 Item 20: Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes
Item 20: Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes
 Tagged class – • instances come in two or more flavors; • contain a tag field indicating the flavor of the instance
Tagged class – • instances come in two or more flavors; • contain a tag field indicating the flavor of the instance
 Tagged classes: • Bad readability • Spend to much memory (contain fields belonging to other flavors) • Fields can’t be final (constructors don’t initialize irrelevant fields) • Constructors must set the tag field and initialize the right data fields – compiler can’t control this. • Type doesn’t gives a clue to its flavor.
Tagged classes: • Bad readability • Spend to much memory (contain fields belonging to other flavors) • Fields can’t be final (constructors don’t initialize irrelevant fields) • Constructors must set the tag field and initialize the right data fields – compiler can’t control this. • Type doesn’t gives a clue to its flavor.
 A tagged class is just imitation of a class hierarchy Refactor tagged class into a hierarchy
A tagged class is just imitation of a class hierarchy Refactor tagged class into a hierarchy
 Item 21: Use function objects to represent strategies
Item 21: Use function objects to represent strategies
 Function object is – An instance of a class that exports exactly one method performing operations on other objects, passed explicitly to the method Example: Comparator
Function object is – An instance of a class that exports exactly one method performing operations on other objects, passed explicitly to the method Example: Comparator
 Concrete strategy • Comparator is concrete strategy for comparison • Typical concrete strategy classes are stateless: has no fields => all instances of the class are functionally equivalent => should be a singleton
Concrete strategy • Comparator is concrete strategy for comparison • Typical concrete strategy classes are stateless: has no fields => all instances of the class are functionally equivalent => should be a singleton
 Concrete strategy classes are often declared as anonymous classes Note that using an anonymous class will create a new instance each time the call is executed • If concrete strategy used once – anonymous class • If concrete strategy is designed for repeated use: • Implementation – private static member class • Export – final public static field • Type – strategy interface
Concrete strategy classes are often declared as anonymous classes Note that using an anonymous class will create a new instance each time the call is executed • If concrete strategy used once – anonymous class • If concrete strategy is designed for repeated use: • Implementation – private static member class • Export – final public static field • Type – strategy interface
 Item 22: Favor static member classes over nonstatic
Item 22: Favor static member classes over nonstatic
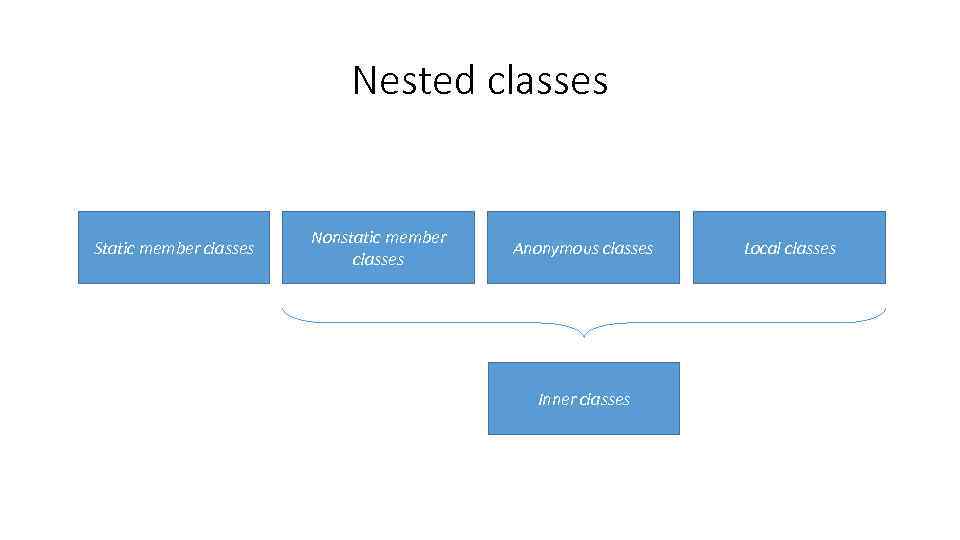 Nested classes Static member classes Nonstatic member classes Anonymous classes Inner classes Local classes
Nested classes Static member classes Nonstatic member classes Anonymous classes Inner classes Local classes
 If you declare a member class that does not require access to an enclosing instance – always put the static modifier in its declaration Nonstatic member class has reference to enclosing instance: • it costs time and resources; • it makes enclosing instance not available for garbage collection.
If you declare a member class that does not require access to an enclosing instance – always put the static modifier in its declaration Nonstatic member class has reference to enclosing instance: • it costs time and resources; • it makes enclosing instance not available for garbage collection.
 Anonymous and local classes should be short – ten a fewer lines
Anonymous and local classes should be short – ten a fewer lines