 Issues at the Turn of the Century How does technology, pop culture, education and segregation effect 1880 s-1910 s America?
Issues at the Turn of the Century How does technology, pop culture, education and segregation effect 1880 s-1910 s America?
 Technology in the City • Louis Sullivan designs the skyscraper, Otis invents elevator • Electric streetcars, elevated trains, subways, steel cabled bridges improve transportation • Urban planning allows for open space in cities [parks]
Technology in the City • Louis Sullivan designs the skyscraper, Otis invents elevator • Electric streetcars, elevated trains, subways, steel cabled bridges improve transportation • Urban planning allows for open space in cities [parks]
 Pop Culture • 8 hour workday gives people more free time • Amusement midways have first ferris wheel & rollercoaster • Spectator sports (boxing & baseball) popular • Vaudeville & Ragtime are popular shows & music
Pop Culture • 8 hour workday gives people more free time • Amusement midways have first ferris wheel & rollercoaster • Spectator sports (boxing & baseball) popular • Vaudeville & Ragtime are popular shows & music
 Discuss: How do Spread of Pop Culture • George Eastman introduces Kodak camera popular ideas & trends spread? • Pulitzer & Hearst begin daily newspapers • 1890: FW Woolworth is 1 st department store (becomes chain) • Sears mailed catalogs allow purchases w/o leaving house Capture the moment
Discuss: How do Spread of Pop Culture • George Eastman introduces Kodak camera popular ideas & trends spread? • Pulitzer & Hearst begin daily newspapers • 1890: FW Woolworth is 1 st department store (becomes chain) • Sears mailed catalogs allow purchases w/o leaving house Capture the moment
 Expanding Public Education • Mandatory schooling for children 8 -16, (literacy rises to 95%) • College enrollment increases to 20% but most African Americans excluded from secondary education • Booker T. Washington: 1) “black schools” that teach skills, 2) once Af-Ams have skills, will be valued by society, ends seg. • WEB Dubois: 1) Niagara movement - college education to create future black leaders • 2) Talented Tenth: those already educated need to legally fight segregation now!
Expanding Public Education • Mandatory schooling for children 8 -16, (literacy rises to 95%) • College enrollment increases to 20% but most African Americans excluded from secondary education • Booker T. Washington: 1) “black schools” that teach skills, 2) once Af-Ams have skills, will be valued by society, ends seg. • WEB Dubois: 1) Niagara movement - college education to create future black leaders • 2) Talented Tenth: those already educated need to legally fight segregation now!
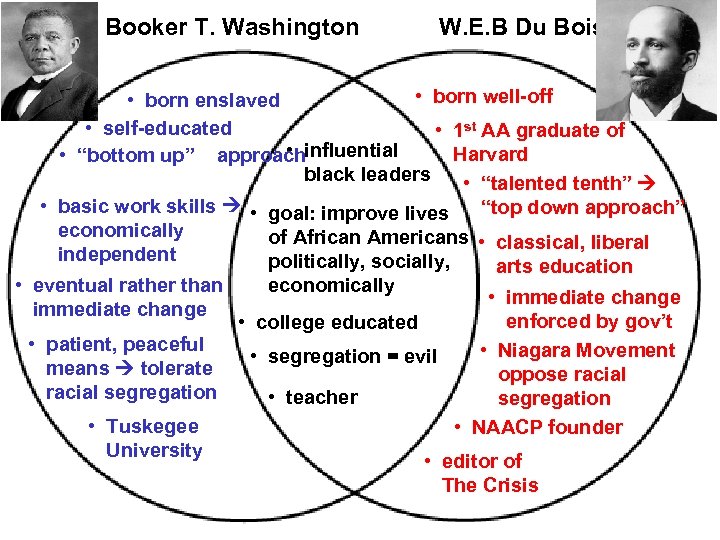 Booker T. Washington W. E. B Du Bois • born well-off • born enslaved • self-educated • 1 st AA graduate of • Harvard • “bottom up” approachinfluential black leaders • “talented tenth” • basic work skills • goal: improve lives “top down approach” economically of African Americans • classical, liberal independent politically, socially, arts education economically • eventual rather than • immediate change enforced by gov’t • college educated • patient, peaceful • Niagara Movement • segregation = evil means tolerate oppose racial segregation • teacher segregation • Tuskegee • NAACP founder University • editor of The Crisis
Booker T. Washington W. E. B Du Bois • born well-off • born enslaved • self-educated • 1 st AA graduate of • Harvard • “bottom up” approachinfluential black leaders • “talented tenth” • basic work skills • goal: improve lives “top down approach” economically of African Americans • classical, liberal independent politically, socially, arts education economically • eventual rather than • immediate change enforced by gov’t • college educated • patient, peaceful • Niagara Movement • segregation = evil means tolerate oppose racial segregation • teacher segregation • Tuskegee • NAACP founder University • editor of The Crisis
 Jim Crow Laws (De jure segregation - legal) • 1877: Southern state laws allowed for segregated public & private facilities (schools, restaurants, public transit, etc Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) • Homer Plessy (1/8 th black) tries to challenge segregation on trains that cross state lines (interstate travel = ICC) • Plessy argues segregated trains violate 14 Am • Sup. Court rules “separate but equal” is not a violation of 14 th Amendment
Jim Crow Laws (De jure segregation - legal) • 1877: Southern state laws allowed for segregated public & private facilities (schools, restaurants, public transit, etc Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) • Homer Plessy (1/8 th black) tries to challenge segregation on trains that cross state lines (interstate travel = ICC) • Plessy argues segregated trains violate 14 Am • Sup. Court rules “separate but equal” is not a violation of 14 th Amendment
 Racial Etiquette (De facto segregation - customary) • Many southerners want blacks to have “step & fetch” mentality & follow “southern” customs • African Americans who didn’t “follow custom” could face violence & death (1, 400 lynched 1882 -1902) Discrimination outside the South (De facto) • North: immigrants & blacks forced into segregated neighborhoods, unions disallow black & Irish membership in jobs -West: many Mexicans forced into debt peonage (forced to work until your debt is paid off), some segregation -West: most Chinese segregated in schools (esp. California)
Racial Etiquette (De facto segregation - customary) • Many southerners want blacks to have “step & fetch” mentality & follow “southern” customs • African Americans who didn’t “follow custom” could face violence & death (1, 400 lynched 1882 -1902) Discrimination outside the South (De facto) • North: immigrants & blacks forced into segregated neighborhoods, unions disallow black & Irish membership in jobs -West: many Mexicans forced into debt peonage (forced to work until your debt is paid off), some segregation -West: most Chinese segregated in schools (esp. California)