acf73a7ce602f733a9af2d82f3ccfef3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 137
 ITIL seminar for managers and senior engineers at ITS -IT governance, IT internal control, ITIL and IT services. Nov. 24. 2010 JICA Expert Go Ota 1
ITIL seminar for managers and senior engineers at ITS -IT governance, IT internal control, ITIL and IT services. Nov. 24. 2010 JICA Expert Go Ota 1
 Agenda Part 0. Introduction Part 1. General Idea of IT governance and service 1 -1. Overview of Internal control and IT supports 1 -2. IT Governance 1 -3. Risk Management 1 -4. ITAC: IT Application Control and Application development 1 -5. Availability Management and Service Continuity Management 1 -6. Protection of Information Assets - Information Security Management 1 -7. IT services and operation Part 2. Recommendation and discussion 2 -1. Roadmap and main activities 2 -2. ITS structure and capacity development (HRD) 2
Agenda Part 0. Introduction Part 1. General Idea of IT governance and service 1 -1. Overview of Internal control and IT supports 1 -2. IT Governance 1 -3. Risk Management 1 -4. ITAC: IT Application Control and Application development 1 -5. Availability Management and Service Continuity Management 1 -6. Protection of Information Assets - Information Security Management 1 -7. IT services and operation Part 2. Recommendation and discussion 2 -1. Roadmap and main activities 2 -2. ITS structure and capacity development (HRD) 2
 0. Introduction 3
0. Introduction 3
 What do user want? Want do users see? What are tasks of IT engineers? 4
What do user want? Want do users see? What are tasks of IT engineers? 4
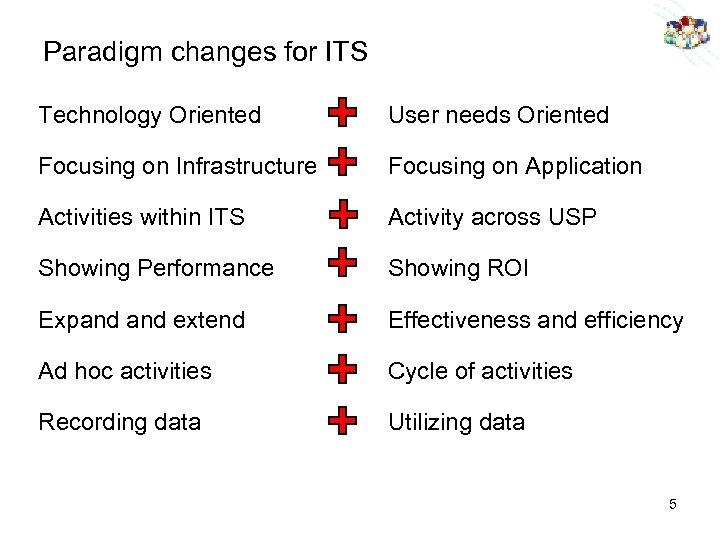 Paradigm changes for ITS Technology Oriented User needs Oriented Focusing on Infrastructure Focusing on Application Activities within ITS Activity across USP Showing Performance Showing ROI Expand extend Effectiveness and efficiency Ad hoc activities Cycle of activities Recording data Utilizing data 5
Paradigm changes for ITS Technology Oriented User needs Oriented Focusing on Infrastructure Focusing on Application Activities within ITS Activity across USP Showing Performance Showing ROI Expand extend Effectiveness and efficiency Ad hoc activities Cycle of activities Recording data Utilizing data 5
 Objectives of ITS Customer Satisfaction : CS • CS is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. It is seen as a key performance indicator within business • In a competitive marketplace where businesses compete for customers, customer satisfaction is seen as a key differentiator and increasingly has become a key element of business strategy. (Wikipedia) Not direct objectives, but: Because ITS achieves CS, ITS should keep appropriate recourses and structure. How does ITS keep them? 6
Objectives of ITS Customer Satisfaction : CS • CS is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. It is seen as a key performance indicator within business • In a competitive marketplace where businesses compete for customers, customer satisfaction is seen as a key differentiator and increasingly has become a key element of business strategy. (Wikipedia) Not direct objectives, but: Because ITS achieves CS, ITS should keep appropriate recourses and structure. How does ITS keep them? 6
 Important ideas of ITIL • Small action and quick win - Don’t think of Appling all of ITIL at one. - To start small activities and get good results soon. • CSIP: Continues Service Improvement Program - ITIL doesn't provide fixed procedures and methods, IT engineer should develop appropriate methods for own situation. - To find problem and improve every time - To visualize process and results, record data and show evidence. • Proactive -To prepare before problem and/or trouble happen KPI: KPI should include how to measure and to show difference before and after. 7
Important ideas of ITIL • Small action and quick win - Don’t think of Appling all of ITIL at one. - To start small activities and get good results soon. • CSIP: Continues Service Improvement Program - ITIL doesn't provide fixed procedures and methods, IT engineer should develop appropriate methods for own situation. - To find problem and improve every time - To visualize process and results, record data and show evidence. • Proactive -To prepare before problem and/or trouble happen KPI: KPI should include how to measure and to show difference before and after. 7
 Presenting and Communicating (CISA IS Audit) Considerations for Communication and Presentation to Executive • Understandable for Exceptive. Because usually they doesn’t know IT technology, Don’t use technical terms. • Finding and recommendation should be made form the viewpoint of business • Short documentation, executives don’t have time to read sick documents. • Showing objective evidence. Executives prefer quantitative information to qualitative one 8
Presenting and Communicating (CISA IS Audit) Considerations for Communication and Presentation to Executive • Understandable for Exceptive. Because usually they doesn’t know IT technology, Don’t use technical terms. • Finding and recommendation should be made form the viewpoint of business • Short documentation, executives don’t have time to read sick documents. • Showing objective evidence. Executives prefer quantitative information to qualitative one 8
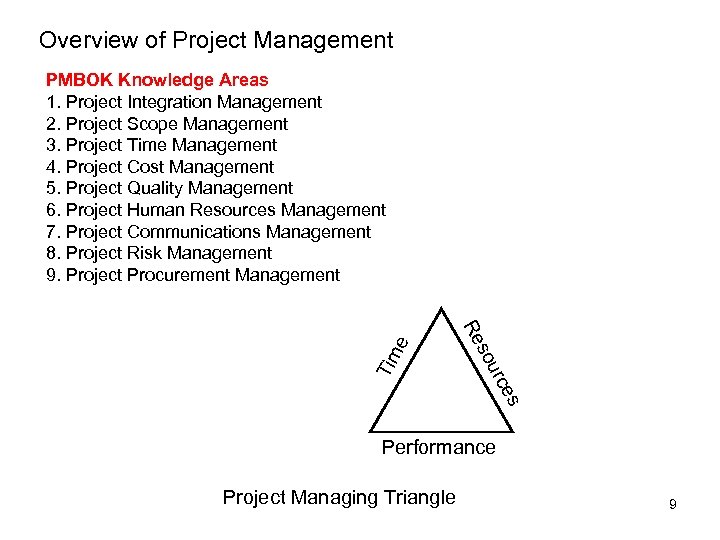 Overview of Project Management es urc Tim so Re e PMBOK Knowledge Areas 1. Project Integration Management 2. Project Scope Management 3. Project Time Management 4. Project Cost Management 5. Project Quality Management 6. Project Human Resources Management 7. Project Communications Management 8. Project Risk Management 9. Project Procurement Management Performance Project Managing Triangle 9
Overview of Project Management es urc Tim so Re e PMBOK Knowledge Areas 1. Project Integration Management 2. Project Scope Management 3. Project Time Management 4. Project Cost Management 5. Project Quality Management 6. Project Human Resources Management 7. Project Communications Management 8. Project Risk Management 9. Project Procurement Management Performance Project Managing Triangle 9
 Part 1. General Idea of IT governance and service 1 -1. Overview of Internal control and IT supports 10
Part 1. General Idea of IT governance and service 1 -1. Overview of Internal control and IT supports 10
 Why IS Audit is needed? Social Background Information System has been becoming a main function for business. • Supporting business activity • Keeping business information • Main interface to customer Innovation of ICT gave information system major role in business Problem of business management • Inappropriate IT system to business strategy • Bug investment for IT system and unclear ROI Problem of security/ risk management • Computer virus/ illegal Access • System trouble and Backup of disaster Effective and Efficient inter management and operation for Information system should be needed Independent Information System Audit 11
Why IS Audit is needed? Social Background Information System has been becoming a main function for business. • Supporting business activity • Keeping business information • Main interface to customer Innovation of ICT gave information system major role in business Problem of business management • Inappropriate IT system to business strategy • Bug investment for IT system and unclear ROI Problem of security/ risk management • Computer virus/ illegal Access • System trouble and Backup of disaster Effective and Efficient inter management and operation for Information system should be needed Independent Information System Audit 11
 Why IS Audit is needed? Legal Background (1) After major corporate and accounting scandals including those affecting Enron, Tyco International, Adelphia, Peregrine Systems and World. Com, the 'Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act' and 'Corporate and Auditing Accountability and Responsibility Act' and commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, Sarbox or SOX, is a United States federal law enacted on July 30, 2002 • Directs SEC to enact rules protecting shareholders & the economy • Honesty in financial reporting • Responsibility at the Top • Demonstrate Compliance by Audits The most contentious aspect of SOX is Section 404, which requires management and the external auditor to report on the adequacy of the company's internal control over financial reporting Internal Control must use Information System now. To evaluate internal control should needs audit for Information system 12
Why IS Audit is needed? Legal Background (1) After major corporate and accounting scandals including those affecting Enron, Tyco International, Adelphia, Peregrine Systems and World. Com, the 'Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act' and 'Corporate and Auditing Accountability and Responsibility Act' and commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, Sarbox or SOX, is a United States federal law enacted on July 30, 2002 • Directs SEC to enact rules protecting shareholders & the economy • Honesty in financial reporting • Responsibility at the Top • Demonstrate Compliance by Audits The most contentious aspect of SOX is Section 404, which requires management and the external auditor to report on the adequacy of the company's internal control over financial reporting Internal Control must use Information System now. To evaluate internal control should needs audit for Information system 12
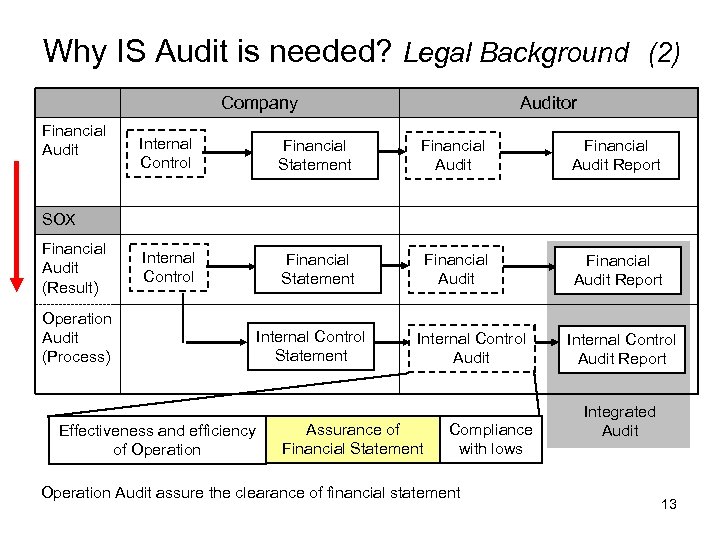 Why IS Audit is needed? Legal Background (2) Company Financial Auditor Internal Control Financial Statement Financial Audit Report SOX Financial Audit (Result) Operation Audit (Process) Effectiveness and efficiency of Operation Internal Control Statement Internal Control Audit Assurance of Financial Statement Compliance with lows Operation Audit assure the clearance of financial statement Internal Control Audit Report Integrated Audit 13
Why IS Audit is needed? Legal Background (2) Company Financial Auditor Internal Control Financial Statement Financial Audit Report SOX Financial Audit (Result) Operation Audit (Process) Effectiveness and efficiency of Operation Internal Control Statement Internal Control Audit Assurance of Financial Statement Compliance with lows Operation Audit assure the clearance of financial statement Internal Control Audit Report Integrated Audit 13
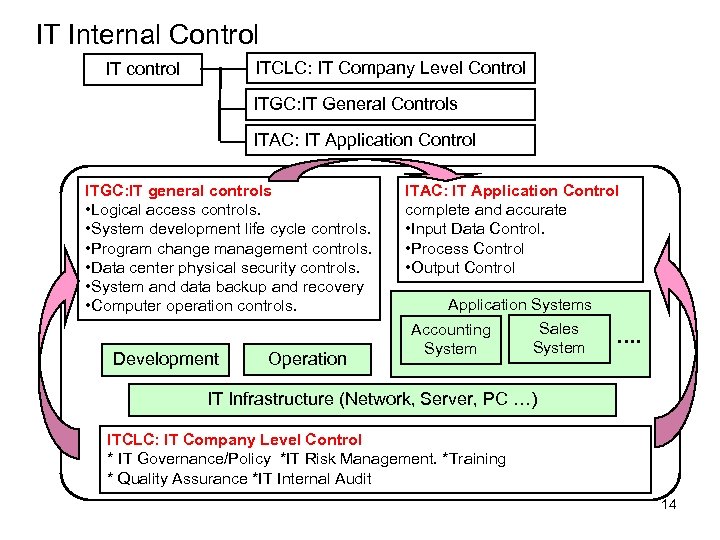 IT Internal Control ITCLC: IT Company Level Control IT control ITGC: IT General Controls ITAC: IT Application Control ITGC: IT general controls • Logical access controls. • System development life cycle controls. • Program change management controls. • Data center physical security controls. • System and data backup and recovery • Computer operation controls. Development Operation ITAC: IT Application Control complete and accurate • Input Data Control. • Process Control • Output Control Application Systems Sales Accounting System …. IT Infrastructure (Network, Server, PC …) ITCLC: IT Company Level Control * IT Governance/Policy *IT Risk Management. *Training * Quality Assurance *IT Internal Audit 14
IT Internal Control ITCLC: IT Company Level Control IT control ITGC: IT General Controls ITAC: IT Application Control ITGC: IT general controls • Logical access controls. • System development life cycle controls. • Program change management controls. • Data center physical security controls. • System and data backup and recovery • Computer operation controls. Development Operation ITAC: IT Application Control complete and accurate • Input Data Control. • Process Control • Output Control Application Systems Sales Accounting System …. IT Infrastructure (Network, Server, PC …) ITCLC: IT Company Level Control * IT Governance/Policy *IT Risk Management. *Training * Quality Assurance *IT Internal Audit 14
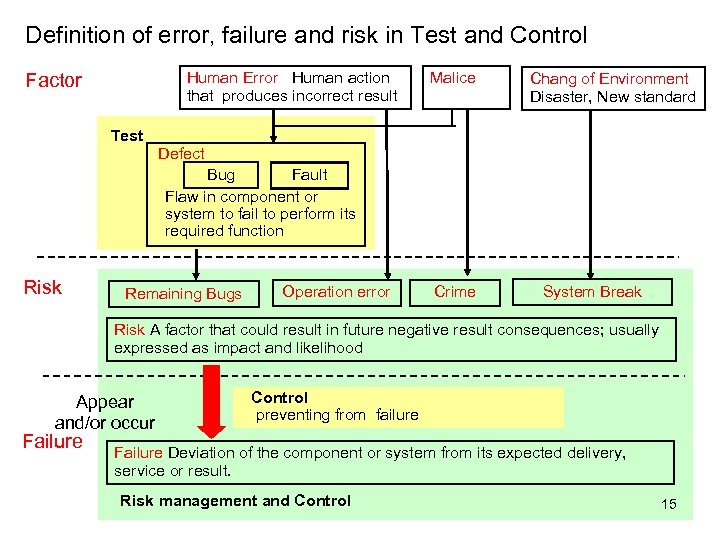 Definition of error, failure and risk in Test and Control Human Error Human action that produces incorrect result Factor Test Malice Chang of Environment Disaster, New standard Defect Bug Fault Flaw in component or system to fail to perform its required function Risk Remaining Bugs Operation error Crime System Break Risk A factor that could result in future negative result consequences; usually expressed as impact and likelihood Appear and/or occur Failure Control preventing from failure Failure Deviation of the component or system from its expected delivery, service or result. Risk management and Control 15
Definition of error, failure and risk in Test and Control Human Error Human action that produces incorrect result Factor Test Malice Chang of Environment Disaster, New standard Defect Bug Fault Flaw in component or system to fail to perform its required function Risk Remaining Bugs Operation error Crime System Break Risk A factor that could result in future negative result consequences; usually expressed as impact and likelihood Appear and/or occur Failure Control preventing from failure Failure Deviation of the component or system from its expected delivery, service or result. Risk management and Control 15
 Where did ITIL come from? Problem of Current IT system and operation * IT system became core of business and social activities, simultaneously it became bigger and more complicated * Cost of IT is not clear, sometimes investment to IT development and operation doesn’t realize user needs. ITIL ( Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is collection of good practices and knowledge/skill for operation of infrastructure and realizes; - Stable and high quality operation of IT infrastructure - Providing clear indicator of ROI for IT operation ( Return of Investment) 16
Where did ITIL come from? Problem of Current IT system and operation * IT system became core of business and social activities, simultaneously it became bigger and more complicated * Cost of IT is not clear, sometimes investment to IT development and operation doesn’t realize user needs. ITIL ( Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is collection of good practices and knowledge/skill for operation of infrastructure and realizes; - Stable and high quality operation of IT infrastructure - Providing clear indicator of ROI for IT operation ( Return of Investment) 16
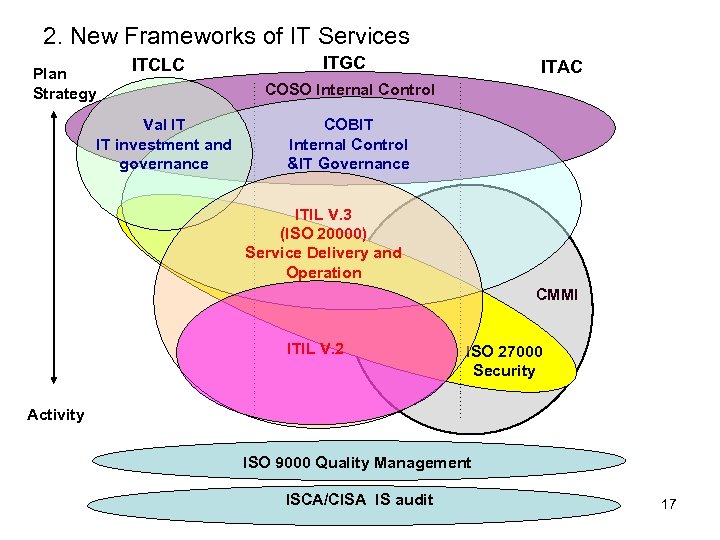 2. New Frameworks of IT Services Plan Strategy ITCLC Val IT IT investment and governance ITGC ITAC COSO Internal Control COBIT Internal Control &IT Governance ITIL V. 3 (ISO 20000) Service Delivery and Operation CMMI ITIL V. 2 ISO 27000 Security Activity ISO 9000 Quality Management ISCA/CISA IS audit 17
2. New Frameworks of IT Services Plan Strategy ITCLC Val IT IT investment and governance ITGC ITAC COSO Internal Control COBIT Internal Control &IT Governance ITIL V. 3 (ISO 20000) Service Delivery and Operation CMMI ITIL V. 2 ISO 27000 Security Activity ISO 9000 Quality Management ISCA/CISA IS audit 17
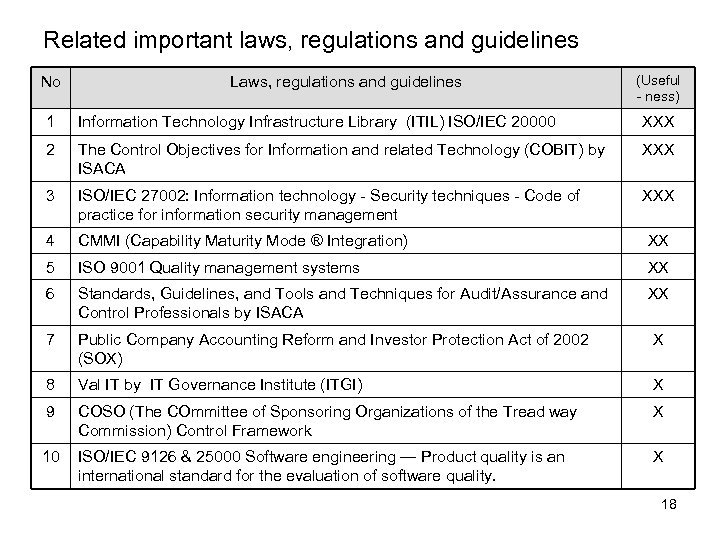 Related important laws, regulations and guidelines No Laws, regulations and guidelines (Useful - ness) 1 Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) ISO/IEC 20000 XXX 2 The Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT) by ISACA XXX 3 ISO/IEC 27002: Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management XXX 4 CMMI (Capability Maturity Mode ® Integration) XX 5 ISO 9001 Quality management systems XX 6 Standards, Guidelines, and Tools and Techniques for Audit/Assurance and Control Professionals by ISACA XX 7 Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act of 2002 (SOX) X 8 Val IT by IT Governance Institute (ITGI) X 9 COSO (The COmmittee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Tread way Commission) Control Framework X 10 ISO/IEC 9126 & 25000 Software engineering — Product quality is an international standard for the evaluation of software quality. X 18
Related important laws, regulations and guidelines No Laws, regulations and guidelines (Useful - ness) 1 Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) ISO/IEC 20000 XXX 2 The Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT) by ISACA XXX 3 ISO/IEC 27002: Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management XXX 4 CMMI (Capability Maturity Mode ® Integration) XX 5 ISO 9001 Quality management systems XX 6 Standards, Guidelines, and Tools and Techniques for Audit/Assurance and Control Professionals by ISACA XX 7 Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act of 2002 (SOX) X 8 Val IT by IT Governance Institute (ITGI) X 9 COSO (The COmmittee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Tread way Commission) Control Framework X 10 ISO/IEC 9126 & 25000 Software engineering — Product quality is an international standard for the evaluation of software quality. X 18
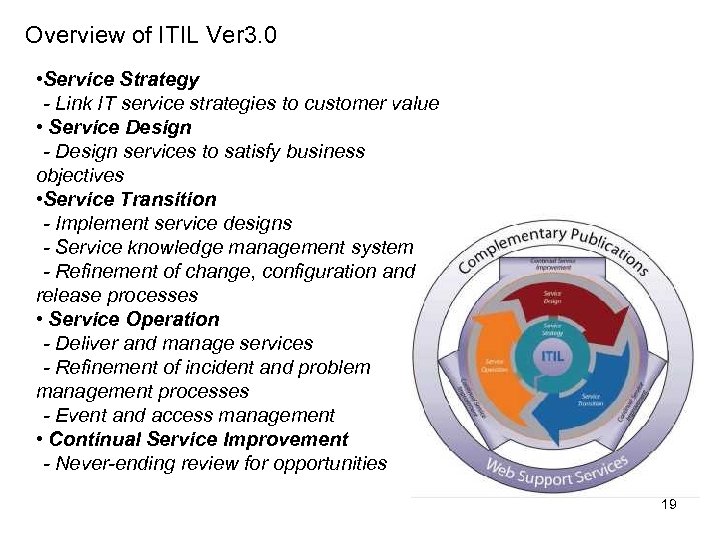 Overview of ITIL Ver 3. 0 • Service Strategy - Link IT service strategies to customer value • Service Design - Design services to satisfy business objectives • Service Transition - Implement service designs - Service knowledge management system - Refinement of change, configuration and release processes • Service Operation - Deliver and manage services - Refinement of incident and problem management processes - Event and access management • Continual Service Improvement - Never-ending review for opportunities 19
Overview of ITIL Ver 3. 0 • Service Strategy - Link IT service strategies to customer value • Service Design - Design services to satisfy business objectives • Service Transition - Implement service designs - Service knowledge management system - Refinement of change, configuration and release processes • Service Operation - Deliver and manage services - Refinement of incident and problem management processes - Event and access management • Continual Service Improvement - Never-ending review for opportunities 19
 Inportanct idea of ITIL • Service Strategy - Link IT service strategies to customer value • Service Design - Design services to satisfy business objectives • Service Transition - Implement service designs - Service knowledge management system - Refinement of change, configuration and release processes • Service Operation - Deliver and manage services - Refinement of incident and problem management processes - Event and access management • Continual Service Improvement - Never-ending review for opportunities 20
Inportanct idea of ITIL • Service Strategy - Link IT service strategies to customer value • Service Design - Design services to satisfy business objectives • Service Transition - Implement service designs - Service knowledge management system - Refinement of change, configuration and release processes • Service Operation - Deliver and manage services - Refinement of incident and problem management processes - Event and access management • Continual Service Improvement - Never-ending review for opportunities 20
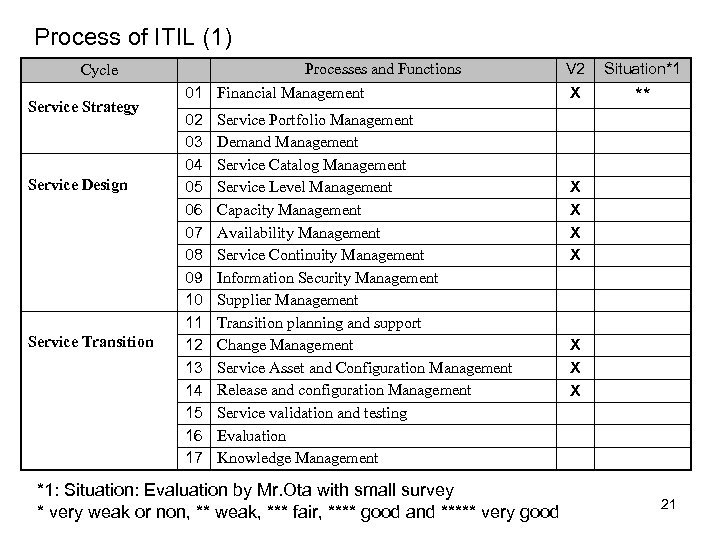 Process of ITIL (1) Processes and Functions Cycle Service Strategy Service Design Service Transition 01 Financial Management 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Service Portfolio Management Demand Management Service Catalog Management Service Level Management Capacity Management Availability Management Service Continuity Management Information Security Management Supplier Management Transition planning and support Change Management Service Asset and Configuration Management Release and configuration Management Service validation and testing Evaluation Knowledge Management *1: Situation: Evaluation by Mr. Ota with small survey * very weak or non, ** weak, *** fair, **** good and ***** very good V 2 Situation*1 X ** X X X X 21
Process of ITIL (1) Processes and Functions Cycle Service Strategy Service Design Service Transition 01 Financial Management 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Service Portfolio Management Demand Management Service Catalog Management Service Level Management Capacity Management Availability Management Service Continuity Management Information Security Management Supplier Management Transition planning and support Change Management Service Asset and Configuration Management Release and configuration Management Service validation and testing Evaluation Knowledge Management *1: Situation: Evaluation by Mr. Ota with small survey * very weak or non, ** weak, *** fair, **** good and ***** very good V 2 Situation*1 X ** X X X X 21
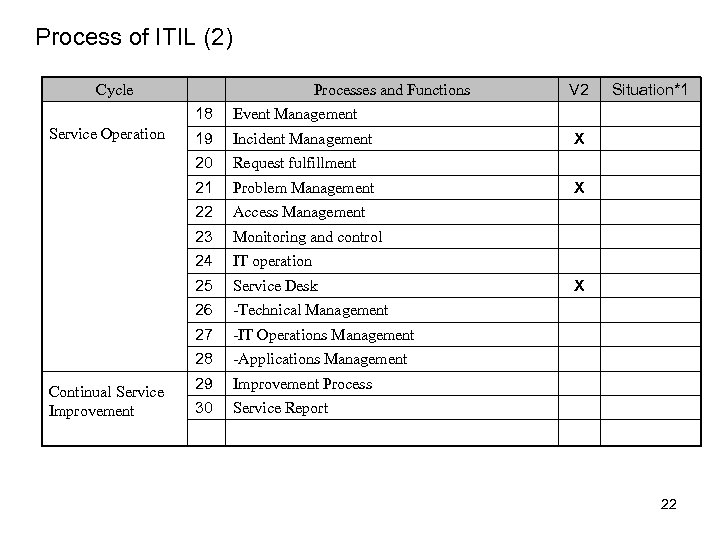 Process of ITIL (2) Cycle Processes and Functions 18 Incident Management Request fulfillment 21 Problem Management 22 Access Management 23 Monitoring and control 24 IT operation 25 Service Desk 26 -Technical Management 27 -IT Operations Management 28 Continual Service Improvement 19 -Applications Management 29 Improvement Process 30 Situation*1 Event Management 20 Service Operation V 2 Service Report X X X 22
Process of ITIL (2) Cycle Processes and Functions 18 Incident Management Request fulfillment 21 Problem Management 22 Access Management 23 Monitoring and control 24 IT operation 25 Service Desk 26 -Technical Management 27 -IT Operations Management 28 Continual Service Improvement 19 -Applications Management 29 Improvement Process 30 Situation*1 Event Management 20 Service Operation V 2 Service Report X X X 22
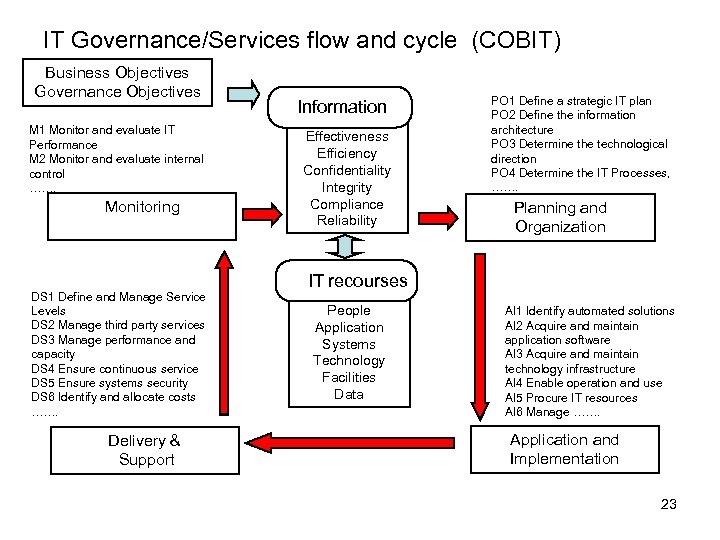 IT Governance/Services flow and cycle (COBIT) Business Objectives Governance Objectives M 1 Monitor and evaluate IT Performance M 2 Monitor and evaluate internal control ……. Monitoring DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage third party services DS 3 Manage performance and capacity DS 4 Ensure continuous service DS 5 Ensure systems security DS 6 Identify and allocate costs ……. Delivery & Support Information Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality Integrity Compliance Reliability PO 1 Define a strategic IT plan PO 2 Define the information architecture PO 3 Determine the technological direction PO 4 Determine the IT Processes, ……. Planning and Organization IT recourses People Application Systems Technology Facilities Data AI 1 Identify automated solutions AI 2 Acquire and maintain application software AI 3 Acquire and maintain technology infrastructure AI 4 Enable operation and use AI 5 Procure IT resources AI 6 Manage ……. Application and Implementation 23
IT Governance/Services flow and cycle (COBIT) Business Objectives Governance Objectives M 1 Monitor and evaluate IT Performance M 2 Monitor and evaluate internal control ……. Monitoring DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage third party services DS 3 Manage performance and capacity DS 4 Ensure continuous service DS 5 Ensure systems security DS 6 Identify and allocate costs ……. Delivery & Support Information Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality Integrity Compliance Reliability PO 1 Define a strategic IT plan PO 2 Define the information architecture PO 3 Determine the technological direction PO 4 Determine the IT Processes, ……. Planning and Organization IT recourses People Application Systems Technology Facilities Data AI 1 Identify automated solutions AI 2 Acquire and maintain application software AI 3 Acquire and maintain technology infrastructure AI 4 Enable operation and use AI 5 Procure IT resources AI 6 Manage ……. Application and Implementation 23
 IT Governance Focus Area: (ITGI) Enterprise governance is a set of responsibilities and practices exercised by the board and executive management with the goal of: • Providing strategic direction • Ensuring that objectives are achieved • Ascertaining that risks are managed appropriately • Verifying that the enterprise’s resources are used responsibly 24
IT Governance Focus Area: (ITGI) Enterprise governance is a set of responsibilities and practices exercised by the board and executive management with the goal of: • Providing strategic direction • Ensuring that objectives are achieved • Ascertaining that risks are managed appropriately • Verifying that the enterprise’s resources are used responsibly 24
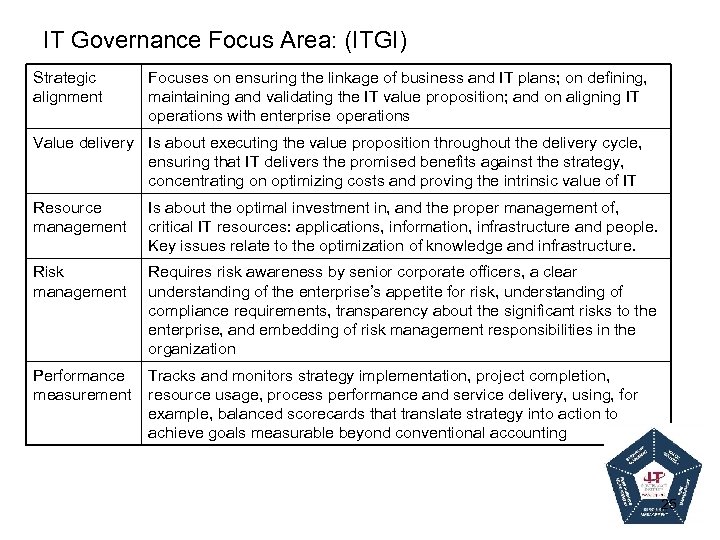 IT Governance Focus Area: (ITGI) Strategic alignment Focuses on ensuring the linkage of business and IT plans; on defining, maintaining and validating the IT value proposition; and on aligning IT operations with enterprise operations Value delivery Is about executing the value proposition throughout the delivery cycle, ensuring that IT delivers the promised benefits against the strategy, concentrating on optimizing costs and proving the intrinsic value of IT Resource management Is about the optimal investment in, and the proper management of, critical IT resources: applications, information, infrastructure and people. Key issues relate to the optimization of knowledge and infrastructure. Risk management Requires risk awareness by senior corporate officers, a clear understanding of the enterprise’s appetite for risk, understanding of compliance requirements, transparency about the significant risks to the enterprise, and embedding of risk management responsibilities in the organization Performance measurement Tracks and monitors strategy implementation, project completion, resource usage, process performance and service delivery, using, for example, balanced scorecards that translate strategy into action to achieve goals measurable beyond conventional accounting 25
IT Governance Focus Area: (ITGI) Strategic alignment Focuses on ensuring the linkage of business and IT plans; on defining, maintaining and validating the IT value proposition; and on aligning IT operations with enterprise operations Value delivery Is about executing the value proposition throughout the delivery cycle, ensuring that IT delivers the promised benefits against the strategy, concentrating on optimizing costs and proving the intrinsic value of IT Resource management Is about the optimal investment in, and the proper management of, critical IT resources: applications, information, infrastructure and people. Key issues relate to the optimization of knowledge and infrastructure. Risk management Requires risk awareness by senior corporate officers, a clear understanding of the enterprise’s appetite for risk, understanding of compliance requirements, transparency about the significant risks to the enterprise, and embedding of risk management responsibilities in the organization Performance measurement Tracks and monitors strategy implementation, project completion, resource usage, process performance and service delivery, using, for example, balanced scorecards that translate strategy into action to achieve goals measurable beyond conventional accounting 25
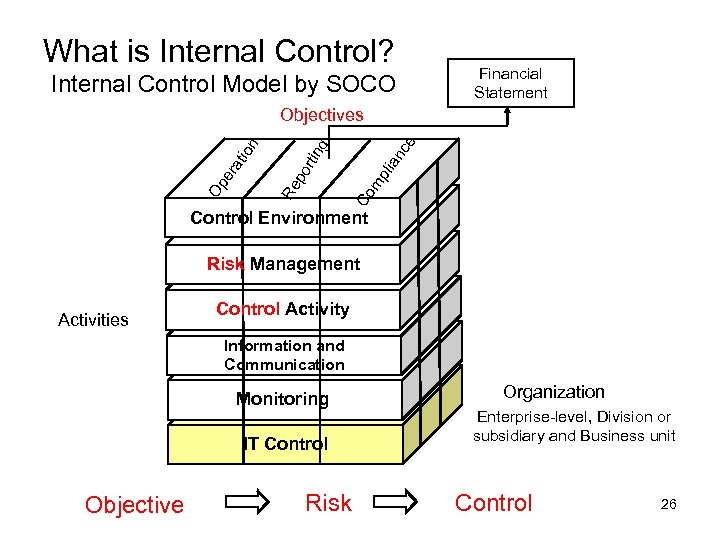 What is Internal Control? Internal Control Model by SOCO Financial Statement ce g pli an rt i n Co m po Re Op er at ion Objectives Control Environment Risk Management Activities Control Activity Information and Communication Monitoring IT Control Objective Risk Organization Enterprise-level, Division or subsidiary and Business unit Control 26
What is Internal Control? Internal Control Model by SOCO Financial Statement ce g pli an rt i n Co m po Re Op er at ion Objectives Control Environment Risk Management Activities Control Activity Information and Communication Monitoring IT Control Objective Risk Organization Enterprise-level, Division or subsidiary and Business unit Control 26
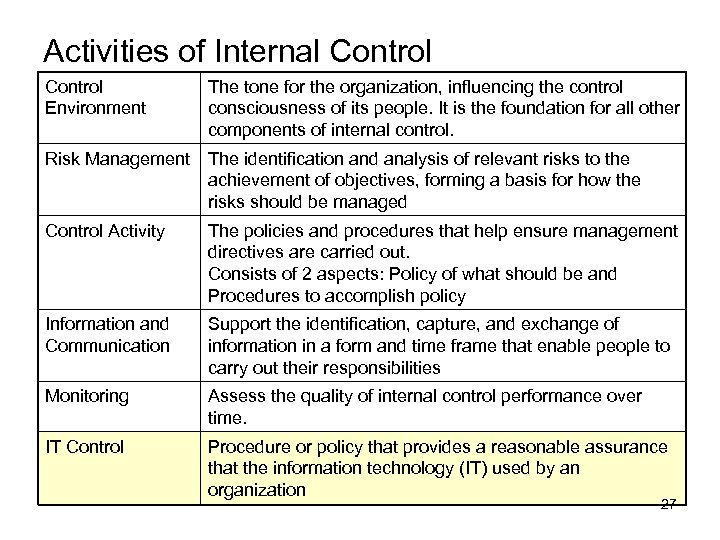 Activities of Internal Control Environment The tone for the organization, influencing the control consciousness of its people. It is the foundation for all other components of internal control. Risk Management The identification and analysis of relevant risks to the achievement of objectives, forming a basis for how the risks should be managed Control Activity The policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out. Consists of 2 aspects: Policy of what should be and Procedures to accomplish policy Information and Communication Support the identification, capture, and exchange of information in a form and time frame that enable people to carry out their responsibilities Monitoring Assess the quality of internal control performance over time. IT Control Procedure or policy that provides a reasonable assurance that the information technology (IT) used by an organization 27
Activities of Internal Control Environment The tone for the organization, influencing the control consciousness of its people. It is the foundation for all other components of internal control. Risk Management The identification and analysis of relevant risks to the achievement of objectives, forming a basis for how the risks should be managed Control Activity The policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out. Consists of 2 aspects: Policy of what should be and Procedures to accomplish policy Information and Communication Support the identification, capture, and exchange of information in a form and time frame that enable people to carry out their responsibilities Monitoring Assess the quality of internal control performance over time. IT Control Procedure or policy that provides a reasonable assurance that the information technology (IT) used by an organization 27
 1 -2. IT Governance 28
1 -2. IT Governance 28
 Concept of IT Governance: Definition & Summary Definition • IT Governance is the responsibility of executives and the board of directors, and consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the enterprise’s IT sustains and extends the organization’s strategies and objectives. (Cobi. T 4. 1) • [IT Governance] Consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the enterprise’s information technology sustains and extends the organization’s strategies and objectives. (IIA International Professional Practices Framework) Summary a) Leadership and Clear Business Ownership b) Aligned Business-Relevant Measures c) Complete and Accurate Inventories d) Linking Technical and Business Risk 29
Concept of IT Governance: Definition & Summary Definition • IT Governance is the responsibility of executives and the board of directors, and consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the enterprise’s IT sustains and extends the organization’s strategies and objectives. (Cobi. T 4. 1) • [IT Governance] Consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the enterprise’s information technology sustains and extends the organization’s strategies and objectives. (IIA International Professional Practices Framework) Summary a) Leadership and Clear Business Ownership b) Aligned Business-Relevant Measures c) Complete and Accurate Inventories d) Linking Technical and Business Risk 29
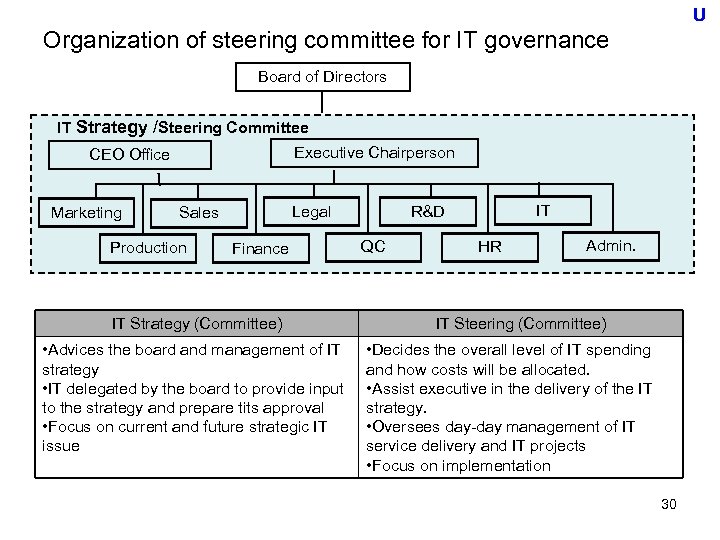 U Organization of steering committee for IT governance Board of Directors IT Strategy /Steering Committee Executive Chairperson CEO Office Marketing Legal Sales Production Finance IT Strategy (Committee) • Advices the board and management of IT strategy • IT delegated by the board to provide input to the strategy and prepare tits approval • Focus on current and future strategic IT issue IT R&D QC HR Admin. IT Steering (Committee) • Decides the overall level of IT spending and how costs will be allocated. • Assist executive in the delivery of the IT strategy. • Oversees day-day management of IT service delivery and IT projects • Focus on implementation 30
U Organization of steering committee for IT governance Board of Directors IT Strategy /Steering Committee Executive Chairperson CEO Office Marketing Legal Sales Production Finance IT Strategy (Committee) • Advices the board and management of IT strategy • IT delegated by the board to provide input to the strategy and prepare tits approval • Focus on current and future strategic IT issue IT R&D QC HR Admin. IT Steering (Committee) • Decides the overall level of IT spending and how costs will be allocated. • Assist executive in the delivery of the IT strategy. • Oversees day-day management of IT service delivery and IT projects • Focus on implementation 30
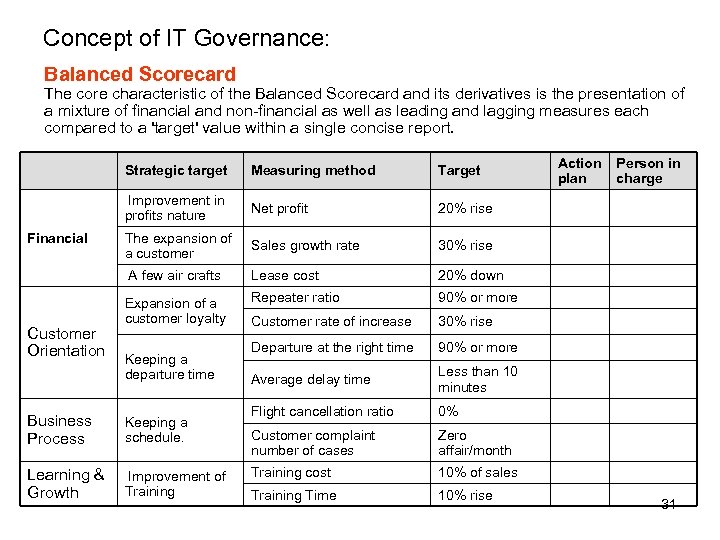 Concept of IT Governance: Balanced Scorecard The core characteristic of the Balanced Scorecard and its derivatives is the presentation of a mixture of financial and non-financial as well as leading and lagging measures each compared to a 'target' value within a single concise report. Customer Orientation Measuring method Target Action plan Person in charge Net profit 20% rise The expansion of a customer Sales growth rate 30% rise A few air crafts Financial Strategic target Improvement in profits nature Lease cost 20% down Expansion of a customer loyalty Repeater ratio 90% or more Customer rate of increase 30% rise Departure at the right time 90% or more Average delay time Less than 10 minutes Flight cancellation ratio 0% Customer complaint number of cases Zero affair/month Training cost 10% of sales Training Time 10% rise Keeping a departure time Business Process Keeping a schedule. Learning & Growth Improvement of Training 31
Concept of IT Governance: Balanced Scorecard The core characteristic of the Balanced Scorecard and its derivatives is the presentation of a mixture of financial and non-financial as well as leading and lagging measures each compared to a 'target' value within a single concise report. Customer Orientation Measuring method Target Action plan Person in charge Net profit 20% rise The expansion of a customer Sales growth rate 30% rise A few air crafts Financial Strategic target Improvement in profits nature Lease cost 20% down Expansion of a customer loyalty Repeater ratio 90% or more Customer rate of increase 30% rise Departure at the right time 90% or more Average delay time Less than 10 minutes Flight cancellation ratio 0% Customer complaint number of cases Zero affair/month Training cost 10% of sales Training Time 10% rise Keeping a departure time Business Process Keeping a schedule. Learning & Growth Improvement of Training 31
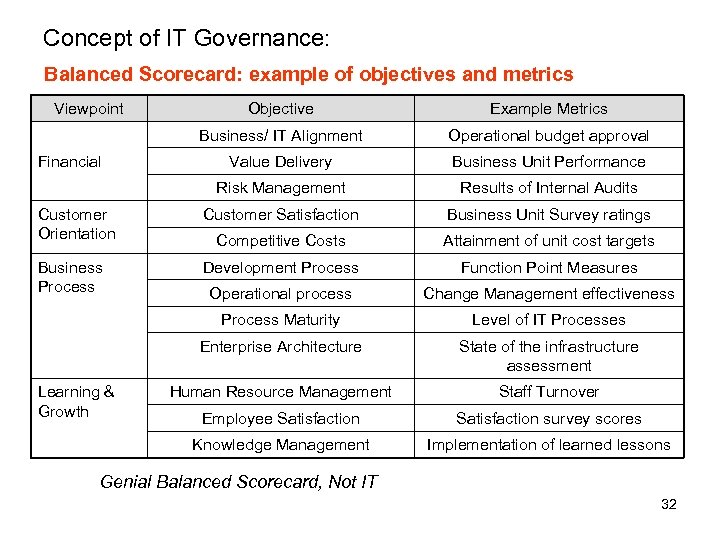 Concept of IT Governance: Balanced Scorecard: example of objectives and metrics Viewpoint Objective Example Metrics Business/ IT Alignment Operational budget approval Value Delivery Business Unit Performance Risk Management Results of Internal Audits Customer Orientation Customer Satisfaction Business Unit Survey ratings Competitive Costs Attainment of unit cost targets Business Process Development Process Function Point Measures Operational process Change Management effectiveness Process Maturity Level of IT Processes Enterprise Architecture State of the infrastructure assessment Human Resource Management Staff Turnover Employee Satisfaction survey scores Knowledge Management Implementation of learned lessons Financial Learning & Growth Genial Balanced Scorecard, Not IT 32
Concept of IT Governance: Balanced Scorecard: example of objectives and metrics Viewpoint Objective Example Metrics Business/ IT Alignment Operational budget approval Value Delivery Business Unit Performance Risk Management Results of Internal Audits Customer Orientation Customer Satisfaction Business Unit Survey ratings Competitive Costs Attainment of unit cost targets Business Process Development Process Function Point Measures Operational process Change Management effectiveness Process Maturity Level of IT Processes Enterprise Architecture State of the infrastructure assessment Human Resource Management Staff Turnover Employee Satisfaction survey scores Knowledge Management Implementation of learned lessons Financial Learning & Growth Genial Balanced Scorecard, Not IT 32
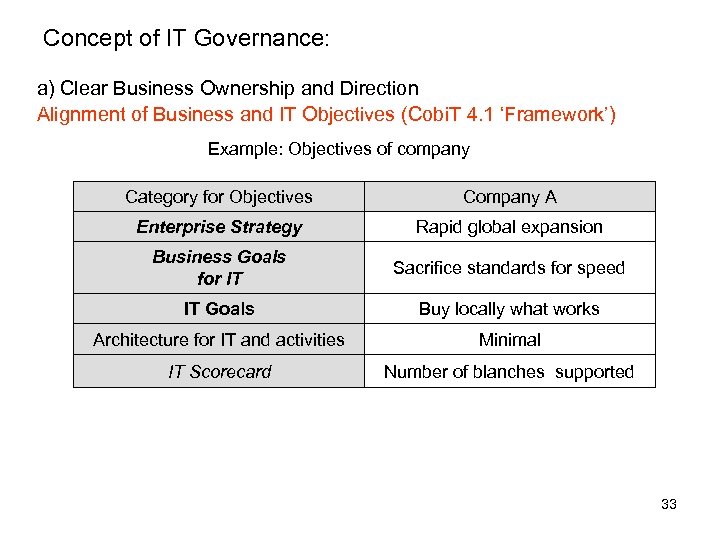 Concept of IT Governance: a) Clear Business Ownership and Direction Alignment of Business and IT Objectives (Cobi. T 4. 1 ‘Framework’) Example: Objectives of company Category for Objectives Company A Enterprise Strategy Rapid global expansion Business Goals for IT Sacrifice standards for speed IT Goals Buy locally what works Architecture for IT and activities Minimal IT Scorecard Number of blanches supported 33
Concept of IT Governance: a) Clear Business Ownership and Direction Alignment of Business and IT Objectives (Cobi. T 4. 1 ‘Framework’) Example: Objectives of company Category for Objectives Company A Enterprise Strategy Rapid global expansion Business Goals for IT Sacrifice standards for speed IT Goals Buy locally what works Architecture for IT and activities Minimal IT Scorecard Number of blanches supported 33
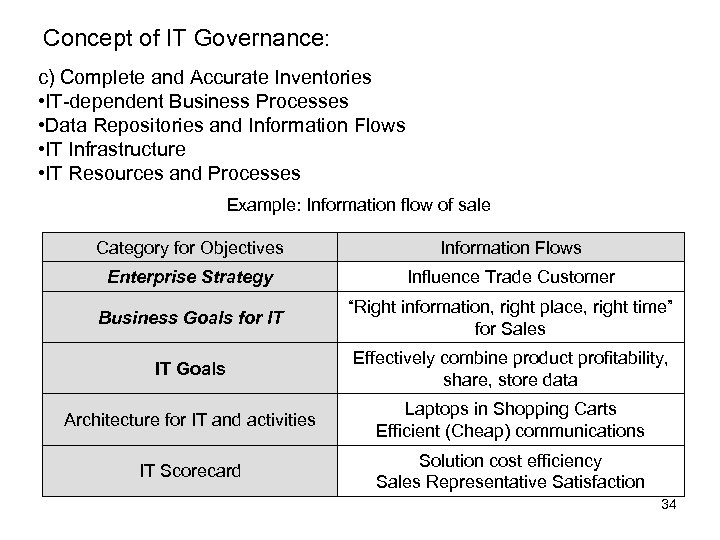 Concept of IT Governance: c) Complete and Accurate Inventories • IT-dependent Business Processes • Data Repositories and Information Flows • IT Infrastructure • IT Resources and Processes Example: Information flow of sale Category for Objectives Information Flows Enterprise Strategy Influence Trade Customer Business Goals for IT “Right information, right place, right time” for Sales IT Goals Effectively combine product profitability, share, store data Architecture for IT and activities Laptops in Shopping Carts Efficient (Cheap) communications IT Scorecard Solution cost efficiency Sales Representative Satisfaction 34
Concept of IT Governance: c) Complete and Accurate Inventories • IT-dependent Business Processes • Data Repositories and Information Flows • IT Infrastructure • IT Resources and Processes Example: Information flow of sale Category for Objectives Information Flows Enterprise Strategy Influence Trade Customer Business Goals for IT “Right information, right place, right time” for Sales IT Goals Effectively combine product profitability, share, store data Architecture for IT and activities Laptops in Shopping Carts Efficient (Cheap) communications IT Scorecard Solution cost efficiency Sales Representative Satisfaction 34
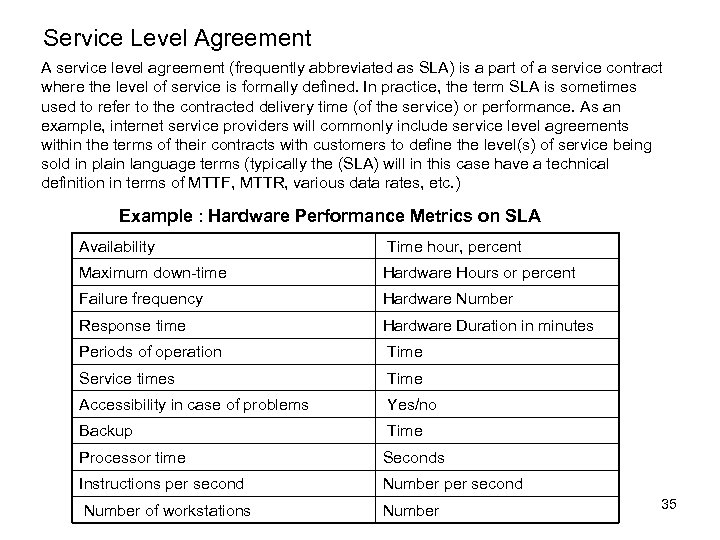 Service Level Agreement A service level agreement (frequently abbreviated as SLA) is a part of a service contract where the level of service is formally defined. In practice, the term SLA is sometimes used to refer to the contracted delivery time (of the service) or performance. As an example, internet service providers will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms (typically the (SLA) will in this case have a technical definition in terms of MTTF, MTTR, various data rates, etc. ) Example : Hardware Performance Metrics on SLA Availability Time hour, percent Maximum down-time Hardware Hours or percent Failure frequency Hardware Number Response time Hardware Duration in minutes Periods of operation Time Service times Time Accessibility in case of problems Yes/no Backup Time Processor time Seconds Instructions per second Number of workstations Number 35
Service Level Agreement A service level agreement (frequently abbreviated as SLA) is a part of a service contract where the level of service is formally defined. In practice, the term SLA is sometimes used to refer to the contracted delivery time (of the service) or performance. As an example, internet service providers will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms (typically the (SLA) will in this case have a technical definition in terms of MTTF, MTTR, various data rates, etc. ) Example : Hardware Performance Metrics on SLA Availability Time hour, percent Maximum down-time Hardware Hours or percent Failure frequency Hardware Number Response time Hardware Duration in minutes Periods of operation Time Service times Time Accessibility in case of problems Yes/no Backup Time Processor time Seconds Instructions per second Number of workstations Number 35
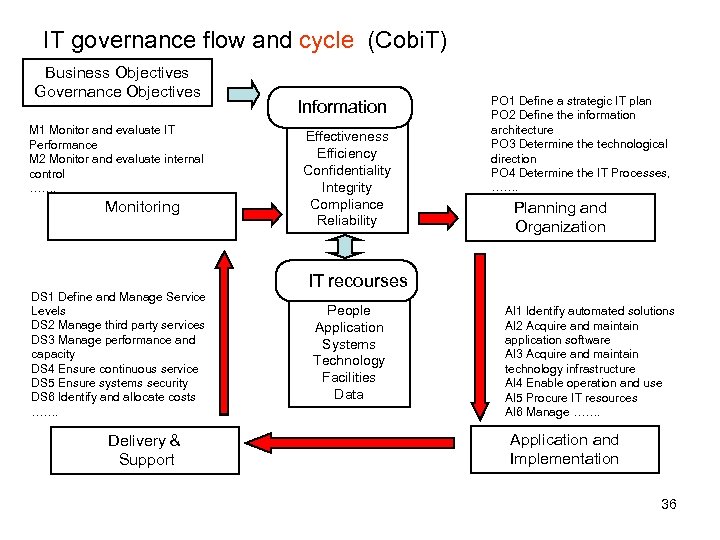 IT governance flow and cycle (Cobi. T) Business Objectives Governance Objectives M 1 Monitor and evaluate IT Performance M 2 Monitor and evaluate internal control ……. Monitoring DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage third party services DS 3 Manage performance and capacity DS 4 Ensure continuous service DS 5 Ensure systems security DS 6 Identify and allocate costs ……. Delivery & Support Information Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality Integrity Compliance Reliability PO 1 Define a strategic IT plan PO 2 Define the information architecture PO 3 Determine the technological direction PO 4 Determine the IT Processes, ……. Planning and Organization IT recourses People Application Systems Technology Facilities Data AI 1 Identify automated solutions AI 2 Acquire and maintain application software AI 3 Acquire and maintain technology infrastructure AI 4 Enable operation and use AI 5 Procure IT resources AI 6 Manage ……. Application and Implementation 36
IT governance flow and cycle (Cobi. T) Business Objectives Governance Objectives M 1 Monitor and evaluate IT Performance M 2 Monitor and evaluate internal control ……. Monitoring DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage third party services DS 3 Manage performance and capacity DS 4 Ensure continuous service DS 5 Ensure systems security DS 6 Identify and allocate costs ……. Delivery & Support Information Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality Integrity Compliance Reliability PO 1 Define a strategic IT plan PO 2 Define the information architecture PO 3 Determine the technological direction PO 4 Determine the IT Processes, ……. Planning and Organization IT recourses People Application Systems Technology Facilities Data AI 1 Identify automated solutions AI 2 Acquire and maintain application software AI 3 Acquire and maintain technology infrastructure AI 4 Enable operation and use AI 5 Procure IT resources AI 6 Manage ……. Application and Implementation 36
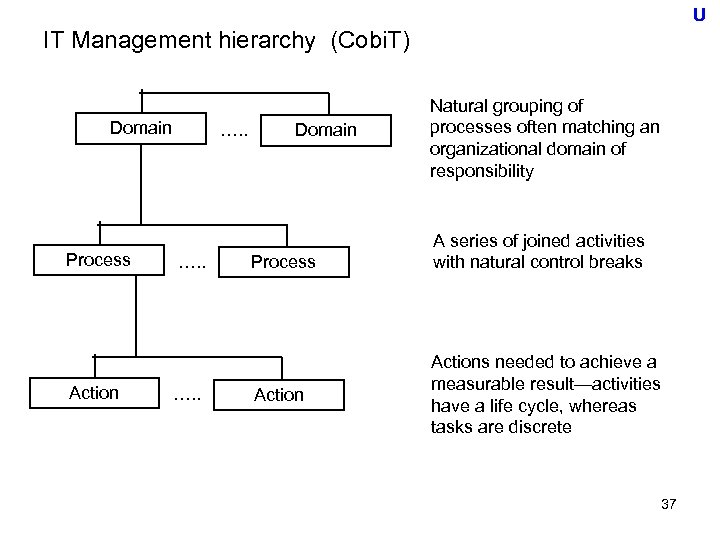 U IT Management hierarchy (Cobi. T) Domain Process Action …. . Domain Process Action Natural grouping of processes often matching an organizational domain of responsibility A series of joined activities with natural control breaks Actions needed to achieve a measurable result—activities have a life cycle, whereas tasks are discrete 37
U IT Management hierarchy (Cobi. T) Domain Process Action …. . Domain Process Action Natural grouping of processes often matching an organizational domain of responsibility A series of joined activities with natural control breaks Actions needed to achieve a measurable result—activities have a life cycle, whereas tasks are discrete 37
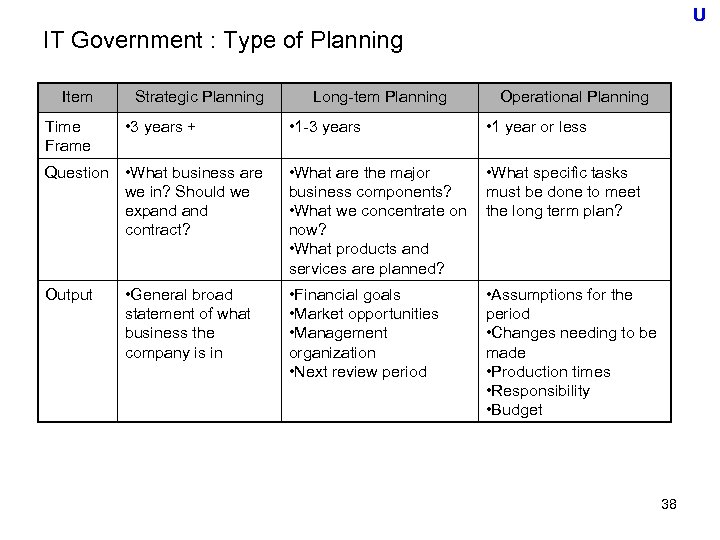 U IT Government : Type of Planning Item Time Frame Strategic Planning • 3 years + Question • What business are we in? Should we expand contract? Output • General broad statement of what business the company is in Long-tem Planning Operational Planning • 1 -3 years • 1 year or less • What are the major business components? • What we concentrate on now? • What products and services are planned? • What specific tasks must be done to meet the long term plan? • Financial goals • Market opportunities • Management organization • Next review period • Assumptions for the period • Changes needing to be made • Production times • Responsibility • Budget 38
U IT Government : Type of Planning Item Time Frame Strategic Planning • 3 years + Question • What business are we in? Should we expand contract? Output • General broad statement of what business the company is in Long-tem Planning Operational Planning • 1 -3 years • 1 year or less • What are the major business components? • What we concentrate on now? • What products and services are planned? • What specific tasks must be done to meet the long term plan? • Financial goals • Market opportunities • Management organization • Next review period • Assumptions for the period • Changes needing to be made • Production times • Responsibility • Budget 38
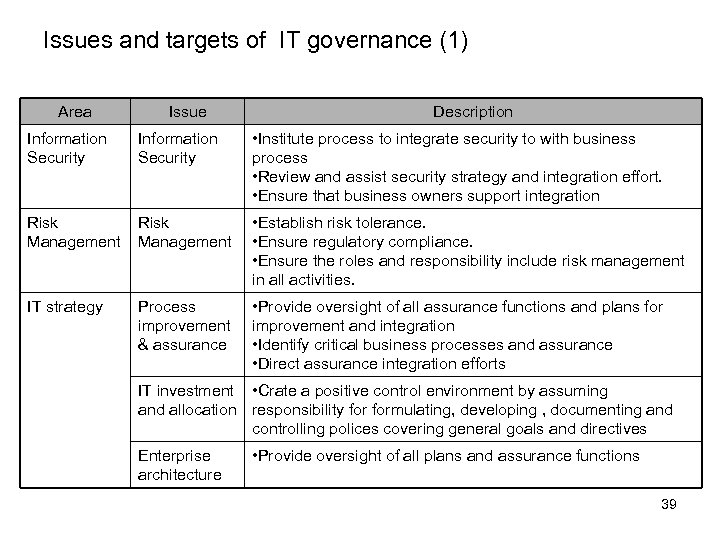 Issues and targets of IT governance (1) Area Issue Description Information Security • Institute process to integrate security to with business process • Review and assist security strategy and integration effort. • Ensure that business owners support integration Risk Management • Establish risk tolerance. • Ensure regulatory compliance. • Ensure the roles and responsibility include risk management in all activities. IT strategy Process improvement & assurance • Provide oversight of all assurance functions and plans for improvement and integration • Identify critical business processes and assurance • Direct assurance integration efforts IT investment • Crate a positive control environment by assuming and allocation responsibility formulating, developing , documenting and controlling polices covering general goals and directives Enterprise architecture • Provide oversight of all plans and assurance functions 39
Issues and targets of IT governance (1) Area Issue Description Information Security • Institute process to integrate security to with business process • Review and assist security strategy and integration effort. • Ensure that business owners support integration Risk Management • Establish risk tolerance. • Ensure regulatory compliance. • Ensure the roles and responsibility include risk management in all activities. IT strategy Process improvement & assurance • Provide oversight of all assurance functions and plans for improvement and integration • Identify critical business processes and assurance • Direct assurance integration efforts IT investment • Crate a positive control environment by assuming and allocation responsibility formulating, developing , documenting and controlling polices covering general goals and directives Enterprise architecture • Provide oversight of all plans and assurance functions 39
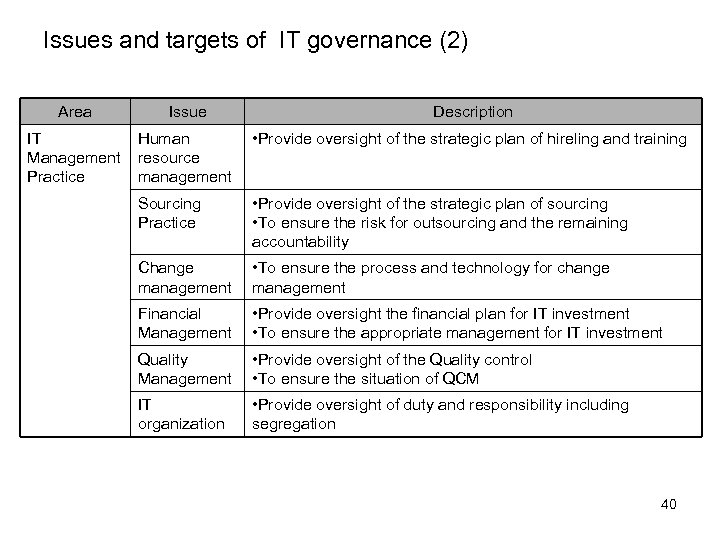 Issues and targets of IT governance (2) Area Issue Description IT Management Practice Human resource management • Provide oversight of the strategic plan of hireling and training Sourcing Practice • Provide oversight of the strategic plan of sourcing • To ensure the risk for outsourcing and the remaining accountability Change management • To ensure the process and technology for change management Financial Management • Provide oversight the financial plan for IT investment • To ensure the appropriate management for IT investment Quality Management • Provide oversight of the Quality control • To ensure the situation of QCM IT organization • Provide oversight of duty and responsibility including segregation 40
Issues and targets of IT governance (2) Area Issue Description IT Management Practice Human resource management • Provide oversight of the strategic plan of hireling and training Sourcing Practice • Provide oversight of the strategic plan of sourcing • To ensure the risk for outsourcing and the remaining accountability Change management • To ensure the process and technology for change management Financial Management • Provide oversight the financial plan for IT investment • To ensure the appropriate management for IT investment Quality Management • Provide oversight of the Quality control • To ensure the situation of QCM IT organization • Provide oversight of duty and responsibility including segregation 40
 1 -3. Risk Management 41
1 -3. Risk Management 41
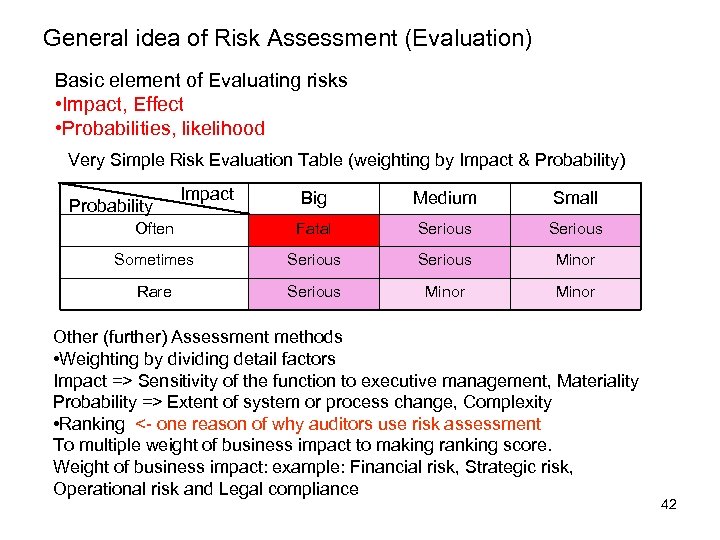 General idea of Risk Assessment (Evaluation) Basic element of Evaluating risks • Impact, Effect • Probabilities, likelihood Very Simple Risk Evaluation Table (weighting by Impact & Probability) Impact Big Medium Small Often Fatal Serious Sometimes Serious Minor Rare Serious Minor Probability Other (further) Assessment methods • Weighting by dividing detail factors Impact => Sensitivity of the function to executive management, Materiality Probability => Extent of system or process change, Complexity • Ranking <- one reason of why auditors use risk assessment To multiple weight of business impact to making ranking score. Weight of business impact: example: Financial risk, Strategic risk, Operational risk and Legal compliance 42
General idea of Risk Assessment (Evaluation) Basic element of Evaluating risks • Impact, Effect • Probabilities, likelihood Very Simple Risk Evaluation Table (weighting by Impact & Probability) Impact Big Medium Small Often Fatal Serious Sometimes Serious Minor Rare Serious Minor Probability Other (further) Assessment methods • Weighting by dividing detail factors Impact => Sensitivity of the function to executive management, Materiality Probability => Extent of system or process change, Complexity • Ranking <- one reason of why auditors use risk assessment To multiple weight of business impact to making ranking score. Weight of business impact: example: Financial risk, Strategic risk, Operational risk and Legal compliance 42
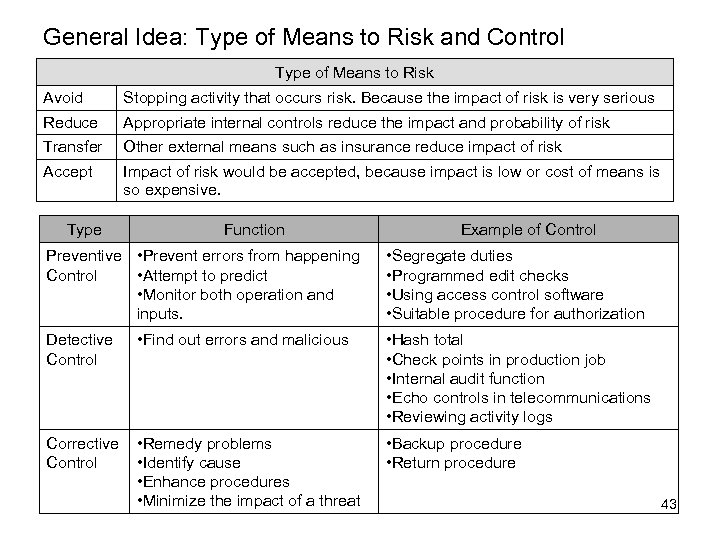 General Idea: Type of Means to Risk and Control Type of Means to Risk Avoid Stopping activity that occurs risk. Because the impact of risk is very serious Reduce Appropriate internal controls reduce the impact and probability of risk Transfer Other external means such as insurance reduce impact of risk Accept Impact of risk would be accepted, because impact is low or cost of means is so expensive. Type Function Preventive • Prevent errors from happening Control • Attempt to predict • Monitor both operation and inputs. Example of Control • Segregate duties • Programmed edit checks • Using access control software • Suitable procedure for authorization Detective Control • Find out errors and malicious • Hash total • Check points in production job • Internal audit function • Echo controls in telecommunications • Reviewing activity logs Corrective Control • Remedy problems • Identify cause • Enhance procedures • Minimize the impact of a threat • Backup procedure • Return procedure 43
General Idea: Type of Means to Risk and Control Type of Means to Risk Avoid Stopping activity that occurs risk. Because the impact of risk is very serious Reduce Appropriate internal controls reduce the impact and probability of risk Transfer Other external means such as insurance reduce impact of risk Accept Impact of risk would be accepted, because impact is low or cost of means is so expensive. Type Function Preventive • Prevent errors from happening Control • Attempt to predict • Monitor both operation and inputs. Example of Control • Segregate duties • Programmed edit checks • Using access control software • Suitable procedure for authorization Detective Control • Find out errors and malicious • Hash total • Check points in production job • Internal audit function • Echo controls in telecommunications • Reviewing activity logs Corrective Control • Remedy problems • Identify cause • Enhance procedures • Minimize the impact of a threat • Backup procedure • Return procedure 43
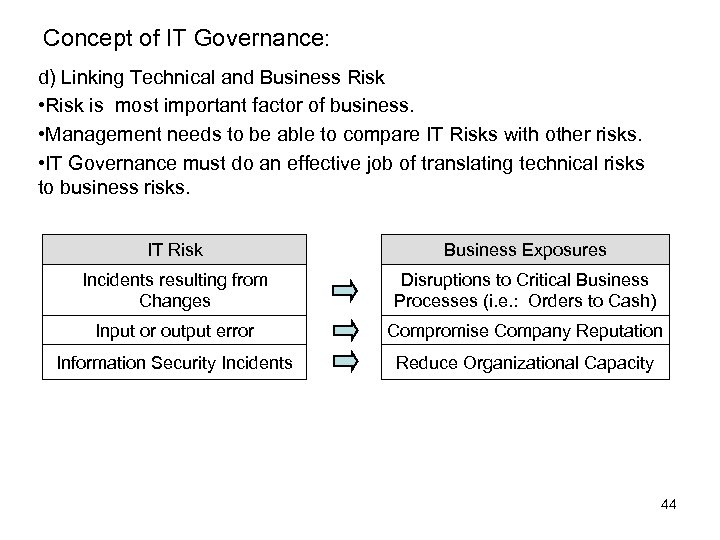 Concept of IT Governance: d) Linking Technical and Business Risk • Risk is most important factor of business. • Management needs to be able to compare IT Risks with other risks. • IT Governance must do an effective job of translating technical risks to business risks. IT Risk Business Exposures Incidents resulting from Changes Disruptions to Critical Business Processes (i. e. : Orders to Cash) Input or output error Compromise Company Reputation Information Security Incidents Reduce Organizational Capacity 44
Concept of IT Governance: d) Linking Technical and Business Risk • Risk is most important factor of business. • Management needs to be able to compare IT Risks with other risks. • IT Governance must do an effective job of translating technical risks to business risks. IT Risk Business Exposures Incidents resulting from Changes Disruptions to Critical Business Processes (i. e. : Orders to Cash) Input or output error Compromise Company Reputation Information Security Incidents Reduce Organizational Capacity 44
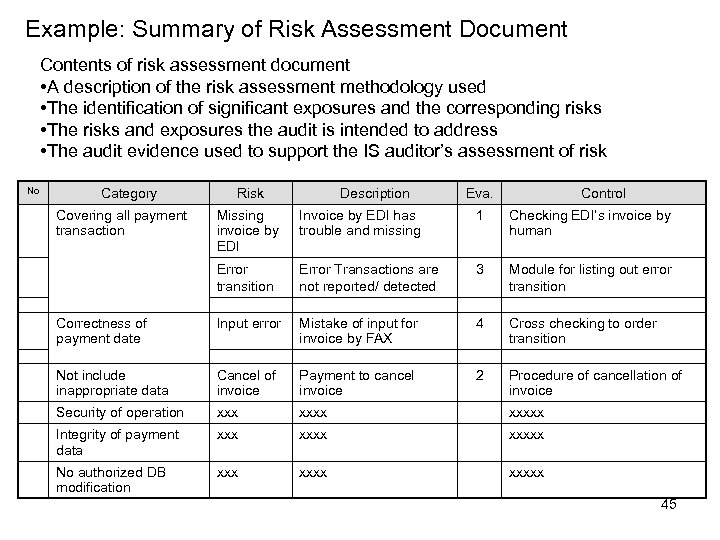 Example: Summary of Risk Assessment Document Contents of risk assessment document • A description of the risk assessment methodology used • The identification of significant exposures and the corresponding risks • The risks and exposures the audit is intended to address • The audit evidence used to support the IS auditor’s assessment of risk No Category Covering all payment transaction Risk Description Eva. Control Missing invoice by EDI Invoice by EDI has trouble and missing 1 Checking EDI’s invoice by human Error transition Error Transactions are not reported/ detected 3 Module for listing out error transition Correctness of payment date Input error Mistake of input for invoice by FAX 4 Cross checking to order transition Not include inappropriate data Cancel of invoice Payment to cancel invoice 2 Procedure of cancellation of invoice Security of operation xxxxx Integrity of payment data xxxxx No authorized DB modification xxxxx 45
Example: Summary of Risk Assessment Document Contents of risk assessment document • A description of the risk assessment methodology used • The identification of significant exposures and the corresponding risks • The risks and exposures the audit is intended to address • The audit evidence used to support the IS auditor’s assessment of risk No Category Covering all payment transaction Risk Description Eva. Control Missing invoice by EDI Invoice by EDI has trouble and missing 1 Checking EDI’s invoice by human Error transition Error Transactions are not reported/ detected 3 Module for listing out error transition Correctness of payment date Input error Mistake of input for invoice by FAX 4 Cross checking to order transition Not include inappropriate data Cancel of invoice Payment to cancel invoice 2 Procedure of cancellation of invoice Security of operation xxxxx Integrity of payment data xxxxx No authorized DB modification xxxxx 45
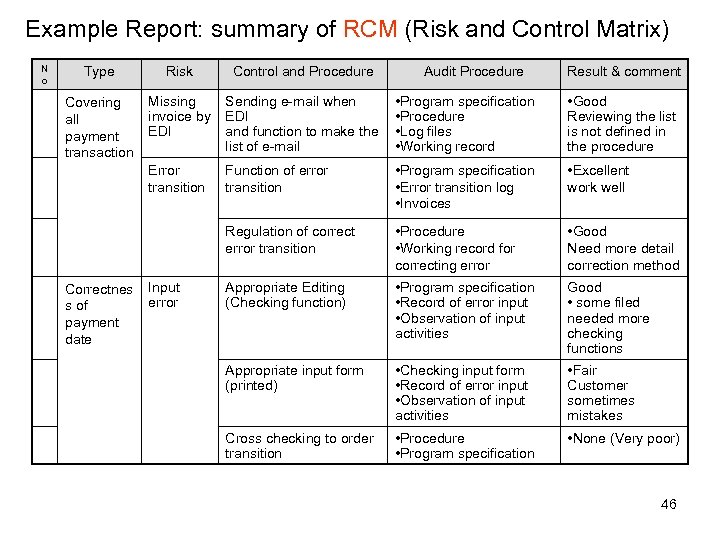 Example Report: summary of RCM (Risk and Control Matrix) N o Type Risk Control and Procedure Covering all payment transaction Missing invoice by EDI Sending e-mail when EDI and function to make the list of e-mail • Program specification • Procedure • Log files • Working record • Good Reviewing the list is not defined in the procedure Error transition Function of error transition • Program specification • Error transition log • Invoices • Excellent work well Regulation of correct error transition • Procedure • Working record for correcting error • Good Need more detail correction method Appropriate Editing (Checking function) • Program specification • Record of error input • Observation of input activities Good • some filed needed more checking functions Appropriate input form (printed) • Checking input form • Record of error input • Observation of input activities • Fair Customer sometimes mistakes Cross checking to order transition • Procedure • Program specification • None (Very poor) Correctnes s of payment date Input error Audit Procedure Result & comment 46
Example Report: summary of RCM (Risk and Control Matrix) N o Type Risk Control and Procedure Covering all payment transaction Missing invoice by EDI Sending e-mail when EDI and function to make the list of e-mail • Program specification • Procedure • Log files • Working record • Good Reviewing the list is not defined in the procedure Error transition Function of error transition • Program specification • Error transition log • Invoices • Excellent work well Regulation of correct error transition • Procedure • Working record for correcting error • Good Need more detail correction method Appropriate Editing (Checking function) • Program specification • Record of error input • Observation of input activities Good • some filed needed more checking functions Appropriate input form (printed) • Checking input form • Record of error input • Observation of input activities • Fair Customer sometimes mistakes Cross checking to order transition • Procedure • Program specification • None (Very poor) Correctnes s of payment date Input error Audit Procedure Result & comment 46
 1 -4. ITAC: IT Application Control and Application development 47
1 -4. ITAC: IT Application Control and Application development 47
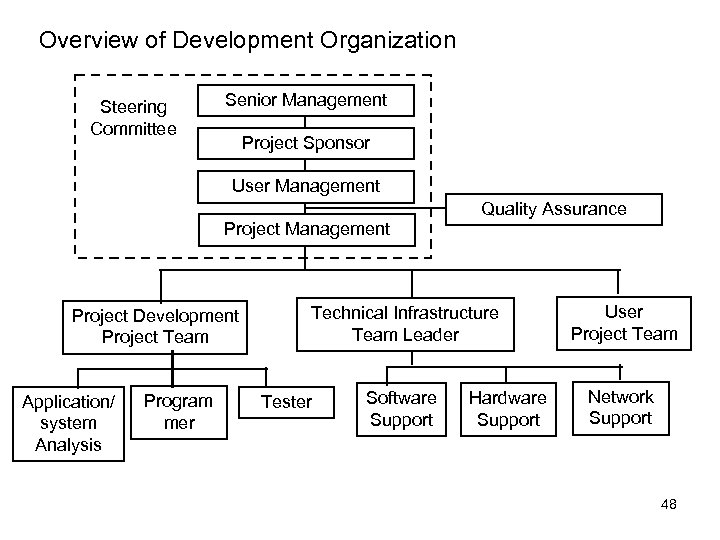 Overview of Development Organization Steering Committee Senior Management Project Sponsor User Management Quality Assurance Project Management Project Development Project Team Application/ system Analysis Program mer Technical Infrastructure Team Leader Tester Software Support Hardware Support User Project Team Network Support 48
Overview of Development Organization Steering Committee Senior Management Project Sponsor User Management Quality Assurance Project Management Project Development Project Team Application/ system Analysis Program mer Technical Infrastructure Team Leader Tester Software Support Hardware Support User Project Team Network Support 48
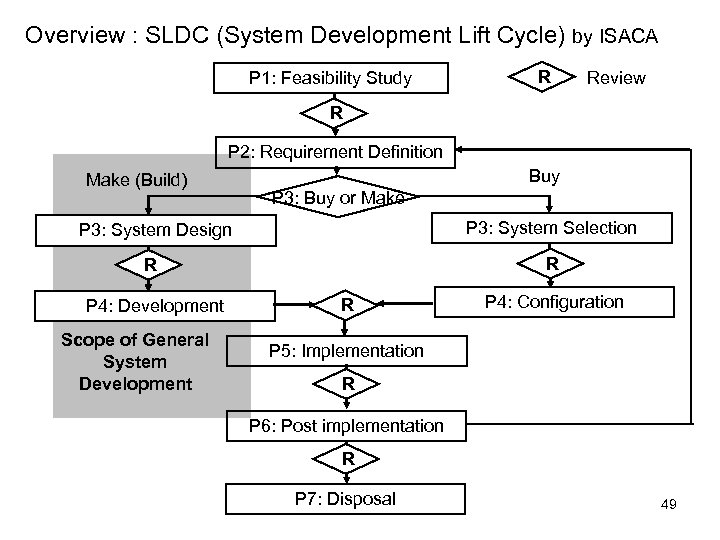 Overview : SLDC (System Development Lift Cycle) by ISACA P 1: Feasibility Study R Review R P 2: Requirement Definition Make (Build) Buy P 3: Buy or Make P 3: System Design P 3: System Selection R R P 4: Development Scope of General System Development R P 4: Configuration P 5: Implementation R P 6: Post implementation R P 7: Disposal 49
Overview : SLDC (System Development Lift Cycle) by ISACA P 1: Feasibility Study R Review R P 2: Requirement Definition Make (Build) Buy P 3: Buy or Make P 3: System Design P 3: System Selection R R P 4: Development Scope of General System Development R P 4: Configuration P 5: Implementation R P 6: Post implementation R P 7: Disposal 49
 Overview of SLDC Phase 1 and 2 Phase 1: Feasibility Study To determine the strategic benefit of new information system and analyze possible resolutions to realize needs • Define business case • Define the objectives with supporting evidence. • List up possible resolutions • Perform preliminary risk assessment • Agree upon an initial budget and expected return on investment (ROI) Phase 2: Requirement definition To create detail definition of needs including inputs, output, current environment and proposed interaction. • Collect specifications (requirements) and supporting evidence. • Identify which standard (technology) will be implemented for the specifications. • Create a quality control plan to ensure that the design complaints to the specifications. 50
Overview of SLDC Phase 1 and 2 Phase 1: Feasibility Study To determine the strategic benefit of new information system and analyze possible resolutions to realize needs • Define business case • Define the objectives with supporting evidence. • List up possible resolutions • Perform preliminary risk assessment • Agree upon an initial budget and expected return on investment (ROI) Phase 2: Requirement definition To create detail definition of needs including inputs, output, current environment and proposed interaction. • Collect specifications (requirements) and supporting evidence. • Identify which standard (technology) will be implemented for the specifications. • Create a quality control plan to ensure that the design complaints to the specifications. 50
 Overview of SLDC Phase 3 and 4 Phase 3: Plan solution and system design/ system selection To plan solution (strategy ) whether make (build) or buy based on the objectives from phase 1 and specifications from phase 2. Case of Build • Make design such as user requirement, basic design, detail design and operation design. ( start development process) Case of buy • Make RFP (Request for Proposal) to select best vendor and product based on specification in Phase 2. • Conduct bidding to select the vender and product Phase 4: Development and configuration Case of Build • Making program and conducting testing Case of buy • Customization is typically limited program configuration settings with a limited number of customized reports. 51
Overview of SLDC Phase 3 and 4 Phase 3: Plan solution and system design/ system selection To plan solution (strategy ) whether make (build) or buy based on the objectives from phase 1 and specifications from phase 2. Case of Build • Make design such as user requirement, basic design, detail design and operation design. ( start development process) Case of buy • Make RFP (Request for Proposal) to select best vendor and product based on specification in Phase 2. • Conduct bidding to select the vender and product Phase 4: Development and configuration Case of Build • Making program and conducting testing Case of buy • Customization is typically limited program configuration settings with a limited number of customized reports. 51
 Overview of SLDC Phase 5, 6 and 7 Phase 5: Implementation To install new system and final user acceptance (mainly function testing) test begins. The system undergoes a process of final certification and approval. Phase 6: post implementation After the system has been in production use, it is reviewed for effectiveness to full fill the original objectives. • Compare performance metrics to the original objectives. • Re-review the specifications and requirement annually. • Implement request for new requirement, update or disposal Phase 7: Disposal Final phase is the proper disposal of equipment and purging data. 52
Overview of SLDC Phase 5, 6 and 7 Phase 5: Implementation To install new system and final user acceptance (mainly function testing) test begins. The system undergoes a process of final certification and approval. Phase 6: post implementation After the system has been in production use, it is reviewed for effectiveness to full fill the original objectives. • Compare performance metrics to the original objectives. • Re-review the specifications and requirement annually. • Implement request for new requirement, update or disposal Phase 7: Disposal Final phase is the proper disposal of equipment and purging data. 52
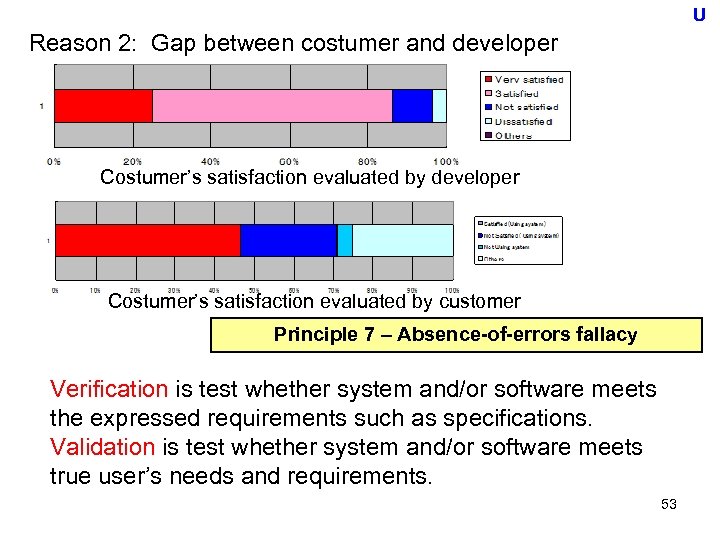 U Reason 2: Gap between costumer and developer Costumer’s satisfaction evaluated by customer Principle 7 – Absence-of-errors fallacy Verification is test whether system and/or software meets the expressed requirements such as specifications. Validation is test whether system and/or software meets true user’s needs and requirements. 53
U Reason 2: Gap between costumer and developer Costumer’s satisfaction evaluated by customer Principle 7 – Absence-of-errors fallacy Verification is test whether system and/or software meets the expressed requirements such as specifications. Validation is test whether system and/or software meets true user’s needs and requirements. 53
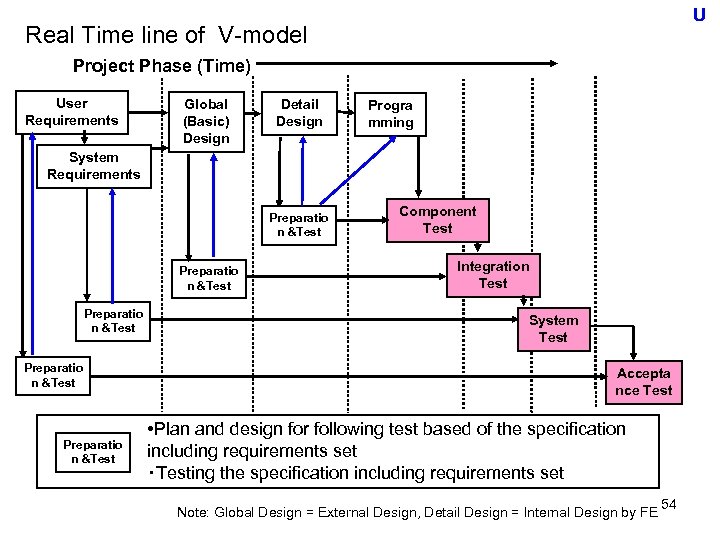 U Real Time line of V-model Project Phase (Time) User Requirements Global (Basic) Design Detail Design Progra mming System Requirements Preparatio n &Test Preparatio n &Test Component Test Integration Test System Test Accepta nce Test • Plan and design for following test based of the specification including requirements set ・Testing the specification including requirements set Note: Global Design = External Design, Detail Design = Internal Design by FE 54
U Real Time line of V-model Project Phase (Time) User Requirements Global (Basic) Design Detail Design Progra mming System Requirements Preparatio n &Test Preparatio n &Test Component Test Integration Test System Test Accepta nce Test • Plan and design for following test based of the specification including requirements set ・Testing the specification including requirements set Note: Global Design = External Design, Detail Design = Internal Design by FE 54
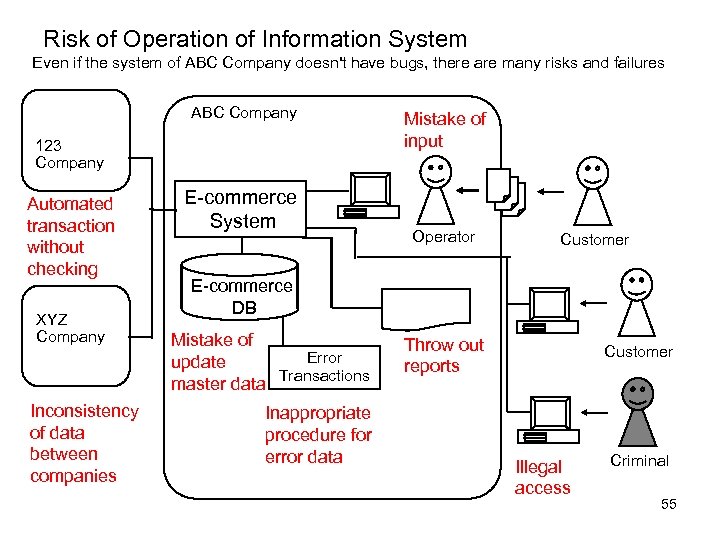 Risk of Operation of Information System Even if the system of ABC Company doesn't have bugs, there are many risks and failures ABC Company 123 Company Automated transaction without checking XYZ Company Inconsistency of data between companies E-commerce System Mistake of input Operator Customer E-commerce DB Mistake of Error update Transactions master data Inappropriate procedure for error data Throw out reports Customer Illegal access Criminal 55
Risk of Operation of Information System Even if the system of ABC Company doesn't have bugs, there are many risks and failures ABC Company 123 Company Automated transaction without checking XYZ Company Inconsistency of data between companies E-commerce System Mistake of input Operator Customer E-commerce DB Mistake of Error update Transactions master data Inappropriate procedure for error data Throw out reports Customer Illegal access Criminal 55
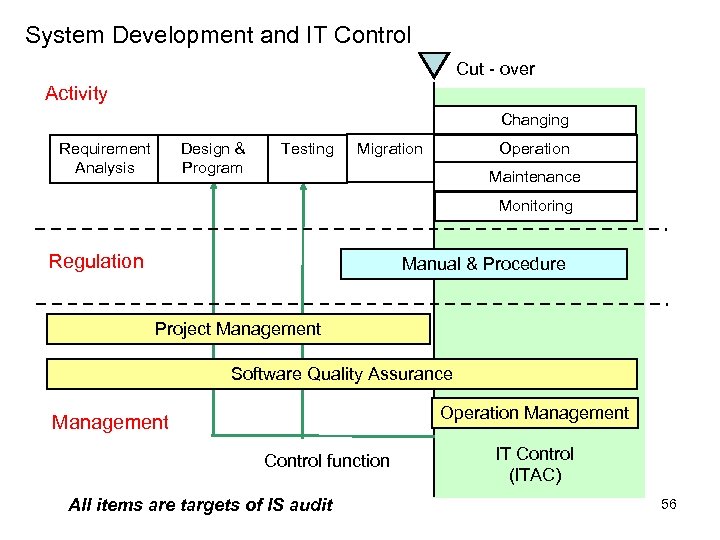 System Development and IT Control Cut - over Activity Changing Requirement Analysis Design & Program Testing Migration Operation Maintenance Monitoring Regulation Manual & Procedure Project Management Software Quality Assurance Operation Management Control function All items are targets of IS audit IT Control (ITAC) 56
System Development and IT Control Cut - over Activity Changing Requirement Analysis Design & Program Testing Migration Operation Maintenance Monitoring Regulation Manual & Procedure Project Management Software Quality Assurance Operation Management Control function All items are targets of IS audit IT Control (ITAC) 56
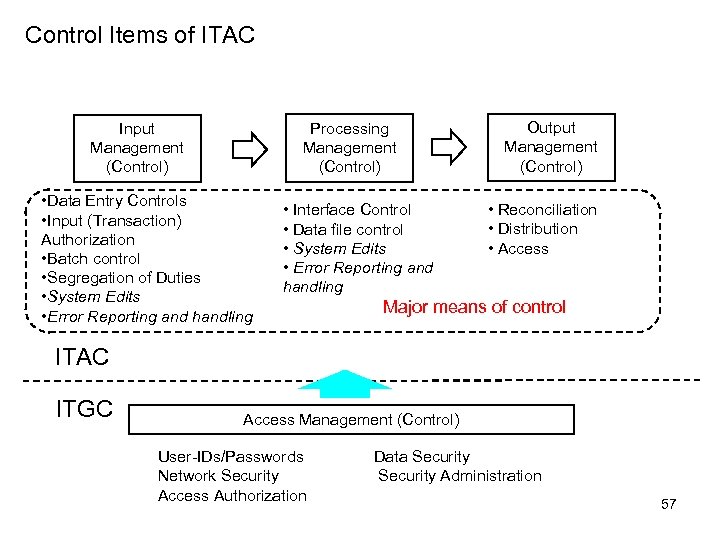 Control Items of ITAC Processing Management (Control) Input Management (Control) • Data Entry Controls • Input (Transaction) Authorization • Batch control • Segregation of Duties • System Edits • Error Reporting and handling • Interface Control • Data file control • System Edits • Error Reporting and handling Output Management (Control) • Reconciliation • Distribution • Access Major means of control ITAC ITGC Access Management (Control) User-IDs/Passwords Network Security Access Authorization Data Security Administration 57
Control Items of ITAC Processing Management (Control) Input Management (Control) • Data Entry Controls • Input (Transaction) Authorization • Batch control • Segregation of Duties • System Edits • Error Reporting and handling • Interface Control • Data file control • System Edits • Error Reporting and handling Output Management (Control) • Reconciliation • Distribution • Access Major means of control ITAC ITGC Access Management (Control) User-IDs/Passwords Network Security Access Authorization Data Security Administration 57
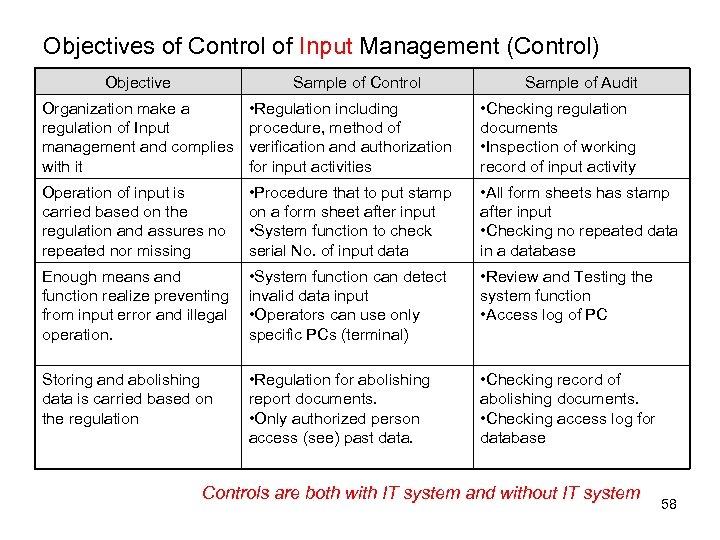 Objectives of Control of Input Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of Input management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for input activities • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of input activity Operation of input is carried based on the regulation and assures no repeated nor missing • Procedure that to put stamp on a form sheet after input • System function to check serial No. of input data • All form sheets has stamp after input • Checking no repeated data in a database Enough means and function realize preventing from input error and illegal operation. • System function can detect invalid data input • Operators can use only specific PCs (terminal) • Review and Testing the system function • Access log of PC Storing and abolishing data is carried based on the regulation • Regulation for abolishing report documents. • Only authorized person access (see) past data. • Checking record of abolishing documents. • Checking access log for database Controls are both with IT system and without IT system 58
Objectives of Control of Input Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of Input management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for input activities • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of input activity Operation of input is carried based on the regulation and assures no repeated nor missing • Procedure that to put stamp on a form sheet after input • System function to check serial No. of input data • All form sheets has stamp after input • Checking no repeated data in a database Enough means and function realize preventing from input error and illegal operation. • System function can detect invalid data input • Operators can use only specific PCs (terminal) • Review and Testing the system function • Access log of PC Storing and abolishing data is carried based on the regulation • Regulation for abolishing report documents. • Only authorized person access (see) past data. • Checking record of abolishing documents. • Checking access log for database Controls are both with IT system and without IT system 58
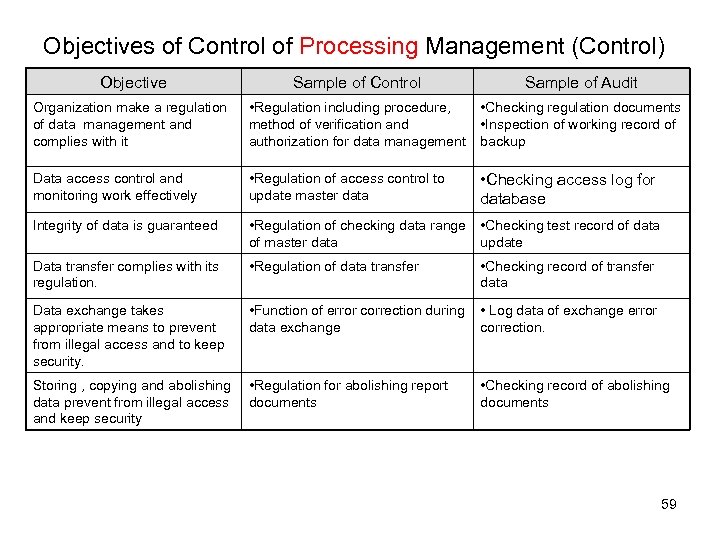 Objectives of Control of Processing Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of data management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for data management • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of backup Data access control and monitoring work effectively • Regulation of access control to update master data • Checking access log for database Integrity of data is guaranteed • Regulation of checking data range • Checking test record of data of master data update Data transfer complies with its regulation. • Regulation of data transfer • Checking record of transfer data Data exchange takes appropriate means to prevent from illegal access and to keep security. • Function of error correction during data exchange • Log data of exchange error correction. Storing , copying and abolishing data prevent from illegal access and keep security • Regulation for abolishing report documents • Checking record of abolishing documents 59
Objectives of Control of Processing Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of data management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for data management • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of backup Data access control and monitoring work effectively • Regulation of access control to update master data • Checking access log for database Integrity of data is guaranteed • Regulation of checking data range • Checking test record of data of master data update Data transfer complies with its regulation. • Regulation of data transfer • Checking record of transfer data Data exchange takes appropriate means to prevent from illegal access and to keep security. • Function of error correction during data exchange • Log data of exchange error correction. Storing , copying and abolishing data prevent from illegal access and keep security • Regulation for abolishing report documents • Checking record of abolishing documents 59
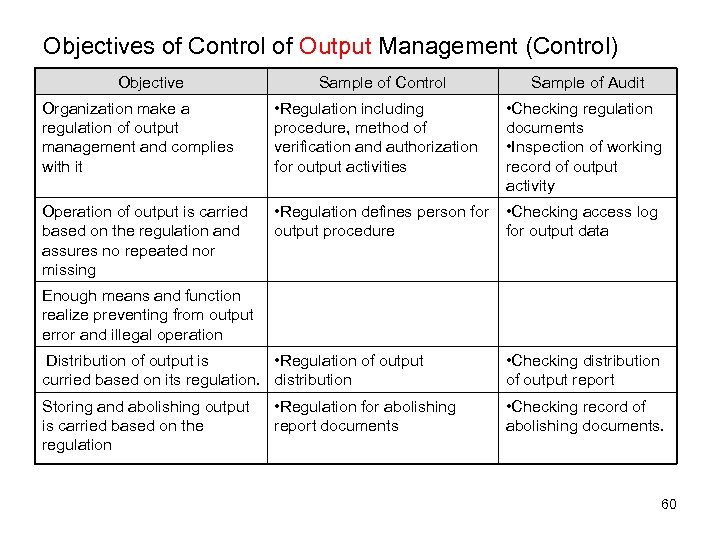 Objectives of Control of Output Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of output management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for output activities • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of output activity Operation of output is carried based on the regulation and assures no repeated nor missing • Regulation defines person for output procedure • Checking access log for output data Enough means and function realize preventing from output error and illegal operation Distribution of output is • Regulation of output curried based on its regulation. distribution Storing and abolishing output is carried based on the regulation • Regulation for abolishing report documents • Checking distribution of output report • Checking record of abolishing documents. 60
Objectives of Control of Output Management (Control) Objective Sample of Control Sample of Audit Organization make a regulation of output management and complies with it • Regulation including procedure, method of verification and authorization for output activities • Checking regulation documents • Inspection of working record of output activity Operation of output is carried based on the regulation and assures no repeated nor missing • Regulation defines person for output procedure • Checking access log for output data Enough means and function realize preventing from output error and illegal operation Distribution of output is • Regulation of output curried based on its regulation. distribution Storing and abolishing output is carried based on the regulation • Regulation for abolishing report documents • Checking distribution of output report • Checking record of abolishing documents. 60
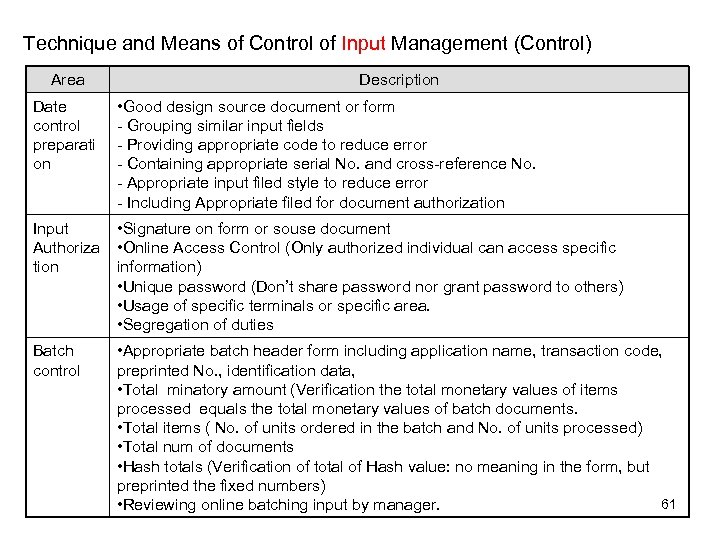 Technique and Means of Control of Input Management (Control) Area Description Date control preparati on • Good design source document or form - Grouping similar input fields - Providing appropriate code to reduce error - Containing appropriate serial No. and cross-reference No. - Appropriate input filed style to reduce error - Including Appropriate filed for document authorization Input Authoriza tion • Signature on form or souse document • Online Access Control (Only authorized individual can access specific information) • Unique password (Don’t share password nor grant password to others) • Usage of specific terminals or specific area. • Segregation of duties Batch control • Appropriate batch header form including application name, transaction code, preprinted No. , identification data, • Total minatory amount (Verification the total monetary values of items processed equals the total monetary values of batch documents. • Total items ( No. of units ordered in the batch and No. of units processed) • Total num of documents • Hash totals (Verification of total of Hash value: no meaning in the form, but preprinted the fixed numbers) 61 • Reviewing online batching input by manager.
Technique and Means of Control of Input Management (Control) Area Description Date control preparati on • Good design source document or form - Grouping similar input fields - Providing appropriate code to reduce error - Containing appropriate serial No. and cross-reference No. - Appropriate input filed style to reduce error - Including Appropriate filed for document authorization Input Authoriza tion • Signature on form or souse document • Online Access Control (Only authorized individual can access specific information) • Unique password (Don’t share password nor grant password to others) • Usage of specific terminals or specific area. • Segregation of duties Batch control • Appropriate batch header form including application name, transaction code, preprinted No. , identification data, • Total minatory amount (Verification the total monetary values of items processed equals the total monetary values of batch documents. • Total items ( No. of units ordered in the batch and No. of units processed) • Total num of documents • Hash totals (Verification of total of Hash value: no meaning in the form, but preprinted the fixed numbers) 61 • Reviewing online batching input by manager.
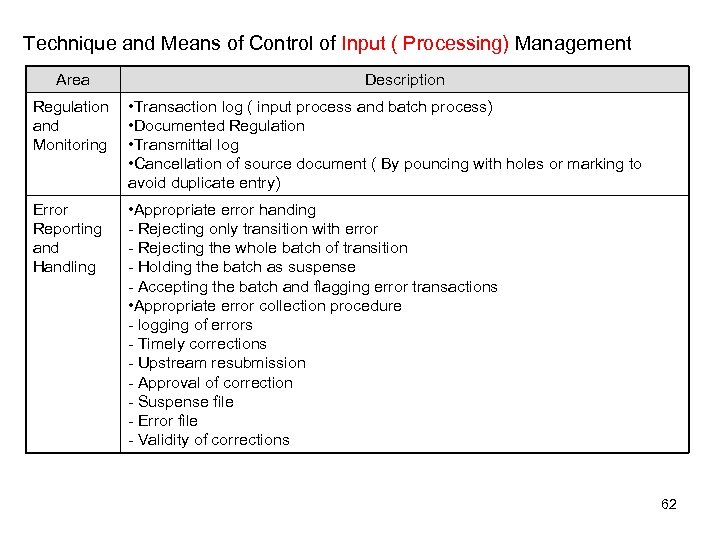 Technique and Means of Control of Input ( Processing) Management Area Description Regulation and Monitoring • Transaction log ( input process and batch process) • Documented Regulation • Transmittal log • Cancellation of source document ( By pouncing with holes or marking to avoid duplicate entry) Error Reporting and Handling • Appropriate error handing - Rejecting only transition with error - Rejecting the whole batch of transition - Holding the batch as suspense - Accepting the batch and flagging error transactions • Appropriate error collection procedure - logging of errors - Timely corrections - Upstream resubmission - Approval of correction - Suspense file - Error file - Validity of corrections 62
Technique and Means of Control of Input ( Processing) Management Area Description Regulation and Monitoring • Transaction log ( input process and batch process) • Documented Regulation • Transmittal log • Cancellation of source document ( By pouncing with holes or marking to avoid duplicate entry) Error Reporting and Handling • Appropriate error handing - Rejecting only transition with error - Rejecting the whole batch of transition - Holding the batch as suspense - Accepting the batch and flagging error transactions • Appropriate error collection procedure - logging of errors - Timely corrections - Upstream resubmission - Approval of correction - Suspense file - Error file - Validity of corrections 62
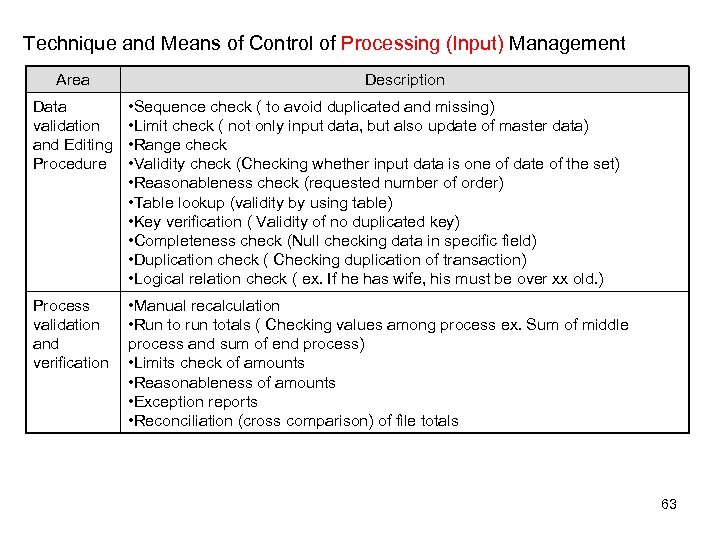 Technique and Means of Control of Processing (Input) Management Area Description Data validation and Editing Procedure • Sequence check ( to avoid duplicated and missing) • Limit check ( not only input data, but also update of master data) • Range check • Validity check (Checking whether input data is one of date of the set) • Reasonableness check (requested number of order) • Table lookup (validity by using table) • Key verification ( Validity of no duplicated key) • Completeness check (Null checking data in specific field) • Duplication check ( Checking duplication of transaction) • Logical relation check ( ex. If he has wife, his must be over xx old. ) Process validation and verification • Manual recalculation • Run to run totals ( Checking values among process ex. Sum of middle process and sum of end process) • Limits check of amounts • Reasonableness of amounts • Exception reports • Reconciliation (cross comparison) of file totals 63
Technique and Means of Control of Processing (Input) Management Area Description Data validation and Editing Procedure • Sequence check ( to avoid duplicated and missing) • Limit check ( not only input data, but also update of master data) • Range check • Validity check (Checking whether input data is one of date of the set) • Reasonableness check (requested number of order) • Table lookup (validity by using table) • Key verification ( Validity of no duplicated key) • Completeness check (Null checking data in specific field) • Duplication check ( Checking duplication of transaction) • Logical relation check ( ex. If he has wife, his must be over xx old. ) Process validation and verification • Manual recalculation • Run to run totals ( Checking values among process ex. Sum of middle process and sum of end process) • Limits check of amounts • Reasonableness of amounts • Exception reports • Reconciliation (cross comparison) of file totals 63
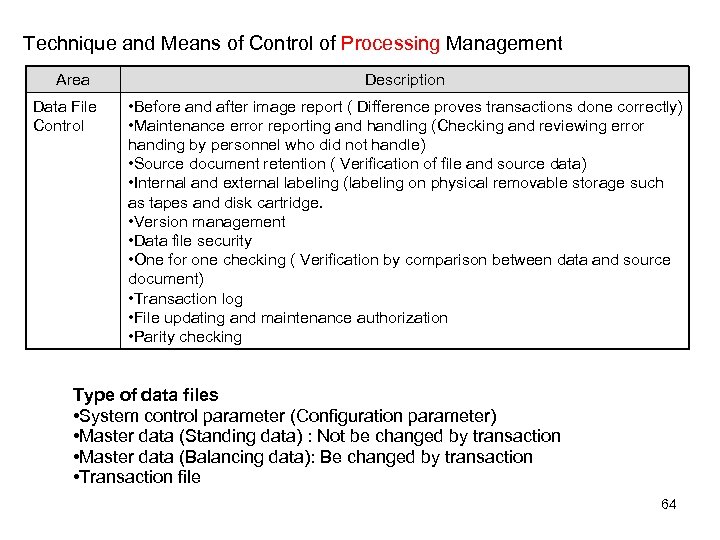 Technique and Means of Control of Processing Management Area Data File Control Description • Before and after image report ( Difference proves transactions done correctly) • Maintenance error reporting and handling (Checking and reviewing error handing by personnel who did not handle) • Source document retention ( Verification of file and source data) • Internal and external labeling (labeling on physical removable storage such as tapes and disk cartridge. • Version management • Data file security • One for one checking ( Verification by comparison between data and source document) • Transaction log • File updating and maintenance authorization • Parity checking Type of data files • System control parameter (Configuration parameter) • Master data (Standing data) : Not be changed by transaction • Master data (Balancing data): Be changed by transaction • Transaction file 64
Technique and Means of Control of Processing Management Area Data File Control Description • Before and after image report ( Difference proves transactions done correctly) • Maintenance error reporting and handling (Checking and reviewing error handing by personnel who did not handle) • Source document retention ( Verification of file and source data) • Internal and external labeling (labeling on physical removable storage such as tapes and disk cartridge. • Version management • Data file security • One for one checking ( Verification by comparison between data and source document) • Transaction log • File updating and maintenance authorization • Parity checking Type of data files • System control parameter (Configuration parameter) • Master data (Standing data) : Not be changed by transaction • Master data (Balancing data): Be changed by transaction • Transaction file 64
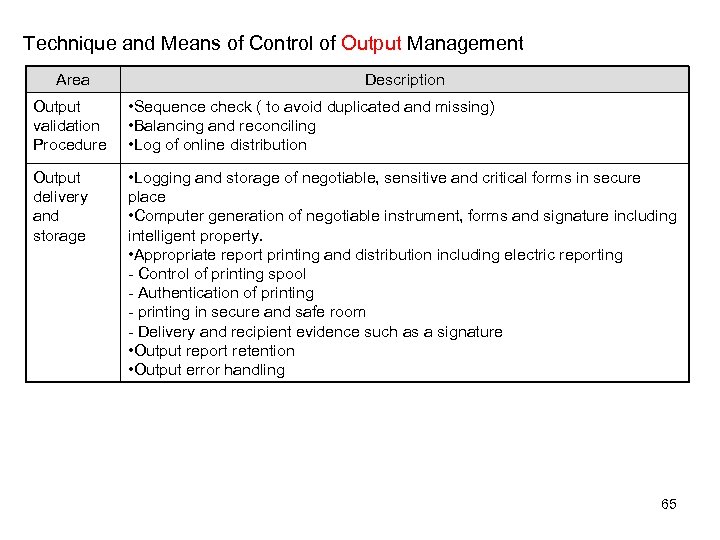 Technique and Means of Control of Output Management Area Description Output validation Procedure • Sequence check ( to avoid duplicated and missing) • Balancing and reconciling • Log of online distribution Output delivery and storage • Logging and storage of negotiable, sensitive and critical forms in secure place • Computer generation of negotiable instrument, forms and signature including intelligent property. • Appropriate report printing and distribution including electric reporting - Control of printing spool - Authentication of printing - printing in secure and safe room - Delivery and recipient evidence such as a signature • Output report retention • Output error handling 65
Technique and Means of Control of Output Management Area Description Output validation Procedure • Sequence check ( to avoid duplicated and missing) • Balancing and reconciling • Log of online distribution Output delivery and storage • Logging and storage of negotiable, sensitive and critical forms in secure place • Computer generation of negotiable instrument, forms and signature including intelligent property. • Appropriate report printing and distribution including electric reporting - Control of printing spool - Authentication of printing - printing in secure and safe room - Delivery and recipient evidence such as a signature • Output report retention • Output error handling 65
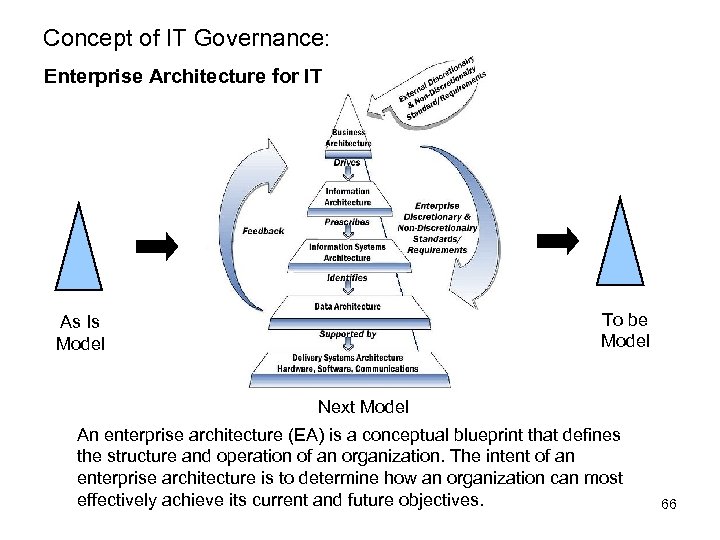 Concept of IT Governance: Enterprise Architecture for IT To be Model As Is Model Next Model An enterprise architecture (EA) is a conceptual blueprint that defines the structure and operation of an organization. The intent of an enterprise architecture is to determine how an organization can most effectively achieve its current and future objectives. 66
Concept of IT Governance: Enterprise Architecture for IT To be Model As Is Model Next Model An enterprise architecture (EA) is a conceptual blueprint that defines the structure and operation of an organization. The intent of an enterprise architecture is to determine how an organization can most effectively achieve its current and future objectives. 66
 1 -5. Availability Management and Service Continuity Management 67
1 -5. Availability Management and Service Continuity Management 67
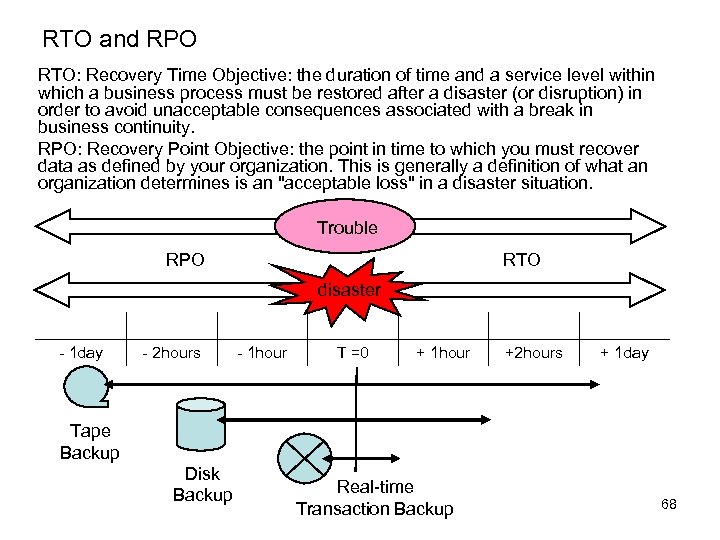 RTO and RPO RTO: Recovery Time Objective: the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster (or disruption) in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. RPO: Recovery Point Objective: the point in time to which you must recover data as defined by your organization. This is generally a definition of what an organization determines is an "acceptable loss" in a disaster situation. Trouble RTO RPO disaster - 1 day - 2 hours - 1 hour T =0 + 1 hour +2 hours + 1 day Tape Backup Disk Backup Real-time Transaction Backup 68
RTO and RPO RTO: Recovery Time Objective: the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster (or disruption) in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. RPO: Recovery Point Objective: the point in time to which you must recover data as defined by your organization. This is generally a definition of what an organization determines is an "acceptable loss" in a disaster situation. Trouble RTO RPO disaster - 1 day - 2 hours - 1 hour T =0 + 1 hour +2 hours + 1 day Tape Backup Disk Backup Real-time Transaction Backup 68
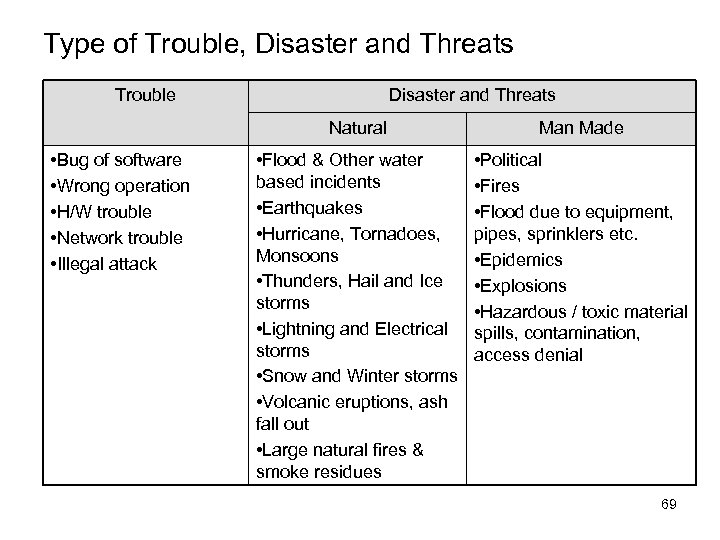 Type of Trouble, Disaster and Threats Trouble Disaster and Threats Natural • Bug of software • Wrong operation • H/W trouble • Network trouble • Illegal attack Man Made • Flood & Other water based incidents • Earthquakes • Hurricane, Tornadoes, Monsoons • Thunders, Hail and Ice storms • Lightning and Electrical storms • Snow and Winter storms • Volcanic eruptions, ash fall out • Large natural fires & smoke residues • Political • Fires • Flood due to equipment, pipes, sprinklers etc. • Epidemics • Explosions • Hazardous / toxic material spills, contamination, access denial 69
Type of Trouble, Disaster and Threats Trouble Disaster and Threats Natural • Bug of software • Wrong operation • H/W trouble • Network trouble • Illegal attack Man Made • Flood & Other water based incidents • Earthquakes • Hurricane, Tornadoes, Monsoons • Thunders, Hail and Ice storms • Lightning and Electrical storms • Snow and Winter storms • Volcanic eruptions, ash fall out • Large natural fires & smoke residues • Political • Fires • Flood due to equipment, pipes, sprinklers etc. • Epidemics • Explosions • Hazardous / toxic material spills, contamination, access denial 69
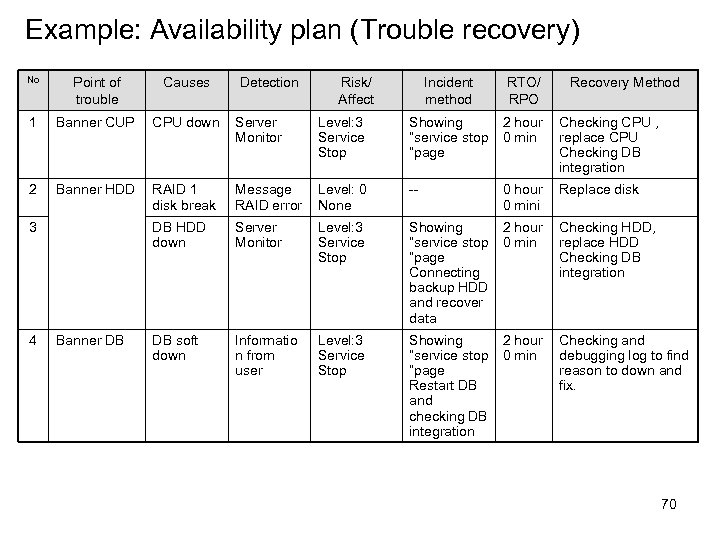 Example: Availability plan (Trouble recovery) No Point of trouble Causes 1 Banner CUP CPU down Server Monitor 2 Banner HDD RAID 1 disk break 4 Banner DB Incident method RTO/ RPO Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page 2 hour 0 min Checking CPU , replace CPU Checking DB integration Message RAID error Level: 0 None -- 0 hour 0 mini Replace disk DB HDD down 3 Detection Risk/ Affect Recovery Method Server Monitor Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page Connecting backup HDD and recover data 2 hour 0 min Checking HDD, replace HDD Checking DB integration DB soft down Informatio n from user Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page Restart DB and checking DB integration 2 hour 0 min Checking and debugging log to find reason to down and fix. 70
Example: Availability plan (Trouble recovery) No Point of trouble Causes 1 Banner CUP CPU down Server Monitor 2 Banner HDD RAID 1 disk break 4 Banner DB Incident method RTO/ RPO Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page 2 hour 0 min Checking CPU , replace CPU Checking DB integration Message RAID error Level: 0 None -- 0 hour 0 mini Replace disk DB HDD down 3 Detection Risk/ Affect Recovery Method Server Monitor Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page Connecting backup HDD and recover data 2 hour 0 min Checking HDD, replace HDD Checking DB integration DB soft down Informatio n from user Level: 3 Service Stop Showing “service stop ”page Restart DB and checking DB integration 2 hour 0 min Checking and debugging log to find reason to down and fix. 70
 Overview of BCP: Business Continuity Plan An ongoing process supported by senior management and funded to insure that the necessary steps are taken to identify the impact of potential losses, maintain viable recovery strategies and recovery plans, and ensure continuity of services through personnel training, plan testing, and maintenance. BCP vs. DRP • BCP vs. DRP Business Continuity Plan (BCP) tells us what essential resources are needed to continue business operations. • The Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) tells us how to bring back those essential resources. The purpose of the DRP is to carry out the BCP 71
Overview of BCP: Business Continuity Plan An ongoing process supported by senior management and funded to insure that the necessary steps are taken to identify the impact of potential losses, maintain viable recovery strategies and recovery plans, and ensure continuity of services through personnel training, plan testing, and maintenance. BCP vs. DRP • BCP vs. DRP Business Continuity Plan (BCP) tells us what essential resources are needed to continue business operations. • The Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) tells us how to bring back those essential resources. The purpose of the DRP is to carry out the BCP 71
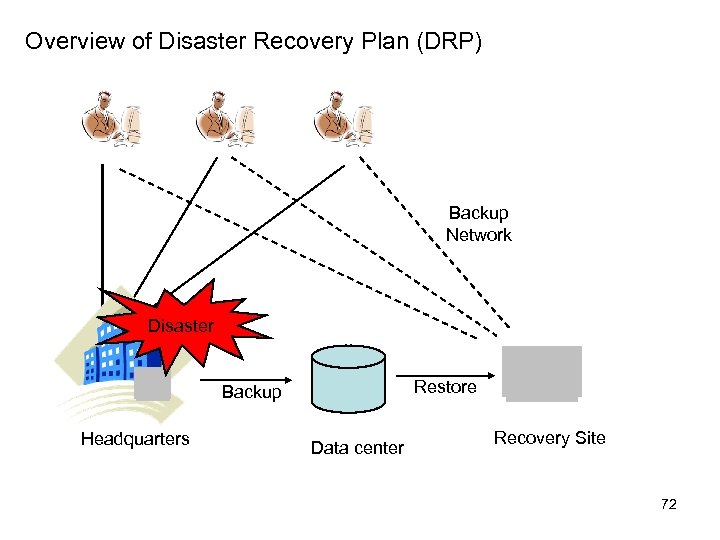 Overview of Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) Backup Network Disaster Restore Backup Headquarters Data center Recovery Site 72
Overview of Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) Backup Network Disaster Restore Backup Headquarters Data center Recovery Site 72
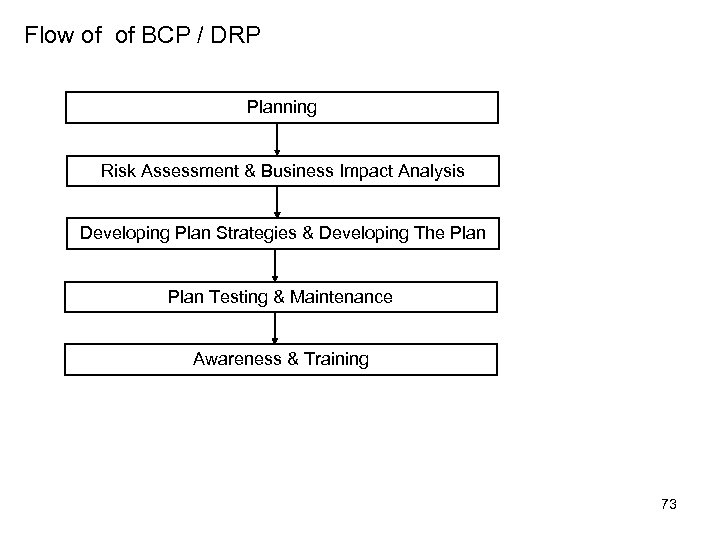 Flow of of BCP / DRP Planning Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Testing & Maintenance Awareness & Training 73
Flow of of BCP / DRP Planning Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Testing & Maintenance Awareness & Training 73
 Flow of of BCP / DRP: Planning • Define BCP vs. DRP for clear understanding by all. • Identify Project Sponsors and Leadership. Defining objectives, policies, critical success factors, scope. Identifying legal and regulatory requirements. • Define standard terms and assumptions. • Develop a Project Plan and Budget. Hard costs and soft costs such as equipment, personnel resources, facilities, etc. 74
Flow of of BCP / DRP: Planning • Define BCP vs. DRP for clear understanding by all. • Identify Project Sponsors and Leadership. Defining objectives, policies, critical success factors, scope. Identifying legal and regulatory requirements. • Define standard terms and assumptions. • Develop a Project Plan and Budget. Hard costs and soft costs such as equipment, personnel resources, facilities, etc. 74
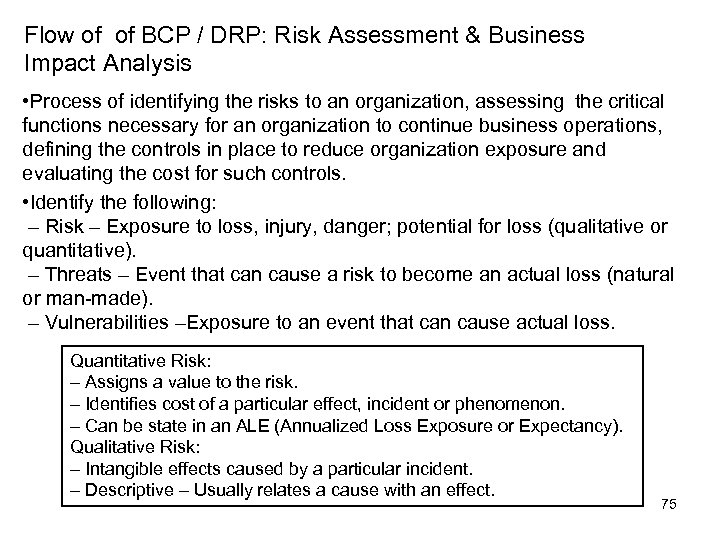 Flow of of BCP / DRP: Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis • Process of identifying the risks to an organization, assessing the critical functions necessary for an organization to continue business operations, defining the controls in place to reduce organization exposure and evaluating the cost for such controls. • Identify the following: – Risk – Exposure to loss, injury, danger; potential for loss (qualitative or quantitative). – Threats – Event that can cause a risk to become an actual loss (natural or man-made). – Vulnerabilities –Exposure to an event that can cause actual loss. Quantitative Risk: – Assigns a value to the risk. – Identifies cost of a particular effect, incident or phenomenon. – Can be state in an ALE (Annualized Loss Exposure or Expectancy). Qualitative Risk: – Intangible effects caused by a particular incident. – Descriptive – Usually relates a cause with an effect. 75
Flow of of BCP / DRP: Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis • Process of identifying the risks to an organization, assessing the critical functions necessary for an organization to continue business operations, defining the controls in place to reduce organization exposure and evaluating the cost for such controls. • Identify the following: – Risk – Exposure to loss, injury, danger; potential for loss (qualitative or quantitative). – Threats – Event that can cause a risk to become an actual loss (natural or man-made). – Vulnerabilities –Exposure to an event that can cause actual loss. Quantitative Risk: – Assigns a value to the risk. – Identifies cost of a particular effect, incident or phenomenon. – Can be state in an ALE (Annualized Loss Exposure or Expectancy). Qualitative Risk: – Intangible effects caused by a particular incident. – Descriptive – Usually relates a cause with an effect. 75
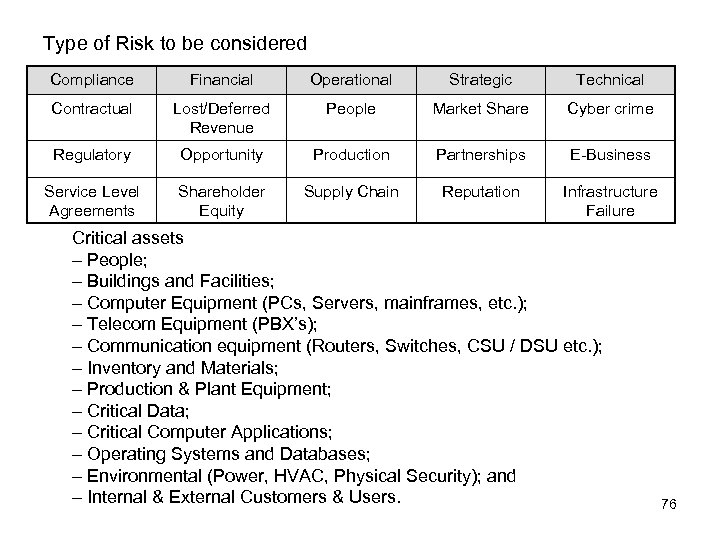 Type of Risk to be considered Compliance Financial Operational Strategic Technical Contractual Lost/Deferred Revenue People Market Share Cyber crime Regulatory Opportunity Production Partnerships E-Business Service Level Agreements Shareholder Equity Supply Chain Reputation Infrastructure Failure Critical assets – People; – Buildings and Facilities; – Computer Equipment (PCs, Servers, mainframes, etc. ); – Telecom Equipment (PBX’s); – Communication equipment (Routers, Switches, CSU / DSU etc. ); – Inventory and Materials; – Production & Plant Equipment; – Critical Data; – Critical Computer Applications; – Operating Systems and Databases; – Environmental (Power, HVAC, Physical Security); and – Internal & External Customers & Users. 76
Type of Risk to be considered Compliance Financial Operational Strategic Technical Contractual Lost/Deferred Revenue People Market Share Cyber crime Regulatory Opportunity Production Partnerships E-Business Service Level Agreements Shareholder Equity Supply Chain Reputation Infrastructure Failure Critical assets – People; – Buildings and Facilities; – Computer Equipment (PCs, Servers, mainframes, etc. ); – Telecom Equipment (PBX’s); – Communication equipment (Routers, Switches, CSU / DSU etc. ); – Inventory and Materials; – Production & Plant Equipment; – Critical Data; – Critical Computer Applications; – Operating Systems and Databases; – Environmental (Power, HVAC, Physical Security); and – Internal & External Customers & Users. 76
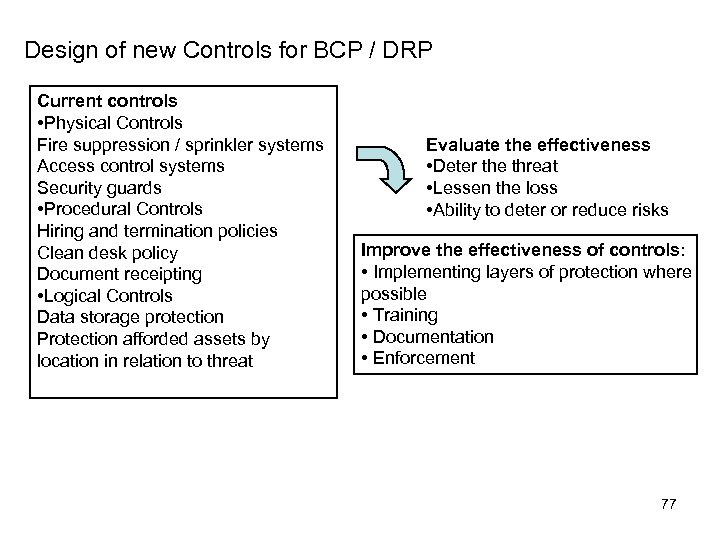 Design of new Controls for BCP / DRP Current controls • Physical Controls Fire suppression / sprinkler systems Access control systems Security guards • Procedural Controls Hiring and termination policies Clean desk policy Document receipting • Logical Controls Data storage protection Protection afforded assets by location in relation to threat Evaluate the effectiveness • Deter the threat • Lessen the loss • Ability to deter or reduce risks Improve the effectiveness of controls: • Implementing layers of protection where possible • Training • Documentation • Enforcement 77
Design of new Controls for BCP / DRP Current controls • Physical Controls Fire suppression / sprinkler systems Access control systems Security guards • Procedural Controls Hiring and termination policies Clean desk policy Document receipting • Logical Controls Data storage protection Protection afforded assets by location in relation to threat Evaluate the effectiveness • Deter the threat • Lessen the loss • Ability to deter or reduce risks Improve the effectiveness of controls: • Implementing layers of protection where possible • Training • Documentation • Enforcement 77
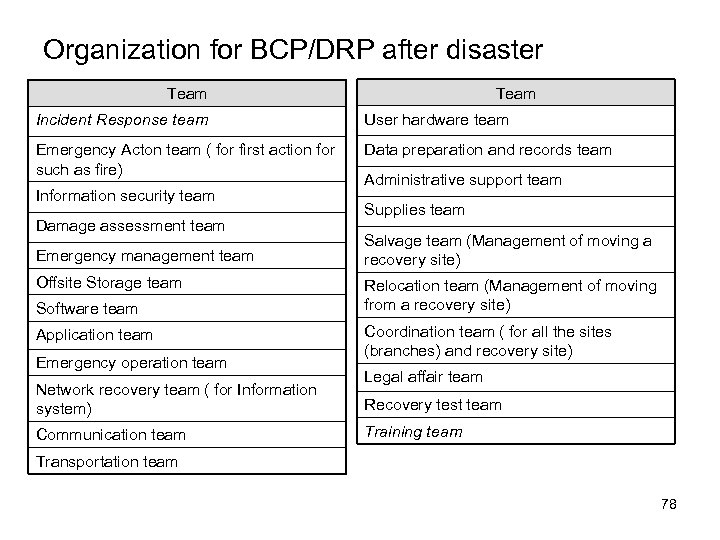 Organization for BCP/DRP after disaster Team Incident Response team User hardware team Emergency Acton team ( for first action for such as fire) Data preparation and records team Information security team Damage assessment team Emergency management team Offsite Storage team Software team Application team Emergency operation team Network recovery team ( for Information system) Communication team Administrative support team Supplies team Salvage team (Management of moving a recovery site) Relocation team (Management of moving from a recovery site) Coordination team ( for all the sites (branches) and recovery site) Legal affair team Recovery test team Training team Transportation team 78
Organization for BCP/DRP after disaster Team Incident Response team User hardware team Emergency Acton team ( for first action for such as fire) Data preparation and records team Information security team Damage assessment team Emergency management team Offsite Storage team Software team Application team Emergency operation team Network recovery team ( for Information system) Communication team Administrative support team Supplies team Salvage team (Management of moving a recovery site) Relocation team (Management of moving from a recovery site) Coordination team ( for all the sites (branches) and recovery site) Legal affair team Recovery test team Training team Transportation team 78
 Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Determine and guide the selection of alternative business recovery operating strategies for recovery of business and information technologies within the recovery time objectives, while maintaining the organization’s critical functions. Identify Requirements for DRP and BCP Strategies • Review business recovery issues from BIA • Review technology recovery issues for each support area • Review non-technology issues for each support area Identify Off-Site storage requirements and Alternative facilities Identify Viable Recovery strategies within business functional areas: • Service Degradation • Internal Recovery (Reciprocal Agreement) • Commercial Recovery Center such as Hot site and Warm site. Consolidating Strategies across the Enterprise • Coordination of Technology Recovery • Enterprise Level Crisis Management • Enterprise Level Media Handling • Centralized strategy for interfacing with local 79
Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Determine and guide the selection of alternative business recovery operating strategies for recovery of business and information technologies within the recovery time objectives, while maintaining the organization’s critical functions. Identify Requirements for DRP and BCP Strategies • Review business recovery issues from BIA • Review technology recovery issues for each support area • Review non-technology issues for each support area Identify Off-Site storage requirements and Alternative facilities Identify Viable Recovery strategies within business functional areas: • Service Degradation • Internal Recovery (Reciprocal Agreement) • Commercial Recovery Center such as Hot site and Warm site. Consolidating Strategies across the Enterprise • Coordination of Technology Recovery • Enterprise Level Crisis Management • Enterprise Level Media Handling • Centralized strategy for interfacing with local 79
 Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Detail Plan (1/2) Content Detail content Plan Scope and Objective • Definition of Standard Terms • Selecting the appropriate Methodology • Scope of Project itself Business Recovery Organization (BRO) and responsibilities • BCP Planning Coordinator • Disaster Recovery Teams • Business Continuity Management Teams Major Plan Components • Reduction • Response • Recovery and Resumption Escalation, notification • Disaster Declaration Procedures and plan activation • Mobilization procedures • Damage assessment concepts • Recovery Site Activation Vital records and offsite storage program • What goes off-site • Inventory of what is off site • How do you get it back 80
Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Detail Plan (1/2) Content Detail content Plan Scope and Objective • Definition of Standard Terms • Selecting the appropriate Methodology • Scope of Project itself Business Recovery Organization (BRO) and responsibilities • BCP Planning Coordinator • Disaster Recovery Teams • Business Continuity Management Teams Major Plan Components • Reduction • Response • Recovery and Resumption Escalation, notification • Disaster Declaration Procedures and plan activation • Mobilization procedures • Damage assessment concepts • Recovery Site Activation Vital records and offsite storage program • What goes off-site • Inventory of what is off site • How do you get it back 80
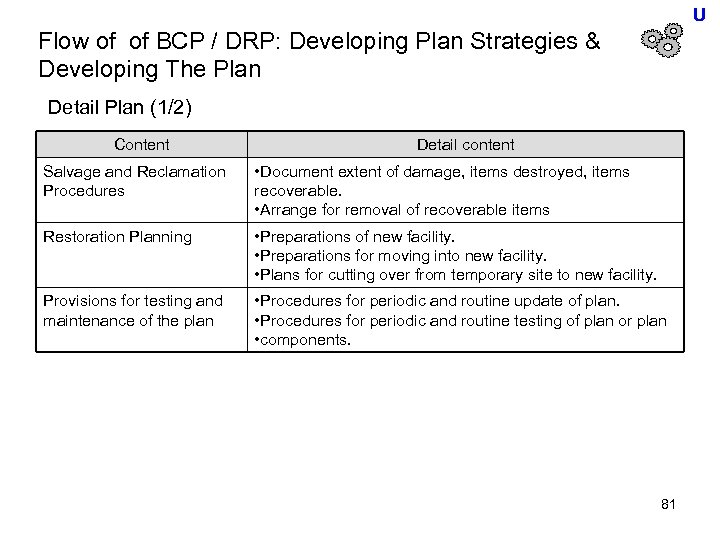 U Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Detail Plan (1/2) Content Detail content Salvage and Reclamation Procedures • Document extent of damage, items destroyed, items recoverable. • Arrange for removal of recoverable items Restoration Planning • Preparations of new facility. • Preparations for moving into new facility. • Plans for cutting over from temporary site to new facility. Provisions for testing and maintenance of the plan • Procedures for periodic and routine update of plan. • Procedures for periodic and routine testing of plan or plan • components. 81
U Flow of of BCP / DRP: Developing Plan Strategies & Developing The Plan Detail Plan (1/2) Content Detail content Salvage and Reclamation Procedures • Document extent of damage, items destroyed, items recoverable. • Arrange for removal of recoverable items Restoration Planning • Preparations of new facility. • Preparations for moving into new facility. • Plans for cutting over from temporary site to new facility. Provisions for testing and maintenance of the plan • Procedures for periodic and routine update of plan. • Procedures for periodic and routine testing of plan or plan • components. 81
 1 -6. Protection of Information Assets - Information Security Management- 82
1 -6. Protection of Information Assets - Information Security Management- 82
 What is “Protection of Information Assets” Information Assets • all elements of information that either share a common usage, purpose, associated risk and/or form of storage. • Something that is considered of worth to the organization. Protection of information assets • Protect against loss of nuclear sensitive/classified information, • Protect against theft of material (both physical and information), • Protect against terrorist action, • Ensure nuclear safety, • Ensure business continuity, • Minimize business risk 83
What is “Protection of Information Assets” Information Assets • all elements of information that either share a common usage, purpose, associated risk and/or form of storage. • Something that is considered of worth to the organization. Protection of information assets • Protect against loss of nuclear sensitive/classified information, • Protect against theft of material (both physical and information), • Protect against terrorist action, • Ensure nuclear safety, • Ensure business continuity, • Minimize business risk 83
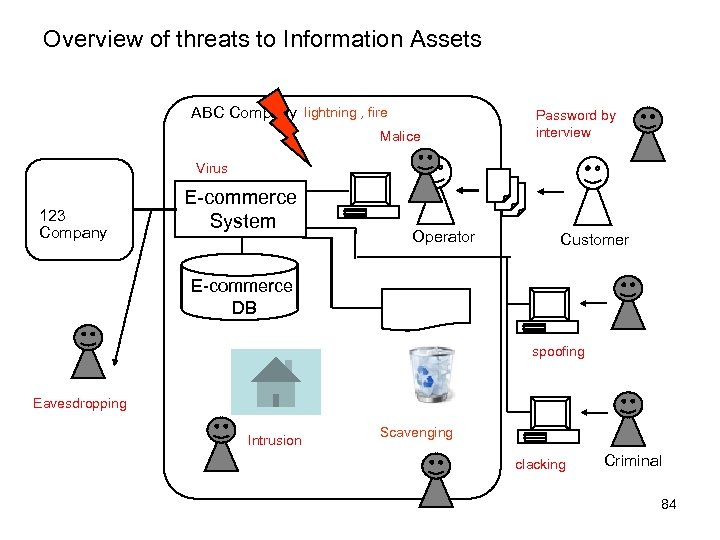 Overview of threats to Information Assets ABC Company lightning , fire Malice Password by interview Virus 123 Company E-commerce System Operator Customer E-commerce DB spoofing Eavesdropping Intrusion Scavenging clacking Criminal 84
Overview of threats to Information Assets ABC Company lightning , fire Malice Password by interview Virus 123 Company E-commerce System Operator Customer E-commerce DB spoofing Eavesdropping Intrusion Scavenging clacking Criminal 84
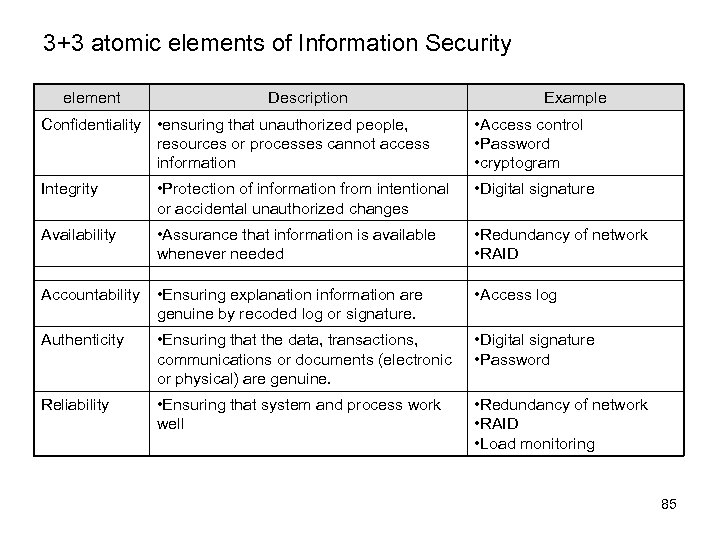 3+3 atomic elements of Information Security element Description Confidentiality • ensuring that unauthorized people, resources or processes cannot access information Example • Access control • Password • cryptogram Integrity • Protection of information from intentional or accidental unauthorized changes • Digital signature Availability • Assurance that information is available whenever needed • Redundancy of network • RAID Accountability • Ensuring explanation information are genuine by recoded log or signature. • Access log Authenticity • Ensuring that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine. • Digital signature • Password Reliability • Ensuring that system and process work well • Redundancy of network • RAID • Load monitoring 85
3+3 atomic elements of Information Security element Description Confidentiality • ensuring that unauthorized people, resources or processes cannot access information Example • Access control • Password • cryptogram Integrity • Protection of information from intentional or accidental unauthorized changes • Digital signature Availability • Assurance that information is available whenever needed • Redundancy of network • RAID Accountability • Ensuring explanation information are genuine by recoded log or signature. • Access log Authenticity • Ensuring that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine. • Digital signature • Password Reliability • Ensuring that system and process work well • Redundancy of network • RAID • Load monitoring 85
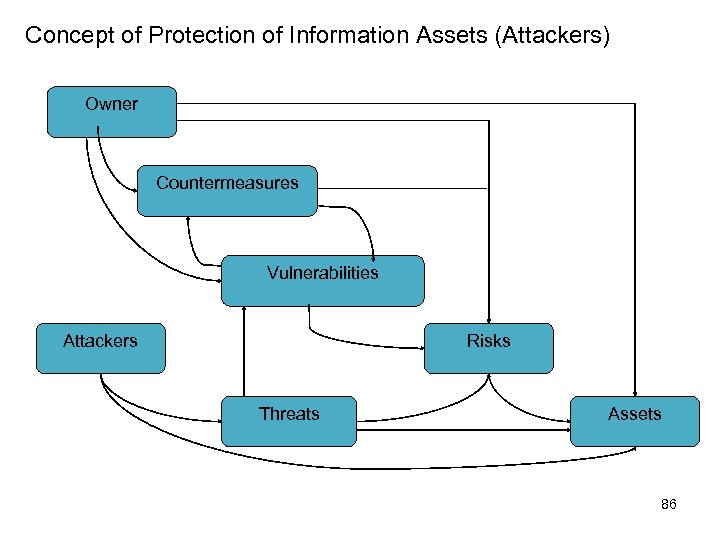 Concept of Protection of Information Assets (Attackers) Owner Countermeasures Vulnerabilities Attackers Risks Threats Assets 86
Concept of Protection of Information Assets (Attackers) Owner Countermeasures Vulnerabilities Attackers Risks Threats Assets 86
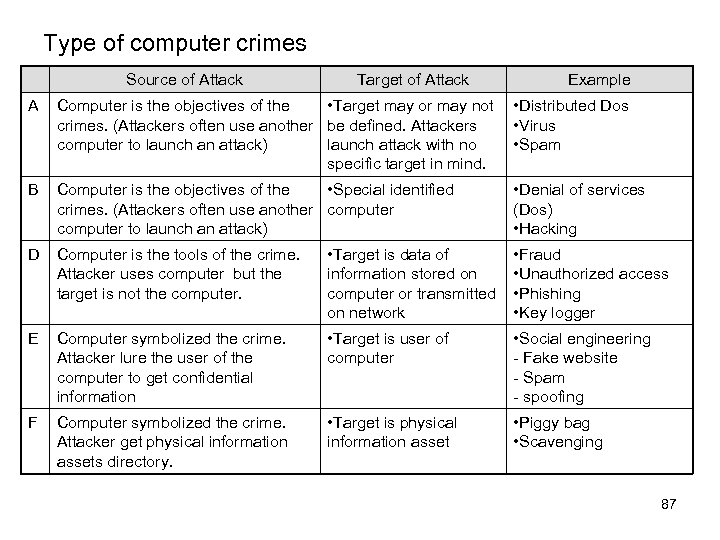 Type of computer crimes Source of Attack Target of Attack Example A Computer is the objectives of the • Target may or may not crimes. (Attackers often use another be defined. Attackers computer to launch an attack) launch attack with no specific target in mind. • Distributed Dos • Virus • Spam B Computer is the objectives of the • Special identified crimes. (Attackers often use another computer to launch an attack) • Denial of services (Dos) • Hacking D Computer is the tools of the crime. Attacker uses computer but the target is not the computer. • Target is data of information stored on computer or transmitted on network • Fraud • Unauthorized access • Phishing • Key logger E Computer symbolized the crime. Attacker lure the user of the computer to get confidential information • Target is user of computer • Social engineering - Fake website - Spam - spoofing F Computer symbolized the crime. Attacker get physical information assets directory. • Target is physical information asset • Piggy bag • Scavenging 87
Type of computer crimes Source of Attack Target of Attack Example A Computer is the objectives of the • Target may or may not crimes. (Attackers often use another be defined. Attackers computer to launch an attack) launch attack with no specific target in mind. • Distributed Dos • Virus • Spam B Computer is the objectives of the • Special identified crimes. (Attackers often use another computer to launch an attack) • Denial of services (Dos) • Hacking D Computer is the tools of the crime. Attacker uses computer but the target is not the computer. • Target is data of information stored on computer or transmitted on network • Fraud • Unauthorized access • Phishing • Key logger E Computer symbolized the crime. Attacker lure the user of the computer to get confidential information • Target is user of computer • Social engineering - Fake website - Spam - spoofing F Computer symbolized the crime. Attacker get physical information assets directory. • Target is physical information asset • Piggy bag • Scavenging 87
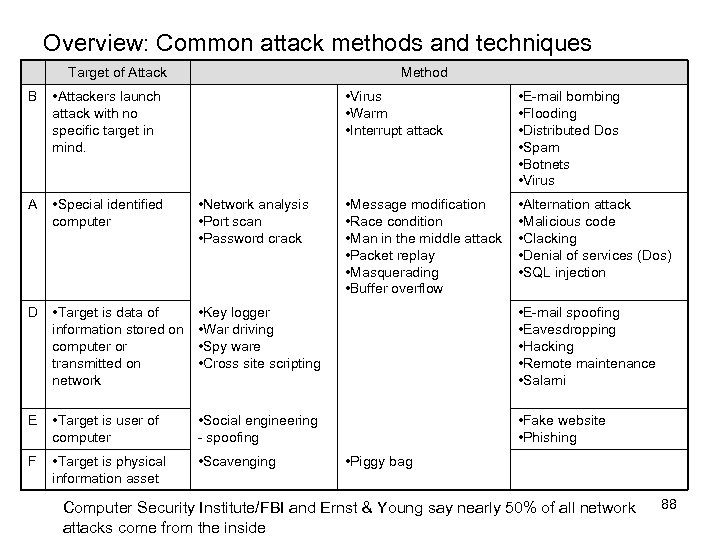 Overview: Common attack methods and techniques Target of Attack Method B • Attackers launch attack with no specific target in mind. • Virus • Warm • Interrupt attack • E-mail bombing • Flooding • Distributed Dos • Spam • Botnets • Virus A • Special identified computer • Network analysis • Port scan • Password crack • Message modification • Race condition • Man in the middle attack • Packet replay • Masquerading • Buffer overflow • Alternation attack • Malicious code • Clacking • Denial of services (Dos) • SQL injection D • Target is data of information stored on computer or transmitted on network • Key logger • War driving • Spy ware • Cross site scripting • E-mail spoofing • Eavesdropping • Hacking • Remote maintenance • Salami E • Target is user of computer • Social engineering - spoofing • Fake website • Phishing F • Target is physical information asset • Scavenging • Piggy bag Computer Security Institute/FBI and Ernst & Young say nearly 50% of all network attacks come from the inside 88
Overview: Common attack methods and techniques Target of Attack Method B • Attackers launch attack with no specific target in mind. • Virus • Warm • Interrupt attack • E-mail bombing • Flooding • Distributed Dos • Spam • Botnets • Virus A • Special identified computer • Network analysis • Port scan • Password crack • Message modification • Race condition • Man in the middle attack • Packet replay • Masquerading • Buffer overflow • Alternation attack • Malicious code • Clacking • Denial of services (Dos) • SQL injection D • Target is data of information stored on computer or transmitted on network • Key logger • War driving • Spy ware • Cross site scripting • E-mail spoofing • Eavesdropping • Hacking • Remote maintenance • Salami E • Target is user of computer • Social engineering - spoofing • Fake website • Phishing F • Target is physical information asset • Scavenging • Piggy bag Computer Security Institute/FBI and Ernst & Young say nearly 50% of all network attacks come from the inside 88
 Security control concept (1) Access Control • Ability to permit or deny the use of resources by a particular entity • The ability to allow only authorized users, programs or processes system or resource access Authentication • Who goes there? • Restrictions on who (or what) can access the system • Verifying the identity of a user, process, or device, often as a prerequisite to allowing access to resources Authorization • Are you allowed to do that? • Restrictions on actions of authenticated users • The right or a permission that is granted to a system entity to access a system resource 89
Security control concept (1) Access Control • Ability to permit or deny the use of resources by a particular entity • The ability to allow only authorized users, programs or processes system or resource access Authentication • Who goes there? • Restrictions on who (or what) can access the system • Verifying the identity of a user, process, or device, often as a prerequisite to allowing access to resources Authorization • Are you allowed to do that? • Restrictions on actions of authenticated users • The right or a permission that is granted to a system entity to access a system resource 89
 Security control concept (2) Need-to-know • Having access to the information that is required to carry out work • ensuring that access to nuclear sensitive assets is limited to only those who have the necessary ‘need to know’ and the appropriate security clearance Defense-in-depth • places multiple barriers between an attacker and your assets • the deeper an attacker tries to go, the more layers they need to get through undetected Least privilege and functions • The minimum level of computer access to an asset in order to effectively carry out work • only a minimal set of users have root access • Users can user only minimum functions 90
Security control concept (2) Need-to-know • Having access to the information that is required to carry out work • ensuring that access to nuclear sensitive assets is limited to only those who have the necessary ‘need to know’ and the appropriate security clearance Defense-in-depth • places multiple barriers between an attacker and your assets • the deeper an attacker tries to go, the more layers they need to get through undetected Least privilege and functions • The minimum level of computer access to an asset in order to effectively carry out work • only a minimal set of users have root access • Users can user only minimum functions 90
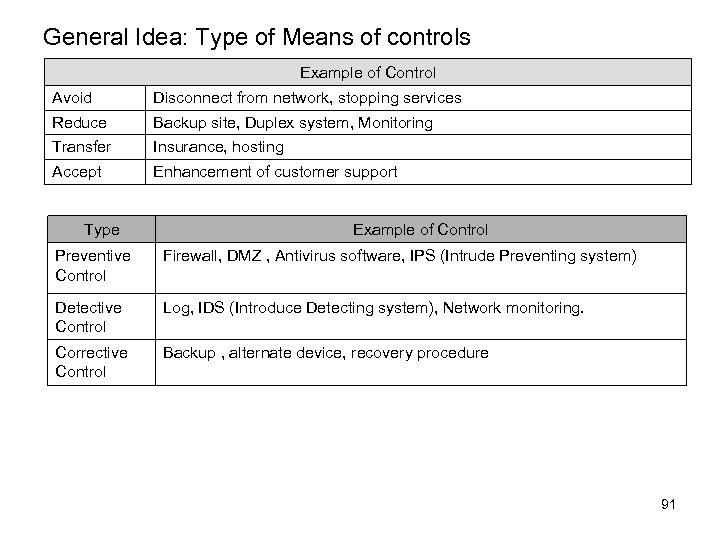 General Idea: Type of Means of controls Example of Control Avoid Disconnect from network, stopping services Reduce Backup site, Duplex system, Monitoring Transfer Insurance, hosting Accept Enhancement of customer support Type Example of Control Preventive Control Firewall, DMZ , Antivirus software, IPS (Intrude Preventing system) Detective Control Log, IDS (Introduce Detecting system), Network monitoring. Corrective Control Backup , alternate device, recovery procedure 91
General Idea: Type of Means of controls Example of Control Avoid Disconnect from network, stopping services Reduce Backup site, Duplex system, Monitoring Transfer Insurance, hosting Accept Enhancement of customer support Type Example of Control Preventive Control Firewall, DMZ , Antivirus software, IPS (Intrude Preventing system) Detective Control Log, IDS (Introduce Detecting system), Network monitoring. Corrective Control Backup , alternate device, recovery procedure 91
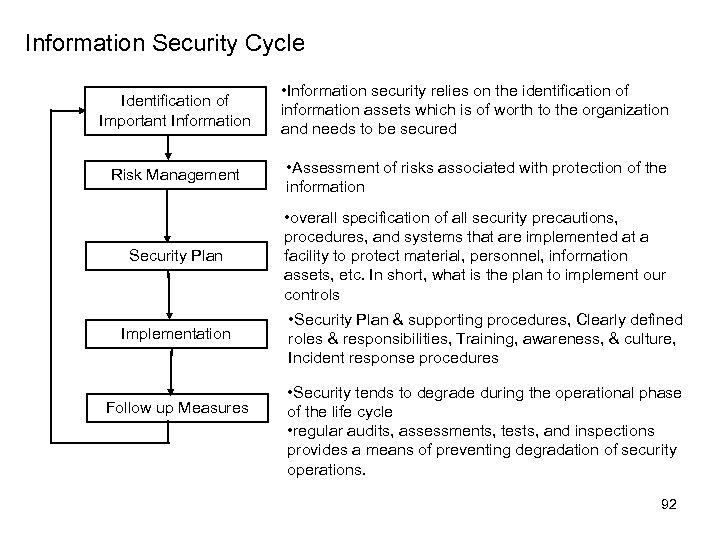 Information Security Cycle Identification of Important Information • Information security relies on the identification of information assets which is of worth to the organization and needs to be secured Risk Management • Assessment of risks associated with protection of the information Security Plan • overall specification of all security precautions, procedures, and systems that are implemented at a facility to protect material, personnel, information assets, etc. In short, what is the plan to implement our controls Implementation Follow up Measures • Security Plan & supporting procedures, Clearly defined roles & responsibilities, Training, awareness, & culture, Incident response procedures • Security tends to degrade during the operational phase of the life cycle • regular audits, assessments, tests, and inspections provides a means of preventing degradation of security operations. 92
Information Security Cycle Identification of Important Information • Information security relies on the identification of information assets which is of worth to the organization and needs to be secured Risk Management • Assessment of risks associated with protection of the information Security Plan • overall specification of all security precautions, procedures, and systems that are implemented at a facility to protect material, personnel, information assets, etc. In short, what is the plan to implement our controls Implementation Follow up Measures • Security Plan & supporting procedures, Clearly defined roles & responsibilities, Training, awareness, & culture, Incident response procedures • Security tends to degrade during the operational phase of the life cycle • regular audits, assessments, tests, and inspections provides a means of preventing degradation of security operations. 92
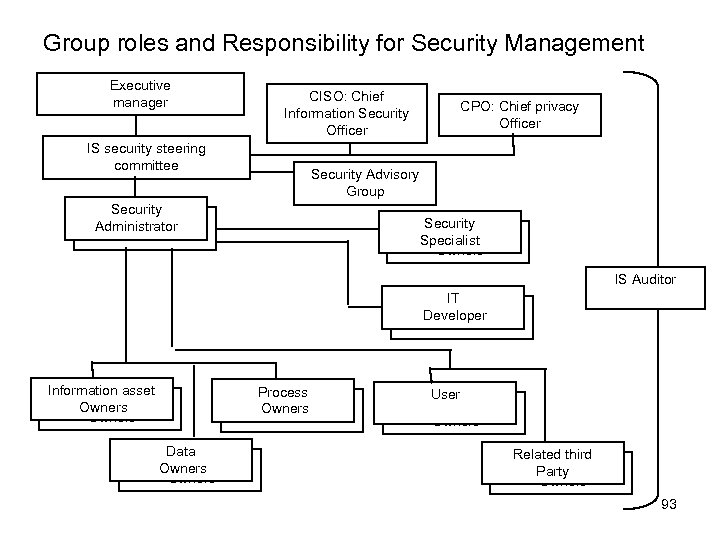 Group roles and Responsibility for Security Management Executive manager IS security steering committee CISO: Chief Information Security Officer CPO: Chief privacy Officer Security Advisory Group Security Process Administrator Owners Security Process Specialist Owners IS Auditor IT Process Developer Owners Information asset Process Owners Data Process Owners User Process Owners Related third Process Party Owners 93
Group roles and Responsibility for Security Management Executive manager IS security steering committee CISO: Chief Information Security Officer CPO: Chief privacy Officer Security Advisory Group Security Process Administrator Owners Security Process Specialist Owners IS Auditor IT Process Developer Owners Information asset Process Owners Data Process Owners User Process Owners Related third Process Party Owners 93
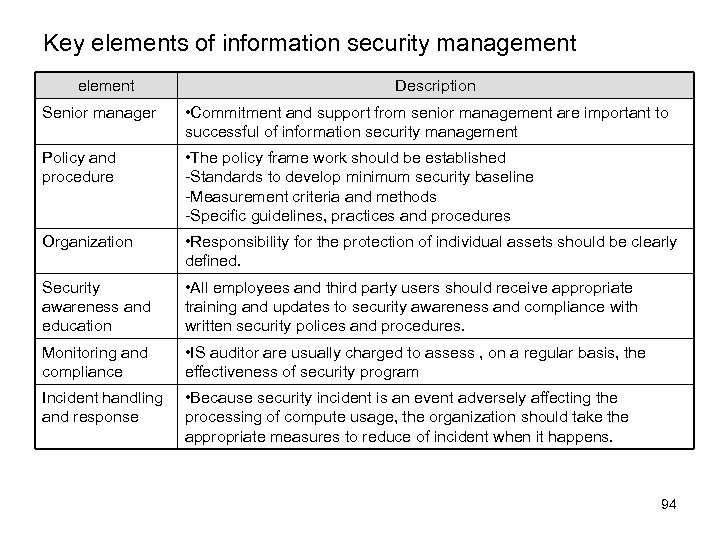 Key elements of information security management element Description Senior manager • Commitment and support from senior management are important to successful of information security management Policy and procedure • The policy frame work should be established -Standards to develop minimum security baseline -Measurement criteria and methods -Specific guidelines, practices and procedures Organization • Responsibility for the protection of individual assets should be clearly defined. Security awareness and education • All employees and third party users should receive appropriate training and updates to security awareness and compliance with written security polices and procedures. Monitoring and compliance • IS auditor are usually charged to assess , on a regular basis, the effectiveness of security program Incident handling and response • Because security incident is an event adversely affecting the processing of compute usage, the organization should take the appropriate measures to reduce of incident when it happens. 94
Key elements of information security management element Description Senior manager • Commitment and support from senior management are important to successful of information security management Policy and procedure • The policy frame work should be established -Standards to develop minimum security baseline -Measurement criteria and methods -Specific guidelines, practices and procedures Organization • Responsibility for the protection of individual assets should be clearly defined. Security awareness and education • All employees and third party users should receive appropriate training and updates to security awareness and compliance with written security polices and procedures. Monitoring and compliance • IS auditor are usually charged to assess , on a regular basis, the effectiveness of security program Incident handling and response • Because security incident is an event adversely affecting the processing of compute usage, the organization should take the appropriate measures to reduce of incident when it happens. 94
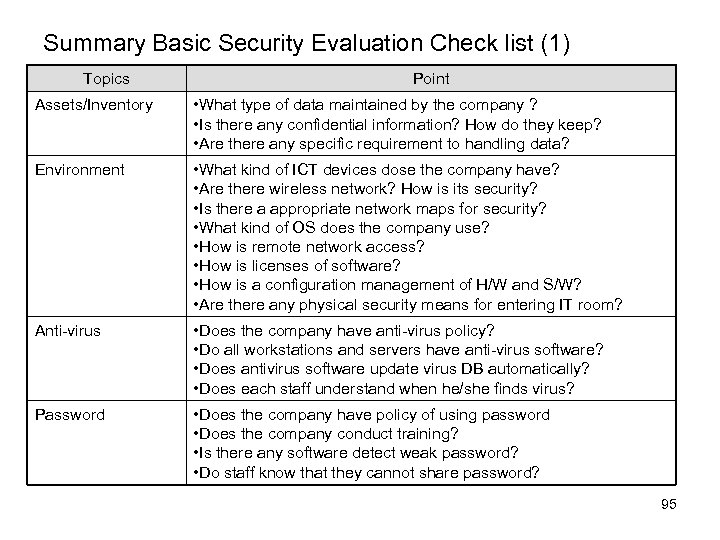 Summary Basic Security Evaluation Check list (1) Topics Point Assets/Inventory • What type of data maintained by the company ? • Is there any confidential information? How do they keep? • Are there any specific requirement to handling data? Environment • What kind of ICT devices dose the company have? • Are there wireless network? How is its security? • Is there a appropriate network maps for security? • What kind of OS does the company use? • How is remote network access? • How is licenses of software? • How is a configuration management of H/W and S/W? • Are there any physical security means for entering IT room? Anti-virus • Does the company have anti-virus policy? • Do all workstations and servers have anti-virus software? • Does antivirus software update virus DB automatically? • Does each staff understand when he/she finds virus? Password • Does the company have policy of using password • Does the company conduct training? • Is there any software detect weak password? • Do staff know that they cannot share password? 95
Summary Basic Security Evaluation Check list (1) Topics Point Assets/Inventory • What type of data maintained by the company ? • Is there any confidential information? How do they keep? • Are there any specific requirement to handling data? Environment • What kind of ICT devices dose the company have? • Are there wireless network? How is its security? • Is there a appropriate network maps for security? • What kind of OS does the company use? • How is remote network access? • How is licenses of software? • How is a configuration management of H/W and S/W? • Are there any physical security means for entering IT room? Anti-virus • Does the company have anti-virus policy? • Do all workstations and servers have anti-virus software? • Does antivirus software update virus DB automatically? • Does each staff understand when he/she finds virus? Password • Does the company have policy of using password • Does the company conduct training? • Is there any software detect weak password? • Do staff know that they cannot share password? 95
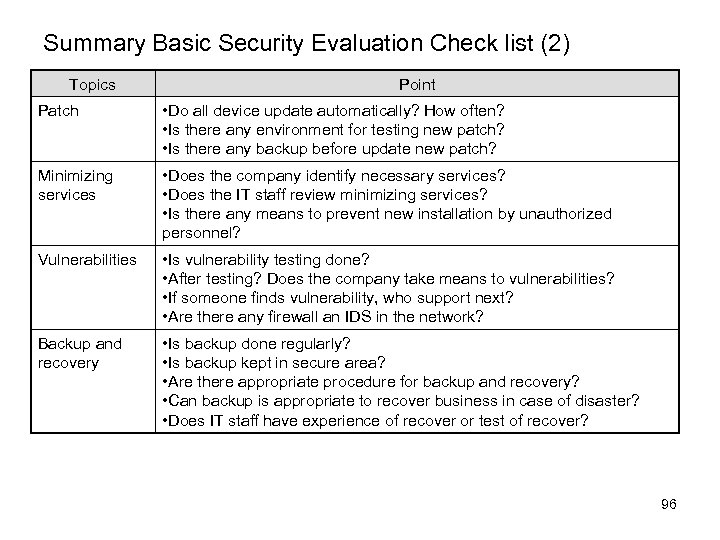 Summary Basic Security Evaluation Check list (2) Topics Point Patch • Do all device update automatically? How often? • Is there any environment for testing new patch? • Is there any backup before update new patch? Minimizing services • Does the company identify necessary services? • Does the IT staff review minimizing services? • Is there any means to prevent new installation by unauthorized personnel? Vulnerabilities • Is vulnerability testing done? • After testing? Does the company take means to vulnerabilities? • If someone finds vulnerability, who support next? • Are there any firewall an IDS in the network? Backup and recovery • Is backup done regularly? • Is backup kept in secure area? • Are there appropriate procedure for backup and recovery? • Can backup is appropriate to recover business in case of disaster? • Does IT staff have experience of recover or test of recover? 96
Summary Basic Security Evaluation Check list (2) Topics Point Patch • Do all device update automatically? How often? • Is there any environment for testing new patch? • Is there any backup before update new patch? Minimizing services • Does the company identify necessary services? • Does the IT staff review minimizing services? • Is there any means to prevent new installation by unauthorized personnel? Vulnerabilities • Is vulnerability testing done? • After testing? Does the company take means to vulnerabilities? • If someone finds vulnerability, who support next? • Are there any firewall an IDS in the network? Backup and recovery • Is backup done regularly? • Is backup kept in secure area? • Are there appropriate procedure for backup and recovery? • Can backup is appropriate to recover business in case of disaster? • Does IT staff have experience of recover or test of recover? 96
 Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing Vulnerability Assessment • Overall network infrastructure is assessed to determine any exploitable vulnerability • Sophisticated tools are used to identify any potential security weaknesses • Devices assessed include firewalls, routers, servers, etc. • Tests are performed to identify system weaknesses from both internal and external threats • Comprehensive report submitted with vulnerabilities found and corrective actions to be taken • Should be performed at regular intervals or after any major changes Penetration Testing • Attempt to scrutinize the true strength of an organization’s security infrastructure against a real attack • Assume the role of a real intruder and attempts to breach the network in a controlled and safe way not affecting your services • Launches a series of attacks on the network using commonly used techniques • Various commercial and open source “hacker” tools will be employed during the tests 97
Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing Vulnerability Assessment • Overall network infrastructure is assessed to determine any exploitable vulnerability • Sophisticated tools are used to identify any potential security weaknesses • Devices assessed include firewalls, routers, servers, etc. • Tests are performed to identify system weaknesses from both internal and external threats • Comprehensive report submitted with vulnerabilities found and corrective actions to be taken • Should be performed at regular intervals or after any major changes Penetration Testing • Attempt to scrutinize the true strength of an organization’s security infrastructure against a real attack • Assume the role of a real intruder and attempts to breach the network in a controlled and safe way not affecting your services • Launches a series of attacks on the network using commonly used techniques • Various commercial and open source “hacker” tools will be employed during the tests 97
 1 -7. IT services and operation 98
1 -7. IT services and operation 98
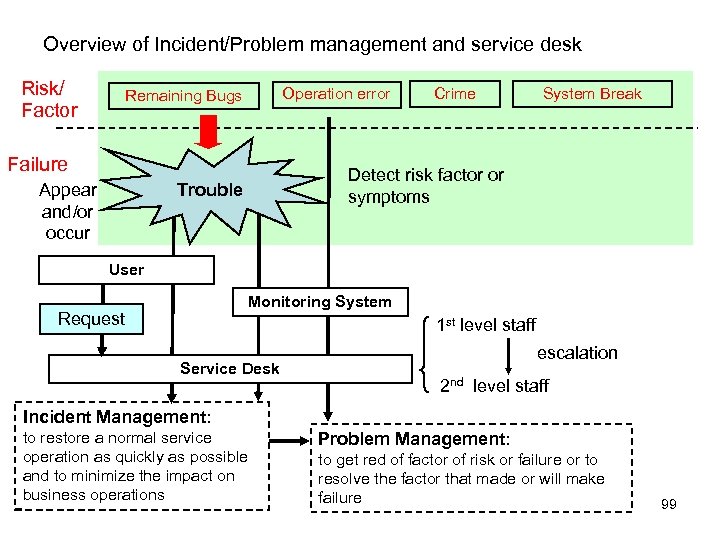 Overview of Incident/Problem management and service desk Risk/ Factor Operation error Remaining Bugs Failure System Break Detect risk factor or symptoms Trouble Appear and/or occur Crime User Monitoring System Request 1 st level staff Service Desk escalation 2 nd level staff Incident Management: to restore a normal service operation as quickly as possible and to minimize the impact on business operations Problem Management: to get red of factor of risk or failure or to resolve the factor that made or will make failure 99
Overview of Incident/Problem management and service desk Risk/ Factor Operation error Remaining Bugs Failure System Break Detect risk factor or symptoms Trouble Appear and/or occur Crime User Monitoring System Request 1 st level staff Service Desk escalation 2 nd level staff Incident Management: to restore a normal service operation as quickly as possible and to minimize the impact on business operations Problem Management: to get red of factor of risk or failure or to resolve the factor that made or will make failure 99
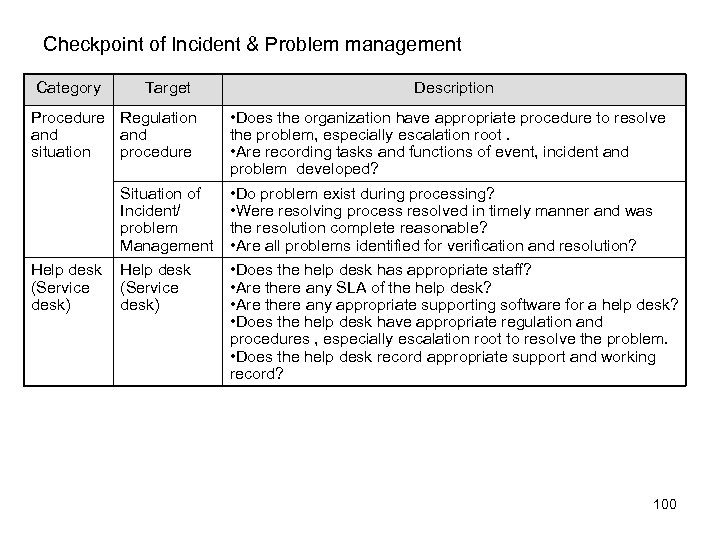 Checkpoint of Incident & Problem management Category Target Description • Does the organization have appropriate procedure to resolve the problem, especially escalation root. • Are recording tasks and functions of event, incident and problem developed? Situation of • Do problem exist during processing? Incident/ • Were resolving process resolved in timely manner and was problem the resolution complete reasonable? Management • Are all problems identified for verification and resolution? Help desk • Does the help desk has appropriate staff? (Service • Are there any SLA of the help desk? desk) • Are there any appropriate supporting software for a help desk? • Does the help desk have appropriate regulation and procedures , especially escalation root to resolve the problem. • Does the help desk record appropriate support and working record? Procedure Regulation and situation procedure Help desk (Service desk) 100
Checkpoint of Incident & Problem management Category Target Description • Does the organization have appropriate procedure to resolve the problem, especially escalation root. • Are recording tasks and functions of event, incident and problem developed? Situation of • Do problem exist during processing? Incident/ • Were resolving process resolved in timely manner and was problem the resolution complete reasonable? Management • Are all problems identified for verification and resolution? Help desk • Does the help desk has appropriate staff? (Service • Are there any SLA of the help desk? desk) • Are there any appropriate supporting software for a help desk? • Does the help desk have appropriate regulation and procedures , especially escalation root to resolve the problem. • Does the help desk record appropriate support and working record? Procedure Regulation and situation procedure Help desk (Service desk) 100
 Overview of Capacity Management Reactive activities: • Monitoring and measuring • Responding and reacting to capacity related events (incidents) Proactive activities: • Predicting future requirement and trends • Budgeting, planning and implementing upgrade. • Seeking ways to improve service performance. • Optimizing the performance of a service 101
Overview of Capacity Management Reactive activities: • Monitoring and measuring • Responding and reacting to capacity related events (incidents) Proactive activities: • Predicting future requirement and trends • Budgeting, planning and implementing upgrade. • Seeking ways to improve service performance. • Optimizing the performance of a service 101
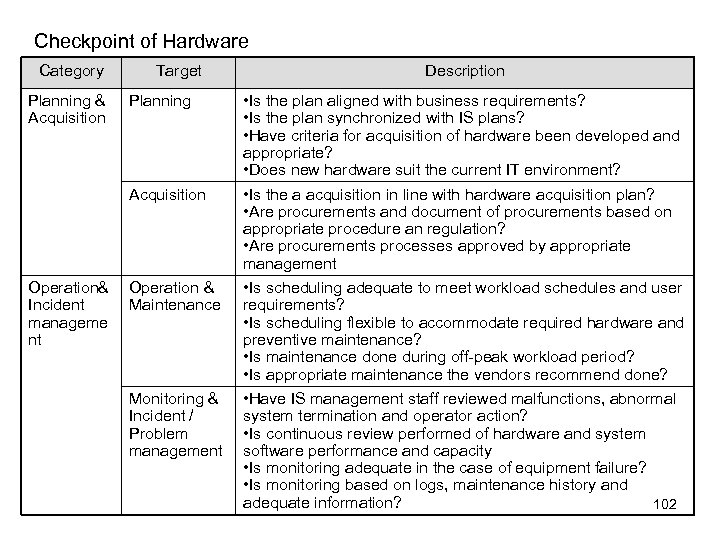 Checkpoint of Hardware Category Planning & Acquisition Target Planning Acquisition Operation& Incident manageme nt Operation & Maintenance Monitoring & Incident / Problem management Description • Is the plan aligned with business requirements? • Is the plan synchronized with IS plans? • Have criteria for acquisition of hardware been developed and appropriate? • Does new hardware suit the current IT environment? • Is the a acquisition in line with hardware acquisition plan? • Are procurements and document of procurements based on appropriate procedure an regulation? • Are procurements processes approved by appropriate management • Is scheduling adequate to meet workload schedules and user requirements? • Is scheduling flexible to accommodate required hardware and preventive maintenance? • Is maintenance done during off-peak workload period? • Is appropriate maintenance the vendors recommend done? • Have IS management staff reviewed malfunctions, abnormal system termination and operator action? • Is continuous review performed of hardware and system software performance and capacity • Is monitoring adequate in the case of equipment failure? • Is monitoring based on logs, maintenance history and adequate information? 102
Checkpoint of Hardware Category Planning & Acquisition Target Planning Acquisition Operation& Incident manageme nt Operation & Maintenance Monitoring & Incident / Problem management Description • Is the plan aligned with business requirements? • Is the plan synchronized with IS plans? • Have criteria for acquisition of hardware been developed and appropriate? • Does new hardware suit the current IT environment? • Is the a acquisition in line with hardware acquisition plan? • Are procurements and document of procurements based on appropriate procedure an regulation? • Are procurements processes approved by appropriate management • Is scheduling adequate to meet workload schedules and user requirements? • Is scheduling flexible to accommodate required hardware and preventive maintenance? • Is maintenance done during off-peak workload period? • Is appropriate maintenance the vendors recommend done? • Have IS management staff reviewed malfunctions, abnormal system termination and operator action? • Is continuous review performed of hardware and system software performance and capacity • Is monitoring adequate in the case of equipment failure? • Is monitoring based on logs, maintenance history and adequate information? 102
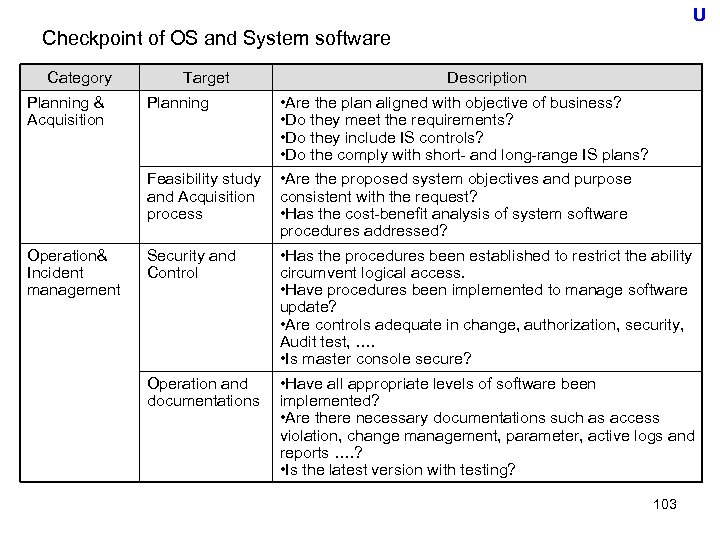 U Checkpoint of OS and System software Category Planning & Acquisition Target Planning Feasibility study and Acquisition process Operation& Incident management Security and Control Operation and documentations Description • Are the plan aligned with objective of business? • Do they meet the requirements? • Do they include IS controls? • Do the comply with short- and long-range IS plans? • Are the proposed system objectives and purpose consistent with the request? • Has the cost-benefit analysis of system software procedures addressed? • Has the procedures been established to restrict the ability circumvent logical access. • Have procedures been implemented to manage software update? • Are controls adequate in change, authorization, security, Audit test, …. • Is master console secure? • Have all appropriate levels of software been implemented? • Are there necessary documentations such as access violation, change management, parameter, active logs and reports …. ? • Is the latest version with testing? 103
U Checkpoint of OS and System software Category Planning & Acquisition Target Planning Feasibility study and Acquisition process Operation& Incident management Security and Control Operation and documentations Description • Are the plan aligned with objective of business? • Do they meet the requirements? • Do they include IS controls? • Do the comply with short- and long-range IS plans? • Are the proposed system objectives and purpose consistent with the request? • Has the cost-benefit analysis of system software procedures addressed? • Has the procedures been established to restrict the ability circumvent logical access. • Have procedures been implemented to manage software update? • Are controls adequate in change, authorization, security, Audit test, …. • Is master console secure? • Have all appropriate levels of software been implemented? • Are there necessary documentations such as access violation, change management, parameter, active logs and reports …. ? • Is the latest version with testing? 103
 Tasks of operation staff • Executing and monitoring scheduled job • Facilitating timely backup • Monitoring unauthorized access and use of sensitive data • Monitoring and reviewing the extent to adherence to IT operation procedures as established by IS and business management • Participating in test of disaster recovery plans • Monitoring the performance, capacity, availability and failure of information resources • Facilitating troubleshooting and incident handling. 104
Tasks of operation staff • Executing and monitoring scheduled job • Facilitating timely backup • Monitoring unauthorized access and use of sensitive data • Monitoring and reviewing the extent to adherence to IT operation procedures as established by IS and business management • Participating in test of disaster recovery plans • Monitoring the performance, capacity, availability and failure of information resources • Facilitating troubleshooting and incident handling. 104
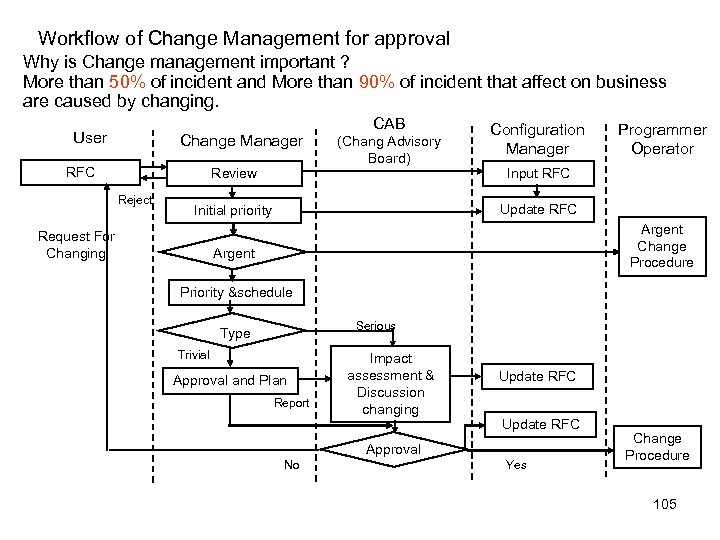 Workflow of Change Management for approval Why is Change management important ? More than 50% of incident and More than 90% of incident that affect on business are caused by changing. User Change Manager RFC Review Reject CAB (Chang Advisory Board) Programmer Operator Input RFC Update RFC Initial priority Request For Changing Configuration Manager Argent Change Procedure Argent Priority &schedule Serious Type Trivial Approval and Plan Report Impact assessment & Discussion changing Update RFC Approval No Yes Change Procedure 105
Workflow of Change Management for approval Why is Change management important ? More than 50% of incident and More than 90% of incident that affect on business are caused by changing. User Change Manager RFC Review Reject CAB (Chang Advisory Board) Programmer Operator Input RFC Update RFC Initial priority Request For Changing Configuration Manager Argent Change Procedure Argent Priority &schedule Serious Type Trivial Approval and Plan Report Impact assessment & Discussion changing Update RFC Approval No Yes Change Procedure 105
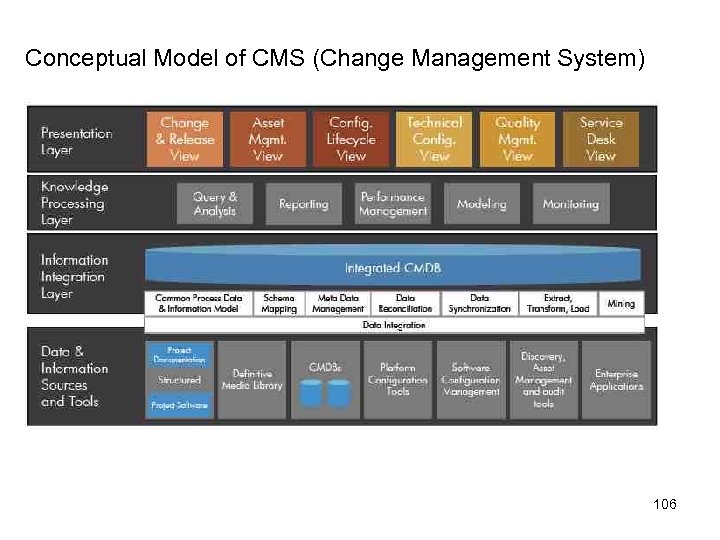 Conceptual Model of CMS (Change Management System) 106
Conceptual Model of CMS (Change Management System) 106
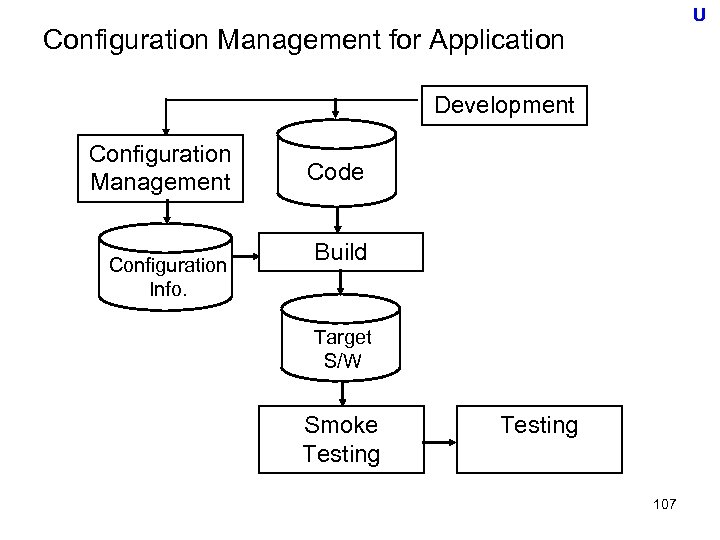 U Configuration Management for Application Development Configuration Management Configuration Info. Code Build Target S/W Smoke Testing 107
U Configuration Management for Application Development Configuration Management Configuration Info. Code Build Target S/W Smoke Testing 107
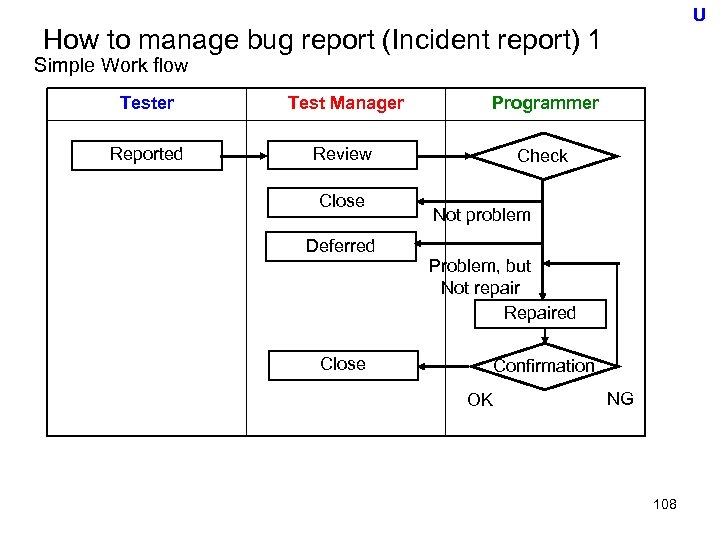 U How to manage bug report (Incident report) 1 Simple Work flow Tester Test Manager Programmer Reported Review Check Close Not problem Deferred Problem, but Not repair Repaired Close Confirmation OK NG 108
U How to manage bug report (Incident report) 1 Simple Work flow Tester Test Manager Programmer Reported Review Check Close Not problem Deferred Problem, but Not repair Repaired Close Confirmation OK NG 108
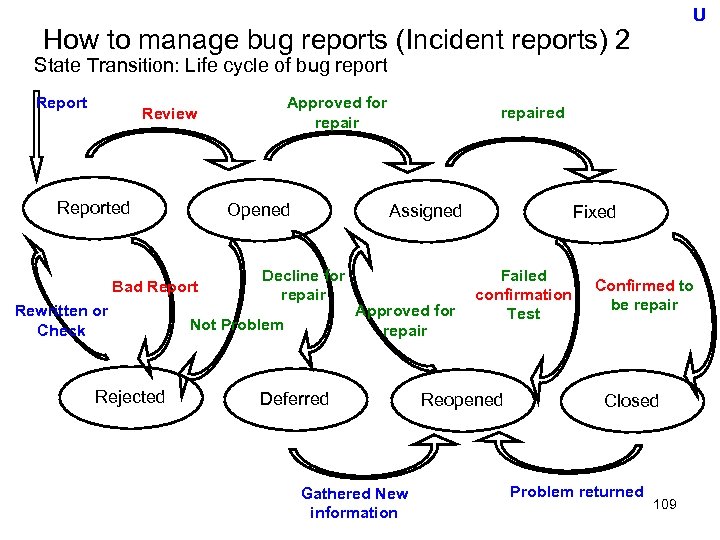 U How to manage bug reports (Incident reports) 2 State Transition: Life cycle of bug report Report Approved for repair Review Reported Opened Bad Report Rewritten or Check Rejected repaired Assigned Decline for repair Not Problem Approved for repair Deferred Gathered New information Fixed Failed confirmation Test Reopened Confirmed to be repair Closed Problem returned 109
U How to manage bug reports (Incident reports) 2 State Transition: Life cycle of bug report Report Approved for repair Review Reported Opened Bad Report Rewritten or Check Rejected repaired Assigned Decline for repair Not Problem Approved for repair Deferred Gathered New information Fixed Failed confirmation Test Reopened Confirmed to be repair Closed Problem returned 109
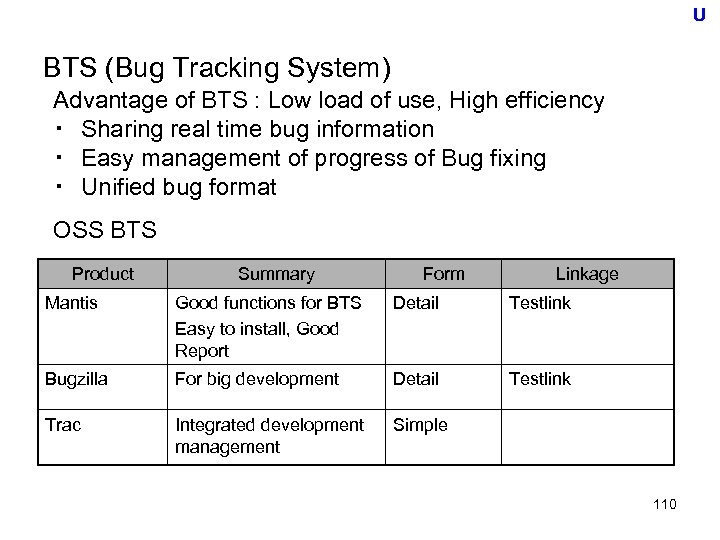 U BTS (Bug Tracking System) Advantage of BTS : Low load of use, High efficiency ・ Sharing real time bug information ・ Easy management of progress of Bug fixing ・ Unified bug format OSS BTS Product Summary Form Linkage Mantis Good functions for BTS Easy to install, Good Report Detail Testlink Bugzilla For big development Detail Testlink Trac Integrated development management Simple 110
U BTS (Bug Tracking System) Advantage of BTS : Low load of use, High efficiency ・ Sharing real time bug information ・ Easy management of progress of Bug fixing ・ Unified bug format OSS BTS Product Summary Form Linkage Mantis Good functions for BTS Easy to install, Good Report Detail Testlink Bugzilla For big development Detail Testlink Trac Integrated development management Simple 110
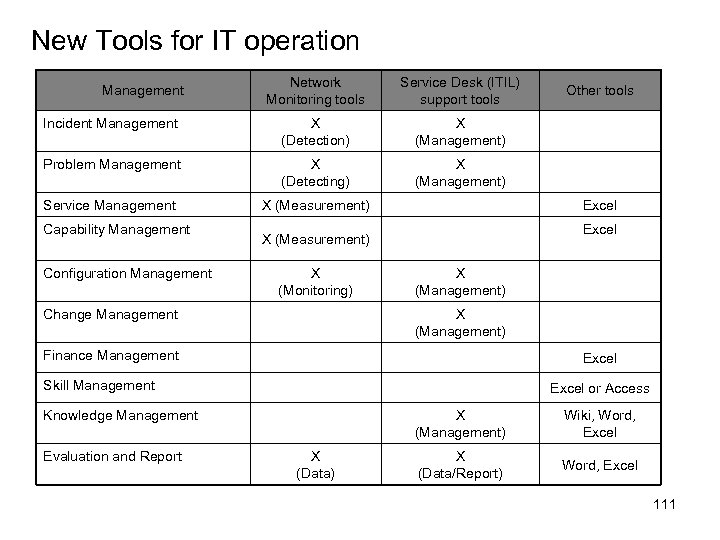 New Tools for IT operation Network Monitoring tools Service Desk (ITIL) support tools Incident Management X (Detection) X (Management) Problem Management X (Detecting) X (Management) Service Management X (Measurement) Management Capability Management Configuration Management Excel X (Measurement) X (Monitoring) Change Management X (Management) Finance Management Excel Skill Management Excel or Access Knowledge Management Evaluation and Report Other tools X (Management) X (Data) Wiki, Word, Excel X (Data/Report) Word, Excel 111
New Tools for IT operation Network Monitoring tools Service Desk (ITIL) support tools Incident Management X (Detection) X (Management) Problem Management X (Detecting) X (Management) Service Management X (Measurement) Management Capability Management Configuration Management Excel X (Measurement) X (Monitoring) Change Management X (Management) Finance Management Excel Skill Management Excel or Access Knowledge Management Evaluation and Report Other tools X (Management) X (Data) Wiki, Word, Excel X (Data/Report) Word, Excel 111
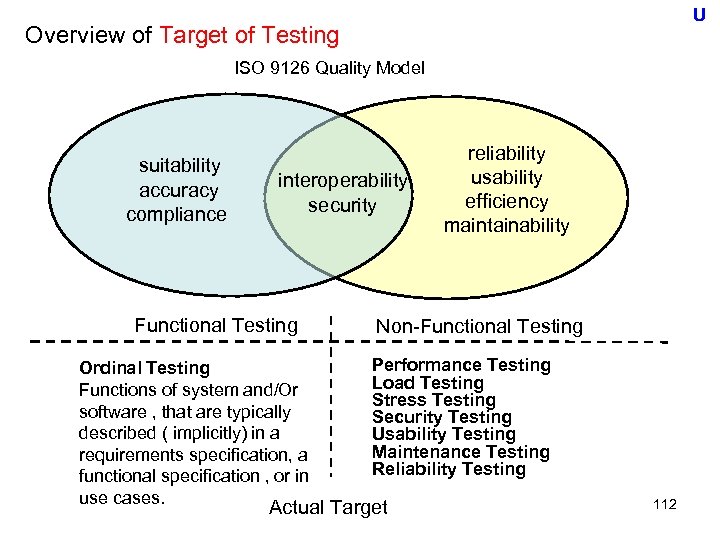 U Overview of Target of Testing ISO 9126 Quality Model suitability accuracy compliance interoperability security Functional Testing Ordinal Testing Functions of system and/Or software , that are typically described ( implicitly) in a requirements specification, a functional specification , or in use cases. reliability usability efficiency maintainability Non-Functional Testing Performance Testing Load Testing Stress Testing Security Testing Usability Testing Maintenance Testing Reliability Testing Actual Target 112
U Overview of Target of Testing ISO 9126 Quality Model suitability accuracy compliance interoperability security Functional Testing Ordinal Testing Functions of system and/Or software , that are typically described ( implicitly) in a requirements specification, a functional specification , or in use cases. reliability usability efficiency maintainability Non-Functional Testing Performance Testing Load Testing Stress Testing Security Testing Usability Testing Maintenance Testing Reliability Testing Actual Target 112
 Part 2. Recommendation and discussion 2 -1. Roadmap and main activities 113
Part 2. Recommendation and discussion 2 -1. Roadmap and main activities 113
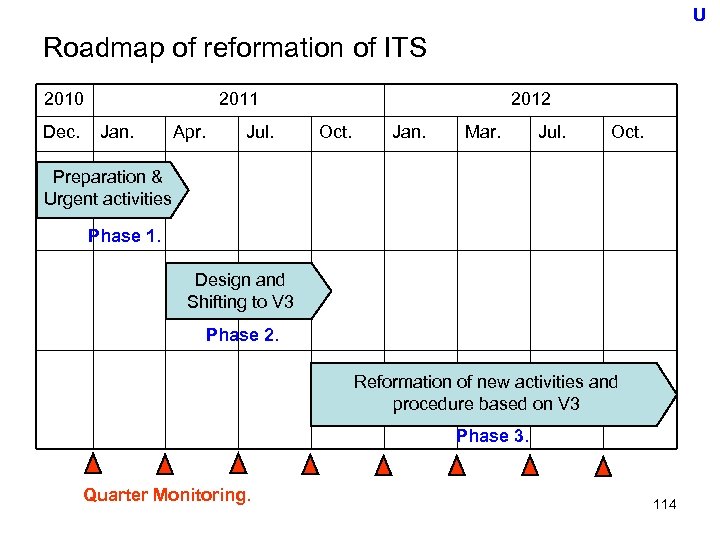 U Roadmap of reformation of ITS 2010 Dec. 2011 Jan. Apr. Jul. 2012 Oct. Jan. Mar. Jul. Oct. Preparation & Urgent activities Phase 1. Design and Shifting to V 3 Phase 2. Reformation of new activities and procedure based on V 3 Phase 3. Quarter Monitoring. 114
U Roadmap of reformation of ITS 2010 Dec. 2011 Jan. Apr. Jul. 2012 Oct. Jan. Mar. Jul. Oct. Preparation & Urgent activities Phase 1. Design and Shifting to V 3 Phase 2. Reformation of new activities and procedure based on V 3 Phase 3. Quarter Monitoring. 114
 Points of ITIL Activities at ITIL (phase 1) • • • User needs Oriented Small action and quick win CSIP: Continues Service Improvement Program Showing ROI and evaluation of KPI Getting agreement of USP management ITIL procedures and functions of ITS are almost good as V 2 level now. ITS needs to shift to cyclic management as V 3. Phase 1 is perpetration for shifting to V 3. 115
Points of ITIL Activities at ITIL (phase 1) • • • User needs Oriented Small action and quick win CSIP: Continues Service Improvement Program Showing ROI and evaluation of KPI Getting agreement of USP management ITIL procedures and functions of ITS are almost good as V 2 level now. ITS needs to shift to cyclic management as V 3. Phase 1 is perpetration for shifting to V 3. 115
 Key tasks of Phase 1 (& 2) Tasks to be shown outside A-1. Formulation of IT Committee for IT governance A-2. Conducting user needs assessment A-3. Accomplishment of enhancement of USP Net A-4. Starting enhancement of application development and control A-5. Enhancement of environment and support of regional campuses A-6. Enhancement of direct user support A-7. Starting plan of academic research services A-8. Possible cost cut with evidence 116
Key tasks of Phase 1 (& 2) Tasks to be shown outside A-1. Formulation of IT Committee for IT governance A-2. Conducting user needs assessment A-3. Accomplishment of enhancement of USP Net A-4. Starting enhancement of application development and control A-5. Enhancement of environment and support of regional campuses A-6. Enhancement of direct user support A-7. Starting plan of academic research services A-8. Possible cost cut with evidence 116
 Key tasks of Phase 1& 2 Tasks to enhance ITS B-1. Employment of new staff B-2. Enhancement of work procedure as ITS level B-3. Modifying strategic plan and getting approval by USP management. B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators B-5. Definite regular monitoring procedure B-6. Planning and conducting training including regional staff B-7. Enhancement of communication among staff 117
Key tasks of Phase 1& 2 Tasks to enhance ITS B-1. Employment of new staff B-2. Enhancement of work procedure as ITS level B-3. Modifying strategic plan and getting approval by USP management. B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators B-5. Definite regular monitoring procedure B-6. Planning and conducting training including regional staff B-7. Enhancement of communication among staff 117
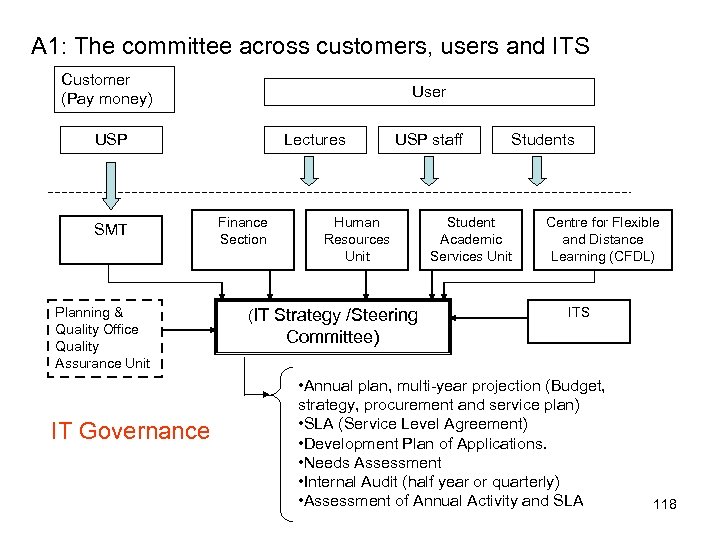 A 1: The committee across customers, users and ITS Customer (Pay money) User USP SMT Planning & Quality Office Quality Assurance Unit IT Governance Lectures Finance Section USP staff Human Resources Unit (IT Strategy /Steering Students Student Academic Services Unit Centre for Flexible and Distance Learning (CFDL) ITS Committee) • Annual plan, multi-year projection (Budget, strategy, procurement and service plan) • SLA (Service Level Agreement) • Development Plan of Applications. • Needs Assessment • Internal Audit (half year or quarterly) • Assessment of Annual Activity and SLA 118
A 1: The committee across customers, users and ITS Customer (Pay money) User USP SMT Planning & Quality Office Quality Assurance Unit IT Governance Lectures Finance Section USP staff Human Resources Unit (IT Strategy /Steering Students Student Academic Services Unit Centre for Flexible and Distance Learning (CFDL) ITS Committee) • Annual plan, multi-year projection (Budget, strategy, procurement and service plan) • SLA (Service Level Agreement) • Development Plan of Applications. • Needs Assessment • Internal Audit (half year or quarterly) • Assessment of Annual Activity and SLA 118
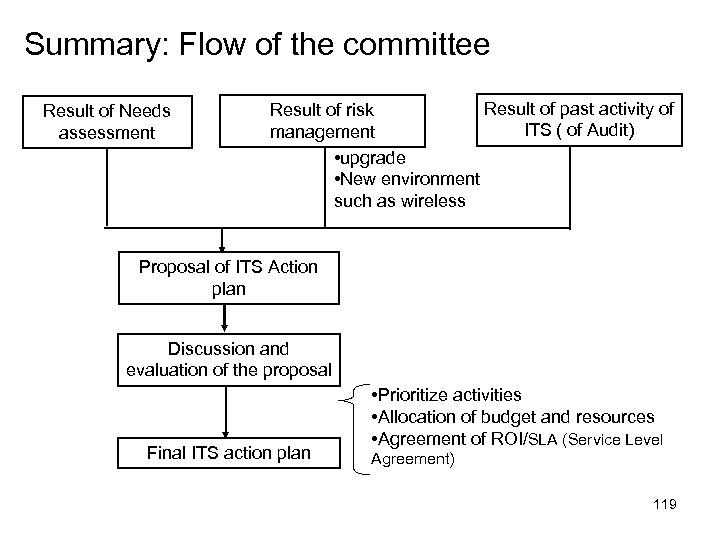 Summary: Flow of the committee Result of Needs assessment Result of past activity of Result of risk ITS ( of Audit) management • upgrade • New environment such as wireless Proposal of ITS Action plan Discussion and evaluation of the proposal Final ITS action plan • Prioritize activities • Allocation of budget and resources • Agreement of ROI/SLA (Service Level Agreement) 119
Summary: Flow of the committee Result of Needs assessment Result of past activity of Result of risk ITS ( of Audit) management • upgrade • New environment such as wireless Proposal of ITS Action plan Discussion and evaluation of the proposal Final ITS action plan • Prioritize activities • Allocation of budget and resources • Agreement of ROI/SLA (Service Level Agreement) 119
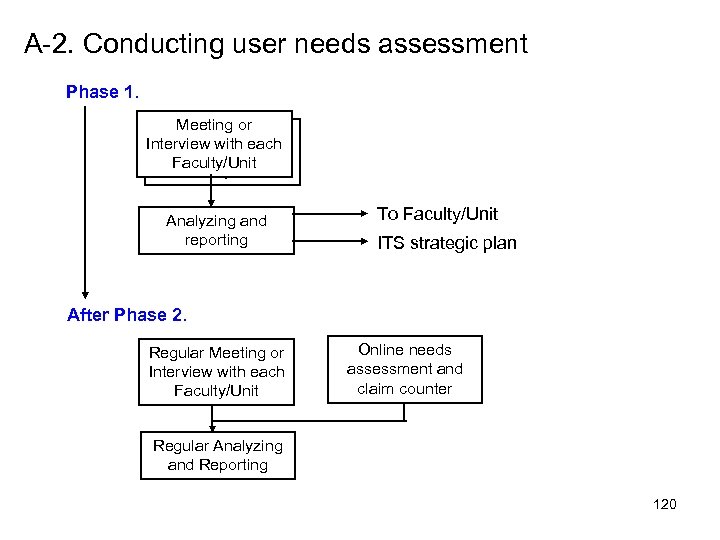 A-2. Conducting user needs assessment Phase 1. Meeting or Interview with each Faculty/Unit Analyzing and reporting To Faculty/Unit ITS strategic plan After Phase 2. Regular Meeting or Interview with each Faculty/Unit Online needs assessment and claim counter Regular Analyzing and Reporting 120
A-2. Conducting user needs assessment Phase 1. Meeting or Interview with each Faculty/Unit Analyzing and reporting To Faculty/Unit ITS strategic plan After Phase 2. Regular Meeting or Interview with each Faculty/Unit Online needs assessment and claim counter Regular Analyzing and Reporting 120
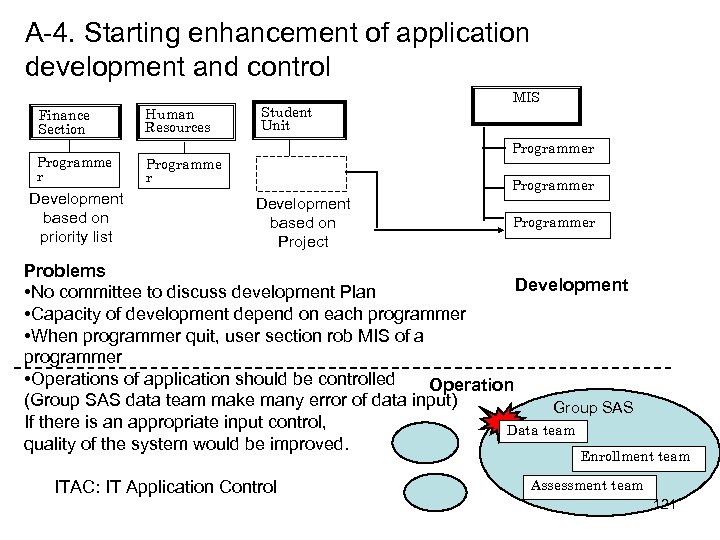 A-4. Starting enhancement of application development and control Finance Section Programme r Development based on priority list Human Resources Student Unit MIS Programmer Programmer Development based on Project Programmer Problems Development • No committee to discuss development Plan • Capacity of development depend on each programmer • When programmer quit, user section rob MIS of a programmer • Operations of application should be controlled Operation (Group SAS data team make many error of data input) Group SAS If there is an appropriate input control, Data team quality of the system would be improved. Enrollment team ITAC: IT Application Control Assessment team 121
A-4. Starting enhancement of application development and control Finance Section Programme r Development based on priority list Human Resources Student Unit MIS Programmer Programmer Development based on Project Programmer Problems Development • No committee to discuss development Plan • Capacity of development depend on each programmer • When programmer quit, user section rob MIS of a programmer • Operations of application should be controlled Operation (Group SAS data team make many error of data input) Group SAS If there is an appropriate input control, Data team quality of the system would be improved. Enrollment team ITAC: IT Application Control Assessment team 121
 A-5. Enhancement of environment and support of regional campuses a. b. c. d. Survey of Number of break down PCs and repairing (and establishment of repairing procedures) Needs assessment for regional campuses and staff Enhancement of communication with regional campus staff Conducting training for regional campus staff 122
A-5. Enhancement of environment and support of regional campuses a. b. c. d. Survey of Number of break down PCs and repairing (and establishment of repairing procedures) Needs assessment for regional campuses and staff Enhancement of communication with regional campus staff Conducting training for regional campus staff 122
 A-6. Enhancement of direct user support a. b. c. Reformation of ITS web sites What kind of information is important for users. Enhancement of announcement of IT usage at USP Finding problem of the current helpdesk as user support and resolving 123
A-6. Enhancement of direct user support a. b. c. Reformation of ITS web sites What kind of information is important for users. Enhancement of announcement of IT usage at USP Finding problem of the current helpdesk as user support and resolving 123
 A-8. Possible cost cut with evidence Example: • • • Improvement of repairing work ( xx PCs / week -> xx PCs/week) Reducing servers: finding unused servers and stopping them Procurement of servers: ITS provide server function. User doesn’t need procure new server H/W. Making a appropriate contact of software license. Charging for special IT services 124
A-8. Possible cost cut with evidence Example: • • • Improvement of repairing work ( xx PCs / week -> xx PCs/week) Reducing servers: finding unused servers and stopping them Procurement of servers: ITS provide server function. User doesn’t need procure new server H/W. Making a appropriate contact of software license. Charging for special IT services 124
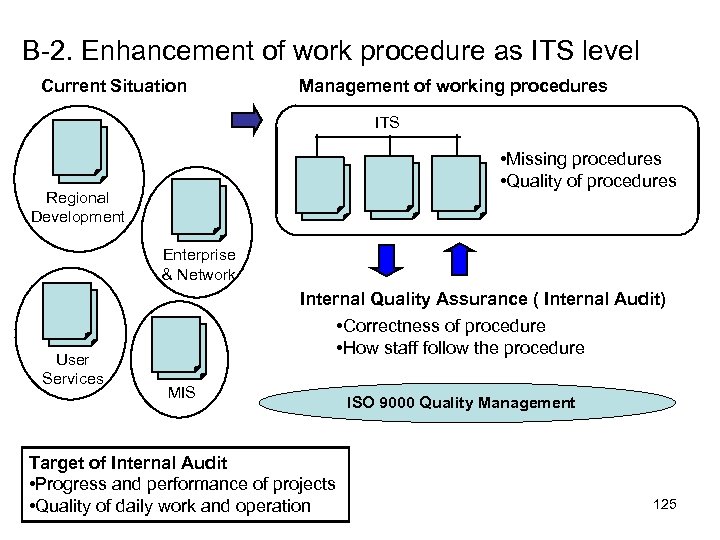 B-2. Enhancement of work procedure as ITS level Current Situation Management of working procedures ITS • Missing procedures • Quality of procedures Regional Development Enterprise & Network User Services Internal Quality Assurance ( Internal Audit) • Correctness of procedure • How staff follow the procedure MIS Target of Internal Audit • Progress and performance of projects • Quality of daily work and operation ISO 9000 Quality Management 125
B-2. Enhancement of work procedure as ITS level Current Situation Management of working procedures ITS • Missing procedures • Quality of procedures Regional Development Enterprise & Network User Services Internal Quality Assurance ( Internal Audit) • Correctness of procedure • How staff follow the procedure MIS Target of Internal Audit • Progress and performance of projects • Quality of daily work and operation ISO 9000 Quality Management 125
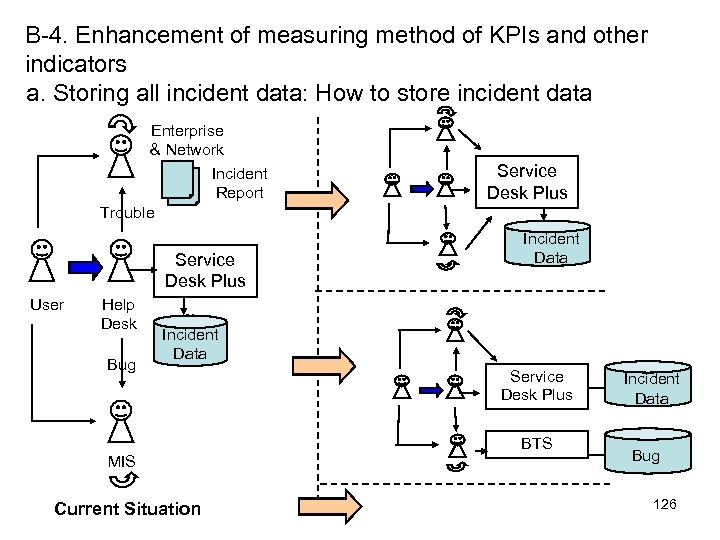 B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators a. Storing all incident data: How to store incident data Enterprise & Network Incident Report Service Desk Plus Trouble Service Desk Plus User Help Desk Bug Incident Data MIS Current Situation Service Desk Plus BTS Incident Data Bug 126
B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators a. Storing all incident data: How to store incident data Enterprise & Network Incident Report Service Desk Plus Trouble Service Desk Plus User Help Desk Bug Incident Data MIS Current Situation Service Desk Plus BTS Incident Data Bug 126
 B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators b. c. d. Evidence to explain number of staff at ITS PC H/W technician, AV H/W technician, Helpdesk, USP net operator and AV operator (Schedule, actual working hour and performance ( num. of repairing H/W , Num. Of user request at Helpdesk) Definition of measuring method of KPIs, Current situation ( or value ) of KPIs Example: • Current breakdown ratio of PCs at regional corpuses is xx%, KPI in 3 months is that the ratio is reduced to yy% • Number of personal Note PC connecting wireless is 800 PCs in 2010, expectation in 2013 up to 1500. ITS establish new wireless network for 2000 PCs until 2013. • Input error ratio of banner is 15% now that makes 20 claims/ week. The xxxxx internal control would reduce the ration 5%. 127
B-4. Enhancement of measuring method of KPIs and other indicators b. c. d. Evidence to explain number of staff at ITS PC H/W technician, AV H/W technician, Helpdesk, USP net operator and AV operator (Schedule, actual working hour and performance ( num. of repairing H/W , Num. Of user request at Helpdesk) Definition of measuring method of KPIs, Current situation ( or value ) of KPIs Example: • Current breakdown ratio of PCs at regional corpuses is xx%, KPI in 3 months is that the ratio is reduced to yy% • Number of personal Note PC connecting wireless is 800 PCs in 2010, expectation in 2013 up to 1500. ITS establish new wireless network for 2000 PCs until 2013. • Input error ratio of banner is 15% now that makes 20 claims/ week. The xxxxx internal control would reduce the ration 5%. 127
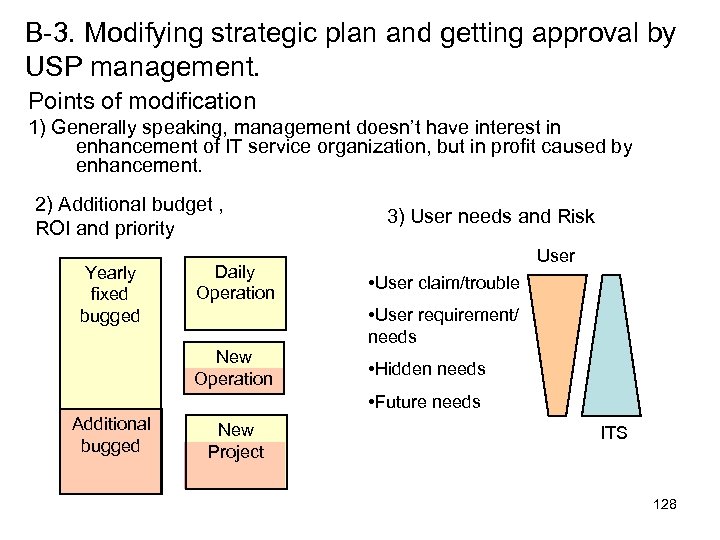 B-3. Modifying strategic plan and getting approval by USP management. Points of modification 1) Generally speaking, management doesn’t have interest in enhancement of IT service organization, but in profit caused by enhancement. 2) Additional budget , ROI and priority Yearly fixed bugged Daily Operation 3) User needs and Risk User • User claim/trouble • User requirement/ needs New Operation • Hidden needs • Future needs Additional bugged New Project ITS 128
B-3. Modifying strategic plan and getting approval by USP management. Points of modification 1) Generally speaking, management doesn’t have interest in enhancement of IT service organization, but in profit caused by enhancement. 2) Additional budget , ROI and priority Yearly fixed bugged Daily Operation 3) User needs and Risk User • User claim/trouble • User requirement/ needs New Operation • Hidden needs • Future needs Additional bugged New Project ITS 128
 2 -2. ITS structure and capacity development (HRD) 129
2 -2. ITS structure and capacity development (HRD) 129
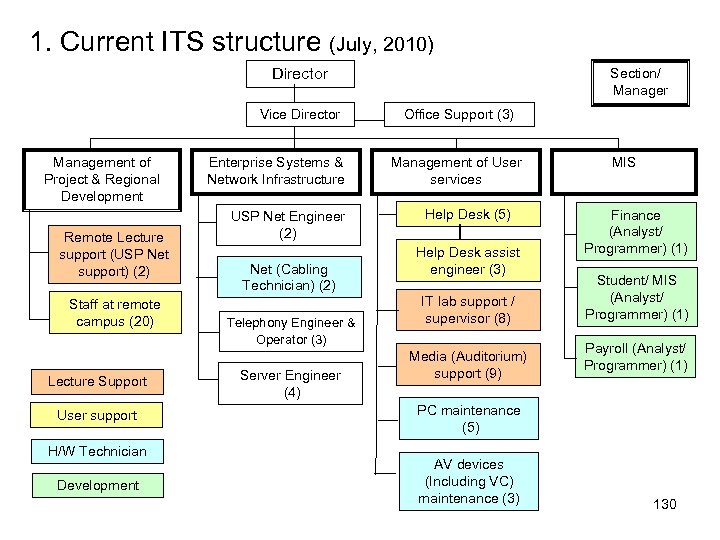 1. Current ITS structure (July, 2010) Director Vice Director Management of Project & Regional Development Remote Lecture support (USP Net support) (2) Staff at remote campus (20) Lecture Support User support H/W Technician Development Enterprise Systems & Network Infrastructure USP Net Engineer (2) Net (Cabling Technician) (2) Telephony Engineer & Operator (3) Server Engineer (4) Section/ Manager Office Support (3) Management of User services Help Desk (5) Help Desk assist engineer (3) IT lab support / supervisor (8) Media (Auditorium) support (9) MIS Finance (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) Student/ MIS (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) Payroll (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) PC maintenance (5) AV devices (Including VC) maintenance (3) 130
1. Current ITS structure (July, 2010) Director Vice Director Management of Project & Regional Development Remote Lecture support (USP Net support) (2) Staff at remote campus (20) Lecture Support User support H/W Technician Development Enterprise Systems & Network Infrastructure USP Net Engineer (2) Net (Cabling Technician) (2) Telephony Engineer & Operator (3) Server Engineer (4) Section/ Manager Office Support (3) Management of User services Help Desk (5) Help Desk assist engineer (3) IT lab support / supervisor (8) Media (Auditorium) support (9) MIS Finance (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) Student/ MIS (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) Payroll (Analyst/ Programmer) (1) PC maintenance (5) AV devices (Including VC) maintenance (3) 130
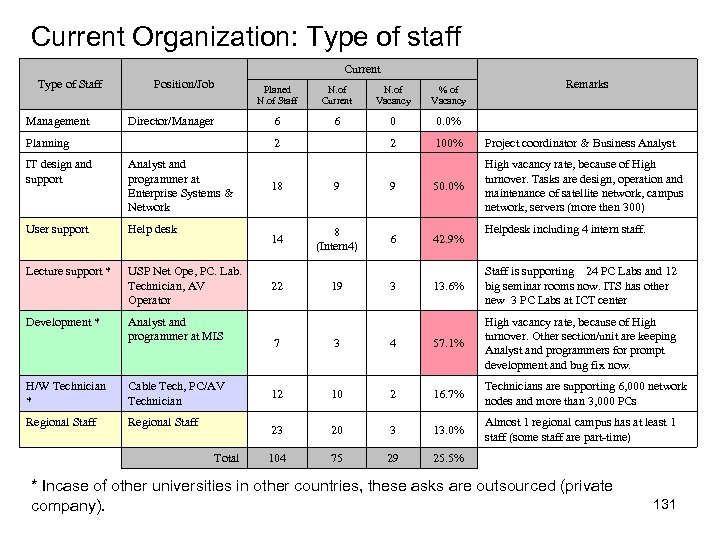 Current Organization: Type of staff Current Type of Staff Management Position/Job N. of Vacancy % of Vacancy 6 0 0. 0% 2 100% Project coordinator & Business Analyst High vacancy rate, because of High turnover. Tasks are design, operation and maintenance of satellite network, campus network, servers (more then 300) 2 IT design and support Analyst and programmer at Enterprise Systems & Network User support Help desk Lecture support * USP Net Ope, PC. Lab. Technician, AV Operator Analyst and programmer at MIS 18 9 9 50. 0% 14 8 (Intern 4) 6 42. 9% 22 19 3 Helpdesk including 4 intern staff. 13. 6% Staff is supporting 24 PC Labs and 12 big seminar rooms now. ITS has other new 3 PC Labs at ICT center Cable Tech, PC/AV Technician Regional Staff Total 7 3 4 57. 1% High vacancy rate, because of High turnover. Other section/unit are keeping Analyst and programmers for prompt development and bug fix now. 12 10 2 16. 7% Technicians are supporting 6, 000 network nodes and more than 3, 000 PCs 23 H/W Technician * N. of Current 6 Director/Manager Planning Development * Remarks Planed N. of Staff 20 3 13. 0% Almost 1 regional campus has at least 1 staff (some staff are part-time) 104 75 29 25. 5% * Incase of other universities in other countries, these asks are outsourced (private company). 131
Current Organization: Type of staff Current Type of Staff Management Position/Job N. of Vacancy % of Vacancy 6 0 0. 0% 2 100% Project coordinator & Business Analyst High vacancy rate, because of High turnover. Tasks are design, operation and maintenance of satellite network, campus network, servers (more then 300) 2 IT design and support Analyst and programmer at Enterprise Systems & Network User support Help desk Lecture support * USP Net Ope, PC. Lab. Technician, AV Operator Analyst and programmer at MIS 18 9 9 50. 0% 14 8 (Intern 4) 6 42. 9% 22 19 3 Helpdesk including 4 intern staff. 13. 6% Staff is supporting 24 PC Labs and 12 big seminar rooms now. ITS has other new 3 PC Labs at ICT center Cable Tech, PC/AV Technician Regional Staff Total 7 3 4 57. 1% High vacancy rate, because of High turnover. Other section/unit are keeping Analyst and programmers for prompt development and bug fix now. 12 10 2 16. 7% Technicians are supporting 6, 000 network nodes and more than 3, 000 PCs 23 H/W Technician * N. of Current 6 Director/Manager Planning Development * Remarks Planed N. of Staff 20 3 13. 0% Almost 1 regional campus has at least 1 staff (some staff are part-time) 104 75 29 25. 5% * Incase of other universities in other countries, these asks are outsourced (private company). 131
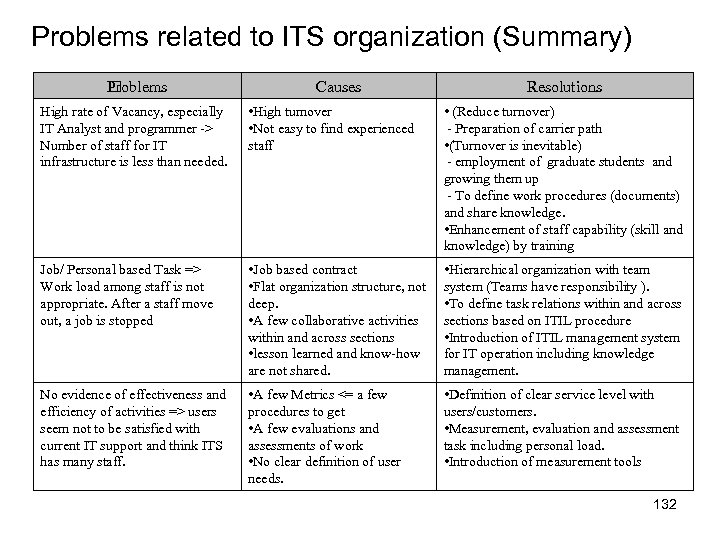 Problems related to ITS organization (Summary) Problems Causes Resolutions High rate of Vacancy, especially IT Analyst and programmer -> Number of staff for IT infrastructure is less than needed. • High turnover • Not easy to find experienced staff • (Reduce turnover) - Preparation of carrier path • (Turnover is inevitable) - employment of graduate students and growing them up - To define work procedures (documents) and share knowledge. • Enhancement of staff capability (skill and knowledge) by training Job/ Personal based Task => Work load among staff is not appropriate. After a staff move out, a job is stopped • Job based contract • Flat organization structure, not deep. • A few collaborative activities within and across sections • lesson learned and know-how are not shared. • Hierarchical organization with team system (Teams have responsibility ). • To define task relations within and across sections based on ITIL procedure • Introduction of ITIL management system for IT operation including knowledge management. No evidence of effectiveness and efficiency of activities => users seem not to be satisfied with current IT support and think ITS has many staff. • A few Metrics <= a few procedures to get • A few evaluations and assessments of work • No clear definition of user needs. • Definition of clear service level with users/customers. • Measurement, evaluation and assessment task including personal load. • Introduction of measurement tools 132
Problems related to ITS organization (Summary) Problems Causes Resolutions High rate of Vacancy, especially IT Analyst and programmer -> Number of staff for IT infrastructure is less than needed. • High turnover • Not easy to find experienced staff • (Reduce turnover) - Preparation of carrier path • (Turnover is inevitable) - employment of graduate students and growing them up - To define work procedures (documents) and share knowledge. • Enhancement of staff capability (skill and knowledge) by training Job/ Personal based Task => Work load among staff is not appropriate. After a staff move out, a job is stopped • Job based contract • Flat organization structure, not deep. • A few collaborative activities within and across sections • lesson learned and know-how are not shared. • Hierarchical organization with team system (Teams have responsibility ). • To define task relations within and across sections based on ITIL procedure • Introduction of ITIL management system for IT operation including knowledge management. No evidence of effectiveness and efficiency of activities => users seem not to be satisfied with current IT support and think ITS has many staff. • A few Metrics <= a few procedures to get • A few evaluations and assessments of work • No clear definition of user needs. • Definition of clear service level with users/customers. • Measurement, evaluation and assessment task including personal load. • Introduction of measurement tools 132
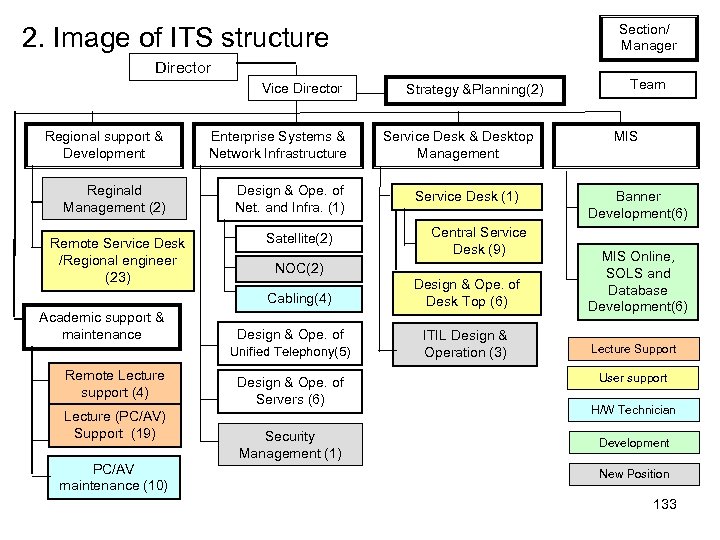 Section/ Manager 2. Image of ITS structure Director Vice Director Regional support & Development Enterprise Systems & Network Infrastructure Reginald Management (2) Design & Ope. of Net. and Infra. (1) Remote Service Desk /Regional engineer (23) Satellite(2) Design & Ope. of Unified Telephony(5) Remote Lecture support (4) Lecture (PC/AV) Support (19) PC/AV maintenance (10) Service Desk & Desktop Management Service Desk (1) Central Service Desk (9) NOC(2) Cabling(4) Academic support & maintenance Strategy &Planning(2) Design & Ope. of Servers (6) Security Management (1) Design & Ope. of Desk Top (6) ITIL Design & Operation (3) Team MIS Banner Development(6) MIS Online, SOLS and Database Development(6) Lecture Support User support H/W Technician Development New Position 133
Section/ Manager 2. Image of ITS structure Director Vice Director Regional support & Development Enterprise Systems & Network Infrastructure Reginald Management (2) Design & Ope. of Net. and Infra. (1) Remote Service Desk /Regional engineer (23) Satellite(2) Design & Ope. of Unified Telephony(5) Remote Lecture support (4) Lecture (PC/AV) Support (19) PC/AV maintenance (10) Service Desk & Desktop Management Service Desk (1) Central Service Desk (9) NOC(2) Cabling(4) Academic support & maintenance Strategy &Planning(2) Design & Ope. of Servers (6) Security Management (1) Design & Ope. of Desk Top (6) ITIL Design & Operation (3) Team MIS Banner Development(6) MIS Online, SOLS and Database Development(6) Lecture Support User support H/W Technician Development New Position 133
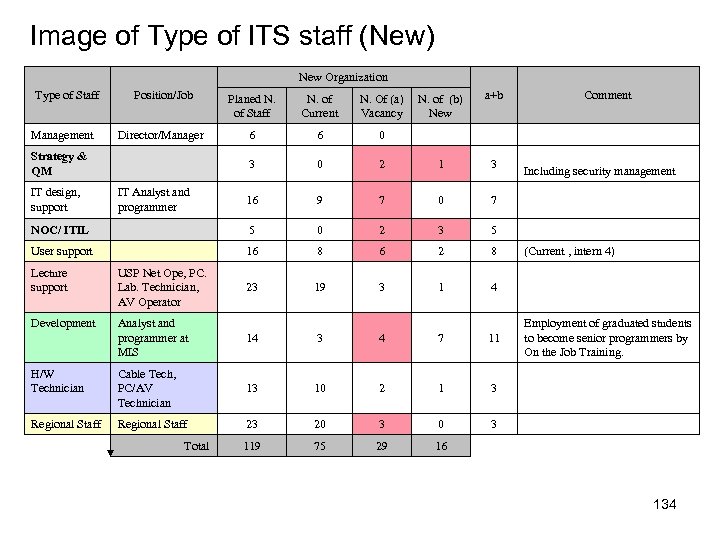 Image of Type of ITS staff (New) New Organization Type of Staff Position/Job Planed N. of Staff N. of Current Director/Manager 6 6 0 3 0 2 1 3 16 9 7 0 7 NOC/ ITIL 5 0 2 3 5 User support 16 8 6 2 8 23 19 3 1 4 Management Strategy & QM IT design, support IT Analyst and programmer N. Of (a) N. of (b) Vacancy New a+b Lecture support USP Net Ope, PC. Lab. Technician, AV Operator Development Analyst and programmer at MIS 14 3 4 7 Cable Tech, PC/AV Technician 13 10 2 1 Regional Staff 23 20 3 0 75 29 16 (Current , intern 4) 3 119 3 Regional Staff Including security management 11 H/W Technician Comment Total Employment of graduated students to become senior programmers by On the Job Training. 134
Image of Type of ITS staff (New) New Organization Type of Staff Position/Job Planed N. of Staff N. of Current Director/Manager 6 6 0 3 0 2 1 3 16 9 7 0 7 NOC/ ITIL 5 0 2 3 5 User support 16 8 6 2 8 23 19 3 1 4 Management Strategy & QM IT design, support IT Analyst and programmer N. Of (a) N. of (b) Vacancy New a+b Lecture support USP Net Ope, PC. Lab. Technician, AV Operator Development Analyst and programmer at MIS 14 3 4 7 Cable Tech, PC/AV Technician 13 10 2 1 Regional Staff 23 20 3 0 75 29 16 (Current , intern 4) 3 119 3 Regional Staff Including security management 11 H/W Technician Comment Total Employment of graduated students to become senior programmers by On the Job Training. 134
 Point of reformation of ITS structure • • Development HR management system Employment of vacant position Restructure of Application development at USP level Communication managers and staff Enhancement of training ( Management of staff skill and skill standards) Development of regional staffs’ capacity Establishment of team system in current structure Utilization of internship and employment of graduated students. What is motivation and incentive of staff? 135
Point of reformation of ITS structure • • Development HR management system Employment of vacant position Restructure of Application development at USP level Communication managers and staff Enhancement of training ( Management of staff skill and skill standards) Development of regional staffs’ capacity Establishment of team system in current structure Utilization of internship and employment of graduated students. What is motivation and incentive of staff? 135
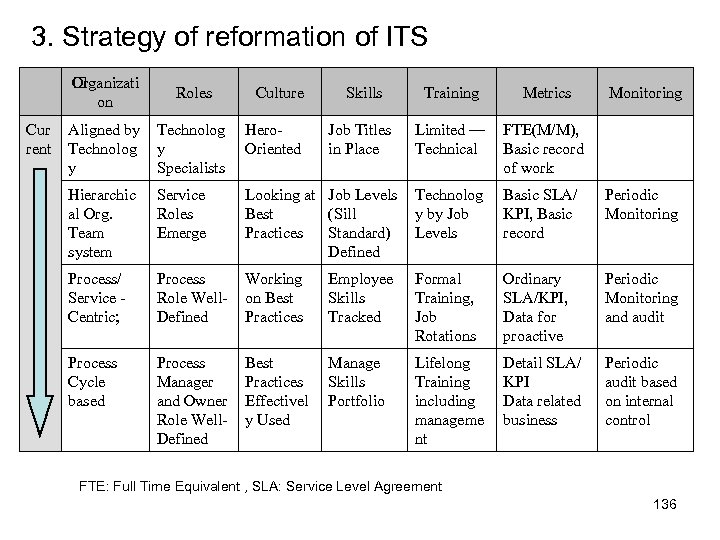 3. Strategy of reformation of ITS Organizati on Cur rent Roles Culture Skills Training Metrics Monitoring Aligned by Technolog y y Specialists Hero. Oriented Job Titles in Place Hierarchic al Org. Team system Service Roles Emerge Looking at Job Levels Technolog Best (Sill y by Job Practices Standard) Levels Defined Basic SLA/ KPI, Basic record Periodic Monitoring Process/ Service Centric; Process Role Well. Defined Working on Best Practices Employee Skills Tracked Formal Training, Job Rotations Ordinary SLA/KPI, Data for proactive Periodic Monitoring and audit Process Cycle based Process Manager and Owner Role Well. Defined Best Practices Effectivel y Used Manage Skills Portfolio Lifelong Training including manageme nt Detail SLA/ KPI Data related business Periodic audit based on internal control Limited — FTE(M/M), Technical Basic record of work FTE: Full Time Equivalent , SLA: Service Level Agreement 136
3. Strategy of reformation of ITS Organizati on Cur rent Roles Culture Skills Training Metrics Monitoring Aligned by Technolog y y Specialists Hero. Oriented Job Titles in Place Hierarchic al Org. Team system Service Roles Emerge Looking at Job Levels Technolog Best (Sill y by Job Practices Standard) Levels Defined Basic SLA/ KPI, Basic record Periodic Monitoring Process/ Service Centric; Process Role Well. Defined Working on Best Practices Employee Skills Tracked Formal Training, Job Rotations Ordinary SLA/KPI, Data for proactive Periodic Monitoring and audit Process Cycle based Process Manager and Owner Role Well. Defined Best Practices Effectivel y Used Manage Skills Portfolio Lifelong Training including manageme nt Detail SLA/ KPI Data related business Periodic audit based on internal control Limited — FTE(M/M), Technical Basic record of work FTE: Full Time Equivalent , SLA: Service Level Agreement 136
 U Thanks for you joining the lecture! Contact: Go Ota e-mail gohome@v 006. vaio. ne. jp Web www. beyondbb. jp (Japanese) 137
U Thanks for you joining the lecture! Contact: Go Ota e-mail gohome@v 006. vaio. ne. jp Web www. beyondbb. jp (Japanese) 137


