69054677571263f77340e089a828be5d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
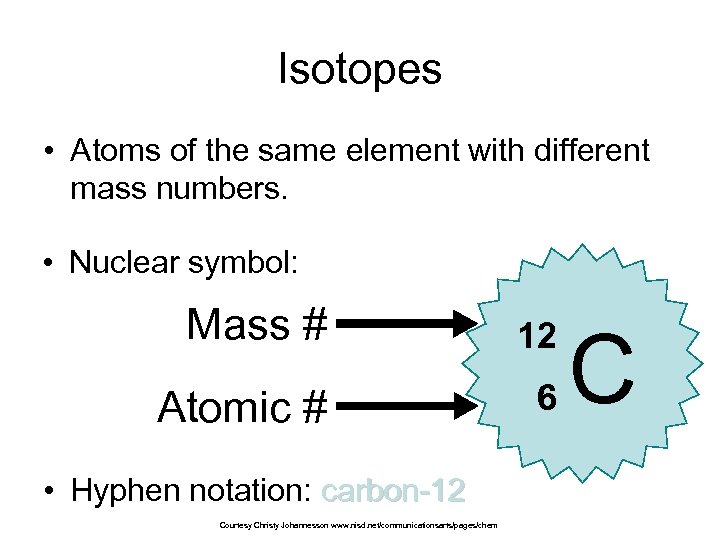 Isotopes • Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. • Nuclear symbol: Mass # 12 Atomic # 6 • Hyphen notation: carbon-12 Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem C
Isotopes • Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. • Nuclear symbol: Mass # 12 Atomic # 6 • Hyphen notation: carbon-12 Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem C
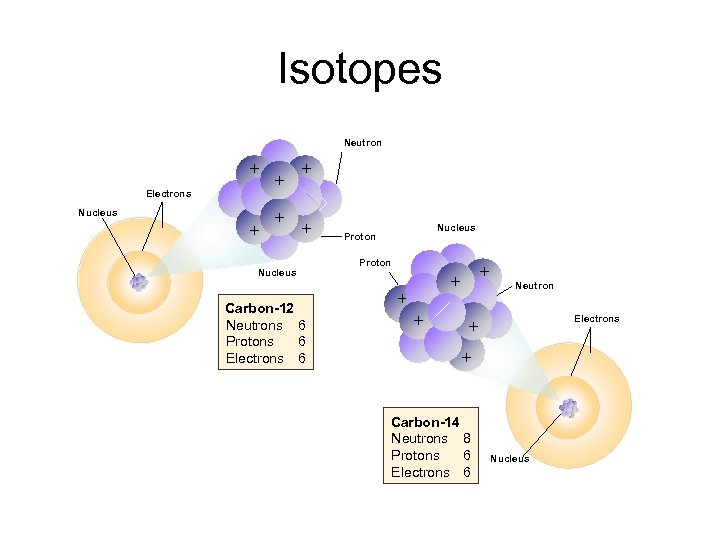 Isotopes Neutron + Electrons Nucleus + + + + + Nucleus Carbon-12 Neutrons 6 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Nucleus Proton + + Neutron Electrons + + Carbon-14 Neutrons 8 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Nucleus
Isotopes Neutron + Electrons Nucleus + + + + + Nucleus Carbon-12 Neutrons 6 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Nucleus Proton + + Neutron Electrons + + Carbon-14 Neutrons 8 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Nucleus
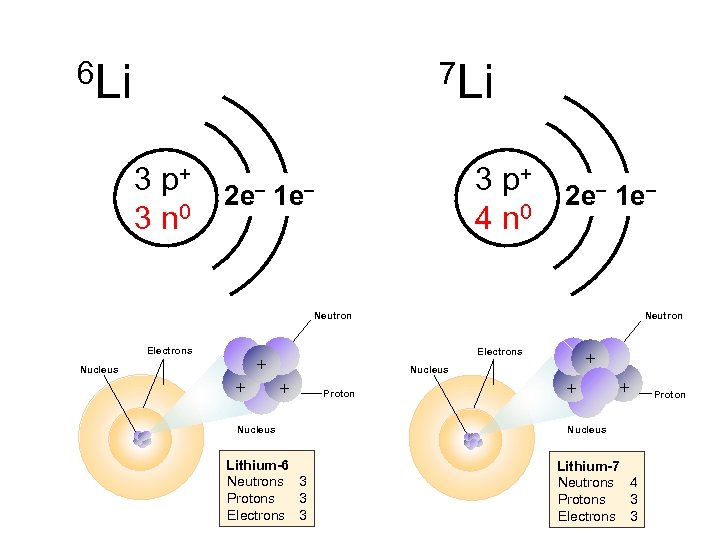 6 Li 7 Li 3 p+ 3 n 0 3 p+ 4 n 0 2 e– 1 e– Neutron Electrons + Electrons + Nucleus Neutron + Nucleus + + Proton Nucleus Lithium-6 Neutrons 3 Protons 3 Electrons 3 + Nucleus Lithium-7 Neutrons 4 Protons 3 Electrons 3 Proton
6 Li 7 Li 3 p+ 3 n 0 3 p+ 4 n 0 2 e– 1 e– Neutron Electrons + Electrons + Nucleus Neutron + Nucleus + + Proton Nucleus Lithium-6 Neutrons 3 Protons 3 Electrons 3 + Nucleus Lithium-7 Neutrons 4 Protons 3 Electrons 3 Proton
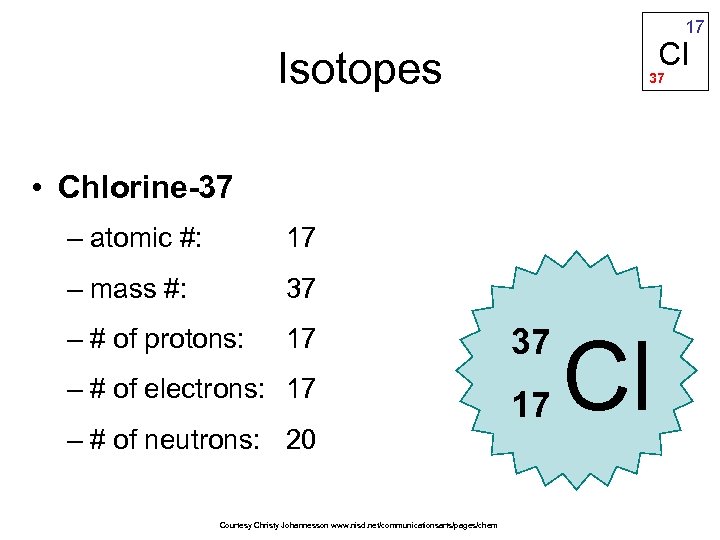 17 Cl Isotopes 37 • Chlorine-37 – atomic #: 17 – mass #: 37 – # of protons: 17 37 – # of electrons: 17 17 – # of neutrons: 20 Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Cl
17 Cl Isotopes 37 • Chlorine-37 – atomic #: 17 – mass #: 37 – # of protons: 17 37 – # of electrons: 17 17 – # of neutrons: 20 Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Cl
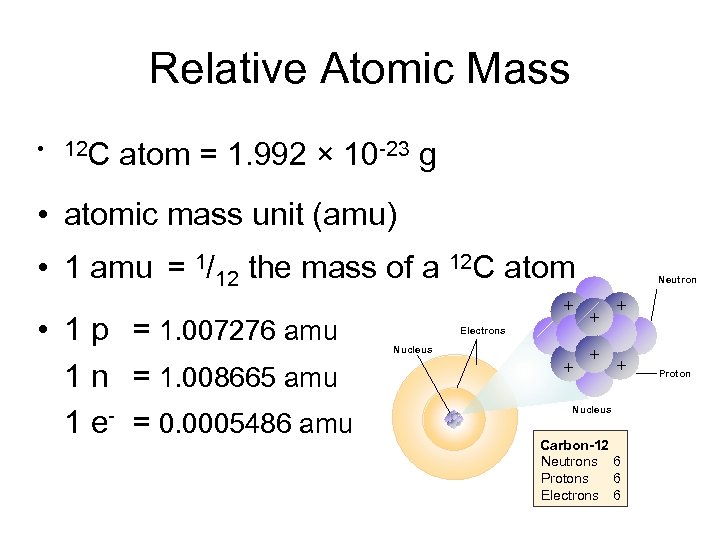 Relative Atomic Mass • 12 C atom = 1. 992 × 10 -23 g • atomic mass unit (amu) • 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of a 12 C atom • 1 p = 1. 007276 amu 1 n = 1. 008665 amu 1 e- = 0. 0005486 amu + Electrons Nucleus + Neutron + + + + Nucleus Carbon-12 Neutrons 6 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Proton
Relative Atomic Mass • 12 C atom = 1. 992 × 10 -23 g • atomic mass unit (amu) • 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of a 12 C atom • 1 p = 1. 007276 amu 1 n = 1. 008665 amu 1 e- = 0. 0005486 amu + Electrons Nucleus + Neutron + + + + Nucleus Carbon-12 Neutrons 6 Protons 6 Electrons 6 Proton
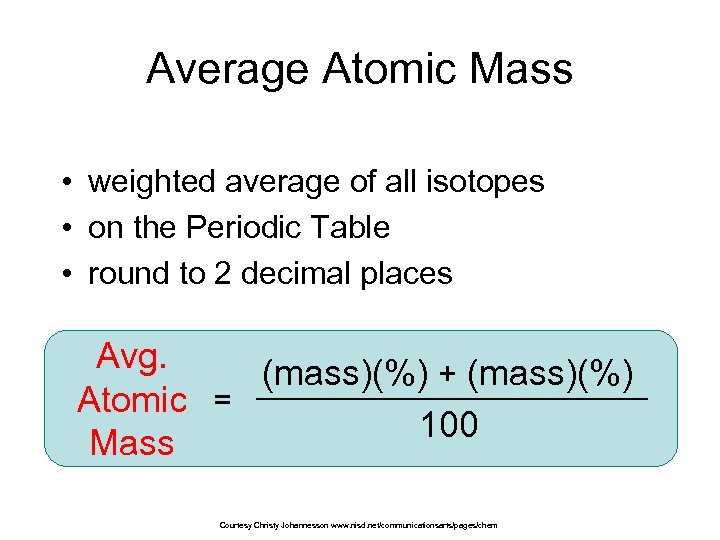 Average Atomic Mass • weighted average of all isotopes • on the Periodic Table • round to 2 decimal places Avg. (mass)(%) + (mass)(%) Atomic = 100 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
Average Atomic Mass • weighted average of all isotopes • on the Periodic Table • round to 2 decimal places Avg. (mass)(%) + (mass)(%) Atomic = 100 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
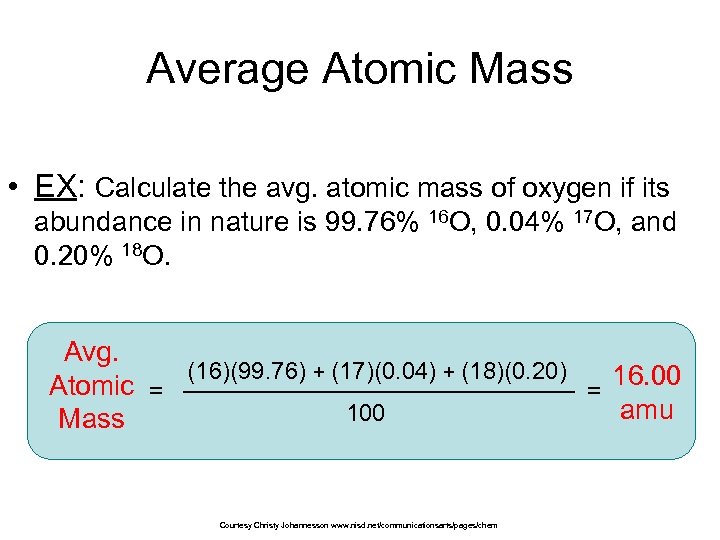 Average Atomic Mass • EX: Calculate the avg. atomic mass of oxygen if its abundance in nature is 99. 76% 16 O, 0. 04% 17 O, and 0. 20% 18 O. Avg. (16)(99. 76) + (17)(0. 04) + (18)(0. 20) 16. 00 Atomic = = amu 100 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
Average Atomic Mass • EX: Calculate the avg. atomic mass of oxygen if its abundance in nature is 99. 76% 16 O, 0. 04% 17 O, and 0. 20% 18 O. Avg. (16)(99. 76) + (17)(0. 04) + (18)(0. 20) 16. 00 Atomic = = amu 100 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
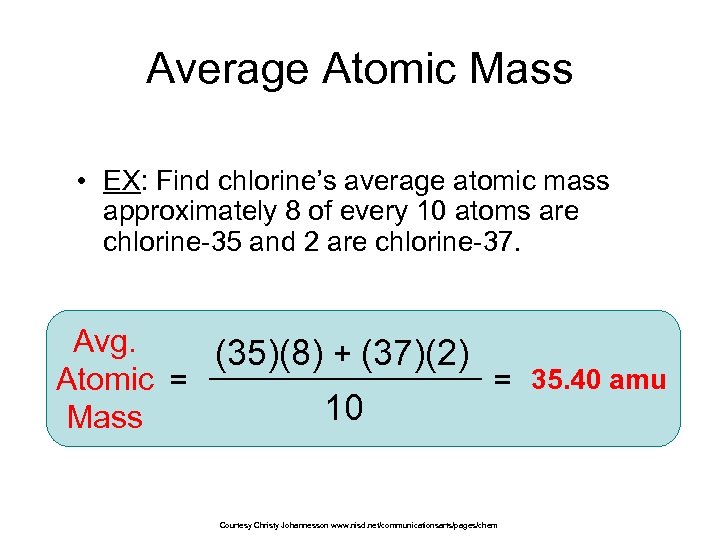 Average Atomic Mass • EX: Find chlorine’s average atomic mass i approximately 8 of every 10 atoms are chlorine-35 and 2 are chlorine-37. Avg. (35)(8) + (37)(2) Atomic = = 35. 40 amu 10 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
Average Atomic Mass • EX: Find chlorine’s average atomic mass i approximately 8 of every 10 atoms are chlorine-35 and 2 are chlorine-37. Avg. (35)(8) + (37)(2) Atomic = = 35. 40 amu 10 Mass Courtesy Christy Johannesson www. nisd. net/communicationsarts/pages/chem
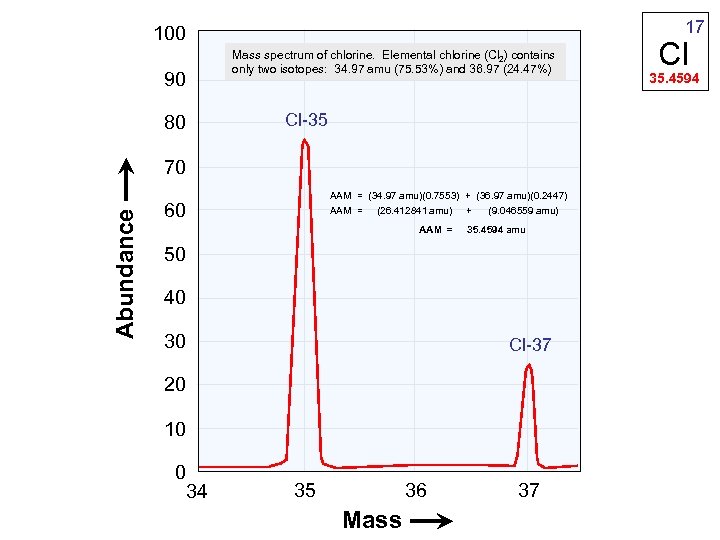 17 100 Mass spectrum of chlorine. Elemental chlorine (Cl 2) contains only two isotopes: 34. 97 amu (75. 53%) and 36. 97 (24. 47%) 90 Cl-35 80 Abundance 70 AAM = (34. 97 amu)(0. 7553) + (36. 97 amu)(0. 2447) AAM = (26. 412841 amu) + (9. 046559 amu) 60 AAM = 35. 4594 amu 50 40 30 Cl-37 20 10 0 34 36 35 Mass 37 Cl 35. 4594
17 100 Mass spectrum of chlorine. Elemental chlorine (Cl 2) contains only two isotopes: 34. 97 amu (75. 53%) and 36. 97 (24. 47%) 90 Cl-35 80 Abundance 70 AAM = (34. 97 amu)(0. 7553) + (36. 97 amu)(0. 2447) AAM = (26. 412841 amu) + (9. 046559 amu) 60 AAM = 35. 4594 amu 50 40 30 Cl-37 20 10 0 34 36 35 Mass 37 Cl 35. 4594
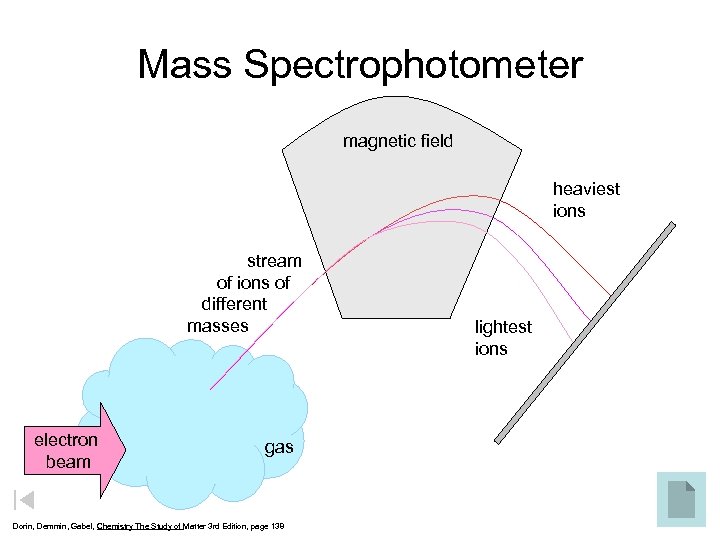 Mass Spectrophotometer magnetic field heaviest ions stream of ions of different masses electron beam gas Dorin, Demmin, Gabel, Chemistry The Study of Matter 3 rd Edition, page 138 lightest ions
Mass Spectrophotometer magnetic field heaviest ions stream of ions of different masses electron beam gas Dorin, Demmin, Gabel, Chemistry The Study of Matter 3 rd Edition, page 138 lightest ions
 Weighing atoms. gas sample enters here ions accelerate towards charged slit magnetic field deflects lightest ions most filament current ionizes the gas The first mass spectrograph was built in 1919 by F. W. Aston, who received the 1922 Nobel Prize for this accomplishment ions separated by mass expose film • mass spectrometry is used to experimentally determine isotopic masses and abundances • interpreting mass spectra • average atomic weights - computed from isotopic masses and abundances - significant figures of tabulated atomic weights gives some idea of natural variation in isotopic abundances Copyright © 1997 -2005 by Fred Senese
Weighing atoms. gas sample enters here ions accelerate towards charged slit magnetic field deflects lightest ions most filament current ionizes the gas The first mass spectrograph was built in 1919 by F. W. Aston, who received the 1922 Nobel Prize for this accomplishment ions separated by mass expose film • mass spectrometry is used to experimentally determine isotopic masses and abundances • interpreting mass spectra • average atomic weights - computed from isotopic masses and abundances - significant figures of tabulated atomic weights gives some idea of natural variation in isotopic abundances Copyright © 1997 -2005 by Fred Senese
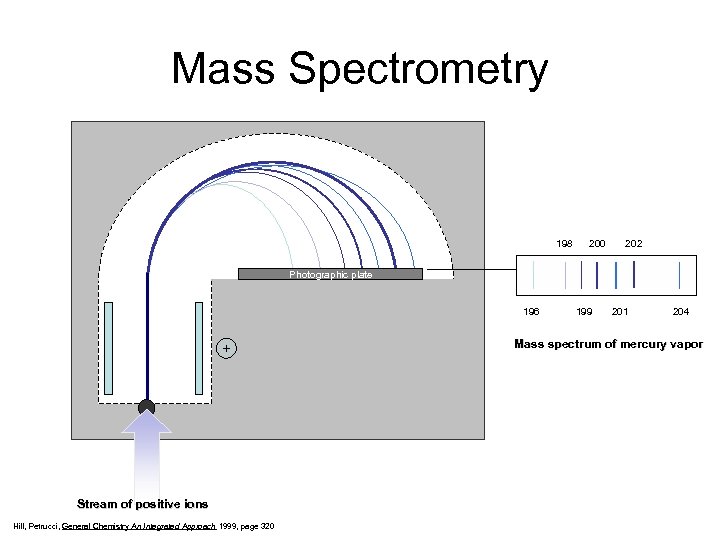 Mass Spectrometry 198 200 202 Photographic plate 196 199 201 204 - + Stream of positive ions Hill, Petrucci, General Chemistry An Integrated Approach 1999, page 320 Mass spectrum of mercury vapor
Mass Spectrometry 198 200 202 Photographic plate 196 199 201 204 - + Stream of positive ions Hill, Petrucci, General Chemistry An Integrated Approach 1999, page 320 Mass spectrum of mercury vapor
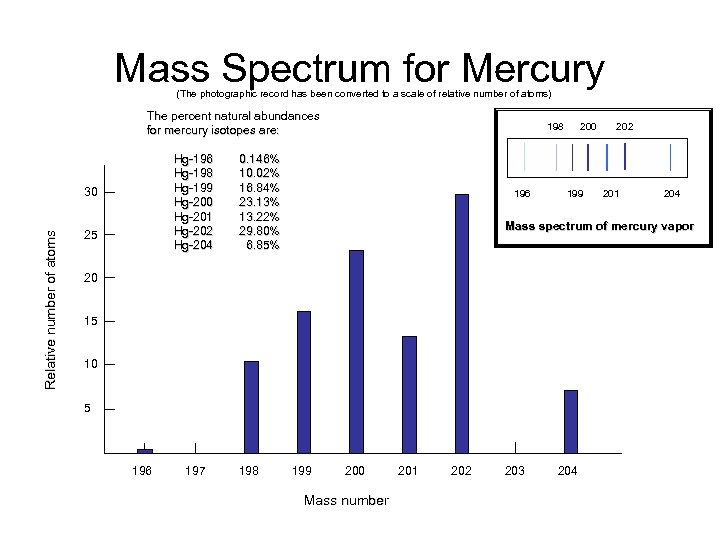 Mass Spectrum for Mercury (The photographic record has been converted to a scale of relative number of atoms) The percent natural abundances for mercury isotopes are: Relative number of atoms 30 25 Hg-196 0. 146% Hg-198 10. 02% Hg-199 16. 84% Hg-200 23. 13% Hg-201 13. 22% Hg-202 29. 80% Hg-204 6. 85% 198 200 202 196 199 201 204 Mass spectrum of mercury vapor 20 15 10 5 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 Mass number
Mass Spectrum for Mercury (The photographic record has been converted to a scale of relative number of atoms) The percent natural abundances for mercury isotopes are: Relative number of atoms 30 25 Hg-196 0. 146% Hg-198 10. 02% Hg-199 16. 84% Hg-200 23. 13% Hg-201 13. 22% Hg-202 29. 80% Hg-204 6. 85% 198 200 202 196 199 201 204 Mass spectrum of mercury vapor 20 15 10 5 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 Mass number
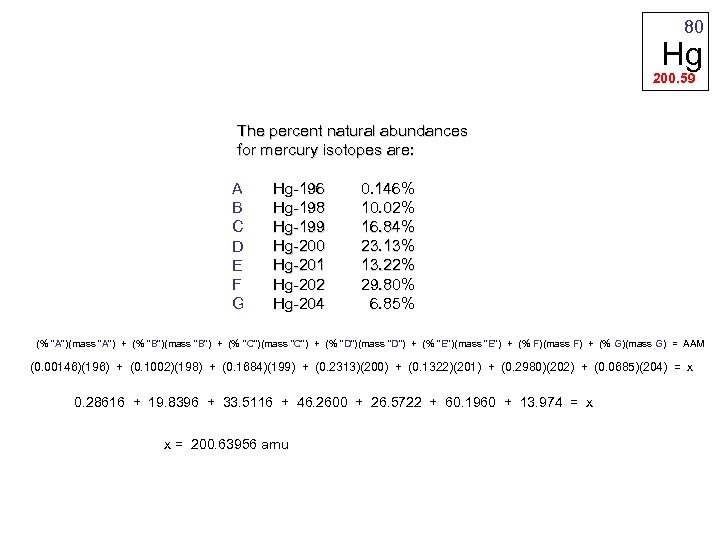 80 Hg 200. 59 The percent natural abundances for mercury isotopes are: Hg-196 0. 146% A Hg-198 10. 02% B Hg-199 16. 84% C Hg-200 23. 13% D Hg-201 13. 22% E Hg-202 29. 80% F Hg-204 6. 85% G (% "A")(mass "A") + (% "B")(mass "B") + (% "C")(mass "C") + (% "D")(mass "D") + (% "E")(mass "E") + (% F)(mass F) + (% G)(mass G) = AAM (0. 00146)(196) + (0. 1002)(198) + (0. 1684)(199) + (0. 2313)(200) + (0. 1322)(201) + (0. 2980)(202) + (0. 0685)(204) = x 0. 28616 + 19. 8396 + 33. 5116 + 46. 2600 + 26. 5722 + 60. 1960 + 13. 974 = x x = 200. 63956 amu
80 Hg 200. 59 The percent natural abundances for mercury isotopes are: Hg-196 0. 146% A Hg-198 10. 02% B Hg-199 16. 84% C Hg-200 23. 13% D Hg-201 13. 22% E Hg-202 29. 80% F Hg-204 6. 85% G (% "A")(mass "A") + (% "B")(mass "B") + (% "C")(mass "C") + (% "D")(mass "D") + (% "E")(mass "E") + (% F)(mass F) + (% G)(mass G) = AAM (0. 00146)(196) + (0. 1002)(198) + (0. 1684)(199) + (0. 2313)(200) + (0. 1322)(201) + (0. 2980)(202) + (0. 0685)(204) = x 0. 28616 + 19. 8396 + 33. 5116 + 46. 2600 + 26. 5722 + 60. 1960 + 13. 974 = x x = 200. 63956 amu
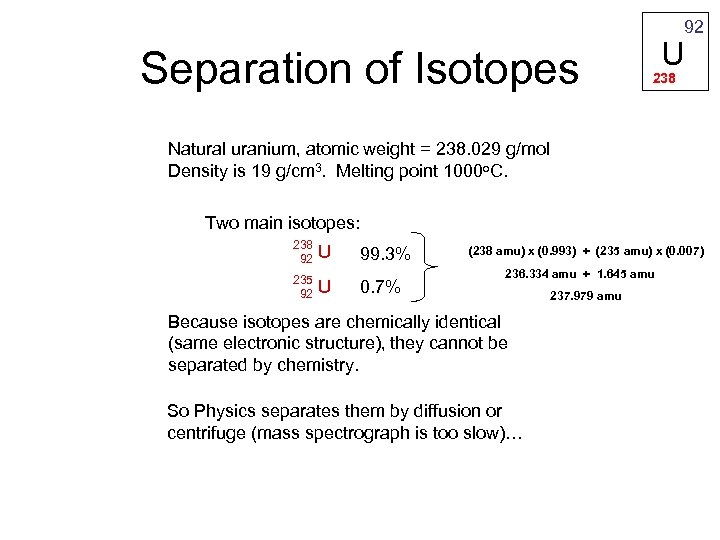 92 Separation of Isotopes U 238 Natural uranium, atomic weight = 238. 029 g/mol Density is 19 g/cm 3. Melting point 1000 o. C. Two main isotopes: 238 92 235 92 U U 99. 3% 0. 7% (238 amu) x (0. 993) + (235 amu) x (0. 007) 236. 334 amu + 1. 645 amu Because isotopes are chemically identical (same electronic structure), they cannot be separated by chemistry. So Physics separates them by diffusion or centrifuge (mass spectrograph is too slow)… 237. 979 amu
92 Separation of Isotopes U 238 Natural uranium, atomic weight = 238. 029 g/mol Density is 19 g/cm 3. Melting point 1000 o. C. Two main isotopes: 238 92 235 92 U U 99. 3% 0. 7% (238 amu) x (0. 993) + (235 amu) x (0. 007) 236. 334 amu + 1. 645 amu Because isotopes are chemically identical (same electronic structure), they cannot be separated by chemistry. So Physics separates them by diffusion or centrifuge (mass spectrograph is too slow)… 237. 979 amu
 17 Cl 35. 453 • Assume you have only two atoms of chlorine. • One atom has a mass of 35 amu (Cl-35) • The other atom has a mass of 36 amu (Cl-36) • What is the average mass of these two isotopes? 35. 5 amu • Looking at the average atomic mass printed on the periodic table. . . approximately what percentage is Cl-35 and Cl-36? 55% Cl-35 and 45% Cl-36 is a good approximation
17 Cl 35. 453 • Assume you have only two atoms of chlorine. • One atom has a mass of 35 amu (Cl-35) • The other atom has a mass of 36 amu (Cl-36) • What is the average mass of these two isotopes? 35. 5 amu • Looking at the average atomic mass printed on the periodic table. . . approximately what percentage is Cl-35 and Cl-36? 55% Cl-35 and 45% Cl-36 is a good approximation
 17 Cl 35. 453 Using our estimated % abundance data 55% Cl-35 and 45% Cl-36 calculate an average atomic mass for chlorine. Average Atomic Mass = (% abundance of isotope "A")(mass "A") + (% "B")(mass "B") AAM = (% abundance of isotope Cl-35)(mass Cl-35) + (% abundance of Cl-36)(mass Cl-36) AAM = (0. 55)(35 amu) + (0. 45)(36 amu) AAM = (19. 25 amu) + (16. 2 amu) AAM = 35. 45 amu
17 Cl 35. 453 Using our estimated % abundance data 55% Cl-35 and 45% Cl-36 calculate an average atomic mass for chlorine. Average Atomic Mass = (% abundance of isotope "A")(mass "A") + (% "B")(mass "B") AAM = (% abundance of isotope Cl-35)(mass Cl-35) + (% abundance of Cl-36)(mass Cl-36) AAM = (0. 55)(35 amu) + (0. 45)(36 amu) AAM = (19. 25 amu) + (16. 2 amu) AAM = 35. 45 amu
 Isotopes Dalton was wrong. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons different mass numbers called isotopes C-12 vs. C-14 California WEB
Isotopes Dalton was wrong. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons different mass numbers called isotopes C-12 vs. C-14 California WEB
 Naming Isotopes • Put the mass number after the name of the element • carbon- 12 • carbon -14 • uranium-235 California WEB
Naming Isotopes • Put the mass number after the name of the element • carbon- 12 • carbon -14 • uranium-235 California WEB
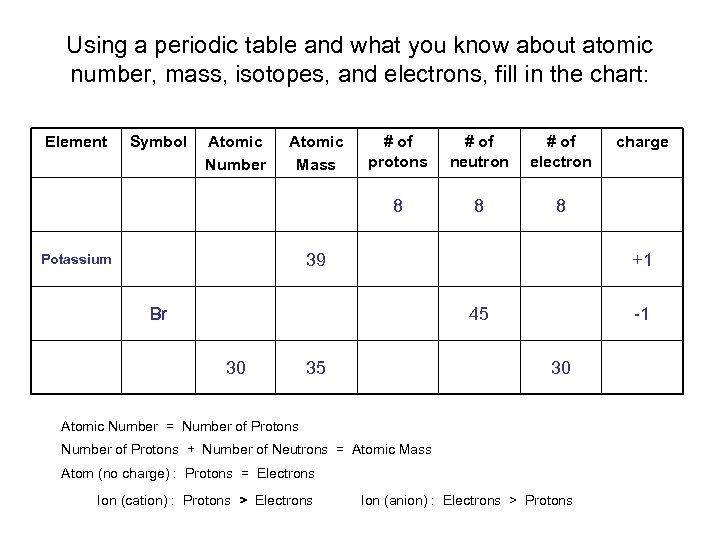 Using a periodic table and what you know about atomic number, mass, isotopes, and electrons, fill in the chart: Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # of protons # of neutron # of electron 8 8 8 39 Potassium +1 Br 45 30 35 -1 30 Atomic Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Atom (no charge) : Protons = Electrons Ion (cation) : Protons > Electrons charge Ion (anion) : Electrons > Protons
Using a periodic table and what you know about atomic number, mass, isotopes, and electrons, fill in the chart: Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # of protons # of neutron # of electron 8 8 8 39 Potassium +1 Br 45 30 35 -1 30 Atomic Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Atom (no charge) : Protons = Electrons Ion (cation) : Protons > Electrons charge Ion (anion) : Electrons > Protons
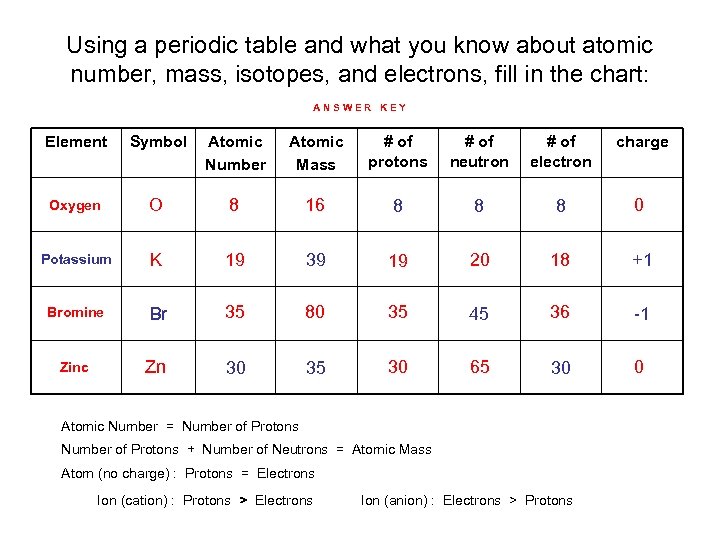 Using a periodic table and what you know about atomic number, mass, isotopes, and electrons, fill in the chart: ANSWER KEY Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # of protons # of neutron # of electron charge Oxygen O 8 16 8 8 8 0 Potassium K 19 39 19 20 18 +1 Bromine Br 35 80 35 45 36 -1 Zinc Zn 30 35 30 65 30 0 Atomic Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Atom (no charge) : Protons = Electrons Ion (cation) : Protons > Electrons Ion (anion) : Electrons > Protons
Using a periodic table and what you know about atomic number, mass, isotopes, and electrons, fill in the chart: ANSWER KEY Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # of protons # of neutron # of electron charge Oxygen O 8 16 8 8 8 0 Potassium K 19 39 19 20 18 +1 Bromine Br 35 80 35 45 36 -1 Zinc Zn 30 35 30 65 30 0 Atomic Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Atom (no charge) : Protons = Electrons Ion (cation) : Protons > Electrons Ion (anion) : Electrons > Protons
 Atomic Mass • • • How heavy is an atom of oxygen? There are different kinds of oxygen atoms. More concerned with average atomic mass. Based on abundance of each element in nature. Don’t use grams because the numbers would be too small
Atomic Mass • • • How heavy is an atom of oxygen? There are different kinds of oxygen atoms. More concerned with average atomic mass. Based on abundance of each element in nature. Don’t use grams because the numbers would be too small
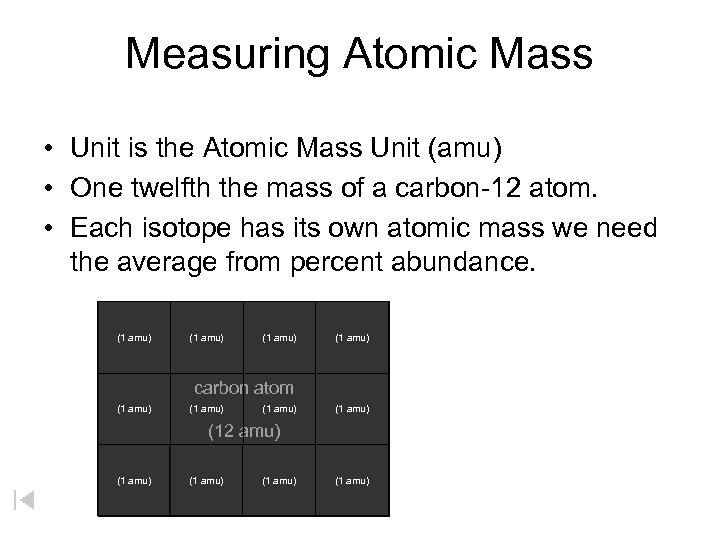 Measuring Atomic Mass • Unit is the Atomic Mass Unit (amu) • One twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • Each isotope has its own atomic mass we need the average from percent abundance. (1 amu) carbon atom (1 amu) (12 amu) (1 amu)
Measuring Atomic Mass • Unit is the Atomic Mass Unit (amu) • One twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • Each isotope has its own atomic mass we need the average from percent abundance. (1 amu) carbon atom (1 amu) (12 amu) (1 amu)
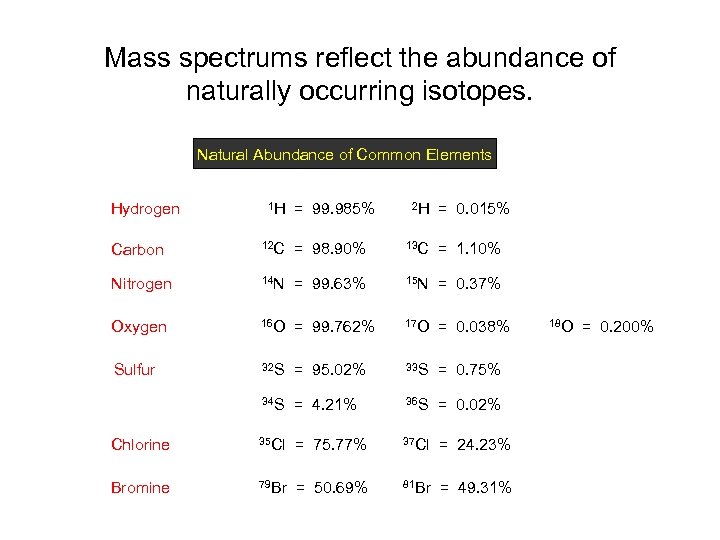 Mass spectrums reflect the abundance of naturally occurring isotopes. Natural Abundance of Common Elements Hydrogen 1 H = 99. 985% 2 H = 0. 015% Carbon 12 C = 98. 90% 13 C = 1. 10% Nitrogen 14 N = 99. 63% 15 N = 0. 37% Oxygen 16 O = 99. 762% 17 O = 0. 038% Sulfur 32 S = 95. 02% 33 S = 0. 75% 34 S = 4. 21% 36 S = 0. 02% Chlorine 35 Cl = 75. 77% 37 Cl = 24. 23% Bromine 79 Br = 50. 69% 81 Br = 49. 31% 18 O = 0. 200%
Mass spectrums reflect the abundance of naturally occurring isotopes. Natural Abundance of Common Elements Hydrogen 1 H = 99. 985% 2 H = 0. 015% Carbon 12 C = 98. 90% 13 C = 1. 10% Nitrogen 14 N = 99. 63% 15 N = 0. 37% Oxygen 16 O = 99. 762% 17 O = 0. 038% Sulfur 32 S = 95. 02% 33 S = 0. 75% 34 S = 4. 21% 36 S = 0. 02% Chlorine 35 Cl = 75. 77% 37 Cl = 24. 23% Bromine 79 Br = 50. 69% 81 Br = 49. 31% 18 O = 0. 200%
 For example…. Methane For carbon 1 in approximately 90 atoms are carbon-13 The rest are carbon-12 the isotope that is 98. 9% abundant. So, for approximately 90 methane molecules… 1 carbon is carbon-13
For example…. Methane For carbon 1 in approximately 90 atoms are carbon-13 The rest are carbon-12 the isotope that is 98. 9% abundant. So, for approximately 90 methane molecules… 1 carbon is carbon-13
 C-13 Where’s Waldo?
C-13 Where’s Waldo?
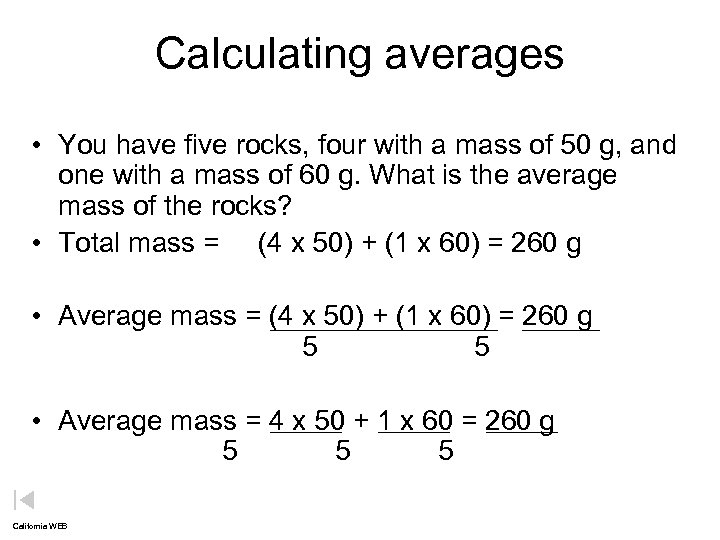 Calculating averages • You have five rocks, four with a mass of 50 g, and one with a mass of 60 g. What is the average mass of the rocks? • Total mass = (4 x 50) + (1 x 60) = 260 g • Average mass = (4 x 50) + (1 x 60) = 260 g 5 • Average mass = 4 x 50 + 1 x 60 = 260 g 5 5 5 California WEB
Calculating averages • You have five rocks, four with a mass of 50 g, and one with a mass of 60 g. What is the average mass of the rocks? • Total mass = (4 x 50) + (1 x 60) = 260 g • Average mass = (4 x 50) + (1 x 60) = 260 g 5 • Average mass = 4 x 50 + 1 x 60 = 260 g 5 5 5 California WEB
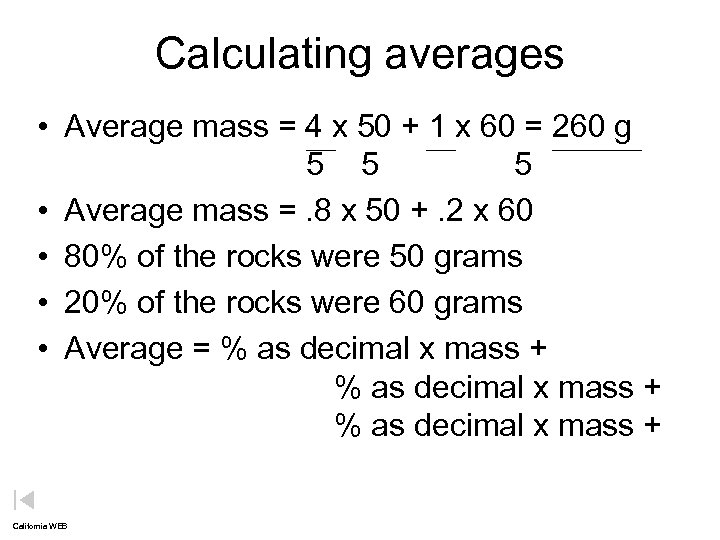 Calculating averages • Average mass = 4 x 50 + 1 x 60 = 260 g 5 5 5 • Average mass =. 8 x 50 +. 2 x 60 • 80% of the rocks were 50 grams • 20% of the rocks were 60 grams • Average = % as decimal x mass + California WEB
Calculating averages • Average mass = 4 x 50 + 1 x 60 = 260 g 5 5 5 • Average mass =. 8 x 50 +. 2 x 60 • 80% of the rocks were 50 grams • 20% of the rocks were 60 grams • Average = % as decimal x mass + California WEB
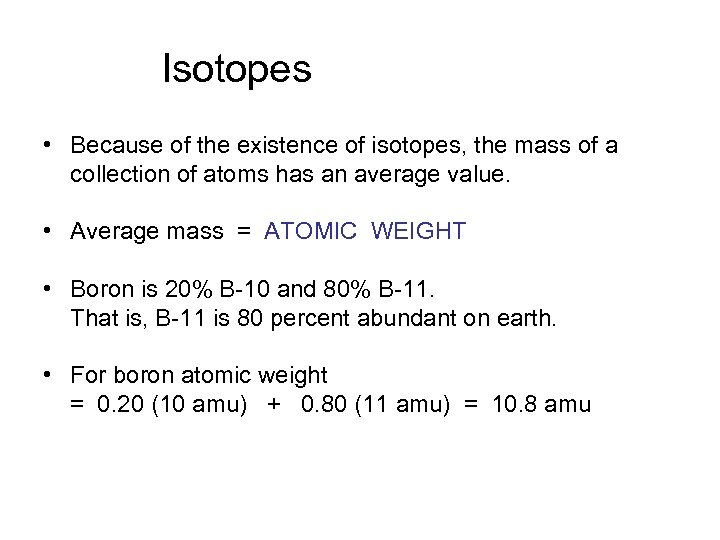 Isotopes • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Boron is 20% B-10 and 80% B-11. That is, B-11 is 80 percent abundant on earth. • For boron atomic weight = 0. 20 (10 amu) + 0. 80 (11 amu) = 10. 8 amu
Isotopes • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Boron is 20% B-10 and 80% B-11. That is, B-11 is 80 percent abundant on earth. • For boron atomic weight = 0. 20 (10 amu) + 0. 80 (11 amu) = 10. 8 amu
 Periodic Table • Dmitri Mendeleev developed the modern periodic table. • Argued that element properties are periodic functions of their atomic weights. • We now know that element properties are periodic functions of their ATOMIC NUMBERS.
Periodic Table • Dmitri Mendeleev developed the modern periodic table. • Argued that element properties are periodic functions of their atomic weights. • We now know that element properties are periodic functions of their ATOMIC NUMBERS.
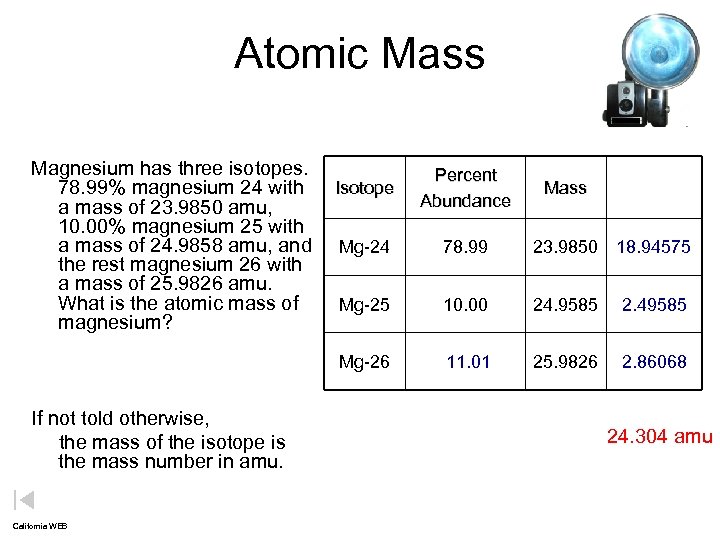 Atomic Mass Magnesium has three isotopes. 78. 99% magnesium 24 with Isotope a mass of 23. 9850 amu, 10. 00% magnesium 25 with a mass of 24. 9858 amu, and Mg-24 the rest magnesium 26 with a mass of 25. 9826 amu. What is the atomic mass of Mg-25 magnesium? Mg-26 If not told otherwise, the mass of the isotope is the mass number in amu. California WEB Percent Abundance Mass 78. 99 23. 9850 18. 94575 10. 00 24. 9585 2. 49585 11. 01 25. 9826 2. 86068 24. 304 amu
Atomic Mass Magnesium has three isotopes. 78. 99% magnesium 24 with Isotope a mass of 23. 9850 amu, 10. 00% magnesium 25 with a mass of 24. 9858 amu, and Mg-24 the rest magnesium 26 with a mass of 25. 9826 amu. What is the atomic mass of Mg-25 magnesium? Mg-26 If not told otherwise, the mass of the isotope is the mass number in amu. California WEB Percent Abundance Mass 78. 99 23. 9850 18. 94575 10. 00 24. 9585 2. 49585 11. 01 25. 9826 2. 86068 24. 304 amu
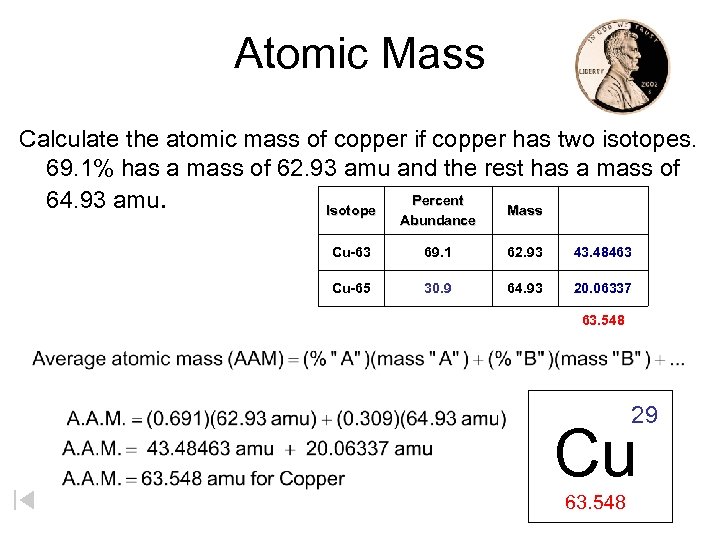 Atomic Mass Calculate the atomic mass of copper if copper has two isotopes. 69. 1% has a mass of 62. 93 amu and the rest has a mass of Percent 64. 93 amu. Isotope Mass Abundance Cu-63 69. 1 62. 93 43. 48463 Cu-65 30. 9 64. 93 20. 06337 63. 548 29 Cu 63. 548
Atomic Mass Calculate the atomic mass of copper if copper has two isotopes. 69. 1% has a mass of 62. 93 amu and the rest has a mass of Percent 64. 93 amu. Isotope Mass Abundance Cu-63 69. 1 62. 93 43. 48463 Cu-65 30. 9 64. 93 20. 06337 63. 548 29 Cu 63. 548
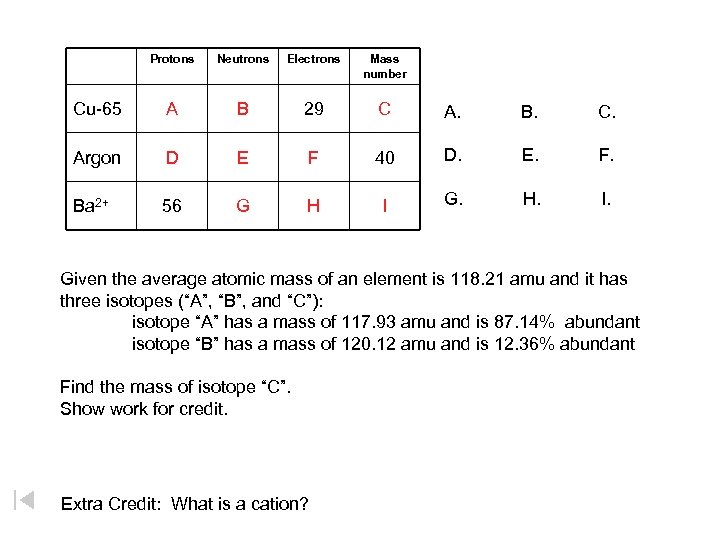 Protons Neutrons Electrons Mass number Cu-65 A B 29 C A. B. C. Argon D E F 40 D. E. F. Ba 2+ 56 G H I G. H. I. Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. Show work for credit. Extra Credit: What is a cation?
Protons Neutrons Electrons Mass number Cu-65 A B 29 C A. B. C. Argon D E F 40 D. E. F. Ba 2+ 56 G H I G. H. I. Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. Show work for credit. Extra Credit: What is a cation?
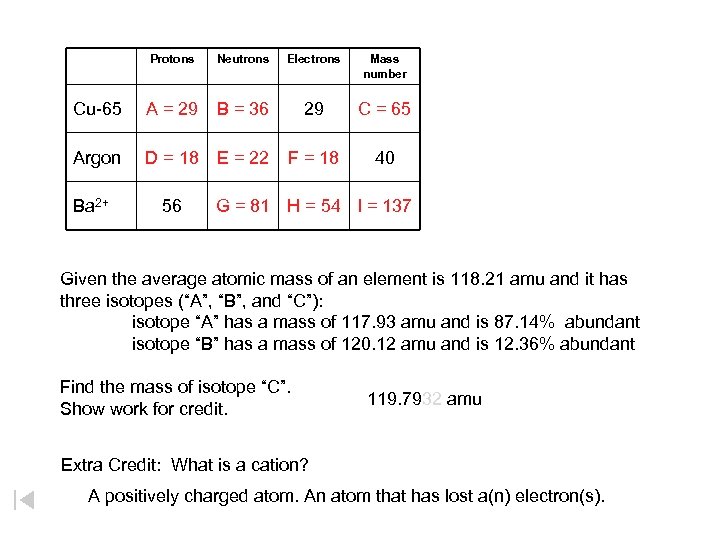 Protons Neutrons Electrons Mass number Cu-65 A = 29 B = 36 29 C = 65 Argon D = 18 E = 22 F = 18 40 Ba 2+ 56 G = 81 H = 54 I = 137 Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. 119. 7932 amu Show work for credit. Extra Credit: What is a cation? A positively charged atom. An atom that has lost a(n) electron(s).
Protons Neutrons Electrons Mass number Cu-65 A = 29 B = 36 29 C = 65 Argon D = 18 E = 22 F = 18 40 Ba 2+ 56 G = 81 H = 54 I = 137 Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. 119. 7932 amu Show work for credit. Extra Credit: What is a cation? A positively charged atom. An atom that has lost a(n) electron(s).
 Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. Show work for credit.
Given the average atomic mass of an element is 118. 21 amu and it has three isotopes (“A”, “B”, and “C”): isotope “A” has a mass of 117. 93 amu and is 87. 14% abundant isotope “B” has a mass of 120. 12 amu and is 12. 36% abundant Find the mass of isotope “C”. Show work for credit.


