788f21cc6e8a652fbe7d6171b72f409d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Issues in HIV prevention with positives in India: The role of stigma & discrimination Maria L Ekstrand, Ph. D Center for AIDS Prevention Studies University of CA, San Francisco
Issues in HIV prevention with positives in India: The role of stigma & discrimination Maria L Ekstrand, Ph. D Center for AIDS Prevention Studies University of CA, San Francisco
 Research teams “Stigma” and “Positive needs” studies Mumbai Shalini Bharat, Ph. D Maninder Setia, MD Brinelle D’Souza, MA Hema Jerajani, MD 2 Bangalore Jayashree Ramakrishna, Ph. D Sara Chandy, MD Girija Singh, MD UCSF Monica Gandhi, MD Christina Lindan, MD Suneeta Krishnan, Ph. D David Huebner, Ph. D Wayne Steward, Ph. D Mirriam Rafiq, MPH
Research teams “Stigma” and “Positive needs” studies Mumbai Shalini Bharat, Ph. D Maninder Setia, MD Brinelle D’Souza, MA Hema Jerajani, MD 2 Bangalore Jayashree Ramakrishna, Ph. D Sara Chandy, MD Girija Singh, MD UCSF Monica Gandhi, MD Christina Lindan, MD Suneeta Krishnan, Ph. D David Huebner, Ph. D Wayne Steward, Ph. D Mirriam Rafiq, MPH
 HIV prevalence in India (estimates) 4. 58 million HIV infected individuals (India’s National AIDS Control Organization) 5 -8 million currently, 20 -25 million by 2010 (US National Intelligence Council)
HIV prevalence in India (estimates) 4. 58 million HIV infected individuals (India’s National AIDS Control Organization) 5 -8 million currently, 20 -25 million by 2010 (US National Intelligence Council)
 HIV prevalence in India: Implications n “AIDS is more devastating than any terrorist attack, any conflict or any weapon of mass destruction. AIDS can destroy countries and destabilize entire regions. ” (Colin Powell) n “India's on the brink of success. And one of the only things that stands in the way of that, achieving the incredible potential that India has, is making sure that there's not a widespread AIDS epidemic. ” (Bill Gates)
HIV prevalence in India: Implications n “AIDS is more devastating than any terrorist attack, any conflict or any weapon of mass destruction. AIDS can destroy countries and destabilize entire regions. ” (Colin Powell) n “India's on the brink of success. And one of the only things that stands in the way of that, achieving the incredible potential that India has, is making sure that there's not a widespread AIDS epidemic. ” (Bill Gates)
 HIV “hot spots” in India 6 Indian states have been classified as "high prevalence", based on antenatal sentinel surveillance: n Maharashtra, n Manipur, Nagaland, n Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. n
HIV “hot spots” in India 6 Indian states have been classified as "high prevalence", based on antenatal sentinel surveillance: n Maharashtra, n Manipur, Nagaland, n Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. n
 Map of India
Map of India
 Who is infected? Higher rates seen among: n Sex workers (Mumbai, South India) n Migrant workers (everywhere) n Truck drivers (esp states along truck routes) n MSM (– only reports in Mumbai & TN) n Drug users (esp. Manipur, Nagaland) n Monogamous wives (in high prev states)
Who is infected? Higher rates seen among: n Sex workers (Mumbai, South India) n Migrant workers (everywhere) n Truck drivers (esp states along truck routes) n MSM (– only reports in Mumbai & TN) n Drug users (esp. Manipur, Nagaland) n Monogamous wives (in high prev states)
 Study of Prevention needs of HIV Infected Men Objectives To examine: 1. sexual behaviors among newly diagnosed HIV+ men. 2. issues related to receiving HIV+ diagnosis; disclosure, social support, healthcare seeking, and depression
Study of Prevention needs of HIV Infected Men Objectives To examine: 1. sexual behaviors among newly diagnosed HIV+ men. 2. issues related to receiving HIV+ diagnosis; disclosure, social support, healthcare seeking, and depression
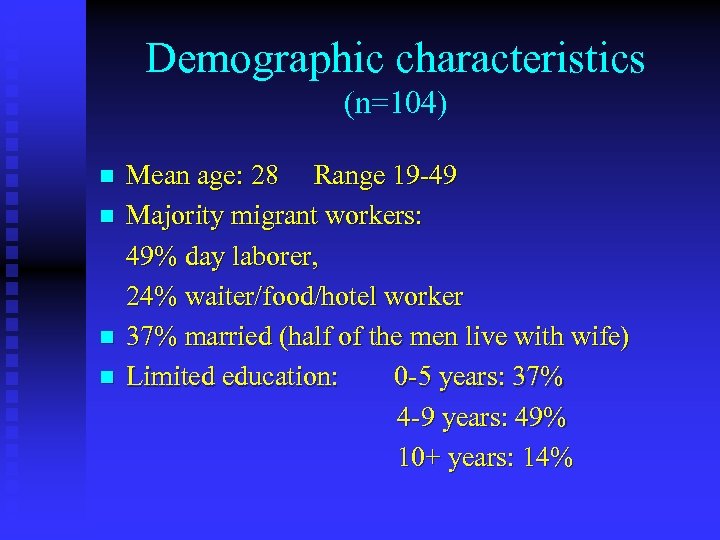 Demographic characteristics (n=104) n n Mean age: 28 Range 19 -49 Majority migrant workers: 49% day laborer, 24% waiter/food/hotel worker 37% married (half of the men live with wife) Limited education: 0 -5 years: 37% 4 -9 years: 49% 10+ years: 14%
Demographic characteristics (n=104) n n Mean age: 28 Range 19 -49 Majority migrant workers: 49% day laborer, 24% waiter/food/hotel worker 37% married (half of the men live with wife) Limited education: 0 -5 years: 37% 4 -9 years: 49% 10+ years: 14%
 Lifetime sexual behaviors (before diagnosis) Ever visited Female Sex Worker: 91% n Intoxicated before FSW visit: 82% n n Number of lifetime FSW partners: u 39% reported 10 or fewer FSW partners u 39% reported 11 -50 FSW partners u 21% reported more than 50 FSW partners Condom use: Never: Sometimes: Always: 39% 56% 5%
Lifetime sexual behaviors (before diagnosis) Ever visited Female Sex Worker: 91% n Intoxicated before FSW visit: 82% n n Number of lifetime FSW partners: u 39% reported 10 or fewer FSW partners u 39% reported 11 -50 FSW partners u 21% reported more than 50 FSW partners Condom use: Never: Sometimes: Always: 39% 56% 5%
 Other lifetime sexual partners (before diagnosis) n n n n Two or more casual female sex partners: 19% Condom use: 95% “never” Two or more regular female sex partners: 58% Condom use: 78% “never” Married: 37% Condom use with wife: 65% “never” Sex/play with a man: 35% (21% two or more) Condom use: 93% “never”
Other lifetime sexual partners (before diagnosis) n n n n Two or more casual female sex partners: 19% Condom use: 95% “never” Two or more regular female sex partners: 58% Condom use: 78% “never” Married: 37% Condom use with wife: 65% “never” Sex/play with a man: 35% (21% two or more) Condom use: 93% “never”
 Condom attitudes Sex with condoms less pleasurable: 58% n Condoms break/slip often: 46% n Safe sex with FSW not worth having: 44% n Condoms difficult to use: 40% n Condoms embarrassing to buy: 40% n Condom promo. is part of gov plot: 40% n Only for pregnancy prevention: 36% n
Condom attitudes Sex with condoms less pleasurable: 58% n Condoms break/slip often: 46% n Safe sex with FSW not worth having: 44% n Condoms difficult to use: 40% n Condoms embarrassing to buy: 40% n Condom promo. is part of gov plot: 40% n Only for pregnancy prevention: 36% n
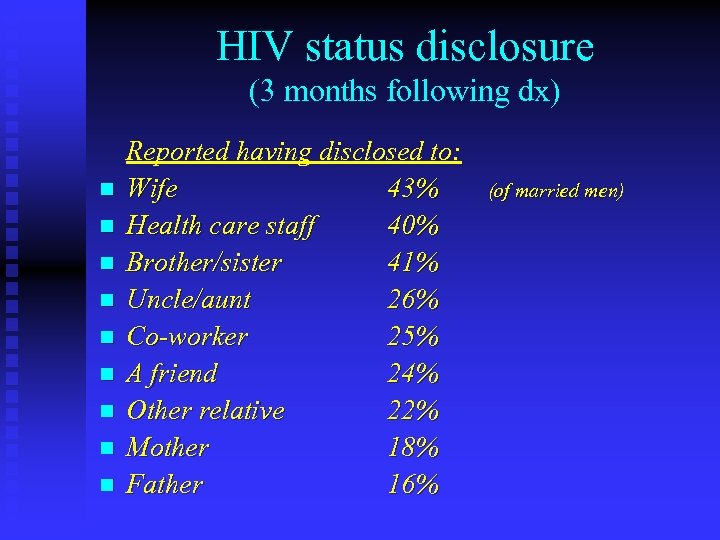 HIV status disclosure (3 months following dx) n n n n n Reported having disclosed to: Wife 43% Health care staff 40% Brother/sister 41% Uncle/aunt 26% Co-worker 25% A friend 24% Other relative 22% Mother 18% Father 16% (of married men)
HIV status disclosure (3 months following dx) n n n n n Reported having disclosed to: Wife 43% Health care staff 40% Brother/sister 41% Uncle/aunt 26% Co-worker 25% A friend 24% Other relative 22% Mother 18% Father 16% (of married men)
 High levels of depression BDI II Scores*: “Normal” “Mild-moderate” “Moderate-severe” “Severe depression” n 25% 19% 40% 26% *Categories based on U. S norms freq used in India
High levels of depression BDI II Scores*: “Normal” “Mild-moderate” “Moderate-severe” “Severe depression” n 25% 19% 40% 26% *Categories based on U. S norms freq used in India
 Issues brought up by participants in semi-structured interviews n n n n Fear of stigma and discrimination! Fear of lack of care and treatment Fear of future inability to support self Worry about inability to marry Worry about inability to have children Requests for medication Requests for legal help Requests for ongoing counseling
Issues brought up by participants in semi-structured interviews n n n n Fear of stigma and discrimination! Fear of lack of care and treatment Fear of future inability to support self Worry about inability to marry Worry about inability to have children Requests for medication Requests for legal help Requests for ongoing counseling
 Role of AIDS stigma n It impacts AIDS prevention and treatment on multiple levels: It is associated with less condom use. u It deters people from getting tested. u It reduces likelihood of disclosure (to family members, sex partners, healthcare staff). u It makes people afraid to seek treatment. u It decreases willingness to provide care and support (healthcare workers and families). u
Role of AIDS stigma n It impacts AIDS prevention and treatment on multiple levels: It is associated with less condom use. u It deters people from getting tested. u It reduces likelihood of disclosure (to family members, sex partners, healthcare staff). u It makes people afraid to seek treatment. u It decreases willingness to provide care and support (healthcare workers and families). u
 Stigma fears are reality-based n A person with HIV/AIDS has no right to marry and start a family. Indian Supreme Court 1998 n Premarital HIV testing mandatory. Current and proposed legislation in A. P. and parts of Maharasthra § Sodomy law an obstacle to HIV prevention with MSM Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code
Stigma fears are reality-based n A person with HIV/AIDS has no right to marry and start a family. Indian Supreme Court 1998 n Premarital HIV testing mandatory. Current and proposed legislation in A. P. and parts of Maharasthra § Sodomy law an obstacle to HIV prevention with MSM Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code
 Stigma and Discrimination - contexts At the community-level -boycotting families with infected members n By schools -refusing admission to PLWHAs, families, n neighbors n By families -refusing care, housing, support
Stigma and Discrimination - contexts At the community-level -boycotting families with infected members n By schools -refusing admission to PLWHAs, families, n neighbors n By families -refusing care, housing, support
 Stigma & Discrimination - contexts n At the workplace (quotes from Bharat, 2000) "Those staff members who know about me, talk about it. They point out at me and say 'Look, he is the one with AIDS'. There has been some difference in the way they behave toward me now - keep distance from me and remain aloof“ "Nobody will want to come near me, eat with me in the canteen, nobody will want to work with me, I'll be an outcast here"
Stigma & Discrimination - contexts n At the workplace (quotes from Bharat, 2000) "Those staff members who know about me, talk about it. They point out at me and say 'Look, he is the one with AIDS'. There has been some difference in the way they behave toward me now - keep distance from me and remain aloof“ "Nobody will want to come near me, eat with me in the canteen, nobody will want to work with me, I'll be an outcast here"
 Stigma & Discrimination n By the health care system: - pregnant women, surgery pts tested and refused care if infected. By landlords: "Media has made HIV look so frightening that we are scared. I understand that it's not contagious, but neighbors had put a lot of pressure. So I asked her to leave. " (NDTV) n
Stigma & Discrimination n By the health care system: - pregnant women, surgery pts tested and refused care if infected. By landlords: "Media has made HIV look so frightening that we are scared. I understand that it's not contagious, but neighbors had put a lot of pressure. So I asked her to leave. " (NDTV) n
 Consequences of stigma & discrimination High levels of depression n Suicides n Homicides n Low levels of disclosure (=more risk) n Less treatment seeking n Increased vulnerability to those offering false hope & quick cures n
Consequences of stigma & discrimination High levels of depression n Suicides n Homicides n Low levels of disclosure (=more risk) n Less treatment seeking n Increased vulnerability to those offering false hope & quick cures n
 Signs of hope? Indian government’s promise of free drugs to some groups in high prevalence states n CIPLA’s generic drugs n Lawyer’s collective working within legal system to end discrimination (Jan 2004 Mumbai) n
Signs of hope? Indian government’s promise of free drugs to some groups in high prevalence states n CIPLA’s generic drugs n Lawyer’s collective working within legal system to end discrimination (Jan 2004 Mumbai) n
 Implications for positive prevention n Prevention programs for PLWAs have to address the needs of the whole person, not just sexual risk taking. This includes: Physical health (ART, OI prophylaxis, nutrition as well as regimen adherence support) 2) Psychological/Psychiatric support to reduce distress and improve coping in both individual, family and group settings - including antidepressant meds. 3) Legal issues – involve e. g. “Lawyers collective” 4) Referrals to networks of HIV positives for support 5) “Social responsibility” issues, e. g. how to handle 1)
Implications for positive prevention n Prevention programs for PLWAs have to address the needs of the whole person, not just sexual risk taking. This includes: Physical health (ART, OI prophylaxis, nutrition as well as regimen adherence support) 2) Psychological/Psychiatric support to reduce distress and improve coping in both individual, family and group settings - including antidepressant meds. 3) Legal issues – involve e. g. “Lawyers collective” 4) Referrals to networks of HIV positives for support 5) “Social responsibility” issues, e. g. how to handle 1)


