5fbb44eed048aaba0f0a41bafc6c45ef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 IT Security Evaluation and Certification Standards and Personal Information Current challenges and future needs in a multilateral perspective Giovanni Iachello College of Computing, Georgia Inst. of Technology giac@cc. gatech. edu Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed
IT Security Evaluation and Certification Standards and Personal Information Current challenges and future needs in a multilateral perspective Giovanni Iachello College of Computing, Georgia Inst. of Technology giac@cc. gatech. edu Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed
 Evaluation and Certification: Why? Verify and validate conformance to requirements – Increase information fluidity Compare among competitors – Better informed decisions Independent quality assessment – Increase credibility Marketing – Increase confidence Regulation (in the future) – Higher protection standards Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 2
Evaluation and Certification: Why? Verify and validate conformance to requirements – Increase information fluidity Compare among competitors – Better informed decisions Independent quality assessment – Increase credibility Marketing – Increase confidence Regulation (in the future) – Higher protection standards Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 2
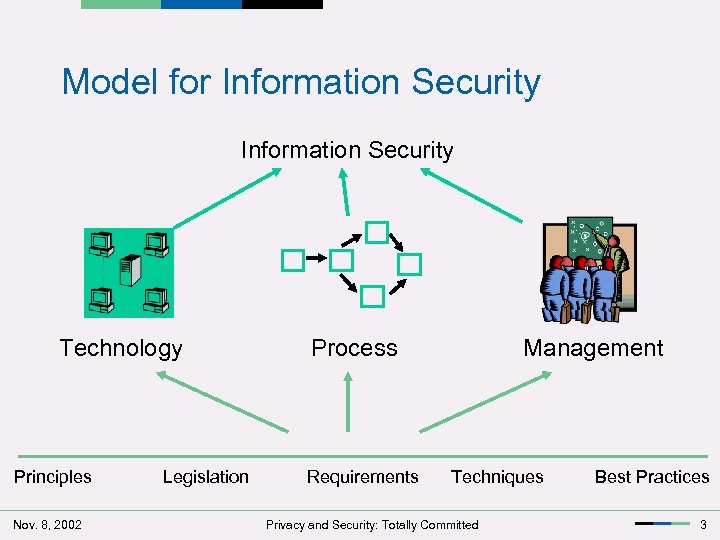 Model for Information Security Technology Principles Nov. 8, 2002 Legislation Process Requirements Management Techniques Privacy and Security: Totally Committed Best Practices 3
Model for Information Security Technology Principles Nov. 8, 2002 Legislation Process Requirements Management Techniques Privacy and Security: Totally Committed Best Practices 3
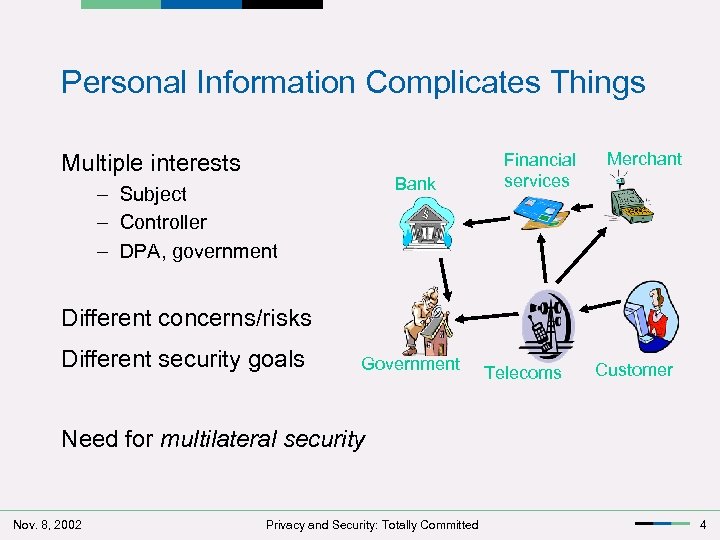 Personal Information Complicates Things Multiple interests Bank – Subject – Controller – DPA, government Financial services Merchant Different concerns/risks Different security goals Government Telecoms Customer Need for multilateral security Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 4
Personal Information Complicates Things Multiple interests Bank – Subject – Controller – DPA, government Financial services Merchant Different concerns/risks Different security goals Government Telecoms Customer Need for multilateral security Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 4
 Common Criteria and PETs Context – – – Modular security requirements framework Addresses products and systems Evaluation and certification Address SW HW FW Derives from 20+ years experience (TCSEC, ITSEC) Security = Functionality + Assurance – Functional requirements “What can the system do to be secure? ” – Assurance requirements “What was done to assure that the TOE does what it shall do / does not what it shouldn't do? ” Why use the Common Criteria (CC)? – Accredited evaluation facilities already exist – Evaluations can be recognized by participating countries – Integrate PET evaluation with security evaluation Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 6
Common Criteria and PETs Context – – – Modular security requirements framework Addresses products and systems Evaluation and certification Address SW HW FW Derives from 20+ years experience (TCSEC, ITSEC) Security = Functionality + Assurance – Functional requirements “What can the system do to be secure? ” – Assurance requirements “What was done to assure that the TOE does what it shall do / does not what it shouldn't do? ” Why use the Common Criteria (CC)? – Accredited evaluation facilities already exist – Evaluations can be recognized by participating countries – Integrate PET evaluation with security evaluation Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 6
 Common Criteria and PETs Older criteria – no privacy! – ITSEC: “security = integrity, confidentiality and availability” (1991) Common Criteria FPR class: good… – Privacy requirements (a. k. a. the “Freiburg class”) – Support anonymity, pseudonymity, unobservability (1995 -) …but not enough! – Information collection, use, retention – Non-security requirements – Unlinkability, trust distribution Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 7
Common Criteria and PETs Older criteria – no privacy! – ITSEC: “security = integrity, confidentiality and availability” (1991) Common Criteria FPR class: good… – Privacy requirements (a. k. a. the “Freiburg class”) – Support anonymity, pseudonymity, unobservability (1995 -) …but not enough! – Information collection, use, retention – Non-security requirements – Unlinkability, trust distribution Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 7
 Enhancing the Common Criteria Derive functional and assurance requirements from FIPs (PETTEP 2001 -2002) – One functional family for each Fair Information Practice – Each requirement supports one or more practices Use abstract properties (Trust, Linkability) to derive functional requirements (IIG Freiburg 1998 -1999) – Trust allocation in multiple administrative domains – Unlinkability – Information retention At the proposal stage – Real world testing is needed Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 8
Enhancing the Common Criteria Derive functional and assurance requirements from FIPs (PETTEP 2001 -2002) – One functional family for each Fair Information Practice – Each requirement supports one or more practices Use abstract properties (Trust, Linkability) to derive functional requirements (IIG Freiburg 1998 -1999) – Trust allocation in multiple administrative domains – Unlinkability – Information retention At the proposal stage – Real world testing is needed Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 8
 Shortcomings of PET Certification Conflicting requirements – Structured to protect centralized systems – New requirements can be inconsistent with old ones Trust – Advanced PETs distribute information so that no trustee can abuse it – Distinct administrative domains, awkward to state within the CC – Need to “step out of the box” Technology is only as good as how it is used – Safeguards can be circumvented or ignored – Information has an inherent strategic value – How to protect a system from its own administrators? Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 9
Shortcomings of PET Certification Conflicting requirements – Structured to protect centralized systems – New requirements can be inconsistent with old ones Trust – Advanced PETs distribute information so that no trustee can abuse it – Distinct administrative domains, awkward to state within the CC – Need to “step out of the box” Technology is only as good as how it is used – Safeguards can be circumvented or ignored – Information has an inherent strategic value – How to protect a system from its own administrators? Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 9
 PET Evaluation/Certification Costs Currently evaluated products 1. 2. Mass-market products – Evaluation paid by the manufacturer Custom products with special security requirements – Evaluation paid by the customer as part of the contract Formal evaluation – – – Very costly Impractical in patchwork systems Impractical for consumer products Unlikely that formal PET evaluation can be made mandatory in the short term Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 10
PET Evaluation/Certification Costs Currently evaluated products 1. 2. Mass-market products – Evaluation paid by the manufacturer Custom products with special security requirements – Evaluation paid by the customer as part of the contract Formal evaluation – – – Very costly Impractical in patchwork systems Impractical for consumer products Unlikely that formal PET evaluation can be made mandatory in the short term Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 10
 …let’s look at the Management side Management and process definition can be used to increase personal information protection How can personal data management be assessed? – Voluntary self-evaluation – U. S. Safe Harbor – Japan Requirements for Personal Information Protection – European Data Protection Laws – Independent assessments Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 12
…let’s look at the Management side Management and process definition can be used to increase personal information protection How can personal data management be assessed? – Voluntary self-evaluation – U. S. Safe Harbor – Japan Requirements for Personal Information Protection – European Data Protection Laws – Independent assessments Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 12
 IT Security Management Evaluation and Certification – ISO 17799 Widely used for many years as British Standard 7799 ISO standardized in 2000 Part 1: Code of practice – Best practices and application guidelines – Policy, infrastructure, asset control, personnel, physical, communications, access control, development & maintenance, compliance Part 2: Specification – What requirements are needed for certification – Not yet ISO standard Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 14
IT Security Management Evaluation and Certification – ISO 17799 Widely used for many years as British Standard 7799 ISO standardized in 2000 Part 1: Code of practice – Best practices and application guidelines – Policy, infrastructure, asset control, personnel, physical, communications, access control, development & maintenance, compliance Part 2: Specification – What requirements are needed for certification – Not yet ISO standard Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 14
 IS 17799 and Personal Information IS 17799 has no provision for personal data management Needs support for privacy requirements – Personal data privacy policy – Accountability – Identification of data protection roles, responsibilities – Management – How and why of personal data lifecycle – Communication – With the data subject and the data protection authority – Challenge Compliance In development, needs to be tested Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 15
IS 17799 and Personal Information IS 17799 has no provision for personal data management Needs support for privacy requirements – Personal data privacy policy – Accountability – Identification of data protection roles, responsibilities – Management – How and why of personal data lifecycle – Communication – With the data subject and the data protection authority – Challenge Compliance In development, needs to be tested Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 15
 Pros and Cons of Management Certification Advantages – Provides assurance on how really the organization is doing in managing the data – Can inform sound management practices – Does not require to evaluate/change installed technology Drawbacks – Not the perfect solution (e. g. “locked closet” and “dusty shelf” problems of ISO 9000) – Done on a per-organization basis – Must be regularly repeated – Cultural resistance Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 16
Pros and Cons of Management Certification Advantages – Provides assurance on how really the organization is doing in managing the data – Can inform sound management practices – Does not require to evaluate/change installed technology Drawbacks – Not the perfect solution (e. g. “locked closet” and “dusty shelf” problems of ISO 9000) – Done on a per-organization basis – Must be regularly repeated – Cultural resistance Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 16
 Summary Personal Information Management Evaluation – Integration of COTS – Legacy systems – Data transfer to third parties – how does the system inform the subject about the data transfer? – Definition of system parameters – how long may information be retained? Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy Enhancing Technology Evaluation – Enforcement of PDC (Personal data constraints) – Automatic purging – Labeling attributes – Control on processing activities – Must be designed into the product – Does not work well with patchwork systems Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 17
Summary Personal Information Management Evaluation – Integration of COTS – Legacy systems – Data transfer to third parties – how does the system inform the subject about the data transfer? – Definition of system parameters – how long may information be retained? Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy Enhancing Technology Evaluation – Enforcement of PDC (Personal data constraints) – Automatic purging – Labeling attributes – Control on processing activities – Must be designed into the product – Does not work well with patchwork systems Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 17
 Conclusions PETs evaluation / certification can help… … but management evaluation is equally important! – Could be more effective in the short run – Could help DPAs to assess organizations – Could help organizations with their privacy management needs and problems Sound process design is fundamental Acknowledgements: IIG, IFIP WG 9. 6, Altoprofilo giac@cc. gatech. edu Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 18
Conclusions PETs evaluation / certification can help… … but management evaluation is equally important! – Could be more effective in the short run – Could help DPAs to assess organizations – Could help organizations with their privacy management needs and problems Sound process design is fundamental Acknowledgements: IIG, IFIP WG 9. 6, Altoprofilo giac@cc. gatech. edu Nov. 8, 2002 Privacy and Security: Totally Committed 18


