Operator Extended Reality Social Media e-Government Data … (what’ s this? ) Lean Operator R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Always Best Connected (ABC) Evolution of VPNs
 Building a Data Path for Operators • • Exploit data related opportunities Move from Bits to Management of Information R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Building a Data Path for Operators • • Exploit data related opportunities Move from Bits to Management of Information R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
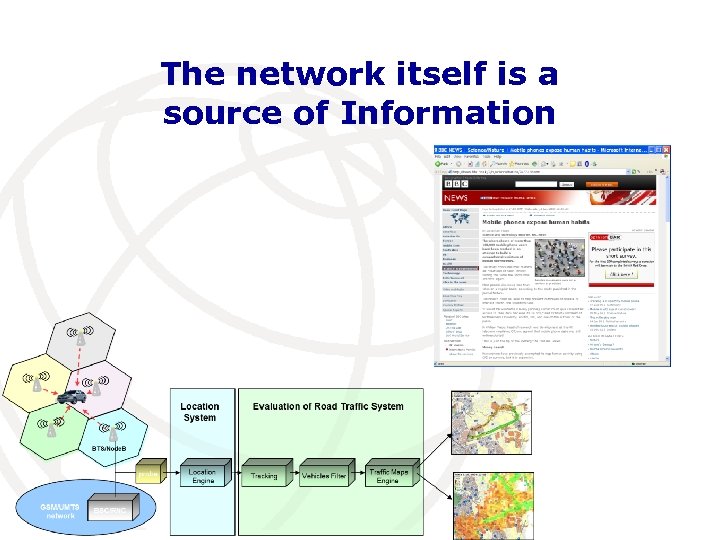 The network itself is a source of Information
The network itself is a source of Information
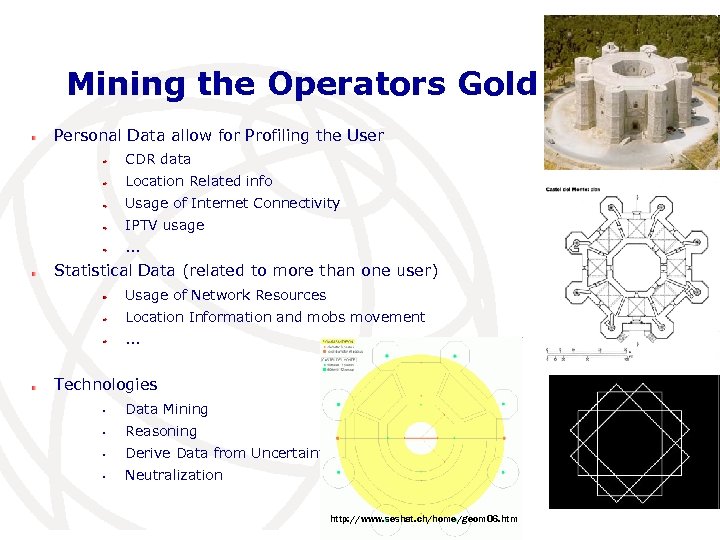 Mining the Operators Gold Mines Personal Data allow for Profiling the User CDR data Location Related info Usage of Internet Connectivity IPTV usage. . . Statistical Data (related to more than one user) Usage of Network Resources Location Information and mobs movement. . . Technologies • Data Mining • Reasoning • Derive Data from Uncertainty • Neutralization 11 http: //www. seshat. ch/home/geom 06. htm
Mining the Operators Gold Mines Personal Data allow for Profiling the User CDR data Location Related info Usage of Internet Connectivity IPTV usage. . . Statistical Data (related to more than one user) Usage of Network Resources Location Information and mobs movement. . . Technologies • Data Mining • Reasoning • Derive Data from Uncertainty • Neutralization 11 http: //www. seshat. ch/home/geom 06. htm
 Internet of Things R. MINERVA, TELECOM ITALIA / FUTURE CENTRE
Internet of Things R. MINERVA, TELECOM ITALIA / FUTURE CENTRE
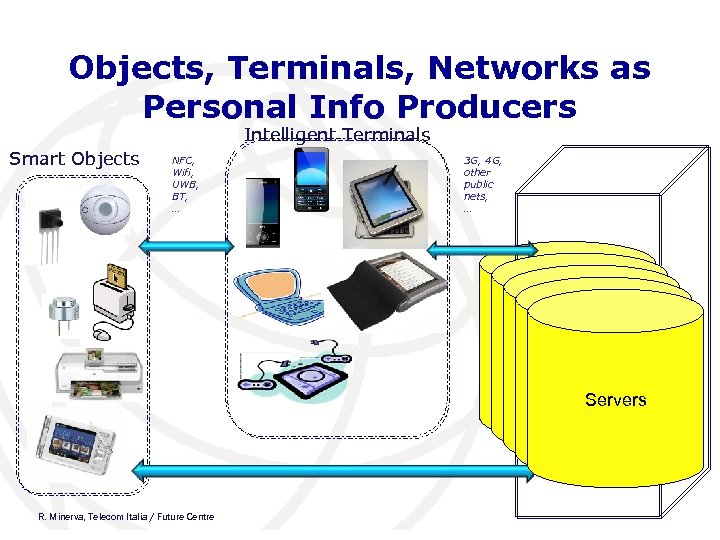 Objects, Terminals, Networks as Personal Info Producers Intelligent Terminals Smart Objects NFC, Wifi, UWB, BT, … 3 G, 4 G, other public nets, … Servers Servers R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Objects, Terminals, Networks as Personal Info Producers Intelligent Terminals Smart Objects NFC, Wifi, UWB, BT, … 3 G, 4 G, other public nets, … Servers Servers R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
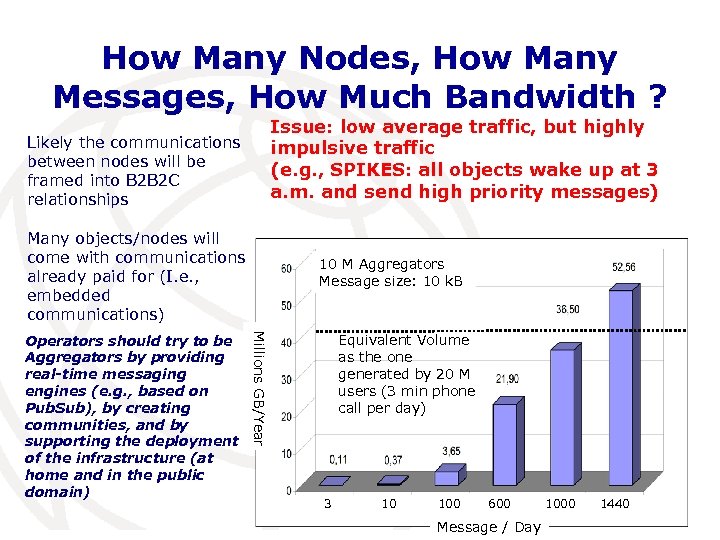 How Many Nodes, How Many Messages, How Much Bandwidth ? Issue: low average traffic, but highly impulsive traffic (e. g. , SPIKES: all objects wake up at 3 a. m. and send high priority messages) Likely the communications between nodes will be framed into B 2 B 2 C relationships Many objects/nodes will come with communications already paid for (I. e. , embedded communications) Millions GB/Year Operators should try to be Aggregators by providing real-time messaging engines (e. g. , based on Pub. Sub), by creating communities, and by supporting the deployment of the infrastructure (at home and in the public domain) 10 M Aggregators Message size: 10 k. B Equivalent Volume as the one generated by 20 M users (3 min phone call per day) 3 10 100 600 Message / Day 1000 1440
How Many Nodes, How Many Messages, How Much Bandwidth ? Issue: low average traffic, but highly impulsive traffic (e. g. , SPIKES: all objects wake up at 3 a. m. and send high priority messages) Likely the communications between nodes will be framed into B 2 B 2 C relationships Many objects/nodes will come with communications already paid for (I. e. , embedded communications) Millions GB/Year Operators should try to be Aggregators by providing real-time messaging engines (e. g. , based on Pub. Sub), by creating communities, and by supporting the deployment of the infrastructure (at home and in the public domain) 10 M Aggregators Message size: 10 k. B Equivalent Volume as the one generated by 20 M users (3 min phone call per day) 3 10 100 600 Message / Day 1000 1440
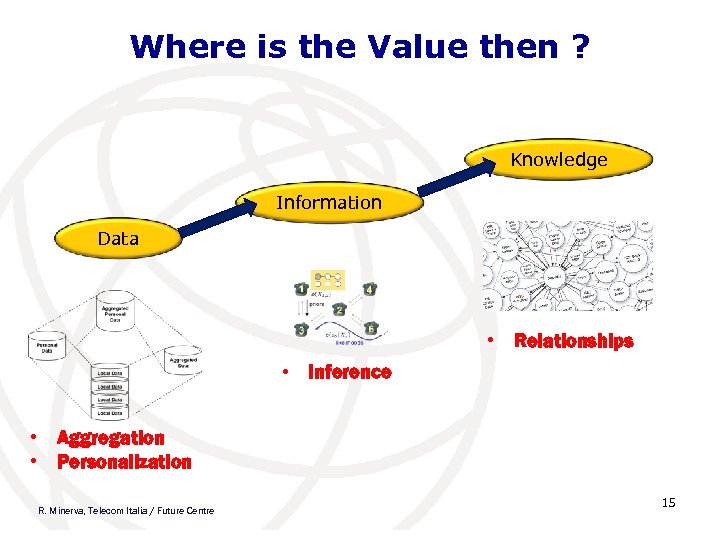 Where is the Value then ? Knowledge Information Data • Relationships • Inference • Aggregation • Personalization R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 15
Where is the Value then ? Knowledge Information Data • Relationships • Inference • Aggregation • Personalization R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 15
 Some Issues with networked data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Some Issues with networked data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
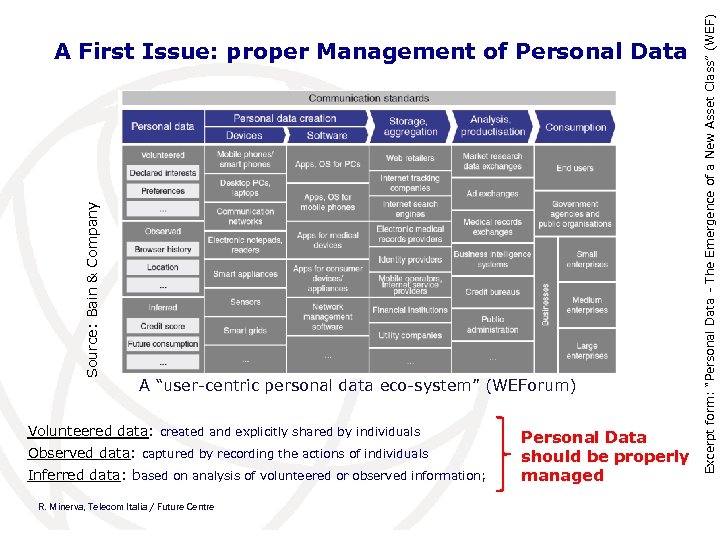 A “user-centric personal data eco-system” (WEForum) Volunteered data: created and explicitly shared by individuals Observed data: captured by recording the actions of individuals Inferred data: based on analysis of volunteered or observed information; R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Personal Data should be properly managed Excerpt form: “Personal Data - The Emergence of a New Asset Class” (WEF) Source: Bain & Company A First Issue: proper Management of Personal Data
A “user-centric personal data eco-system” (WEForum) Volunteered data: created and explicitly shared by individuals Observed data: captured by recording the actions of individuals Inferred data: based on analysis of volunteered or observed information; R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Personal Data should be properly managed Excerpt form: “Personal Data - The Emergence of a New Asset Class” (WEF) Source: Bain & Company A First Issue: proper Management of Personal Data
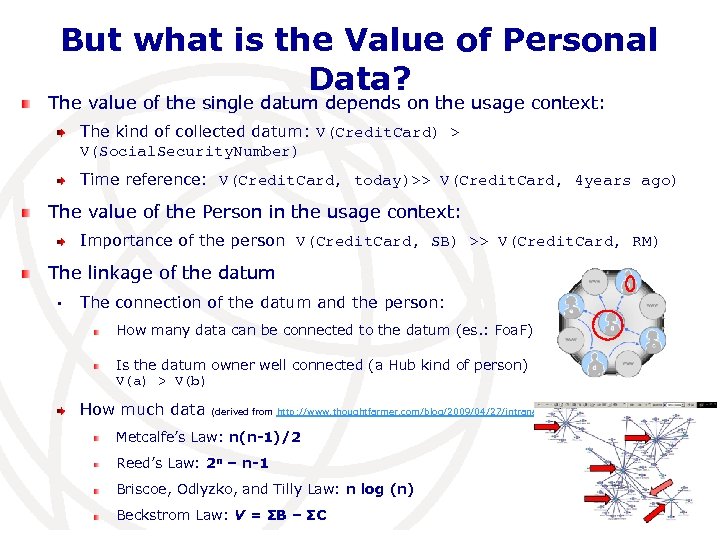 But what is the Value of Personal Data? The value of the single datum depends on the usage context: The kind of collected datum: V(Credit. Card) > V(Social. Security. Number) Time reference: V(Credit. Card, today)>> V(Credit. Card, 4 years ago) The value of the Person in the usage context: Importance of the person V(Credit. Card, SB) >> V(Credit. Card, RM) The linkage of the datum • The connection of the datum and the person: How many data can be connected to the datum (es. : Foa. F) Is the datum owner well connected (a Hub kind of person) V(a) > V(b) How much data (derived from http: //www. thoughtfarmer. com/blog/2009/04/27/intranet-roi/ ) Metcalfe’s Law: n(n-1)/2 Reed’s Law: 2 n – n-1 Briscoe, Odlyzko, and Tilly Law: n log (n) Beckstrom Law: V = ΣB – ΣC
But what is the Value of Personal Data? The value of the single datum depends on the usage context: The kind of collected datum: V(Credit. Card) > V(Social. Security. Number) Time reference: V(Credit. Card, today)>> V(Credit. Card, 4 years ago) The value of the Person in the usage context: Importance of the person V(Credit. Card, SB) >> V(Credit. Card, RM) The linkage of the datum • The connection of the datum and the person: How many data can be connected to the datum (es. : Foa. F) Is the datum owner well connected (a Hub kind of person) V(a) > V(b) How much data (derived from http: //www. thoughtfarmer. com/blog/2009/04/27/intranet-roi/ ) Metcalfe’s Law: n(n-1)/2 Reed’s Law: 2 n – n-1 Briscoe, Odlyzko, and Tilly Law: n log (n) Beckstrom Law: V = ΣB – ΣC
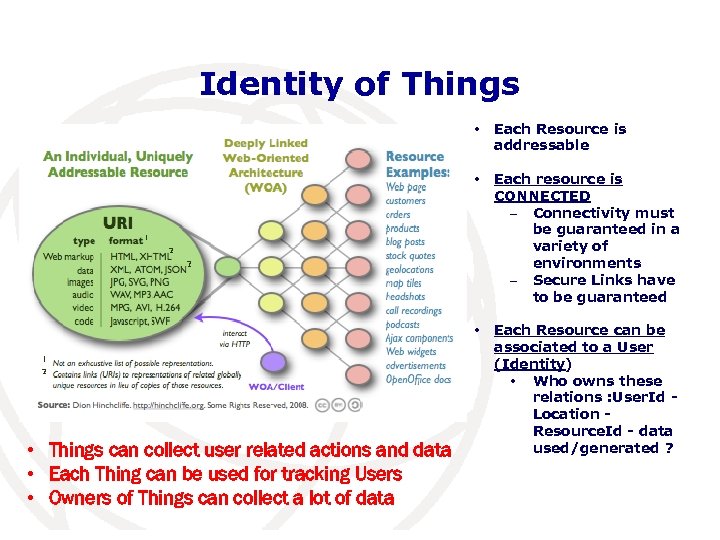 Identity of Things • • Each resource is CONNECTED – Connectivity must be guaranteed in a variety of environments – Secure Links have to be guaranteed • • Things can collect user related actions and data • Each Thing can be used for tracking Users • Owners of Things can collect a lot of data Each Resource is addressable Each Resource can be associated to a User (Identity) • Who owns these relations : User. Id - Location - Resource. Id - data used/generated ?
Identity of Things • • Each resource is CONNECTED – Connectivity must be guaranteed in a variety of environments – Secure Links have to be guaranteed • • Things can collect user related actions and data • Each Thing can be used for tracking Users • Owners of Things can collect a lot of data Each Resource is addressable Each Resource can be associated to a User (Identity) • Who owns these relations : User. Id - Location - Resource. Id - data used/generated ?
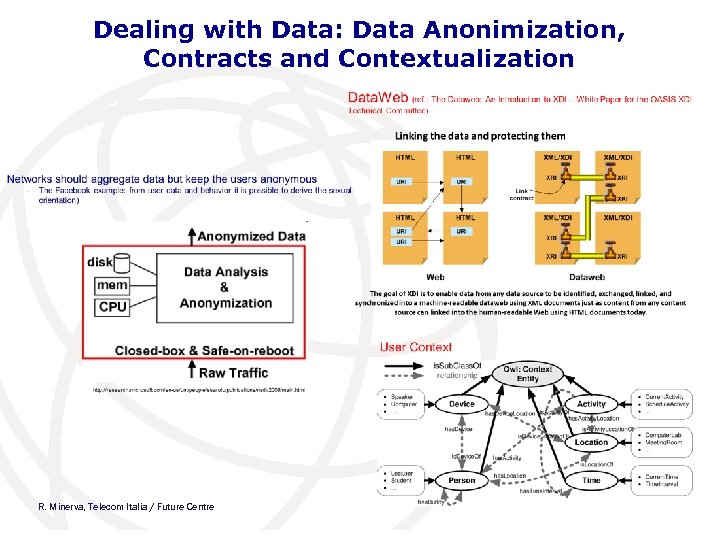 Dealing with Data: Data Anonimization, Contracts and Contextualization R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Dealing with Data: Data Anonimization, Contracts and Contextualization R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
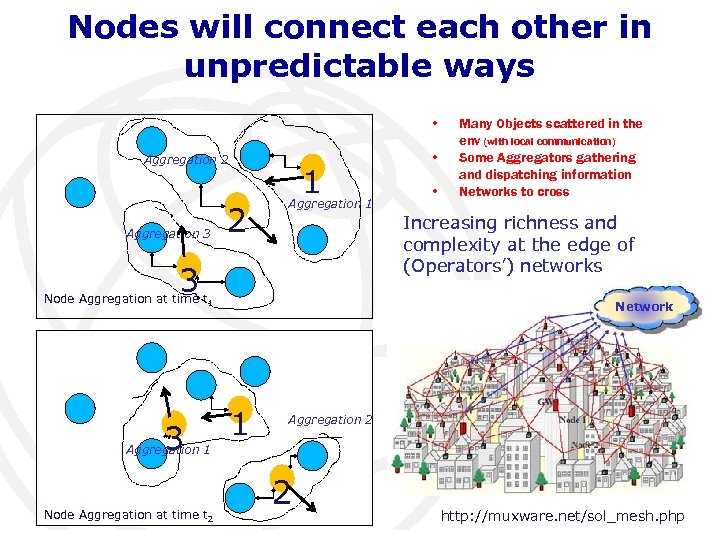 Nodes will connect each other in unpredictable ways • Aggregation 2 Aggregation 3 2 1 Aggregation 1 • Increasing richness and complexity at the edge of (Operators’) networks 3 Node Aggregation at time t 1 3 • Many Objects scattered in the env (with local communication) Some Aggregators gathering and dispatching information Networks to cross Network 1 Aggregation 2 Aggregation 1 Node Aggregation at time t 2 2 http: //muxware. net/sol_mesh. php
Nodes will connect each other in unpredictable ways • Aggregation 2 Aggregation 3 2 1 Aggregation 1 • Increasing richness and complexity at the edge of (Operators’) networks 3 Node Aggregation at time t 1 3 • Many Objects scattered in the env (with local communication) Some Aggregators gathering and dispatching information Networks to cross Network 1 Aggregation 2 Aggregation 1 Node Aggregation at time t 2 2 http: //muxware. net/sol_mesh. php
 A Second Issue: Complexity is moving to the edge Functionalities and data generation/consumption and storage in the edge Networks will comprise smart objects and processing, storage, communication resources Data and Info will be the user target and not mere connectivity Complexity coalesces at the edges (more nodes and more capabilities) • While big networks are flattening and becoming simpler (less nodes) • Local aggregation vs. average coverage Aggregation of intelligent points will be mainly unpredictable and even if high average connectivity capabilities will be provided, such a dynamic concentration will challenge the networks capabilities • Competition for scarce resources for a limited period of time Terminals will have a key role Terminals as an integral part of the communication environment Mobility will be assumed for the majority of terminals Need to control new complex systems without human intervention • The Operator's network needs to support and help in this new context R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
A Second Issue: Complexity is moving to the edge Functionalities and data generation/consumption and storage in the edge Networks will comprise smart objects and processing, storage, communication resources Data and Info will be the user target and not mere connectivity Complexity coalesces at the edges (more nodes and more capabilities) • While big networks are flattening and becoming simpler (less nodes) • Local aggregation vs. average coverage Aggregation of intelligent points will be mainly unpredictable and even if high average connectivity capabilities will be provided, such a dynamic concentration will challenge the networks capabilities • Competition for scarce resources for a limited period of time Terminals will have a key role Terminals as an integral part of the communication environment Mobility will be assumed for the majority of terminals Need to control new complex systems without human intervention • The Operator's network needs to support and help in this new context R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
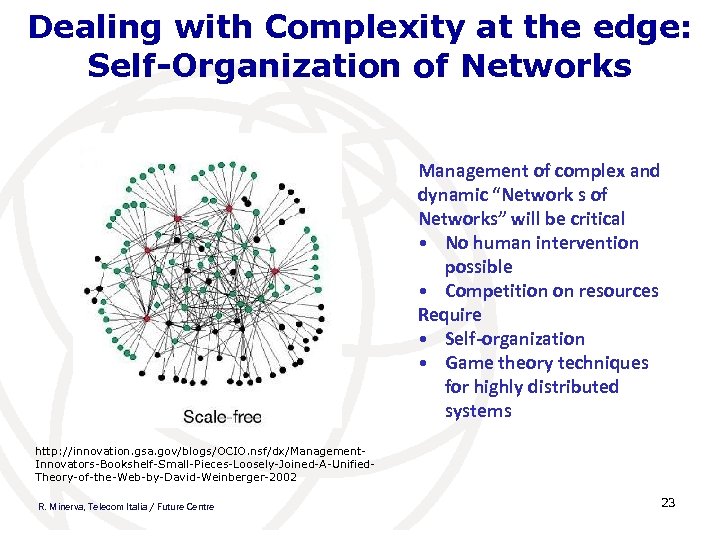 Dealing with Complexity at the edge: Self-Organization of Networks Management of complex and dynamic “Network s of Networks” will be critical • No human intervention possible • Competition on resources Require • Self-organization • Game theory techniques for highly distributed systems http: //innovation. gsa. gov/blogs/OCIO. nsf/dx/Management. Innovators-Bookshelf-Small-Pieces-Loosely-Joined-A-Unified. Theory-of-the-Web-by-David-Weinberger-2002 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 23
Dealing with Complexity at the edge: Self-Organization of Networks Management of complex and dynamic “Network s of Networks” will be critical • No human intervention possible • Competition on resources Require • Self-organization • Game theory techniques for highly distributed systems http: //innovation. gsa. gov/blogs/OCIO. nsf/dx/Management. Innovators-Bookshelf-Small-Pieces-Loosely-Joined-A-Unified. Theory-of-the-Web-by-David-Weinberger-2002 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 23
 A Tussle: Future Internet and Identity There is a need for an Identity Layer in the Future Internet For identify people For identify things To relate things, people and places For freeing people from Identity Providers People have the right to exist independently from a provider People are the owners of their identity (and names), homonymies should be managed in a far way (way just one Mario Rossi when there are plenty …) Open framework Many options, and, in certain circumstances, support for Certification by a provider (a bank), the government, others Need for a lot of standardization and discussion Need to safeguard and protect the ownership of data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
A Tussle: Future Internet and Identity There is a need for an Identity Layer in the Future Internet For identify people For identify things To relate things, people and places For freeing people from Identity Providers People have the right to exist independently from a provider People are the owners of their identity (and names), homonymies should be managed in a far way (way just one Mario Rossi when there are plenty …) Open framework Many options, and, in certain circumstances, support for Certification by a provider (a bank), the government, others Need for a lot of standardization and discussion Need to safeguard and protect the ownership of data R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
 A Bit of Technology R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
A Bit of Technology R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
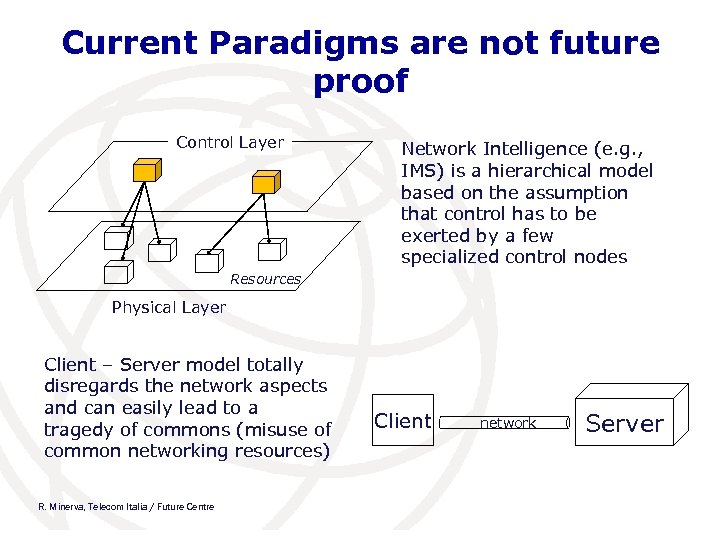 Current Paradigms are not future proof Control Layer Network Intelligence (e. g. , IMS) is a hierarchical model based on the assumption that control has to be exerted by a few specialized control nodes Resources Physical Layer Client – Server model totally disregards the network aspects and can easily lead to a tragedy of commons (misuse of common networking resources) R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Client network Server
Current Paradigms are not future proof Control Layer Network Intelligence (e. g. , IMS) is a hierarchical model based on the assumption that control has to be exerted by a few specialized control nodes Resources Physical Layer Client – Server model totally disregards the network aspects and can easily lead to a tragedy of commons (misuse of common networking resources) R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Client network Server
 Ossification of Internet and Perspective for the Future Internet Security. Currently it is tackled as an issue at the edge, while the network(s) could contribute to relieve some issues (e. g. , DDOS) Mobility, the current Internet has not been designed for an optimal management of mobility, the Future Internet has to deal with a multitude of highly mobile objects (mobility built in) Network Identity, Users are not recognized and managed in the network, they are managed only at the edges (specific servers or applications) Integration of Applications and Transport/Control Layers. Currently there are not consolidated interfaces that allow for a better cooperation between the Network and the Apps. Many applications do not use resources properly (e. g. , p 2 p applications do retrieve data from far away hosts) Edges are becoming themselves Networks. There is the need to understand manage the dynamics around Networks of Networks: i. e. , complex systems that impulsively request resources and use them while these resources have been designed to support statistically determined needs 27 Focus on data and info and not on transport of bits
Ossification of Internet and Perspective for the Future Internet Security. Currently it is tackled as an issue at the edge, while the network(s) could contribute to relieve some issues (e. g. , DDOS) Mobility, the current Internet has not been designed for an optimal management of mobility, the Future Internet has to deal with a multitude of highly mobile objects (mobility built in) Network Identity, Users are not recognized and managed in the network, they are managed only at the edges (specific servers or applications) Integration of Applications and Transport/Control Layers. Currently there are not consolidated interfaces that allow for a better cooperation between the Network and the Apps. Many applications do not use resources properly (e. g. , p 2 p applications do retrieve data from far away hosts) Edges are becoming themselves Networks. There is the need to understand manage the dynamics around Networks of Networks: i. e. , complex systems that impulsively request resources and use them while these resources have been designed to support statistically determined needs 27 Focus on data and info and not on transport of bits
 Enabling technologies autonomic capabilities and bio-inspired algorithms (e. g. , gossiping, self-organization algorithms), to deal with complexity; (self-organized) P 2 P overlays for clustering components, to guarantee scalability, reliability, and abstraction from underlying network; resources virtualization, based on abstraction for coping with heterogeneity and on the definition of dynamic slices for multiple allocations; programmable “intelligent” mechanisms, e. g. , based on auctions, game theory, etc. , for optimized resource allocation and use; cognitive cross layering, to allow the network to perceive conditions, decide and act autonomically to reach local/global/end-to-end goals in an optimal way, in cooperation with autonomic and self-organizing behavior of resources; grid Computing to better integrate different resources (computing storage and network and to integrate new ones (sensors. , actuators, micromachinery, . . . ) Information centric networking to better collect and use the needed wanted data information R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
Enabling technologies autonomic capabilities and bio-inspired algorithms (e. g. , gossiping, self-organization algorithms), to deal with complexity; (self-organized) P 2 P overlays for clustering components, to guarantee scalability, reliability, and abstraction from underlying network; resources virtualization, based on abstraction for coping with heterogeneity and on the definition of dynamic slices for multiple allocations; programmable “intelligent” mechanisms, e. g. , based on auctions, game theory, etc. , for optimized resource allocation and use; cognitive cross layering, to allow the network to perceive conditions, decide and act autonomically to reach local/global/end-to-end goals in an optimal way, in cooperation with autonomic and self-organizing behavior of resources; grid Computing to better integrate different resources (computing storage and network and to integrate new ones (sensors. , actuators, micromachinery, . . . ) Information centric networking to better collect and use the needed wanted data information R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
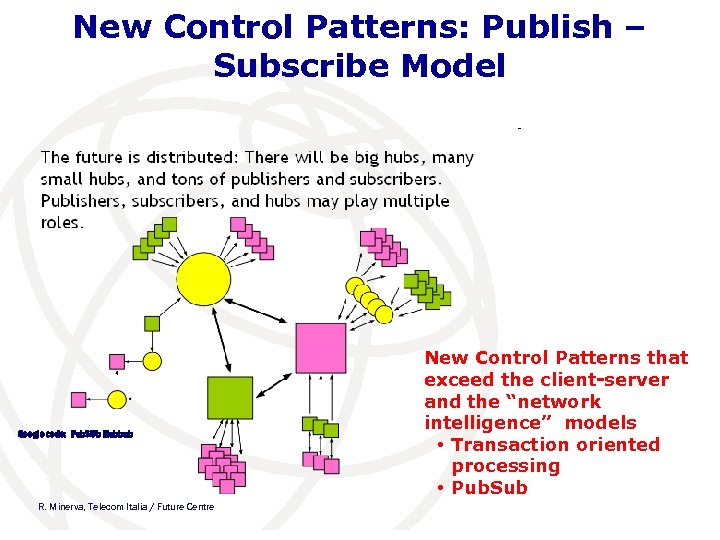 New Control Patterns: Publish – Subscribe Model Google code: Pub. SUb Hubbub R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre New Control Patterns that exceed the client-server and the “network intelligence” models • Transaction oriented processing • Pub. Sub
New Control Patterns: Publish – Subscribe Model Google code: Pub. SUb Hubbub R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre New Control Patterns that exceed the client-server and the “network intelligence” models • Transaction oriented processing • Pub. Sub
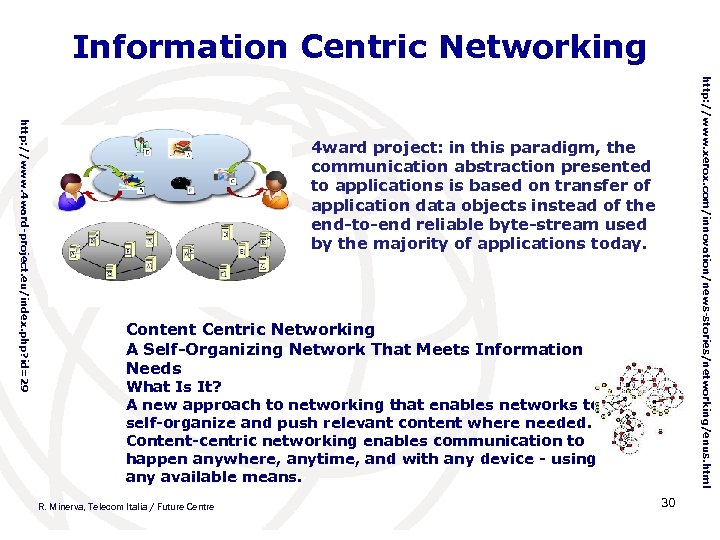 Information Centric Networking Content Centric Networking A Self-Organizing Network That Meets Information Needs What Is It? A new approach to networking that enables networks to self-organize and push relevant content where needed. Content-centric networking enables communication to happen anywhere, anytime, and with any device - using any available means. R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 30 http: //www. xerox. com/innovation/news-stories/networking/enus. html http: //www. 4 ward-project. eu/index. php? id=29 4 ward project: in this paradigm, the communication abstraction presented to applications is based on transfer of application data objects instead of the end-to-end reliable byte-stream used by the majority of applications today.
Information Centric Networking Content Centric Networking A Self-Organizing Network That Meets Information Needs What Is It? A new approach to networking that enables networks to self-organize and push relevant content where needed. Content-centric networking enables communication to happen anywhere, anytime, and with any device - using any available means. R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 30 http: //www. xerox. com/innovation/news-stories/networking/enus. html http: //www. 4 ward-project. eu/index. php? id=29 4 ward project: in this paradigm, the communication abstraction presented to applications is based on transfer of application data objects instead of the end-to-end reliable byte-stream used by the majority of applications today.
 What Role and Architecture for Operators ? R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
What Role and Architecture for Operators ? R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
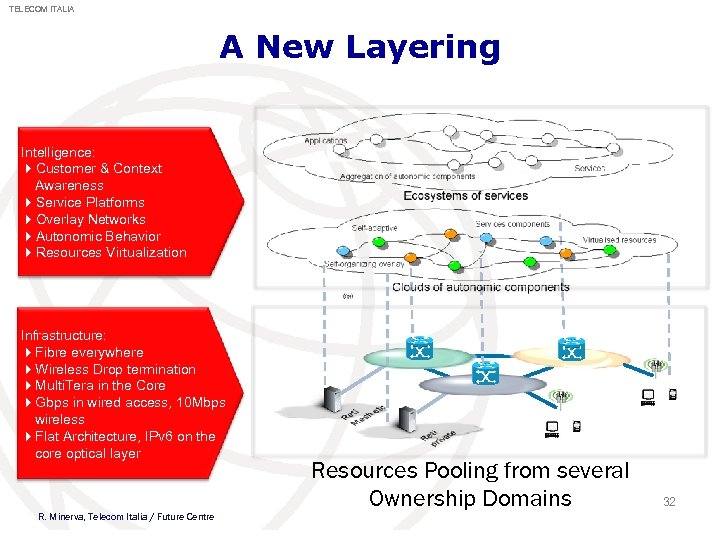 TELECOM ITALIA A New Layering Intelligence: 4 Customer & Context Awareness 4 Service Platforms 4 Overlay Networks 4 Autonomic Behavior 4 Resources Virtualization Infrastructure: 4 Fibre everywhere 4 Wireless Drop termination 4 Multi. Tera in the Core 4 Gbps in wired access, 10 Mbps wireless 4 Flat Architecture, IPv 6 on the core optical layer R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Resources Pooling from several Ownership Domains 32
TELECOM ITALIA A New Layering Intelligence: 4 Customer & Context Awareness 4 Service Platforms 4 Overlay Networks 4 Autonomic Behavior 4 Resources Virtualization Infrastructure: 4 Fibre everywhere 4 Wireless Drop termination 4 Multi. Tera in the Core 4 Gbps in wired access, 10 Mbps wireless 4 Flat Architecture, IPv 6 on the core optical layer R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Resources Pooling from several Ownership Domains 32
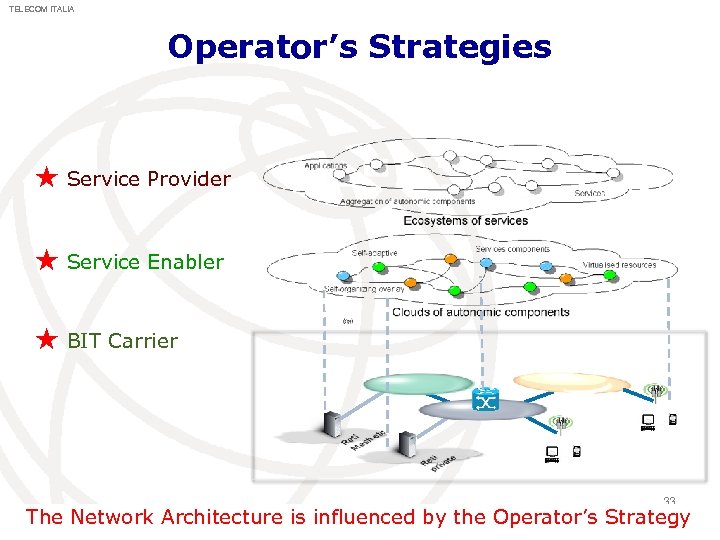 TELECOM ITALIA Operator’s Strategies ★ Service Provider ★ Service Enabler ★ BIT Carrier 33 The Network Architecture is influenced by the Operator’s Strategy
TELECOM ITALIA Operator’s Strategies ★ Service Provider ★ Service Enabler ★ BIT Carrier 33 The Network Architecture is influenced by the Operator’s Strategy
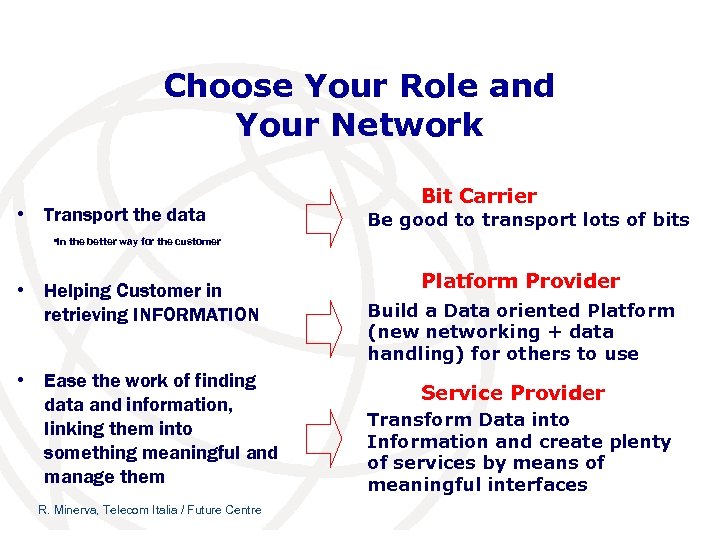 Choose Your Role and Your Network • Transport the data Bit Carrier Be good to transport lots of bits • in the better way for the customer • Helping Customer in retrieving INFORMATION • Ease the work of finding data and information, linking them into something meaningful and manage them R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Platform Provider Build a Data oriented Platform (new networking + data handling) for others to use Service Provider Transform Data into Information and create plenty of services by means of meaningful interfaces
Choose Your Role and Your Network • Transport the data Bit Carrier Be good to transport lots of bits • in the better way for the customer • Helping Customer in retrieving INFORMATION • Ease the work of finding data and information, linking them into something meaningful and manage them R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Platform Provider Build a Data oriented Platform (new networking + data handling) for others to use Service Provider Transform Data into Information and create plenty of services by means of meaningful interfaces
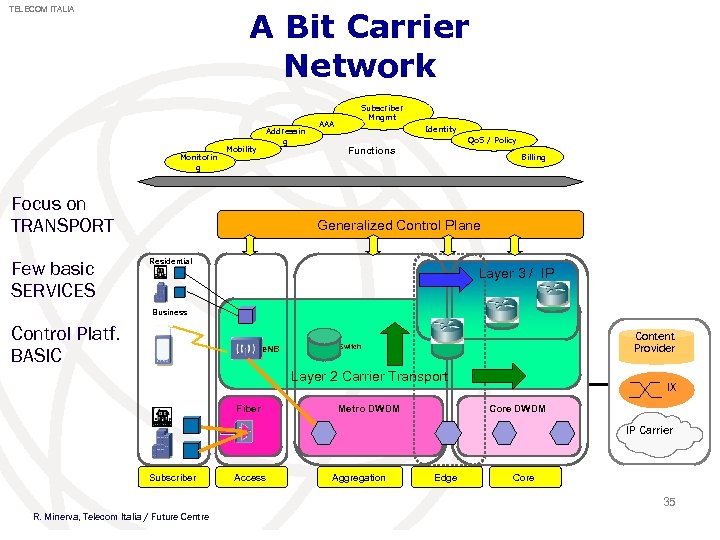 TELECOM ITALIA A Bit Carrier Network Monitorin g Mobility Addressin g Focus on TRANSPORT Few basic SERVICES AAA Subscriber Mngmt Identity Qo. S / Policy Functions Billing Generalized Control Plane Residential Layer 3 / IP Business Control Platf. BASIC e. NB Content Provider Switch Layer 2 Carrier Transport Fiber Metro DWDM IX Core DWDM IP Carrier Subscriber Access Aggregation Edge Core 35 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
TELECOM ITALIA A Bit Carrier Network Monitorin g Mobility Addressin g Focus on TRANSPORT Few basic SERVICES AAA Subscriber Mngmt Identity Qo. S / Policy Functions Billing Generalized Control Plane Residential Layer 3 / IP Business Control Platf. BASIC e. NB Content Provider Switch Layer 2 Carrier Transport Fiber Metro DWDM IX Core DWDM IP Carrier Subscriber Access Aggregation Edge Core 35 R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre
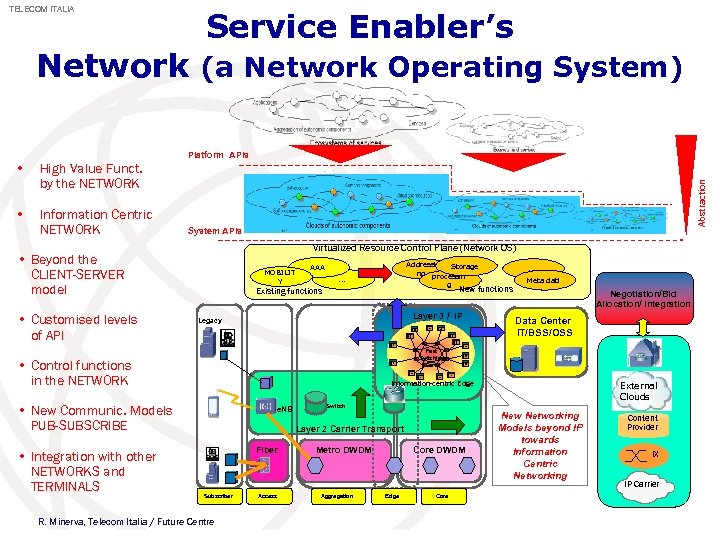 TELECOM ITALIA Service Enabler’s Network (a Network Operating System) Platform APIs High Value Funct. by the NETWORK • Information Centric NETWORK System APIs Virtualized Resource Control Plane (Network OS) • Beyond the CLIENT-SERVER model • Customised levels of API Abstraction • MOBILIT Y . . . g Existing functions . . . Meta dati New functions Layer 3 / IP Legacy Negotiation/Bid Allocation/ Integration Data Center IT/BSS/OSS Fast Switching Core • Control functions in the NETWORK Information-centric Edge • New Communic. Models PUB-SUBSCRIBE • Integration with other NETWORKS and TERMINALS Addressi Storage ng processin AAA e. NB Switch Layer 2 Carrier Transport Fiber Subscriber R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Access External Clouds Metro DWDM Aggregation Core DWDM Edge Core New Networking Models beyond IP towards Information Centric Networking Content Provider IX IP Carrier 36
TELECOM ITALIA Service Enabler’s Network (a Network Operating System) Platform APIs High Value Funct. by the NETWORK • Information Centric NETWORK System APIs Virtualized Resource Control Plane (Network OS) • Beyond the CLIENT-SERVER model • Customised levels of API Abstraction • MOBILIT Y . . . g Existing functions . . . Meta dati New functions Layer 3 / IP Legacy Negotiation/Bid Allocation/ Integration Data Center IT/BSS/OSS Fast Switching Core • Control functions in the NETWORK Information-centric Edge • New Communic. Models PUB-SUBSCRIBE • Integration with other NETWORKS and TERMINALS Addressi Storage ng processin AAA e. NB Switch Layer 2 Carrier Transport Fiber Subscriber R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Access External Clouds Metro DWDM Aggregation Core DWDM Edge Core New Networking Models beyond IP towards Information Centric Networking Content Provider IX IP Carrier 36
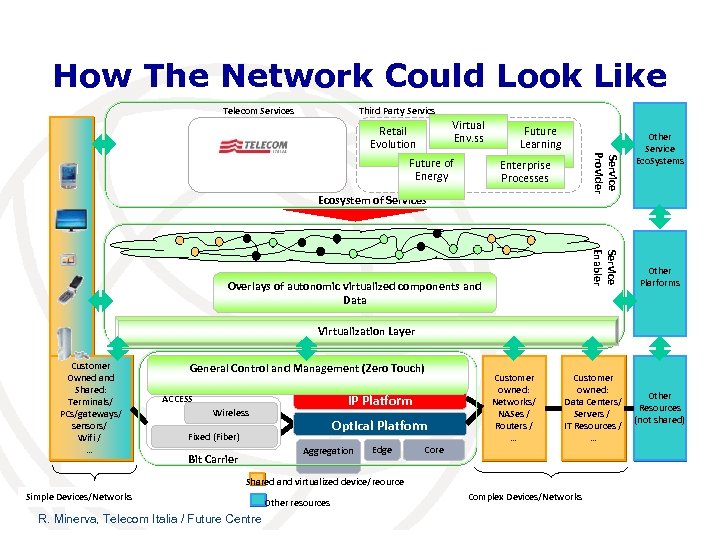 How The Network Could Look Like Telecom Services Third Party Servics Virtual Env. ss Retail Evolution Service Provider Future of Energy Future Learning Enterprise Processes Ecosystem of Services Service Enabler Overlays of autonomic virtualized components and Data Other Service Eco. Systems Other Plarforms Virtualization Layer Customer Owned and Shared: Terminals/ PCs/gateways/ sensors/ Wifi / … General Control and Management (Zero Touch) IP Platform ACCESS Wireless Optical Platform Fixed (Fiber) Aggregation Bit Carrier Edge Core Customer owned: Networks/ NASes / Routers / … Customer owned: Data Centers/ Servers / IT Resources / … Shared and virtualized device/reource Simple Devices/Networks R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Other resources Complex Devices/Networks Other Resources (not shared)
How The Network Could Look Like Telecom Services Third Party Servics Virtual Env. ss Retail Evolution Service Provider Future of Energy Future Learning Enterprise Processes Ecosystem of Services Service Enabler Overlays of autonomic virtualized components and Data Other Service Eco. Systems Other Plarforms Virtualization Layer Customer Owned and Shared: Terminals/ PCs/gateways/ sensors/ Wifi / … General Control and Management (Zero Touch) IP Platform ACCESS Wireless Optical Platform Fixed (Fiber) Aggregation Bit Carrier Edge Core Customer owned: Networks/ NASes / Routers / … Customer owned: Data Centers/ Servers / IT Resources / … Shared and virtualized device/reource Simple Devices/Networks R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre Other resources Complex Devices/Networks Other Resources (not shared)
 My 2 ¢ suggestions What T. I. is doing Working on alternative models for dealing with personal data Working on a Network OS with open APIs Working on zero-touch networks (e. g. , AFI) Working on ICN (European projects) Working on a new view of Identity R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre What should be done Future Internet will be dominated by Tussles: looking at networks and architecture with more user flavor (involving more user associations ? ) Propose an open framework for Identity and related issues (profiling, data ownership, …) Push for a shift from bits to data and ICN A Great Initiative for User Controlled Network of Networks and Data ?
My 2 ¢ suggestions What T. I. is doing Working on alternative models for dealing with personal data Working on a Network OS with open APIs Working on zero-touch networks (e. g. , AFI) Working on ICN (European projects) Working on a new view of Identity R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre What should be done Future Internet will be dominated by Tussles: looking at networks and architecture with more user flavor (involving more user associations ? ) Propose an open framework for Identity and related issues (profiling, data ownership, …) Push for a shift from bits to data and ICN A Great Initiative for User Controlled Network of Networks and Data ?
 Thank you! Roberto Minerva TORINO - Italy Phone: +39 011 228 7027 Email: roberto. minerva@telecomitalia. com R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 39
Thank you! Roberto Minerva TORINO - Italy Phone: +39 011 228 7027 Email: roberto. minerva@telecomitalia. com R. Minerva, Telecom Italia / Future Centre 39


