8a64235e949679775f48fb187de128e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67

 IT Essentials I v. 3 Module 5 Windows 9 x Operating Systems © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
IT Essentials I v. 3 Module 5 Windows 9 x Operating Systems © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
 Module 5 Windows 9 x Operating Systems 5. 1 – The Windows 9 x File Structure and File Management System 5. 2 – Windows Management with Control Panel 5. 3 – System Tools 5. 4 – Preparing a Hard Drive for OS Installation 5. 5 – Installing Windows 9 x 5. 6 – Troubleshooting the Installation Process
Module 5 Windows 9 x Operating Systems 5. 1 – The Windows 9 x File Structure and File Management System 5. 2 – Windows Management with Control Panel 5. 3 – System Tools 5. 4 – Preparing a Hard Drive for OS Installation 5. 5 – Installing Windows 9 x 5. 6 – Troubleshooting the Installation Process
 The Windows 9 x File Structure and File Management System
The Windows 9 x File Structure and File Management System
 Naming Files in Windows • The terms directory and folder are used interchangeably to describe a place to store information. • Files are now referred to as documents. • A sub-folder is simply a folder within a folder.
Naming Files in Windows • The terms directory and folder are used interchangeably to describe a place to store information. • Files are now referred to as documents. • A sub-folder is simply a folder within a folder.
 Naming Files in Windows • The characters / ; : * ? " < > should not be used because they are associated with special functions when executing commands from a prompt. • If used, a warning displays prompting the user to rename a file. • Allowable characters include all other characters and numbers available on a standard keyboard. • Uppercase characters are treated the same as lowercase in Windows.
Naming Files in Windows • The characters / ; : * ? " < > should not be used because they are associated with special functions when executing commands from a prompt. • If used, a warning displays prompting the user to rename a file. • Allowable characters include all other characters and numbers available on a standard keyboard. • Uppercase characters are treated the same as lowercase in Windows.
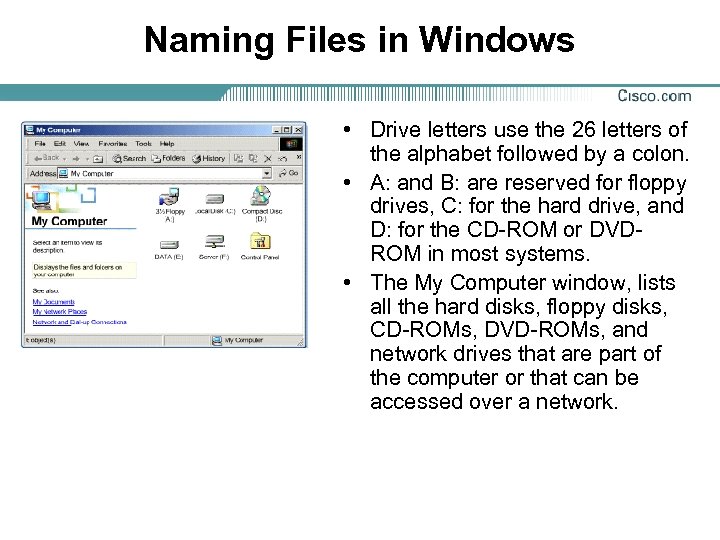 Naming Files in Windows • Drive letters use the 26 letters of the alphabet followed by a colon. • A: and B: are reserved for floppy drives, C: for the hard drive, and D: for the CD-ROM or DVDROM in most systems. • The My Computer window, lists all the hard disks, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs, and network drives that are part of the computer or that can be accessed over a network.
Naming Files in Windows • Drive letters use the 26 letters of the alphabet followed by a colon. • A: and B: are reserved for floppy drives, C: for the hard drive, and D: for the CD-ROM or DVDROM in most systems. • The My Computer window, lists all the hard disks, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs, and network drives that are part of the computer or that can be accessed over a network.
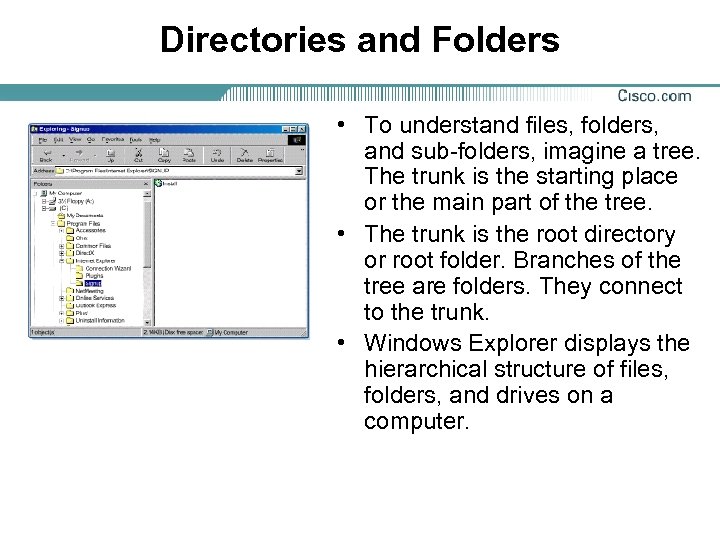 Directories and Folders • To understand files, folders, and sub-folders, imagine a tree. The trunk is the starting place or the main part of the tree. • The trunk is the root directory or root folder. Branches of the tree are folders. They connect to the trunk. • Windows Explorer displays the hierarchical structure of files, folders, and drives on a computer.
Directories and Folders • To understand files, folders, and sub-folders, imagine a tree. The trunk is the starting place or the main part of the tree. • The trunk is the root directory or root folder. Branches of the tree are folders. They connect to the trunk. • Windows Explorer displays the hierarchical structure of files, folders, and drives on a computer.
 Directories and Folders • There are three main parts to this window. • The general area at the top is known as the Title Bar, the area on the left in a window pane is labeled Folders, and the right window pane contains file names and possibly file details such as size and type. • These files can be viewed in different modes by selecting the View icon on the title bar.
Directories and Folders • There are three main parts to this window. • The general area at the top is known as the Title Bar, the area on the left in a window pane is labeled Folders, and the right window pane contains file names and possibly file details such as size and type. • These files can be viewed in different modes by selecting the View icon on the title bar.
 Directories and Folders • To make a folder, use the scroll bar between the left and right window panes and in the left window pane, locate and click on the Desktop. • With the Desktop highlighted, move the cursor over to the right window pane and right-click in a blank area. • Choose New and then Folder.
Directories and Folders • To make a folder, use the scroll bar between the left and right window panes and in the left window pane, locate and click on the Desktop. • With the Desktop highlighted, move the cursor over to the right window pane and right-click in a blank area. • Choose New and then Folder.
 Directories and Folders • The folder can be renamed later by clicking once on the folder to highlight it and pressing the F 2 key. • The name highlights. Type the new name. • A folder name can have up to 255 characters and must only use valid characters.
Directories and Folders • The folder can be renamed later by clicking once on the folder to highlight it and pressing the F 2 key. • The name highlights. Type the new name. • A folder name can have up to 255 characters and must only use valid characters.
 Using a Text Editing Application to Create a File (document) • Files can be created in Windows using Word. Pad or Notepad. • The document can be saved in Rich Text Format (RTF) to the Desktop or to the Word for Windows format.
Using a Text Editing Application to Create a File (document) • Files can be created in Windows using Word. Pad or Notepad. • The document can be saved in Rich Text Format (RTF) to the Desktop or to the Word for Windows format.
 Copy, Cut or Create Shortcuts • Another folder can be created inside the previous folder and files or documents can be copied into this folder. • By right-clicking on an item, other options will appear such as Copy, Move, or Create Shortcuts.
Copy, Cut or Create Shortcuts • Another folder can be created inside the previous folder and files or documents can be copied into this folder. • By right-clicking on an item, other options will appear such as Copy, Move, or Create Shortcuts.
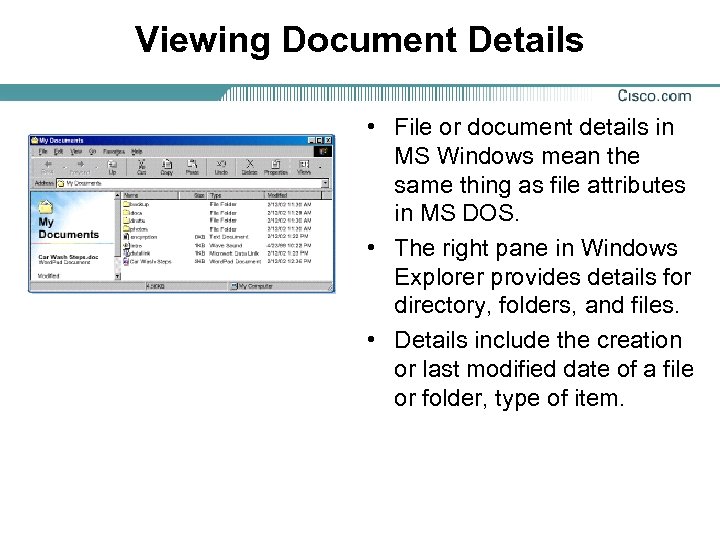 Viewing Document Details • File or document details in MS Windows mean the same thing as file attributes in MS DOS. • The right pane in Windows Explorer provides details for directory, folders, and files. • Details include the creation or last modified date of a file or folder, type of item.
Viewing Document Details • File or document details in MS Windows mean the same thing as file attributes in MS DOS. • The right pane in Windows Explorer provides details for directory, folders, and files. • Details include the creation or last modified date of a file or folder, type of item.
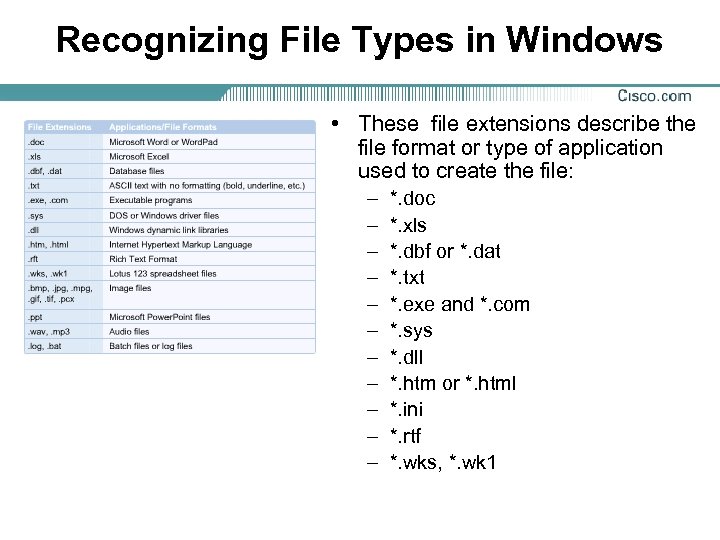 Recognizing File Types in Windows • These file extensions describe the file format or type of application used to create the file: – – – *. doc *. xls *. dbf or *. dat *. txt *. exe and *. com *. sys *. dll *. htm or *. html *. ini *. rtf *. wks, *. wk 1
Recognizing File Types in Windows • These file extensions describe the file format or type of application used to create the file: – – – *. doc *. xls *. dbf or *. dat *. txt *. exe and *. com *. sys *. dll *. htm or *. html *. ini *. rtf *. wks, *. wk 1
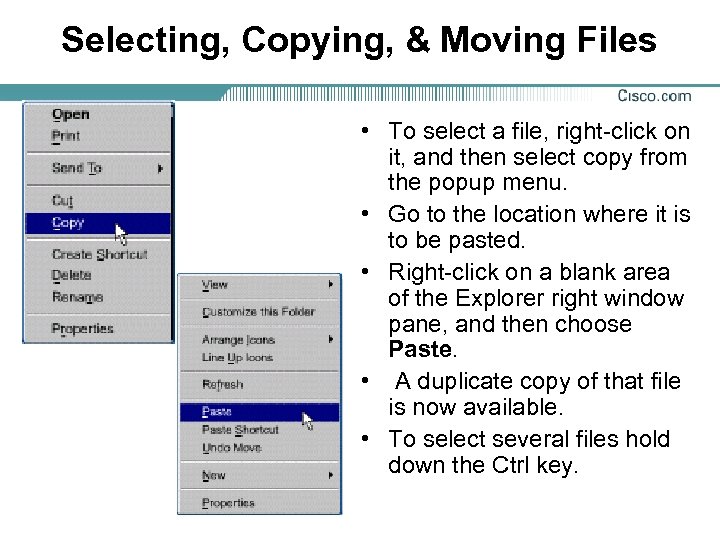 Selecting, Copying, & Moving Files • To select a file, right-click on it, and then select copy from the popup menu. • Go to the location where it is to be pasted. • Right-click on a blank area of the Explorer right window pane, and then choose Paste. • A duplicate copy of that file is now available. • To select several files hold down the Ctrl key.
Selecting, Copying, & Moving Files • To select a file, right-click on it, and then select copy from the popup menu. • Go to the location where it is to be pasted. • Right-click on a blank area of the Explorer right window pane, and then choose Paste. • A duplicate copy of that file is now available. • To select several files hold down the Ctrl key.
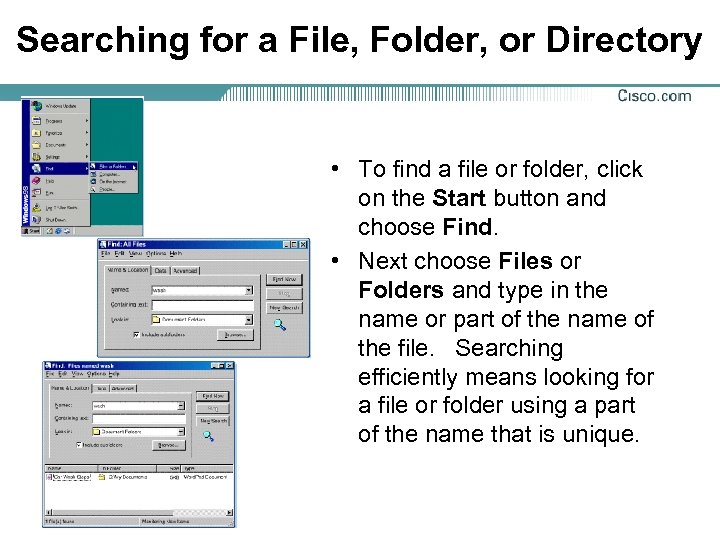 Searching for a File, Folder, or Directory • To find a file or folder, click on the Start button and choose Find. • Next choose Files or Folders and type in the name or part of the name of the file. Searching efficiently means looking for a file or folder using a part of the name that is unique.
Searching for a File, Folder, or Directory • To find a file or folder, click on the Start button and choose Find. • Next choose Files or Folders and type in the name or part of the name of the file. Searching efficiently means looking for a file or folder using a part of the name that is unique.
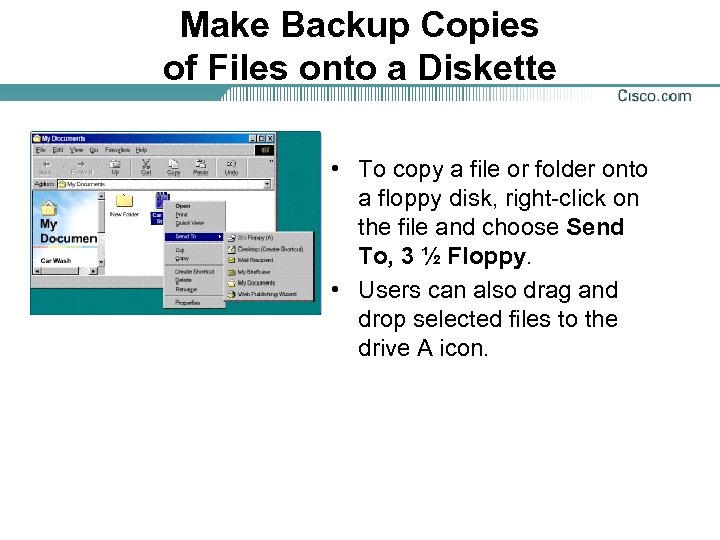 Make Backup Copies of Files onto a Diskette • To copy a file or folder onto a floppy disk, right-click on the file and choose Send To, 3 ½ Floppy. • Users can also drag and drop selected files to the drive A icon.
Make Backup Copies of Files onto a Diskette • To copy a file or folder onto a floppy disk, right-click on the file and choose Send To, 3 ½ Floppy. • Users can also drag and drop selected files to the drive A icon.
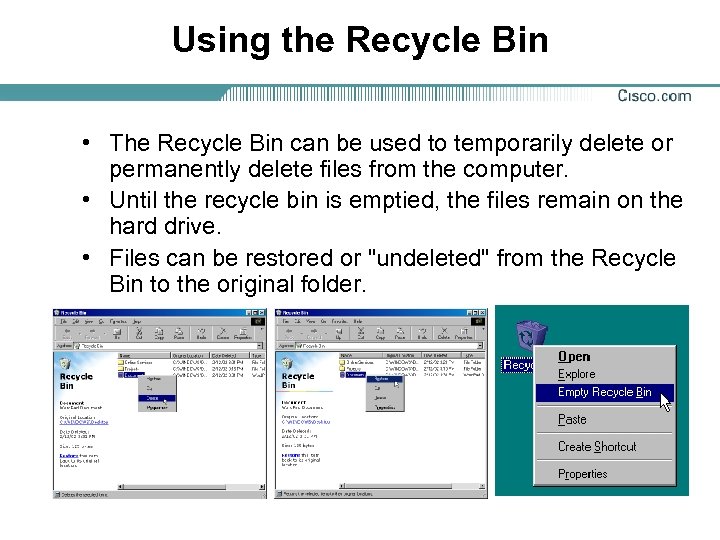 Using the Recycle Bin • The Recycle Bin can be used to temporarily delete or permanently delete files from the computer. • Until the recycle bin is emptied, the files remain on the hard drive. • Files can be restored or "undeleted" from the Recycle Bin to the original folder.
Using the Recycle Bin • The Recycle Bin can be used to temporarily delete or permanently delete files from the computer. • Until the recycle bin is emptied, the files remain on the hard drive. • Files can be restored or "undeleted" from the Recycle Bin to the original folder.
 Windows Management with Control Panel
Windows Management with Control Panel
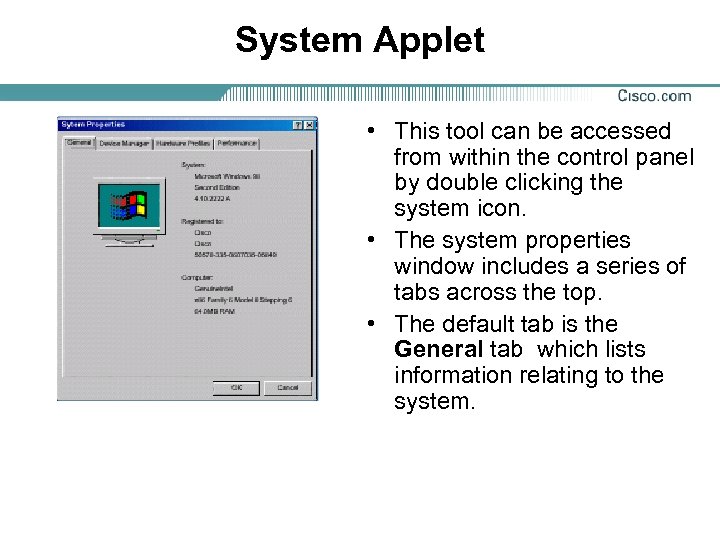 System Applet • This tool can be accessed from within the control panel by double clicking the system icon. • The system properties window includes a series of tabs across the top. • The default tab is the General tab which lists information relating to the system.
System Applet • This tool can be accessed from within the control panel by double clicking the system icon. • The system properties window includes a series of tabs across the top. • The default tab is the General tab which lists information relating to the system.
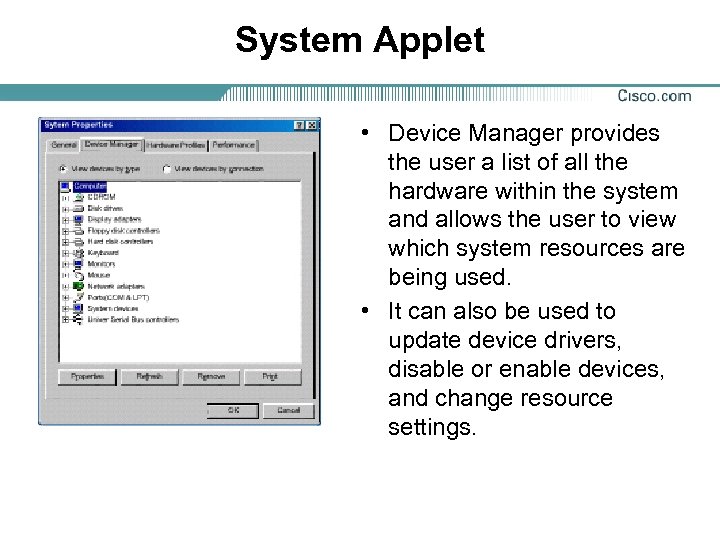 System Applet • Device Manager provides the user a list of all the hardware within the system and allows the user to view which system resources are being used. • It can also be used to update device drivers, disable or enable devices, and change resource settings.
System Applet • Device Manager provides the user a list of all the hardware within the system and allows the user to view which system resources are being used. • It can also be used to update device drivers, disable or enable devices, and change resource settings.
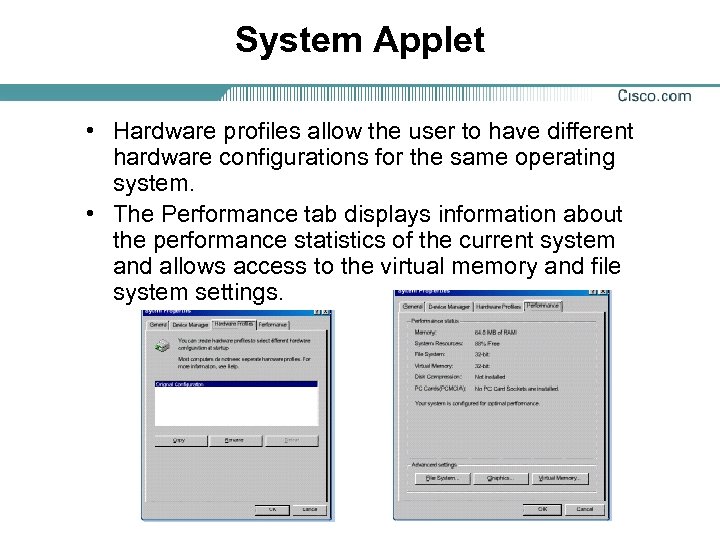 System Applet • Hardware profiles allow the user to have different hardware configurations for the same operating system. • The Performance tab displays information about the performance statistics of the current system and allows access to the virtual memory and file system settings.
System Applet • Hardware profiles allow the user to have different hardware configurations for the same operating system. • The Performance tab displays information about the performance statistics of the current system and allows access to the virtual memory and file system settings.
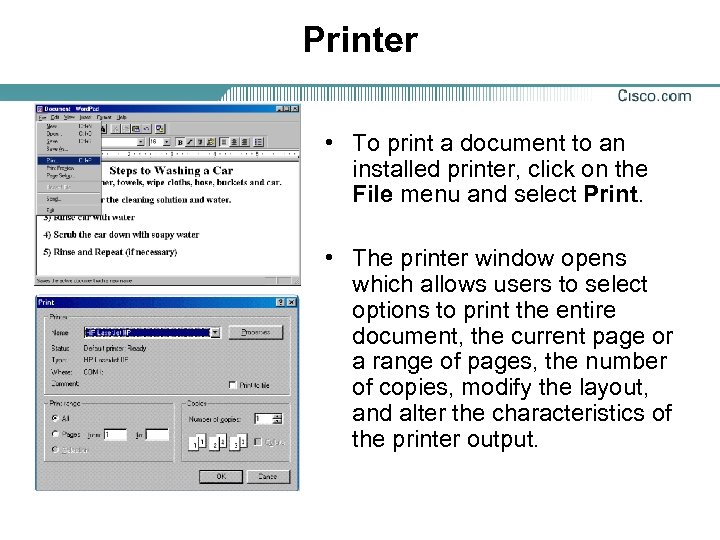 Printer • To print a document to an installed printer, click on the File menu and select Print. • The printer window opens which allows users to select options to print the entire document, the current page or a range of pages, the number of copies, modify the layout, and alter the characteristics of the printer output.
Printer • To print a document to an installed printer, click on the File menu and select Print. • The printer window opens which allows users to select options to print the entire document, the current page or a range of pages, the number of copies, modify the layout, and alter the characteristics of the printer output.
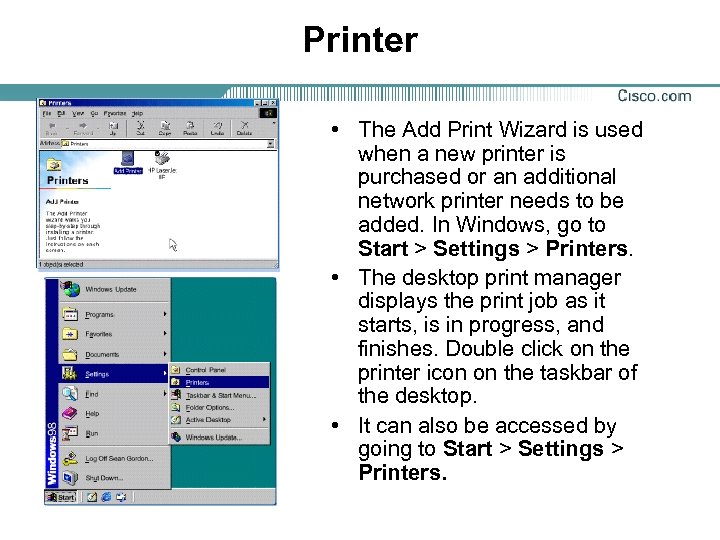 Printer • The Add Print Wizard is used when a new printer is purchased or an additional network printer needs to be added. In Windows, go to Start > Settings > Printers. • The desktop print manager displays the print job as it starts, is in progress, and finishes. Double click on the printer icon on the taskbar of the desktop. • It can also be accessed by going to Start > Settings > Printers.
Printer • The Add Print Wizard is used when a new printer is purchased or an additional network printer needs to be added. In Windows, go to Start > Settings > Printers. • The desktop print manager displays the print job as it starts, is in progress, and finishes. Double click on the printer icon on the taskbar of the desktop. • It can also be accessed by going to Start > Settings > Printers.
 Printer • The desktop print manager displays the print job as it starts and finishes. • The options available in the Printer menu including Pause printing, Purge Print Documents, and the Properties of the printer.
Printer • The desktop print manager displays the print job as it starts and finishes. • The options available in the Printer menu including Pause printing, Purge Print Documents, and the Properties of the printer.
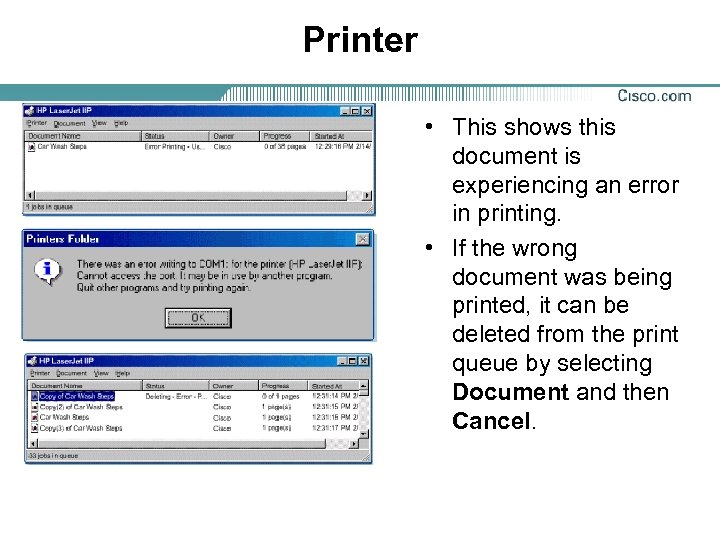 Printer • This shows this document is experiencing an error in printing. • If the wrong document was being printed, it can be deleted from the print queue by selecting Document and then Cancel.
Printer • This shows this document is experiencing an error in printing. • If the wrong document was being printed, it can be deleted from the print queue by selecting Document and then Cancel.
 Add/Remove Programs • When uninstalling an application, go into the Add/Remove Programs utility and click the "Uninstall…" button to uninstall the software. • This will assure that the uninstalled application is removed from the system together with all of its associated pieces.
Add/Remove Programs • When uninstalling an application, go into the Add/Remove Programs utility and click the "Uninstall…" button to uninstall the software. • This will assure that the uninstalled application is removed from the system together with all of its associated pieces.
 Add/Remove Hardware • The Add/Remove Hardware utility automates the addition of a new piece of hardware to the system. • The wizard searches the computer for new hardware and installs the appropriate drivers. • If the appropriate driver is not found automatically, it provides the ability to manually select the type of device from a list and installs drivers from a specific location.
Add/Remove Hardware • The Add/Remove Hardware utility automates the addition of a new piece of hardware to the system. • The wizard searches the computer for new hardware and installs the appropriate drivers. • If the appropriate driver is not found automatically, it provides the ability to manually select the type of device from a list and installs drivers from a specific location.
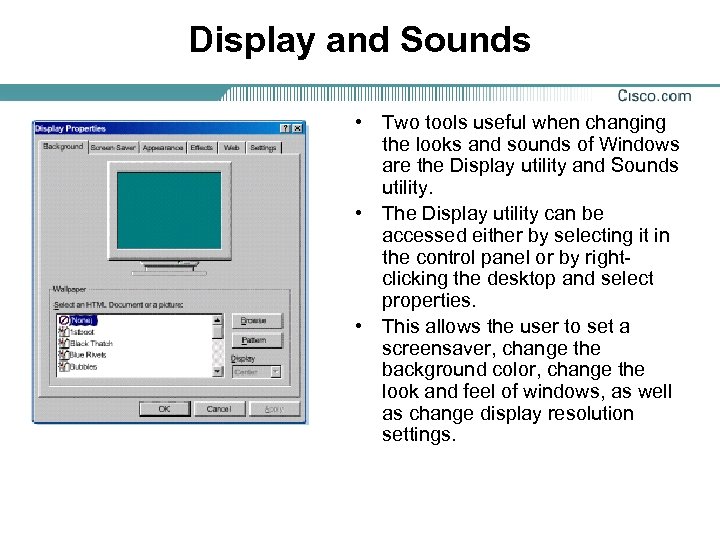 Display and Sounds • Two tools useful when changing the looks and sounds of Windows are the Display utility and Sounds utility. • The Display utility can be accessed either by selecting it in the control panel or by rightclicking the desktop and select properties. • This allows the user to set a screensaver, change the background color, change the look and feel of windows, as well as change display resolution settings.
Display and Sounds • Two tools useful when changing the looks and sounds of Windows are the Display utility and Sounds utility. • The Display utility can be accessed either by selecting it in the control panel or by rightclicking the desktop and select properties. • This allows the user to set a screensaver, change the background color, change the look and feel of windows, as well as change display resolution settings.
 Display and Sounds • The Sounds utility allows the user to choose which sounds are played for different system events. • Themes may also be used to coordinate the background, the look and feel of windows, and the sounds.
Display and Sounds • The Sounds utility allows the user to choose which sounds are played for different system events. • Themes may also be used to coordinate the background, the look and feel of windows, and the sounds.
 System Tools
System Tools
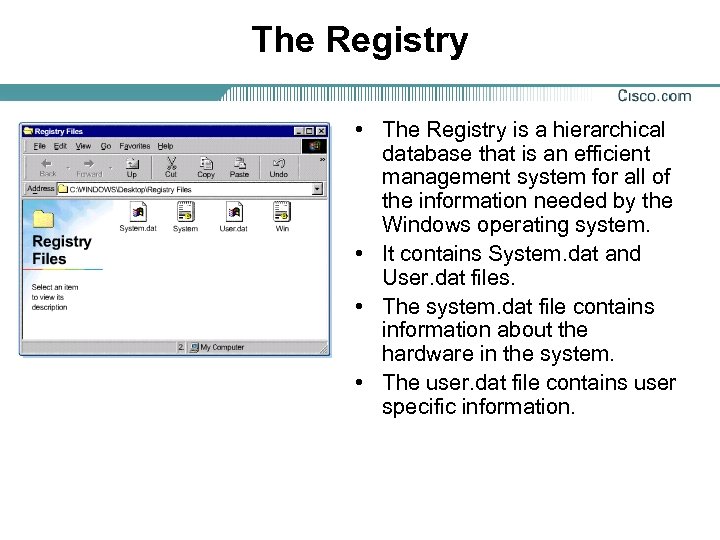 The Registry • The Registry is a hierarchical database that is an efficient management system for all of the information needed by the Windows operating system. • It contains System. dat and User. dat files. • The system. dat file contains information about the hardware in the system. • The user. dat file contains user specific information.
The Registry • The Registry is a hierarchical database that is an efficient management system for all of the information needed by the Windows operating system. • It contains System. dat and User. dat files. • The system. dat file contains information about the hardware in the system. • The user. dat file contains user specific information.
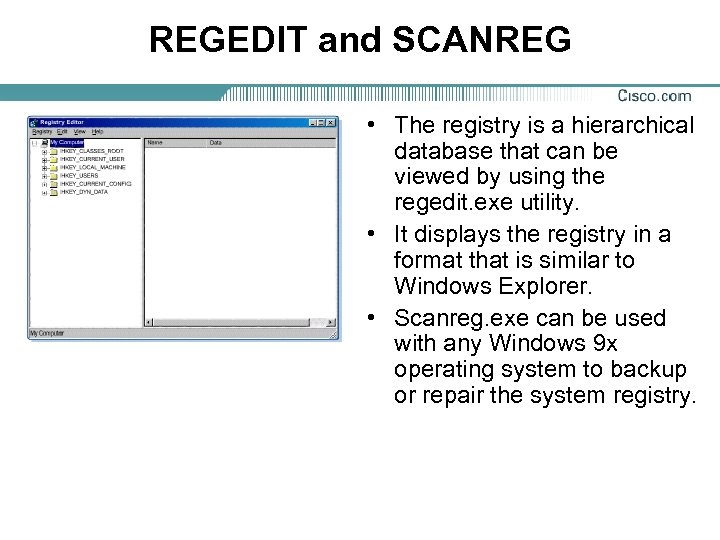 REGEDIT and SCANREG • The registry is a hierarchical database that can be viewed by using the regedit. exe utility. • It displays the registry in a format that is similar to Windows Explorer. • Scanreg. exe can be used with any Windows 9 x operating system to backup or repair the system registry.
REGEDIT and SCANREG • The registry is a hierarchical database that can be viewed by using the regedit. exe utility. • It displays the registry in a format that is similar to Windows Explorer. • Scanreg. exe can be used with any Windows 9 x operating system to backup or repair the system registry.
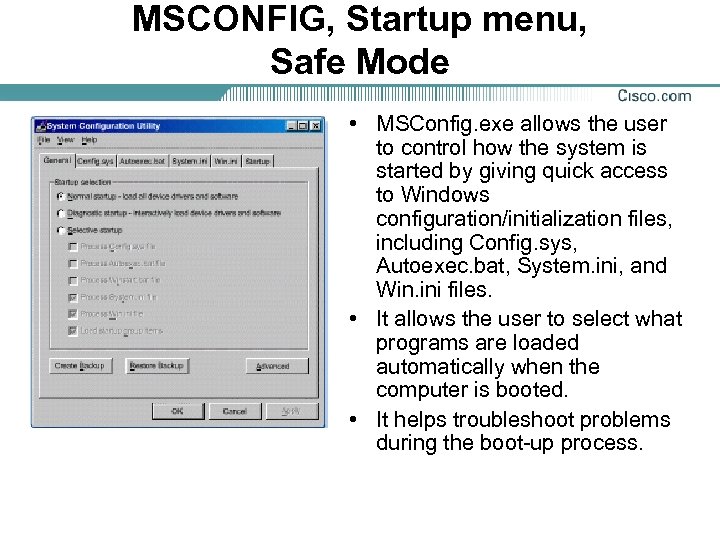 MSCONFIG, Startup menu, Safe Mode • MSConfig. exe allows the user to control how the system is started by giving quick access to Windows configuration/initialization files, including Config. sys, Autoexec. bat, System. ini, and Win. ini files. • It allows the user to select what programs are loaded automatically when the computer is booted. • It helps troubleshoot problems during the boot-up process.
MSCONFIG, Startup menu, Safe Mode • MSConfig. exe allows the user to control how the system is started by giving quick access to Windows configuration/initialization files, including Config. sys, Autoexec. bat, System. ini, and Win. ini files. • It allows the user to select what programs are loaded automatically when the computer is booted. • It helps troubleshoot problems during the boot-up process.
 WSCRIPT. EXE, HWINFO. EXE, ASD. EXE • The wscript. exe command allows the configuration of the properties related to the Windows scripting host.
WSCRIPT. EXE, HWINFO. EXE, ASD. EXE • The wscript. exe command allows the configuration of the properties related to the Windows scripting host.
 WSCRIPT. EXE, HWINFO. EXE, ASD. EXE • Hwinfo. exe is a utility that gives a detailed collection of information about the computer. • ASD. exe skips a driver when the operating system fails during boot-up. • Use whenever there is a problem with a driver that cannot be solved by booting into safe mode.
WSCRIPT. EXE, HWINFO. EXE, ASD. EXE • Hwinfo. exe is a utility that gives a detailed collection of information about the computer. • ASD. exe skips a driver when the operating system fails during boot-up. • Use whenever there is a problem with a driver that cannot be solved by booting into safe mode.
 Preparing a Hard Drive for OS Installation
Preparing a Hard Drive for OS Installation
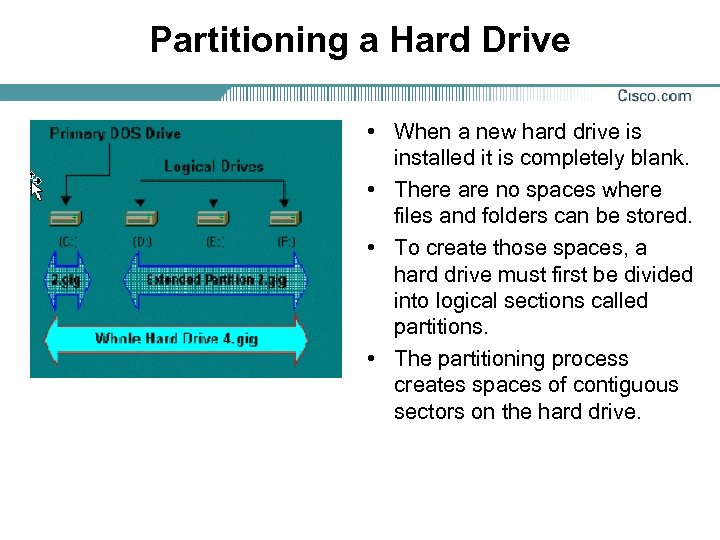 Partitioning a Hard Drive • When a new hard drive is installed it is completely blank. • There are no spaces where files and folders can be stored. • To create those spaces, a hard drive must first be divided into logical sections called partitions. • The partitioning process creates spaces of contiguous sectors on the hard drive.
Partitioning a Hard Drive • When a new hard drive is installed it is completely blank. • There are no spaces where files and folders can be stored. • To create those spaces, a hard drive must first be divided into logical sections called partitions. • The partitioning process creates spaces of contiguous sectors on the hard drive.
 Partitioning a Hard Drive • Typically with DOS, when the hard drive is divided into more than one partition, the first partition is referred to as the primary partition, while the second is called the extended partition. • DOS can have up to four separate primary partitions, or three primary and one extended, two primary and one extended, or just one primary and one extended partition on one hard drive, depending on the user’s needs. • DOS can have up to four separate partitions on any one hard disk. • The extended partition uses the free hard disk space, and is normally assigned all the available space outside the primary partition(s).
Partitioning a Hard Drive • Typically with DOS, when the hard drive is divided into more than one partition, the first partition is referred to as the primary partition, while the second is called the extended partition. • DOS can have up to four separate primary partitions, or three primary and one extended, two primary and one extended, or just one primary and one extended partition on one hard drive, depending on the user’s needs. • DOS can have up to four separate partitions on any one hard disk. • The extended partition uses the free hard disk space, and is normally assigned all the available space outside the primary partition(s).
 Partitioning a Hard Drive • When a hard drive is partitioned, the extended partition uses up all free hard disk space not included in the primary partition(s). • There can be only one extended partition per disk, it can be subdivided into multiple (up to 23) sections called logical drives. • Having multiple logical drives inside the extended partition provides some advantages: – Rapid retrieval of information – Multiple operating systems – Logical drives physically separate information for organizational and security reasons
Partitioning a Hard Drive • When a hard drive is partitioned, the extended partition uses up all free hard disk space not included in the primary partition(s). • There can be only one extended partition per disk, it can be subdivided into multiple (up to 23) sections called logical drives. • Having multiple logical drives inside the extended partition provides some advantages: – Rapid retrieval of information – Multiple operating systems – Logical drives physically separate information for organizational and security reasons
 Partitioning a Hard Drive • FDISK is the partitioning program for MS-DOS, Windows 9 x (95, 98, and Millennium Edition [ME]), UNIX, and Linux. • When partitioning a hard drive, the FDISK program creates the disk boot sector.
Partitioning a Hard Drive • FDISK is the partitioning program for MS-DOS, Windows 9 x (95, 98, and Millennium Edition [ME]), UNIX, and Linux. • When partitioning a hard drive, the FDISK program creates the disk boot sector.
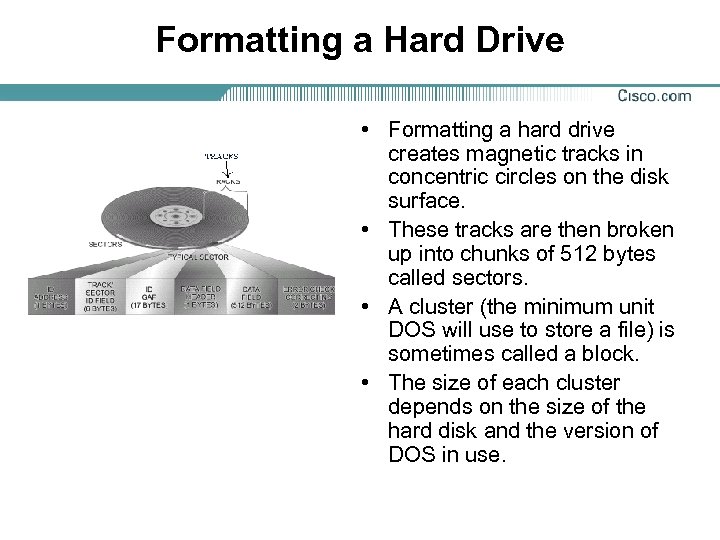 Formatting a Hard Drive • Formatting a hard drive creates magnetic tracks in concentric circles on the disk surface. • These tracks are then broken up into chunks of 512 bytes called sectors. • A cluster (the minimum unit DOS will use to store a file) is sometimes called a block. • The size of each cluster depends on the size of the hard disk and the version of DOS in use.
Formatting a Hard Drive • Formatting a hard drive creates magnetic tracks in concentric circles on the disk surface. • These tracks are then broken up into chunks of 512 bytes called sectors. • A cluster (the minimum unit DOS will use to store a file) is sometimes called a block. • The size of each cluster depends on the size of the hard disk and the version of DOS in use.
 Formatting a Hard Drive • During formatting, a special file, called the File Allocation Table (FAT) is created and located in the disk sector 0. • FAT is a reference table that the operating system uses to locate files on the disk. • There are two important concepts about formatting a hard drive that need to be understood: – Low-level formatting routine marks off the disk into sectors and cylinders, and defines their placement on the disk – High-level format routine is performed by the format command in MS-DOS. This procedure creates logical structures on the disk that tells the system what files are on the disk and where they can be found
Formatting a Hard Drive • During formatting, a special file, called the File Allocation Table (FAT) is created and located in the disk sector 0. • FAT is a reference table that the operating system uses to locate files on the disk. • There are two important concepts about formatting a hard drive that need to be understood: – Low-level formatting routine marks off the disk into sectors and cylinders, and defines their placement on the disk – High-level format routine is performed by the format command in MS-DOS. This procedure creates logical structures on the disk that tells the system what files are on the disk and where they can be found
 Installing Windows 9 x
Installing Windows 9 x
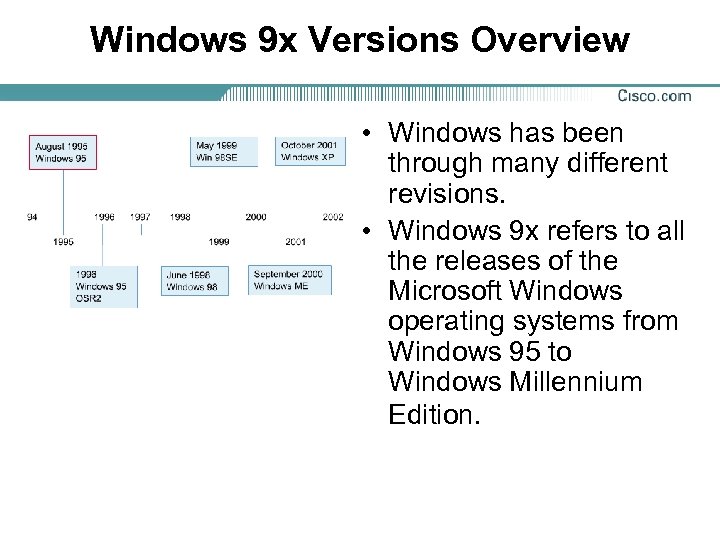 Windows 9 x Versions Overview • Windows has been through many different revisions. • Windows 9 x refers to all the releases of the Microsoft Windows operating systems from Windows 95 to Windows Millennium Edition.
Windows 9 x Versions Overview • Windows has been through many different revisions. • Windows 9 x refers to all the releases of the Microsoft Windows operating systems from Windows 95 to Windows Millennium Edition.
 Requirements for Installing Windows 98 • To install Windows 98, the following minimum hardware platform is required: • An 486 DX 66 Mhz or faster processor, operating with at least 16 MB of RAM. • The system must possess a keyboard, a mouse, and a 16 -color VGA monitor or better (SVGA recommended).
Requirements for Installing Windows 98 • To install Windows 98, the following minimum hardware platform is required: • An 486 DX 66 Mhz or faster processor, operating with at least 16 MB of RAM. • The system must possess a keyboard, a mouse, and a 16 -color VGA monitor or better (SVGA recommended).
 Requirements for Installing Windows 98 • The system hard drive needs to have between 255 and 355 MB of free space available to successfully install Windows 98 full version on a FAT 16 drive, or between 175 and 255 MB drive space on a FAT 32 drive. • To upgrade from Windows 95 requires about 195 MB of free hard disk space, but may range from between 120 MB and 255 MB. • Sometimes a modem is required to download device drivers upgrades from sources on the Internet. The minimum required is a 14. 4 kbps (28. 8 kbps or faster is recommended). • 3. 5 -inch high-density floppy disk drive and CD-ROM drive (32 speed is recommended).
Requirements for Installing Windows 98 • The system hard drive needs to have between 255 and 355 MB of free space available to successfully install Windows 98 full version on a FAT 16 drive, or between 175 and 255 MB drive space on a FAT 32 drive. • To upgrade from Windows 95 requires about 195 MB of free hard disk space, but may range from between 120 MB and 255 MB. • Sometimes a modem is required to download device drivers upgrades from sources on the Internet. The minimum required is a 14. 4 kbps (28. 8 kbps or faster is recommended). • 3. 5 -inch high-density floppy disk drive and CD-ROM drive (32 speed is recommended).
 Understanding the Windows 98 Installation Steps • The steps of the installation procedure are divided into four phases: • Preparing to run Windows 98 Setup • Collecting information about the computer • Copying Windows 98 Files and restarting the computer • Setting Up Hardware and Finalizing Settings
Understanding the Windows 98 Installation Steps • The steps of the installation procedure are divided into four phases: • Preparing to run Windows 98 Setup • Collecting information about the computer • Copying Windows 98 Files and restarting the computer • Setting Up Hardware and Finalizing Settings
 Windows 98 Setup Options • Windows 98 can be installed from the CD-ROM after the system is booted from a floppy disk, or the system may be booted from the installation CD itself. • Another option is to copy all the files to the hard drive and perform an internal installation from the hard drive.
Windows 98 Setup Options • Windows 98 can be installed from the CD-ROM after the system is booted from a floppy disk, or the system may be booted from the installation CD itself. • Another option is to copy all the files to the hard drive and perform an internal installation from the hard drive.
 Upgrade Installation • Windows 95 users can upgrade to Windows 98 for added features and usability • The upgrade from Windows 98 to Windows ME is simple and very straightforward • A Windows ME upgrade can be uninstalled only once on the same system.
Upgrade Installation • Windows 95 users can upgrade to Windows 98 for added features and usability • The upgrade from Windows 98 to Windows ME is simple and very straightforward • A Windows ME upgrade can be uninstalled only once on the same system.
 Troubleshooting the Installation Process
Troubleshooting the Installation Process
 Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • When troubleshooting the PC, it is good practice to begin from the outside of the system and move inwards. Proceed in a systematic way as follows: 1. Start the system in a logical order to see what symptoms are produced. 2. Isolate the problem as either software-related or hardware-related. 3. After determining the nature of the problem, isolate it to a particular section of the hardware or software. 4. Determine the appropriate solution, implement it, and verify that the problem is solved.
Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • When troubleshooting the PC, it is good practice to begin from the outside of the system and move inwards. Proceed in a systematic way as follows: 1. Start the system in a logical order to see what symptoms are produced. 2. Isolate the problem as either software-related or hardware-related. 3. After determining the nature of the problem, isolate it to a particular section of the hardware or software. 4. Determine the appropriate solution, implement it, and verify that the problem is solved.
 Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • If Windows 98 becomes unavailable, shut off the computer, and turn it back on. • During this process, listen for a beep or wait for a few seconds and press and hold the left Ctrl key on the keyboard. • This will open a Windows 98 Startup menu. From the list of options, choose Safe Mode, to boot Windows in a Safe Mode.
Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • If Windows 98 becomes unavailable, shut off the computer, and turn it back on. • During this process, listen for a beep or wait for a few seconds and press and hold the left Ctrl key on the keyboard. • This will open a Windows 98 Startup menu. From the list of options, choose Safe Mode, to boot Windows in a Safe Mode.
 Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • In Safe mode, Windows loads only the basic devices it needs to run. • In Windows Safe Mode, check the device manager to ensure that there are no conflicts with any devices causing the system to not operate properly.
Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • In Safe mode, Windows loads only the basic devices it needs to run. • In Windows Safe Mode, check the device manager to ensure that there are no conflicts with any devices causing the system to not operate properly.
 Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • Scandisk searches the disk drive for disconnected file clusters and converts them into a form that can be checked and manipulated. • It detects and delete crosslinked files from the disk drive.
Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • Scandisk searches the disk drive for disconnected file clusters and converts them into a form that can be checked and manipulated. • It detects and delete crosslinked files from the disk drive.
 Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • The Defrag program realigns the positioning of the related file clusters to speed up the disk drive operation. • It does this by making the files more easily read by the system. • As a rule, always run Scandisk prior to Defrag.
Systematic Troubleshooting Techniques and Finding Help • The Defrag program realigns the positioning of the related file clusters to speed up the disk drive operation. • It does this by making the files more easily read by the system. • As a rule, always run Scandisk prior to Defrag.
 Windows 98 Setup Errors • Setup errors are probably the most important set of problems to deal with. • Understanding the error codes generated by the operating system can save a lot of time when troubleshooting Windows installation problems.
Windows 98 Setup Errors • Setup errors are probably the most important set of problems to deal with. • Understanding the error codes generated by the operating system can save a lot of time when troubleshooting Windows installation problems.
 System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • System Properties has four categories of information that can be accessed by clicking on the tabs: • General • Device Manager • Hardware Profiles • Performance
System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • System Properties has four categories of information that can be accessed by clicking on the tabs: • General • Device Manager • Hardware Profiles • Performance
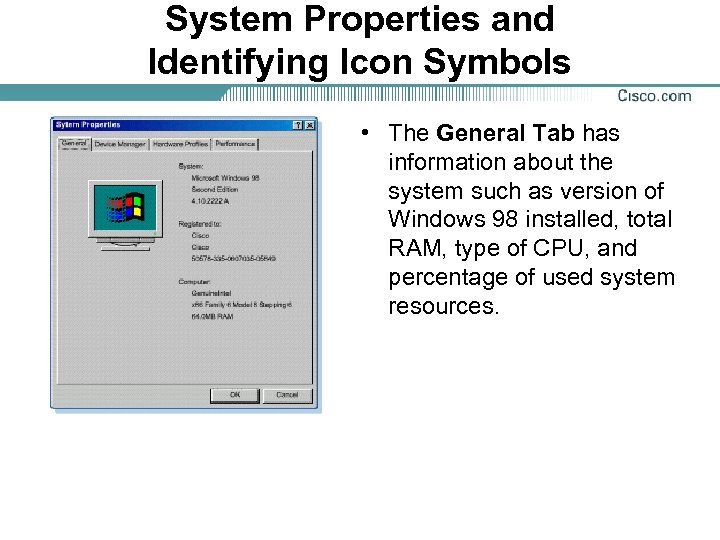 System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • The General Tab has information about the system such as version of Windows 98 installed, total RAM, type of CPU, and percentage of used system resources.
System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • The General Tab has information about the system such as version of Windows 98 installed, total RAM, type of CPU, and percentage of used system resources.
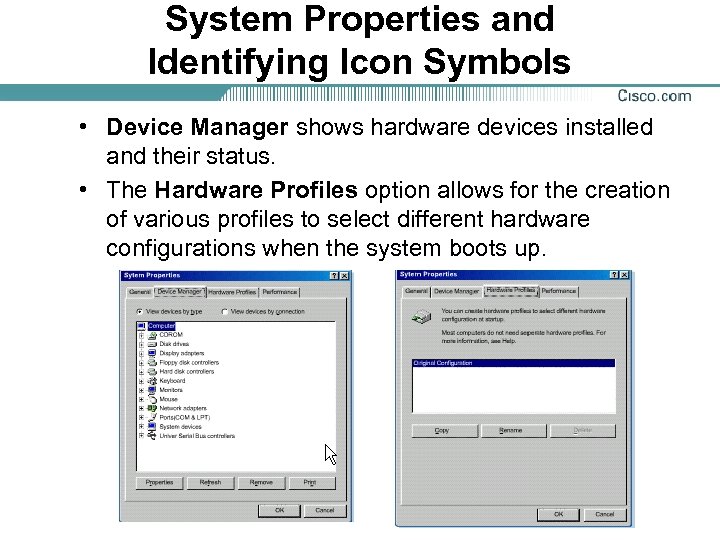 System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • Device Manager shows hardware devices installed and their status. • The Hardware Profiles option allows for the creation of various profiles to select different hardware configurations when the system boots up.
System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • Device Manager shows hardware devices installed and their status. • The Hardware Profiles option allows for the creation of various profiles to select different hardware configurations when the system boots up.
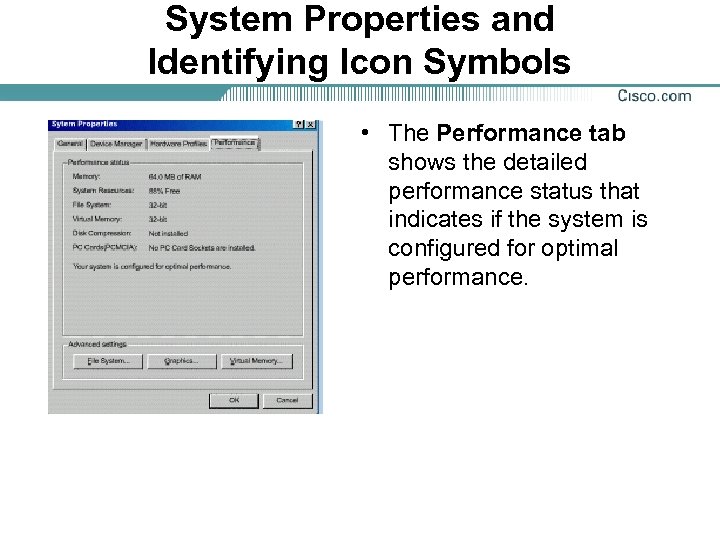 System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • The Performance tab shows the detailed performance status that indicates if the system is configured for optimal performance.
System Properties and Identifying Icon Symbols • The Performance tab shows the detailed performance status that indicates if the system is configured for optimal performance.
 Adding Software Drivers • A device driver is software specially designed to enable the computer to "see" the hardware or devices installed within the system. • Such devices include CD-ROM drives, hard drives, and expansion cards. • They can also include an external device such as a mouse or keyboard. • The device driver not only allows the basic system to recognize the presence of a device, but actually enables it to work with the device.
Adding Software Drivers • A device driver is software specially designed to enable the computer to "see" the hardware or devices installed within the system. • Such devices include CD-ROM drives, hard drives, and expansion cards. • They can also include an external device such as a mouse or keyboard. • The device driver not only allows the basic system to recognize the presence of a device, but actually enables it to work with the device.
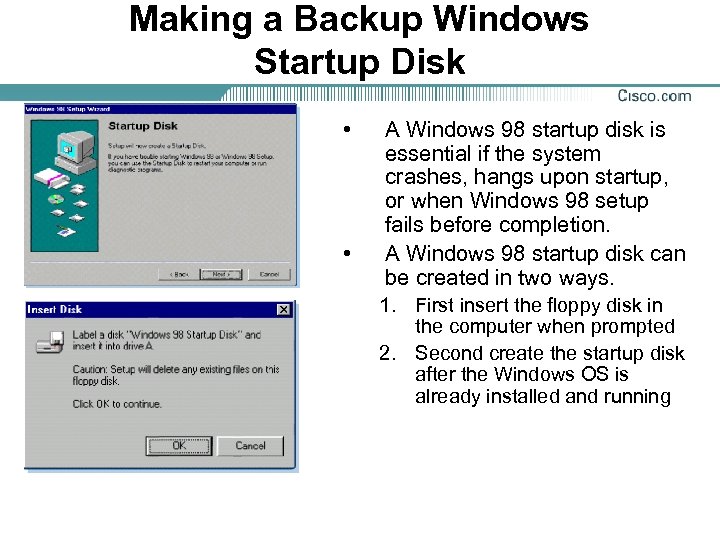 Making a Backup Windows Startup Disk • • A Windows 98 startup disk is essential if the system crashes, hangs upon startup, or when Windows 98 setup fails before completion. A Windows 98 startup disk can be created in two ways. 1. First insert the floppy disk in the computer when prompted 2. Second create the startup disk after the Windows OS is already installed and running
Making a Backup Windows Startup Disk • • A Windows 98 startup disk is essential if the system crashes, hangs upon startup, or when Windows 98 setup fails before completion. A Windows 98 startup disk can be created in two ways. 1. First insert the floppy disk in the computer when prompted 2. Second create the startup disk after the Windows OS is already installed and running
 Uninstalling Windows 98 • The uninstall procedure will allow the system to return to a previous version of the Windows operating system. • In some instances, uninstalling Windows 98 is the only solution left when an attempted upgrade fails, especially if no system backup was done before trying to upgrade.
Uninstalling Windows 98 • The uninstall procedure will allow the system to return to a previous version of the Windows operating system. • In some instances, uninstalling Windows 98 is the only solution left when an attempted upgrade fails, especially if no system backup was done before trying to upgrade.
 Uninstalling Windows 98 • Windows 98 can be uninstalled when: – You upgraded from a previous version of Windows – The "Save uninstall information" option was selected during Windows 98 setup • Windows 98 cannot be uninstalled when: – The conditions mentioned above are not met – The two files Winundo. dat and Winundo. ini become corrupted or deleted – The hard disk was compressed prior to the Windows 98 OS installation – The hard disk was compressed, or converted to FAT 32 AFTER installing Windows 98
Uninstalling Windows 98 • Windows 98 can be uninstalled when: – You upgraded from a previous version of Windows – The "Save uninstall information" option was selected during Windows 98 setup • Windows 98 cannot be uninstalled when: – The conditions mentioned above are not met – The two files Winundo. dat and Winundo. ini become corrupted or deleted – The hard disk was compressed prior to the Windows 98 OS installation – The hard disk was compressed, or converted to FAT 32 AFTER installing Windows 98



