4454c7532990553cf48b4374c7357b97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 ISSUES FOR AMEDA DEPOSITORIES IN MANAGING RISK IN THE CURRENT ENVIRONMENT April 2010
ISSUES FOR AMEDA DEPOSITORIES IN MANAGING RISK IN THE CURRENT ENVIRONMENT April 2010
 Agenda § TM Depository Risk Definitions & Country Categories § Risk Comparisons: AMEDA vs Rest of the World with Key Issues Page 2 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Agenda § TM Depository Risk Definitions & Country Categories § Risk Comparisons: AMEDA vs Rest of the World with Key Issues Page 2 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
 Risk Definitions § Asset Commitment Risk - The period of time from when control of securities or cash is given up until receipt of countervalue. § Liquidity Risk - The risk that insufficient securities and or funds are available to meet commitments; the obligation will be covered some time later. § Counterparty Risk - The risk that a counterparty (i. e. , a participant) will not settle its obligations for full value at any time. § Asset Servicing Risk - The risk that a participant may incur a loss arising from missed or inaccurate information provided by the depository, or from incorrectly executed instructions, in respect of corporate actions and proxy voting. § Financial Risk - The ability of the CSD to operate as a financially viable company. Page 3 § Operational Risk - The risk that deficiencies in information systems or internal controls, human errors or management failures will result in losses. © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd. PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL
Risk Definitions § Asset Commitment Risk - The period of time from when control of securities or cash is given up until receipt of countervalue. § Liquidity Risk - The risk that insufficient securities and or funds are available to meet commitments; the obligation will be covered some time later. § Counterparty Risk - The risk that a counterparty (i. e. , a participant) will not settle its obligations for full value at any time. § Asset Servicing Risk - The risk that a participant may incur a loss arising from missed or inaccurate information provided by the depository, or from incorrectly executed instructions, in respect of corporate actions and proxy voting. § Financial Risk - The ability of the CSD to operate as a financially viable company. Page 3 § Operational Risk - The risk that deficiencies in information systems or internal controls, human errors or management failures will result in losses. © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd. PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL
 Country Categories § Middle East Countries and CSDs § § § § Page 4 Bahrain – CDS Egypt – MCDR Israel – TASECH Jordan – SDC Kuwait – KCC Lebanon – Midclear Morocco – Maroclear Oman – MDSRC Palestine – CDS Qatar – Qatar Exchange Saudi Arabia – Tadawul Tunisia – Sticodevam UAE – DFM UAE Nasdaq Dubai African Countries and CSDs § § Kenya – CDSC Mauritius – CDS Nigeria – CSCS South Africa – Strate Additional CSDs in Country Average § § § Kenya – CBK Mauritius – BOM West Africa – DCBR Zambia – Lu. SE Zambia – Bo. Z Additional CSDs in Country Average § AMEDA CSDs Under preparation Lebanon – CBL § § Ghana – GSD UAE - ADX PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Country Categories § Middle East Countries and CSDs § § § § Page 4 Bahrain – CDS Egypt – MCDR Israel – TASECH Jordan – SDC Kuwait – KCC Lebanon – Midclear Morocco – Maroclear Oman – MDSRC Palestine – CDS Qatar – Qatar Exchange Saudi Arabia – Tadawul Tunisia – Sticodevam UAE – DFM UAE Nasdaq Dubai African Countries and CSDs § § Kenya – CDSC Mauritius – CDS Nigeria – CSCS South Africa – Strate Additional CSDs in Country Average § § § Kenya – CBK Mauritius – BOM West Africa – DCBR Zambia – Lu. SE Zambia – Bo. Z Additional CSDs in Country Average § AMEDA CSDs Under preparation Lebanon – CBL § § Ghana – GSD UAE - ADX PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
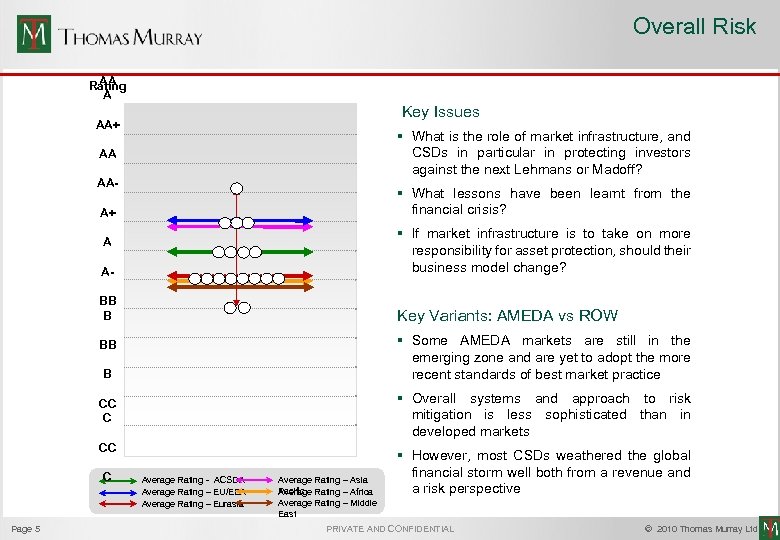 Overall Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § What is the role of market infrastructure, and CSDs in particular in protecting investors against the next Lehmans or Madoff? AA AA- § What lessons have been learnt from the financial crisis? A+ A- § If market infrastructure is to take on more responsibility for asset protection, should their business model change? BB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW A § Some AMEDA markets are still in the emerging zone and are yet to adopt the more recent standards of best market practice BB B § Overall systems and approach to risk mitigation is less sophisticated than in developed markets CC C Page 5 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § However, most CSDs weathered the global financial storm well both from a revenue and a risk perspective PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Overall Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § What is the role of market infrastructure, and CSDs in particular in protecting investors against the next Lehmans or Madoff? AA AA- § What lessons have been learnt from the financial crisis? A+ A- § If market infrastructure is to take on more responsibility for asset protection, should their business model change? BB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW A § Some AMEDA markets are still in the emerging zone and are yet to adopt the more recent standards of best market practice BB B § Overall systems and approach to risk mitigation is less sophisticated than in developed markets CC C Page 5 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § However, most CSDs weathered the global financial storm well both from a revenue and a risk perspective PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
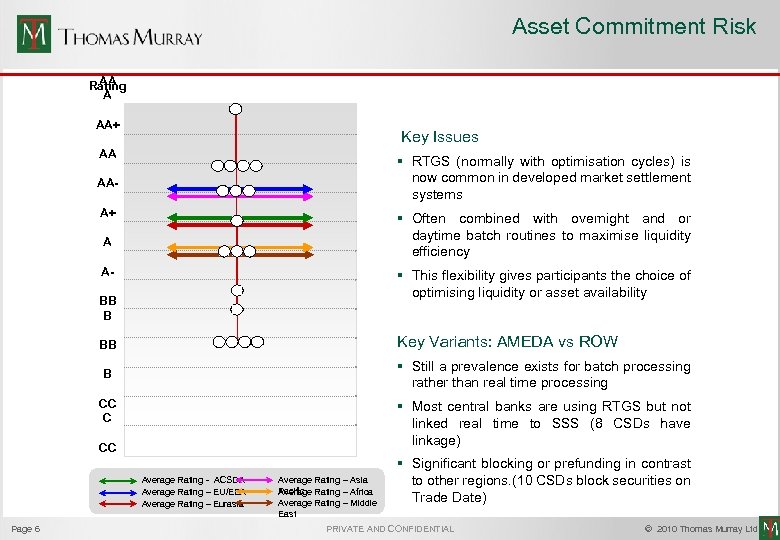 Asset Commitment Risk AA Rating A AA+ Key Issues AA § RTGS (normally with optimisation cycles) is now common in developed market settlement systems AAA+ § Often combined with overnight and or daytime batch routines to maximise liquidity efficiency A A- § This flexibility gives participants the choice of optimising liquidity or asset availability BB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § Still a prevalence exists for batch processing rather than real time processing B CC C § Most central banks are using RTGS but not linked real time to SSS (8 CSDs have linkage) CC C Page 6 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Significant blocking or prefunding in contrast to other regions. (10 CSDs block securities on Trade Date) PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Asset Commitment Risk AA Rating A AA+ Key Issues AA § RTGS (normally with optimisation cycles) is now common in developed market settlement systems AAA+ § Often combined with overnight and or daytime batch routines to maximise liquidity efficiency A A- § This flexibility gives participants the choice of optimising liquidity or asset availability BB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § Still a prevalence exists for batch processing rather than real time processing B CC C § Most central banks are using RTGS but not linked real time to SSS (8 CSDs have linkage) CC C Page 6 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Significant blocking or prefunding in contrast to other regions. (10 CSDs block securities on Trade Date) PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
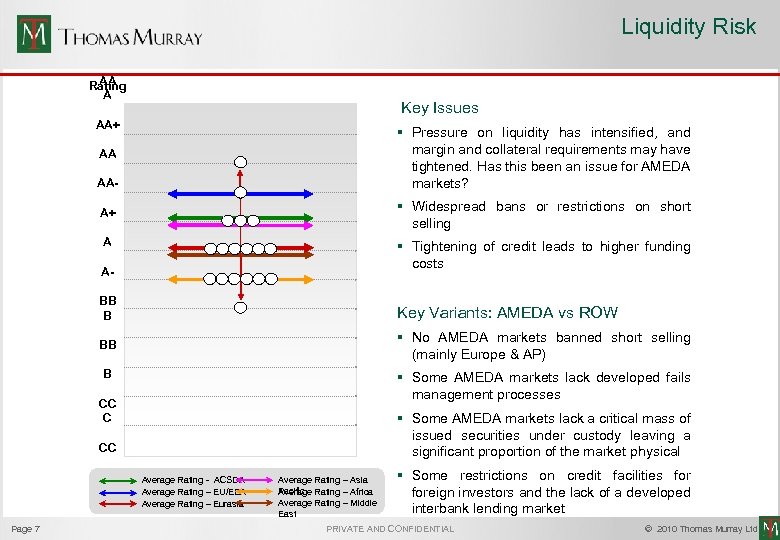 Liquidity Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § Pressure on liquidity has intensified, and margin and collateral requirements may have tightened. Has this been an issue for AMEDA markets? AA AA- § Widespread bans or restrictions on short selling A+ A § Tightening of credit leads to higher funding costs ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § No AMEDA markets banned short selling (mainly Europe & AP) B § Some AMEDA markets lack developed fails management processes CC C § Some AMEDA markets lack a critical mass of issued securities under custody leaving a significant proportion of the market physical CC C Page 7 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Some restrictions on credit facilities foreign investors and the lack of a developed interbank lending market PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Liquidity Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § Pressure on liquidity has intensified, and margin and collateral requirements may have tightened. Has this been an issue for AMEDA markets? AA AA- § Widespread bans or restrictions on short selling A+ A § Tightening of credit leads to higher funding costs ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § No AMEDA markets banned short selling (mainly Europe & AP) B § Some AMEDA markets lack developed fails management processes CC C § Some AMEDA markets lack a critical mass of issued securities under custody leaving a significant proportion of the market physical CC C Page 7 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Some restrictions on credit facilities foreign investors and the lack of a developed interbank lending market PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
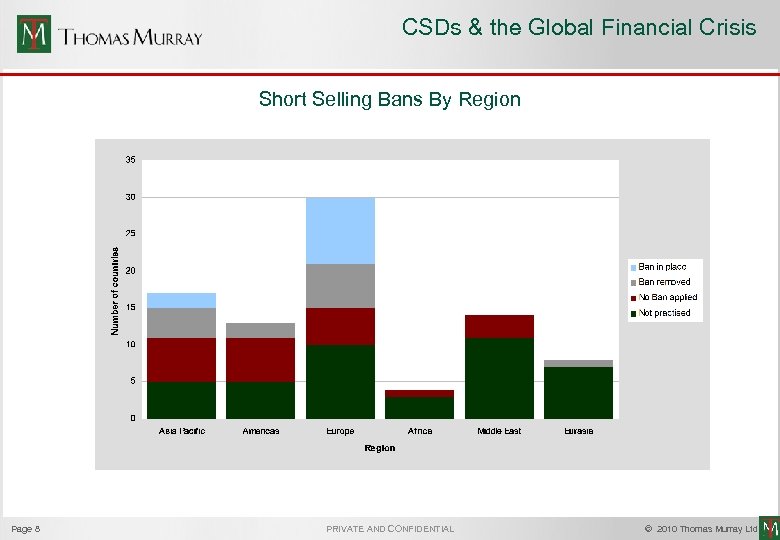 CSDs & the Global Financial Crisis Short Selling Bans By Region Page 8 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
CSDs & the Global Financial Crisis Short Selling Bans By Region Page 8 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
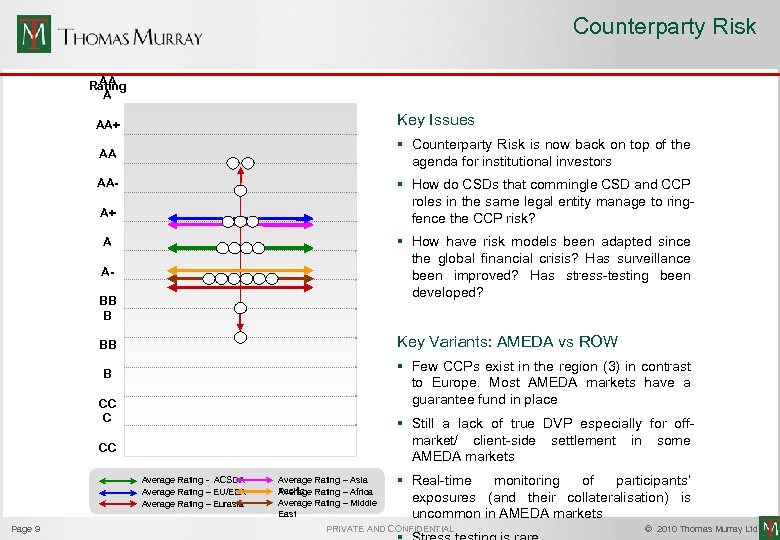 Counterparty Risk AA Rating A AA+ Key Issues AA § Counterparty Risk is now back on top of the agenda for institutional investors § How do CSDs that commingle CSD and CCP roles in the same legal entity manage to ringfence the CCP risk? AAA+ § How have risk models been adapted since the global financial crisis? Has surveillance been improved? Has stress-testing been developed? A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § Few CCPs exist in the region (3) in contrast to Europe. Most AMEDA markets have a guarantee fund in place B CC C § Still a lack of true DVP especially for offmarket/ client-side settlement in some AMEDA markets CC C Page 9 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Real-time monitoring of participants’ exposures (and their collateralisation) is uncommon in AMEDA markets PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Counterparty Risk AA Rating A AA+ Key Issues AA § Counterparty Risk is now back on top of the agenda for institutional investors § How do CSDs that commingle CSD and CCP roles in the same legal entity manage to ringfence the CCP risk? AAA+ § How have risk models been adapted since the global financial crisis? Has surveillance been improved? Has stress-testing been developed? A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB § Few CCPs exist in the region (3) in contrast to Europe. Most AMEDA markets have a guarantee fund in place B CC C § Still a lack of true DVP especially for offmarket/ client-side settlement in some AMEDA markets CC C Page 9 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Real-time monitoring of participants’ exposures (and their collateralisation) is uncommon in AMEDA markets PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
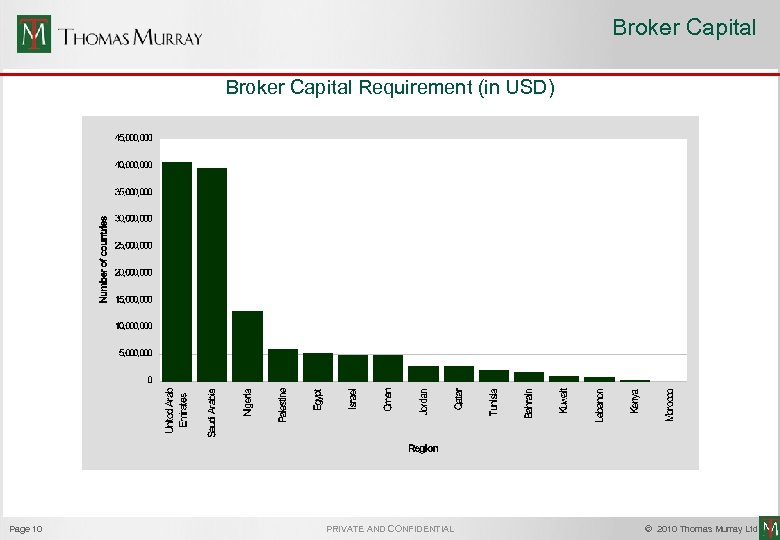 Broker Capital Requirement (in USD) Page 10 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Broker Capital Requirement (in USD) Page 10 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
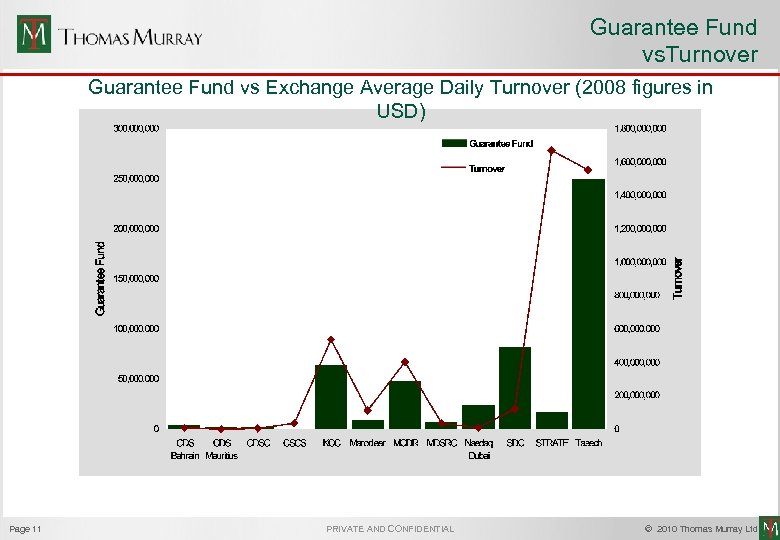 Guarantee Fund vs. Turnover Guarantee Fund vs Exchange Average Daily Turnover (2008 figures in USD) Page 11 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Guarantee Fund vs. Turnover Guarantee Fund vs Exchange Average Daily Turnover (2008 figures in USD) Page 11 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
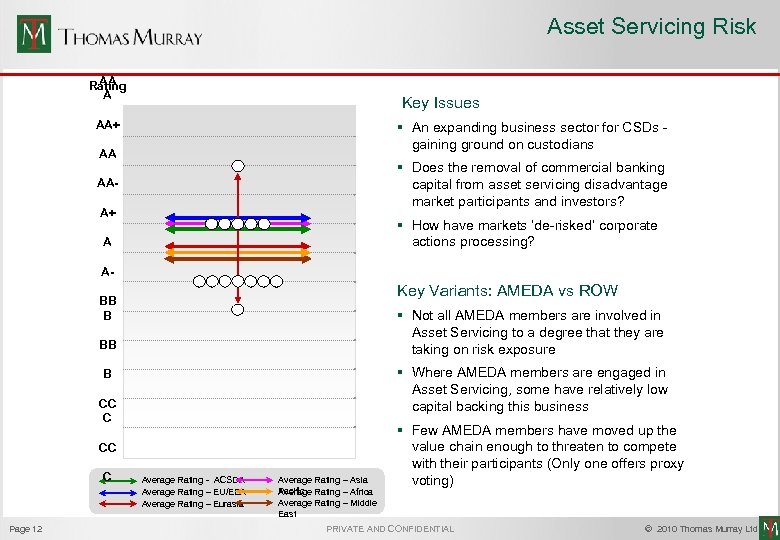 Asset Servicing Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § An expanding business sector for CSDs gaining ground on custodians AA § Does the removal of commercial banking capital from asset servicing disadvantage market participants and investors? AAA+ § How have markets ‘de-risked’ corporate actions processing? A A- Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB B § Not all AMEDA members are involved in Asset Servicing to a degree that they are taking on risk exposure BB § Where AMEDA members are engaged in Asset Servicing, some have relatively low capital backing this business B CC C Page 12 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Few AMEDA members have moved up the value chain enough to threaten to compete with their participants (Only one offers proxy voting) PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Asset Servicing Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § An expanding business sector for CSDs gaining ground on custodians AA § Does the removal of commercial banking capital from asset servicing disadvantage market participants and investors? AAA+ § How have markets ‘de-risked’ corporate actions processing? A A- Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW BB B § Not all AMEDA members are involved in Asset Servicing to a degree that they are taking on risk exposure BB § Where AMEDA members are engaged in Asset Servicing, some have relatively low capital backing this business B CC C Page 12 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East § Few AMEDA members have moved up the value chain enough to threaten to compete with their participants (Only one offers proxy voting) PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
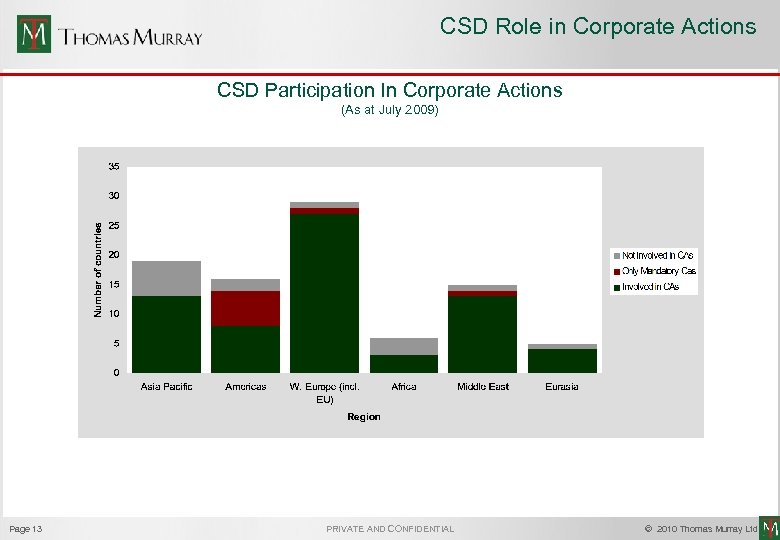 CSD Role in Corporate Actions CSD Participation In Corporate Actions (As at July 2009) Page 13 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
CSD Role in Corporate Actions CSD Participation In Corporate Actions (As at July 2009) Page 13 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
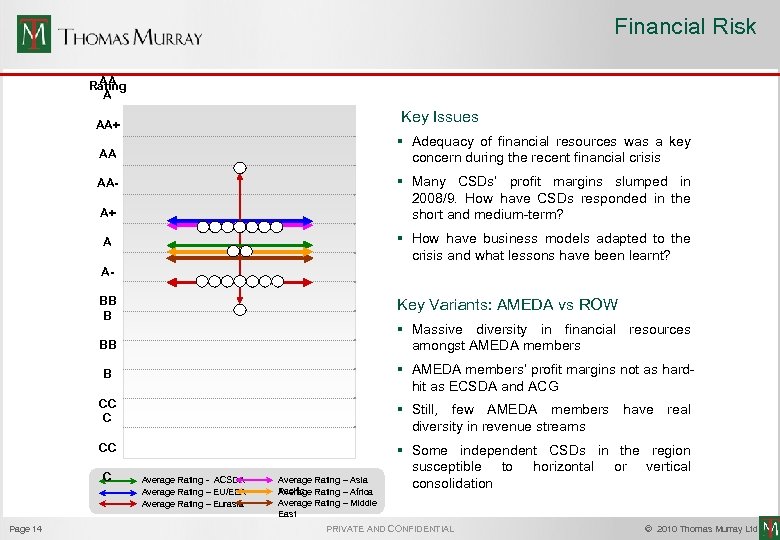 Financial Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § Adequacy of financial resources was a key concern during the recent financial crisis AA § Many CSDs’ profit margins slumped in 2008/9. How have CSDs responded in the short and medium-term? AAA+ § How have business models adapted to the crisis and what lessons have been learnt? A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW § Massive diversity in financial resources amongst AMEDA members BB § AMEDA members’ profit margins not as hardhit as ECSDA and ACG B CC C § Still, few AMEDA members have real diversity in revenue streams CC § Some independent CSDs in the region susceptible to horizontal or vertical consolidation C Page 14 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Financial Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § Adequacy of financial resources was a key concern during the recent financial crisis AA § Many CSDs’ profit margins slumped in 2008/9. How have CSDs responded in the short and medium-term? AAA+ § How have business models adapted to the crisis and what lessons have been learnt? A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW § Massive diversity in financial resources amongst AMEDA members BB § AMEDA members’ profit margins not as hardhit as ECSDA and ACG B CC C § Still, few AMEDA members have real diversity in revenue streams CC § Some independent CSDs in the region susceptible to horizontal or vertical consolidation C Page 14 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
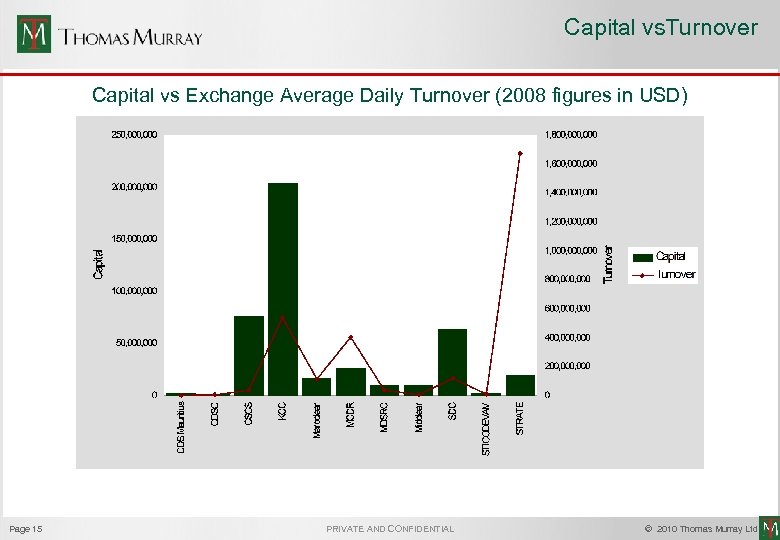 Capital vs. Turnover Capital vs Exchange Average Daily Turnover (2008 figures in USD) Page 15 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Capital vs. Turnover Capital vs Exchange Average Daily Turnover (2008 figures in USD) Page 15 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
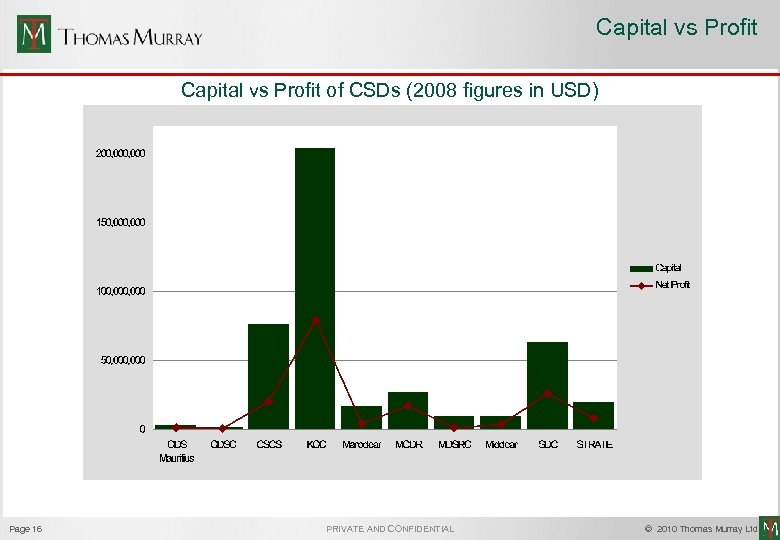 Capital vs Profit of CSDs (2008 figures in USD) Page 16 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Capital vs Profit of CSDs (2008 figures in USD) Page 16 PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
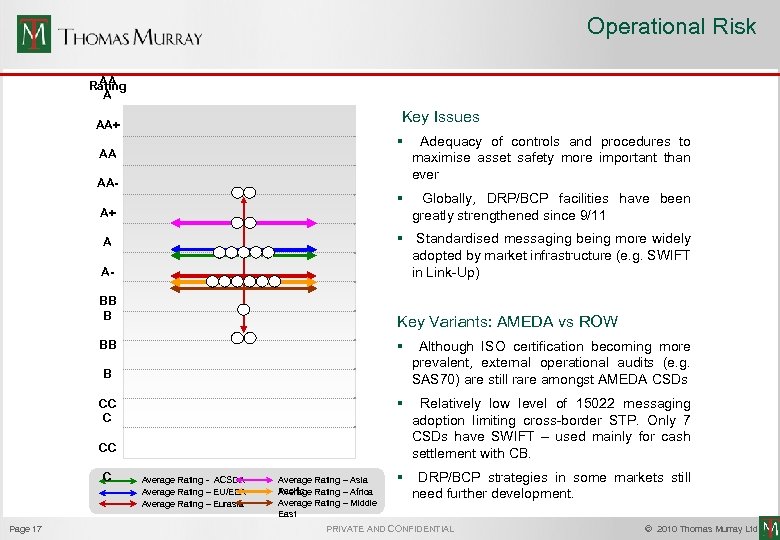 Operational Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § AA- Adequacy of controls and procedures to maximise asset safety more important than ever § AA Globally, DRP/BCP facilities have been greatly strengthened since 9/11 A+ § Standardised messaging being more widely adopted by market infrastructure (e. g. SWIFT in Link-Up) A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW § Although ISO certification becoming more prevalent, external operational audits (e. g. SAS 70) are still rare amongst AMEDA CSDs § BB Relatively low level of 15022 messaging adoption limiting cross-border STP. Only 7 CSDs have SWIFT – used mainly for cash settlement with CB. § DRP/BCP strategies in some markets still need further development. B CC C Page 17 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.
Operational Risk AA Rating A Key Issues AA+ § AA- Adequacy of controls and procedures to maximise asset safety more important than ever § AA Globally, DRP/BCP facilities have been greatly strengthened since 9/11 A+ § Standardised messaging being more widely adopted by market infrastructure (e. g. SWIFT in Link-Up) A ABB B Key Variants: AMEDA vs ROW § Although ISO certification becoming more prevalent, external operational audits (e. g. SAS 70) are still rare amongst AMEDA CSDs § BB Relatively low level of 15022 messaging adoption limiting cross-border STP. Only 7 CSDs have SWIFT – used mainly for cash settlement with CB. § DRP/BCP strategies in some markets still need further development. B CC C Page 17 Average Rating - ACSDA Average Rating – EU/EEA Average Rating – Eurasia Average Rating – Asia Pacific Rating – Africa Average Rating – Middle East PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL © 2010 Thomas Murray Ltd.


