2de0873a17b0db790294b6eed019f8ac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 ISYS 363 Information Systems for Management David Chao
ISYS 363 Information Systems for Management David Chao
 A Technology News Bay Area Apartment Complex To ‘DNA Print’ Dog Waste http: //news. yahoo. com/blogs/san-francisco/bay-area-apartment -complex-dna-print-dog-waste-150618123. html • A Redwood City apartment complex expects to be the first in the Bay Area to "DNA print" the solid waste from pets as a hightech solution to the age-old and often gross dilemma of owners who refuse to curb their dogs.
A Technology News Bay Area Apartment Complex To ‘DNA Print’ Dog Waste http: //news. yahoo. com/blogs/san-francisco/bay-area-apartment -complex-dna-print-dog-waste-150618123. html • A Redwood City apartment complex expects to be the first in the Bay Area to "DNA print" the solid waste from pets as a hightech solution to the age-old and often gross dilemma of owners who refuse to curb their dogs.
 Wireless Parking San Francisco • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=y. Vq 9 pda m 14 M
Wireless Parking San Francisco • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=y. Vq 9 pda m 14 M
 PG&E Smart Meter Wireless Communication • http: //www. pge. com/smartmeter/ • Energy Alerts – let you know when you’re moving into higher-priced electric tiers so you can manage your energy use and save. • Understanding your electric charges – http: //www. pge. com/myhome/myaccount/charges/ • Track energy use online – http: //www. pge. com/myhome/myaccount/syp-myaccount/
PG&E Smart Meter Wireless Communication • http: //www. pge. com/smartmeter/ • Energy Alerts – let you know when you’re moving into higher-priced electric tiers so you can manage your energy use and save. • Understanding your electric charges – http: //www. pge. com/myhome/myaccount/charges/ • Track energy use online – http: //www. pge. com/myhome/myaccount/syp-myaccount/
 Information Technology • Support day-to-day business operations • Create new way of doing business – Example: • Making reservations – United Airelines- http: //www. united. com/ – Select your seats – Web check-In • Mobile check-in with web-enabled mobile phones : – http: //www. cathaypacific. com/cpa/en_INTL/manageyourtrip/m obileservices/mobilecheckin – Save your check-in confirmation with the barcode on your mobile device
Information Technology • Support day-to-day business operations • Create new way of doing business – Example: • Making reservations – United Airelines- http: //www. united. com/ – Select your seats – Web check-In • Mobile check-in with web-enabled mobile phones : – http: //www. cathaypacific. com/cpa/en_INTL/manageyourtrip/m obileservices/mobilecheckin – Save your check-in confirmation with the barcode on your mobile device
 Mobile Banking • Mobile banking (M-Banking) is a term used for performing balance checks, account transactions, payments, credit applications and other banking transactions through a mobile device such as a mobile phone or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). • Bank of America: http: //www. bankofamerica. com/onlinebanking/index. cfm? template=mo bile_web • US Bank: – http: //www. usbank. com/mobile/index. html
Mobile Banking • Mobile banking (M-Banking) is a term used for performing balance checks, account transactions, payments, credit applications and other banking transactions through a mobile device such as a mobile phone or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). • Bank of America: http: //www. bankofamerica. com/onlinebanking/index. cfm? template=mo bile_web • US Bank: – http: //www. usbank. com/mobile/index. html
 Technology Life Cycle • • Problem Solution Service Competition: • Yahoo Map vs Google Map • Google search vs Bing. com • Obsolete
Technology Life Cycle • • Problem Solution Service Competition: • Yahoo Map vs Google Map • Google search vs Bing. com • Obsolete
 Digital Entrepreneur • People who develop new technologies. – Search engines, map, browser, etc. • People who use the technologies innovatively. – Most popular i. Phone applications: • http: //www. apple. com/webapps/index. html – Twitter applications: • http: //www. techcrunch. com/2009/02/19/the-top-20 twitter-applications/
Digital Entrepreneur • People who develop new technologies. – Search engines, map, browser, etc. • People who use the technologies innovatively. – Most popular i. Phone applications: • http: //www. apple. com/webapps/index. html – Twitter applications: • http: //www. techcrunch. com/2009/02/19/the-top-20 twitter-applications/
 Why study information systems? • An end-user perspective – Enhance personal productivity, and the productivity of their work groups and department. – Increase your opportunities for success: • be aware of the management problems and opportunities presented by the information technology.
Why study information systems? • An end-user perspective – Enhance personal productivity, and the productivity of their work groups and department. – Increase your opportunities for success: • be aware of the management problems and opportunities presented by the information technology.
 Why study information systems? • An enterprise perspective: Information systems play a vital role in the success of an enterprise. – Efficient operations – Effective management – Competitive advantage
Why study information systems? • An enterprise perspective: Information systems play a vital role in the success of an enterprise. – Efficient operations – Effective management – Competitive advantage
 Business Are Becoming Internetworked Enterprises • The internet and Internet-like networks (intranets and extranets) have become the primary information technology infrastructure that supports the business operations of many organizations. • Electronic commerce: – The buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products, services, and information over a variety of computer networks. • Globalization: – Global markets, global production facilities, global partners, global competitors, global customers.
Business Are Becoming Internetworked Enterprises • The internet and Internet-like networks (intranets and extranets) have become the primary information technology infrastructure that supports the business operations of many organizations. • Electronic commerce: – The buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products, services, and information over a variety of computer networks. • Globalization: – Global markets, global production facilities, global partners, global competitors, global customers.
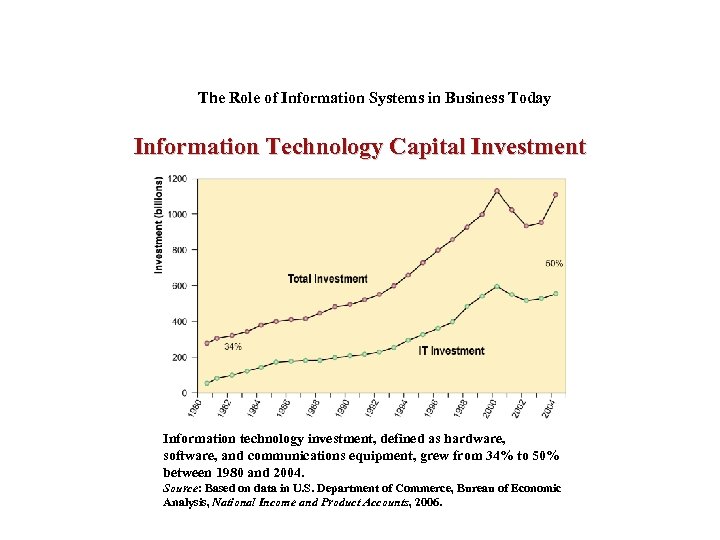 The Role of Information Systems in Business Today Information Technology Capital Investment Information technology investment, defined as hardware, software, and communications equipment, grew from 34% to 50% between 1980 and 2004. Source: Based on data in U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, National Income and Product Accounts, 2006.
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today Information Technology Capital Investment Information technology investment, defined as hardware, software, and communications equipment, grew from 34% to 50% between 1980 and 2004. Source: Based on data in U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, National Income and Product Accounts, 2006.
 Techies might finally be able to move into top management • More Chief Information Officers (CIOs) are reporting directly to CEOs. • More CIOs are being included on management committees. • In a recent survey of executives at capital market firms, 89% believed that technology managers would assume greater responsibilities.
Techies might finally be able to move into top management • More Chief Information Officers (CIOs) are reporting directly to CEOs. • More CIOs are being included on management committees. • In a recent survey of executives at capital market firms, 89% believed that technology managers would assume greater responsibilities.
 Geek-Suit http: //www. nri. co. jp/english/opinion/papers/2009/pdf/np 2009143. pdf
Geek-Suit http: //www. nri. co. jp/english/opinion/papers/2009/pdf/np 2009143. pdf
 Course Introduction • IT – Introduction to information technology – Computer hardware, software, network – IT management • IS – Introduction to information systems – Information system components – Types of information systems • PC – personal computing – Advanced spreadsheet techniques in decision support. – Introduction to database and database application development – Internet techniques
Course Introduction • IT – Introduction to information technology – Computer hardware, software, network – IT management • IS – Introduction to information systems – Information system components – Types of information systems • PC – personal computing – Advanced spreadsheet techniques in decision support. – Introduction to database and database application development – Internet techniques
 What is Information Technology? • A term used to refer to a wide variety of items and abilities used in the creation, storage, and dispersal of data, information and knowledge. – Data: Raw facts, figures, and details. • Numerical, text, multimedia – Information: An organized, meaningful, and useful interpretation of data. – Knowledge: Insight of a subject matter.
What is Information Technology? • A term used to refer to a wide variety of items and abilities used in the creation, storage, and dispersal of data, information and knowledge. – Data: Raw facts, figures, and details. • Numerical, text, multimedia – Information: An organized, meaningful, and useful interpretation of data. – Knowledge: Insight of a subject matter.
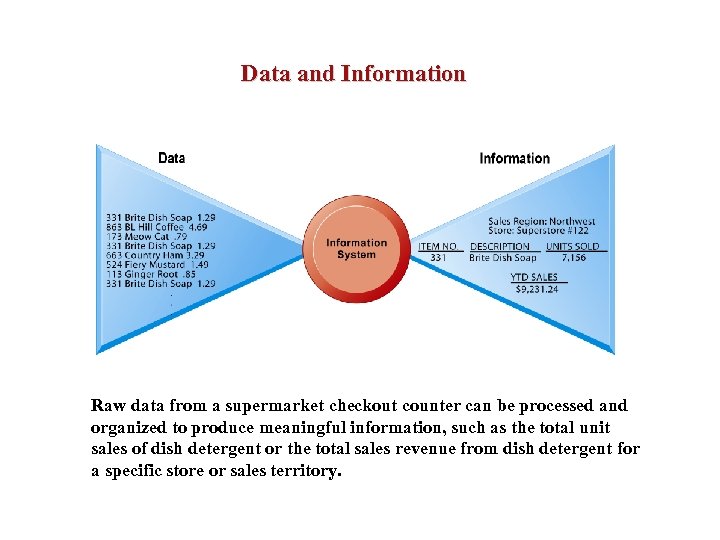 Data and Information Raw data from a supermarket checkout counter can be processed and organized to produce meaningful information, such as the total unit sales of dish detergent or the total sales revenue from dish detergent for a specific store or sales territory.
Data and Information Raw data from a supermarket checkout counter can be processed and organized to produce meaningful information, such as the total unit sales of dish detergent or the total sales revenue from dish detergent for a specific store or sales territory.
 Hardware • Input devices • CPU and primary storage – RAM - temporary storage – Processor • Control Unit - decoder • Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU) • Output devices • Secondary storage devices • Communication devices
Hardware • Input devices • CPU and primary storage – RAM - temporary storage – Processor • Control Unit - decoder • Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU) • Output devices • Secondary storage devices • Communication devices
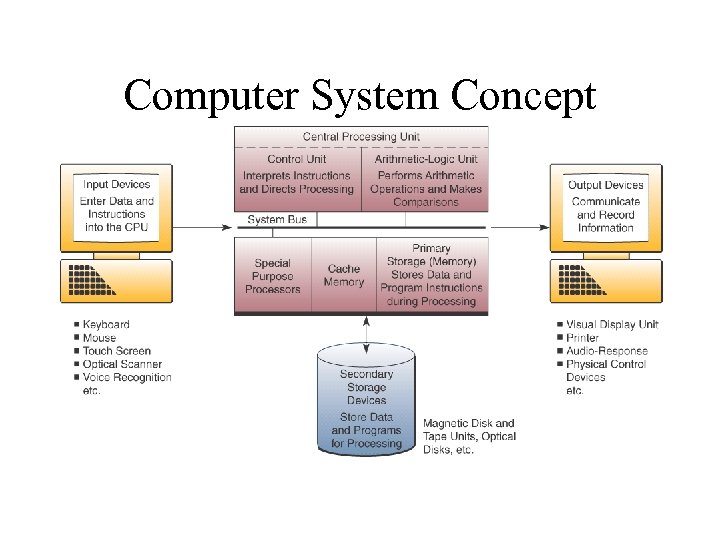 Computer System Concept
Computer System Concept
 Types of Computer Systems • Micro/Minicomputers – Personal computing, workstation, network server. – Departmental and workgroup systems, network server, workstation. • Mainframes – Speed: MIPS million instructions per second • 26 MIPS to about 17, 801 MIPS – Enterprisewide systems – for organizations have to deal with huge amounts of data. Giga-record or tera-record files are not unusual. – Data mining and warehousing • Supercomputers – Speed: Floating-point operations per second • 20 peta flops – Supercomputers are often purpose-built for one or a very few specific institutional tasks (E. g. Simulation and Modeling). – Scientific calculations • Networked computer systems – WAN, LAN, PAN
Types of Computer Systems • Micro/Minicomputers – Personal computing, workstation, network server. – Departmental and workgroup systems, network server, workstation. • Mainframes – Speed: MIPS million instructions per second • 26 MIPS to about 17, 801 MIPS – Enterprisewide systems – for organizations have to deal with huge amounts of data. Giga-record or tera-record files are not unusual. – Data mining and warehousing • Supercomputers – Speed: Floating-point operations per second • 20 peta flops – Supercomputers are often purpose-built for one or a very few specific institutional tasks (E. g. Simulation and Modeling). – Scientific calculations • Networked computer systems – WAN, LAN, PAN
 Personal Area Network • A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer devices (including telephones and personal digital assistants) close to one person. The devices may or may not belong to the person in question. The reach of a PAN is typically a few meters. • Blue. Tooth: It is an industrial specification for wireless PANs. Bluetooth provides a way to connect and exchange information between devices such as mobile phones, laptops, PCs, printers, digital cameras and video game consoles via a short-range radio frequency.
Personal Area Network • A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer devices (including telephones and personal digital assistants) close to one person. The devices may or may not belong to the person in question. The reach of a PAN is typically a few meters. • Blue. Tooth: It is an industrial specification for wireless PANs. Bluetooth provides a way to connect and exchange information between devices such as mobile phones, laptops, PCs, printers, digital cameras and video game consoles via a short-range radio frequency.
 Bluetooth Applications • Business applications: – http: //www. informit. com/articles/article. aspx? p =24243 • Bluetooth Social Networking – http: //www. btflirt. com/
Bluetooth Applications • Business applications: – http: //www. informit. com/articles/article. aspx? p =24243 • Bluetooth Social Networking – http: //www. btflirt. com/
 Storage Device • Terabytes of storage • RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks): – Arrays of disk drives that provides a fault tolerant capability by storing multiple copies of data on several disks. • Mirroring
Storage Device • Terabytes of storage • RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks): – Arrays of disk drives that provides a fault tolerant capability by storing multiple copies of data on several disks. • Mirroring
 Storage Network • Storage Area Network, SAN: – A storage area network is an architecture to attach remote computer storage devices to servers in such a way that the devices appear as locally attached to the operating system.
Storage Network • Storage Area Network, SAN: – A storage area network is an architecture to attach remote computer storage devices to servers in such a way that the devices appear as locally attached to the operating system.
 Data Center • A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. • Modular Data Center – Data Center Containers: • Google: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. Rw. PSFp. LX 8 I • Microsoft: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=PPno. Kb 9 f. Tk. A
Data Center • A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. • Modular Data Center – Data Center Containers: • Google: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. Rw. PSFp. LX 8 I • Microsoft: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=PPno. Kb 9 f. Tk. A
 Where to put data center? • The cost of electric power, labor, taxes, natural disasters and land are key factors when choosing a data center location. – http: //www. computerworld. com/s/article/300809/Low_Cost_Locat ions? taxonomy. Id=155&intsrc=kc_feat&taxonomy. Name=servers – http: //news. idg. no/cw/art. cfm? id=6 ECF 9 E 56 -17 A 40 F 78 -31 EAB 0750688 E 73 E# – http: //www. informit. com/articles/article. aspx? p=417091
Where to put data center? • The cost of electric power, labor, taxes, natural disasters and land are key factors when choosing a data center location. – http: //www. computerworld. com/s/article/300809/Low_Cost_Locat ions? taxonomy. Id=155&intsrc=kc_feat&taxonomy. Name=servers – http: //news. idg. no/cw/art. cfm? id=6 ECF 9 E 56 -17 A 40 F 78 -31 EAB 0750688 E 73 E# – http: //www. informit. com/articles/article. aspx? p=417091
 Radio Frequency Identification • RFID is a system for tagging and identifying objects. – Antenna to send and receive signals. – RFID reader • Applications: – An alternative to bar code • Supermarket – Tracking objects
Radio Frequency Identification • RFID is a system for tagging and identifying objects. – Antenna to send and receive signals. – RFID reader • Applications: – An alternative to bar code • Supermarket – Tracking objects
 RFID AN RFID tag is small compared to current bar-code labels.
RFID AN RFID tag is small compared to current bar-code labels.
 Passive & Active RFID • A passive RFID tag does not contain a battery; the power is supplied by the reader. When radio waves from the reader are encountered by a passive rfid tag, the coiled antenna within the tag forms a magnetic field. The tag draws power from it, energizing the circuits in the tag. The tag then sends the information encoded in the tag's memory. • An active RFID tag is equipped with a battery that can be used as a partial or complete source of power for the tag's circuitry and antenna. Active RFID always broadcasts or beacons its signal.
Passive & Active RFID • A passive RFID tag does not contain a battery; the power is supplied by the reader. When radio waves from the reader are encountered by a passive rfid tag, the coiled antenna within the tag forms a magnetic field. The tag draws power from it, energizing the circuits in the tag. The tag then sends the information encoded in the tag's memory. • An active RFID tag is equipped with a battery that can be used as a partial or complete source of power for the tag's circuitry and antenna. Active RFID always broadcasts or beacons its signal.
 A few interesting RFID applications – RFID tags help you to choose clothes • http: //blogs. zdnet. com/emergingtech/? p=719 – Ford embeds RFID tech into new trucks and vans • http: //www. computerworld. com/action/article. do? command =view. Article. Basic&article. Id=9061580&intsrc=hm_list – Digital watermark to prevent counterfeit: • http: //www. industryweek. com/articles/new_rfid_ device_helps_fight_counterfeiting_15439. aspx
A few interesting RFID applications – RFID tags help you to choose clothes • http: //blogs. zdnet. com/emergingtech/? p=719 – Ford embeds RFID tech into new trucks and vans • http: //www. computerworld. com/action/article. do? command =view. Article. Basic&article. Id=9061580&intsrc=hm_list – Digital watermark to prevent counterfeit: • http: //www. industryweek. com/articles/new_rfid_ device_helps_fight_counterfeiting_15439. aspx
 Software • System software – Operating system • Application software – University’s registration system • Application development software
Software • System software – Operating system • Application software – University’s registration system • Application development software
 Operating system functions – User interface – Resource management (managing hardware) – Task management (managing the accomplishment of tasks) – File management (managing data and program files) – Utilities (providing a variety of supporting services)
Operating system functions – User interface – Resource management (managing hardware) – Task management (managing the accomplishment of tasks) – File management (managing data and program files) – Utilities (providing a variety of supporting services)
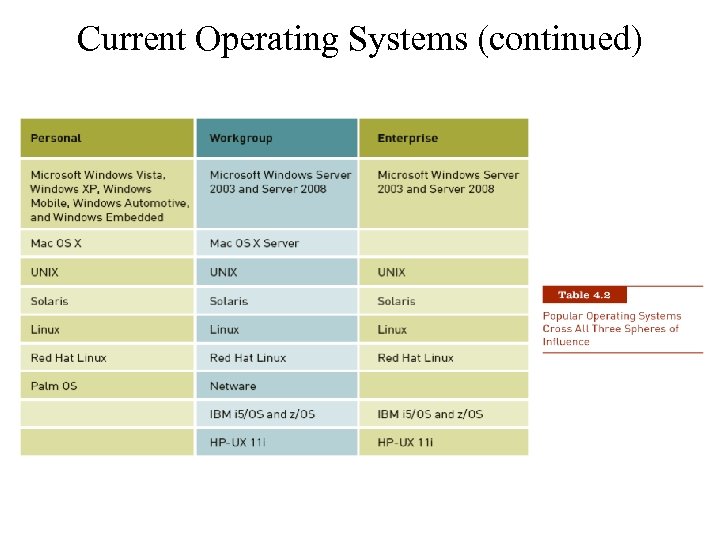 Current Operating Systems (continued)
Current Operating Systems (continued)
 Today’s Operating Systems • Personal computers: – IBM PC compatible: • Microsoft windows, Unix-like systems such as Linux. – Apple Macintosh: • Mac OS X, Linux • Workgroup computers: – MS Windows Server, Mac OS X Server, Linux. Solaris • Mainframe computers: – IBM z/OS, Linux
Today’s Operating Systems • Personal computers: – IBM PC compatible: • Microsoft windows, Unix-like systems such as Linux. – Apple Macintosh: • Mac OS X, Linux • Workgroup computers: – MS Windows Server, Mac OS X Server, Linux. Solaris • Mainframe computers: – IBM z/OS, Linux
 Linux and Open Source • A Linux system is sometimes referred to as GNU/Linux. – GNU – free software • Linux has been more widely ported to different computing platforms than any other operating system. • Linux is the most prominent example of free software and of open source development. Its underlying source code is available for anyone to use, modify, and redistribute freely, and in some instances the entire operating system consists of free/open source software.
Linux and Open Source • A Linux system is sometimes referred to as GNU/Linux. – GNU – free software • Linux has been more widely ported to different computing platforms than any other operating system. • Linux is the most prominent example of free software and of open source development. Its underlying source code is available for anyone to use, modify, and redistribute freely, and in some instances the entire operating system consists of free/open source software.
 Free Software: http: //www. gnu. org/ • “Free software” is a matter of liberty, not price. To understand the concept, you should think of “free” as in “free speech”, not as in “free beer”. • Free software is a matter of the users' freedom to run, copy, distribute, study, change and improve the software. More precisely, it refers to four kinds of freedom, for the users of the software: • The freedom to run the program, for any purpose (freedom 0). • The freedom to study how the program works, and adapt it to your needs (freedom 1). Access to the source code is a precondition for this. • The freedom to redistribute copies so you can help your neighbor (freedom 2). • The freedom to improve the program, and release your improvements to the public, so that the whole community benefits (freedom 3). Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
Free Software: http: //www. gnu. org/ • “Free software” is a matter of liberty, not price. To understand the concept, you should think of “free” as in “free speech”, not as in “free beer”. • Free software is a matter of the users' freedom to run, copy, distribute, study, change and improve the software. More precisely, it refers to four kinds of freedom, for the users of the software: • The freedom to run the program, for any purpose (freedom 0). • The freedom to study how the program works, and adapt it to your needs (freedom 1). Access to the source code is a precondition for this. • The freedom to redistribute copies so you can help your neighbor (freedom 2). • The freedom to improve the program, and release your improvements to the public, so that the whole community benefits (freedom 3). Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
 Operating Systems for Mobile Devices • Mobile devices: – Pocket PC/PDA – Smartphones – Portable media center • Smartphone Operating systems, the most important software in any smartphone: http: //communication. howstuffworks. com/smartphone 2. htm – Windows Mobile, Windows Phone – Palm OS – Symbian OS for Nokia – i. OS for i. Phone/i. Pad – Android for Google phone
Operating Systems for Mobile Devices • Mobile devices: – Pocket PC/PDA – Smartphones – Portable media center • Smartphone Operating systems, the most important software in any smartphone: http: //communication. howstuffworks. com/smartphone 2. htm – Windows Mobile, Windows Phone – Palm OS – Symbian OS for Nokia – i. OS for i. Phone/i. Pad – Android for Google phone
 Virtualization • Virtualization is a technology that makes it possible to run multiple operating systems and multiple applications on the same computer at the same time, increasing the utilization and flexibility of hardware. – Average server utilization rate – 10% • Reduce costs • Green computing • A virtual machine is a software container that can run its own operating systems and applications as if it were a physical computer. A virtual machine behaves exactly like a physical computer and contains its own virtual (ie, software-based) CPU, RAM hard disk and network interface card (NIC). An operating system can’t tell the difference between a virtual machine and a physical machine, nor can applications or other computers on a network. • Vendors: VMware, Parallels, etc.
Virtualization • Virtualization is a technology that makes it possible to run multiple operating systems and multiple applications on the same computer at the same time, increasing the utilization and flexibility of hardware. – Average server utilization rate – 10% • Reduce costs • Green computing • A virtual machine is a software container that can run its own operating systems and applications as if it were a physical computer. A virtual machine behaves exactly like a physical computer and contains its own virtual (ie, software-based) CPU, RAM hard disk and network interface card (NIC). An operating system can’t tell the difference between a virtual machine and a physical machine, nor can applications or other computers on a network. • Vendors: VMware, Parallels, etc.
 Application development software • Low level language • High level language – third generation – fourth generation • Word processing, desktop publishing, spreadsheet, database management, graphic presentation, etc. – MS Office – Open. Office. Org » http: //www. openoffice. org/
Application development software • Low level language • High level language – third generation – fourth generation • Word processing, desktop publishing, spreadsheet, database management, graphic presentation, etc. – MS Office – Open. Office. Org » http: //www. openoffice. org/
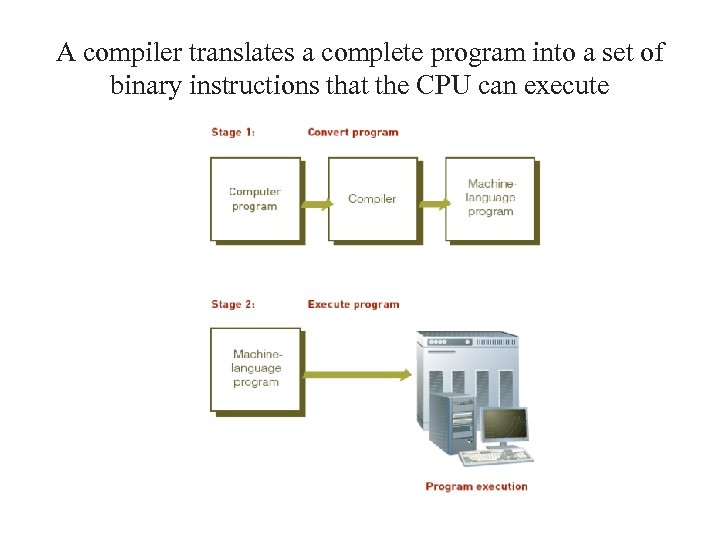 A compiler translates a complete program into a set of binary instructions that the CPU can execute
A compiler translates a complete program into a set of binary instructions that the CPU can execute
 Object-oriented development tools – – Graphical user interface Component programming Event-driven programming Code generator/Wizard • Object example: – Excel’s cell, chart • Object-oriented tool example: • VB. Net • Java
Object-oriented development tools – – Graphical user interface Component programming Event-driven programming Code generator/Wizard • Object example: – Excel’s cell, chart • Object-oriented tool example: • VB. Net • Java
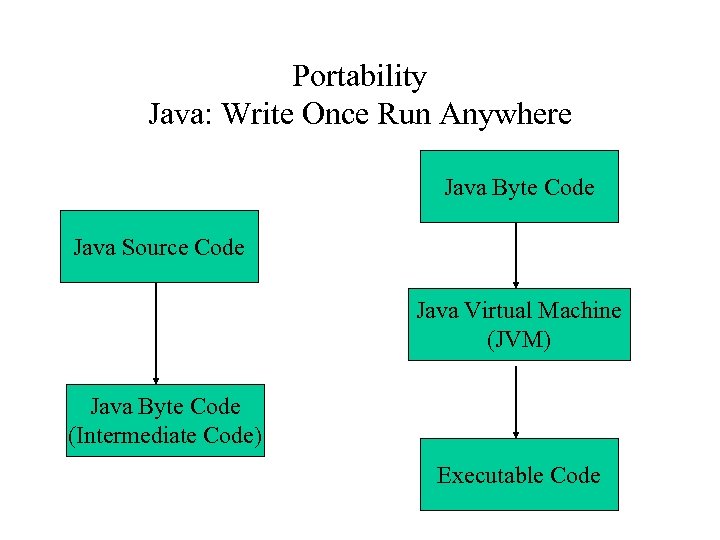 Portability Java: Write Once Run Anywhere Java Byte Code Java Source Code Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Java Byte Code (Intermediate Code) Executable Code
Portability Java: Write Once Run Anywhere Java Byte Code Java Source Code Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Java Byte Code (Intermediate Code) Executable Code
 Microsoft’s. Net • Language must compliance with Common Language Specification, CLS. • Compile the language into Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) code. • The MSIL code is then executed in the Common Language Runtime (CLR), which conceptually is same as the JVM, where it is translated into machine code by a compiler. • Microsoft. Net is a server-side technology. It runs on any servers that implement the. Net system.
Microsoft’s. Net • Language must compliance with Common Language Specification, CLS. • Compile the language into Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) code. • The MSIL code is then executed in the Common Language Runtime (CLR), which conceptually is same as the JVM, where it is translated into machine code by a compiler. • Microsoft. Net is a server-side technology. It runs on any servers that implement the. Net system.
 Software as a Service, Saa. S • Saa. S is a model of software deployment where an application is hosted as a service provided to customers across the Internet. – Saa. S alleviates the customer's burden of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support. • no upfront investment in software development – Conversely, customers relinquish control over software versions or changing requirements; – Costs to use the service become a continuous expense, rather than a single expense at time of purchase.
Software as a Service, Saa. S • Saa. S is a model of software deployment where an application is hosted as a service provided to customers across the Internet. – Saa. S alleviates the customer's burden of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support. • no upfront investment in software development – Conversely, customers relinquish control over software versions or changing requirements; – Costs to use the service become a continuous expense, rather than a single expense at time of purchase.
 What is cloud computing? • Cloud computing is a style of computing in which computing resources are provided as a service over the Internet. Users need not have knowledge of, expertise in, or control over the technology infrastructure in the "cloud" that supports them. • Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ae_DKNw. K_ms &eurl=http%3 A%2 F%2 Fpardalis. squarespace. com %2 F&feature=player_embedded
What is cloud computing? • Cloud computing is a style of computing in which computing resources are provided as a service over the Internet. Users need not have knowledge of, expertise in, or control over the technology infrastructure in the "cloud" that supports them. • Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ae_DKNw. K_ms &eurl=http%3 A%2 F%2 Fpardalis. squarespace. com %2 F&feature=player_embedded
 Companies Offer Saa. S • Sales. Force. com: – http: //www. salesforce. com/ • Workday: – http: //www. workday. com/index. php • Google Docs: – Demo: http: //www. google. com/apps/intl/en/business/collaboratio n. html#docs – Login: docs. google. com • Microsoft Windows. Live – https: //login. live. com/ – Sky. Drive
Companies Offer Saa. S • Sales. Force. com: – http: //www. salesforce. com/ • Workday: – http: //www. workday. com/index. php • Google Docs: – Demo: http: //www. google. com/apps/intl/en/business/collaboratio n. html#docs – Login: docs. google. com • Microsoft Windows. Live – https: //login. live. com/ – Sky. Drive
 Examples of Cloud Computing • Saa. S • Utility computing Companies such as Amazon. com, Sun, and IBM, now offer storage and virtual servers that others can access on demand. • Platform as a service, Paa. S This form of cloud computing delivers development environments as a service. You build your own applications that run on the provider's infrastructure and are delivered to your users via the Internet from the provider's servers. – Mainframe, Linux, Windows Server, etc. • Service commerce platforms: software personal assistant. This cloud computing offers a service hub that users interact with: http: //www. reardencommerce. com/
Examples of Cloud Computing • Saa. S • Utility computing Companies such as Amazon. com, Sun, and IBM, now offer storage and virtual servers that others can access on demand. • Platform as a service, Paa. S This form of cloud computing delivers development environments as a service. You build your own applications that run on the provider's infrastructure and are delivered to your users via the Internet from the provider's servers. – Mainframe, Linux, Windows Server, etc. • Service commerce platforms: software personal assistant. This cloud computing offers a service hub that users interact with: http: //www. reardencommerce. com/
 Who owns the data? • Privacy: http: //venturebeat. com/2009/02/17/is-facebook-really-using -its-new-terms-of-service-to-own-your-data / • Facebook introduced a new terms of service agreement in Feb. 09: – You hereby grant Facebook an irrevocable, perpetual, non-exclusive, transferable, fully paid, worldwide license (with the right to sublicense) to (a) use, copy, publish, stream, store, retain, publicly perform or display, transmit, scan, reformat, modify, edit, …. . • Security: http: //www. ecommercetimes. com/story/Pinning-Down. Enterprise-Data-Security-in-the-Cloud-67093. html? wlc=1252360837 • Top reasons why big businesses are reluctant to adopt Saa. S : http: //www. executivebrief. com/blogs/the-pros-andcons-of-saas-part-2/
Who owns the data? • Privacy: http: //venturebeat. com/2009/02/17/is-facebook-really-using -its-new-terms-of-service-to-own-your-data / • Facebook introduced a new terms of service agreement in Feb. 09: – You hereby grant Facebook an irrevocable, perpetual, non-exclusive, transferable, fully paid, worldwide license (with the right to sublicense) to (a) use, copy, publish, stream, store, retain, publicly perform or display, transmit, scan, reformat, modify, edit, …. . • Security: http: //www. ecommercetimes. com/story/Pinning-Down. Enterprise-Data-Security-in-the-Cloud-67093. html? wlc=1252360837 • Top reasons why big businesses are reluctant to adopt Saa. S : http: //www. executivebrief. com/blogs/the-pros-andcons-of-saas-part-2/
 IT and New Business Model • New products, services, and business models: – Business model: describes how company produces, delivers, and sells product or service to create wealth – Information systems and technology a major enabling tool for new products, services, business models • E. g. Netflix’s Internet-based DVD rentals
IT and New Business Model • New products, services, and business models: – Business model: describes how company produces, delivers, and sells product or service to create wealth – Information systems and technology a major enabling tool for new products, services, business models • E. g. Netflix’s Internet-based DVD rentals


