f5e329e2506e951b60624789d5b3f2e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 IT Security & Privacy n MIS 6800 Group Six n Professor: Dr. Mary Lacity n Group Members • Liang Liu • Timothy Beecher • Kadambari Goel • Jonathan Riek • Wilfrid Hutagalung Fall 2005, UMSL 1
IT Security & Privacy n MIS 6800 Group Six n Professor: Dr. Mary Lacity n Group Members • Liang Liu • Timothy Beecher • Kadambari Goel • Jonathan Riek • Wilfrid Hutagalung Fall 2005, UMSL 1
 What Keeps CIO's up at Night Security… Survey on CIO's concerns § On Management: No. 3 in 2004, 2003 § On Applications: No. 1 in 2004 Luftman, J. , and Mc. Lean, E. , “Key Issues for IT Executives, ” MISQ Executive, Vol. 4, 2, 2005, pp. 269 -286 2
What Keeps CIO's up at Night Security… Survey on CIO's concerns § On Management: No. 3 in 2004, 2003 § On Applications: No. 1 in 2004 Luftman, J. , and Mc. Lean, E. , “Key Issues for IT Executives, ” MISQ Executive, Vol. 4, 2, 2005, pp. 269 -286 2
 Agenda n n Introduction – Liang Liu Case Studies n Threat and Vulnerability Assessment Tim Beecher: Interviewed Kathy Forrester, CIO at Fleishman Hillard n n n Strategy, Architecture and Design Kadambari Goel: Interviewed Gaurav Huria, Project Manager at AT&T Threat and Vulnerability Management Jonathan Riek: Interviewed John Todd, Senior LAN Administrator at First Data Corporation Conclusion - Wilfrid Hutagalung 3
Agenda n n Introduction – Liang Liu Case Studies n Threat and Vulnerability Assessment Tim Beecher: Interviewed Kathy Forrester, CIO at Fleishman Hillard n n n Strategy, Architecture and Design Kadambari Goel: Interviewed Gaurav Huria, Project Manager at AT&T Threat and Vulnerability Management Jonathan Riek: Interviewed John Todd, Senior LAN Administrator at First Data Corporation Conclusion - Wilfrid Hutagalung 3
 Introduction n Definition n Importance n Relationship n Functional Inventory n CISO n Legal and Regulatory 4
Introduction n Definition n Importance n Relationship n Functional Inventory n CISO n Legal and Regulatory 4
 Definitions n IT Security n Privacy is to provide protection of information systems against unauthorized access to or modification of information, whether in storage, processing or transit, and against the denial of service to authorized users or the provision of service to unauthorized users, including those measures necessary to detect, document, and counter such threats • The right “to be left alone” – 1890 • Informational self-determination – Current Source for Security: U. S. National Information Systems Security Glossary Source for Privacy: Warren, S. D. and Brandeis, L. D. (1890): Harvard Law Review, 5, pp 205 5
Definitions n IT Security n Privacy is to provide protection of information systems against unauthorized access to or modification of information, whether in storage, processing or transit, and against the denial of service to authorized users or the provision of service to unauthorized users, including those measures necessary to detect, document, and counter such threats • The right “to be left alone” – 1890 • Informational self-determination – Current Source for Security: U. S. National Information Systems Security Glossary Source for Privacy: Warren, S. D. and Brandeis, L. D. (1890): Harvard Law Review, 5, pp 205 5
 Importance of Security & Privacy – Vital to E-Commerce n Build Customer Trust n Laws and Regulations n Part of IT Infrastructure – Federal & State – Most systems cannot run without security: Abz insurance system 7 weeks outage due to the Siennax subcontracting with Blue. X – Verisign n Can be Costly – Losses and Expenditures 6
Importance of Security & Privacy – Vital to E-Commerce n Build Customer Trust n Laws and Regulations n Part of IT Infrastructure – Federal & State – Most systems cannot run without security: Abz insurance system 7 weeks outage due to the Siennax subcontracting with Blue. X – Verisign n Can be Costly – Losses and Expenditures 6
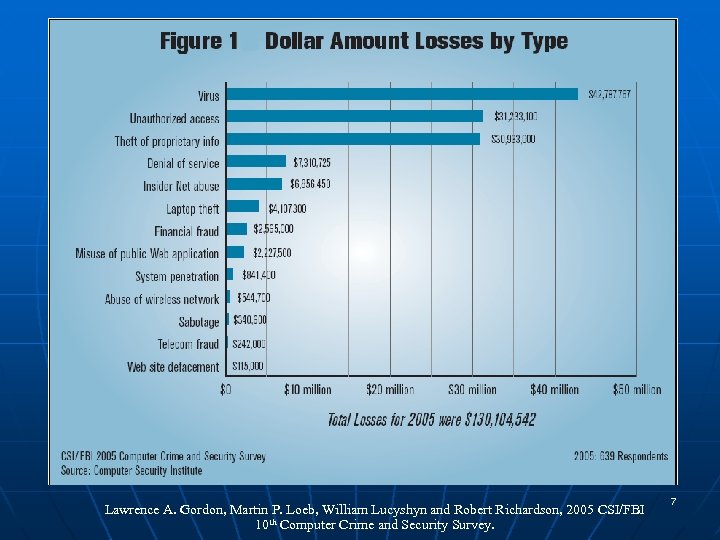 Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 7
Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 7
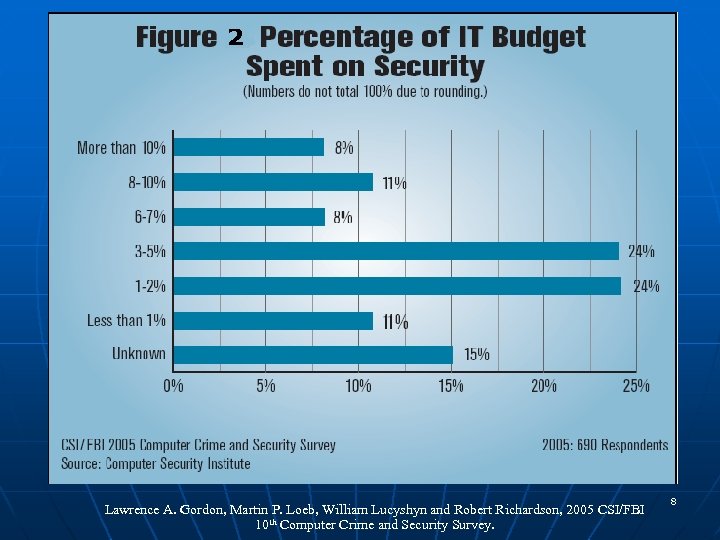 Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 8
Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 8
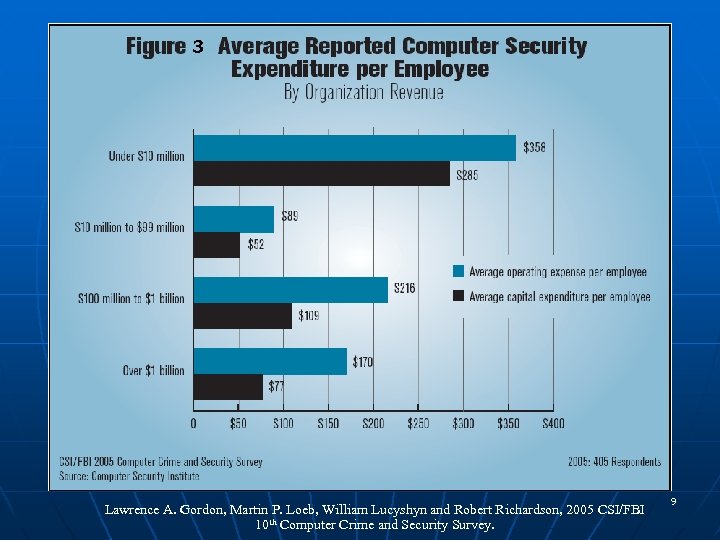 Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 9
Lawrence A. Gordon, Martin P. Loeb, William Lucyshyn and Robert Richardson, 2005 CSI/FBI 10 th Computer Crime and Security Survey. 9
 Relationship between Security and Privacy n Complementary – Reinforces each other n Contradictory n n - Conflicts each other Which one is more important? • Privacy – Customers • Security - Corporations Avoid two extremes • Complete Lack of Security • Complete Privacy 10
Relationship between Security and Privacy n Complementary – Reinforces each other n Contradictory n n - Conflicts each other Which one is more important? • Privacy – Customers • Security - Corporations Avoid two extremes • Complete Lack of Security • Complete Privacy 10
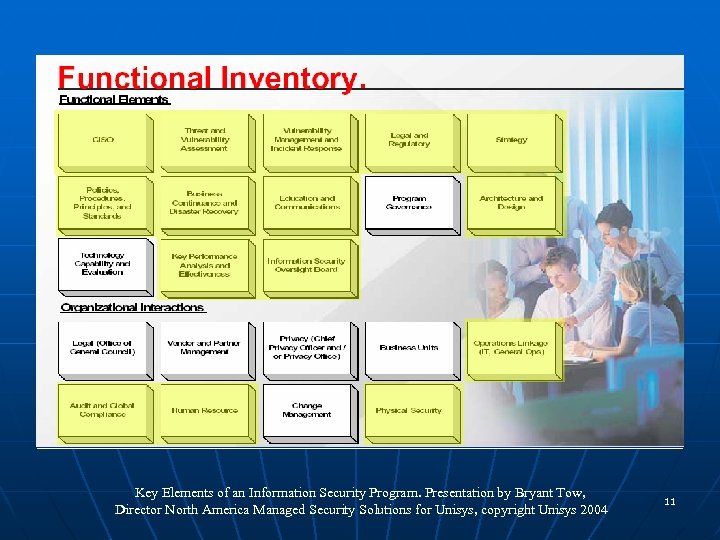 Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 11
Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 11
 CISO (CSO) n More Jobs for CISO • 2005 – 40% Companies • 2004 – 31% Companies • Weakness in Strategic Planning and Regulatory Compliance n CISO is NOT just for IT - protect all business’s info assets n Best report to CEO n Think like a CFO n Implement a Process-Oriented Portfolio Strategy IDG’s CIO Magazine & Price Waterhouse Coopers Survey September 2005 12
CISO (CSO) n More Jobs for CISO • 2005 – 40% Companies • 2004 – 31% Companies • Weakness in Strategic Planning and Regulatory Compliance n CISO is NOT just for IT - protect all business’s info assets n Best report to CEO n Think like a CFO n Implement a Process-Oriented Portfolio Strategy IDG’s CIO Magazine & Price Waterhouse Coopers Survey September 2005 12
 Legal and Regulatory n n Major Federal and State Laws • Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act n The Financial Modernization Act of 1999 or GLB • Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002) • Patriot Act (2001 after 9/11) • HIPAA – Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act (1996) • California’s SB 1386 (July, 2003) CIO Magazine • 38% Co. not in compliance with Sarbanes-Oxley • 23% Co. not in compliance with HIPAA • 15% not in compliance with California’s SB 1386 IDG’s CIO Magazine & Price Waterhouse Coopers Survey September 2005 13
Legal and Regulatory n n Major Federal and State Laws • Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act n The Financial Modernization Act of 1999 or GLB • Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002) • Patriot Act (2001 after 9/11) • HIPAA – Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act (1996) • California’s SB 1386 (July, 2003) CIO Magazine • 38% Co. not in compliance with Sarbanes-Oxley • 23% Co. not in compliance with HIPAA • 15% not in compliance with California’s SB 1386 IDG’s CIO Magazine & Price Waterhouse Coopers Survey September 2005 13
 Threat & Vulnerability Assessment 14
Threat & Vulnerability Assessment 14
 Fleishman-Hillard- Overview n n n Global communications agency with offices in 59 cities around the world 2, 000 employees rely on the quality of its data to address a wide range of client needs, from new product introductions and marketing promotions to crisis management Staffers need remote connectivity 15
Fleishman-Hillard- Overview n n n Global communications agency with offices in 59 cities around the world 2, 000 employees rely on the quality of its data to address a wide range of client needs, from new product introductions and marketing promotions to crisis management Staffers need remote connectivity 15
 Fleishman-Hillard- CIO Profile § Kathy Forrester - Chief Information Officer, Senior Vice President, and Senior Partner § Oversees the company's worldwide information service groups and supporting information technology needs, including network/data center services for the company's core lines of business § With Fleishman-Hillard for the past 10 years § Has an IT budget of 7 -8 million dollars and 4% goes directly to IT Security 16
Fleishman-Hillard- CIO Profile § Kathy Forrester - Chief Information Officer, Senior Vice President, and Senior Partner § Oversees the company's worldwide information service groups and supporting information technology needs, including network/data center services for the company's core lines of business § With Fleishman-Hillard for the past 10 years § Has an IT budget of 7 -8 million dollars and 4% goes directly to IT Security 16
 Average Daily Data Usage Fleishman Hillard n • • 4 Terabytes Terabyte - 1024 GB, 1, 048, 576 MB, 8, 388, 608 KB, 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 Bytes and 8, 796, 093, 022, 208 bits AT&T n • • 1. 6 Petabytes Petabyte - 1024 TB, 1, 048, 576 GB, 1, 073, 741, 824 MB, 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 KB, 1, 125, 899, 906, 842, 624 Bytes and 9, 007, 199, 254, 740, 992 bits http: //www. glossary-tech. com/byte. htm 17
Average Daily Data Usage Fleishman Hillard n • • 4 Terabytes Terabyte - 1024 GB, 1, 048, 576 MB, 8, 388, 608 KB, 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 Bytes and 8, 796, 093, 022, 208 bits AT&T n • • 1. 6 Petabytes Petabyte - 1024 TB, 1, 048, 576 GB, 1, 073, 741, 824 MB, 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 KB, 1, 125, 899, 906, 842, 624 Bytes and 9, 007, 199, 254, 740, 992 bits http: //www. glossary-tech. com/byte. htm 17
 Fleishman Hillard - Services n Internet Protect n Firewall Services n Intrusion Detection n Secure E-Mail Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-HIllard, Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 18
Fleishman Hillard - Services n Internet Protect n Firewall Services n Intrusion Detection n Secure E-Mail Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-HIllard, Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 18
 Common Threats User n • • • Giving out passwords Leaving workstations Leaving laptops at airports Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors n • • Sloppy coding Audit Hackers n • Career Data Base Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 19
Common Threats User n • • • Giving out passwords Leaving workstations Leaving laptops at airports Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors n • • Sloppy coding Audit Hackers n • Career Data Base Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 19
 Common Threats- continued n n n Viruses • Trojans • I love you virus Spiders • Continually attacking the firewall Distributed Denial of Service (DDo. S) • DDo. S attacks can overwhelm web servers and saturate a company's Internet connections thus resulting in the inability to maintain efficient communications, commerce, and ultimately connectivity Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 20
Common Threats- continued n n n Viruses • Trojans • I love you virus Spiders • Continually attacking the firewall Distributed Denial of Service (DDo. S) • DDo. S attacks can overwhelm web servers and saturate a company's Internet connections thus resulting in the inability to maintain efficient communications, commerce, and ultimately connectivity Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 20
 Proactive Assessment n n Perform threat analysis of current and emerging solutions to detect, trace and filter the unwanted traffic as soon as possible User Training - 20 & 40 minute training sessions on the common threats & risks to all employees, clients, subcontractors Hackers, Viruses, Spiders, DDos • The only real proactive activities are to learn from past encounters and to implement/invest in the best firewalls and anti-virus Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors • Research • Actively monitor • Ensure they know your system Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard. Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. Cullen, S. , Seddon, P. , and Willcocks, “Managing Outsourcing: The Life Cycle Imperative, ” MIS Quarterly Executive, March 2005, pp. 229 -246 21
Proactive Assessment n n Perform threat analysis of current and emerging solutions to detect, trace and filter the unwanted traffic as soon as possible User Training - 20 & 40 minute training sessions on the common threats & risks to all employees, clients, subcontractors Hackers, Viruses, Spiders, DDos • The only real proactive activities are to learn from past encounters and to implement/invest in the best firewalls and anti-virus Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors • Research • Actively monitor • Ensure they know your system Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard. Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. Cullen, S. , Seddon, P. , and Willcocks, “Managing Outsourcing: The Life Cycle Imperative, ” MIS Quarterly Executive, March 2005, pp. 229 -246 21
 Reactive Assessment n n Provide near real time threat analysis of current attacks Early Warning - allows most real-time attacks (viruses, worms and DDo. S attacks) to be addressed and mitigated before a hacker releases them Once help desk lights up is usually when most security departments discover that there has been a breach Communicate threat information through training sessions to establish active threat levels for organizations Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 22
Reactive Assessment n n Provide near real time threat analysis of current attacks Early Warning - allows most real-time attacks (viruses, worms and DDo. S attacks) to be addressed and mitigated before a hacker releases them Once help desk lights up is usually when most security departments discover that there has been a breach Communicate threat information through training sessions to establish active threat levels for organizations Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 22
 Reactive Assessment- continued n n n Information is one of the most valuable assets of any company Security breaches can happen everyday to anyone whether you're a large enterprise or a small business Steps 1. Quick detection and mitigation techniques 2. Building and keeping network security infrastructure updated against newer vulnerabilities 3. Enforce security policies 4. Review data gathered during security incidents Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 23
Reactive Assessment- continued n n n Information is one of the most valuable assets of any company Security breaches can happen everyday to anyone whether you're a large enterprise or a small business Steps 1. Quick detection and mitigation techniques 2. Building and keeping network security infrastructure updated against newer vulnerabilities 3. Enforce security policies 4. Review data gathered during security incidents Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 23
 Reactive Assessment- continued n n Users • Giving out passwords n Fingerprint scans instead of numeric passwords n ID cards that changes passwords every second • Leaving workstations n Setting a screen saver to appear when computer is inactive for 30 sec and can only be activated with a password • Leaving laptops at airports n Future plan is to try to disable the device remotely Hackers • Find and report them Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 24
Reactive Assessment- continued n n Users • Giving out passwords n Fingerprint scans instead of numeric passwords n ID cards that changes passwords every second • Leaving workstations n Setting a screen saver to appear when computer is inactive for 30 sec and can only be activated with a password • Leaving laptops at airports n Future plan is to try to disable the device remotely Hackers • Find and report them Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 24
 Reactive Assessment- continued n n Viruses, Spiders & DDo. S • Find and isolate affected areas • Contact anti-virus companies to see if they can help but usually they are too slow and have a guy in-house that can write a code to get ride of the virus or spider Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors • Sloppy code - Correct their work to ensure that breaches will not happen again Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 25
Reactive Assessment- continued n n Viruses, Spiders & DDo. S • Find and isolate affected areas • Contact anti-virus companies to see if they can help but usually they are too slow and have a guy in-house that can write a code to get ride of the virus or spider Outsourcing/Sub-Contractors • Sloppy code - Correct their work to ensure that breaches will not happen again Kathy Forrester, CIO of Fleishman-Hillard Interviewed in person by Jim Beecher, October 26, 2005. 25
 Architecture and Design 26
Architecture and Design 26
 IT Security In Demand Recent IDC Survey n n Number of computer security specialists will grow 3 times than the IT field as a whole Survey of more than 5, 000 Security Managers worldwide indicated growth of nearly 15% during 2004 n Hiring is expected to increase by nearly 14% during each of the next 4 years n Overall Growth in the IT Professional ranks at about 5% Nikki Swartz- Information Management Journal: Jan/Feb 2005 Vol. 39, Issue 1, pg 18 27
IT Security In Demand Recent IDC Survey n n Number of computer security specialists will grow 3 times than the IT field as a whole Survey of more than 5, 000 Security Managers worldwide indicated growth of nearly 15% during 2004 n Hiring is expected to increase by nearly 14% during each of the next 4 years n Overall Growth in the IT Professional ranks at about 5% Nikki Swartz- Information Management Journal: Jan/Feb 2005 Vol. 39, Issue 1, pg 18 27
 Security Efforts Still Lacking n n Architecture & Design Expenditures account for over 58% of an Organization’s IT Budget & is growing at 11% a year Financial Institutions, Energy Companies spend the most on their Architecture & Design Budget as compared to Manufacturing Industries 41% Respondents spend about 5 -10% (Unsecure) 73% Reviewed their Disaster Recovery Planning after 9/11 But Only 1 in 10 said it was Top Priority Nikki Swartz- Information Management Journal: Jan/Feb 2003 Vol. 37, Issue 1, pg 15 Bruce R Lewis, Terry Anthony Byrd - European Journal of Information Systems: June 2003 Vol. 12, Issue 2, pg 93 28
Security Efforts Still Lacking n n Architecture & Design Expenditures account for over 58% of an Organization’s IT Budget & is growing at 11% a year Financial Institutions, Energy Companies spend the most on their Architecture & Design Budget as compared to Manufacturing Industries 41% Respondents spend about 5 -10% (Unsecure) 73% Reviewed their Disaster Recovery Planning after 9/11 But Only 1 in 10 said it was Top Priority Nikki Swartz- Information Management Journal: Jan/Feb 2003 Vol. 37, Issue 1, pg 15 Bruce R Lewis, Terry Anthony Byrd - European Journal of Information Systems: June 2003 Vol. 12, Issue 2, pg 93 28
 Need for Architecture & Design n n Quick decision making has led to Fast and Open Access to corporate networks increasing Security Threats New Weapon in developing sustained Competitive Advantage Ensures Availability, Confidentiality & Integrity of Information Systems Foundation for Managing Information Assets & Tangible Benefits for Continuity of Business Practices Provides Support for Global Business Strategies & Catalyst for Globalization Process 29 29 Bruce R Lewis, Terry Anthony Byrd - European Journal of Information Systems: June 2003 Vol. 12, Issue 2, pg 93
Need for Architecture & Design n n Quick decision making has led to Fast and Open Access to corporate networks increasing Security Threats New Weapon in developing sustained Competitive Advantage Ensures Availability, Confidentiality & Integrity of Information Systems Foundation for Managing Information Assets & Tangible Benefits for Continuity of Business Practices Provides Support for Global Business Strategies & Catalyst for Globalization Process 29 29 Bruce R Lewis, Terry Anthony Byrd - European Journal of Information Systems: June 2003 Vol. 12, Issue 2, pg 93
 Network Security Architecture & Design n n n From Reactive to Proactive Approach Authentication : “Who are you? ” Process of verifying the Identity of a Participant Authorization : “Should you be doing that. ” Process of determining whether a Participant may use or access a resource Analysis of Current and Emerging Solutions Design Technological Information Security Controls for Business Solutions Impact of Design Requirements on User Experience 30 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
Network Security Architecture & Design n n n From Reactive to Proactive Approach Authentication : “Who are you? ” Process of verifying the Identity of a Participant Authorization : “Should you be doing that. ” Process of determining whether a Participant may use or access a resource Analysis of Current and Emerging Solutions Design Technological Information Security Controls for Business Solutions Impact of Design Requirements on User Experience 30 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
 AT&T - Overview Third-Quarter 2005 Earnings: October 21 st 2005 n Third-quarter earnings per diluted share of $0. 64 n Consolidated revenue of $6. 6 billion n Operating income of $955 million n Third-quarter cash from operating activities of $1. 4 billion n Increased full-year 2005 revenue and operating margin guidance Major products the company sells n Internet Protocol & Enhanced Services (IP&E-services) n Data Services n LD and Local Voice n Outsourcing, Professional Services & Other Characteristics of their customers n Bundled Services n Standalone LD, Transactional & Other Services n Local Customers 31 www. att. com, viewed October 30 th, 2005
AT&T - Overview Third-Quarter 2005 Earnings: October 21 st 2005 n Third-quarter earnings per diluted share of $0. 64 n Consolidated revenue of $6. 6 billion n Operating income of $955 million n Third-quarter cash from operating activities of $1. 4 billion n Increased full-year 2005 revenue and operating margin guidance Major products the company sells n Internet Protocol & Enhanced Services (IP&E-services) n Data Services n LD and Local Voice n Outsourcing, Professional Services & Other Characteristics of their customers n Bundled Services n Standalone LD, Transactional & Other Services n Local Customers 31 www. att. com, viewed October 30 th, 2005
 Organization Chart n n n n Hossein Eslambolchi joined AT&T Bell Labs in 1986 Became CTO & President of AT&T Labs in Sept 2001 Company CIO in 2002 Earns more than $4. 2 million a year, making him one of the highest-paid CIO's in the world Allocates roughly 20% of his time to operations, 25% to labs, 25% to CTO job & 30% to CIO issues Has more than 300 patents granted or pending 24 -by-7 kind of guy who operates at 100 miles an hour Presented by Information Week, Networking Pipeline Nov 29, 2004 "IP Will Eat Everything" By Paul Travis 32
Organization Chart n n n n Hossein Eslambolchi joined AT&T Bell Labs in 1986 Became CTO & President of AT&T Labs in Sept 2001 Company CIO in 2002 Earns more than $4. 2 million a year, making him one of the highest-paid CIO's in the world Allocates roughly 20% of his time to operations, 25% to labs, 25% to CTO job & 30% to CIO issues Has more than 300 patents granted or pending 24 -by-7 kind of guy who operates at 100 miles an hour Presented by Information Week, Networking Pipeline Nov 29, 2004 "IP Will Eat Everything" By Paul Travis 32
 Dealing With Threats Commonly Faced Risks n DDo. S Attacks n Unauthorized Data Access n VIRUS n WORMS n Trojans Security Services Offered n Internet Protect n Firewall Services n Intrusion Detection n Secure E-Mail Gateway n Token Authentication Services Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 33
Dealing With Threats Commonly Faced Risks n DDo. S Attacks n Unauthorized Data Access n VIRUS n WORMS n Trojans Security Services Offered n Internet Protect n Firewall Services n Intrusion Detection n Secure E-Mail Gateway n Token Authentication Services Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 33
 Service Offering from AT&T n n n Internet Protect as a Leading Security Offer for Preventing Attacks before they Materialize Proactive Approach for Malicious Intruders & Unauthorized Activities by providing a Robust, all Inclusive Information Security Portal Distributed Denial of Service (DDo. S) Defense Attacks for the most Nefarious Activities passing on the Internet next to Worms & Viruses Quality of Data Analysis carrying over 1. 6 Petabytes of data daily Advanced Intelligence Gathering 34 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
Service Offering from AT&T n n n Internet Protect as a Leading Security Offer for Preventing Attacks before they Materialize Proactive Approach for Malicious Intruders & Unauthorized Activities by providing a Robust, all Inclusive Information Security Portal Distributed Denial of Service (DDo. S) Defense Attacks for the most Nefarious Activities passing on the Internet next to Worms & Viruses Quality of Data Analysis carrying over 1. 6 Petabytes of data daily Advanced Intelligence Gathering 34 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
 Details of Service n n Internet Protect. SM is a security Alerting and Notification service that offers advanced information regarding potential Real-Time attacks that are in the early formation stages This service Detects and Mitigates DDo. S & other Flood attacks to Customer Systems within the core of the IP backbone First step involves Identification of an attack & then Mitigating the detected attack before traffic reaches the Customer’s Network In DDo. S Defense if a denial of service attack is detected, the traffic is routed to a network mitigation farm, where the malicious DDo. S attack packets are identified and dropped while the valid traffic is allowed to pass 35 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
Details of Service n n Internet Protect. SM is a security Alerting and Notification service that offers advanced information regarding potential Real-Time attacks that are in the early formation stages This service Detects and Mitigates DDo. S & other Flood attacks to Customer Systems within the core of the IP backbone First step involves Identification of an attack & then Mitigating the detected attack before traffic reaches the Customer’s Network In DDo. S Defense if a denial of service attack is detected, the traffic is routed to a network mitigation farm, where the malicious DDo. S attack packets are identified and dropped while the valid traffic is allowed to pass 35 Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005
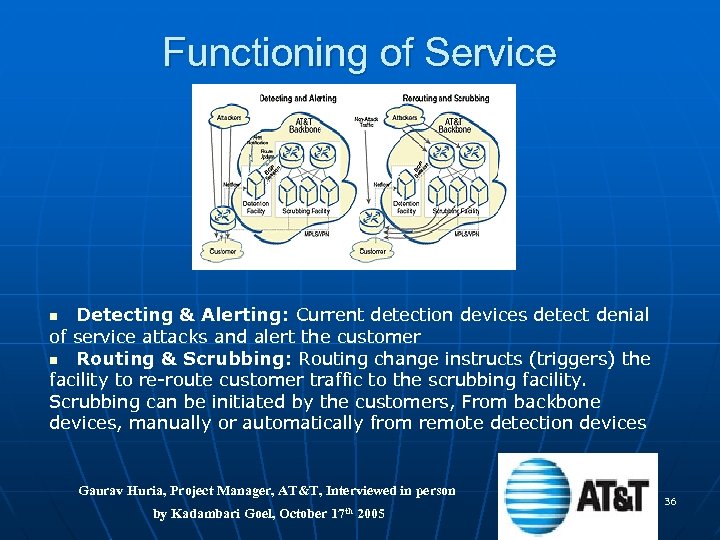 Functioning of Service Detecting & Alerting: Current detection devices detect denial of service attacks and alert the customer n Routing & Scrubbing: Routing change instructs (triggers) the facility to re-route customer traffic to the scrubbing facility. Scrubbing can be initiated by the customers, From backbone devices, manually or automatically from remote detection devices n Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 36
Functioning of Service Detecting & Alerting: Current detection devices detect denial of service attacks and alert the customer n Routing & Scrubbing: Routing change instructs (triggers) the facility to re-route customer traffic to the scrubbing facility. Scrubbing can be initiated by the customers, From backbone devices, manually or automatically from remote detection devices n Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 36
 Benefits & Challenges Benefits n Early Warning n Advanced Intelligence n Gathering, Detecting & Mitgation n Detection & Trace Back of Attacks n Filtering techniques for different types of Attacks Challenges n Time consuming n Cost Associated n Real Time Monitoring Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 37
Benefits & Challenges Benefits n Early Warning n Advanced Intelligence n Gathering, Detecting & Mitgation n Detection & Trace Back of Attacks n Filtering techniques for different types of Attacks Challenges n Time consuming n Cost Associated n Real Time Monitoring Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 37
 Security Model n n n Create a Policy Statement beginning with assessing the risk to the network and building a team to respond Conduct a Risk Analysis by identifying portions of your network, assign a threat rating to each portion, and apply an appropriate level of security Establish a Security Team with participants from each of your company's operational areas Approve Security Changes which is defining changes to network equipment that have a possible impact on the overall security of the network (firewall configuration) Monitor Security of Your Network detecting changes in the network that indicate a security violation 38
Security Model n n n Create a Policy Statement beginning with assessing the risk to the network and building a team to respond Conduct a Risk Analysis by identifying portions of your network, assign a threat rating to each portion, and apply an appropriate level of security Establish a Security Team with participants from each of your company's operational areas Approve Security Changes which is defining changes to network equipment that have a possible impact on the overall security of the network (firewall configuration) Monitor Security of Your Network detecting changes in the network that indicate a security violation 38
 Security Model- continued n n n Implement changes to prevent further access to the violation Restore normal network operations Define and implement controls to limit risk of identified vulnerability Develop and maintain effective disaster recovery plan Review the process as a final effort in creating and maintaining a security policy Ensure that information security program activities align with organizational goals Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 www. cisco. com, viewed October 30 th, 2005 39
Security Model- continued n n n Implement changes to prevent further access to the violation Restore normal network operations Define and implement controls to limit risk of identified vulnerability Develop and maintain effective disaster recovery plan Review the process as a final effort in creating and maintaining a security policy Ensure that information security program activities align with organizational goals Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 www. cisco. com, viewed October 30 th, 2005 39
 AT&T n Good Security Policy detailing outline to Users' Roles & Responsibilities n Incident Response Team in case of Threat n Auditing the Network n Risk Analysis n Upgrading the Network from New Vulnerabilities Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 40
AT&T n Good Security Policy detailing outline to Users' Roles & Responsibilities n Incident Response Team in case of Threat n Auditing the Network n Risk Analysis n Upgrading the Network from New Vulnerabilities Gaurav Huria, Project Manager, AT&T, Interviewed in person by Kadambari Goel, October 17 th 2005 40
 Threat & Vulnerability Management 41
Threat & Vulnerability Management 41
 Ongoing Management Process n n n Assessment showed us what we need, why we need it, and how to learn from incidents Architecture and Design illustrated key components and capabilities of a solid strategy Management will show the day to day processes, communication, and departmental interaction 42
Ongoing Management Process n n n Assessment showed us what we need, why we need it, and how to learn from incidents Architecture and Design illustrated key components and capabilities of a solid strategy Management will show the day to day processes, communication, and departmental interaction 42
 First Data Corporation n n Third largest payment processing company in the world Oldest portion of business – Western Union, founded in 1871 First company to process both Visa and Master. Card transactions in 1976 Now: 1100 financial transactions per second, and 36 billion transactions to date Manage over 406 million cardholder accounts 43 http: //ir. firstdata. com/profile. cfm, viewed November 2, 2005
First Data Corporation n n Third largest payment processing company in the world Oldest portion of business – Western Union, founded in 1871 First company to process both Visa and Master. Card transactions in 1976 Now: 1100 financial transactions per second, and 36 billion transactions to date Manage over 406 million cardholder accounts 43 http: //ir. firstdata. com/profile. cfm, viewed November 2, 2005
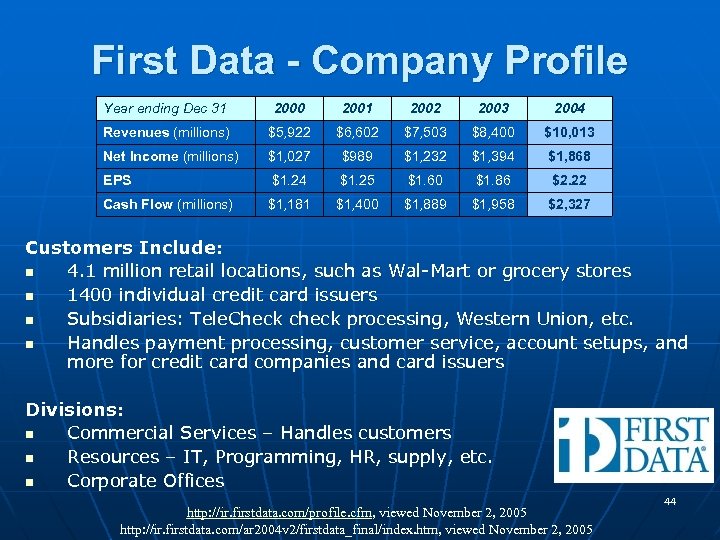 First Data - Company Profile Year ending Dec 31 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Revenues (millions) $5, 922 $6, 602 $7, 503 $8, 400 $10, 013 Net Income (millions) $1, 027 $989 $1, 232 $1, 394 $1, 868 EPS $1. 24 $1. 25 $1. 60 $1. 86 $2. 22 Cash Flow (millions) $1, 181 $1, 400 $1, 889 $1, 958 $2, 327 Customers Include: n 4. 1 million retail locations, such as Wal-Mart or grocery stores n 1400 individual credit card issuers n Subsidiaries: Tele. Check check processing, Western Union, etc. n Handles payment processing, customer service, account setups, and more for credit card companies and card issuers Divisions: n Commercial Services – Handles customers n Resources – IT, Programming, HR, supply, etc. n Corporate Offices http: //ir. firstdata. com/profile. cfm, viewed November 2, 2005 http: //ir. firstdata. com/ar 2004 v 2/firstdata_final/index. htm, viewed November 2, 2005 44
First Data - Company Profile Year ending Dec 31 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Revenues (millions) $5, 922 $6, 602 $7, 503 $8, 400 $10, 013 Net Income (millions) $1, 027 $989 $1, 232 $1, 394 $1, 868 EPS $1. 24 $1. 25 $1. 60 $1. 86 $2. 22 Cash Flow (millions) $1, 181 $1, 400 $1, 889 $1, 958 $2, 327 Customers Include: n 4. 1 million retail locations, such as Wal-Mart or grocery stores n 1400 individual credit card issuers n Subsidiaries: Tele. Check check processing, Western Union, etc. n Handles payment processing, customer service, account setups, and more for credit card companies and card issuers Divisions: n Commercial Services – Handles customers n Resources – IT, Programming, HR, supply, etc. n Corporate Offices http: //ir. firstdata. com/profile. cfm, viewed November 2, 2005 http: //ir. firstdata. com/ar 2004 v 2/firstdata_final/index. htm, viewed November 2, 2005 44
 First Data - CIO Profile n n Guy Battista - Chief Information Officer and Executive Vice President Overseeing the company's Information Services Group and supporting information technology needs, including network/data center services for the company's core lines of business n More than 30 years of IT background, 14 years at First Data n Annual compensation unknown, but stock options alone in 2004 totaled $3. 3 million http: //www. firstdata. com/abt_bio_battista. jsp , viewed November 2, 2005 45 http: //www. forbes. com/finance/mktguideapps/personinfo/From. Person. Id. Person. Tearsheet. jhtml? passed. Person. Id=391436, Viewed November 2, 2005
First Data - CIO Profile n n Guy Battista - Chief Information Officer and Executive Vice President Overseeing the company's Information Services Group and supporting information technology needs, including network/data center services for the company's core lines of business n More than 30 years of IT background, 14 years at First Data n Annual compensation unknown, but stock options alone in 2004 totaled $3. 3 million http: //www. firstdata. com/abt_bio_battista. jsp , viewed November 2, 2005 45 http: //www. forbes. com/finance/mktguideapps/personinfo/From. Person. Id. Person. Tearsheet. jhtml? passed. Person. Id=391436, Viewed November 2, 2005
 Vulnerability Management Proactive n n Policies • Serve as a guide, deterrent, or both • User or hardware / software based • User example – password security policies • Hardware / Software example: Wireless access (802. 11) Monitoring and Reporting • Constant and consistent tracking of key areas for vulnerability or weakness • Monitoring often done by remote from a home office location or by outsourced firm to reduce bias Jill R. Aitoro, “Cyber Security -- Federal cybersecurity: a work in progress”, VARbusiness July 11, 2005, Iss. 2115; pg. G. 23 46
Vulnerability Management Proactive n n Policies • Serve as a guide, deterrent, or both • User or hardware / software based • User example – password security policies • Hardware / Software example: Wireless access (802. 11) Monitoring and Reporting • Constant and consistent tracking of key areas for vulnerability or weakness • Monitoring often done by remote from a home office location or by outsourced firm to reduce bias Jill R. Aitoro, “Cyber Security -- Federal cybersecurity: a work in progress”, VARbusiness July 11, 2005, Iss. 2115; pg. G. 23 46
 Proactive - continued n n Business Continuation / Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) • Mirrored data centers – real time remote replication of data • Traditional “Point-in-Time” backups n Example – tape backups • Monitoring and Management n Backup team monitoring backup completeness, links between data centers, etc. • Prevent loss of backup data Updates to key components • Antivirus and Anti Spam • Operating System updates • Firmware updates for firewalls / network hardware 47 Data Protection and Disaster Recovery of Local and Remote File Servers Julie Herd Goodman. Computer Technology Review. Los Angeles: Aug/Sep 2005. Vol. 25, Iss. 5; pg. 29, 2 pgs
Proactive - continued n n Business Continuation / Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) • Mirrored data centers – real time remote replication of data • Traditional “Point-in-Time” backups n Example – tape backups • Monitoring and Management n Backup team monitoring backup completeness, links between data centers, etc. • Prevent loss of backup data Updates to key components • Antivirus and Anti Spam • Operating System updates • Firmware updates for firewalls / network hardware 47 Data Protection and Disaster Recovery of Local and Remote File Servers Julie Herd Goodman. Computer Technology Review. Los Angeles: Aug/Sep 2005. Vol. 25, Iss. 5; pg. 29, 2 pgs
 Incident Response - Reactive n n n Dedicated response team with vast resources Follow a prescribed plan – work carefully through a set plan to ensure that resources are brought online in the right order, and that all critical data is present. Prioritization of resources – ensure that business critical systems are given priority James Ryan, Alex Rosenbaum, Scott Carpenter. “Getting a Handle on Incidents”, Security Management. Arlington: April 2005. Vol. 49, Iss. 4; pg. 66, 7 pgs 48
Incident Response - Reactive n n n Dedicated response team with vast resources Follow a prescribed plan – work carefully through a set plan to ensure that resources are brought online in the right order, and that all critical data is present. Prioritization of resources – ensure that business critical systems are given priority James Ryan, Alex Rosenbaum, Scott Carpenter. “Getting a Handle on Incidents”, Security Management. Arlington: April 2005. Vol. 49, Iss. 4; pg. 66, 7 pgs 48
 Education and Communication n Ethics and awareness training • Helps to prevent Social Engineering - the process of obtaining confidential information by manipulation of legitimate users • Ongoing training for all users on common schemes and weaknesses, proper password handling, importance of data privacy, etc. • First Data does this through regular required online classroom sessions, with follow-up testing and user tracking Issue reporting • Open line to company users to report a potential or real time vulnerability Reporting to senior management • Important policy changes • Business Continuation and Disaster Recovery plans • Realistic perspective and likelihood of threat and potential impact on business operations Robert P Moffie, David L Baumer, Ralph B Tower. “Identity Theft and Data Security”, Internal Auditing. Sept/Oct 2005. Vol. 20, Iss. 5; pg. 29, 9 pgs 49
Education and Communication n Ethics and awareness training • Helps to prevent Social Engineering - the process of obtaining confidential information by manipulation of legitimate users • Ongoing training for all users on common schemes and weaknesses, proper password handling, importance of data privacy, etc. • First Data does this through regular required online classroom sessions, with follow-up testing and user tracking Issue reporting • Open line to company users to report a potential or real time vulnerability Reporting to senior management • Important policy changes • Business Continuation and Disaster Recovery plans • Realistic perspective and likelihood of threat and potential impact on business operations Robert P Moffie, David L Baumer, Ralph B Tower. “Identity Theft and Data Security”, Internal Auditing. Sept/Oct 2005. Vol. 20, Iss. 5; pg. 29, 9 pgs 49
 Policies, Procedures & Standards n n n Software / Hardware enforced policies: • USB storage devices • Password renewal and complexity policy • Remote access policies • Encryption policies User based policies: • Focus on areas that cannot easily or completely be limited by technology • No viewing of consumer data on laptops around non-FDC employees • Restriction on editing of sensitive code with family or friends in the room • Internet browsing policy Written principles and standards • Emphasis on protective behavior overall cuts down on risk of social engineering George V Hulme. “Data Breaches: Turn Back The Tide”, Business Credit. New York: October 2005. Vol. 107, Iss. 9; pg. 34, 5 pgs 50
Policies, Procedures & Standards n n n Software / Hardware enforced policies: • USB storage devices • Password renewal and complexity policy • Remote access policies • Encryption policies User based policies: • Focus on areas that cannot easily or completely be limited by technology • No viewing of consumer data on laptops around non-FDC employees • Restriction on editing of sensitive code with family or friends in the room • Internet browsing policy Written principles and standards • Emphasis on protective behavior overall cuts down on risk of social engineering George V Hulme. “Data Breaches: Turn Back The Tide”, Business Credit. New York: October 2005. Vol. 107, Iss. 9; pg. 34, 5 pgs 50
 Organizational Interaction n Departments or entities typically involved: • Physical Security • Vendors and Partners • Legal / Privacy • Operations • Audit / Global Compliance • Human Resources Physical Security at First Data: • Electronic security pass cards • Video surveillance • Guards Human Resources at First Data • Responsible for distributing and tracking all training George V Hulme. “Data Breaches: Turn Back The Tide”, Business Credit. New York: October 2005. Vol. 107, Iss. 9; pg. 34, 5 pgs 51
Organizational Interaction n Departments or entities typically involved: • Physical Security • Vendors and Partners • Legal / Privacy • Operations • Audit / Global Compliance • Human Resources Physical Security at First Data: • Electronic security pass cards • Video surveillance • Guards Human Resources at First Data • Responsible for distributing and tracking all training George V Hulme. “Data Breaches: Turn Back The Tide”, Business Credit. New York: October 2005. Vol. 107, Iss. 9; pg. 34, 5 pgs 51
 Performance & Effectiveness Evaluation n Track number and type of incidents that occur, find ways to avoid n Regularly test user awareness and knowledge n n Oversight Board • Group of users and managers from all areas of the company • Can provide valuable input on ease of use, alignment with organizational goals, and more • Security process should be a business enabler, not disabler, and a confidence builder to users Uses of results: • Ongoing reassessment • Design modifications • Real time training enhancements or changes Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 52
Performance & Effectiveness Evaluation n Track number and type of incidents that occur, find ways to avoid n Regularly test user awareness and knowledge n n Oversight Board • Group of users and managers from all areas of the company • Can provide valuable input on ease of use, alignment with organizational goals, and more • Security process should be a business enabler, not disabler, and a confidence builder to users Uses of results: • Ongoing reassessment • Design modifications • Real time training enhancements or changes Key Elements of an Information Security Program. Presentation by Bryant Tow, Director North America Managed Security Solutions for Unisys, copyright Unisys 2004 52
 First Data – Ongoing Challenges n Overall Mindset – Improved focus on the proactive n Learning for previous challenges n Heightened focus on consumer data security n Stronger hardware and software based policies 53
First Data – Ongoing Challenges n Overall Mindset – Improved focus on the proactive n Learning for previous challenges n Heightened focus on consumer data security n Stronger hardware and software based policies 53
 Management Best Practices 54
Management Best Practices 54
 Info. Sec Management Best Practice n n 1. Security Policy - Demonstrate management commitment to, and support for information security 2. Organizational Security - Develop a management framework for the coordination and management of information security in the organization; allocate information security responsibility 3. Asset Classification & Control -Maintain an appropriate level of protection for all critical or sensitive assets 4. Personnel Security - Reduce the risk of error, theft, fraud, or misuse of computer resources by promoting user training and awareness regarding risks and threats to information Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 55
Info. Sec Management Best Practice n n 1. Security Policy - Demonstrate management commitment to, and support for information security 2. Organizational Security - Develop a management framework for the coordination and management of information security in the organization; allocate information security responsibility 3. Asset Classification & Control -Maintain an appropriate level of protection for all critical or sensitive assets 4. Personnel Security - Reduce the risk of error, theft, fraud, or misuse of computer resources by promoting user training and awareness regarding risks and threats to information Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 55
 Best Practice- continued n n n 5. Physical & Environmental Security - Prevent unauthorized access to information processing facilities and prevent damage to information and to the organization's premises 6. Communications & Operations Management - Reduce the risk of failure and its consequences by ensuring the proper and secure use of information processing facilities and by developing incident response procedures 7. Access Control - Control access to information to ensure the protection of networked systems and the detection of unauthorized activities. Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 56
Best Practice- continued n n n 5. Physical & Environmental Security - Prevent unauthorized access to information processing facilities and prevent damage to information and to the organization's premises 6. Communications & Operations Management - Reduce the risk of failure and its consequences by ensuring the proper and secure use of information processing facilities and by developing incident response procedures 7. Access Control - Control access to information to ensure the protection of networked systems and the detection of unauthorized activities. Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 56
 Best Practice- continued n n n 8. Systems Development and Maintenance - Prevent the loss, modification, or misuse of information in operating systems and application software 9. Business Continuity Management - Ability to react rapidly to the interruption of critical activities resulting from failures, incidents, natural disasters, or catastrophes 10. Compliance - Ensure that all laws and regulations are respected and that existing policies comply with the security policy in order to ensure that the objectives laid out by senior management are met Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 57
Best Practice- continued n n n 8. Systems Development and Maintenance - Prevent the loss, modification, or misuse of information in operating systems and application software 9. Business Continuity Management - Ability to react rapidly to the interruption of critical activities resulting from failures, incidents, natural disasters, or catastrophes 10. Compliance - Ensure that all laws and regulations are respected and that existing policies comply with the security policy in order to ensure that the objectives laid out by senior management are met Information Security Management Best Practice Based on ISO/IEC 177799 Information Management Journal, Jul/Aug 2005 Vol. 39 Iss. 4 57
 Mapping The Cases Into Best Practices n Don't bring home Zip drives, USB devices n Not allowed to ping n Instant messaging tools kept minimum n Blocking unwanted web pages and port numbers Examples of Security Policy Implementation 58
Mapping The Cases Into Best Practices n Don't bring home Zip drives, USB devices n Not allowed to ping n Instant messaging tools kept minimum n Blocking unwanted web pages and port numbers Examples of Security Policy Implementation 58
 Mapping-continued n Establish joint security team n Creation of Chief Information Security Officer Organizational Security Management Framework n Assign threat ratings to portions of customer's network system Asset Classification and Control 59
Mapping-continued n Establish joint security team n Creation of Chief Information Security Officer Organizational Security Management Framework n Assign threat ratings to portions of customer's network system Asset Classification and Control 59
 Mapping-continued n Building User Awareness (eg. through training) Personnel Security n Using Password-protected screen saver, ID cards with auto-changing password -Physical and Environmental Security -Access Control n Early Warning System & Communicating Threat Information Communications and Operations Management 60
Mapping-continued n Building User Awareness (eg. through training) Personnel Security n Using Password-protected screen saver, ID cards with auto-changing password -Physical and Environmental Security -Access Control n Early Warning System & Communicating Threat Information Communications and Operations Management 60
 Mapping-continued n n Continuously analyze Threats and Implement most updated Security Technology Make the needed Security Changes Systems Development and Maintenance n n Automatically Routing the oncoming attack to a Network Mitigation Farm Mirrored data centers Business Continuity Management 61
Mapping-continued n n Continuously analyze Threats and Implement most updated Security Technology Make the needed Security Changes Systems Development and Maintenance n n Automatically Routing the oncoming attack to a Network Mitigation Farm Mirrored data centers Business Continuity Management 61
 CONCLUSION n Information security threat increases as computer and network systems are growing more complex and more business processes are integrating with computer/network systems n Information Security is a real and significant aspect in IT/IS systems all over the world n It has become mandatory by law (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) instead of just an optional facility n Best Practice Frameworks are available that can be used to help organizations build a good and sound information security system 62
CONCLUSION n Information security threat increases as computer and network systems are growing more complex and more business processes are integrating with computer/network systems n Information Security is a real and significant aspect in IT/IS systems all over the world n It has become mandatory by law (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) instead of just an optional facility n Best Practice Frameworks are available that can be used to help organizations build a good and sound information security system 62
 ? 63
? 63


