961140dd16270d53398cdc6b7beae905.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 ITCE 720 A Autonomic Wireless Networking Fall 2009 Prof. Chansu Yu chansuyu@gmail. com c. yu 91@csuohio. edu 1
ITCE 720 A Autonomic Wireless Networking Fall 2009 Prof. Chansu Yu chansuyu@gmail. com c. yu 91@csuohio. edu 1
 Who am I Industry Experience at Gold. Star/LG (1984 -1997) Handheld PC at LG Inc. Microsoft’s Windows CE q Hitachi’s SH 3 Microprocessor q Design Issues Interrupt latencies q Power modes & Energy saving q Cache performance (Accessible cache) q ARM Support (Virtual cache) q 2
Who am I Industry Experience at Gold. Star/LG (1984 -1997) Handheld PC at LG Inc. Microsoft’s Windows CE q Hitachi’s SH 3 Microprocessor q Design Issues Interrupt latencies q Power modes & Energy saving q Cache performance (Accessible cache) q ARM Support (Virtual cache) q 2
 Who am I PC BIOS (Basic Input/Output Systems) Project at Gold. Star Inc. q Clean room process q Specification writing team : aware of BIOS code q Bios writing team : virgin engineers q. I was in the Specification team to work on POST (Power -on-self-test) & HDD (hard disk drive) 3
Who am I PC BIOS (Basic Input/Output Systems) Project at Gold. Star Inc. q Clean room process q Specification writing team : aware of BIOS code q Bios writing team : virgin engineers q. I was in the Specification team to work on POST (Power -on-self-test) & HDD (hard disk drive) 3
 Who am I Academic experience ICU (1998 -2001) q Cleveland State University (2001 -Current), USA q Projects in academia Web. Cam with Blue Cord Technology Co. q Remote monitor with ETRI q Energy-aware mobile networking q TDMA-based sensor networks q Current projects q q q Performability in Mobile Wireless Networks (NSF) Exploring Data Access in Internet-based Wireless Mobile Networks (NSF) Low-power Wireless Networking in Software Radio Systems (Fenn) Improving Work Zone Safety using Sensor Networks (CSU) Seamless Connectivity and High Fidelity Communications in Multihop Wireless Mesh Networks (NSF, pending) 4
Who am I Academic experience ICU (1998 -2001) q Cleveland State University (2001 -Current), USA q Projects in academia Web. Cam with Blue Cord Technology Co. q Remote monitor with ETRI q Energy-aware mobile networking q TDMA-based sensor networks q Current projects q q q Performability in Mobile Wireless Networks (NSF) Exploring Data Access in Internet-based Wireless Mobile Networks (NSF) Low-power Wireless Networking in Software Radio Systems (Fenn) Improving Work Zone Safety using Sensor Networks (CSU) Seamless Connectivity and High Fidelity Communications in Multihop Wireless Mesh Networks (NSF, pending) 4
 Cleveland, OHIO 1796: Established in 1796 by Cleveland 1930: City population is 1 M and the 5 th 2008: City population is 0. 5 M 1951: Disc jockey Alan Freed at radio station WJW began playing a certain type of music for a multi-racial audience. Freed coined the phrease "rock and roll" to describe the rollicking R&B music. He organized the first rock and roll concert called "The Moondog Coronation Ball“ Severance Hall (1931, Cleveland Orchestra) Cleveland Clinic (1921, Ranking 3 after Johns Hopkins and Mayo) 5
Cleveland, OHIO 1796: Established in 1796 by Cleveland 1930: City population is 1 M and the 5 th 2008: City population is 0. 5 M 1951: Disc jockey Alan Freed at radio station WJW began playing a certain type of music for a multi-racial audience. Freed coined the phrease "rock and roll" to describe the rollicking R&B music. He organized the first rock and roll concert called "The Moondog Coronation Ball“ Severance Hall (1931, Cleveland Orchestra) Cleveland Clinic (1921, Ranking 3 after Johns Hopkins and Mayo) 5
 Le. Bron James (24), Cleveland Cavaliers The No. 1 overall pick in the 2003 NBA draft ($20 M/year contract @ 2008, one of the highest-paid athlete in US) 1983: Gordon Gund purchased @ $20 M 2005: Gordon Gund sold @ $375 M Value @ 2007: $455 M ($202 M @ 2002) 32 -of-41 regular season games were sold out (50% in 2002) 17 games televised in China (0 in 2002) Cleveland Cavaliers won the first Eastern Conference Championship in 2007 6
Le. Bron James (24), Cleveland Cavaliers The No. 1 overall pick in the 2003 NBA draft ($20 M/year contract @ 2008, one of the highest-paid athlete in US) 1983: Gordon Gund purchased @ $20 M 2005: Gordon Gund sold @ $375 M Value @ 2007: $455 M ($202 M @ 2002) 32 -of-41 regular season games were sold out (50% in 2002) 17 games televised in China (0 in 2002) Cleveland Cavaliers won the first Eastern Conference Championship in 2007 6
 Shin-Soo Choo (27), Cleveland Indians 7
Shin-Soo Choo (27), Cleveland Indians 7
 Introduction 8
Introduction 8
 Evolution of Computing Single user systems Batch processing Time-sharing Networked computing Mobile computing & Ubiquitous computing Autonomic computing (mobile devices + wireless communication + autonomic networking) 9
Evolution of Computing Single user systems Batch processing Time-sharing Networked computing Mobile computing & Ubiquitous computing Autonomic computing (mobile devices + wireless communication + autonomic networking) 9
 Mobile Computing Goal q Access information anywhere, anytime Aliases q Nomadic computing, wireless computing, ubiquitous computing, wearable computing Entire new class of applications New massive markets q Personal computing + consumer electronics + wireless communication q Collaborative computing, vehicle dispatching, point of sale, mail enabled applications, filtered information provision, … q 10
Mobile Computing Goal q Access information anywhere, anytime Aliases q Nomadic computing, wireless computing, ubiquitous computing, wearable computing Entire new class of applications New massive markets q Personal computing + consumer electronics + wireless communication q Collaborative computing, vehicle dispatching, point of sale, mail enabled applications, filtered information provision, … q 10
 1. Mobile Computers 11
1. Mobile Computers 11
 Information at your Fingertips Handheld or Pocket PC, PDA q PC players - easy interface on a computer : Apple Newton, HP Palmtop, Microsoft Windows CE q Electronics players - computing on home appliance : Sharp Zaurus, Philips Velo, Psion Series, 3 Com (USR) Palm. Pilot Starts from and targets PC metaphor (users) q q q Shrunken PC user interface : ex) stylus for mouse Simple PIM applications : Personal Information Mgmt Strong connectivity to Windows PC via IR or Serial PCMCIA, USB, Ir. DA, Mini-card, Flash ROM Stand-alone device but can add networks 12
Information at your Fingertips Handheld or Pocket PC, PDA q PC players - easy interface on a computer : Apple Newton, HP Palmtop, Microsoft Windows CE q Electronics players - computing on home appliance : Sharp Zaurus, Philips Velo, Psion Series, 3 Com (USR) Palm. Pilot Starts from and targets PC metaphor (users) q q q Shrunken PC user interface : ex) stylus for mouse Simple PIM applications : Personal Information Mgmt Strong connectivity to Windows PC via IR or Serial PCMCIA, USB, Ir. DA, Mini-card, Flash ROM Stand-alone device but can add networks 12
 Mobility Issues Bandwidth restrictions and variability Location-aware network operation User may wake up in a new environment q Dynamic replication of data q Querying wireless data & location-based responses Bursty network activity during connections & handling disconnections Disconnection OS and File System Issues - allow for disconnected operation q Database System Issues - when disconnected, based on local data q 13
Mobility Issues Bandwidth restrictions and variability Location-aware network operation User may wake up in a new environment q Dynamic replication of data q Querying wireless data & location-based responses Bursty network activity during connections & handling disconnections Disconnection OS and File System Issues - allow for disconnected operation q Database System Issues - when disconnected, based on local data q 13
 Portability Issues Battery power restrictions Risks to data Physical damage, loss, theft q unauthorized access q encrypt data stored on mobiles q backup critical data to fixed (reliable) hosts q Small user interface Small displays due to battery power and aspect ratio constraints q Cannot open too many windows q Difficult to click on miniature icons q Input Graffiti, (Dictionary-based) Expectation q Gesture or handwriting recognition with Stylus Pen Voice matching or voice recognition 14
Portability Issues Battery power restrictions Risks to data Physical damage, loss, theft q unauthorized access q encrypt data stored on mobiles q backup critical data to fixed (reliable) hosts q Small user interface Small displays due to battery power and aspect ratio constraints q Cannot open too many windows q Difficult to click on miniature icons q Input Graffiti, (Dictionary-based) Expectation q Gesture or handwriting recognition with Stylus Pen Voice matching or voice recognition 14
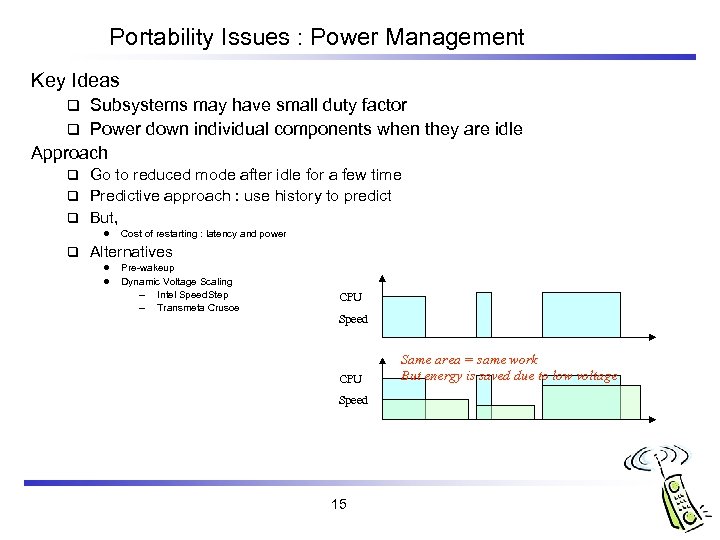 Portability Issues : Power Management Key Ideas Subsystems may have small duty factor q Power down individual components when they are idle Approach q Go to reduced mode after idle for a few time q Predictive approach : use history to predict q But, q l q Cost of restarting : latency and power Alternatives l l Pre-wakeup Dynamic Voltage Scaling – Intel Speed. Step – Transmeta Crusoe CPU Speed 15 Same area = same work But energy is saved due to low voltage
Portability Issues : Power Management Key Ideas Subsystems may have small duty factor q Power down individual components when they are idle Approach q Go to reduced mode after idle for a few time q Predictive approach : use history to predict q But, q l q Cost of restarting : latency and power Alternatives l l Pre-wakeup Dynamic Voltage Scaling – Intel Speed. Step – Transmeta Crusoe CPU Speed 15 Same area = same work But energy is saved due to low voltage
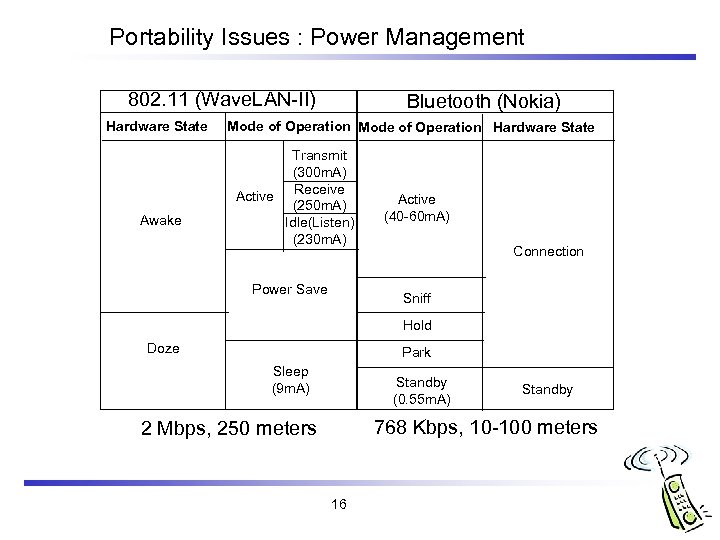 Portability Issues : Power Management 802. 11 (Wave. LAN-II) Hardware State Awake Bluetooth (Nokia) Mode of Operation Hardware State Transmit (300 m. A) Receive Active (250 m. A) Idle(Listen) (230 m. A) Power Save Active (40 -60 m. A) Connection Sniff Hold Doze Park Sleep (9 m. A) Standby (0. 55 m. A) Standby 768 Kbps, 10 -100 meters 2 Mbps, 250 meters 16
Portability Issues : Power Management 802. 11 (Wave. LAN-II) Hardware State Awake Bluetooth (Nokia) Mode of Operation Hardware State Transmit (300 m. A) Receive Active (250 m. A) Idle(Listen) (230 m. A) Power Save Active (40 -60 m. A) Connection Sniff Hold Doze Park Sleep (9 m. A) Standby (0. 55 m. A) Standby 768 Kbps, 10 -100 meters 2 Mbps, 250 meters 16
 2. Wireless Communication Main research challenges due to mobility variable communication conditions q energy limitations q Effects on different layers of OSI hierarchy mobile communication : physical/MAC layer q mobile computing : data link/network/transport layer q Research Issues q Mobile Networking - Network Layer Mobile IP l Location Management l Multicasting l Ad-hoc networking l q Mobile Networking - Transport Layer 17
2. Wireless Communication Main research challenges due to mobility variable communication conditions q energy limitations q Effects on different layers of OSI hierarchy mobile communication : physical/MAC layer q mobile computing : data link/network/transport layer q Research Issues q Mobile Networking - Network Layer Mobile IP l Location Management l Multicasting l Ad-hoc networking l q Mobile Networking - Transport Layer 17
 Mobile Networking How the network/transport layer protocols are affected in mobile and wireless environment Mobility Management - Network Layer q Mobile unit's physical location is no longer determines its network address does not know where a given user is l how to route messages l q Approaches Internet community: mobile IP (extends IP, connectionless) l Cellular communication community: location management (connection-oriented) l 18
Mobile Networking How the network/transport layer protocols are affected in mobile and wireless environment Mobility Management - Network Layer q Mobile unit's physical location is no longer determines its network address does not know where a given user is l how to route messages l q Approaches Internet community: mobile IP (extends IP, connectionless) l Cellular communication community: location management (connection-oriented) l 18
 Location (Mobility) Management Mobility management q Find an adequate tradeoff between searching and informing l l Searching by the system Informing by the mobile hosts – when MHs receives messages frequently – when MHs does not move between cells often Multicasting Possible to receive no / multiple identical messages q Multicasting is a challenge q l l l how to guarantee “exactly once” or “at least once” delivery in an efficient manner MCAST protocol is proposed how to maintain a “group view” - the set of MSSs for multicasting 19
Location (Mobility) Management Mobility management q Find an adequate tradeoff between searching and informing l l Searching by the system Informing by the mobile hosts – when MHs receives messages frequently – when MHs does not move between cells often Multicasting Possible to receive no / multiple identical messages q Multicasting is a challenge q l l l how to guarantee “exactly once” or “at least once” delivery in an efficient manner MCAST protocol is proposed how to maintain a “group view” - the set of MSSs for multicasting 19
 Mobile Ad-hoc Networking Ultimate challenge for mobile networking Mobile terminals can form networks without participation of the fixed infrastructure, arise in rapid-deployment situations emergency service at a disaster site q military operations in a remote area q business meetings held in venues without network infra q sensor networks q Highly dynamic frequent change of routing table q a given terminal can serve as a router now but no longer be a short time later q 20
Mobile Ad-hoc Networking Ultimate challenge for mobile networking Mobile terminals can form networks without participation of the fixed infrastructure, arise in rapid-deployment situations emergency service at a disaster site q military operations in a remote area q business meetings held in venues without network infra q sensor networks q Highly dynamic frequent change of routing table q a given terminal can serve as a router now but no longer be a short time later q 20
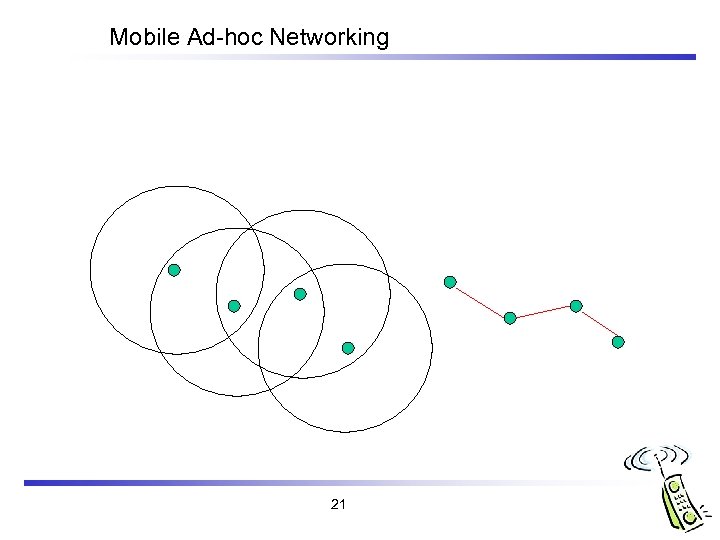 Mobile Ad-hoc Networking 21
Mobile Ad-hoc Networking 21
 3. Embedded Systems Hardware Embedded processors & embedded peripherals q Interfacing q Interacts with environments Sensing and controlling externals l Real-time constrains l l q I/O : System bus, I 2 C, Parallel, Serial, IR, RF, PCMCIA Software q Embedded OS l Palm OS, Windows CE, Embedded Linux, … Cross development & Emulation q Workload characterization q 22
3. Embedded Systems Hardware Embedded processors & embedded peripherals q Interfacing q Interacts with environments Sensing and controlling externals l Real-time constrains l l q I/O : System bus, I 2 C, Parallel, Serial, IR, RF, PCMCIA Software q Embedded OS l Palm OS, Windows CE, Embedded Linux, … Cross development & Emulation q Workload characterization q 22
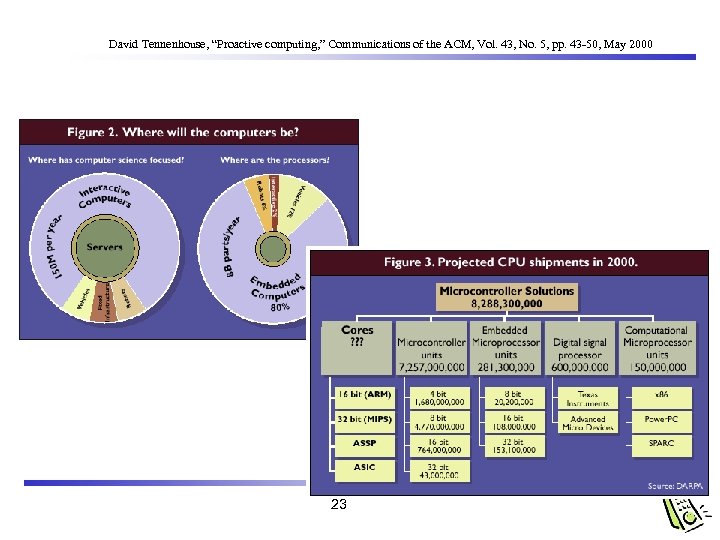 David Tennenhouse, “Proactive computing, ” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 43, No. 5, pp. 43 -50, May 2000 23
David Tennenhouse, “Proactive computing, ” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 43, No. 5, pp. 43 -50, May 2000 23
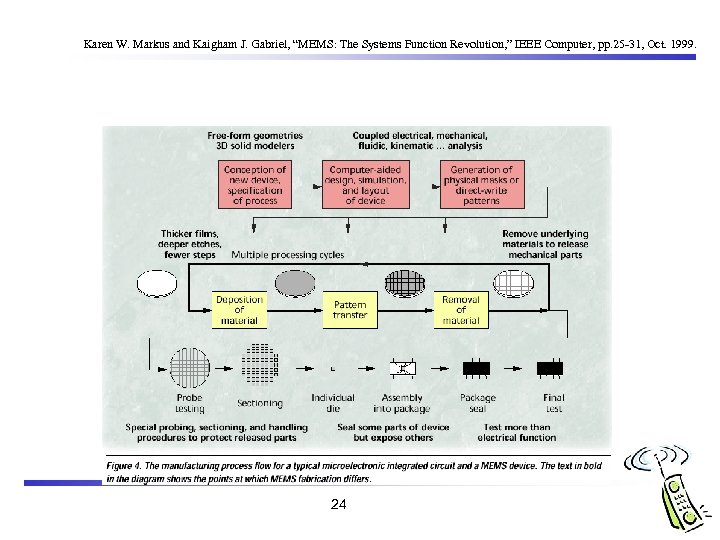 Karen W. Markus and Kaigham J. Gabriel, “MEMS: The Systems Function Revolution, ” IEEE Computer, pp. 25 -31, Oct. 1999. 24
Karen W. Markus and Kaigham J. Gabriel, “MEMS: The Systems Function Revolution, ” IEEE Computer, pp. 25 -31, Oct. 1999. 24
 25
25
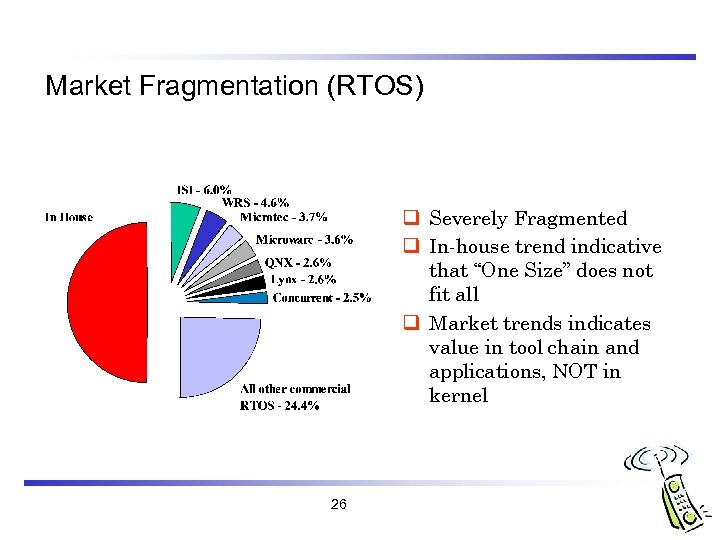 Market Fragmentation (RTOS) q Severely Fragmented q In-house trend indicative that “One Size” does not fit all q Market trends indicates value in tool chain and applications, NOT in kernel 26
Market Fragmentation (RTOS) q Severely Fragmented q In-house trend indicative that “One Size” does not fit all q Market trends indicates value in tool chain and applications, NOT in kernel 26
 Workload Characterization Jakob Engblom Studied Embedded Programs 13 applications, 337 kloc q Various industrial applications: q l Telecomm, Vehicles, Consumer Products, … Embedded, partially real-time programs q Medium-capacity 8 - and 16 -bit CPUs: q l q Z 80, 68 HC 11, C 166, MELPS 7000, H 8, … Medium-to-large European companies 27
Workload Characterization Jakob Engblom Studied Embedded Programs 13 applications, 337 kloc q Various industrial applications: q l Telecomm, Vehicles, Consumer Products, … Embedded, partially real-time programs q Medium-capacity 8 - and 16 -bit CPUs: q l q Z 80, 68 HC 11, C 166, MELPS 7000, H 8, … Medium-to-large European companies 27
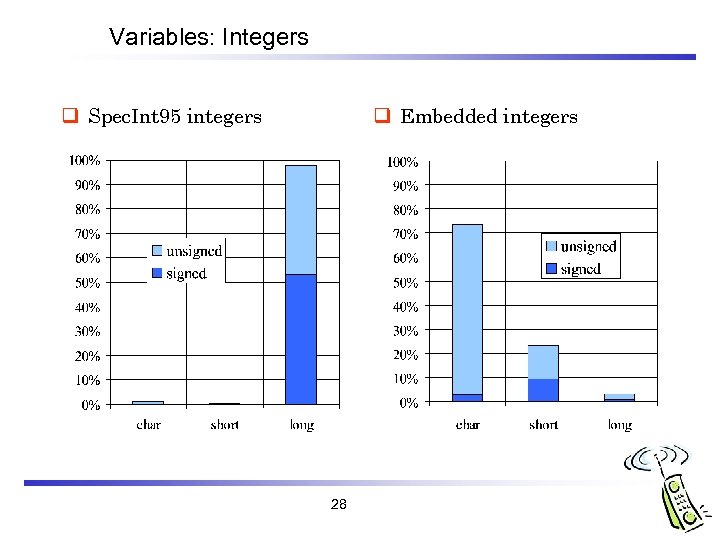 Variables: Integers q Spec. Int 95 integers q Embedded integers 28
Variables: Integers q Spec. Int 95 integers q Embedded integers 28
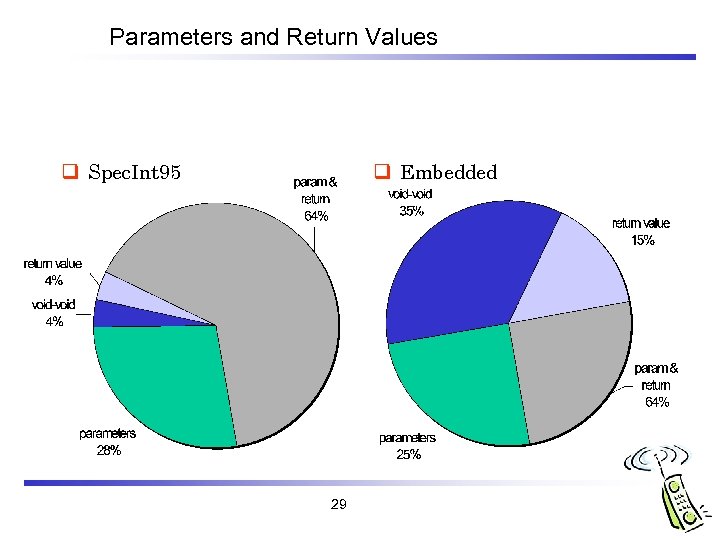 Parameters and Return Values q Spec. Int 95 q Embedded 29
Parameters and Return Values q Spec. Int 95 q Embedded 29
 4. Ubiquitous Computing Whenever people learn something sufficiently well, they cease to be aware of it Location-based services, shared meeting applications <-> Virtual reality : make a world inside the computer Hundreds of computers in a room “share situations” Examples Active Badge - door control, phone call forwarding, terminal preference q Tab - instant votes, library map q 30
4. Ubiquitous Computing Whenever people learn something sufficiently well, they cease to be aware of it Location-based services, shared meeting applications <-> Virtual reality : make a world inside the computer Hundreds of computers in a room “share situations” Examples Active Badge - door control, phone call forwarding, terminal preference q Tab - instant votes, library map q 30
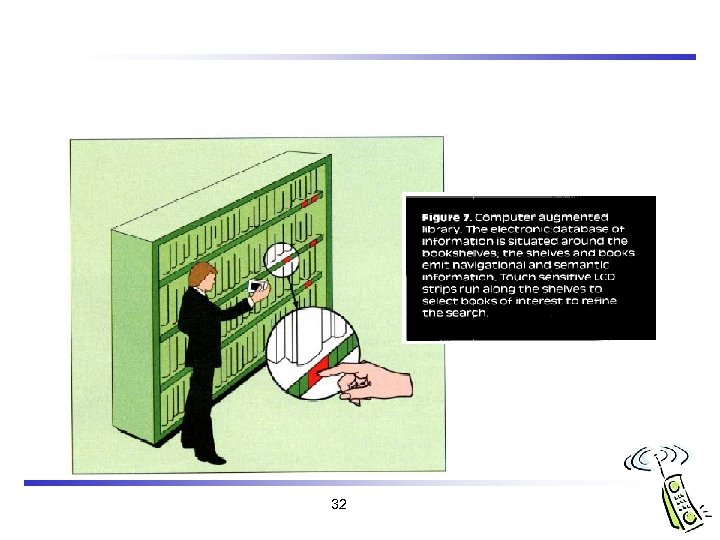
 G. W. Fitzmaurice, “Situated Information Spaces and Spatially Aware Palmtop Computers, ” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 39 -49, Jul. 1993 (this issue contains many other related articles including M. Weiser’s). 31
G. W. Fitzmaurice, “Situated Information Spaces and Spatially Aware Palmtop Computers, ” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 39 -49, Jul. 1993 (this issue contains many other related articles including M. Weiser’s). 31
 32
32
 Active Badges Purpose q locating individuals within a building by determining the location of their Active Badge (and thus, telephone calls can be routed) Method This small device worn by personnel transmits a unique infra-red signal every 10 seconds (for 0. 1 sec to reduce collision probability) q Each office within a building is equipped with one or more networked sensors which detect these transmissions q The location of the badge (and hence its wearer) can thus be determined on the basis of information provided by these sensors q 33
Active Badges Purpose q locating individuals within a building by determining the location of their Active Badge (and thus, telephone calls can be routed) Method This small device worn by personnel transmits a unique infra-red signal every 10 seconds (for 0. 1 sec to reduce collision probability) q Each office within a building is equipped with one or more networked sensors which detect these transmissions q The location of the badge (and hence its wearer) can thus be determined on the basis of information provided by these sensors q 33
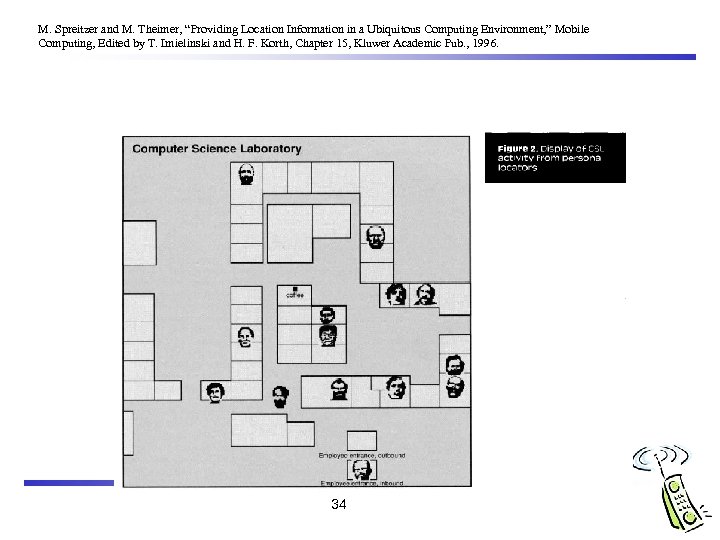 M. Spreitzer and M. Theimer, “Providing Location Information in a Ubiquitous Computing Environment, ” Mobile Computing, Edited by T. Imielinski and H. F. Korth, Chapter 15, Kluwer Academic Pub. , 1996. 34
M. Spreitzer and M. Theimer, “Providing Location Information in a Ubiquitous Computing Environment, ” Mobile Computing, Edited by T. Imielinski and H. F. Korth, Chapter 15, Kluwer Academic Pub. , 1996. 34
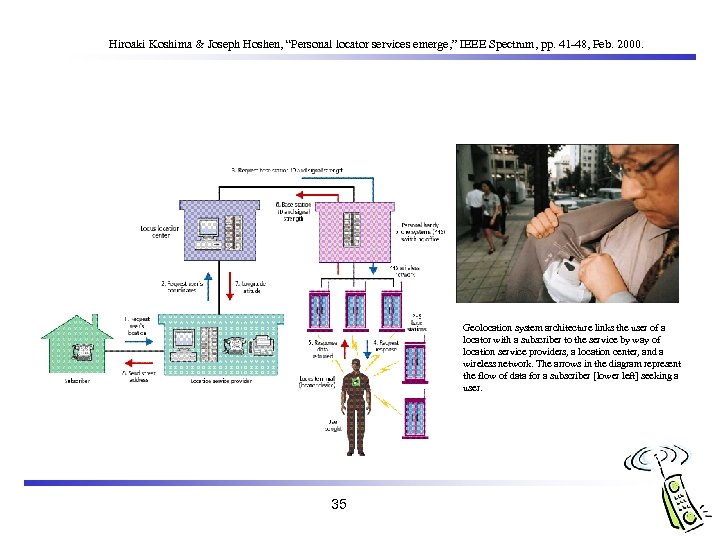 Hiroaki Koshima & Joseph Hoshen, “Personal locator services emerge, ” IEEE Spectrum, pp. 41 -48, Feb. 2000. Geolocation system architecture links the user of a locator with a subscriber to the service by way of location service providers, a location center, and a wireless network. The arrows in the diagram represent the flow of data for a subscriber [lower left] seeking a user. 35
Hiroaki Koshima & Joseph Hoshen, “Personal locator services emerge, ” IEEE Spectrum, pp. 41 -48, Feb. 2000. Geolocation system architecture links the user of a locator with a subscriber to the service by way of location service providers, a location center, and a wireless network. The arrows in the diagram represent the flow of data for a subscriber [lower left] seeking a user. 35
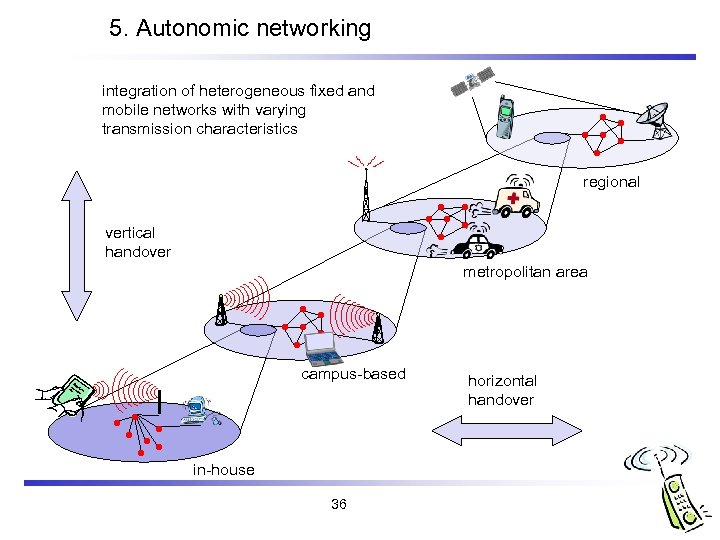 5. Autonomic networking integration of heterogeneous fixed and mobile networks with varying transmission characteristics regional vertical handover metropolitan area campus-based in-house 36 horizontal handover
5. Autonomic networking integration of heterogeneous fixed and mobile networks with varying transmission characteristics regional vertical handover metropolitan area campus-based in-house 36 horizontal handover
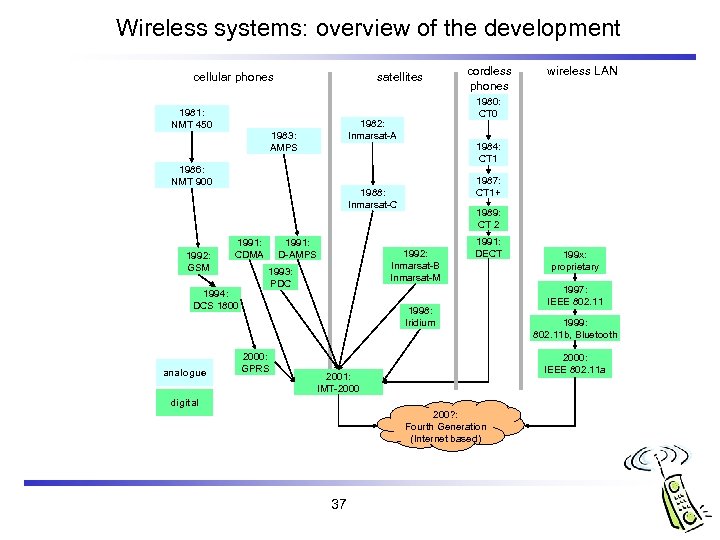 Wireless systems: overview of the development cellular phones 1981: NMT 450 satellites 1986: NMT 900 1992: GSM 1994: DCS 1800 analogue 1984: CT 1 1987: CT 1+ 1988: Inmarsat-C 1991: CDMA 1991: D-AMPS 1989: CT 2 1992: Inmarsat-B Inmarsat-M 1993: PDC 1991: DECT 1998: Iridium 2000: GPRS 199 x: proprietary 1997: IEEE 802. 11 1999: 802. 11 b, Bluetooth 2000: IEEE 802. 11 a 2001: IMT-2000 digital 200? : Fourth Generation (Internet based) 37 wireless LAN 1980: CT 0 1982: Inmarsat-A 1983: AMPS cordless phones
Wireless systems: overview of the development cellular phones 1981: NMT 450 satellites 1986: NMT 900 1992: GSM 1994: DCS 1800 analogue 1984: CT 1 1987: CT 1+ 1988: Inmarsat-C 1991: CDMA 1991: D-AMPS 1989: CT 2 1992: Inmarsat-B Inmarsat-M 1993: PDC 1991: DECT 1998: Iridium 2000: GPRS 199 x: proprietary 1997: IEEE 802. 11 1999: 802. 11 b, Bluetooth 2000: IEEE 802. 11 a 2001: IMT-2000 digital 200? : Fourth Generation (Internet based) 37 wireless LAN 1980: CT 0 1982: Inmarsat-A 1983: AMPS cordless phones
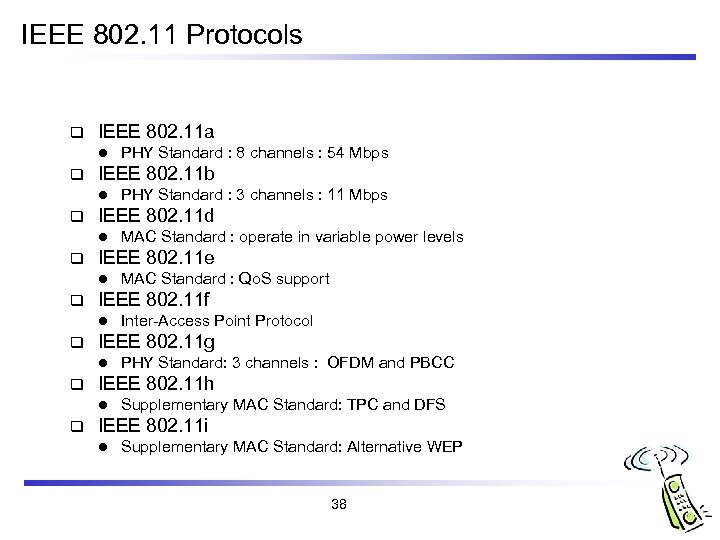 IEEE 802. 11 Protocols q IEEE 802. 11 a l q IEEE 802. 11 b l q PHY Standard: 3 channels : OFDM and PBCC IEEE 802. 11 h l q Inter-Access Point Protocol IEEE 802. 11 g l q MAC Standard : Qo. S support IEEE 802. 11 f l q MAC Standard : operate in variable power levels IEEE 802. 11 e l q PHY Standard : 3 channels : 11 Mbps IEEE 802. 11 d l q PHY Standard : 8 channels : 54 Mbps Supplementary MAC Standard: TPC and DFS IEEE 802. 11 i l Supplementary MAC Standard: Alternative WEP 38
IEEE 802. 11 Protocols q IEEE 802. 11 a l q IEEE 802. 11 b l q PHY Standard: 3 channels : OFDM and PBCC IEEE 802. 11 h l q Inter-Access Point Protocol IEEE 802. 11 g l q MAC Standard : Qo. S support IEEE 802. 11 f l q MAC Standard : operate in variable power levels IEEE 802. 11 e l q PHY Standard : 3 channels : 11 Mbps IEEE 802. 11 d l q PHY Standard : 8 channels : 54 Mbps Supplementary MAC Standard: TPC and DFS IEEE 802. 11 i l Supplementary MAC Standard: Alternative WEP 38
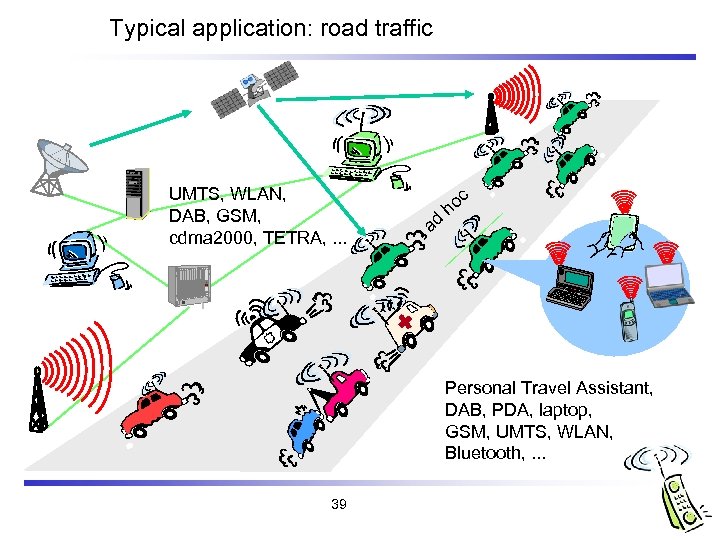 Typical application: road traffic UMTS, WLAN, DAB, GSM, cdma 2000, TETRA, . . . c ad ho Personal Travel Assistant, DAB, PDA, laptop, GSM, UMTS, WLAN, Bluetooth, . . . 39
Typical application: road traffic UMTS, WLAN, DAB, GSM, cdma 2000, TETRA, . . . c ad ho Personal Travel Assistant, DAB, PDA, laptop, GSM, UMTS, WLAN, Bluetooth, . . . 39
 Autonomic Wireless Networking Diverse systems and solutions motivate us to consider self-* networks Applications and services are not ported onto a preexisting network, but the network itself grows out of the applications and the services that end users want Service-driven, situated, self-controlled, self-organized, technologyindependent, and scalable Network is not just a “data transport engine” but more like an “information transport/processing engine” 40
Autonomic Wireless Networking Diverse systems and solutions motivate us to consider self-* networks Applications and services are not ported onto a preexisting network, but the network itself grows out of the applications and the services that end users want Service-driven, situated, self-controlled, self-organized, technologyindependent, and scalable Network is not just a “data transport engine” but more like an “information transport/processing engine” 40
 Software-defined and Cognitive Radios Cognitive radio is “an intelligent wireless communication system that is aware of its environment … adapts to statistical variations in the input stimuli, with two primary objectives in mind – highly reliable communication and efficient utilization of the radio spectrum. ” (Simon Haykin, IEEE JSAC, 2005) Three fundamental cognitive tasks are radio-scene analysis, channel-state estimation and predictive modeling, and transmit power control and dynamic spectrum management Technical foundation of cognitive radio is software-defined radio platform GNU Radio and USRP SORA (MSR China) Cal. Radio (UC) Etc. 41
Software-defined and Cognitive Radios Cognitive radio is “an intelligent wireless communication system that is aware of its environment … adapts to statistical variations in the input stimuli, with two primary objectives in mind – highly reliable communication and efficient utilization of the radio spectrum. ” (Simon Haykin, IEEE JSAC, 2005) Three fundamental cognitive tasks are radio-scene analysis, channel-state estimation and predictive modeling, and transmit power control and dynamic spectrum management Technical foundation of cognitive radio is software-defined radio platform GNU Radio and USRP SORA (MSR China) Cal. Radio (UC) Etc. 41
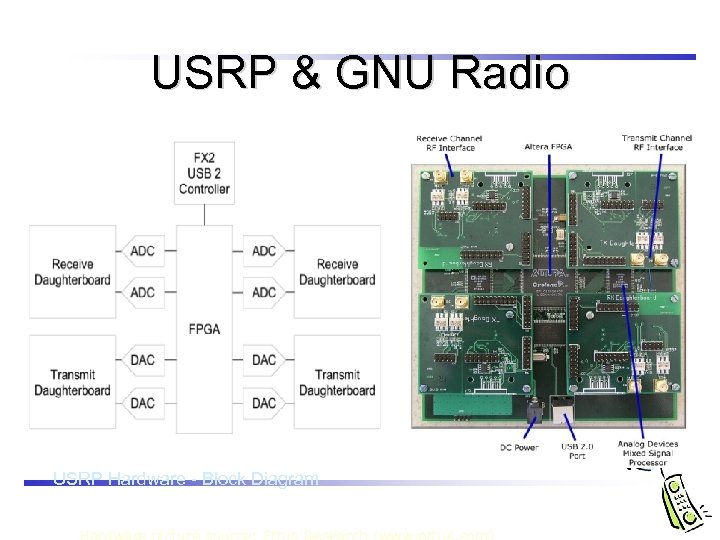 USRP & GNU Radio USRP Hardware - Block Diagram Fig. source - http: //www. nd. edu/~jnl/sdr/docs/tutorials/4. pdf
USRP & GNU Radio USRP Hardware - Block Diagram Fig. source - http: //www. nd. edu/~jnl/sdr/docs/tutorials/4. pdf
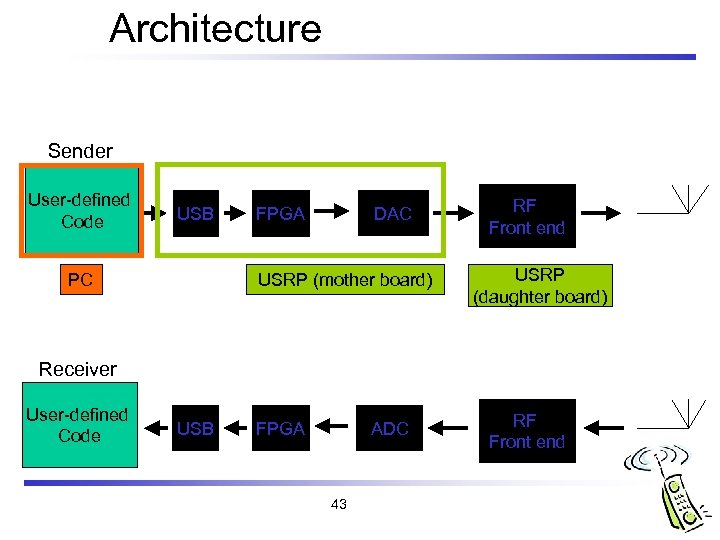 Architecture Sender User-defined Code USB PC DAC FPGA USRP (mother board) RF Front end USRP (daughter board) Receiver User-defined Code USB ADC FPGA 43 RF Front end
Architecture Sender User-defined Code USB PC DAC FPGA USRP (mother board) RF Front end USRP (daughter board) Receiver User-defined Code USB ADC FPGA 43 RF Front end
 ACM Mobi. Com’ 07 44
ACM Mobi. Com’ 07 44
 ACM Sig. Comm’ 07 45
ACM Sig. Comm’ 07 45
 IEEE Workshop. . , 2006 46
IEEE Workshop. . , 2006 46
 BBN Technical Memo, 2006 Revised and published in IEEE MILCOM, 2007 47
BBN Technical Memo, 2006 Revised and published in IEEE MILCOM, 2007 47


