4b5a886f5500293ad8eda1201d6ad700.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 ITS 602 • Purposes of the course – Review the history of US telecommunications as a case study – Examine the basics of regulation, especially as they apply to telecommunications and information – Identify the major issues of current concern
ITS 602 • Purposes of the course – Review the history of US telecommunications as a case study – Examine the basics of regulation, especially as they apply to telecommunications and information – Identify the major issues of current concern
 Some questions to consider • Do we need regulation? • Does history matter? • Why didn’t the U. S. Telecom Act of 1996 work?
Some questions to consider • Do we need regulation? • Does history matter? • Why didn’t the U. S. Telecom Act of 1996 work?
 Boundaries • Type – – Jurisdictional Regulatory category Service Technology • Set by – Law – Regulator – Courts
Boundaries • Type – – Jurisdictional Regulatory category Service Technology • Set by – Law – Regulator – Courts
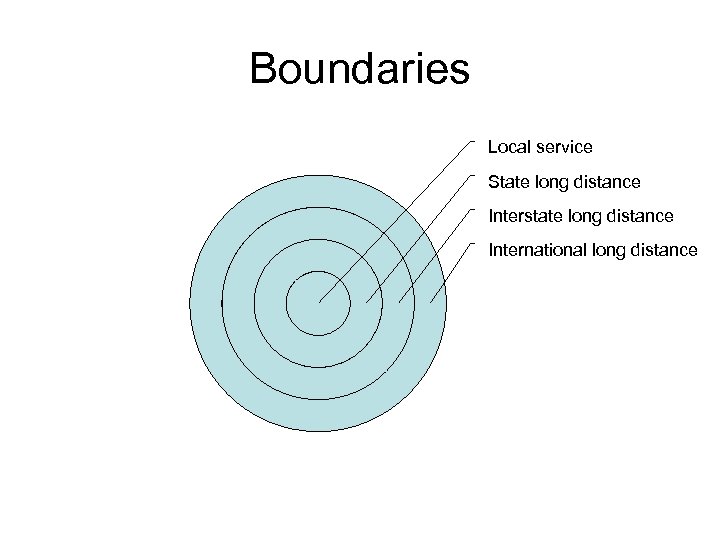 Boundaries Local service State long distance Interstate long distance International long distance
Boundaries Local service State long distance Interstate long distance International long distance
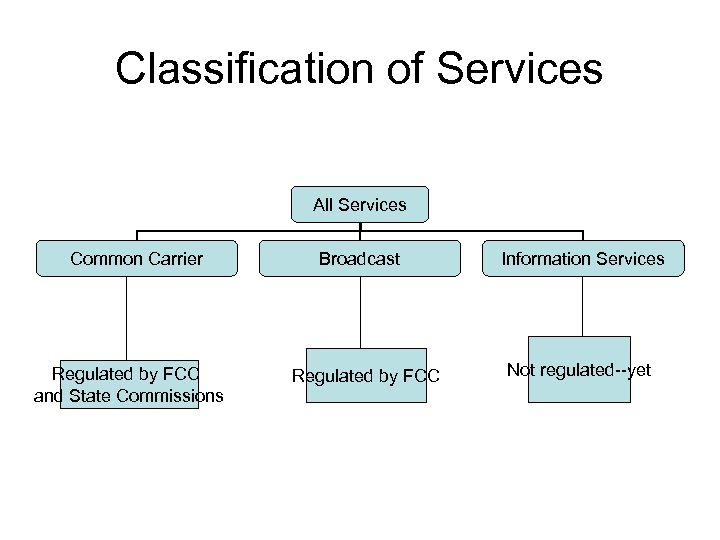 Classification of Services All Services Common Carrier Regulated by FCC and State Commissions Broadcast Regulated by FCC Information Services Not regulated--yet
Classification of Services All Services Common Carrier Regulated by FCC and State Commissions Broadcast Regulated by FCC Information Services Not regulated--yet
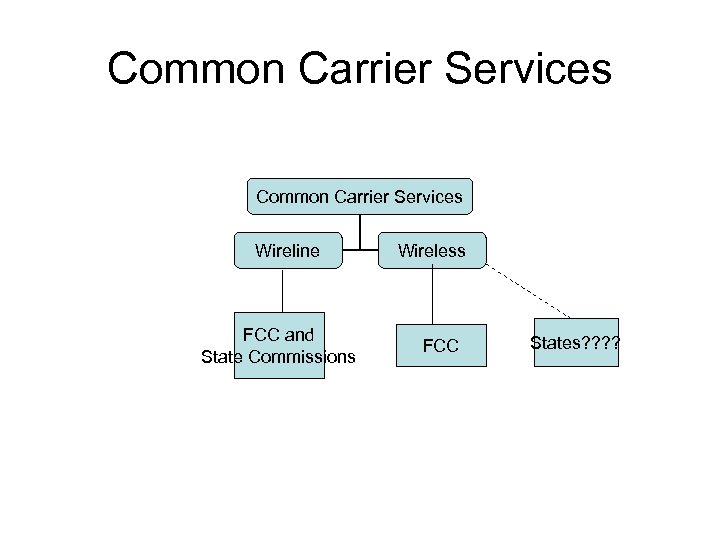 Common Carrier Services Wireline FCC and State Commissions Wireless FCC States? ?
Common Carrier Services Wireline FCC and State Commissions Wireless FCC States? ?
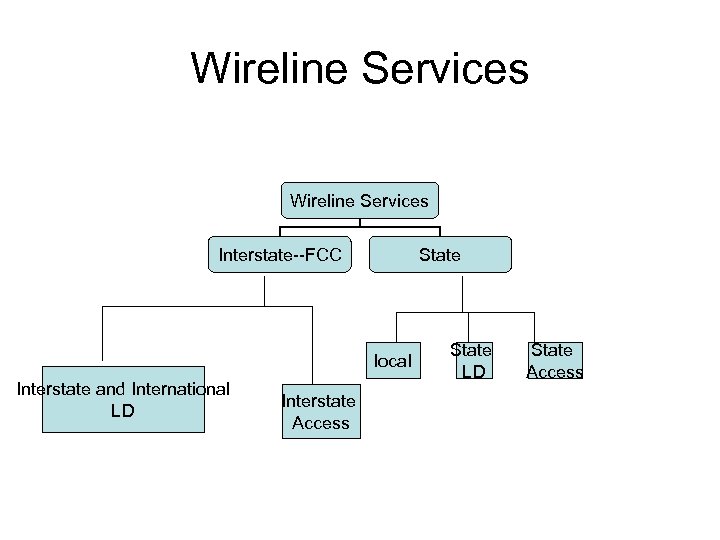 Wireline Services Interstate--FCC State local Interstate and International LD Interstate Access State LD State Access
Wireline Services Interstate--FCC State local Interstate and International LD Interstate Access State LD State Access
 The Players • Regulators (federal and state) • Service providers – Wireline providers – Wireless providers – Cable providers – Vo. IP providers • Customers – Residential, small business, large business, service providers themselves
The Players • Regulators (federal and state) • Service providers – Wireline providers – Wireless providers – Cable providers – Vo. IP providers • Customers – Residential, small business, large business, service providers themselves
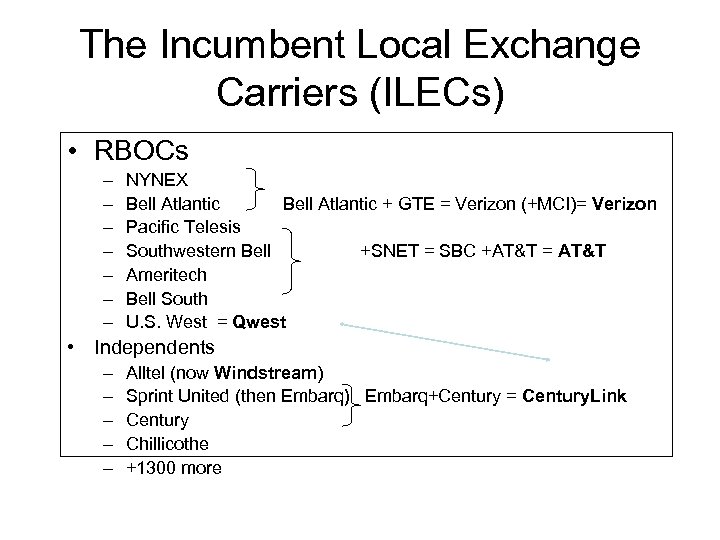 The Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers (ILECs) • RBOCs – – – – NYNEX Bell Atlantic + GTE = Verizon (+MCI)= Verizon Pacific Telesis Southwestern Bell +SNET = SBC +AT&T = AT&T Ameritech Bell South U. S. West = Qwest • Independents – – – Alltel (now Windstream) Sprint United (then Embarq) Embarq+Century = Century. Link Century Chillicothe +1300 more
The Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers (ILECs) • RBOCs – – – – NYNEX Bell Atlantic + GTE = Verizon (+MCI)= Verizon Pacific Telesis Southwestern Bell +SNET = SBC +AT&T = AT&T Ameritech Bell South U. S. West = Qwest • Independents – – – Alltel (now Windstream) Sprint United (then Embarq) Embarq+Century = Century. Link Century Chillicothe +1300 more
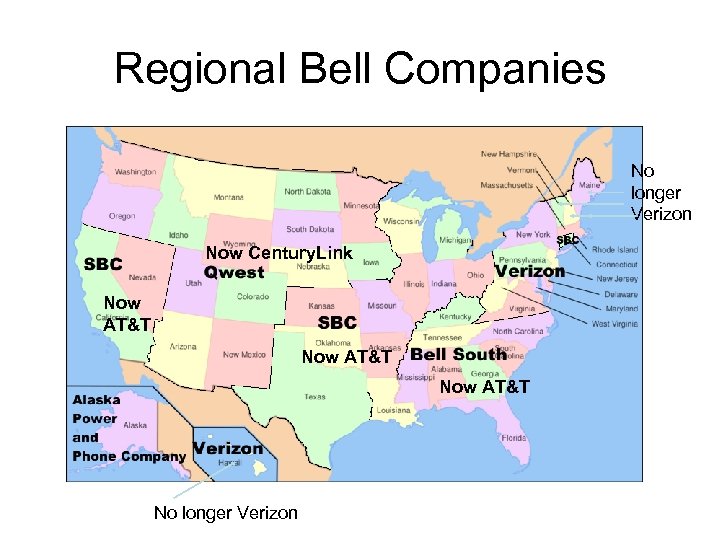 Regional Bell Companies No longer Verizon Now Century. Link Now AT&T No longer Verizon
Regional Bell Companies No longer Verizon Now Century. Link Now AT&T No longer Verizon
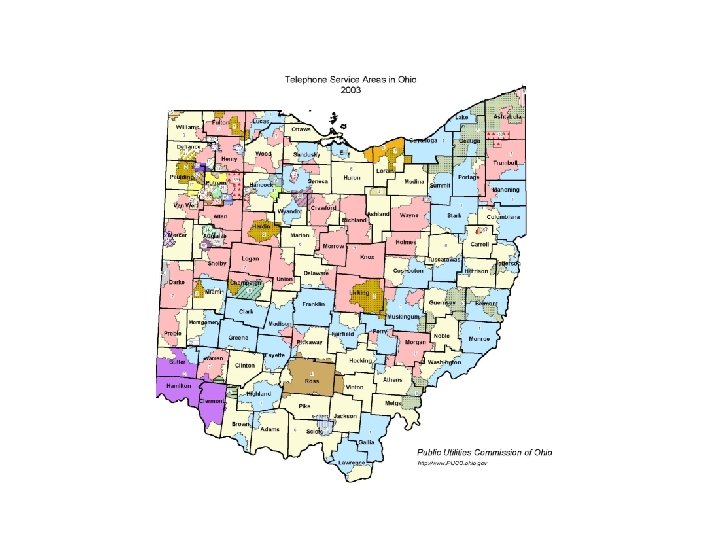
 ILECs in Ohio • 43 in total • Largest include: – – AT&T (4 million lines) Frontier (900, 000 lines) (purchase of Verizon) Cincinnati Bell (800, 000 lines) Century. Link (purchase of Sprint’s Embarq and United properties) – Windstream (formerly Alltel and Western Reserve) – Chillicothe (37, 000 lines) – Champaign (12, 500 lines)
ILECs in Ohio • 43 in total • Largest include: – – AT&T (4 million lines) Frontier (900, 000 lines) (purchase of Verizon) Cincinnati Bell (800, 000 lines) Century. Link (purchase of Sprint’s Embarq and United properties) – Windstream (formerly Alltel and Western Reserve) – Chillicothe (37, 000 lines) – Champaign (12, 500 lines)
 And now today also. . . • Vo. IP providers – Interconnected – Nomadic • Wireless providers
And now today also. . . • Vo. IP providers – Interconnected – Nomadic • Wireless providers
 Who provides what? • In 1950 (all one monopoly) – International and Interstate Long Distance: “old” AT&T Long Lines – Local: “old” AT&T Local Operating Companies and the Independents – State Long Distance: “old” AT&T Local Operating Companies and Independents – Wireless—not much • After 1984 (Local companies and Long distance companies) – International and Interstate Long Distance: The New AT&T, MCI, Sprint, plus other Long Distance companies – Local: RBOCs and Independents – State Long Distance: RBOCs and Independents, and, after a few years, the long distance companies
Who provides what? • In 1950 (all one monopoly) – International and Interstate Long Distance: “old” AT&T Long Lines – Local: “old” AT&T Local Operating Companies and the Independents – State Long Distance: “old” AT&T Local Operating Companies and Independents – Wireless—not much • After 1984 (Local companies and Long distance companies) – International and Interstate Long Distance: The New AT&T, MCI, Sprint, plus other Long Distance companies – Local: RBOCs and Independents – State Long Distance: RBOCs and Independents, and, after a few years, the long distance companies
 • After 1996 (supposed to be competition everywhere) – International and Interstate Long Distance: AT&T, MCI, Sprint, other long distance companies, RBOCs – Local: RBOCs, Independents, competitive providers (CLECs) – State Long Distance: RBOCs, Independents, CLECs, AT&T, MCI, Sprint, other long distance companies
• After 1996 (supposed to be competition everywhere) – International and Interstate Long Distance: AT&T, MCI, Sprint, other long distance companies, RBOCs – Local: RBOCs, Independents, competitive providers (CLECs) – State Long Distance: RBOCs, Independents, CLECs, AT&T, MCI, Sprint, other long distance companies
 Competition from new providers/technologies • Wireless providers – Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint (Nextel) • Internet access – Cable modem services—cable television companies – DSL—Local telephone companies and competitive providers (CLECs) • Vo. IP providers
Competition from new providers/technologies • Wireless providers – Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint (Nextel) • Internet access – Cable modem services—cable television companies – DSL—Local telephone companies and competitive providers (CLECs) • Vo. IP providers
 Lots of mergers • Mergers: – Wireless • Cingular and AT&T Wireless • Sprint and Nextel – Wireline • SBC and AT&T and Bell South • Verizon and MCI • More mergers, sales and acquisitions to come
Lots of mergers • Mergers: – Wireless • Cingular and AT&T Wireless • Sprint and Nextel – Wireline • SBC and AT&T and Bell South • Verizon and MCI • More mergers, sales and acquisitions to come
 Industry Consolidation • Biggest local telephone companies – Verizon and AT&T • Biggest wireless providers – Verizon and AT&T – And now AT&T wants to buy T-Mobile • Biggest long distance providers – AT&T (owned by former SBC) – MCI (owned by Verizon)
Industry Consolidation • Biggest local telephone companies – Verizon and AT&T • Biggest wireless providers – Verizon and AT&T – And now AT&T wants to buy T-Mobile • Biggest long distance providers – AT&T (owned by former SBC) – MCI (owned by Verizon)
 Changes in ILEC Business plans • Verizon is shedding rural properties • Maine, NH, and Vermont sold to Fairpoint—went bankrupt • Hawaii sold to private equity firm—went bankrupt • Former GTE properties in 9 states sold to Frontier (including Athens, Ohio)—will it go bankrupt? ? • Ramping up wireless • Shifts from copper to broadband from circuit switching to IP networks – AT&T’s U-Verse and Verizon’s FIOS
Changes in ILEC Business plans • Verizon is shedding rural properties • Maine, NH, and Vermont sold to Fairpoint—went bankrupt • Hawaii sold to private equity firm—went bankrupt • Former GTE properties in 9 states sold to Frontier (including Athens, Ohio)—will it go bankrupt? ? • Ramping up wireless • Shifts from copper to broadband from circuit switching to IP networks – AT&T’s U-Verse and Verizon’s FIOS
 So, what do we have today? • Cross platform competition • Bundling of services – Cable companies • Cable TV, Cable Modem, Digital Phone (triple play) • And Wireless ? ? (quadruple play) – Telephone companies • Wireline telephone, DSL, Wireless (triple play • And IPTV? ? (quadruple play) – Issues of pricing and service bundling? ?
So, what do we have today? • Cross platform competition • Bundling of services – Cable companies • Cable TV, Cable Modem, Digital Phone (triple play) • And Wireless ? ? (quadruple play) – Telephone companies • Wireline telephone, DSL, Wireless (triple play • And IPTV? ? (quadruple play) – Issues of pricing and service bundling? ?
 Issues of concern • Broadband deployment • Regulatory status of Vo. IP • Network neutrality (or can the FCC regulate the broadband network) • Universal service—is it necessary? Who pays for it? How much should it cost? What should be included? • Regulatory parity in cross platform competition • Viability of competition, and the potential for monopoly • And more. . .
Issues of concern • Broadband deployment • Regulatory status of Vo. IP • Network neutrality (or can the FCC regulate the broadband network) • Universal service—is it necessary? Who pays for it? How much should it cost? What should be included? • Regulatory parity in cross platform competition • Viability of competition, and the potential for monopoly • And more. . .
 So…. . • What is the role of the regulator?
So…. . • What is the role of the regulator?


