187c4eaf3b06c4bf2441013d3d9a3c24.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 IT Governance Dr. Andrew Schwarz Associate Professor, ISDS May 19, 2010
IT Governance Dr. Andrew Schwarz Associate Professor, ISDS May 19, 2010
 The Importance of IT Governance • The IT Governance Global Status Report (2004) – 80% of CEO’s recognized that “IT governance or some thereof is required” to resolve “IT issues” – 57% of CEOs looked to IT governance to align IT strategy (and 53% to manage IT risks) – The report concluded that “solutions in this domain are not yet available” • Gartner – Firms with superior IT governance have at least 20% higher profits (ROA) than firms with poor governance given the same strategic objectives • Blind consulting report – 87% of executives believe that IT is critical to their companies’ strategic success – 33% of leaders reported that IT is very involved – 30% reported business executive responsible for strategy works closely with IT division Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
The Importance of IT Governance • The IT Governance Global Status Report (2004) – 80% of CEO’s recognized that “IT governance or some thereof is required” to resolve “IT issues” – 57% of CEOs looked to IT governance to align IT strategy (and 53% to manage IT risks) – The report concluded that “solutions in this domain are not yet available” • Gartner – Firms with superior IT governance have at least 20% higher profits (ROA) than firms with poor governance given the same strategic objectives • Blind consulting report – 87% of executives believe that IT is critical to their companies’ strategic success – 33% of leaders reported that IT is very involved – 30% reported business executive responsible for strategy works closely with IT division Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Characteristics of High IT Governance Performers • • • More focused strategies – Greater differentiation between customer intimacy, product innovation, or operational excellence Clearer business objectives for IT investment – Greater differentiation between supporting new ways of doing business, improving flexibility, or facilitating customer communication High level executive participation in IT governance – Greater involvement, impact of CEO, COO, Business Heads, Business Unit CIOs and CFO – Who could accurately describe IT governance arrangements Stable IT governance, fewer changes year to year Well functioning formal exception processes Formal communication methods Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Characteristics of High IT Governance Performers • • • More focused strategies – Greater differentiation between customer intimacy, product innovation, or operational excellence Clearer business objectives for IT investment – Greater differentiation between supporting new ways of doing business, improving flexibility, or facilitating customer communication High level executive participation in IT governance – Greater involvement, impact of CEO, COO, Business Heads, Business Unit CIOs and CFO – Who could accurately describe IT governance arrangements Stable IT governance, fewer changes year to year Well functioning formal exception processes Formal communication methods Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Governance and Strategy • If strategy is where we are headed, governance defines how we make the decisions that we need to execute our strategy • Research has suggested that structure follows strategy (Chandler) – Strategy dictates what the organization needs • Single product, single plant, single function organizations tend to be single-owner with no clear functional differentiation of strategic, administrative, and operating decisions • Single product, multi-plant, multi-function organizations tend to have a functional structure • Multi product, multi-plant, multi-function organizations tend to have a multi-divisional structure Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Governance and Strategy • If strategy is where we are headed, governance defines how we make the decisions that we need to execute our strategy • Research has suggested that structure follows strategy (Chandler) – Strategy dictates what the organization needs • Single product, single plant, single function organizations tend to be single-owner with no clear functional differentiation of strategic, administrative, and operating decisions • Single product, multi-plant, multi-function organizations tend to have a functional structure • Multi product, multi-plant, multi-function organizations tend to have a multi-divisional structure Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Governance and Strategy (2) • However, structure also restricts strategy – Organization can restrict the ability of the organization to quickly react to changing market conditions • Thus, there is a mutually enhancing relationship between strategy and structure – However, at a higher level, it is crucial that strategy and structure align with one another • Alignment is therefore the degree to which the information technology mission, objectives, plans, and technology support and are supported by the business mission, objectives, plans, and business processes Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Governance and Strategy (2) • However, structure also restricts strategy – Organization can restrict the ability of the organization to quickly react to changing market conditions • Thus, there is a mutually enhancing relationship between strategy and structure – However, at a higher level, it is crucial that strategy and structure align with one another • Alignment is therefore the degree to which the information technology mission, objectives, plans, and technology support and are supported by the business mission, objectives, plans, and business processes Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
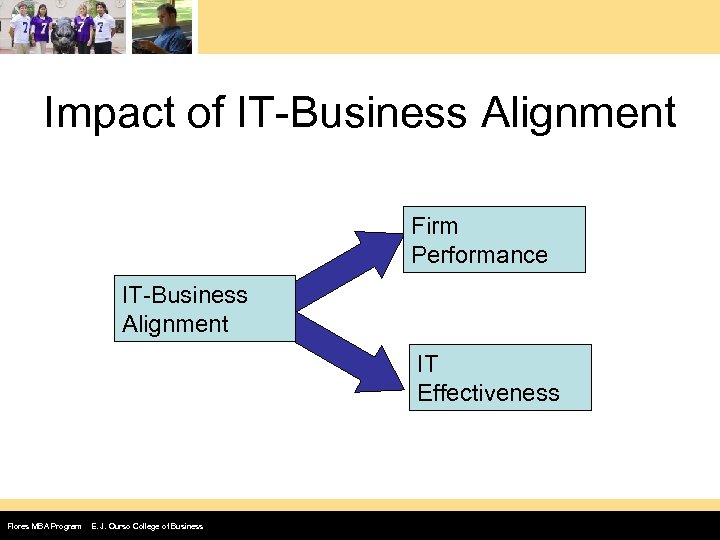 Impact of IT-Business Alignment Firm Performance IT-Business Alignment IT Effectiveness Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Impact of IT-Business Alignment Firm Performance IT-Business Alignment IT Effectiveness Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
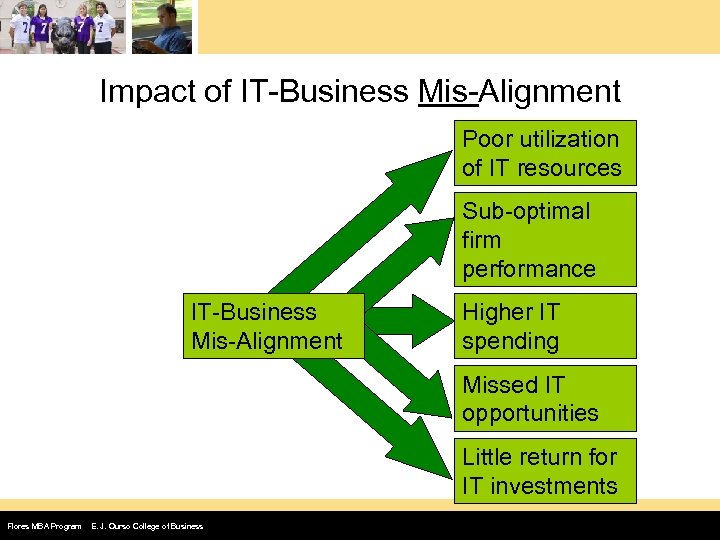 Impact of IT-Business Mis-Alignment Poor utilization of IT resources Sub-optimal firm performance IT-Business Mis-Alignment Higher IT spending Missed IT opportunities Little return for IT investments Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Impact of IT-Business Mis-Alignment Poor utilization of IT resources Sub-optimal firm performance IT-Business Mis-Alignment Higher IT spending Missed IT opportunities Little return for IT investments Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Types of Alignment • Strategic alignment – Congruence of the firm’s IS strategy with the business strategy • Structural alignment – Congruence of the business and IS structures within the organization • Social alignment – The level of mutual understanding of and commitment to the business and IT mission, objectives and plans Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Types of Alignment • Strategic alignment – Congruence of the firm’s IS strategy with the business strategy • Structural alignment – Congruence of the business and IS structures within the organization • Social alignment – The level of mutual understanding of and commitment to the business and IT mission, objectives and plans Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Key Issues in Strategic Alignment • Key considerations – Linked business and IS missions, priorities, and strategies – Interconnected business and IS planning processes, and resulting plans • Goal – IS priorities, capabilities, decisions, and actions to support those of the entire business Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Key Issues in Strategic Alignment • Key considerations – Linked business and IS missions, priorities, and strategies – Interconnected business and IS planning processes, and resulting plans • Goal – IS priorities, capabilities, decisions, and actions to support those of the entire business Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Key Issues in Structural Alignment • Key considerations – Location of IT decision-making rights – Reporting relationships – (De)centralization of IT services and infrastructure – Deployment of IT personnel • Goal – IT and business structures to support organizational objectives Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Key Issues in Structural Alignment • Key considerations – Location of IT decision-making rights – Reporting relationships – (De)centralization of IT services and infrastructure – Deployment of IT personnel • Goal – IT and business structures to support organizational objectives Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Key Issues in Social Alignment • Key considerations – Ensure line and IS executives are communicating – Obtain buy-in from line executive commitment to IS issues and initiatives • Goal – Ensure both business and IS executives have a similar view of the role of IT in the firm Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Key Issues in Social Alignment • Key considerations – Ensure line and IS executives are communicating – Obtain buy-in from line executive commitment to IS issues and initiatives • Goal – Ensure both business and IS executives have a similar view of the role of IT in the firm Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Study #1: European Firms • Randomly selected 500 organizations across Europe – Annual survey of IT diffusion – CIO or IT executive respondent • Data modeled for organizations participating in two subsequent years – 58 firms in 2003 and 2004 Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Study #1: European Firms • Randomly selected 500 organizations across Europe – Annual survey of IT diffusion – CIO or IT executive respondent • Data modeled for organizations participating in two subsequent years – 58 firms in 2003 and 2004 Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
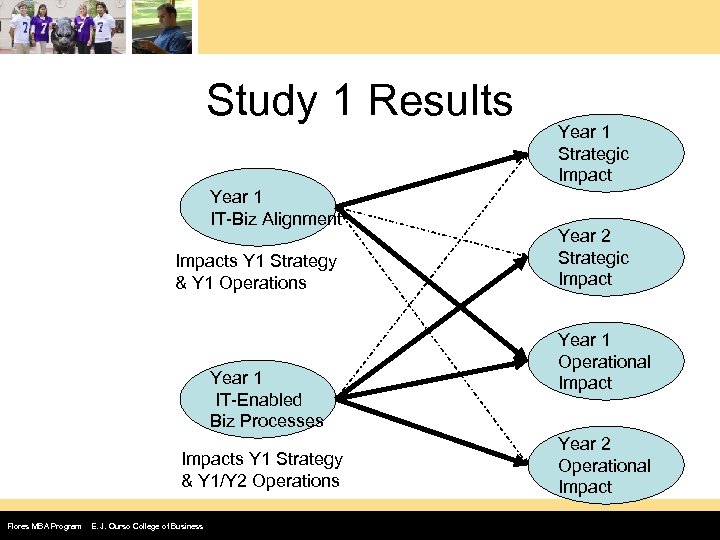 Study 1 Results Year 1 IT-Biz Alignment Impacts Y 1 Strategy & Y 1 Operations Year 1 IT-Enabled Biz Processes Impacts Y 1 Strategy & Y 1/Y 2 Operations Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business Year 1 Strategic Impact Year 2 Strategic Impact Year 1 Operational Impact Year 2 Operational Impact
Study 1 Results Year 1 IT-Biz Alignment Impacts Y 1 Strategy & Y 1 Operations Year 1 IT-Enabled Biz Processes Impacts Y 1 Strategy & Y 1/Y 2 Operations Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business Year 1 Strategic Impact Year 2 Strategic Impact Year 1 Operational Impact Year 2 Operational Impact
 Study #2: German Banks • 1, 020 questionnaires mailed to Germany’s largest banks – Chief Lending or Chief Credit Officer • Data modeled for those returning the survey – 136 fully answered Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Study #2: German Banks • 1, 020 questionnaires mailed to Germany’s largest banks – Chief Lending or Chief Credit Officer • Data modeled for those returning the survey – 136 fully answered Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
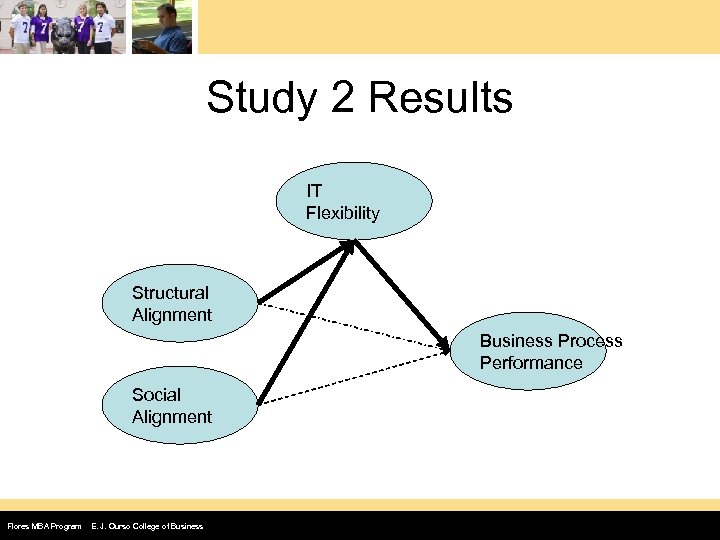 Study 2 Results IT Flexibility Structural Alignment Business Process Performance Social Alignment Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Study 2 Results IT Flexibility Structural Alignment Business Process Performance Social Alignment Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 IT Governance Defined • The assignment of decision rights and the accountability framework to encourage desirable behavior in the use of IT • Governance is really composed of three things – What decisions are to be made – Who will make each of those decisions – What process will be used to make and communicate those decisions Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
IT Governance Defined • The assignment of decision rights and the accountability framework to encourage desirable behavior in the use of IT • Governance is really composed of three things – What decisions are to be made – Who will make each of those decisions – What process will be used to make and communicate those decisions Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Decision Categories 1) IT Principles • 2) High-level statements about how IT will be used to create business value IT infrastructure strategies • 3) State the approach for building shared and standard IT services across the enterprise (typically technical) IT architecture • 4) The technical choices that will meet business needs Business application needs • 5) Where the business defines its’ application needs IT investment and prioritization • Flores MBA Program Defines the process for moving IT-based investments through justification, approval, and accountability E. J. Ourso College of Business
Decision Categories 1) IT Principles • 2) High-level statements about how IT will be used to create business value IT infrastructure strategies • 3) State the approach for building shared and standard IT services across the enterprise (typically technical) IT architecture • 4) The technical choices that will meet business needs Business application needs • 5) Where the business defines its’ application needs IT investment and prioritization • Flores MBA Program Defines the process for moving IT-based investments through justification, approval, and accountability E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Decision Makers • Governance defines two types of rights – Decision rights = who has the right and responsibility to make a decision about how IT is used – Input right = who has the right to provide input to a decision, but not make a decision? Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Decision Makers • Governance defines two types of rights – Decision rights = who has the right and responsibility to make a decision about how IT is used – Input right = who has the right to provide input to a decision, but not make a decision? Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
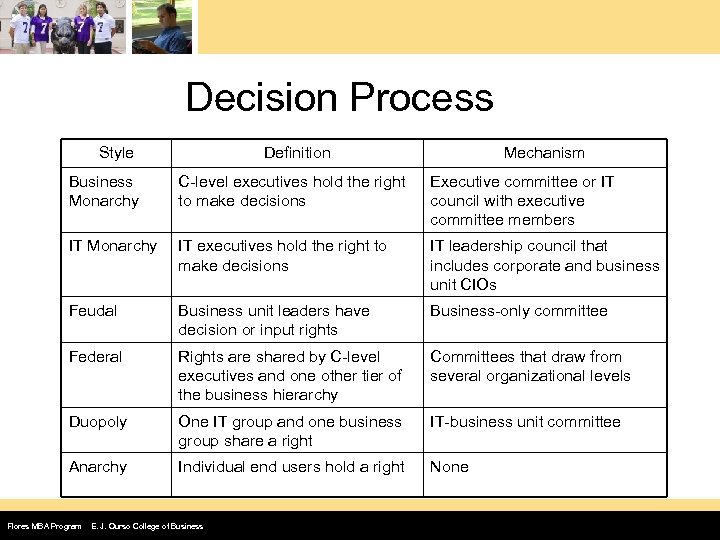 Decision Process Style Definition Mechanism Business Monarchy C-level executives hold the right to make decisions Executive committee or IT council with executive committee members IT Monarchy IT executives hold the right to make decisions IT leadership council that includes corporate and business unit CIOs Feudal Business unit leaders have decision or input rights Business-only committee Federal Rights are shared by C-level executives and one other tier of the business hierarchy Committees that draw from several organizational levels Duopoly One IT group and one business group share a right IT-business unit committee Anarchy Individual end users hold a right None Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Decision Process Style Definition Mechanism Business Monarchy C-level executives hold the right to make decisions Executive committee or IT council with executive committee members IT Monarchy IT executives hold the right to make decisions IT leadership council that includes corporate and business unit CIOs Feudal Business unit leaders have decision or input rights Business-only committee Federal Rights are shared by C-level executives and one other tier of the business hierarchy Committees that draw from several organizational levels Duopoly One IT group and one business group share a right IT-business unit committee Anarchy Individual end users hold a right None Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Allocating Decision and Input Right • Governance is concerned with who gets to make the decisions for the 5 areas versus who gets input – What role do users play? – What role does top management play? – Are there decisions that should be made by IT versus those that should be made other business units? • Who has the decision and input rights? – IT dominates or – User dominates Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Allocating Decision and Input Right • Governance is concerned with who gets to make the decisions for the 5 areas versus who gets input – What role do users play? – What role does top management play? – Are there decisions that should be made by IT versus those that should be made other business units? • Who has the decision and input rights? – IT dominates or – User dominates Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Drivers towards User Dominance • • • User demand Need for flexibility Easy to buy pre-packaged software Users desire to control their own destiny Need for global firm, but local sensitivities Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Drivers towards User Dominance • • • User demand Need for flexibility Easy to buy pre-packaged software Users desire to control their own destiny Need for global firm, but local sensitivities Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Drivers towards IT Dominance • IT has skills that business unit does not • Need for standardization and ensuring system stability • Business leaders not adept at envisioning possibilities with IT, nor at determining feasibility • Need for corporate-wide data management – Eliminate stovepipes • IT better at cost estimation and analysis Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Drivers towards IT Dominance • IT has skills that business unit does not • Need for standardization and ensuring system stability • Business leaders not adept at envisioning possibilities with IT, nor at determining feasibility • Need for corporate-wide data management – Eliminate stovepipes • IT better at cost estimation and analysis Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
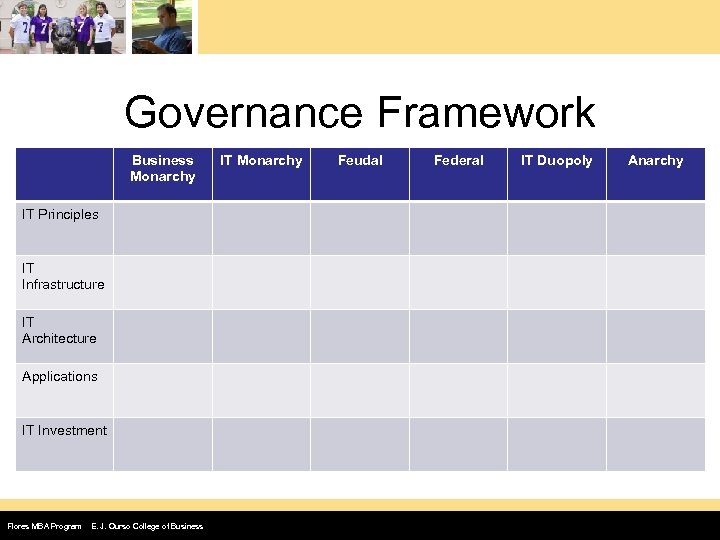 Governance Framework Business Monarchy IT Principles IT Infrastructure IT Architecture Applications IT Investment Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business IT Monarchy Feudal Federal IT Duopoly Anarchy
Governance Framework Business Monarchy IT Principles IT Infrastructure IT Architecture Applications IT Investment Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business IT Monarchy Feudal Federal IT Duopoly Anarchy
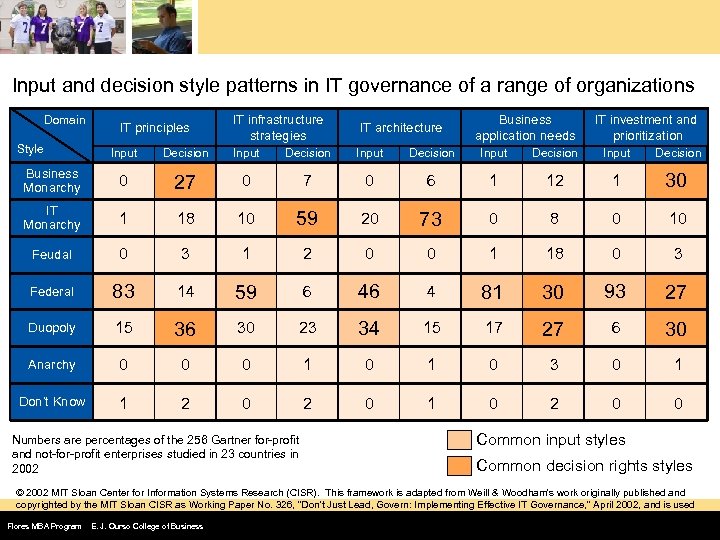 Input and decision style patterns in IT governance of a range of organizations Domain Style IT principles IT infrastructure strategies IT architecture Business application needs IT investment and prioritization Input Decision Input Decision Business Monarchy 0 27 27 0 6 1 12 1 30 IT Monarchy 1 18 10 59 20 73 0 8 0 10 Feudal 0 3 1 2 0 0 1 18 0 3 Federal 83 14 59 6 46 4 81 30 93 27 Duopoly 15 36 30 23 34 15 17 27 6 30 Anarchy 0 0 0 1 0 3 0 1 Don’t Know 1 2 0 1 0 2 0 0 Numbers are percentages of the 256 Gartner for-profit and not-for-profit enterprises studied in 23 countries in 2002 Common input styles Common decision rights styles © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (CISR). This framework is adapted from Weill & Woodham's work originally published and copyrighted by the MIT Sloan CISR as Working Paper No. 326, "Don't Just Lead, Govern: Implementing Effective IT Governance, " April 2002, and is used by Gartner with permission. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Input and decision style patterns in IT governance of a range of organizations Domain Style IT principles IT infrastructure strategies IT architecture Business application needs IT investment and prioritization Input Decision Input Decision Business Monarchy 0 27 27 0 6 1 12 1 30 IT Monarchy 1 18 10 59 20 73 0 8 0 10 Feudal 0 3 1 2 0 0 1 18 0 3 Federal 83 14 59 6 46 4 81 30 93 27 Duopoly 15 36 30 23 34 15 17 27 6 30 Anarchy 0 0 0 1 0 3 0 1 Don’t Know 1 2 0 1 0 2 0 0 Numbers are percentages of the 256 Gartner for-profit and not-for-profit enterprises studied in 23 countries in 2002 Common input styles Common decision rights styles © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (CISR). This framework is adapted from Weill & Woodham's work originally published and copyrighted by the MIT Sloan CISR as Working Paper No. 326, "Don't Just Lead, Govern: Implementing Effective IT Governance, " April 2002, and is used by Gartner with permission. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
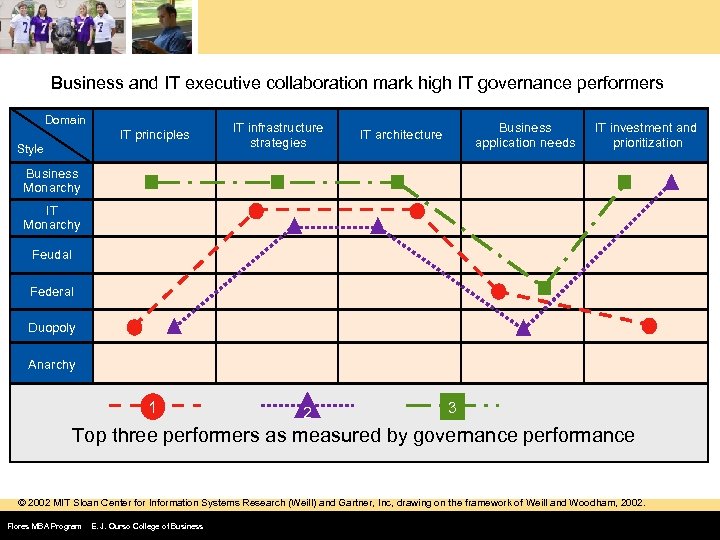 Business and IT executive collaboration mark high IT governance performers Domain IT principles Style IT infrastructure strategies Business application needs IT architecture IT investment and prioritization Business Monarchy IT Monarchy Feudal Federal Duopoly Anarchy 1 2 3 Top three performers as measured by governance performance © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc, drawing on the framework of Weill and Woodham, 2002. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Business and IT executive collaboration mark high IT governance performers Domain IT principles Style IT infrastructure strategies Business application needs IT architecture IT investment and prioritization Business Monarchy IT Monarchy Feudal Federal Duopoly Anarchy 1 2 3 Top three performers as measured by governance performance © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc, drawing on the framework of Weill and Woodham, 2002. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
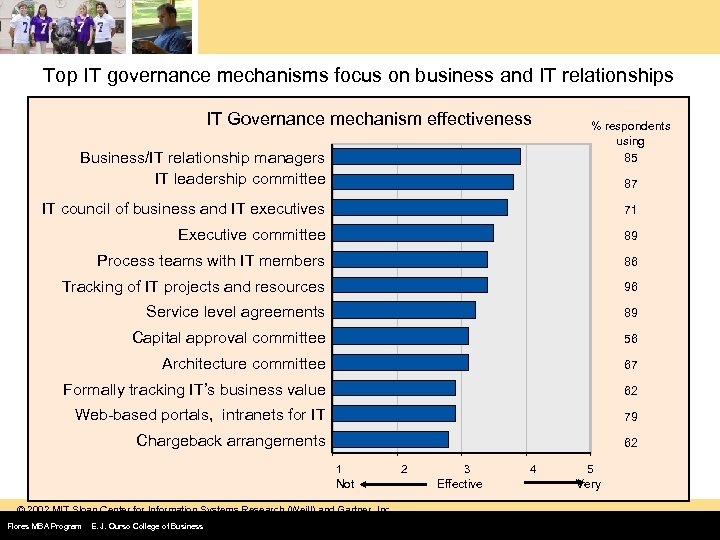 Top IT governance mechanisms focus on business and IT relationships IT Governance mechanism effectiveness Business/IT relationship managers IT leadership committee % respondents using 85 87 IT council of business and IT executives 71 Executive committee 89 Process teams with IT members 86 Tracking of IT projects and resources 96 Service level agreements 89 Capital approval committee 56 Architecture committee 67 Formally tracking IT’s business value 62 Web-based portals, intranets for IT 79 Chargeback arrangements 62 1 Not © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business 2 3 Effective 4 5 Very
Top IT governance mechanisms focus on business and IT relationships IT Governance mechanism effectiveness Business/IT relationship managers IT leadership committee % respondents using 85 87 IT council of business and IT executives 71 Executive committee 89 Process teams with IT members 86 Tracking of IT projects and resources 96 Service level agreements 89 Capital approval committee 56 Architecture committee 67 Formally tracking IT’s business value 62 Web-based portals, intranets for IT 79 Chargeback arrangements 62 1 Not © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business 2 3 Effective 4 5 Very
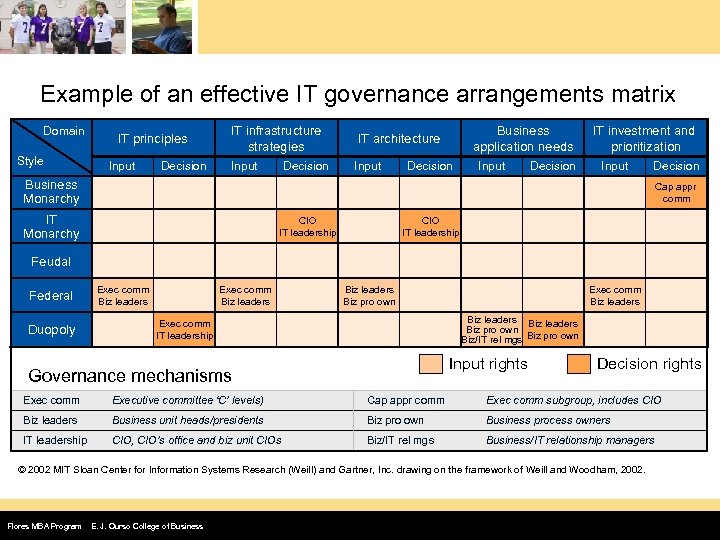 Example of an effective IT governance arrangements matrix Domain Style IT principles Input Decision IT infrastructure strategies IT architecture Input Decision Business application needs Decision Input Decision IT investment and prioritization Input Decision Business Monarchy Cap appr comm IT Monarchy CIO IT leadership Feudal Federal Duopoly Exec comm Biz leaders Biz leaders Biz pro own Biz/IT rel mgs Biz pro own Exec comm IT leadership Input rights Governance mechanisms Decision rights Exec comm Executive committee ‘C’ levels) Cap appr comm Exec comm subgroup, includes CIO Biz leaders Business unit heads/presidents Biz pro own Business process owners IT leadership CIO, CIO’s office and biz unit CIOs Biz/IT rel mgs Business/IT relationship managers © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc. drawing on the framework of Weill and Woodham, 2002. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Example of an effective IT governance arrangements matrix Domain Style IT principles Input Decision IT infrastructure strategies IT architecture Input Decision Business application needs Decision Input Decision IT investment and prioritization Input Decision Business Monarchy Cap appr comm IT Monarchy CIO IT leadership Feudal Federal Duopoly Exec comm Biz leaders Biz leaders Biz pro own Biz/IT rel mgs Biz pro own Exec comm IT leadership Input rights Governance mechanisms Decision rights Exec comm Executive committee ‘C’ levels) Cap appr comm Exec comm subgroup, includes CIO Biz leaders Business unit heads/presidents Biz pro own Business process owners IT leadership CIO, CIO’s office and biz unit CIOs Biz/IT rel mgs Business/IT relationship managers © 2002 MIT Sloan Center for Information Systems Research (Weill) and Gartner, Inc. drawing on the framework of Weill and Woodham, 2002. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Governance Best Practices • There is no one “best” governance arrangement – Tends to be…. • Those seeking synergies among business units enforce-top down decisions • Those with autonomous business units emphasize local decision making • Those with both synergy and autonomy try to encourage faster decision making Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Governance Best Practices • There is no one “best” governance arrangement – Tends to be…. • Those seeking synergies among business units enforce-top down decisions • Those with autonomous business units emphasize local decision making • Those with both synergy and autonomy try to encourage faster decision making Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 What is your Business Orientation? • Autonomy – Highly localized pressures – Business processes distinct • Synergy – High standardization pressures – Business processes integrated • Agility – High speed, flexibility pressures – Business processes adaptable Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
What is your Business Orientation? • Autonomy – Highly localized pressures – Business processes distinct • Synergy – High standardization pressures – Business processes integrated • Agility – High speed, flexibility pressures – Business processes adaptable Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Business & IT Orientation • Autonomy – Emphasize BU decisions, negotiation, peer socialization • Synergy – Emphasize enterprise-wide styles and mechanisms • Agility – Emphasize IT’s role in agility, the use of principles, education Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Business & IT Orientation • Autonomy – Emphasize BU decisions, negotiation, peer socialization • Synergy – Emphasize enterprise-wide styles and mechanisms • Agility – Emphasize IT’s role in agility, the use of principles, education Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Implement key IT governance styles and mechanisms for your business orientation Synergistic enterprises Agility-focused enterprises Autonomy-focused enterprises Decisionmaking styles • Tight corporate coupling between business and IT executives • Top down mandated technology decision making • Business and IT leaders combine for specific purposes • Enterprise-wide arrangements emphasize coordination & learning • IT works with individual business units and process owners • Emphasis on local business decision making Focus of key mechanisms • Well developed business and decision processes • Executive-level committees • High level centrally reporting business-IT relationship managers • Extensive use of IT principles • Business ownership of IT projects • Planned IT-business education experiences • Transparency and Communication • CIOs work through 1/1 negotiation • Standards achieved through socialization and peer pressure • Business-IT service arrangements are in place Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Implement key IT governance styles and mechanisms for your business orientation Synergistic enterprises Agility-focused enterprises Autonomy-focused enterprises Decisionmaking styles • Tight corporate coupling between business and IT executives • Top down mandated technology decision making • Business and IT leaders combine for specific purposes • Enterprise-wide arrangements emphasize coordination & learning • IT works with individual business units and process owners • Emphasis on local business decision making Focus of key mechanisms • Well developed business and decision processes • Executive-level committees • High level centrally reporting business-IT relationship managers • Extensive use of IT principles • Business ownership of IT projects • Planned IT-business education experiences • Transparency and Communication • CIOs work through 1/1 negotiation • Standards achieved through socialization and peer pressure • Business-IT service arrangements are in place Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Top Performing Enterprises • Top-performing enterprises govern IT differently from each other and from average enterprises • Firms leading on growth decentralize more of their IT decision rights and place IT capabilities in the business units • Firms leading on profit centralize more decision rights; senior business leaders make the major IT decisions • Top performers design their IT governance to reinforce their performance goals and link IT governance to the governance of their other key enterprise assets and desired behaviors. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Top Performing Enterprises • Top-performing enterprises govern IT differently from each other and from average enterprises • Firms leading on growth decentralize more of their IT decision rights and place IT capabilities in the business units • Firms leading on profit centralize more decision rights; senior business leaders make the major IT decisions • Top performers design their IT governance to reinforce their performance goals and link IT governance to the governance of their other key enterprise assets and desired behaviors. Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Emerging Trends • Organizational governance is less likely to be centralized or decentralized – Hybrid, federal, or dispersed allocation of decision rights – Focus on demand side and supply side governance – Management of risk, finance, and outsourcing will become significant • We do not know how to do this yet • Emerging models for governance – Emergence/proliferation of new organizational roles • CIOs will have to balance their roles between – Managing the “IT business of the business” – Seeding, stimulating, influencing, and driving IT-enabled business innovation Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Emerging Trends • Organizational governance is less likely to be centralized or decentralized – Hybrid, federal, or dispersed allocation of decision rights – Focus on demand side and supply side governance – Management of risk, finance, and outsourcing will become significant • We do not know how to do this yet • Emerging models for governance – Emergence/proliferation of new organizational roles • CIOs will have to balance their roles between – Managing the “IT business of the business” – Seeding, stimulating, influencing, and driving IT-enabled business innovation Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
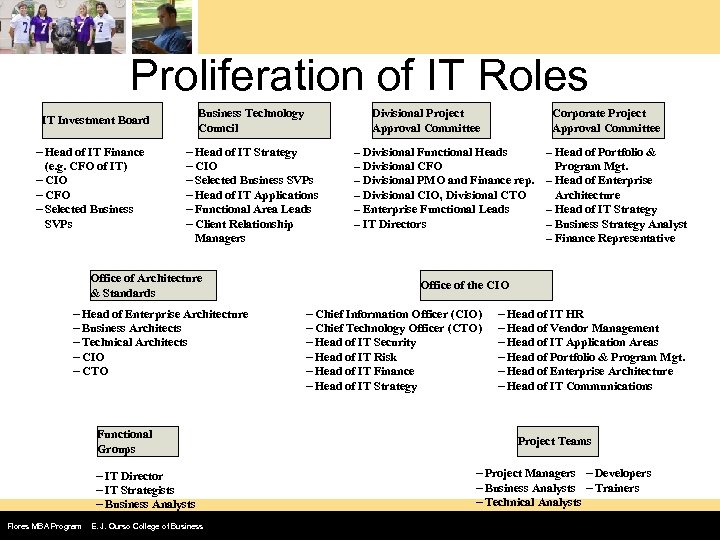 Proliferation of IT Roles Business Technology Council IT Investment Board – Head of IT Finance (e. g. CFO of IT) – CIO – CFO – Selected Business SVPs – Head of IT Strategy – CIO – Selected Business SVPs – Head of IT Applications – Functional Area Leads – Client Relationship Managers Office of Architecture & Standards – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Business Architects – Technical Architects – CIO – CTO Functional Groups – IT Director – IT Strategists – Business Analysts Flores MBA Program Divisional Project Approval Committee E. J. Ourso College of Business – – – Corporate Project Approval Committee Divisional Functional Heads Divisional CFO Divisional PMO and Finance rep. Divisional CIO, Divisional CTO Enterprise Functional Leads IT Directors Head of Portfolio & Program Mgt. – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Head of IT Strategy – Business Strategy Analyst – Finance Representative – Office of the CIO – Chief Information Officer (CIO) – Chief Technology Officer (CTO) – Head of IT Security – Head of IT Risk – Head of IT Finance – Head of IT Strategy – Head of IT HR – Head of Vendor Management – Head of IT Application Areas – Head of Portfolio & Program Mgt. – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Head of IT Communications Project Teams – Project Managers – Developers – Business Analysts – Trainers – Technical Analysts
Proliferation of IT Roles Business Technology Council IT Investment Board – Head of IT Finance (e. g. CFO of IT) – CIO – CFO – Selected Business SVPs – Head of IT Strategy – CIO – Selected Business SVPs – Head of IT Applications – Functional Area Leads – Client Relationship Managers Office of Architecture & Standards – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Business Architects – Technical Architects – CIO – CTO Functional Groups – IT Director – IT Strategists – Business Analysts Flores MBA Program Divisional Project Approval Committee E. J. Ourso College of Business – – – Corporate Project Approval Committee Divisional Functional Heads Divisional CFO Divisional PMO and Finance rep. Divisional CIO, Divisional CTO Enterprise Functional Leads IT Directors Head of Portfolio & Program Mgt. – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Head of IT Strategy – Business Strategy Analyst – Finance Representative – Office of the CIO – Chief Information Officer (CIO) – Chief Technology Officer (CTO) – Head of IT Security – Head of IT Risk – Head of IT Finance – Head of IT Strategy – Head of IT HR – Head of Vendor Management – Head of IT Application Areas – Head of Portfolio & Program Mgt. – Head of Enterprise Architecture – Head of IT Communications Project Teams – Project Managers – Developers – Business Analysts – Trainers – Technical Analysts
 How do I Know if I am Successful? Financial Goals How should we appear to stockholder? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Customer Goals How should we appear to our customer? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business Internal Business Process What business processes should we excel at? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Learning and Growth Goals How will we improve internally? Vision: Metrics: Performance:
How do I Know if I am Successful? Financial Goals How should we appear to stockholder? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Customer Goals How should we appear to our customer? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business Internal Business Process What business processes should we excel at? Vision: Metrics: Performance: Learning and Growth Goals How will we improve internally? Vision: Metrics: Performance:
 Concluding Thoughts • Getting governance right matters • Proliferation of methodologies – COBIG, Val. IT, and others • All helping you to allocate decision and input rights using different approaches • Innovation matters Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Concluding Thoughts • Getting governance right matters • Proliferation of methodologies – COBIG, Val. IT, and others • All helping you to allocate decision and input rights using different approaches • Innovation matters Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
 Thank You! Dr. Andrew Schwarz Louisiana State University E. J. Ourso College of Business aschwarz@lsu. edu Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business
Thank You! Dr. Andrew Schwarz Louisiana State University E. J. Ourso College of Business aschwarz@lsu. edu Flores MBA Program E. J. Ourso College of Business


