88d413b6aaf356bba6b63fe983627642.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 ISO/CCSDS Open Archival Information System (OAIS) Reference Model D Giaretta Chairman of CCSDS Panel 2 Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
ISO/CCSDS Open Archival Information System (OAIS) Reference Model D Giaretta Chairman of CCSDS Panel 2 Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 What are ‘Open Archival Information Systems’ • OPEN – Reference Model standard(s) being developed with participation open to all – Clearly defined interfaces – (i. e. Does not imply uncontrolled access) • ARCHIVAL INFORMATION SYSTEM – Hardware, software and people who are discharging their responsibilities to acquire, preserve and disseminate information
What are ‘Open Archival Information Systems’ • OPEN – Reference Model standard(s) being developed with participation open to all – Clearly defined interfaces – (i. e. Does not imply uncontrolled access) • ARCHIVAL INFORMATION SYSTEM – Hardware, software and people who are discharging their responsibilities to acquire, preserve and disseminate information
 . . . • INFORMATION – Any type of knowledge that can be exchanged – Independent of the forms (i. e. Physical or digital) used to represent the information • OAIS Archive – one that meets the minimum requirements given later – need for CERTIFICATION procedure
. . . • INFORMATION – Any type of knowledge that can be exchanged – Independent of the forms (i. e. Physical or digital) used to represent the information • OAIS Archive – one that meets the minimum requirements given later – need for CERTIFICATION procedure
 CCSDS Panel 2 involvement • ISO Technical Committee (TC) 20: Aircraft and Space Vehicles, and its Sub-Committee (SC) 13: Space Data and Information Transfer Systems – Promote standards for “archiving” space data
CCSDS Panel 2 involvement • ISO Technical Committee (TC) 20: Aircraft and Space Vehicles, and its Sub-Committee (SC) 13: Space Data and Information Transfer Systems – Promote standards for “archiving” space data
 . . . Panel 2 • Proposal made to Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems and ISO TC 20/SC 13 – Develop a ‘Reference Model’ to establish common terms and concepts – Ensure broad participation, including traditional archives – Focus on data in electronic forms, but recognise that other forms exist in most archives – Follow up with additional archive standards efforts as appropriate
. . . Panel 2 • Proposal made to Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems and ISO TC 20/SC 13 – Develop a ‘Reference Model’ to establish common terms and concepts – Ensure broad participation, including traditional archives – Focus on data in electronic forms, but recognise that other forms exist in most archives – Follow up with additional archive standards efforts as appropriate
 Why CCSDS Panel 2? • Close association between ISO TC 20/SC 13 and CCSDS • The archive work complements other Panel 2 work • Space Data is extremely expensive to obtain. Long term preservation and sharing is very important - hence the importance of archiving to CCSDS members • It is not possible to distinguish between information obtained from space and that obtained by other means
Why CCSDS Panel 2? • Close association between ISO TC 20/SC 13 and CCSDS • The archive work complements other Panel 2 work • Space Data is extremely expensive to obtain. Long term preservation and sharing is very important - hence the importance of archiving to CCSDS members • It is not possible to distinguish between information obtained from space and that obtained by other means
 Timescales • Panel 2 will produce the ISO Draft International Standard (DIS) for the OAIS by May 1998 • The DIS will be submitted to the ISO process • Work will follow to produce related standards based on the Reference Model
Timescales • Panel 2 will produce the ISO Draft International Standard (DIS) for the OAIS by May 1998 • The DIS will be submitted to the ISO process • Work will follow to produce related standards based on the Reference Model
 Related work • Work led by NASA members of CCSDS • Many US workshops involving industry, National Archive, military etc. • Workshop held in France • Several International workshops • Details available on the WWW http: //bolero. gsfc. nasa. gov/nost/isoas
Related work • Work led by NASA members of CCSDS • Many US workshops involving industry, National Archive, military etc. • Workshop held in France • Several International workshops • Details available on the WWW http: //bolero. gsfc. nasa. gov/nost/isoas
 Rationale • Growth in computer power, network bandwidth leads to increasing use of electronic forms for information - e. g. Digital data • Many organisations are now performing an “archival” task • Preserving digital data for the long term is more difficult than for paper – hardware and software becomes obsolete (years not decades)
Rationale • Growth in computer power, network bandwidth leads to increasing use of electronic forms for information - e. g. Digital data • Many organisations are now performing an “archival” task • Preserving digital data for the long term is more difficult than for paper – hardware and software becomes obsolete (years not decades)
 ‘Long-Term’ Archive Problems • The archived information must be useable by consumers who are separated in time, distance and background from the producers – producers no longer available • cannot answer questions on ad-hoc basis – producers’ software not supported - may be obsolete • knowledge captured by the software becomes unavailable – documentation is lost over time
‘Long-Term’ Archive Problems • The archived information must be useable by consumers who are separated in time, distance and background from the producers – producers no longer available • cannot answer questions on ad-hoc basis – producers’ software not supported - may be obsolete • knowledge captured by the software becomes unavailable – documentation is lost over time
 . . . problems • the user community will change over time – new community will be unfamiliar with the background to the information – may use different analysis environment – may want to combine information from many sources
. . . problems • the user community will change over time – new community will be unfamiliar with the background to the information – may use different analysis environment – may want to combine information from many sources
 . . . . problems • The archive will change over time – migration to new technology - hardware/software • may require reorganisation of information • Possible changes in implicit relationships – migration to different institutions • Possible changes to management, data structure, file format
. . . . problems • The archive will change over time – migration to new technology - hardware/software • may require reorganisation of information • Possible changes in implicit relationships – migration to different institutions • Possible changes to management, data structure, file format
 Reference Model • A Reference Model is needed to provide a common framework for discussion & description • A major aim is to facilitate a much wider understanding of what is required to preserve information for the long term • Facilitates description and comparison of archives • Provides a basis for further standardisation – help broaden the market for commercial providers
Reference Model • A Reference Model is needed to provide a common framework for discussion & description • A major aim is to facilitate a much wider understanding of what is required to preserve information for the long term • Facilitates description and comparison of archives • Provides a basis for further standardisation – help broaden the market for commercial providers
 . . . Reference Model • We are particularly concerned with Long-Term Preservation of digital information – long term is long enough to be concerned about changing technologies – not just bit preservation – starting point for model addressing non-digital information
. . . Reference Model • We are particularly concerned with Long-Term Preservation of digital information – long term is long enough to be concerned about changing technologies – not just bit preservation – starting point for model addressing non-digital information
 . . . Reference Model • But this work is also of use for “Short-Term archives” because – technological change is rapid (years, not decades) – the short-term archive may eventually hand information over to another, longer-term, archive
. . . Reference Model • But this work is also of use for “Short-Term archives” because – technological change is rapid (years, not decades) – the short-term archive may eventually hand information over to another, longer-term, archive
 OAIS Concepts Environment Information Responsibilities
OAIS Concepts Environment Information Responsibilities
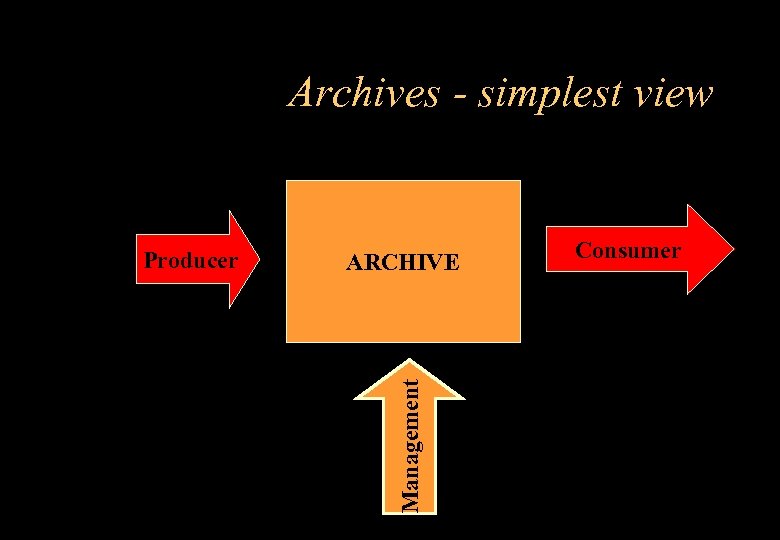 Archives - simplest view ARCHIVE Management Producer Consumer
Archives - simplest view ARCHIVE Management Producer Consumer
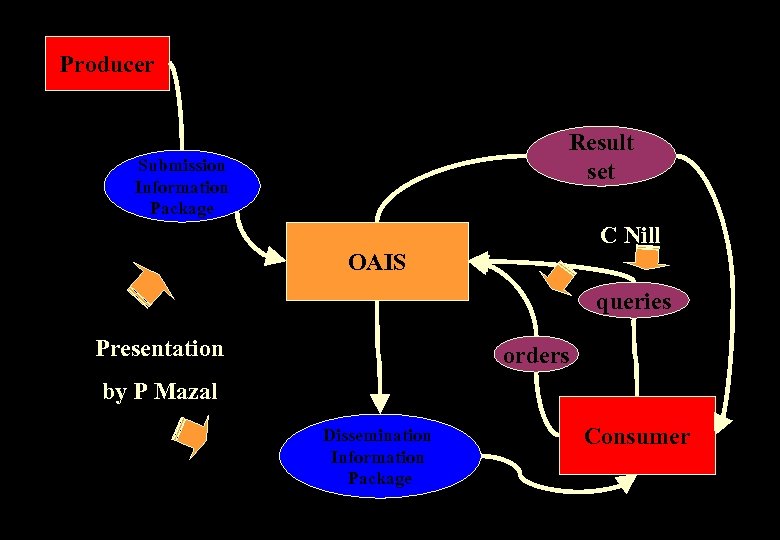 Producer Result set Submission Information Package C Nill OAIS queries Presentation orders by P Mazal Dissemination Information Package Consumer
Producer Result set Submission Information Package C Nill OAIS queries Presentation orders by P Mazal Dissemination Information Package Consumer
 OAIS Concepts • Environment • Information • Responsibilities
OAIS Concepts • Environment • Information • Responsibilities
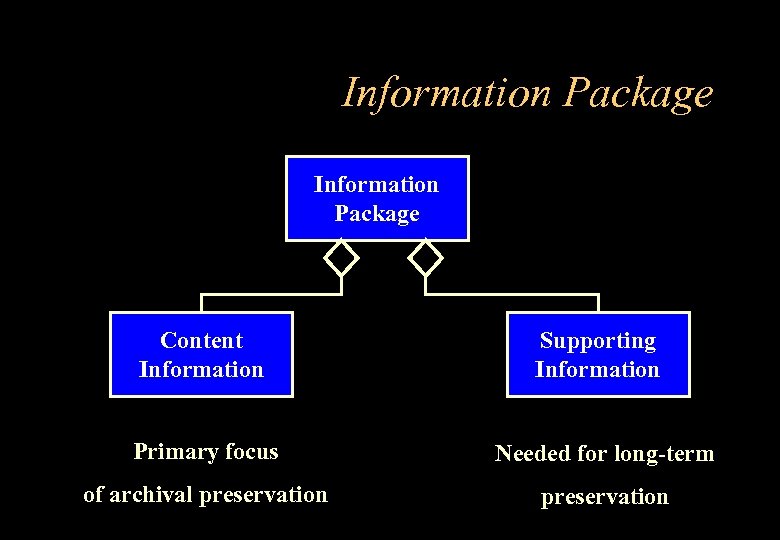 Information Package Content Information Supporting Information Primary focus Needed for long-term of archival preservation
Information Package Content Information Supporting Information Primary focus Needed for long-term of archival preservation
 Information Package components • Content Info • Supporting Information e. g. – is itself understandable by some designated community e. g. the information in a file – could be a physical object – needs Representation Information e. g. to give meaning to a bit sequence in a file – how the Content Info. came into being – who has held it – how it relates to other information – how its integrity is ensured – also has Representation Information
Information Package components • Content Info • Supporting Information e. g. – is itself understandable by some designated community e. g. the information in a file – could be a physical object – needs Representation Information e. g. to give meaning to a bit sequence in a file – how the Content Info. came into being – who has held it – how it relates to other information – how its integrity is ensured – also has Representation Information
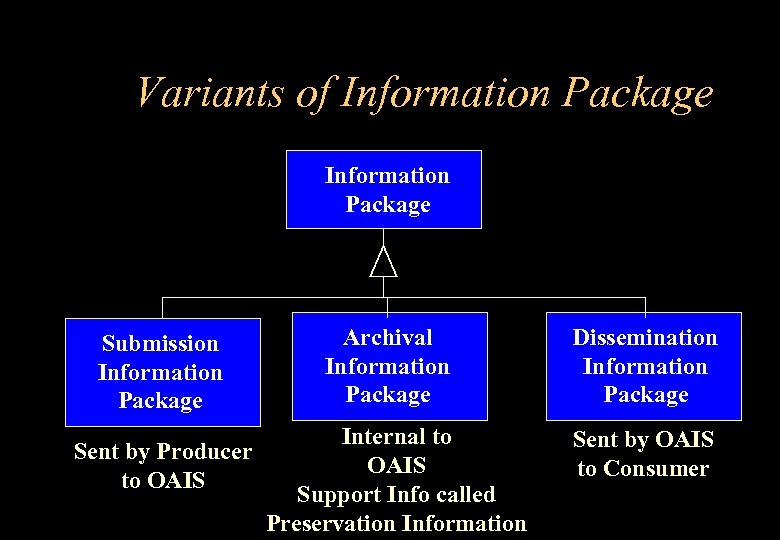 Variants of Information Package Submission Information Package Sent by Producer to OAIS Archival Information Package Internal to OAIS Support Info called Preservation Information Dissemination Information Package Sent by OAIS to Consumer
Variants of Information Package Submission Information Package Sent by Producer to OAIS Archival Information Package Internal to OAIS Support Info called Preservation Information Dissemination Information Package Sent by OAIS to Consumer
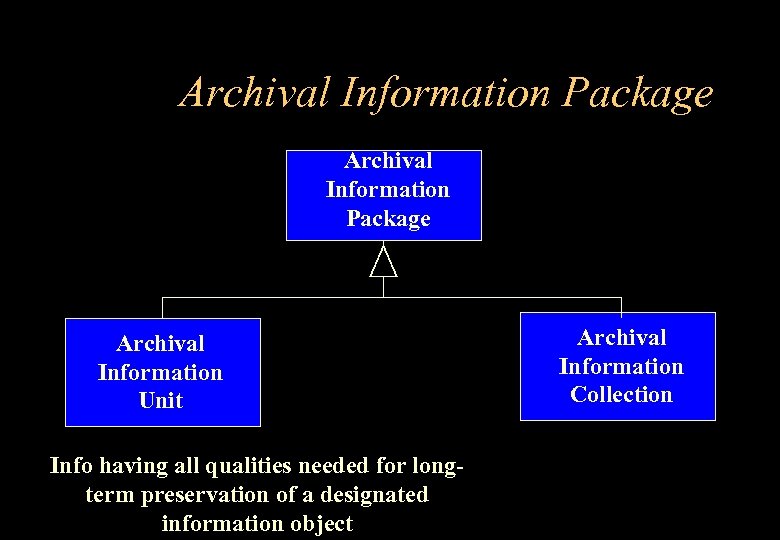 Archival Information Package Archival Information Unit Info having all qualities needed for longterm preservation of a designated information object Archival Information Collection
Archival Information Package Archival Information Unit Info having all qualities needed for longterm preservation of a designated information object Archival Information Collection
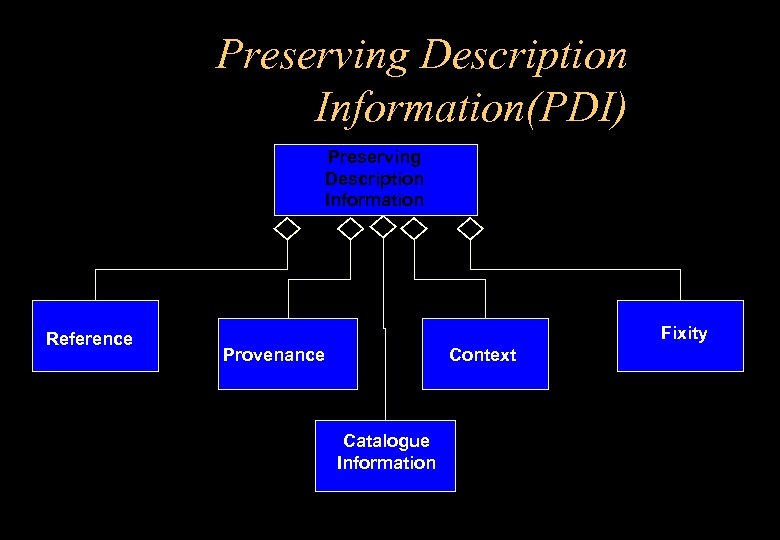 Preserving Description Information(PDI) Preserving Description Information Reference Fixity Provenance Context Catalogue Information
Preserving Description Information(PDI) Preserving Description Information Reference Fixity Provenance Context Catalogue Information
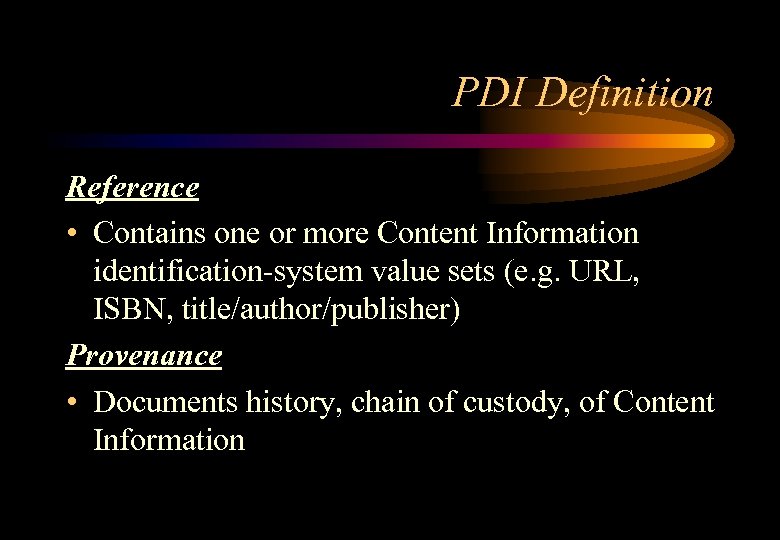 PDI Definition Reference • Contains one or more Content Information identification-system value sets (e. g. URL, ISBN, title/author/publisher) Provenance • Documents history, chain of custody, of Content Information
PDI Definition Reference • Contains one or more Content Information identification-system value sets (e. g. URL, ISBN, title/author/publisher) Provenance • Documents history, chain of custody, of Content Information
 . . . PDI definition Context • Documents relationships of Content Info. to environment – Technical (e. g. Mapping to physical media) – Social (e. g. Why it was created) Catalogue • Optional info extracted from Content Info - to be used in searches
. . . PDI definition Context • Documents relationships of Content Info. to environment – Technical (e. g. Mapping to physical media) – Social (e. g. Why it was created) Catalogue • Optional info extracted from Content Info - to be used in searches
 . . . . PDI definition Fixity • Describes mechanisms (authentication) used to ensure Content Information has not been altered in an undocumented manner. – Encryption, digital signature, physical security, time stamping etc.
. . . . PDI definition Fixity • Describes mechanisms (authentication) used to ensure Content Information has not been altered in an undocumented manner. – Encryption, digital signature, physical security, time stamping etc.
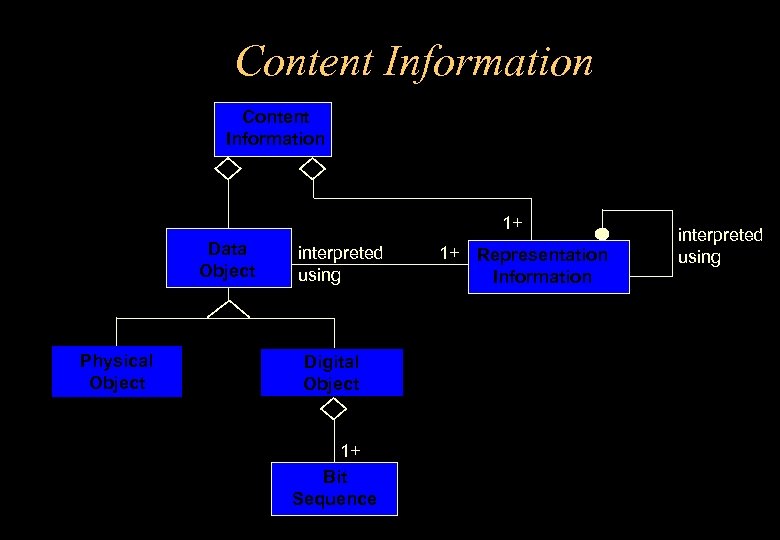 Content Information 1+ Data Object Physical Object interpreted using Digital Object 1+ Bit Sequence 1+ Representation Information interpreted using
Content Information 1+ Data Object Physical Object interpreted using Digital Object 1+ Bit Sequence 1+ Representation Information interpreted using
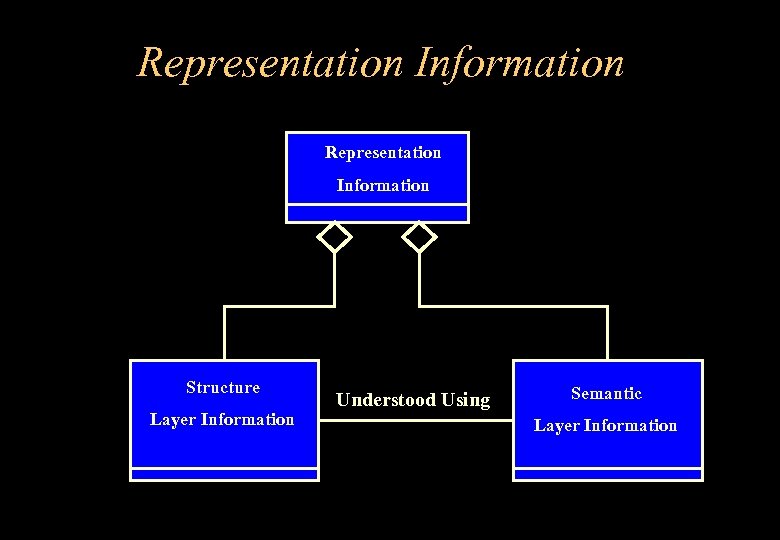 Representation Information Structure Layer Information Understood Using Semantic Layer Information
Representation Information Structure Layer Information Understood Using Semantic Layer Information
 . . . Representation Information • Representations will be discussed in following presentation by P Mazal
. . . Representation Information • Representations will be discussed in following presentation by P Mazal
 OAIS Concepts Environment Information Responsibilities
OAIS Concepts Environment Information Responsibilities
 OAIS Responsibilities • Negotiates & accepts Submission IPs • Determines communities which need to be able to understand Content Information • Ensures information to be preserved is understandable to designated communities • Assumes sufficient control of info. to be able to ensure long-term preservation • Follows policies & procedures to ensure information is preserved • makes the information available to the designated communities in appropriate forms
OAIS Responsibilities • Negotiates & accepts Submission IPs • Determines communities which need to be able to understand Content Information • Ensures information to be preserved is understandable to designated communities • Assumes sufficient control of info. to be able to ensure long-term preservation • Follows policies & procedures to ensure information is preserved • makes the information available to the designated communities in appropriate forms
 Negotiates and Accepts SIPs • Establishes criteria to determine types of information to be accepted • uses conceptual Submission Information Package (SIP) – separates Content Info. from Preserving Description Info.
Negotiates and Accepts SIPs • Establishes criteria to determine types of information to be accepted • uses conceptual Submission Information Package (SIP) – separates Content Info. from Preserving Description Info.
 Determines Designated Consumer Communities • Designated consumer community determines the Submission Information Package • Concern about evolution of the Designated Community
Determines Designated Consumer Communities • Designated consumer community determines the Submission Information Package • Concern about evolution of the Designated Community
 Ensures Information is Independently Usable • Usable by the designated community • Complex topic
Ensures Information is Independently Usable • Usable by the designated community • Complex topic
 Assumes Sufficient Control for Preservation • Must be able to change the data structures as necessary • Control changes by others
Assumes Sufficient Control for Preservation • Must be able to change the data structures as necessary • Control changes by others
 Follows Established Preservation Policies & Procedures • Transformations and migrations - tracable back to original information • Long-term technology evolution plan needed
Follows Established Preservation Policies & Procedures • Transformations and migrations - tracable back to original information • Long-term technology evolution plan needed
 Makes the information available • Makes the IP’s visible and available to consumers • user selections/searches • variety of distribution media
Makes the information available • Makes the IP’s visible and available to consumers • user selections/searches • variety of distribution media
 OAIS Models • Functional Model, High Level Data Flows • Transformations • Migration
OAIS Models • Functional Model, High Level Data Flows • Transformations • Migration
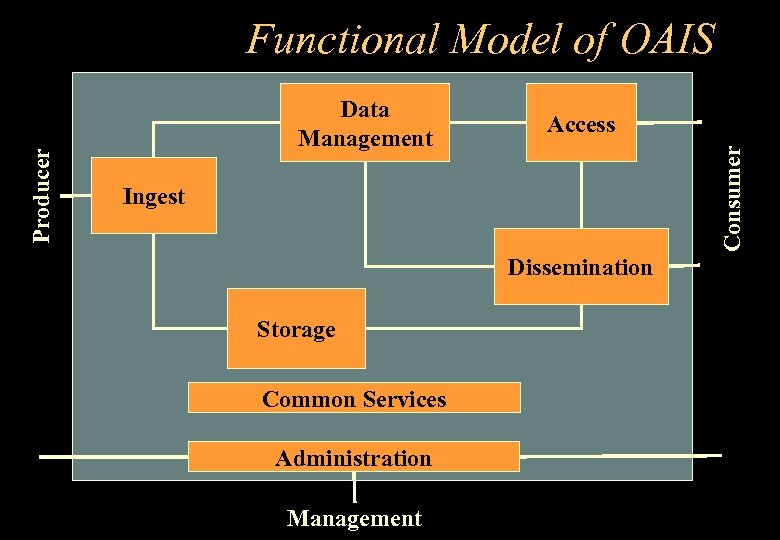 Data Management Access Consumer Producer Functional Model of OAIS Ingest Dissemination Storage Common Services Administration Management
Data Management Access Consumer Producer Functional Model of OAIS Ingest Dissemination Storage Common Services Administration Management
 OAIS Common Services - examples • • • Inter-process communications name services temporary storage allocation exception handling security directory services
OAIS Common Services - examples • • • Inter-process communications name services temporary storage allocation exception handling security directory services
 INGEST Provides the services to accept and validate input and prepare for storage and management • • Scheduling Staging Review Conversion Extract Metadata from SIP Transfer Initiation (to storage) Ingest Reporting
INGEST Provides the services to accept and validate input and prepare for storage and management • • Scheduling Staging Review Conversion Extract Metadata from SIP Transfer Initiation (to storage) Ingest Reporting
 STORAGE Services and function for storage and retrieval of AIP and component data objects • • Transfer Receiving (from Ingest) Hierarchy Management Physical Migration Error Checking Backup Duplication Storage Reporting
STORAGE Services and function for storage and retrieval of AIP and component data objects • • Transfer Receiving (from Ingest) Hierarchy Management Physical Migration Error Checking Backup Duplication Storage Reporting
 DATA MANAGEMENT Services and functions for populating, maintaining and querying wide variety of metadata • • • Report Request Report Generation Update Metadata Maintenance Database Administration Data Management Reporting
DATA MANAGEMENT Services and functions for populating, maintaining and querying wide variety of metadata • • • Report Request Report Generation Update Metadata Maintenance Database Administration Data Management Reporting
 ADMINISTRATION Manages all the system activities • • Acquisition Configuration Management Physical Access Control Planning and Scheduling Monitoring Accounting Customer Service Data Engineering
ADMINISTRATION Manages all the system activities • • Acquisition Configuration Management Physical Access Control Planning and Scheduling Monitoring Accounting Customer Service Data Engineering
 ACCESS Supports user in determining existence, description, location and availability of information of interest • • • Access Control Overview/Browse Query Retrieve Manipulate Display Order Advanced Development Access Reporting
ACCESS Supports user in determining existence, description, location and availability of information of interest • • • Access Control Overview/Browse Query Retrieve Manipulate Display Order Advanced Development Access Reporting
 DISSEMINATION Services and function to fulfill requests for data • • • Receive data orders Monitor orders Retrieve data Retrieve metadata Generate ancillary data Format data Off-line delivery On-line delivery Confirm delivery Delivery Reporting
DISSEMINATION Services and function to fulfill requests for data • • • Receive data orders Monitor orders Retrieve data Retrieve metadata Generate ancillary data Format data Off-line delivery On-line delivery Confirm delivery Delivery Reporting
 . . . OAIS Models • Functional Model, High Level Data Flows • Transformations • Migration
. . . OAIS Models • Functional Model, High Level Data Flows • Transformations • Migration
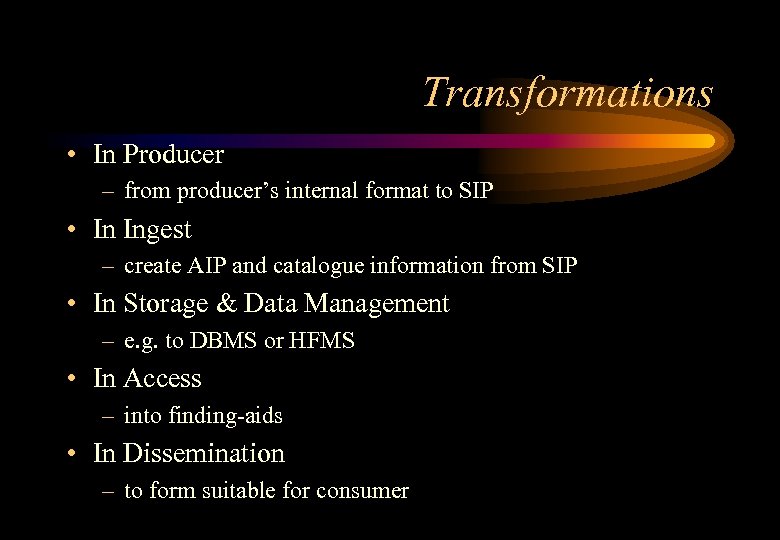 Transformations • In Producer – from producer’s internal format to SIP • In Ingest – create AIP and catalogue information from SIP • In Storage & Data Management – e. g. to DBMS or HFMS • In Access – into finding-aids • In Dissemination – to form suitable for consumer
Transformations • In Producer – from producer’s internal format to SIP • In Ingest – create AIP and catalogue information from SIP • In Storage & Data Management – e. g. to DBMS or HFMS • In Access – into finding-aids • In Dissemination – to form suitable for consumer
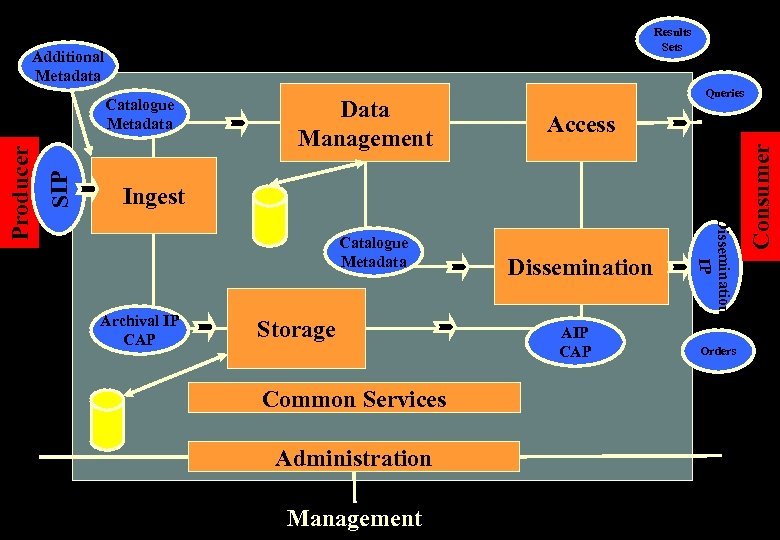 Results Sets Additional Metadata Access Ingest Catalogue Metadata Archival IP CAP Storage Common Services Administration Management Dissemination AIP CAP Orders Consumer SIP Data Management Queries Dissemination IP Producer Catalogue Metadata
Results Sets Additional Metadata Access Ingest Catalogue Metadata Archival IP CAP Storage Common Services Administration Management Dissemination AIP CAP Orders Consumer SIP Data Management Queries Dissemination IP Producer Catalogue Metadata
 OAIS Models • Functional Model. . • Transformations • Migration
OAIS Models • Functional Model. . • Transformations • Migration
 Migration perspectives • Migration should preserve the INFORMATION - need not preserve the BITS • Transformed dataset equivalent to the old if there is a known inverse transformation
Migration perspectives • Migration should preserve the INFORMATION - need not preserve the BITS • Transformed dataset equivalent to the old if there is a known inverse transformation
 Media Migration • New storage medium • If bit-for bit migration possible – new medium same storage density as old – often this will not be the case
Media Migration • New storage medium • If bit-for bit migration possible – new medium same storage density as old – often this will not be the case
 Transformed Logical Structures • Changes in volumes, directory structure, files and records possible
Transformed Logical Structures • Changes in volumes, directory structure, files and records possible
 Transformed Data Objects • Basic data - character, integer, floating – rules to maintain information content with change of representation • Complex objects built up from these • Troubles e. g. if integer is pointer into data
Transformed Data Objects • Basic data - character, integer, floating – rules to maintain information content with change of representation • Complex objects built up from these • Troubles e. g. if integer is pointer into data
 Archive Classifications • • • Acknowledged degree of permanence Digital Information preservation level Degree of opaqueness of AIP Dissemination methods Active vs Final Archive Diversity of collection Institutional vs Non-institutional Archival storage types Distributed vs Centralised
Archive Classifications • • • Acknowledged degree of permanence Digital Information preservation level Degree of opaqueness of AIP Dissemination methods Active vs Final Archive Diversity of collection Institutional vs Non-institutional Archival storage types Distributed vs Centralised
 Possible areas for Standards to follow • • • interfaces between OAIS type archives submission to OAIS dissemination from OAIS search & retrieve metadata from OAIS information migration
Possible areas for Standards to follow • • • interfaces between OAIS type archives submission to OAIS dissemination from OAIS search & retrieve metadata from OAIS information migration
 Conclusion • Full document in MS Word is available from: http: //bolero. gsfc. nasa. gov/nost/isoas • Your comments and participation are strongly encouraged • To participate at any level contact: d. giaretta@rl. ac. uk (01235 -446235)
Conclusion • Full document in MS Word is available from: http: //bolero. gsfc. nasa. gov/nost/isoas • Your comments and participation are strongly encouraged • To participate at any level contact: d. giaretta@rl. ac. uk (01235 -446235)


