357cf0a29f7becef8acdf92e20b5263b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques" Using the User Requirements Notation Daniel Amyot Q. 18/17 Rapporteur SITE, University of Ottawa, Canada damyot@site. uottawa. ca SCHOOL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA, CANADA
ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques" Using the User Requirements Notation Daniel Amyot Q. 18/17 Rapporteur SITE, University of Ottawa, Canada damyot@site. uottawa. ca SCHOOL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA, CANADA
 About this presentation n n What is the User Requirements Notation (URN)? What can we model with URN? What answers can these models provide? What are the typical/potential usages? URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 2
About this presentation n n What is the User Requirements Notation (URN)? What can we model with URN? What answers can these models provide? What are the typical/potential usages? URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 2
 URN – Main objectives n n Focus on early stages of development with goals and scenarios From user requirements to system functional and non -functional requirements No messages, components, or component states required Reusability – of argumentations (goal patterns and analysis) – of scenarios (patterns and architectural alternatives) n n Early performance analysis Traceability and transformations to other languages – Particularly MSC, SDL, TTCN, and UML URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 3
URN – Main objectives n n Focus on early stages of development with goals and scenarios From user requirements to system functional and non -functional requirements No messages, components, or component states required Reusability – of argumentations (goal patterns and analysis) – of scenarios (patterns and architectural alternatives) n n Early performance analysis Traceability and transformations to other languages – Particularly MSC, SDL, TTCN, and UML URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 3
 Current Proposal for URN n n Draft documents for Z. 150, Z. 151, Z. 152 Combined use of two complementary notations: – Goal-oriented Requirement Language (GRL) for NFRs (http: //www. cs. toronto. edu/km/GRL/) – Use Case Maps (UCM) for Functional Requirements (http: //www. Use. Case. Maps. org/) n n Create ITU-T standard by end of 2003 http: //www. Use. Case. Maps. org/urn/ URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 4
Current Proposal for URN n n Draft documents for Z. 150, Z. 151, Z. 152 Combined use of two complementary notations: – Goal-oriented Requirement Language (GRL) for NFRs (http: //www. cs. toronto. edu/km/GRL/) – Use Case Maps (UCM) for Functional Requirements (http: //www. Use. Case. Maps. org/) n n Create ITU-T standard by end of 2003 http: //www. Use. Case. Maps. org/urn/ URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 4
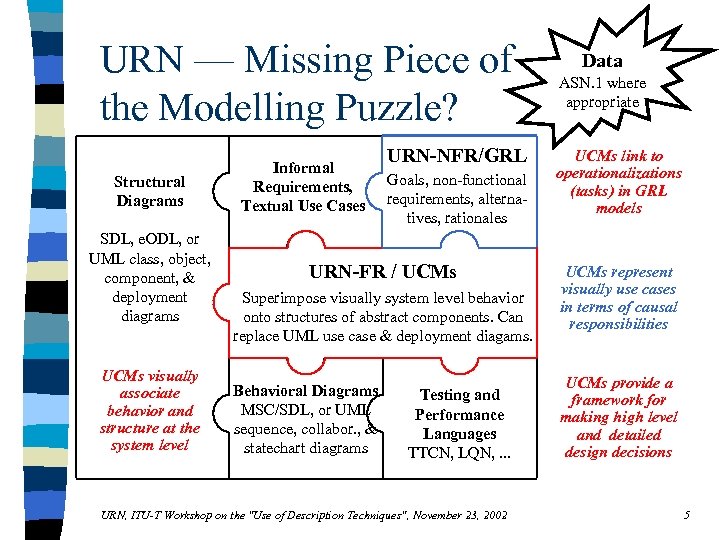 URN — Missing Piece of the Modelling Puzzle? Structural Diagrams SDL, e. ODL, or UML class, object, component, & deployment diagrams UCMs visually associate behavior and structure at the system level Informal Requirements, Textual Use Cases ? ? URN-NFR/GRL Goals, non-functional requirements, alternatives, rationales Data ASN. 1 where appropriate UCMs link to operationalizations (tasks) in GRL models URN-FR / UCMs MSC, UML Use Superimpose visually system level behavior Case Diagram & onto structures of abstract components. Can Activity Diagram replace UML use case & deployment diagams. UCMs represent visually use cases in terms of causal responsibilities Behavioral Diagrams MSC/SDL, or UML sequence, collabor. , & statechart diagrams UCMs provide a framework for making high level and detailed design decisions Testing and Performance Languages TTCN, LQN, . . . URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 5
URN — Missing Piece of the Modelling Puzzle? Structural Diagrams SDL, e. ODL, or UML class, object, component, & deployment diagrams UCMs visually associate behavior and structure at the system level Informal Requirements, Textual Use Cases ? ? URN-NFR/GRL Goals, non-functional requirements, alternatives, rationales Data ASN. 1 where appropriate UCMs link to operationalizations (tasks) in GRL models URN-FR / UCMs MSC, UML Use Superimpose visually system level behavior Case Diagram & onto structures of abstract components. Can Activity Diagram replace UML use case & deployment diagams. UCMs represent visually use cases in terms of causal responsibilities Behavioral Diagrams MSC/SDL, or UML sequence, collabor. , & statechart diagrams UCMs provide a framework for making high level and detailed design decisions Testing and Performance Languages TTCN, LQN, . . . URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 5
 GRL in a Nutshell n Goal-oriented Requirement Language – graphical notation – connects requirements of requirements to business objectives – allows reasoning about (non-functional) requirements n GRL models the “why” aspect – objectives, alternatives, as well as decision rationale – no operational details n Supports goal analysis and evaluations URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 6
GRL in a Nutshell n Goal-oriented Requirement Language – graphical notation – connects requirements of requirements to business objectives – allows reasoning about (non-functional) requirements n GRL models the “why” aspect – objectives, alternatives, as well as decision rationale – no operational details n Supports goal analysis and evaluations URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 6
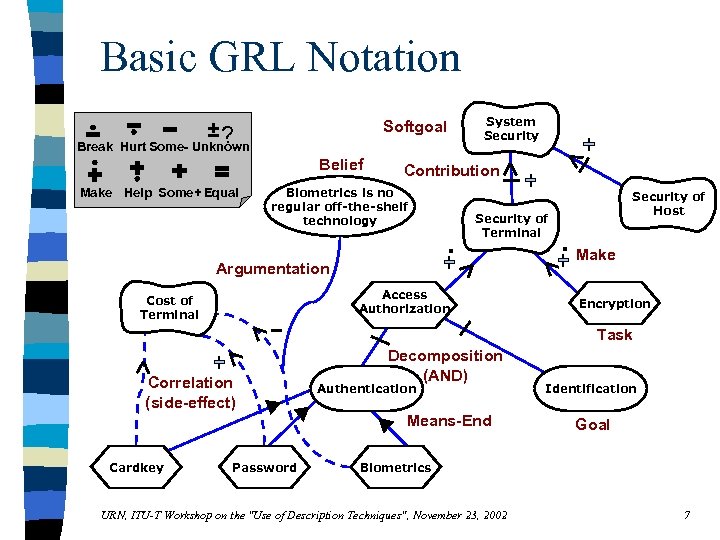 Basic GRL Notation Softgoal ? Break Hurt Some- Unknown Belief Make Help Some+ Equal System Security Contribution Biometrics is no regular off-the-shelf technology Argumentation . Security of Terminal Access Authorization Cost of Terminal Security of Host . Make Encryption Task Correlation (side-effect) Decomposition (AND) Authentication Means-End Cardkey Password Identification Goal Biometrics URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 7
Basic GRL Notation Softgoal ? Break Hurt Some- Unknown Belief Make Help Some+ Equal System Security Contribution Biometrics is no regular off-the-shelf technology Argumentation . Security of Terminal Access Authorization Cost of Terminal Security of Host . Make Encryption Task Correlation (side-effect) Decomposition (AND) Authentication Means-End Cardkey Password Identification Goal Biometrics URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 7
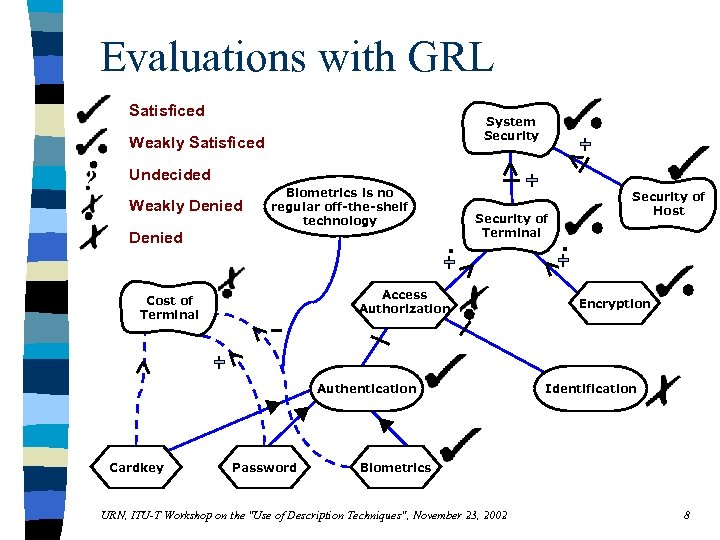 Evaluations with GRL Satisficed System Security Weakly Satisficed Undecided Weakly Denied Biometrics is no regular off-the-shelf technology Denied . Security of Terminal Access Authorization Cost of Terminal Authentication Cardkey Password Security of Host . Encryption Identification Biometrics URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 8
Evaluations with GRL Satisficed System Security Weakly Satisficed Undecided Weakly Denied Biometrics is no regular off-the-shelf technology Denied . Security of Terminal Access Authorization Cost of Terminal Authentication Cardkey Password Security of Host . Encryption Identification Biometrics URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 8
 UCMs in a Nutshell n Use Case Maps – graphical scenario notation – causal relationships between responsibilities – scenario elements may (optionally) be allocated to components n UCMs model the “what” aspects – functional requirements as scenarios – integration and reusability of scenarios – guidance for architecture and detailed behaviour n Performance analysis, conflict detection URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 9
UCMs in a Nutshell n Use Case Maps – graphical scenario notation – causal relationships between responsibilities – scenario elements may (optionally) be allocated to components n UCMs model the “what” aspects – functional requirements as scenarios – integration and reusability of scenarios – guidance for architecture and detailed behaviour n Performance analysis, conflict detection URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 9
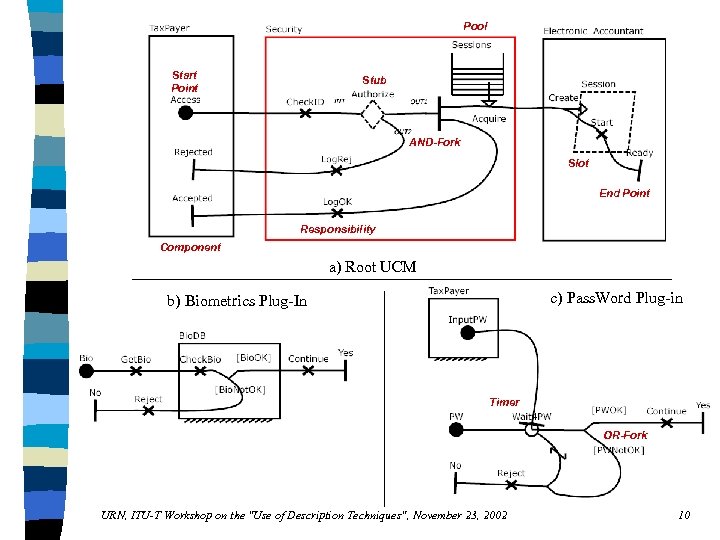 Pool Start Point Stub AND-Fork Slot End Point Responsibility Component a) Root UCM c) Pass. Word Plug-in b) Biometrics Plug-In Timer OR-Fork URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 10
Pool Start Point Stub AND-Fork Slot End Point Responsibility Component a) Root UCM c) Pass. Word Plug-in b) Biometrics Plug-In Timer OR-Fork URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 10
 GRL - UCM Relationship n Goal-based approach – Focuses on answering “why” questions n Scenario-based approach – Focuses on answering “what” questions n Goals are operationalized into tasks and tasks are elaborated in (mapped to) UCM scenarios – Focuses on answering “how” questions n GRL goals can guide the selection of a particular architecture for the UCM scenarios URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 11
GRL - UCM Relationship n Goal-based approach – Focuses on answering “why” questions n Scenario-based approach – Focuses on answering “what” questions n Goals are operationalized into tasks and tasks are elaborated in (mapped to) UCM scenarios – Focuses on answering “how” questions n GRL goals can guide the selection of a particular architecture for the UCM scenarios URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 11
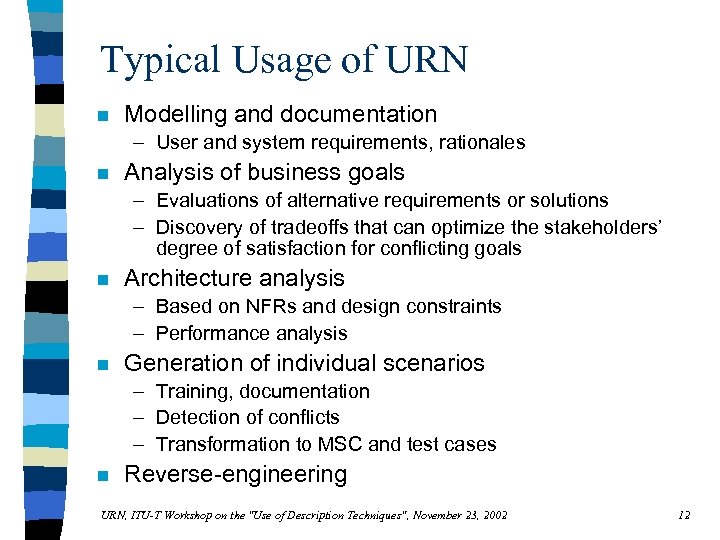 Typical Usage of URN n Modelling and documentation – User and system requirements, rationales n Analysis of business goals – Evaluations of alternative requirements or solutions – Discovery of tradeoffs that can optimize the stakeholders’ degree of satisfaction for conflicting goals n Architecture analysis – Based on NFRs and design constraints – Performance analysis n Generation of individual scenarios – Training, documentation – Detection of conflicts – Transformation to MSC and test cases n Reverse-engineering URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 12
Typical Usage of URN n Modelling and documentation – User and system requirements, rationales n Analysis of business goals – Evaluations of alternative requirements or solutions – Discovery of tradeoffs that can optimize the stakeholders’ degree of satisfaction for conflicting goals n Architecture analysis – Based on NFRs and design constraints – Performance analysis n Generation of individual scenarios – Training, documentation – Detection of conflicts – Transformation to MSC and test cases n Reverse-engineering URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 12
 Experiences with GRL n Used on industrial projects – New family of Web-based telephone sets – Documentation of discussions involving multiple stakeholders – Visualization and analysis of conflicting goals – Evaluation of architectural solutions, and rationales for the retained solution – Proved to be very helpful for keeping discussions on track and for avoiding repeating the same discussions over and over again. – Accelerated the reaching of an agreement and – Improved (short-term and long-term) understanding. n Used in academic projects – Security applications – Web-based systems (in combination with UCMs) – Architectural/performance tradeoffs at a qualitative level URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 13
Experiences with GRL n Used on industrial projects – New family of Web-based telephone sets – Documentation of discussions involving multiple stakeholders – Visualization and analysis of conflicting goals – Evaluation of architectural solutions, and rationales for the retained solution – Proved to be very helpful for keeping discussions on track and for avoiding repeating the same discussions over and over again. – Accelerated the reaching of an agreement and – Improved (short-term and long-term) understanding. n Used in academic projects – Security applications – Web-based systems (in combination with UCMs) – Architectural/performance tradeoffs at a qualitative level URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 13
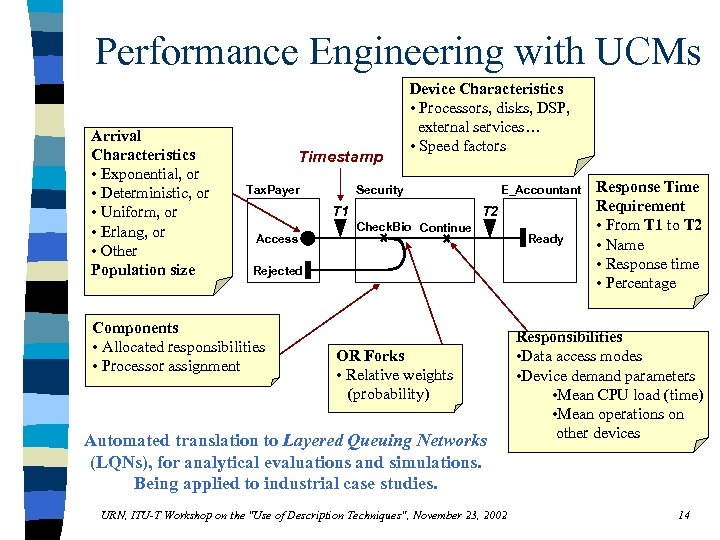 Performance Engineering with UCMs Arrival Characteristics • Exponential, or • Deterministic, or • Uniform, or • Erlang, or • Other Population size Timestamp Tax. Payer Device Characteristics • Processors, disks, DSP, external services… • Speed factors Security T 1 Access E_Accountant T 2 Check. Bio Continue Rejected Components • Allocated responsibilities • Processor assignment OR Forks • Relative weights (probability) Automated translation to Layered Queuing Networks (LQNs), for analytical evaluations and simulations. Being applied to industrial case studies. URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 Ready Response Time Requirement • From T 1 to T 2 • Name • Response time • Percentage Responsibilities • Data access modes • Device demand parameters • Mean CPU load (time) • Mean operations on other devices 14
Performance Engineering with UCMs Arrival Characteristics • Exponential, or • Deterministic, or • Uniform, or • Erlang, or • Other Population size Timestamp Tax. Payer Device Characteristics • Processors, disks, DSP, external services… • Speed factors Security T 1 Access E_Accountant T 2 Check. Bio Continue Rejected Components • Allocated responsibilities • Processor assignment OR Forks • Relative weights (probability) Automated translation to Layered Queuing Networks (LQNs), for analytical evaluations and simulations. Being applied to industrial case studies. URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 Ready Response Time Requirement • From T 1 to T 2 • Name • Response time • Percentage Responsibilities • Data access modes • Device demand parameters • Mean CPU load (time) • Mean operations on other devices 14
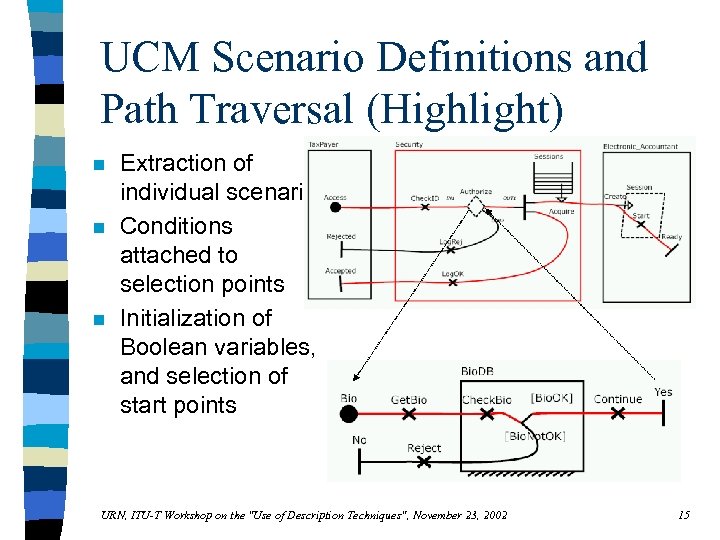 UCM Scenario Definitions and Path Traversal (Highlight) n n n Extraction of individual scenarios Conditions attached to selection points Initialization of Boolean variables, and selection of start points URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 15
UCM Scenario Definitions and Path Traversal (Highlight) n n n Extraction of individual scenarios Conditions attached to selection points Initialization of Boolean variables, and selection of start points URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 15
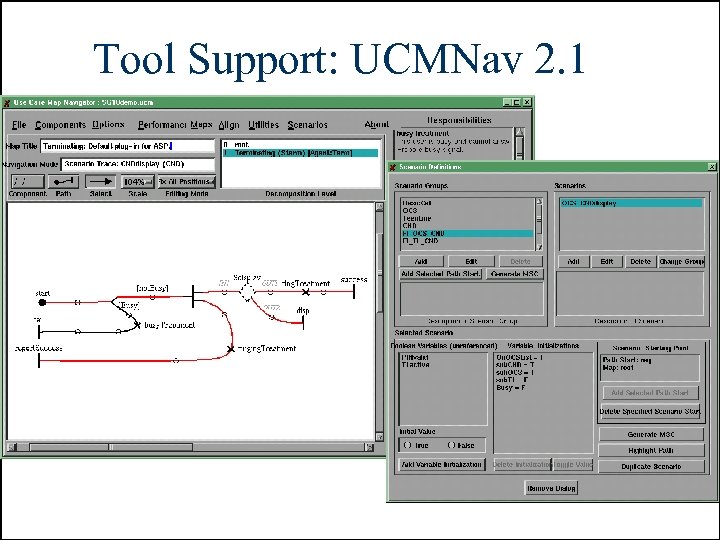 Tool Support: UCMNav 2. 1 URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 16
Tool Support: UCMNav 2. 1 URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 16
 From UCM Requirements to More Detailed Design Models n Requires: – Path Data Model (global Booleans variables) – Scenario Definitions – Path Traversal Mechanism – Mapping Rules (MSC, UML, TTCN, LQN, LOTOS. . . ) URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 17
From UCM Requirements to More Detailed Design Models n Requires: – Path Data Model (global Booleans variables) – Scenario Definitions – Path Traversal Mechanism – Mapping Rules (MSC, UML, TTCN, LQN, LOTOS. . . ) URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 17
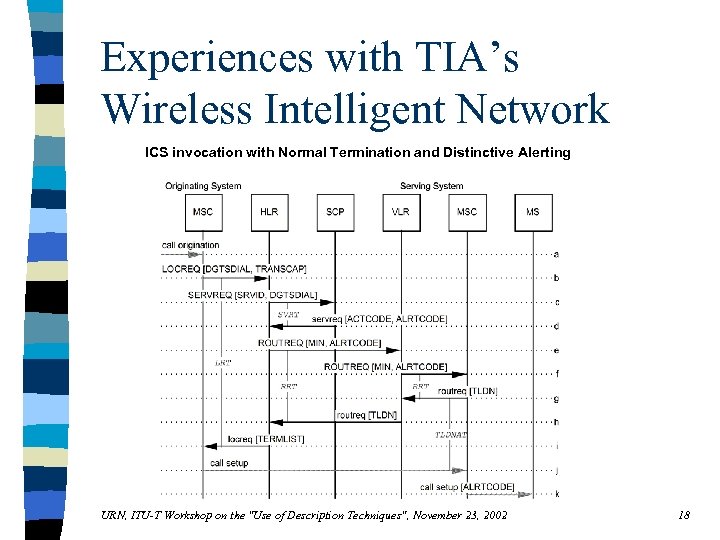 Experiences with TIA’s Wireless Intelligent Network ICS invocation with Normal Termination and Distinctive Alerting URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 18
Experiences with TIA’s Wireless Intelligent Network ICS invocation with Normal Termination and Distinctive Alerting URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 18
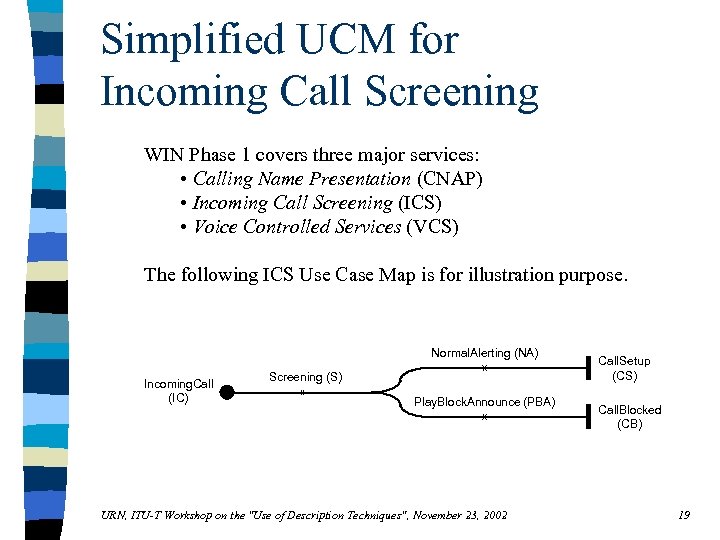 Simplified UCM for Incoming Call Screening WIN Phase 1 covers three major services: • Calling Name Presentation (CNAP) • Incoming Call Screening (ICS) • Voice Controlled Services (VCS) The following ICS Use Case Map is for illustration purpose. Normal. Alerting (NA) Incoming. Call (IC) Screening (S) Play. Block. Announce (PBA) URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 Call. Setup (CS) Call. Blocked (CB) 19
Simplified UCM for Incoming Call Screening WIN Phase 1 covers three major services: • Calling Name Presentation (CNAP) • Incoming Call Screening (ICS) • Voice Controlled Services (VCS) The following ICS Use Case Map is for illustration purpose. Normal. Alerting (NA) Incoming. Call (IC) Screening (S) Play. Block. Announce (PBA) URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 Call. Setup (CS) Call. Blocked (CB) 19
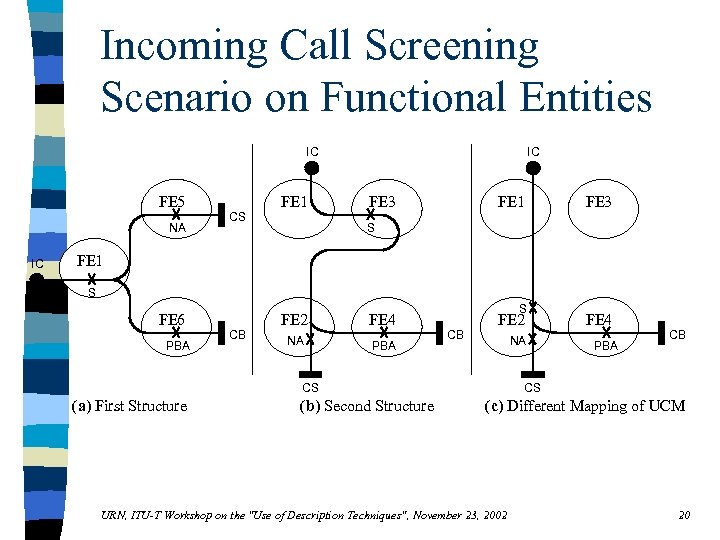 Incoming Call Screening Scenario on Functional Entities IC FE 5 NA IC CS FE 1 IC FE 3 FE 1 FE 3 S FE 1 S FE 6 PBA CB FE 2 FE 4 NA PBA S CB FE 2 NA CS (a) First Structure (b) Second Structure FE 4 PBA CB CS (c) Different Mapping of UCM URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 20
Incoming Call Screening Scenario on Functional Entities IC FE 5 NA IC CS FE 1 IC FE 3 FE 1 FE 3 S FE 1 S FE 6 PBA CB FE 2 FE 4 NA PBA S CB FE 2 NA CS (a) First Structure (b) Second Structure FE 4 PBA CB CS (c) Different Mapping of UCM URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 20
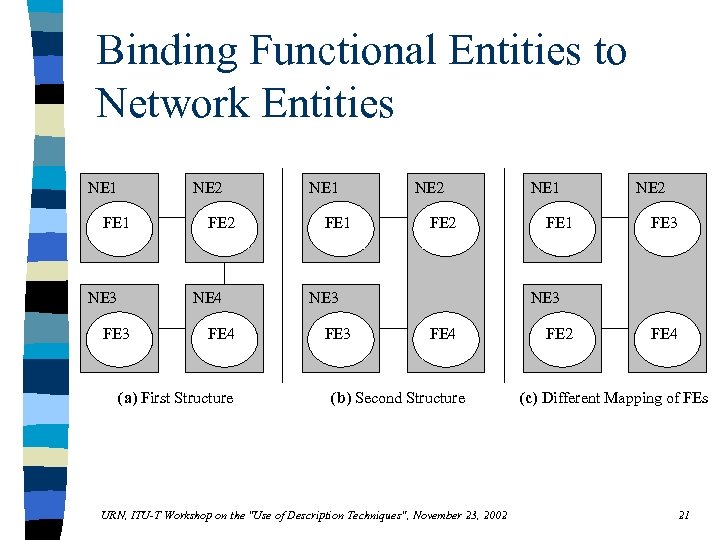 Binding Functional Entities to Network Entities NE 1 NE 2 FE 1 NE 3 FE 2 NE 4 FE 3 FE 4 (a) First Structure NE 1 FE 1 NE 2 FE 2 NE 3 FE 3 NE 1 FE 1 NE 2 FE 3 NE 3 FE 4 (b) Second Structure URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 FE 4 (c) Different Mapping of FEs 21
Binding Functional Entities to Network Entities NE 1 NE 2 FE 1 NE 3 FE 2 NE 4 FE 3 FE 4 (a) First Structure NE 1 FE 1 NE 2 FE 2 NE 3 FE 3 NE 1 FE 1 NE 2 FE 3 NE 3 FE 4 (b) Second Structure URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 FE 4 (c) Different Mapping of FEs 21
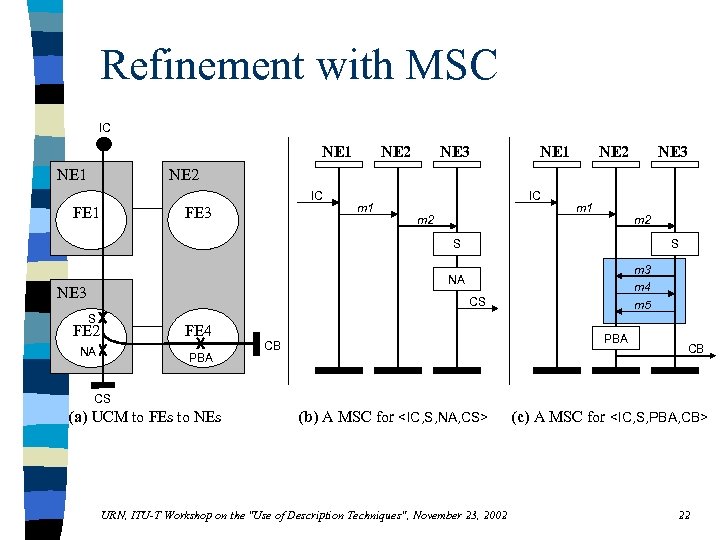 Refinement with MSC IC NE 1 NE 2 NE 3 NE 2 IC FE 1 FE 3 m 1 IC m 2 m 1 m 2 S S m 3 m 4 m 5 NA NE 3 CS S FE 2 FE 4 NA PBA CB CB CS (a) UCM to FEs to NEs (b) A MSC for
Refinement with MSC IC NE 1 NE 2 NE 3 NE 2 IC FE 1 FE 3 m 1 IC m 2 m 1 m 2 S S m 3 m 4 m 5 NA NE 3 CS S FE 2 FE 4 NA PBA CB CB CS (a) UCM to FEs to NEs (b) A MSC for
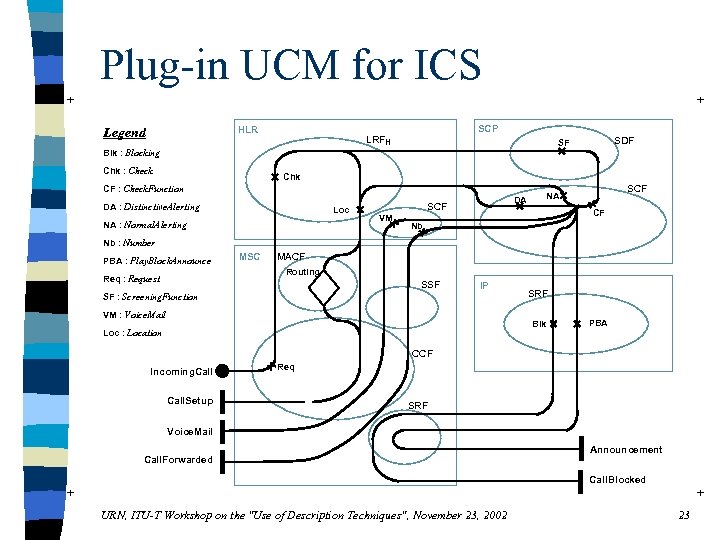 Plug-in UCM for ICS + + HLR Legend SCP LRFH Chk : Check SDF SF Blk : Blocking Chk CF : Check. Function DA : Distinctive. Alerting Loc NA : Normal. Alerting SCF VM SCF NA DA CF Nb Nb : Number PBA : Play. Block. Announce MSC MACF Routing Req : Request SSF SF : Screening. Function IP VM : Voice. Mail SRF Blk Loc : Location PBA CCF Incoming. Call. Setup Req SRF Voice. Mail Call. Forwarded Announcement Call. Blocked + + URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 23
Plug-in UCM for ICS + + HLR Legend SCP LRFH Chk : Check SDF SF Blk : Blocking Chk CF : Check. Function DA : Distinctive. Alerting Loc NA : Normal. Alerting SCF VM SCF NA DA CF Nb Nb : Number PBA : Play. Block. Announce MSC MACF Routing Req : Request SSF SF : Screening. Function IP VM : Voice. Mail SRF Blk Loc : Location PBA CCF Incoming. Call. Setup Req SRF Voice. Mail Call. Forwarded Announcement Call. Blocked + + URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 23
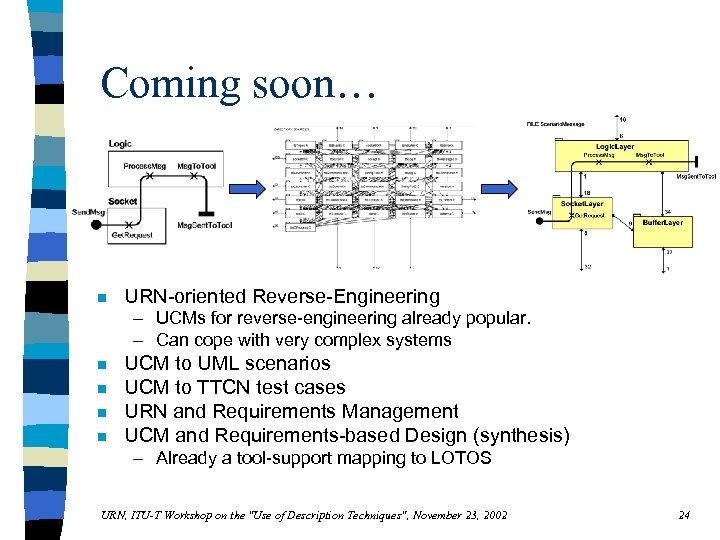 Coming soon… n URN-oriented Reverse-Engineering – UCMs for reverse-engineering already popular. – Can cope with very complex systems n n UCM to UML scenarios UCM to TTCN test cases URN and Requirements Management UCM and Requirements-based Design (synthesis) – Already a tool-support mapping to LOTOS URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 24
Coming soon… n URN-oriented Reverse-Engineering – UCMs for reverse-engineering already popular. – Can cope with very complex systems n n UCM to UML scenarios UCM to TTCN test cases URN and Requirements Management UCM and Requirements-based Design (synthesis) – Already a tool-support mapping to LOTOS URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 24
 Conclusions n URN – Allows engineers to specify or discover requirements for a proposed system or an evolving system, and review such requirements for correctness and completeness. – Is usable in industry and in standardization bodies – Combines goals and scenarios – Helps bridging the gap between informal and formal concepts, and between requirements models and design models – Big benefits for little modelling investment, even when used informally n GRL – For incomplete, tentative, (non-functional) requirements – Capture goals, objectives, alternatives and rationales n UCM – For operational and functional requirements – Enables analysis and transformations – Architectural alternatives and dynamic systems URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 25
Conclusions n URN – Allows engineers to specify or discover requirements for a proposed system or an evolving system, and review such requirements for correctness and completeness. – Is usable in industry and in standardization bodies – Combines goals and scenarios – Helps bridging the gap between informal and formal concepts, and between requirements models and design models – Big benefits for little modelling investment, even when used informally n GRL – For incomplete, tentative, (non-functional) requirements – Capture goals, objectives, alternatives and rationales n UCM – For operational and functional requirements – Enables analysis and transformations – Architectural alternatives and dynamic systems URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 25
 7 th Feature Interaction Workshop Ottawa, June 9 -11, 2003 http: //www. site. uottawa. ca/fiw 03/ Submission deadline: December 9 URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 26
7 th Feature Interaction Workshop Ottawa, June 9 -11, 2003 http: //www. site. uottawa. ca/fiw 03/ Submission deadline: December 9 URN, ITU-T Workshop on the "Use of Description Techniques", November 23, 2002 26


