2ca9d75a6a1b246469ce1e2f1033247d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization The mi. RNA Revolution mi. RNA biogenesis, function, regulation, and analysis Eric Lader, Ph. D Senior Director, R&D eric. lader@qiagen. com - 1 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization The mi. RNA Revolution mi. RNA biogenesis, function, regulation, and analysis Eric Lader, Ph. D Senior Director, R&D eric. lader@qiagen. com - 1 - Sample & Assay Technologies
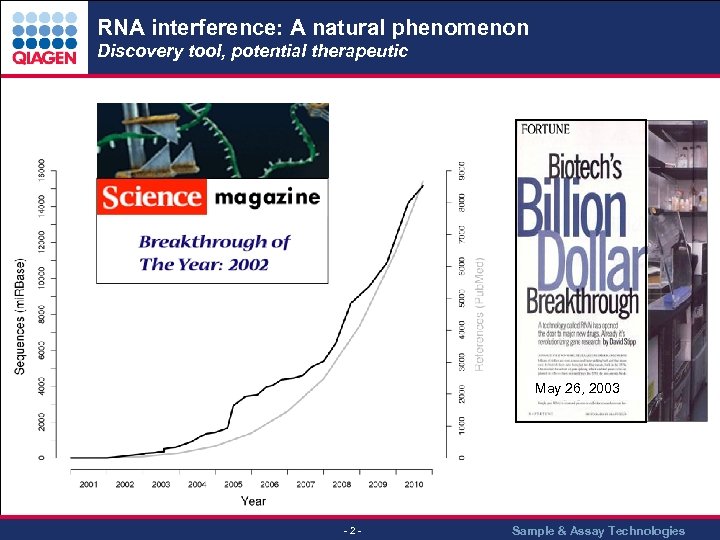 RNA interference: A natural phenomenon Discovery tool, potential therapeutic May 26, 2003 - 2 - Sample & Assay Technologies
RNA interference: A natural phenomenon Discovery tool, potential therapeutic May 26, 2003 - 2 - Sample & Assay Technologies
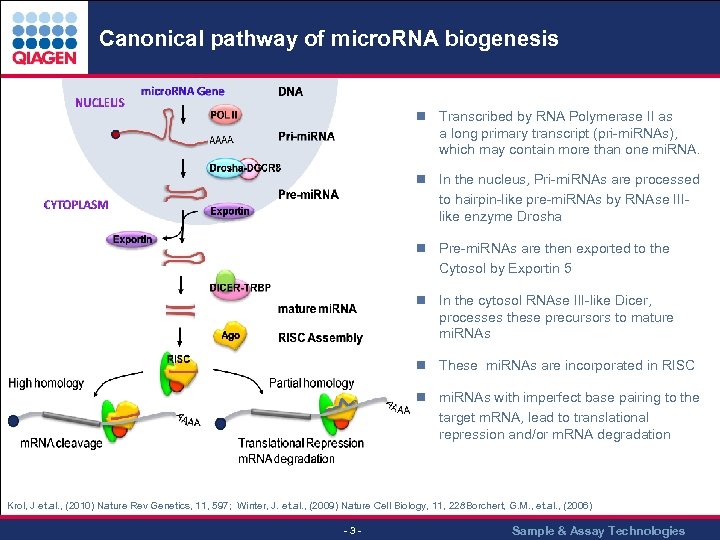 Canonical pathway of micro. RNA biogenesis n Transcribed by RNA Polymerase II as a long primary transcript (pri-mi. RNAs), which may contain more than one mi. RNA. n In the nucleus, Pri-mi. RNAs are processed to hairpin-like pre-mi. RNAs by RNAse IIIlike enzyme Drosha n Pre-mi. RNAs are then exported to the Cytosol by Exportin 5 n In the cytosol RNAse III-like Dicer, processes these precursors to mature mi. RNAs n These mi. RNAs are incorporated in RISC n mi. RNAs with imperfect base pairing to the target m. RNA, lead to translational repression and/or m. RNA degradation Krol, J et. al. , (2010) Nature Rev Genetics, 11, 597; Winter, J. et. al. , (2009) Nature Cell Biology, 11, 228 orchert, G. M. , et. al. , (2006) B - 3 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Canonical pathway of micro. RNA biogenesis n Transcribed by RNA Polymerase II as a long primary transcript (pri-mi. RNAs), which may contain more than one mi. RNA. n In the nucleus, Pri-mi. RNAs are processed to hairpin-like pre-mi. RNAs by RNAse IIIlike enzyme Drosha n Pre-mi. RNAs are then exported to the Cytosol by Exportin 5 n In the cytosol RNAse III-like Dicer, processes these precursors to mature mi. RNAs n These mi. RNAs are incorporated in RISC n mi. RNAs with imperfect base pairing to the target m. RNA, lead to translational repression and/or m. RNA degradation Krol, J et. al. , (2010) Nature Rev Genetics, 11, 597; Winter, J. et. al. , (2009) Nature Cell Biology, 11, 228 orchert, G. M. , et. al. , (2006) B - 3 - Sample & Assay Technologies
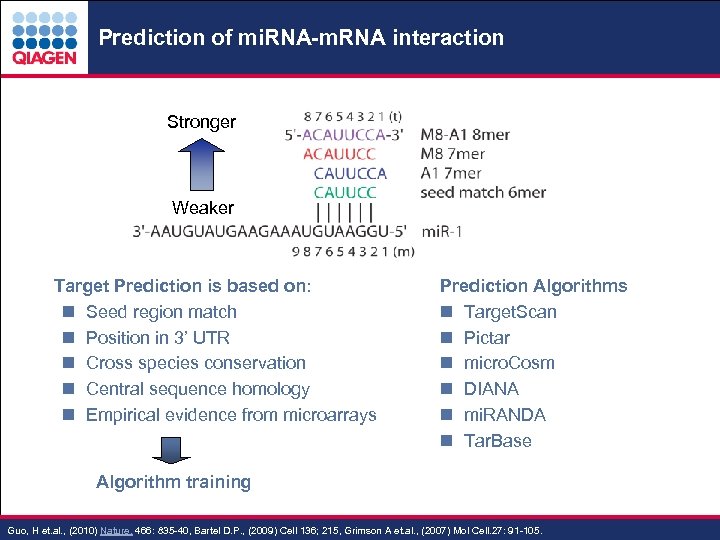 Prediction of mi. RNA-m. RNA interaction Stronger Weaker . Target Prediction is based on: n Seed region match n Position in 3’ UTR n Cross species conservation n Central sequence homology n Empirical evidence from microarrays Prediction Algorithms n Target. Scan n Pictar n micro. Cosm n DIANA n mi. RANDA n Tar. Base Algorithm training - 4 Guo, H et. al. , (2010) Nature. 466: 835 -40, Bartel D. P. , (2009) Cell 136; 215, Grimson A et. al. , (2007) Mol Cell. 27: 91 -105. Sample & Assay Technologies
Prediction of mi. RNA-m. RNA interaction Stronger Weaker . Target Prediction is based on: n Seed region match n Position in 3’ UTR n Cross species conservation n Central sequence homology n Empirical evidence from microarrays Prediction Algorithms n Target. Scan n Pictar n micro. Cosm n DIANA n mi. RANDA n Tar. Base Algorithm training - 4 Guo, H et. al. , (2010) Nature. 466: 835 -40, Bartel D. P. , (2009) Cell 136; 215, Grimson A et. al. , (2007) Mol Cell. 27: 91 -105. Sample & Assay Technologies
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Genomics Generating Diversity in the mi. RNome - 5 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Genomics Generating Diversity in the mi. RNome - 5 - Sample & Assay Technologies
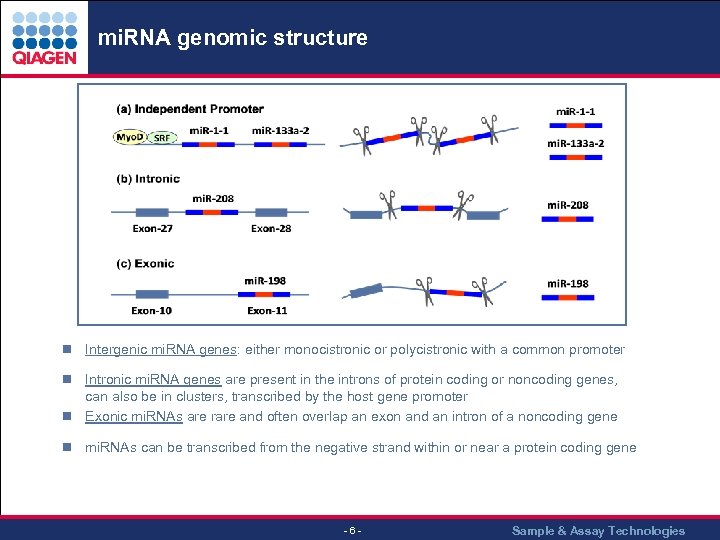 mi. RNA genomic structure n Intergenic mi. RNA genes: either monocistronic or polycistronic with a common promoter n Intronic mi. RNA genes are present in the introns of protein coding or noncoding genes, can also be in clusters, transcribed by the host gene promoter n Exonic mi. RNAs are rare and often overlap an exon and an intron of a noncoding gene n mi. RNAs can be transcribed from the negative strand within or near a protein coding gene - 6 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNA genomic structure n Intergenic mi. RNA genes: either monocistronic or polycistronic with a common promoter n Intronic mi. RNA genes are present in the introns of protein coding or noncoding genes, can also be in clusters, transcribed by the host gene promoter n Exonic mi. RNAs are rare and often overlap an exon and an intron of a noncoding gene n mi. RNAs can be transcribed from the negative strand within or near a protein coding gene - 6 - Sample & Assay Technologies
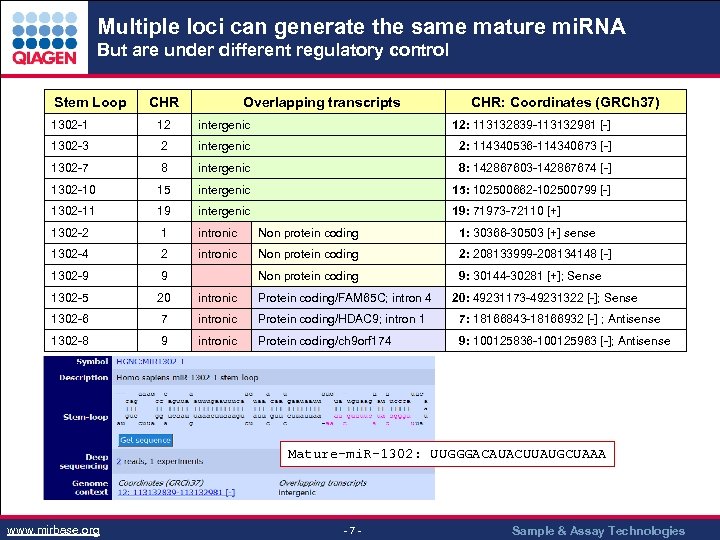 Multiple loci can generate the same mature mi. RNA But are under different regulatory control Stem Loop CHR Overlapping transcripts CHR: Coordinates (GRCh 37) 1302 -1 12 intergenic 12: 113132839 -113132981 [-] 1302 -3 2 intergenic 2: 114340536 -114340673 [-] 1302 -7 8 intergenic 8: 142867603 -142867674 [-] 1302 -10 15 intergenic 15: 102500662 -102500799 [-] 1302 -11 19 intergenic 19: 71973 -72110 [+] 1302 -2 1 intronic Non protein coding 1: 30366 -30503 [+] sense 1302 -4 2 intronic Non protein coding 2: 208133999 -208134148 [-] 1302 -9 9 Non protein coding 9: 30144 -30281 [+]; Sense 1302 -5 20 intronic Protein coding/FAM 65 C; intron 4 1302 -6 7 intronic Protein coding/HDAC 9; intron 1 7: 18166843 -18166932 [-] ; Antisense 1302 -8 9 intronic Protein coding/ch 9 orf 174 9: 100125836 -100125963 [-]; Antisense 20: 49231173 -49231322 [-]; Sense Mature-mi. R-1302: UUGGGACAUACUUAUGCUAAA www. mirbase. org - 7 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Multiple loci can generate the same mature mi. RNA But are under different regulatory control Stem Loop CHR Overlapping transcripts CHR: Coordinates (GRCh 37) 1302 -1 12 intergenic 12: 113132839 -113132981 [-] 1302 -3 2 intergenic 2: 114340536 -114340673 [-] 1302 -7 8 intergenic 8: 142867603 -142867674 [-] 1302 -10 15 intergenic 15: 102500662 -102500799 [-] 1302 -11 19 intergenic 19: 71973 -72110 [+] 1302 -2 1 intronic Non protein coding 1: 30366 -30503 [+] sense 1302 -4 2 intronic Non protein coding 2: 208133999 -208134148 [-] 1302 -9 9 Non protein coding 9: 30144 -30281 [+]; Sense 1302 -5 20 intronic Protein coding/FAM 65 C; intron 4 1302 -6 7 intronic Protein coding/HDAC 9; intron 1 7: 18166843 -18166932 [-] ; Antisense 1302 -8 9 intronic Protein coding/ch 9 orf 174 9: 100125836 -100125963 [-]; Antisense 20: 49231173 -49231322 [-]; Sense Mature-mi. R-1302: UUGGGACAUACUUAUGCUAAA www. mirbase. org - 7 - Sample & Assay Technologies
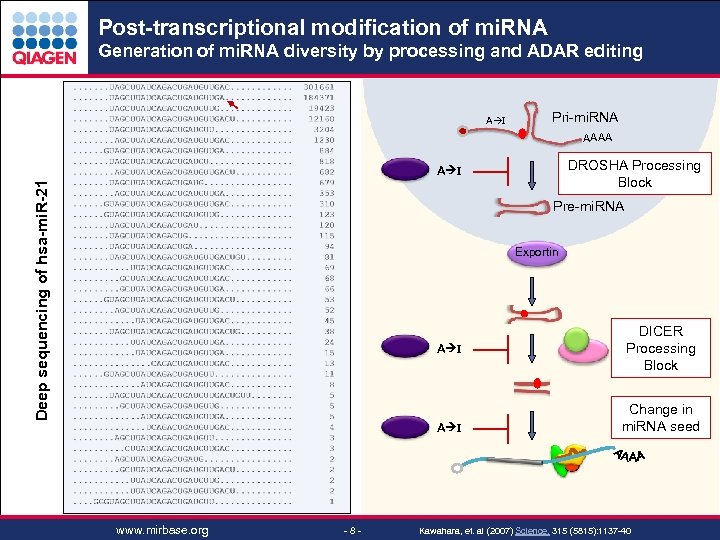 Post-transcriptional modification of mi. RNA Generation of mi. RNA diversity by processing and ADAR editing A I Pri-mi. RNA AAAA DROSHA Processing Block Deep sequencing of hsa-mi. R-21 A I Pre-mi. RNA Exportin A I www. mirbase. org - 8 - DICER Processing Block Change in mi. RNA seed Kawahara, et. al (2007) Science. 315 (5815): 1137 -40 Sample & Assay Technologies
Post-transcriptional modification of mi. RNA Generation of mi. RNA diversity by processing and ADAR editing A I Pri-mi. RNA AAAA DROSHA Processing Block Deep sequencing of hsa-mi. R-21 A I Pre-mi. RNA Exportin A I www. mirbase. org - 8 - DICER Processing Block Change in mi. RNA seed Kawahara, et. al (2007) Science. 315 (5815): 1137 -40 Sample & Assay Technologies
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA in Disease - 9 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA in Disease - 9 - Sample & Assay Technologies
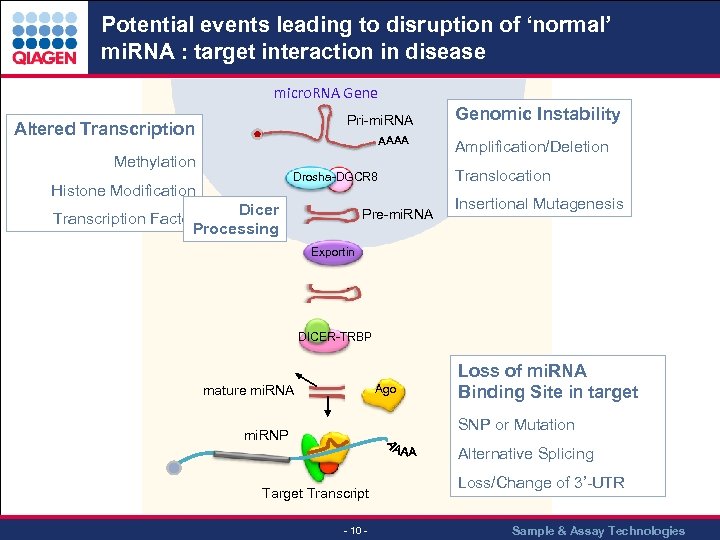 Potential events leading to disruption of ‘normal’ mi. RNA : target interaction in disease micro. RNA Gene Pri-mi. RNA Altered Transcription AAAA Methylation Drosha-DGCR 8 Histone Modification Drosha Dicer Transcription Factor Processing Pre-mi. RNA Genomic Instability Amplification/Deletion Translocation Insertional Mutagenesis Exportin DICER-TRBP Ago mature mi. RNA Loss of mi. RNA Binding Site in target SNP or Mutation mi. RNP Alternative Splicing Target Transcript - 10 - Loss/Change of 3’-UTR Sample & Assay Technologies
Potential events leading to disruption of ‘normal’ mi. RNA : target interaction in disease micro. RNA Gene Pri-mi. RNA Altered Transcription AAAA Methylation Drosha-DGCR 8 Histone Modification Drosha Dicer Transcription Factor Processing Pre-mi. RNA Genomic Instability Amplification/Deletion Translocation Insertional Mutagenesis Exportin DICER-TRBP Ago mature mi. RNA Loss of mi. RNA Binding Site in target SNP or Mutation mi. RNP Alternative Splicing Target Transcript - 10 - Loss/Change of 3’-UTR Sample & Assay Technologies
 Circa 2005: Unique mi. RNA signatures are found in human cancer n mi. RNAs located in genomic regions amplified in cancers (e. g. mi. R 12 -92 cluster) can function as oncogenes, whereas mi. RNAs located in portions of chromosomes deleted in cancers (e. g. mi. R-15 a-mi. R-161 cluster) can function as tumor suppressors. n Abnormal expression of mi. RNAs has been found in both solid and hematopoietic tumors. n mi. RNA expression fingerprints correlate with clinical and biological characteristics of tumors, including tissue type, differentiation, aggression and response to therapy. n The race was on to develop mi. RNA biomarkers and therapeutics! - 11 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Circa 2005: Unique mi. RNA signatures are found in human cancer n mi. RNAs located in genomic regions amplified in cancers (e. g. mi. R 12 -92 cluster) can function as oncogenes, whereas mi. RNAs located in portions of chromosomes deleted in cancers (e. g. mi. R-15 a-mi. R-161 cluster) can function as tumor suppressors. n Abnormal expression of mi. RNAs has been found in both solid and hematopoietic tumors. n mi. RNA expression fingerprints correlate with clinical and biological characteristics of tumors, including tissue type, differentiation, aggression and response to therapy. n The race was on to develop mi. RNA biomarkers and therapeutics! - 11 - Sample & Assay Technologies
 Circa 2011: A growing picture of mi. RNA dysregulation in cancer . . In the last 5 years, a substantial number of studies and reviews have associated the presence of various mi. RNAs with cell proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, and differentiation in cancer cells. For example; n Deletions of mi. RNA-regulated genes have been detected in more than 65% of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases, in 50% of mantle-cell lymphomas, in 16% to 40% of multiple myelomas, and in 60% of prostate cancers. n Other mi. RNA abnormalities have been reported in a wide variety of o Human neoplasms, including other hematologic malignancies such as promyelocytic leukemia; o Benign tumors such as leiomyoma and pituitary adenoma o Multiple types of carcinomas, including pancreatic, esophageal, thyroid, lung, and breast o Neuroblastomas and glioblastomas. - 12 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Circa 2011: A growing picture of mi. RNA dysregulation in cancer . . In the last 5 years, a substantial number of studies and reviews have associated the presence of various mi. RNAs with cell proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, and differentiation in cancer cells. For example; n Deletions of mi. RNA-regulated genes have been detected in more than 65% of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases, in 50% of mantle-cell lymphomas, in 16% to 40% of multiple myelomas, and in 60% of prostate cancers. n Other mi. RNA abnormalities have been reported in a wide variety of o Human neoplasms, including other hematologic malignancies such as promyelocytic leukemia; o Benign tumors such as leiomyoma and pituitary adenoma o Multiple types of carcinomas, including pancreatic, esophageal, thyroid, lung, and breast o Neuroblastomas and glioblastomas. - 12 - Sample & Assay Technologies
 mi. RNA as ‘drug’, mi. RNA as ‘target of drug’ Google “mi. RNA drug” - 13 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNA as ‘drug’, mi. RNA as ‘target of drug’ Google “mi. RNA drug” - 13 - Sample & Assay Technologies
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Isolation Technologies - 14 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Isolation Technologies - 14 - Sample & Assay Technologies
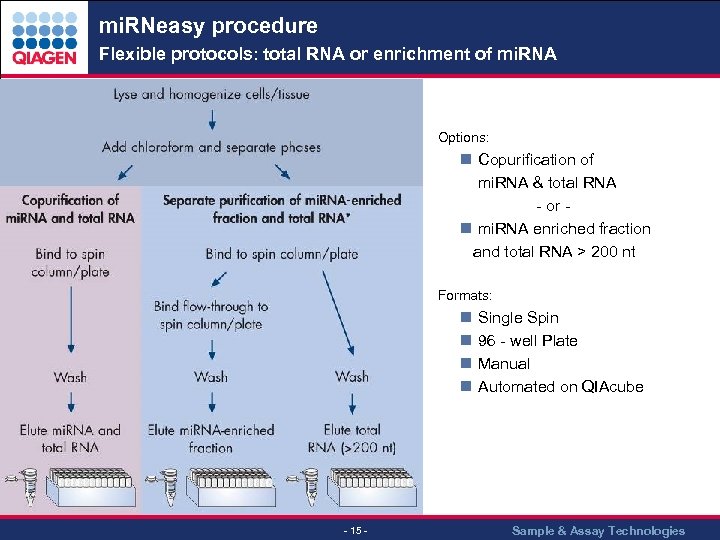 mi. RNeasy procedure Flexible protocols: total RNA or enrichment of mi. RNA Options: n Copurification of mi. RNA & total RNA - or n mi. RNA enriched fraction and total RNA > 200 nt Formats: n Single Spin n 96 - well Plate n Manual n Automated on QIAcube - 15 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNeasy procedure Flexible protocols: total RNA or enrichment of mi. RNA Options: n Copurification of mi. RNA & total RNA - or n mi. RNA enriched fraction and total RNA > 200 nt Formats: n Single Spin n 96 - well Plate n Manual n Automated on QIAcube - 15 - Sample & Assay Technologies
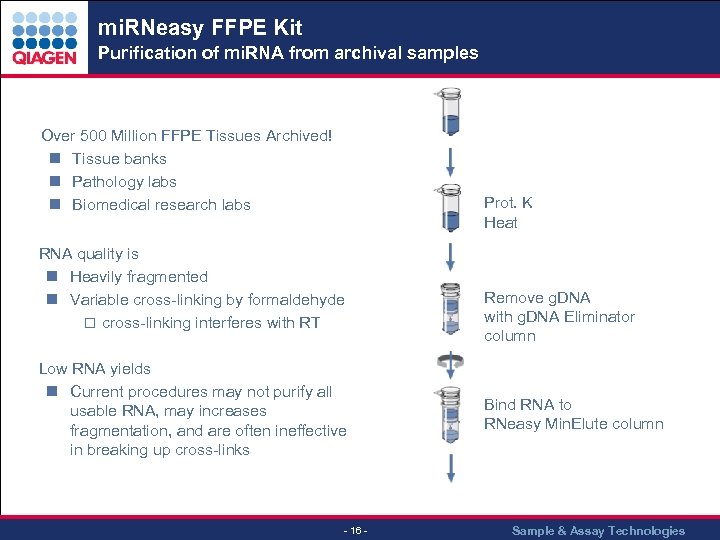 mi. RNeasy FFPE Kit Purification of mi. RNA from archival samples . . . Over 500 Million FFPE Tissues Archived! n Tissue banks n Pathology labs n Biomedical research labs Prot. K Heat RNA quality is n Heavily fragmented n Variable cross-linking by formaldehyde o cross-linking interferes with RT Low RNA yields n Current procedures may not purify all usable RNA, may increases fragmentation, and are often ineffective in breaking up cross-links - 16 - Remove g. DNA with g. DNA Eliminator column Bind RNA to RNeasy Min. Elute column Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNeasy FFPE Kit Purification of mi. RNA from archival samples . . . Over 500 Million FFPE Tissues Archived! n Tissue banks n Pathology labs n Biomedical research labs Prot. K Heat RNA quality is n Heavily fragmented n Variable cross-linking by formaldehyde o cross-linking interferes with RT Low RNA yields n Current procedures may not purify all usable RNA, may increases fragmentation, and are often ineffective in breaking up cross-links - 16 - Remove g. DNA with g. DNA Eliminator column Bind RNA to RNeasy Min. Elute column Sample & Assay Technologies
 mi. RNeasy Mini Kit Purification of circulating mi. RNA QIAzol - 17 - Bind Wash Elute Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNeasy Mini Kit Purification of circulating mi. RNA QIAzol - 17 - Bind Wash Elute Sample & Assay Technologies
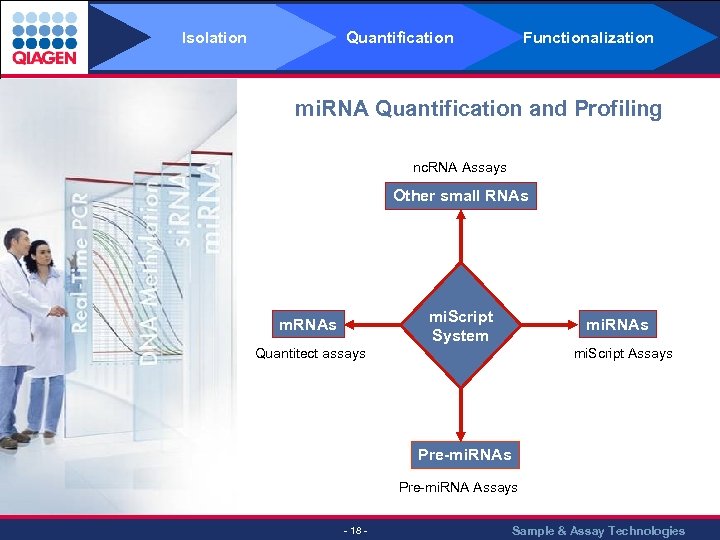 Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Quantification and Profiling nc. RNA Assays Other small RNAs mi. Script System m. RNAs mi. RNAs Quantitect assays mi. Script Assays Pre-mi. RNA Assays - 18 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Quantification and Profiling nc. RNA Assays Other small RNAs mi. Script System m. RNAs mi. RNAs Quantitect assays mi. Script Assays Pre-mi. RNA Assays - 18 - Sample & Assay Technologies
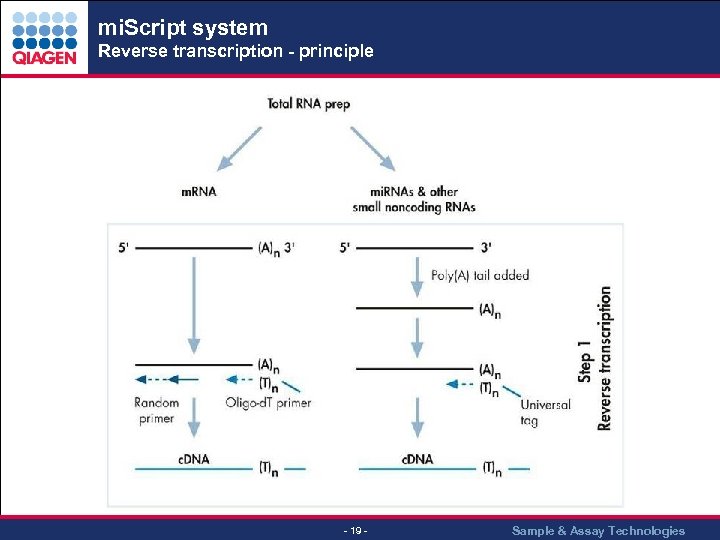 mi. Script system Reverse transcription - principle - 19 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script system Reverse transcription - principle - 19 - Sample & Assay Technologies
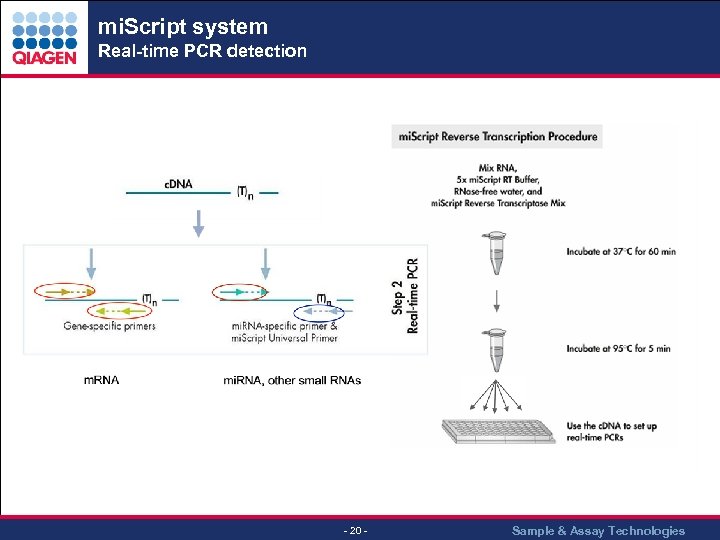 mi. Script system Real-time PCR detection - 20 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script system Real-time PCR detection - 20 - Sample & Assay Technologies
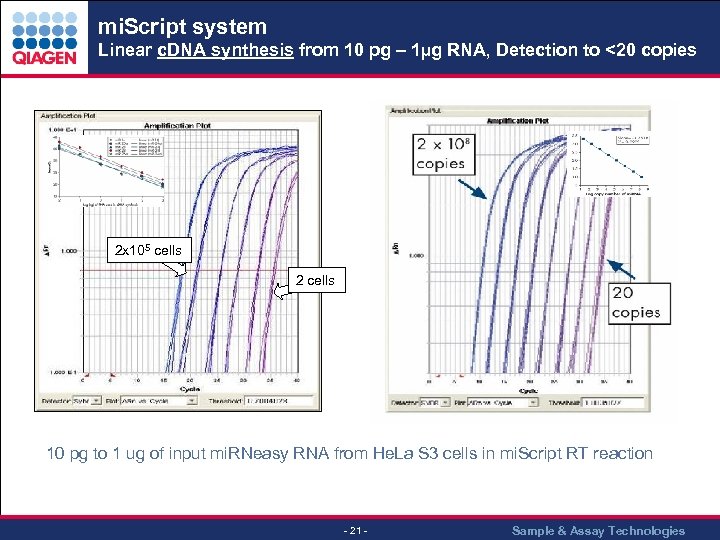 mi. Script system Linear c. DNA synthesis from 10 pg – 1µg RNA, Detection to <20 copies 2 x 105 cells 2 cells 10 pg to 1 ug of input mi. RNeasy RNA from He. La S 3 cells in mi. Script RT reaction - 21 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script system Linear c. DNA synthesis from 10 pg – 1µg RNA, Detection to <20 copies 2 x 105 cells 2 cells 10 pg to 1 ug of input mi. RNeasy RNA from He. La S 3 cells in mi. Script RT reaction - 21 - Sample & Assay Technologies
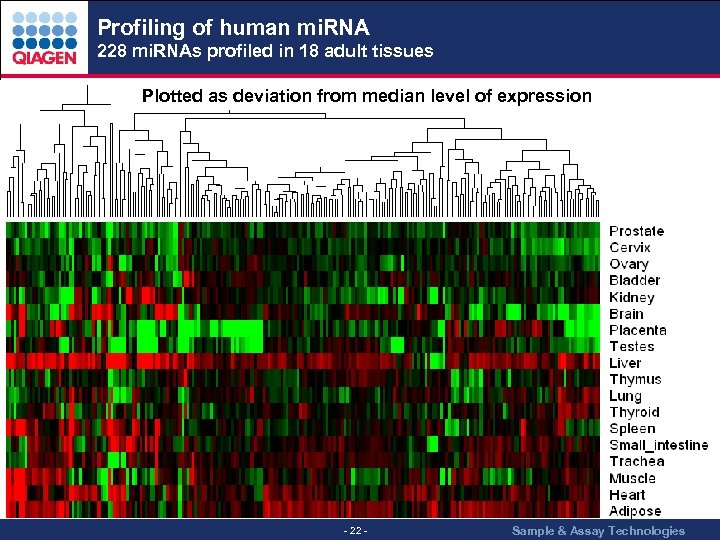 Profiling of human mi. RNA 228 mi. RNAs profiled in 18 adult tissues Plotted as deviation from median level of expression - 22 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Profiling of human mi. RNA 228 mi. RNAs profiled in 18 adult tissues Plotted as deviation from median level of expression - 22 - Sample & Assay Technologies
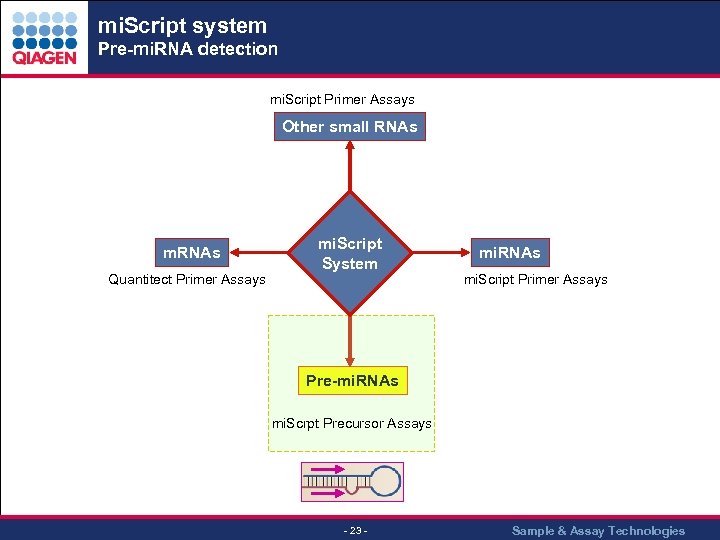 mi. Script system Pre-mi. RNA detection mi. Script Primer Assays Other small RNAs m. RNAs Quantitect Primer Assays mi. Script System mi. RNAs mi. Script Primer Assays Pre-mi. RNAs mi. Scrpt Precursor Assays - 23 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script system Pre-mi. RNA detection mi. Script Primer Assays Other small RNAs m. RNAs Quantitect Primer Assays mi. Script System mi. RNAs mi. Script Primer Assays Pre-mi. RNAs mi. Scrpt Precursor Assays - 23 - Sample & Assay Technologies
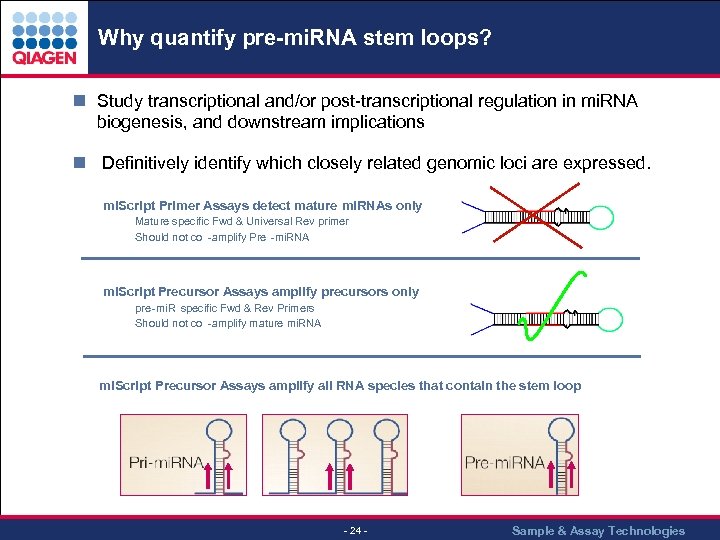 Why quantify pre-mi. RNA stem loops? n Study transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional regulation in mi. RNA biogenesis, and downstream implications n Definitively identify which closely related genomic loci are expressed. mi. Script Primer Assays detect mature mi. RNAs only Mature specific Fwd & Universal Rev primer Should not co -amplify Pre -mi. RNA mi. Script Precursor Assays amplify precursors only Pre pre -mi. R specific Fwd & Rev Primers Should not co -amplify mature mi. RNA mi. Script Precursor Assays amplify all RNA species that contain the stem loop - 24 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Why quantify pre-mi. RNA stem loops? n Study transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional regulation in mi. RNA biogenesis, and downstream implications n Definitively identify which closely related genomic loci are expressed. mi. Script Primer Assays detect mature mi. RNAs only Mature specific Fwd & Universal Rev primer Should not co -amplify Pre -mi. RNA mi. Script Precursor Assays amplify precursors only Pre pre -mi. R specific Fwd & Rev Primers Should not co -amplify mature mi. RNA mi. Script Precursor Assays amplify all RNA species that contain the stem loop - 24 - Sample & Assay Technologies
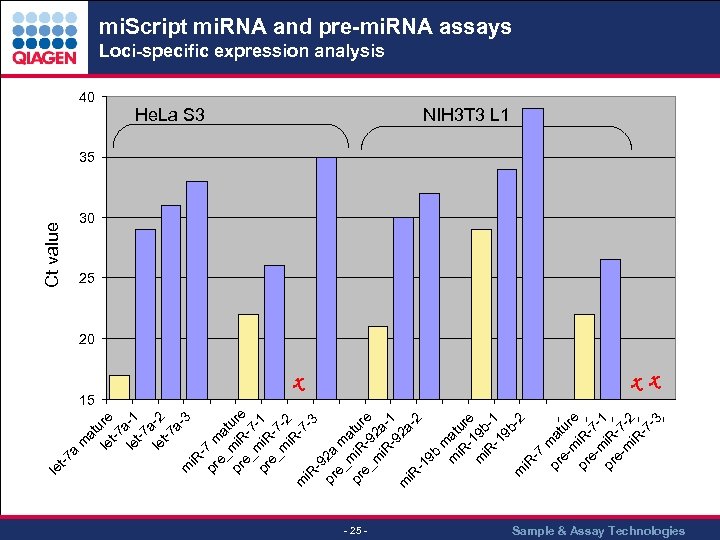 i. R pr 7 m e_ a t pr mi. R ure e_ -7 pr mi. R -1 e_ -7 m -2 i. R -7 m i. R -3 -9 pr 2 a e_ m a pr mi. R tur e_ -9 e m 2 a i. R -1 -9 2 a m i. R -2 -1 9 b m m at i. R ur - e m 19 b i. R -1 -1 9 b -2 m i. R -7 pr mat eu m re pr i. R e- -7 m pr i. R 1 e- -7 m -2 i. R -7 -3 Ct value 40 m at u le re t-7 le a-1 t-7 a le -2 t-7 a 3 a m -7 le t mi. Script mi. RNA and pre-mi. RNA assays Loci-specific expression analysis He. La S 3 15 NIH 3 T 3 L 1 35 30 25 20 x x x - 25 - Sample & Assay Technologies
i. R pr 7 m e_ a t pr mi. R ure e_ -7 pr mi. R -1 e_ -7 m -2 i. R -7 m i. R -3 -9 pr 2 a e_ m a pr mi. R tur e_ -9 e m 2 a i. R -1 -9 2 a m i. R -2 -1 9 b m m at i. R ur - e m 19 b i. R -1 -1 9 b -2 m i. R -7 pr mat eu m re pr i. R e- -7 m pr i. R 1 e- -7 m -2 i. R -7 -3 Ct value 40 m at u le re t-7 le a-1 t-7 a le -2 t-7 a 3 a m -7 le t mi. Script mi. RNA and pre-mi. RNA assays Loci-specific expression analysis He. La S 3 15 NIH 3 T 3 L 1 35 30 25 20 x x x - 25 - Sample & Assay Technologies
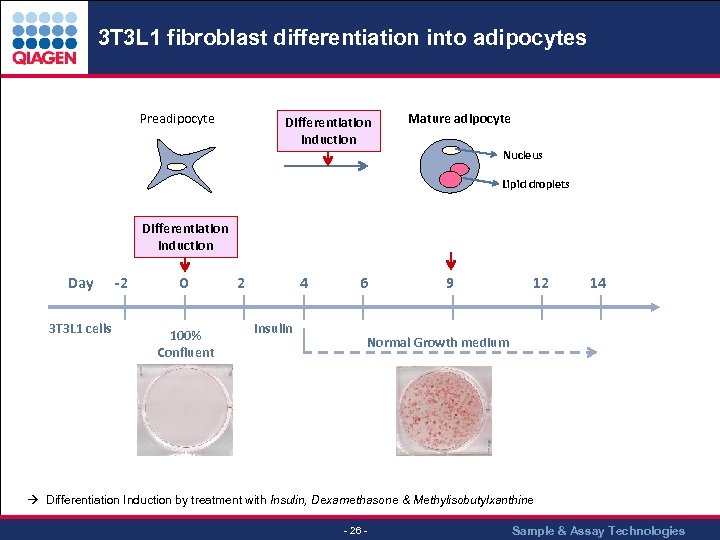 3 T 3 L 1 fibroblast differentiation into adipocytes Preadipocyte Differentiation Induction Mature adipocyte Nucleus Lipid droplets Differentiation Induction Day 3 T 3 L 1 cells -2 0 100% Confluent 2 4 6 Insulin 9 12 14 Normal Growth medium Differentiation Induction by treatment with Insulin, Dexamethasone & Methylisobutylxanthine - 26 - Sample & Assay Technologies
3 T 3 L 1 fibroblast differentiation into adipocytes Preadipocyte Differentiation Induction Mature adipocyte Nucleus Lipid droplets Differentiation Induction Day 3 T 3 L 1 cells -2 0 100% Confluent 2 4 6 Insulin 9 12 14 Normal Growth medium Differentiation Induction by treatment with Insulin, Dexamethasone & Methylisobutylxanthine - 26 - Sample & Assay Technologies
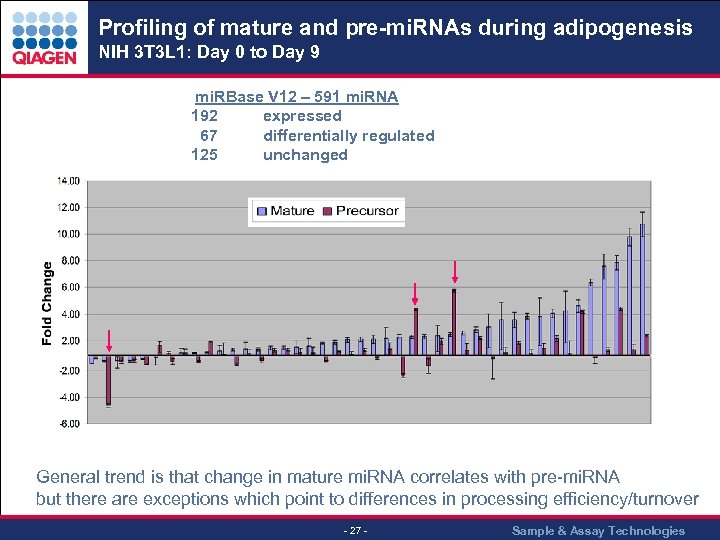 Profiling of mature and pre-mi. RNAs during adipogenesis NIH 3 T 3 L 1: Day 0 to Day 9 mi. RBase V 12 – 591 mi. RNA 192 expressed 67 differentially regulated 125 unchanged General trend is that change in mature mi. RNA correlates with pre-mi. RNA but there are exceptions which point to differences in processing efficiency/turnover - 27 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Profiling of mature and pre-mi. RNAs during adipogenesis NIH 3 T 3 L 1: Day 0 to Day 9 mi. RBase V 12 – 591 mi. RNA 192 expressed 67 differentially regulated 125 unchanged General trend is that change in mature mi. RNA correlates with pre-mi. RNA but there are exceptions which point to differences in processing efficiency/turnover - 27 - Sample & Assay Technologies
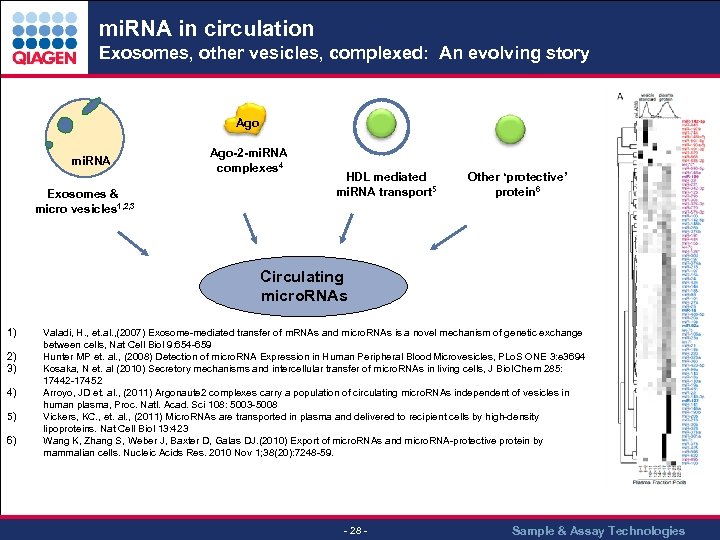 mi. RNA in circulation Exosomes, other vesicles, complexed: An evolving story Ago mi. RNA Exosomes & micro vesicles 1, 2, 3 Ago-2 -mi. RNA complexes 4 HDL mediated mi. RNA transport 5 Other ‘protective’ protein 6 Circulating micro. RNAs 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Valadi, H. , et. al. , (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of m. RNAs and micro. RNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells, Nat Cell Biol 9: 654 -659 Hunter MP et. al. , (2008) Detection of micro. RNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Microvesicles, PLo. S ONE 3: e 3694 Kosaka, N et. al (2010) Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of micro. RNAs in living cells, J Biol Chem 285: 17442 -17452 Arroyo, JD et. al. , (2011) Argonaute 2 complexes carry a population of circulating micro. RNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 108: 5003 -5008 Vickers, KC. , et. al. , (2011) Micro. RNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol 13: 423 Wang K, Zhang S, Weber J, Baxter D, Galas DJ. (2010) Export of micro. RNAs and micro. RNA-protective protein by mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Nov 1; 38(20): 7248 -59. - 28 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNA in circulation Exosomes, other vesicles, complexed: An evolving story Ago mi. RNA Exosomes & micro vesicles 1, 2, 3 Ago-2 -mi. RNA complexes 4 HDL mediated mi. RNA transport 5 Other ‘protective’ protein 6 Circulating micro. RNAs 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Valadi, H. , et. al. , (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of m. RNAs and micro. RNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells, Nat Cell Biol 9: 654 -659 Hunter MP et. al. , (2008) Detection of micro. RNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Microvesicles, PLo. S ONE 3: e 3694 Kosaka, N et. al (2010) Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of micro. RNAs in living cells, J Biol Chem 285: 17442 -17452 Arroyo, JD et. al. , (2011) Argonaute 2 complexes carry a population of circulating micro. RNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 108: 5003 -5008 Vickers, KC. , et. al. , (2011) Micro. RNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol 13: 423 Wang K, Zhang S, Weber J, Baxter D, Galas DJ. (2010) Export of micro. RNAs and micro. RNA-protective protein by mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Nov 1; 38(20): 7248 -59. - 28 - Sample & Assay Technologies
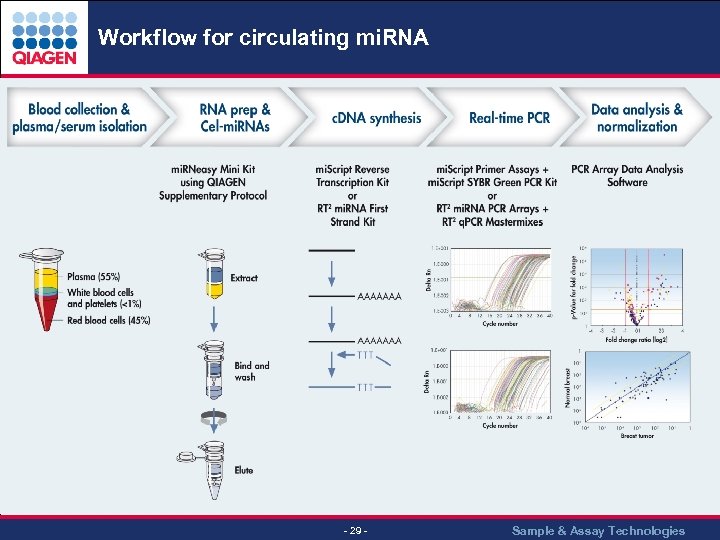 Workflow for circulating mi. RNA - 29 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Workflow for circulating mi. RNA - 29 - Sample & Assay Technologies
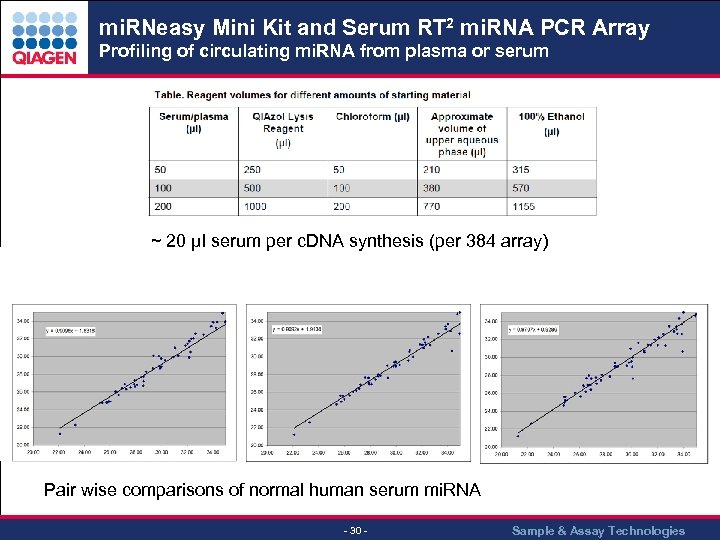 mi. RNeasy Mini Kit and Serum RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Array Profiling of circulating mi. RNA from plasma or serum ~ 20 µl serum per c. DNA synthesis (per 384 array) Pair wise comparisons of normal human serum mi. RNA - 30 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. RNeasy Mini Kit and Serum RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Array Profiling of circulating mi. RNA from plasma or serum ~ 20 µl serum per c. DNA synthesis (per 384 array) Pair wise comparisons of normal human serum mi. RNA - 30 - Sample & Assay Technologies
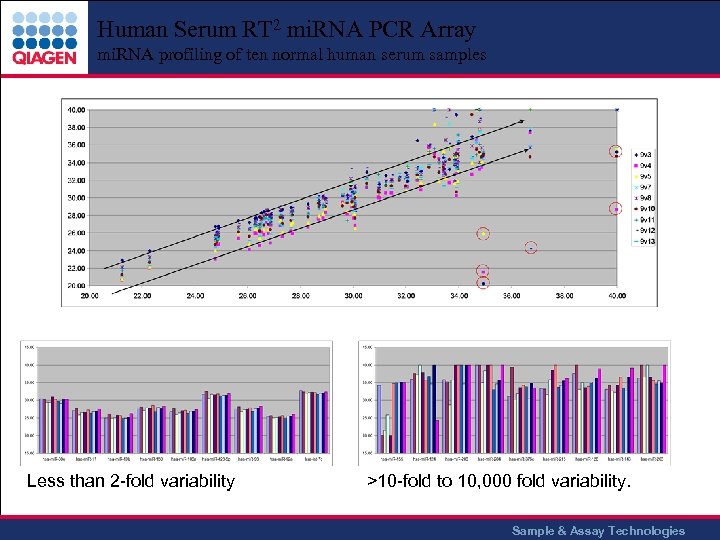 Human Serum RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Array mi. RNA profiling of ten normal human serum samples Less than 2 -fold variability >10 -fold to 10, 000 fold variability. Sample & Assay Technologies
Human Serum RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Array mi. RNA profiling of ten normal human serum samples Less than 2 -fold variability >10 -fold to 10, 000 fold variability. Sample & Assay Technologies
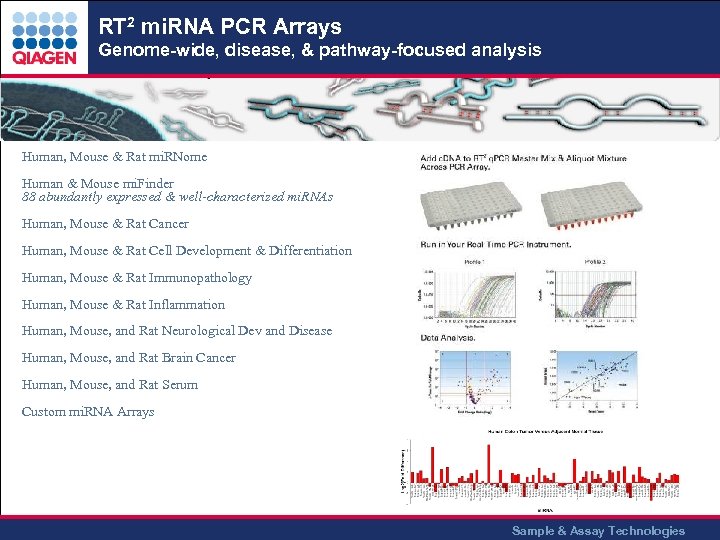 RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Arrays Genome-wide, disease, & pathway-focused analysis Human, Mouse & Rat mi. RNome Human & Mouse mi. Finder 88 abundantly expressed & well-characterized mi. RNAs Human, Mouse & Rat Cancer Human, Mouse & Rat Cell Development & Differentiation Human, Mouse & Rat Immunopathology Human, Mouse & Rat Inflammation Human, Mouse, and Rat Neurological Dev and Disease Human, Mouse, and Rat Brain Cancer Human, Mouse, and Rat Serum Custom mi. RNA Arrays Sample & Assay Technologies
RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Arrays Genome-wide, disease, & pathway-focused analysis Human, Mouse & Rat mi. RNome Human & Mouse mi. Finder 88 abundantly expressed & well-characterized mi. RNAs Human, Mouse & Rat Cancer Human, Mouse & Rat Cell Development & Differentiation Human, Mouse & Rat Immunopathology Human, Mouse & Rat Inflammation Human, Mouse, and Rat Neurological Dev and Disease Human, Mouse, and Rat Brain Cancer Human, Mouse, and Rat Serum Custom mi. RNA Arrays Sample & Assay Technologies
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Functionalization - 33 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Isolation Quantification Functionalization mi. RNA Functionalization - 33 - Sample & Assay Technologies
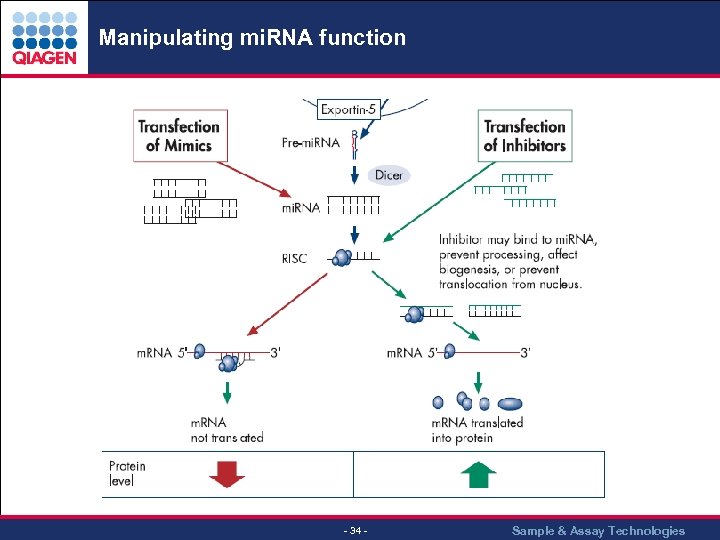 Manipulating mi. RNA function - 34 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Manipulating mi. RNA function - 34 - Sample & Assay Technologies
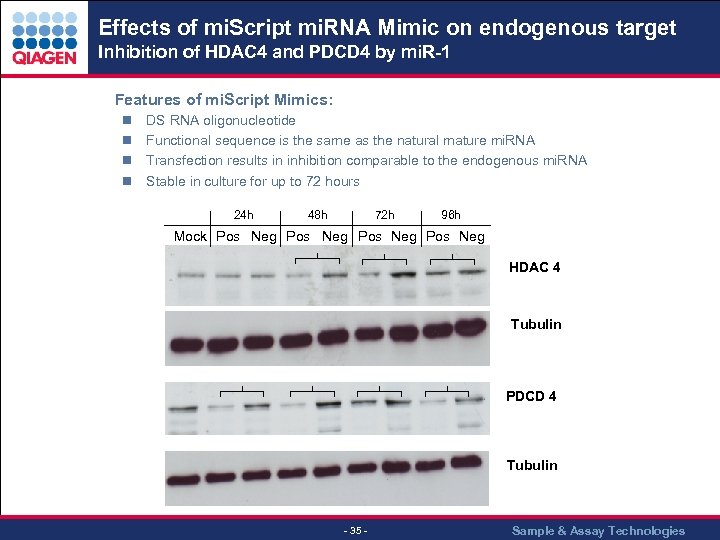 Effects of mi. Script mi. RNA Mimic on endogenous target Inhibition of HDAC 4 and PDCD 4 by mi. R-1. Features of mi. Script Mimics: n n DS RNA oligonucleotide Functional sequence is the same as the natural mature mi. RNA Transfection results in inhibition comparable to the endogenous mi. RNA Stable in culture for up to 72 hours 24 h 48 h 72 h 96 h Mock Pos Neg 250 HDAC 4 130 Tubulin 55 PDCD 4 55 Tubulin 55 - 35 - Sample & Assay Technologies
Effects of mi. Script mi. RNA Mimic on endogenous target Inhibition of HDAC 4 and PDCD 4 by mi. R-1. Features of mi. Script Mimics: n n DS RNA oligonucleotide Functional sequence is the same as the natural mature mi. RNA Transfection results in inhibition comparable to the endogenous mi. RNA Stable in culture for up to 72 hours 24 h 48 h 72 h 96 h Mock Pos Neg 250 HDAC 4 130 Tubulin 55 PDCD 4 55 Tubulin 55 - 35 - Sample & Assay Technologies
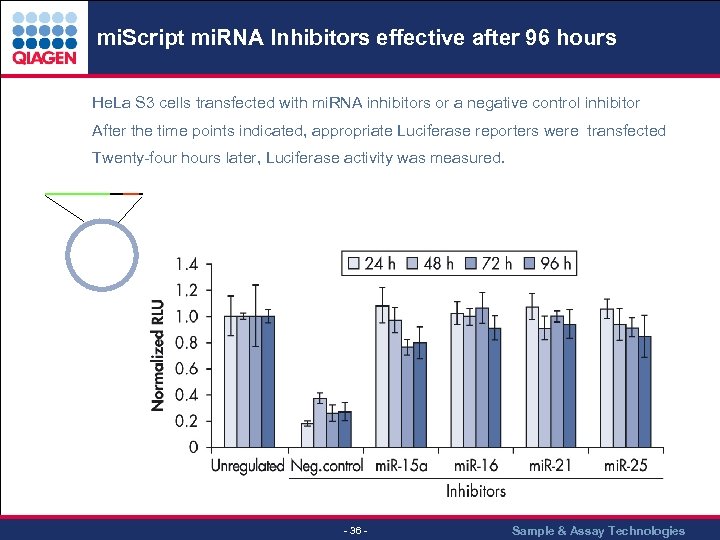 mi. Script mi. RNA Inhibitors effective after 96 hours. . . He. La S 3 cells transfected with mi. RNA inhibitors or a negative control inhibitor After the time points indicated, appropriate Luciferase reporters were transfected Twenty-four hours later, Luciferase activity was measured. - 36 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script mi. RNA Inhibitors effective after 96 hours. . . He. La S 3 cells transfected with mi. RNA inhibitors or a negative control inhibitor After the time points indicated, appropriate Luciferase reporters were transfected Twenty-four hours later, Luciferase activity was measured. - 36 - Sample & Assay Technologies
 mi. Script mi. RNA Mimic & Inhibitor controls Mimic negative control All. Stars Negative Control si. RNA n No homology to any mammalian gene. n Validated for non-effects in microarray and phenotype assays. n Validated for RISC entry Mimic positive control Syn-hsa-mi. R-1 mimic n Not expressed under most culture conditions, only expressed in muscle cells n To check for optimal conditions by using mi. Script PCR mi. R-1 Inhibitor negative control mi. Script Inhibitor Negative Control n Target the sequence of mi. Script mimic negative control Inhibitor positive control Anti-hsa-mi. R-1 inhibitor n To check for optimal conditions in combination with Syn-hsa-mi. R-1 mimic Transfection control All. Stars Hs Cell Death Control si. RNA n Cell death = successful transfection n To run in every experiment - 37 - Sample & Assay Technologies
mi. Script mi. RNA Mimic & Inhibitor controls Mimic negative control All. Stars Negative Control si. RNA n No homology to any mammalian gene. n Validated for non-effects in microarray and phenotype assays. n Validated for RISC entry Mimic positive control Syn-hsa-mi. R-1 mimic n Not expressed under most culture conditions, only expressed in muscle cells n To check for optimal conditions by using mi. Script PCR mi. R-1 Inhibitor negative control mi. Script Inhibitor Negative Control n Target the sequence of mi. Script mimic negative control Inhibitor positive control Anti-hsa-mi. R-1 inhibitor n To check for optimal conditions in combination with Syn-hsa-mi. R-1 mimic Transfection control All. Stars Hs Cell Death Control si. RNA n Cell death = successful transfection n To run in every experiment - 37 - Sample & Assay Technologies
 www. qiagen. com/Gene. Globe - 38 - Sample & Assay Technologies
www. qiagen. com/Gene. Globe - 38 - Sample & Assay Technologies
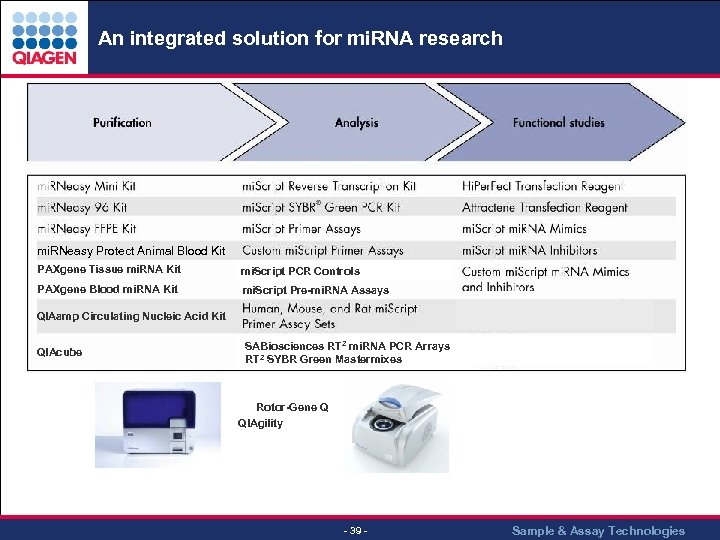 An integrated solution for mi. RNA research mi. RNeasy Protect Animal Blood Kit PAXgene Tissue mi. RNA Kit mi. Script PCR Controls PAXgene Blood mi. RNA Kit mi. Script Pre-mi. RNA Assays QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit QIAcube SABiosciences RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Arrays RT 2 SYBR Green Mastermixes Rotor-Gene Q QIAgility - 39 - Sample & Assay Technologies
An integrated solution for mi. RNA research mi. RNeasy Protect Animal Blood Kit PAXgene Tissue mi. RNA Kit mi. Script PCR Controls PAXgene Blood mi. RNA Kit mi. Script Pre-mi. RNA Assays QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit QIAcube SABiosciences RT 2 mi. RNA PCR Arrays RT 2 SYBR Green Mastermixes Rotor-Gene Q QIAgility - 39 - Sample & Assay Technologies


