b74f7b24af0931fcbc97ca1b22af72d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 ISOM MIS 3150 Data and Info Mgmt: XML Arijit Sengupta
ISOM MIS 3150 Data and Info Mgmt: XML Arijit Sengupta
 Learning Objectives ISOM • Learn what XML is • Learn the various ways in which XML is used • Learn the key companion technologies • See how XML is being used in industry as a meta-language
Learning Objectives ISOM • Learn what XML is • Learn the various ways in which XML is used • Learn the key companion technologies • See how XML is being used in industry as a meta-language
 Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
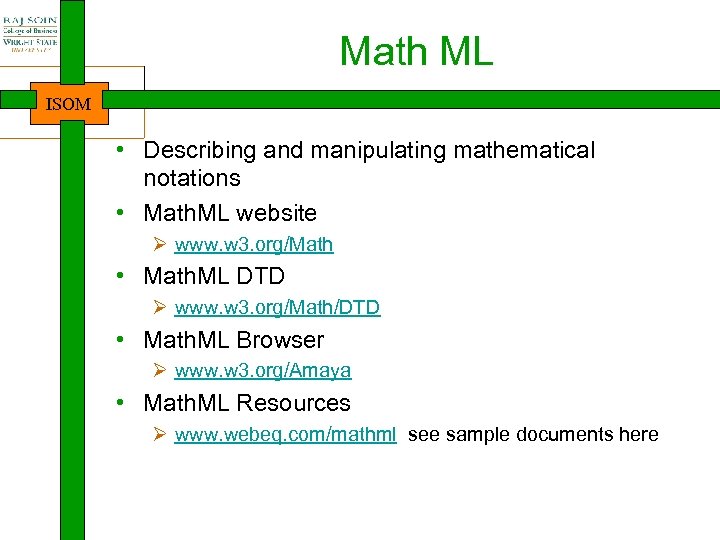
 Overview What is XML? ISOM • • A tag-based meta language Designed for structured data representation Represents data hierarchically (in a tree) Provides context to data (makes it meaningful) Ø Self-describing data • Separates presentation (HTML) from data (XML) • An open W 3 C standard • A subset of SGML Ø vs. HTML, which is an implementation of SGML
Overview What is XML? ISOM • • A tag-based meta language Designed for structured data representation Represents data hierarchically (in a tree) Provides context to data (makes it meaningful) Ø Self-describing data • Separates presentation (HTML) from data (XML) • An open W 3 C standard • A subset of SGML Ø vs. HTML, which is an implementation of SGML
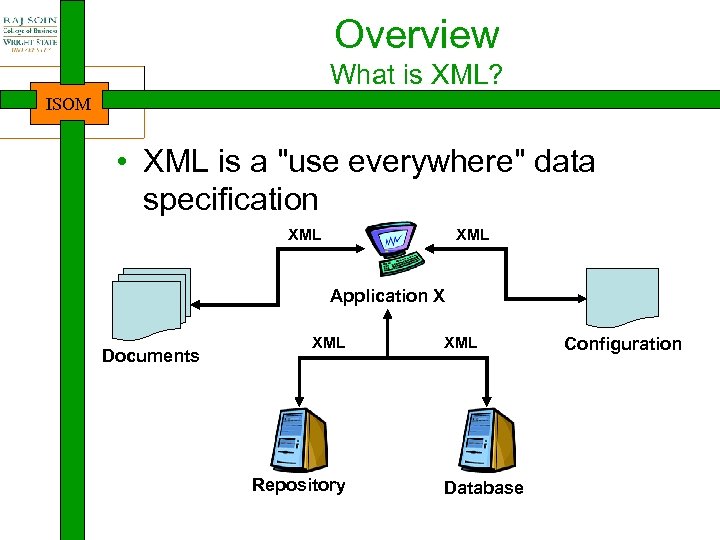 Overview What is XML? ISOM • XML is a "use everywhere" data specification XML Application X Documents XML Repository XML Database Configuration
Overview What is XML? ISOM • XML is a "use everywhere" data specification XML Application X Documents XML Repository XML Database Configuration
 Overview Documents vs. Data ISOM • XML is used to represent two main types of things: ØDocuments • Lots of text with tags to identify and annotate portions of the document ØData • Hierarchical data structures
Overview Documents vs. Data ISOM • XML is used to represent two main types of things: ØDocuments • Lots of text with tags to identify and annotate portions of the document ØData • Hierarchical data structures
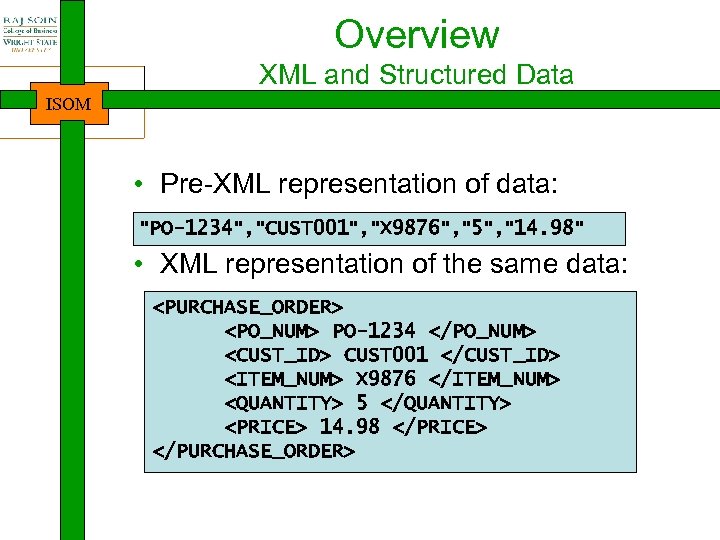 Overview XML and Structured Data ISOM • Pre-XML representation of data: "PO-1234", "CUST 001", "X 9876", "5", "14. 98" • XML representation of the same data:
Overview XML and Structured Data ISOM • Pre-XML representation of data: "PO-1234", "CUST 001", "X 9876", "5", "14. 98" • XML representation of the same data:
 Overview Benefits of XML ISOM • Open W 3 C standard • Representation of data across heterogeneous environments Ø Cross platform Ø Allows for high degree of interoperability • Strict rules Ø Syntax Ø Structure Ø Case sensitive
Overview Benefits of XML ISOM • Open W 3 C standard • Representation of data across heterogeneous environments Ø Cross platform Ø Allows for high degree of interoperability • Strict rules Ø Syntax Ø Structure Ø Case sensitive
 Overview Who Uses XML? ISOM • Submissions by Ø Microsoft Ø IBM Ø Hewlett-Packard Ø Fujitsu Laboratories Ø Sun Microsystems Ø Netscape (AOL), and others… • Technologies using XML Ø SOAP, eb. XML, Biz. Talk, Web. Sphere, many others…
Overview Who Uses XML? ISOM • Submissions by Ø Microsoft Ø IBM Ø Hewlett-Packard Ø Fujitsu Laboratories Ø Sun Microsystems Ø Netscape (AOL), and others… • Technologies using XML Ø SOAP, eb. XML, Biz. Talk, Web. Sphere, many others…
 Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
 Syntax and Structure Components of an XML Document ISOM • Elements Ø Each element has a beginning and ending tag •
Syntax and Structure Components of an XML Document ISOM • Elements Ø Each element has a beginning and ending tag •
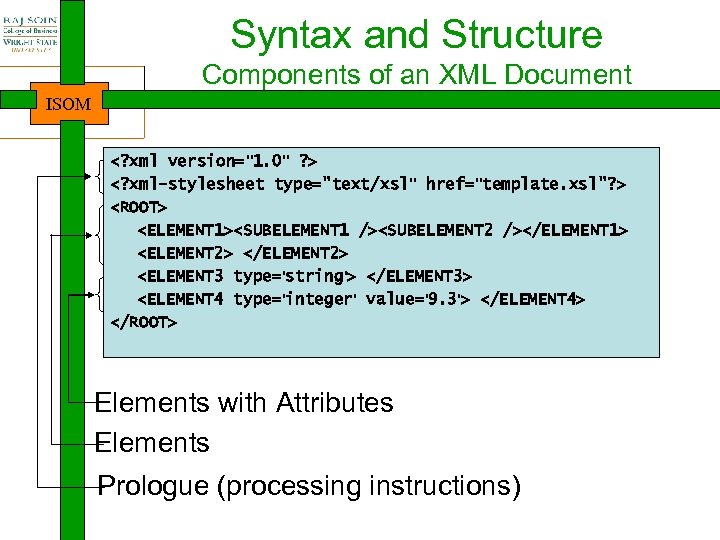 Syntax and Structure Components of an XML Document ISOM
Syntax and Structure Components of an XML Document ISOM
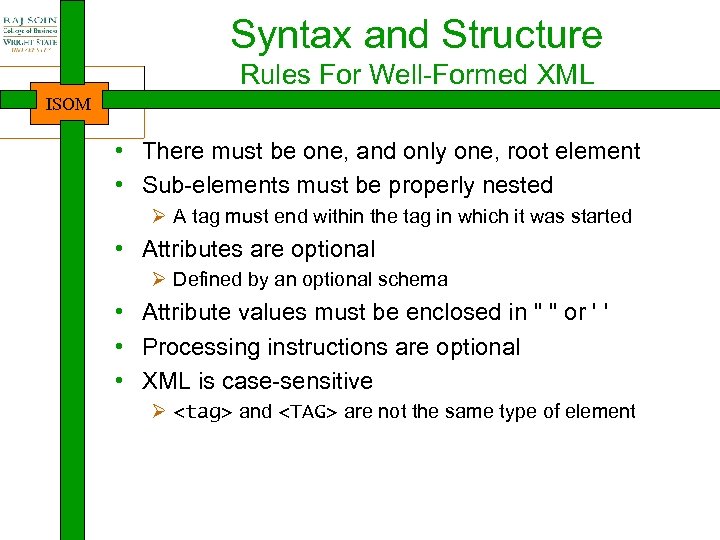 Syntax and Structure Rules For Well-Formed XML ISOM • There must be one, and only one, root element • Sub-elements must be properly nested Ø A tag must end within the tag in which it was started • Attributes are optional Ø Defined by an optional schema • Attribute values must be enclosed in " " or ' ' • Processing instructions are optional • XML is case-sensitive Ø
Syntax and Structure Rules For Well-Formed XML ISOM • There must be one, and only one, root element • Sub-elements must be properly nested Ø A tag must end within the tag in which it was started • Attributes are optional Ø Defined by an optional schema • Attribute values must be enclosed in " " or ' ' • Processing instructions are optional • XML is case-sensitive Ø
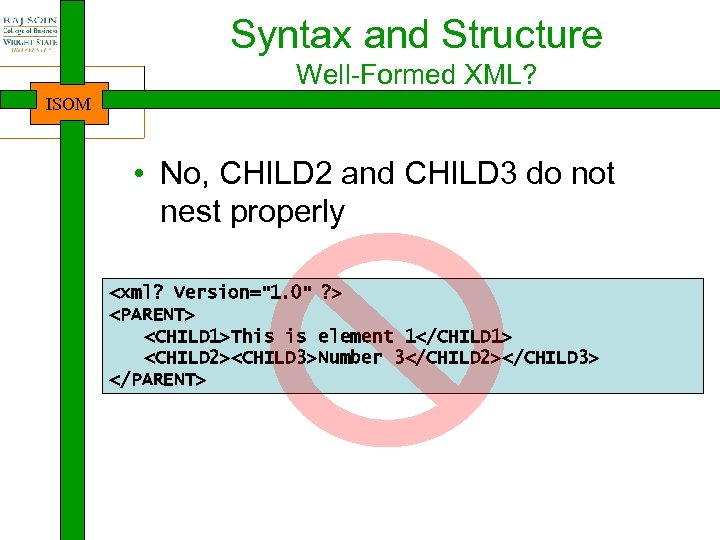 Syntax and Structure Well-Formed XML? ISOM • No, CHILD 2 and CHILD 3 do not nest properly
Syntax and Structure Well-Formed XML? ISOM • No, CHILD 2 and CHILD 3 do not nest properly
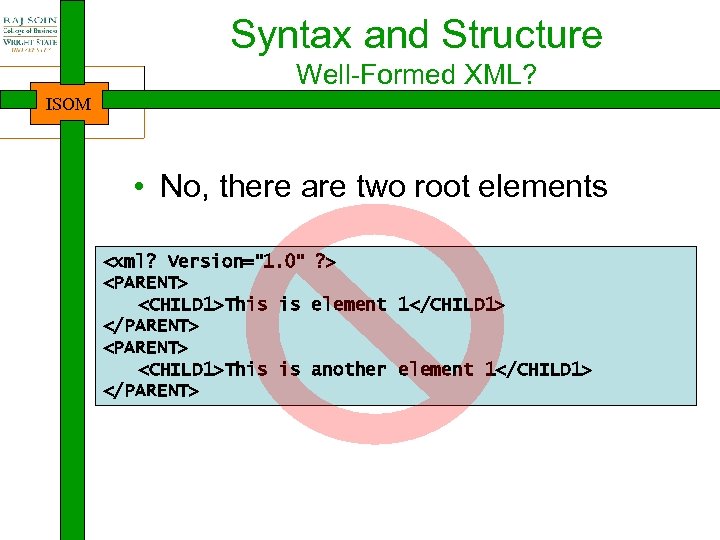 Syntax and Structure Well-Formed XML? ISOM • No, there are two root elements
Syntax and Structure Well-Formed XML? ISOM • No, there are two root elements
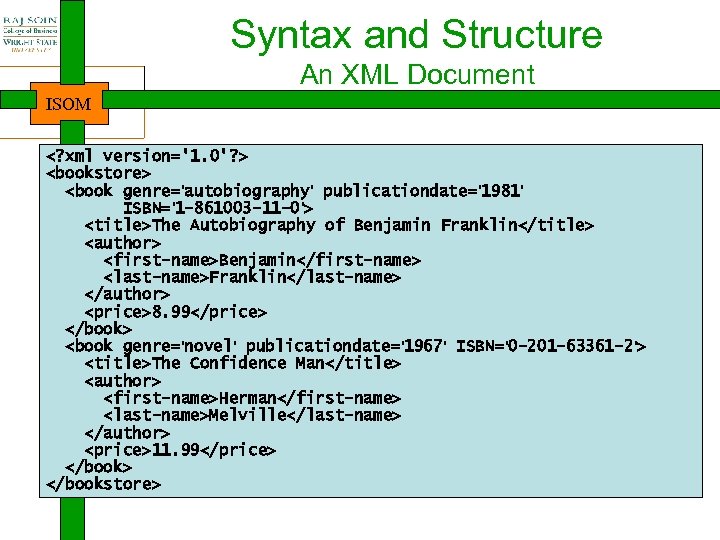 Syntax and Structure An XML Document ISOM
Syntax and Structure An XML Document ISOM
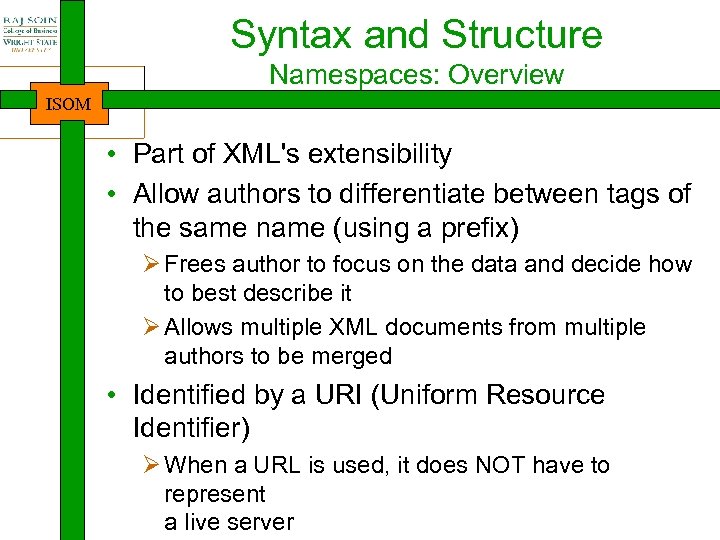 Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Overview ISOM • Part of XML's extensibility • Allow authors to differentiate between tags of the same name (using a prefix) Ø Frees author to focus on the data and decide how to best describe it Ø Allows multiple XML documents from multiple authors to be merged • Identified by a URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) Ø When a URL is used, it does NOT have to represent a live server
Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Overview ISOM • Part of XML's extensibility • Allow authors to differentiate between tags of the same name (using a prefix) Ø Frees author to focus on the data and decide how to best describe it Ø Allows multiple XML documents from multiple authors to be merged • Identified by a URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) Ø When a URL is used, it does NOT have to represent a live server
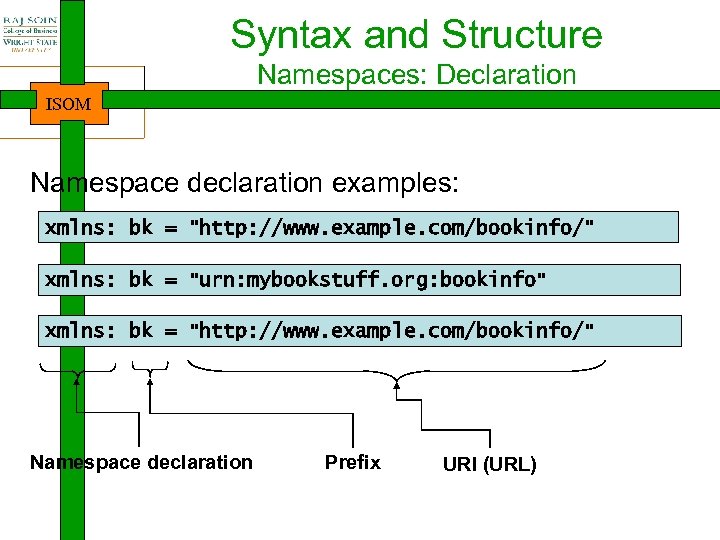 Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Declaration ISOM Namespace declaration examples: xmlns: bk = "http: //www. example. com/bookinfo/" xmlns: bk = "urn: mybookstuff. org: bookinfo" xmlns: bk = "http: //www. example. com/bookinfo/" Namespace declaration Prefix URI (URL)
Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Declaration ISOM Namespace declaration examples: xmlns: bk = "http: //www. example. com/bookinfo/" xmlns: bk = "urn: mybookstuff. org: bookinfo" xmlns: bk = "http: //www. example. com/bookinfo/" Namespace declaration Prefix URI (URL)
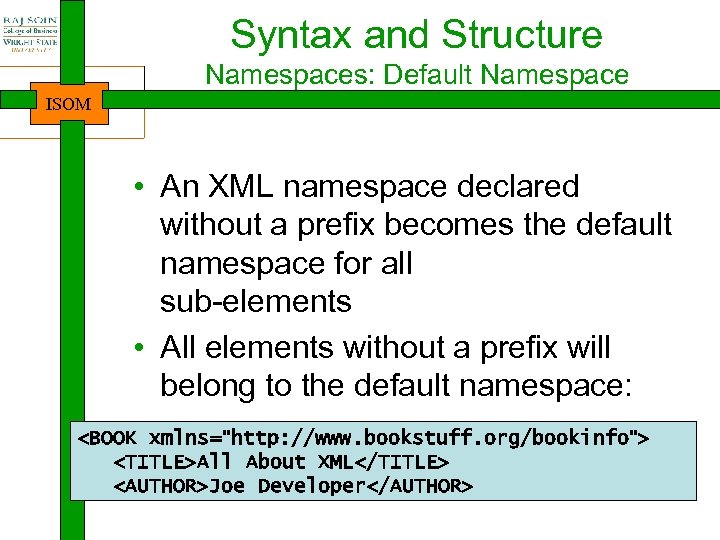 Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Default Namespace ISOM • An XML namespace declared without a prefix becomes the default namespace for all sub-elements • All elements without a prefix will belong to the default namespace:
Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Default Namespace ISOM • An XML namespace declared without a prefix becomes the default namespace for all sub-elements • All elements without a prefix will belong to the default namespace:
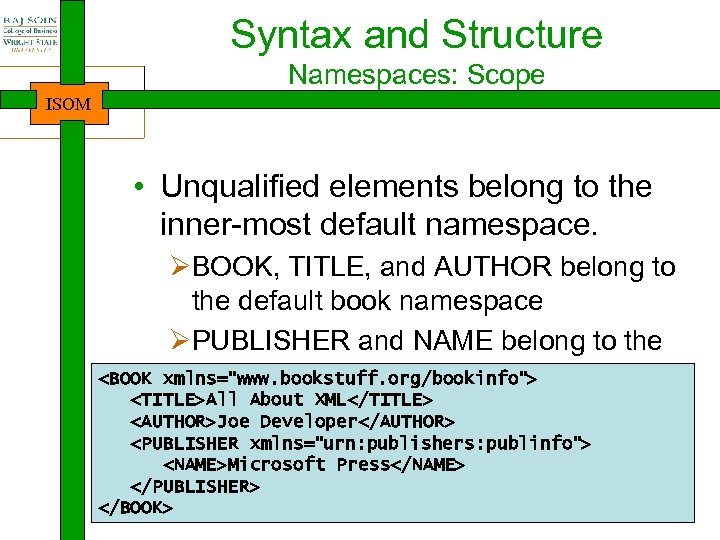 Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Scope ISOM • Unqualified elements belong to the inner-most default namespace. ØBOOK, TITLE, and AUTHOR belong to the default book namespace ØPUBLISHER and NAME belong to the default publisher namespace xmlns="www. bookstuff. org/bookinfo">
Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Scope ISOM • Unqualified elements belong to the inner-most default namespace. ØBOOK, TITLE, and AUTHOR belong to the default book namespace ØPUBLISHER and NAME belong to the default publisher namespace xmlns="www. bookstuff. org/bookinfo">
 Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Attributes ISOM • Unqualified attributes do NOT belong to any namespace ØEven if there is a default namespace • This differs from elements, which belong to the default namespace
Syntax and Structure Namespaces: Attributes ISOM • Unqualified attributes do NOT belong to any namespace ØEven if there is a default namespace • This differs from elements, which belong to the default namespace
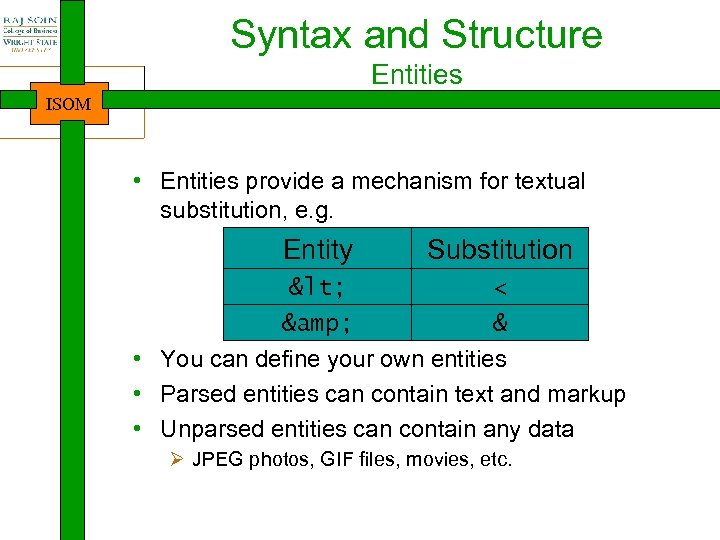 Syntax and Structure Entities ISOM • Entities provide a mechanism for textual substitution, e. g. Entity Substitution < & < & • You can define your own entities • Parsed entities can contain text and markup • Unparsed entities can contain any data Ø JPEG photos, GIF files, movies, etc.
Syntax and Structure Entities ISOM • Entities provide a mechanism for textual substitution, e. g. Entity Substitution < & < & • You can define your own entities • Parsed entities can contain text and markup • Unparsed entities can contain any data Ø JPEG photos, GIF files, movies, etc.
 Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
Agenda ISOM • • Overview Syntax and Structure The XML Alphabet Soup XML as a meta-language
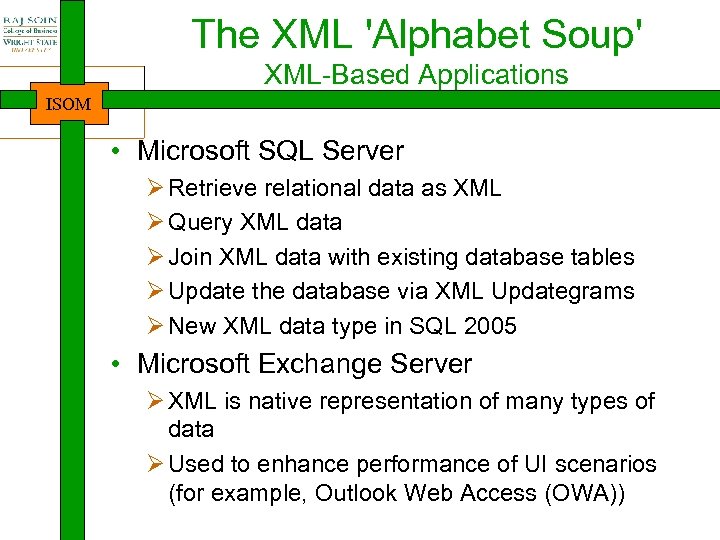
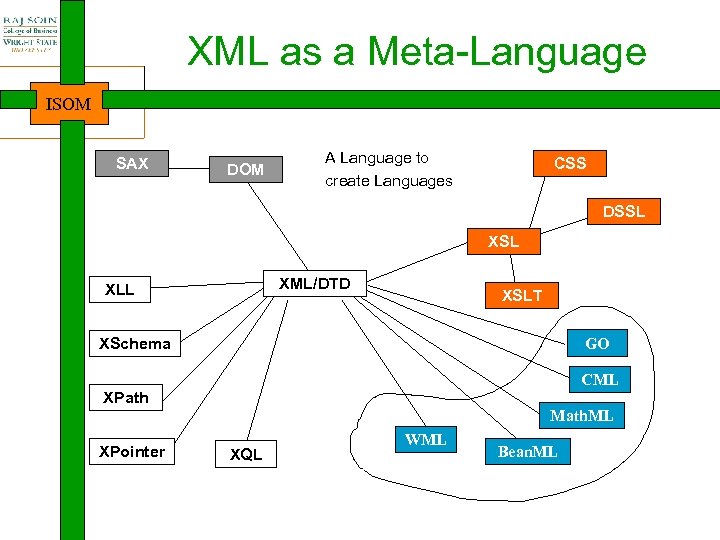
 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM • XML itself is fairly simple • Most of the learning curve is knowing about all of the related technologies
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM • XML itself is fairly simple • Most of the learning curve is knowing about all of the related technologies
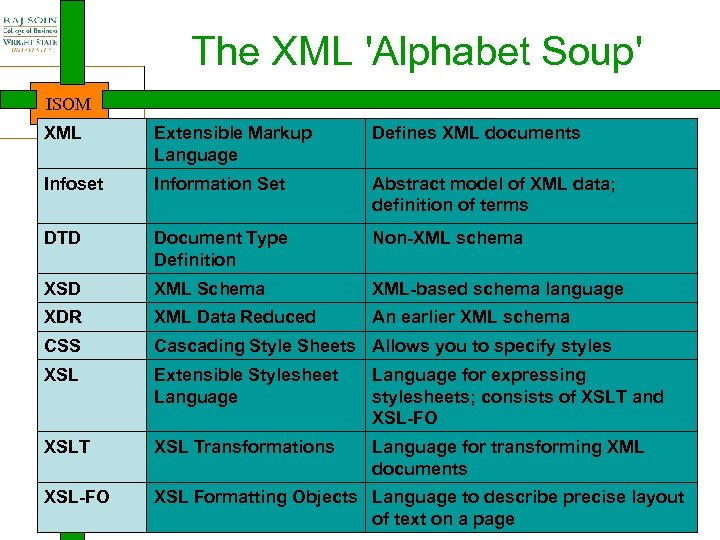 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM XML Extensible Markup Language Defines XML documents Infoset Information Set Abstract model of XML data; definition of terms DTD Document Type Definition Non-XML schema XSD XML Schema XML-based schema language XDR XML Data Reduced An earlier XML schema CSS Cascading Style Sheets Allows you to specify styles XSL Extensible Stylesheet Language for expressing stylesheets; consists of XSLT and XSL-FO XSLT XSL Transformations Language for transforming XML documents XSL-FO XSL Formatting Objects Language to describe precise layout of text on a page
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM XML Extensible Markup Language Defines XML documents Infoset Information Set Abstract model of XML data; definition of terms DTD Document Type Definition Non-XML schema XSD XML Schema XML-based schema language XDR XML Data Reduced An earlier XML schema CSS Cascading Style Sheets Allows you to specify styles XSL Extensible Stylesheet Language for expressing stylesheets; consists of XSLT and XSL-FO XSLT XSL Transformations Language for transforming XML documents XSL-FO XSL Formatting Objects Language to describe precise layout of text on a page
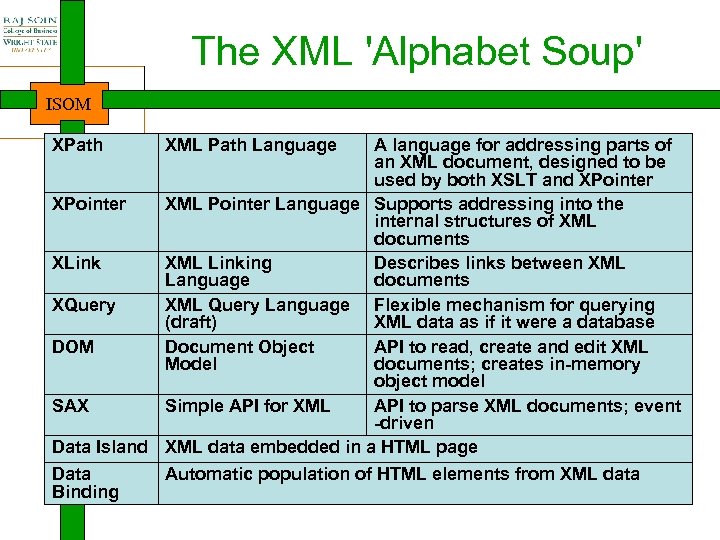 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM XPath XML Path Language A language for addressing parts of an XML document, designed to be used by both XSLT and XPointer XML Pointer Language Supports addressing into the internal structures of XML documents XLink XML Linking Describes links between XML Language documents XQuery XML Query Language Flexible mechanism for querying (draft) XML data as if it were a database DOM Document Object API to read, create and edit XML Model documents; creates in-memory object model SAX Simple API for XML API to parse XML documents; event -driven Data Island XML data embedded in a HTML page Data Automatic population of HTML elements from XML data Binding
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' ISOM XPath XML Path Language A language for addressing parts of an XML document, designed to be used by both XSLT and XPointer XML Pointer Language Supports addressing into the internal structures of XML documents XLink XML Linking Describes links between XML Language documents XQuery XML Query Language Flexible mechanism for querying (draft) XML data as if it were a database DOM Document Object API to read, create and edit XML Model documents; creates in-memory object model SAX Simple API for XML API to parse XML documents; event -driven Data Island XML data embedded in a HTML page Data Automatic population of HTML elements from XML data Binding
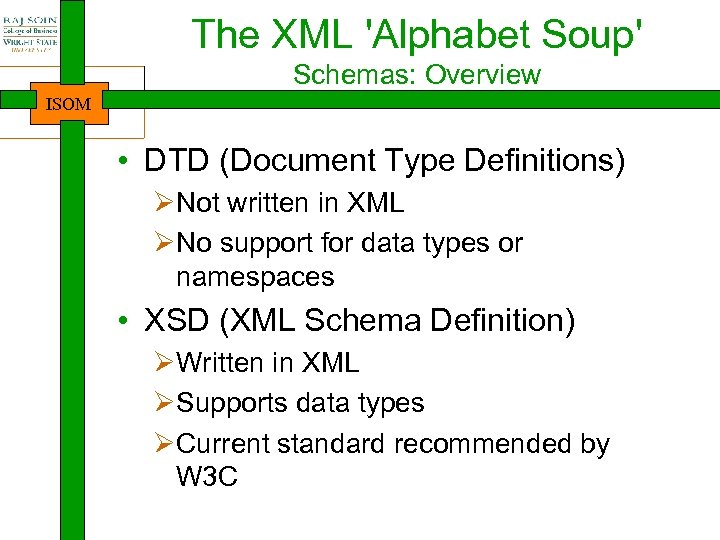 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Overview ISOM • DTD (Document Type Definitions) ØNot written in XML ØNo support for data types or namespaces • XSD (XML Schema Definition) ØWritten in XML ØSupports data types ØCurrent standard recommended by W 3 C
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Overview ISOM • DTD (Document Type Definitions) ØNot written in XML ØNo support for data types or namespaces • XSD (XML Schema Definition) ØWritten in XML ØSupports data types ØCurrent standard recommended by W 3 C
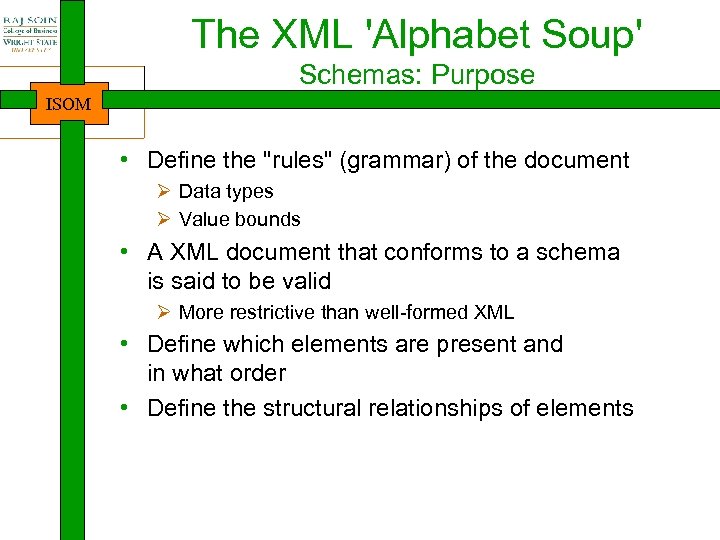 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Purpose ISOM • Define the "rules" (grammar) of the document Ø Data types Ø Value bounds • A XML document that conforms to a schema is said to be valid Ø More restrictive than well-formed XML • Define which elements are present and in what order • Define the structural relationships of elements
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Purpose ISOM • Define the "rules" (grammar) of the document Ø Data types Ø Value bounds • A XML document that conforms to a schema is said to be valid Ø More restrictive than well-formed XML • Define which elements are present and in what order • Define the structural relationships of elements
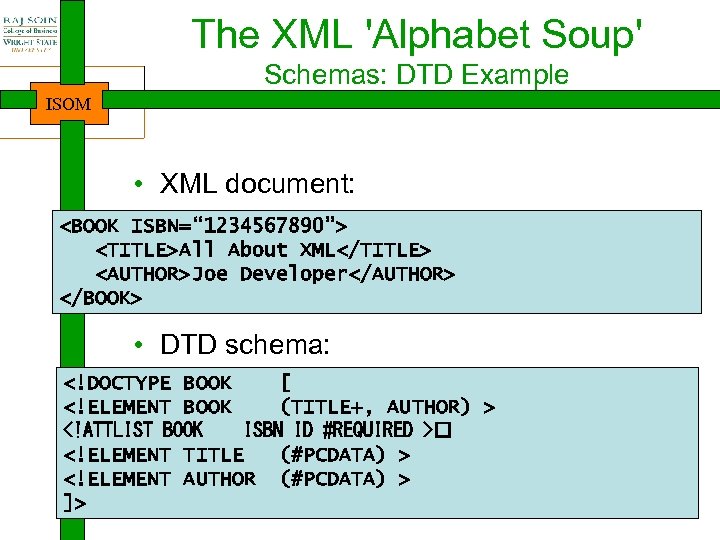 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: DTD Example ISOM • XML document:
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: DTD Example ISOM • XML document:
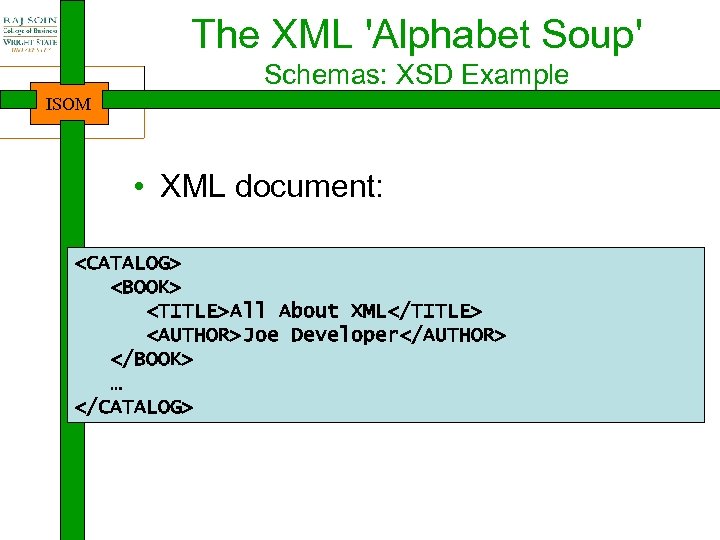 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: XSD Example ISOM • XML document:
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: XSD Example ISOM • XML document:
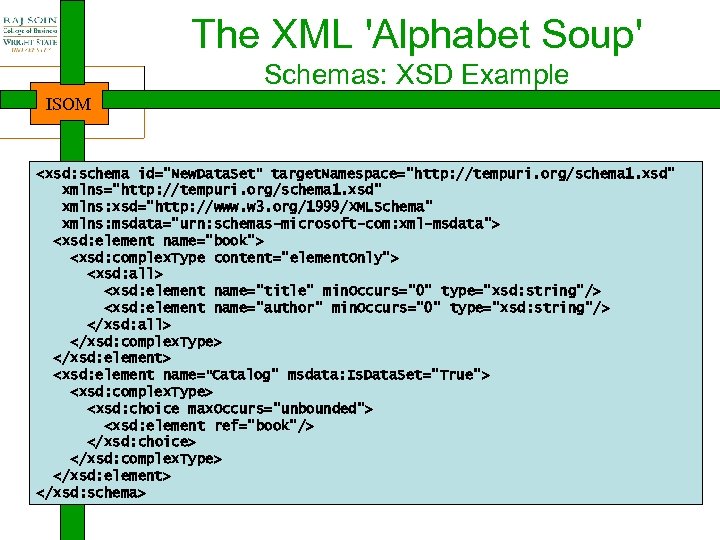 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: XSD Example ISOM
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: XSD Example ISOM
 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Why You Should Use XSD ISOM • Newest W 3 C Standard • Broad support for data types • Reusable "components" Ø Simple data types Ø Complex data types • • • Extensible Inheritance support Namespace support Ability to map to relational database tables XSD support in Visual Studio. NET
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Schemas: Why You Should Use XSD ISOM • Newest W 3 C Standard • Broad support for data types • Reusable "components" Ø Simple data types Ø Complex data types • • • Extensible Inheritance support Namespace support Ability to map to relational database tables XSD support in Visual Studio. NET
 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: XSL ISOM • Language for expressing document styles • Specifies the presentation of XML ØMore powerful than CSS • Consists of: ØXSLT ØXPath ØXSL Formatting Objects (XSL-FO)
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: XSL ISOM • Language for expressing document styles • Specifies the presentation of XML ØMore powerful than CSS • Consists of: ØXSLT ØXPath ØXSL Formatting Objects (XSL-FO)
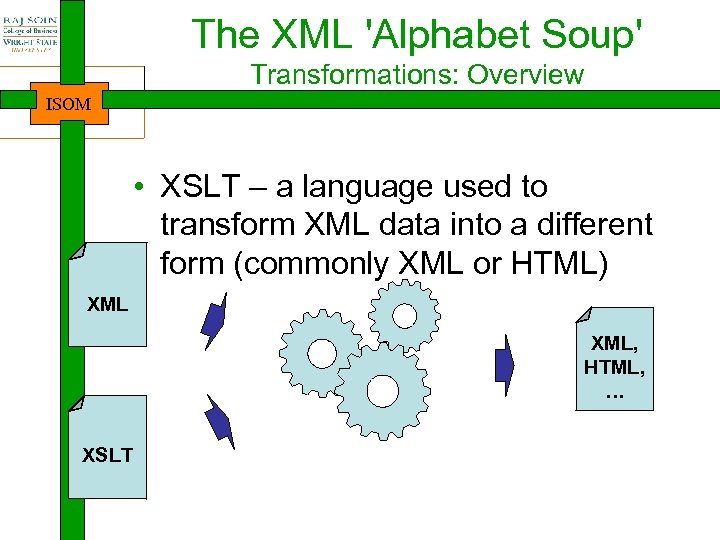 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: Overview ISOM • XSLT – a language used to transform XML data into a different form (commonly XML or HTML) XML, HTML, … XSLT
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: Overview ISOM • XSLT – a language used to transform XML data into a different form (commonly XML or HTML) XML, HTML, … XSLT
 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: XSLT ISOM • The language used for converting XML documents into other forms • Describes how the document is transformed • Expressed as an XML document (. xsl) • Template rules Ø Patterns match nodes in source document Ø Templates instantiated to form part of result document • Uses XPath for querying, sorting, etc.
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Transformations: XSLT ISOM • The language used for converting XML documents into other forms • Describes how the document is transformed • Expressed as an XML document (. xsl) • Template rules Ø Patterns match nodes in source document Ø Templates instantiated to form part of result document • Uses XPath for querying, sorting, etc.
 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath (XML Path Language) ISOM • General purpose query language for identifying nodes in an XML document • Declarative (vs. procedural) • Contextual – the results depend on current node • Supports standard comparison, Boolean and mathematical operators (=, <, and, or, *, +, etc. )
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath (XML Path Language) ISOM • General purpose query language for identifying nodes in an XML document • Declarative (vs. procedural) • Contextual – the results depend on current node • Supports standard comparison, Boolean and mathematical operators (=, <, and, or, *, +, etc. )
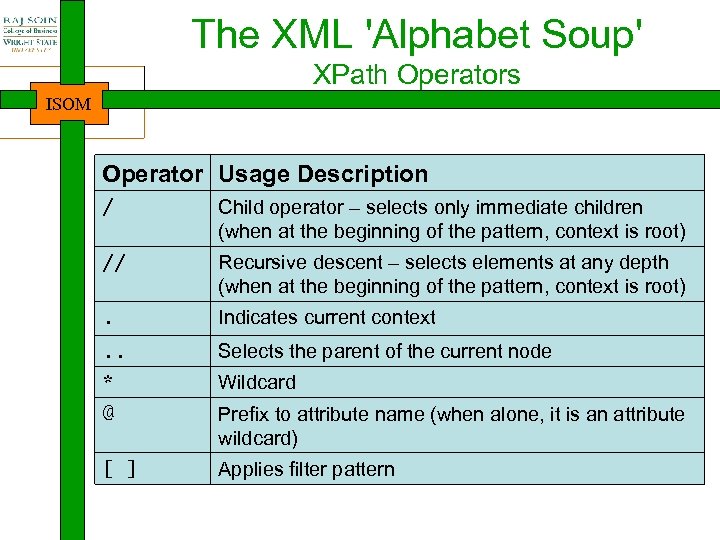 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath Operators ISOM Operator Usage Description / Child operator – selects only immediate children (when at the beginning of the pattern, context is root) // Recursive descent – selects elements at any depth (when at the beginning of the pattern, context is root) . Indicates current context . . Selects the parent of the current node * Wildcard @ Prefix to attribute name (when alone, it is an attribute wildcard) [ ] Applies filter pattern
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath Operators ISOM Operator Usage Description / Child operator – selects only immediate children (when at the beginning of the pattern, context is root) // Recursive descent – selects elements at any depth (when at the beginning of the pattern, context is root) . Indicates current context . . Selects the parent of the current node * Wildcard @ Prefix to attribute name (when alone, it is an attribute wildcard) [ ] Applies filter pattern
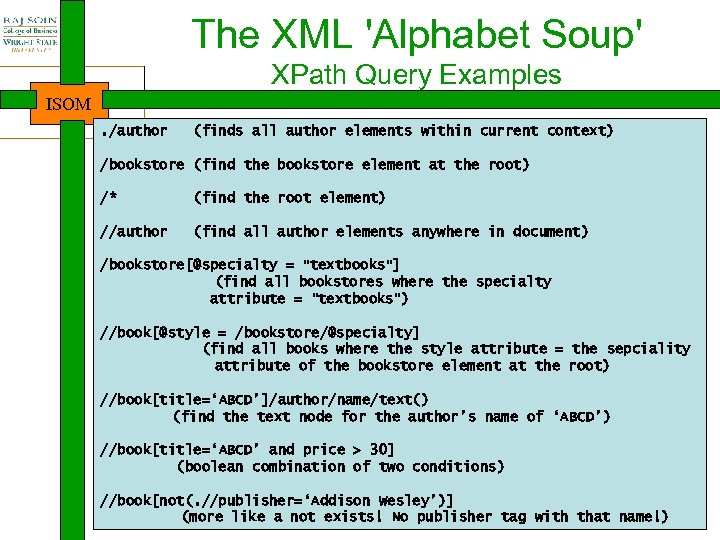 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath Query Examples ISOM. /author (finds all author elements within current context) /bookstore (find the bookstore element at the root) /* (find the root element) //author (find all author elements anywhere in document) /bookstore[@specialty = "textbooks"] (find all bookstores where the specialty attribute = "textbooks") //book[@style = /bookstore/@specialty] (find all books where the style attribute = the sepciality attribute of the bookstore element at the root) //book[title=‘ABCD’]/author/name/text() (find the text node for the author’s name of ‘ABCD’) //book[title=‘ABCD’ and price > 30] (boolean combination of two conditions) //book[not(. //publisher=‘Addison Wesley’)] (more like a not exists! No publisher tag with that name!)
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' XPath Query Examples ISOM. /author (finds all author elements within current context) /bookstore (find the bookstore element at the root) /* (find the root element) //author (find all author elements anywhere in document) /bookstore[@specialty = "textbooks"] (find all bookstores where the specialty attribute = "textbooks") //book[@style = /bookstore/@specialty] (find all books where the style attribute = the sepciality attribute of the bookstore element at the root) //book[title=‘ABCD’]/author/name/text() (find the text node for the author’s name of ‘ABCD’) //book[title=‘ABCD’ and price > 30] (boolean combination of two conditions) //book[not(. //publisher=‘Addison Wesley’)] (more like a not exists! No publisher tag with that name!)
![More XPath Examples ISOM Path Expression Result /bookstore/book[1] Selects the first book element that More XPath Examples ISOM Path Expression Result /bookstore/book[1] Selects the first book element that](https://present5.com/presentation/b74f7b24af0931fcbc97ca1b22af72d0/image-41.jpg) More XPath Examples ISOM Path Expression Result /bookstore/book[1] Selects the first book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[last()] Selects the last book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[last()-1] Selects the last but one book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[position()<3] Selects the first two book elements that are children of the bookstore element //title[@lang] Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang //title[@lang='eng'] Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang with a value of 'eng' /bookstore/book[price>35. 00] Selects all the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35. 00 /bookstore/book[price>35. 00]/title Selects all the title elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35. 00
More XPath Examples ISOM Path Expression Result /bookstore/book[1] Selects the first book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[last()] Selects the last book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[last()-1] Selects the last but one book element that is the child of the bookstore element /bookstore/book[position()<3] Selects the first two book elements that are children of the bookstore element //title[@lang] Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang //title[@lang='eng'] Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang with a value of 'eng' /bookstore/book[price>35. 00] Selects all the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35. 00 /bookstore/book[price>35. 00]/title Selects all the title elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35. 00
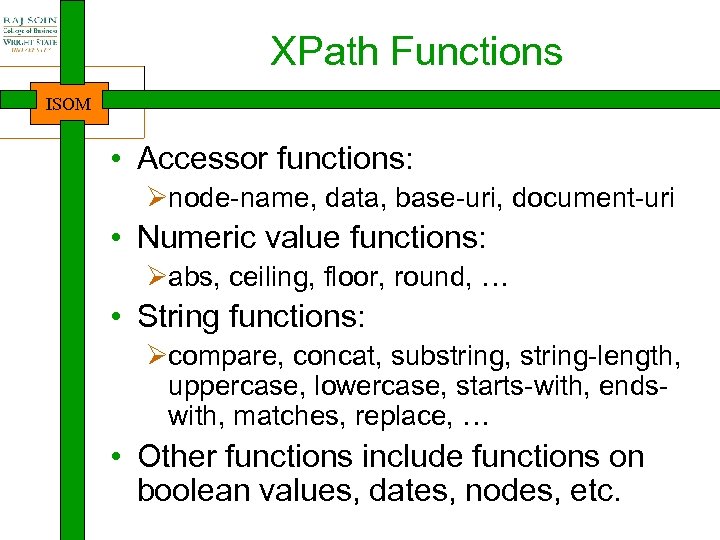 XPath Functions ISOM • Accessor functions: Ønode-name, data, base-uri, document-uri • Numeric value functions: Øabs, ceiling, floor, round, … • String functions: Øcompare, concat, substring, string-length, uppercase, lowercase, starts-with, endswith, matches, replace, … • Other functions include functions on boolean values, dates, nodes, etc.
XPath Functions ISOM • Accessor functions: Ønode-name, data, base-uri, document-uri • Numeric value functions: Øabs, ceiling, floor, round, … • String functions: Øcompare, concat, substring, string-length, uppercase, lowercase, starts-with, endswith, matches, replace, … • Other functions include functions on boolean values, dates, nodes, etc.
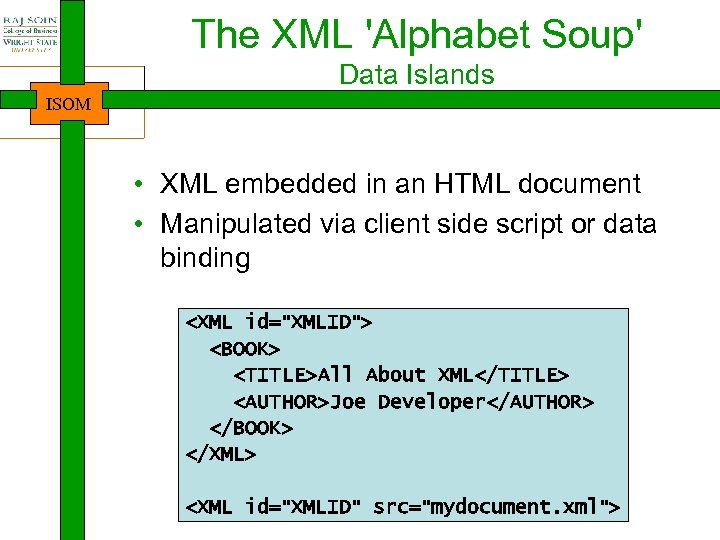 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Data Islands ISOM • XML embedded in an HTML document • Manipulated via client side script or data binding
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Data Islands ISOM • XML embedded in an HTML document • Manipulated via client side script or data binding
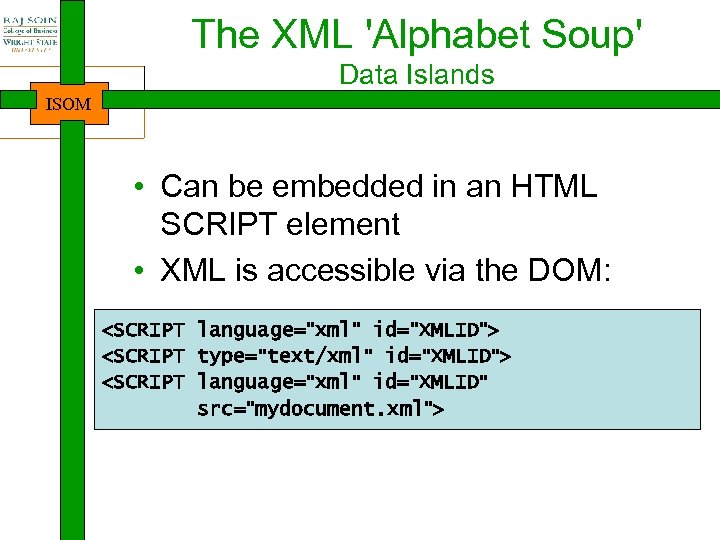 The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Data Islands ISOM • Can be embedded in an HTML SCRIPT element • XML is accessible via the DOM:
The XML 'Alphabet Soup' Data Islands ISOM • Can be embedded in an HTML SCRIPT element • XML is accessible via the DOM: