2076b9be382e1e0ea539832b8cd961e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Islamic Banking : A Journey to the Basics MURAT ÇETİNKAYA Executive Vice President Kuwait Turkish Participation Bank Istanbul 2011

Agenda 1. What does “Islamic banking” stand for? 2. What relevance does Islamic banking have in the modern financial system? 3. What are the current trends and areas of growth? 4. Where does Turkish experience stand in Islamic banking? 5. Kuwait Finance House (KFH) and Kuwait Turkish Participation Bank

From niche to critical mass · Increasing market presence − − − Growing at 15 to 20% per annum Size estimated at USD 900 billion globally New markets welcoming Islamic banks and products · Market-driven proposition − − − Retail demand has historically the backbone of the industry Sensitivities to principles more visible on retail deposit But corporates and even sovereigns showed appetite for the products Market-driven product development proved to be successful Self-regulating organisations accompanied global Islamic banking boom · Global scale − − − More than 250 Islamic banks worldwide operating in over 75 countries A wide range of interest varying from U. K. to Singapore Widening customer base including sovereigns to top global corporates to tap Islamic finance markets
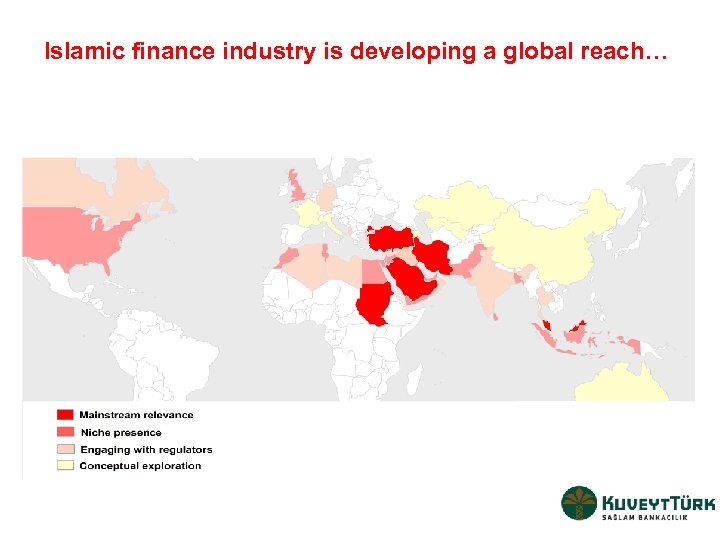
Islamic finance industry is developing a global reach…
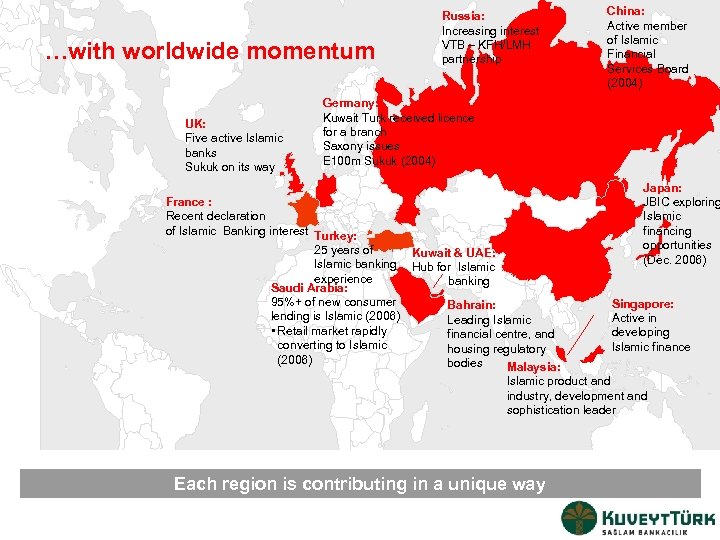
…with worldwide momentum UK: Five active Islamic banks Sukuk on its way Russia: Increasing interest VTB – KFH/LMH partnership China: Active member of Islamic Financial Services Board (2004) Germany: Kuwait Turk received licence for a branch Saxony issues E 100 m Sukuk (2004) France : Recent declaration of Islamic Banking interest Turkey: 25 years of Kuwait & UAE: Islamic banking Hub for Islamic experience banking Saudi Arabia: 95%+ of new consumer Bahrain: lending is Islamic (2006) Leading Islamic • Retail market rapidly financial centre, and converting to Islamic housing regulatory (2006) bodies Malaysia: Japan: JBIC exploring Islamic financing opportunities (Dec. 2006) Singapore: Active in developing Islamic finance Islamic product and industry, development and sophistication leader Each region is contributing in a unique way
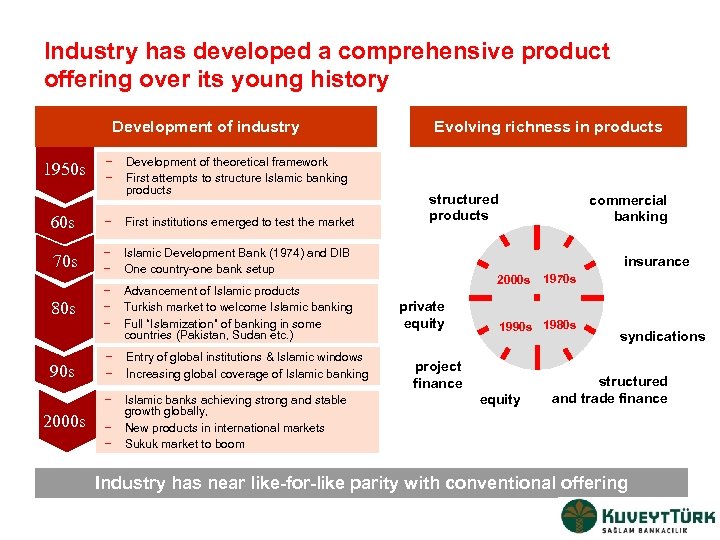
Industry has developed a comprehensive product offering over its young history Development of industry 1950 s − − Development of theoretical framework First attempts to structure Islamic banking products 60 s − First institutions emerged to test the market 70 s − − 80 s Advancement of Islamic products Turkish market to welcome Islamic banking Full “Islamization” of banking in some countries (Pakistan, Sudan etc. ) − − Entry of global institutions & Islamic windows İncreasing global coverage of Islamic banking − Islamic banks achieving strong and stable growth globally, New products in international markets Sukuk market to boom structured products Islamic Development Bank (1974) and DIB One country-one bank setup − − − Evolving richness in products 90 s 2000 s − − commercial banking insurance 2000 s private equity 1970 s 1990 s 1980 s project finance equity syndications structured and trade finance Industry has near like-for-like parity with conventional offering
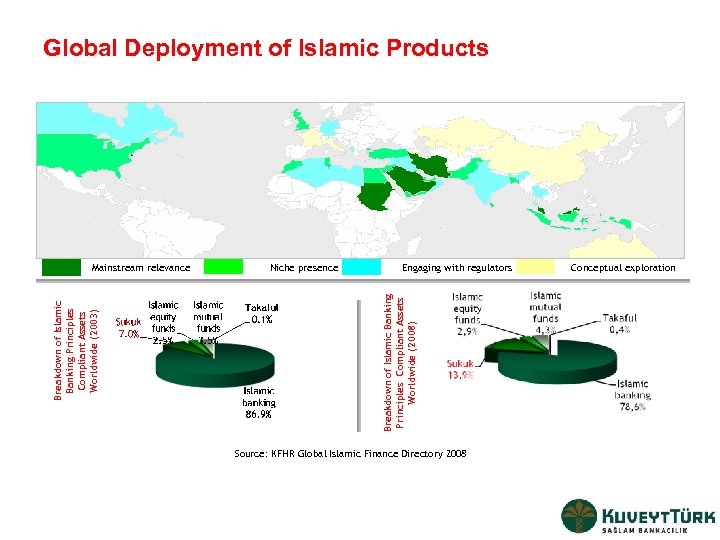
Global Deployment of Islamic Products Niche presence Engaging with regulators Breakdown of Islamic Banking Principles Compliant Assets Worldwide (2008) Breakdown of Islamic Banking Principles Compliant Assets Worldwide (2003) Mainstream relevance Source: KFHR Global Islamic Finance Directory 2008 Conceptual exploration

The industry has not yet reached its potential · Still new markets exist that did not yet meet with Islamic banking and finance · The global Islamic insurance (Takaful) market is estimated to reach USD 20 billion · Most Islamic financial institutions are highly liquid, and seek new asset classes and markets to diversify – New treasury products and investment securities are to emerge – Capital markets developments: New sukuk issuances expected to tap the market · Islamic finance has also gained popularity in Muslim-minority countries – Germany issued the first Islamic Eurobond (2004) – Five Islamic banks in UK · Trends of convergence and conversion – Islamic banks introducing new products and services to compete with the conventional banks, – Conventional banks aiming to tap Islamic banking markets and expand their product base
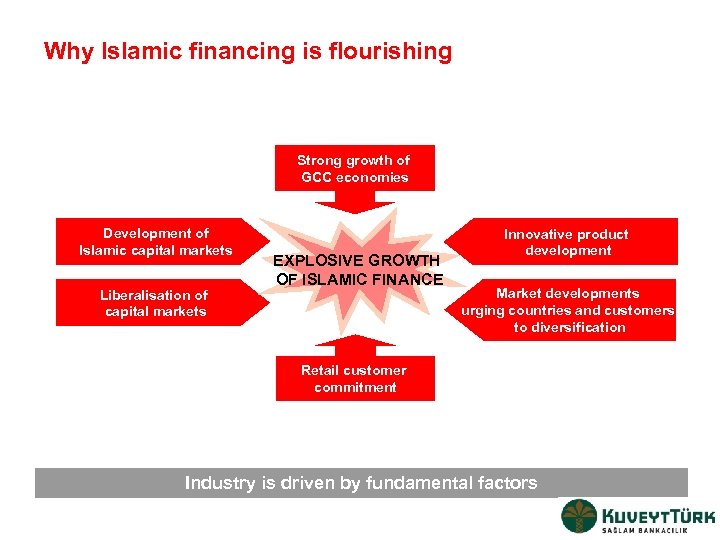
Why Islamic financing is flourishing Strong growth of GCC economies Development of Islamic capital markets Liberalisation of capital markets EXPLOSIVE GROWTH OF ISLAMIC FINANCE Innovative product development Market developments urging countries and customers to diversification Retail customer commitment Industry is driven by fundamental factors
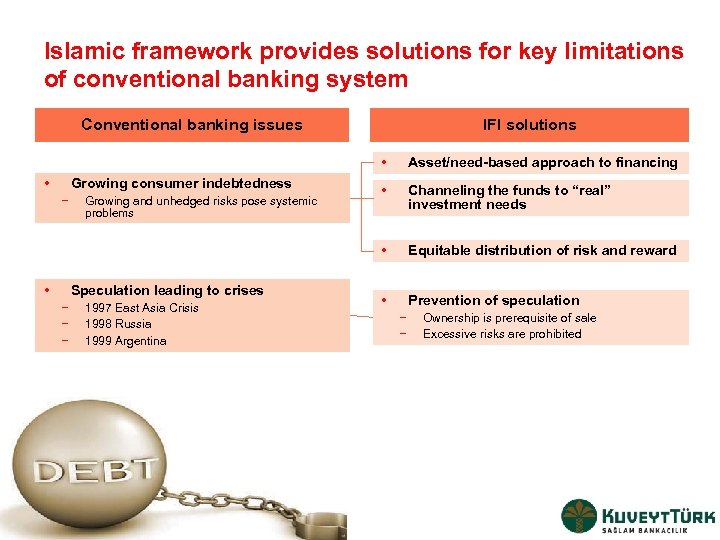
Islamic framework provides solutions for key limitations of conventional banking system Conventional banking issues IFI solutions • Growing consumer indebtedness − • Growing and unhedged risks pose systemic problems Speculation leading to crises − − − 1997 East Asia Crisis 1998 Russia 1999 Argentina • Channeling the funds to “real” investment needs • • Asset/need-based approach to financing Equitable distribution of risk and reward • Prevention of speculation − − Ownership is prerequisite of sale Excessive risks are prohibited
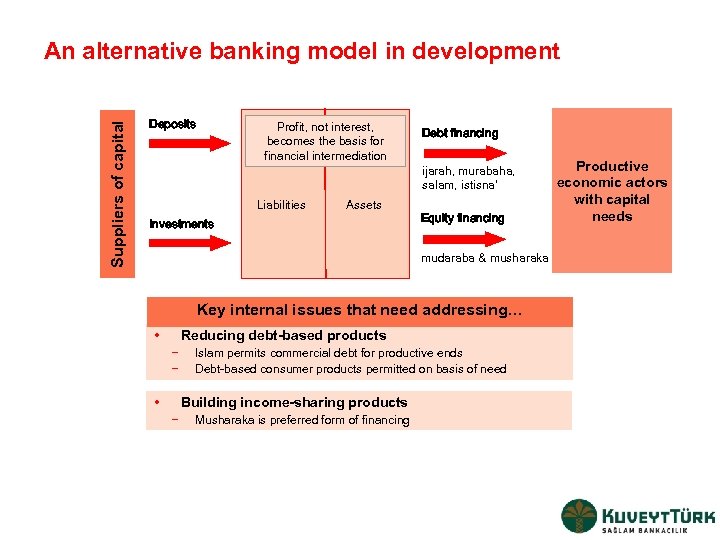
Suppliers of capital An alternative banking model in development Deposits Profit, not interest, becomes the basis for financial intermediation Liabilities Assets Investments Debt financing ijarah, murabaha, salam, istisna‘ Equity financing mudaraba & musharaka Key internal issues that need addressing… • Reducing debt-based products − − • Islam permits commercial debt for productive ends Debt-based consumer products permitted on basis of need Building income-sharing products − Musharaka is preferred form of financing Productive economic actors with capital needs

Tested strength in the financial crisis · Islamic banking, a booming $US 1 trillion global industry that prohibits speculation and high levels of debt, has been relatively unscathed by the credit crunch. · Islamic banking model’s basic principles of – financing “real” trade and economic activities, – no financing of speculation – No engagement in debt trading – Asset backed and project-financing approach to help hedging risks · As a result, the lessons from the crisis; – Islamic banking is inherently stable – Islamic banks outperformed the conventional financial institutions
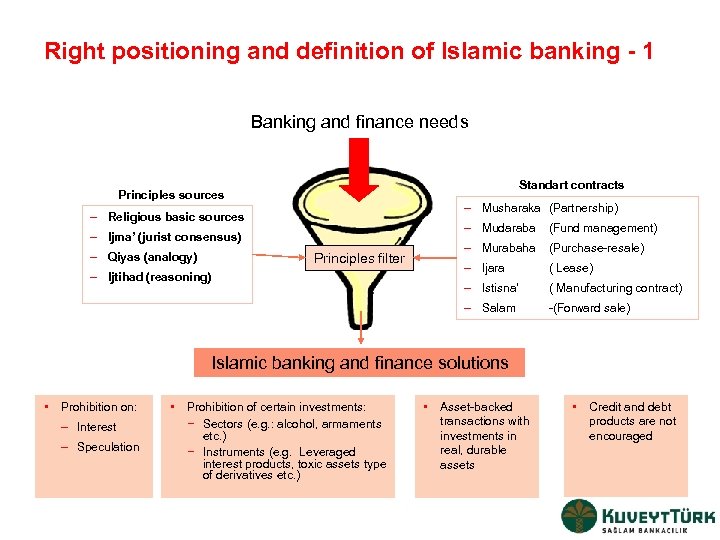
Right positioning and definition of Islamic banking - 1 Banking and finance needs Standart contracts Principles sources – Musharaka (Partnership) – Religious basic sources – Mudaraba – Ijara – Ijtihad (reasoning) ( Lease) – Istisna’ Principles filter (Purchase-resale) ( Manufacturing contract) – Salam – Qiyas (analogy) (Fund management) – Murabaha – Ijma’ (jurist consensus) -(Forward sale) Islamic banking and finance solutions • Prohibition on: – Interest – Speculation • Prohibition of certain investments: − Sectors (e. g. : alcohol, armaments etc. ) − Instruments (e. g. Leveraged interest products, toxic assets type of derivatives etc. ) • Asset-backed transactions with investments in real, durable assets • Credit and debt products are not encouraged
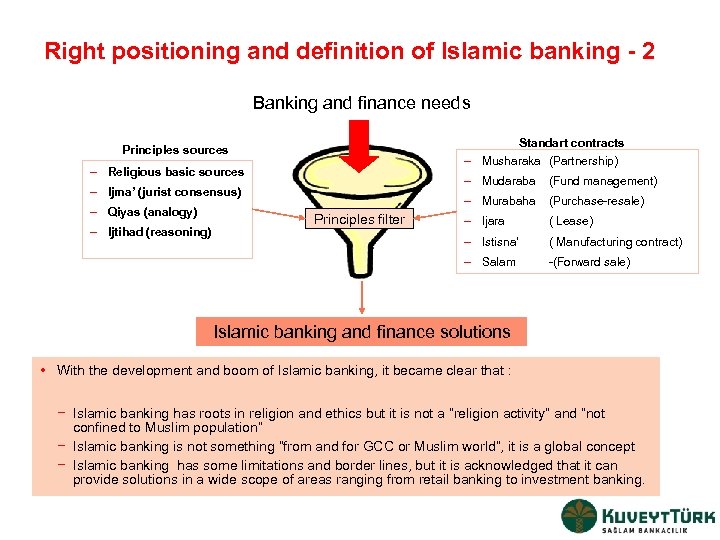
Right positioning and definition of Islamic banking - 2 Banking and finance needs Standart contracts Principles sources – Musharaka (Partnership) – Religious basic sources – Mudaraba – Ijtihad (reasoning) – Ijara ( Lease) – Istisna’ Principles filter (Purchase-resale) ( Manufacturing contract) – Salam – Qiyas (analogy) (Fund management) – Murabaha – Ijma’ (jurist consensus) -(Forward sale) Islamic banking and finance solutions • With the development and boom of Islamic banking, it became clear that : − Islamic banking has roots in religion and ethics but it is not a “religion activity” and “not confined to Muslim population” − Islamic banking is not something “from and for GCC or Muslim world”, it is a global concept − Islamic banking has some limitations and border lines, but it is acknowledged that it can provide solutions in a wide scope of areas ranging from retail banking to investment banking.
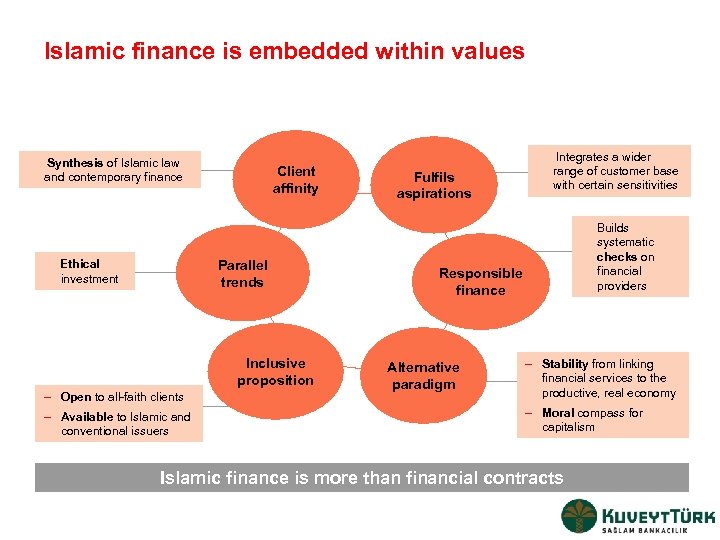
Islamic finance is embedded within values Synthesis of Islamic law and contemporary finance Client affinity Parallel trends Ethical investment Inclusive proposition – Open to all-faith clients – Available to Islamic and conventional issuers Fulfils aspirations Integrates a wider range of customer base with certain sensitivities Builds systematic checks on financial providers Responsible finance Alternative paradigm – Stability from linking financial services to the productive, real economy – Moral compass for capitalism Islamic finance is more than financial contracts
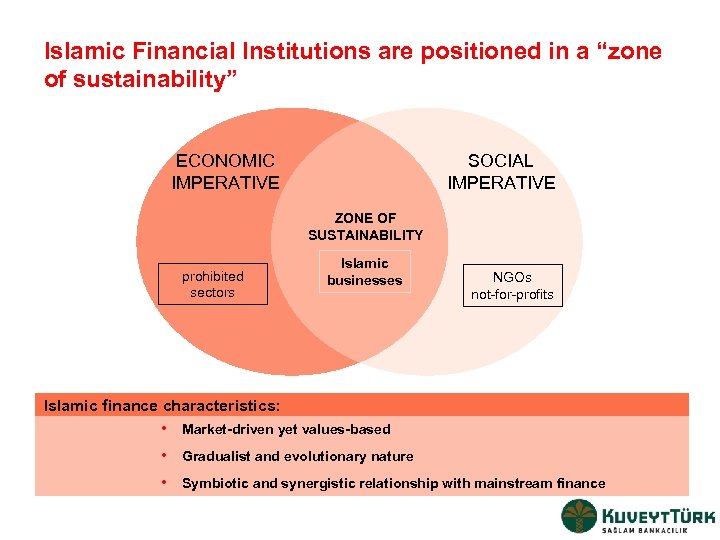
Islamic Financial Institutions are positioned in a “zone of sustainability” ECONOMIC IMPERATIVE SOCIAL IMPERATIVE ZONE OF SUSTAINABILITY prohibited sectors Islamic businesses NGOs not-for-profits Islamic finance characteristics: • Market-driven yet values-based • Gradualist and evolutionary nature • Symbiotic and synergistic relationship with mainstream finance

Self-regulatory organizations bring credibility through standardization of practices AAO-IFI · Benchmark of Islamic accounting standards (1991) Bahrain − − 56 accounting, auditing, governance and Shariah standards Enhancing clarity, transparency and harmonisation IIFM · Development of global Islamic capital and money market Bahrain − − Promoting active and regulated trading and capital flows Catalyzing trading infrastructure, product innovation and information flows GCIBFI · Promoting industry in theory and practice − − Disseminating Shariah concepts & multilateral understanding between IFIs and public Improving IFI practices, cooperation, professionalism and transparency · Standard-setting body of regulatory and supervisory agencies − − Complementing Basel II Capital Accord Key standards: risk management, capital adequacy & corporate governance · Creation of active Islamic inter-bank market Bahrain − − Creating secondary market for short-term Shariah-compliant treasury products Enabling IFI management of liquidity mismatch IIRA · Reference point for IFI ratings − − Issuing sovereign, credit, Shariah quality and corporate governance ratings Providing effective tool for informed investment decision-making (2001) Bahrain IFSB (2002) Malaysia LMC (2002) (2005) Bahrain

Industry is reaching mainstream relevance in global financial system Relevance in countries with already developed Islamic banking • Widens the bankable population and customer base − − − • Increases bankable population of economy Increases product base in the system Attracts more deposits/funds from the customers Enhances stability of financial model − Asset-based framework links financial services to real economy Relevance to new-comers • • Reaching a broader market Alternative source of funding − − • Debt issuance with the widest acceptance Attract “new-to-industry” investors Gateway to OIC markets − − Regional preference of Islamic investors Infrastructure investment opportunities

A number of factors need to be engaged to bring success • Dedicated people − − Key enablers • Greatest intangible to enable Islamic finance and build its future Human capital development: bankers and scholars Committed sponsorship − − • Academic input to formulate visionary framework and development Capital sponsorship to bring plans to life Proactive engagement − Regulators, practitioners and scholars to set a common agenda Need for co-ordination to enable further development

The way ahead …. . i Current expanding reach and richness of Islamic finance – Despite the absence of an enabling framework – But at a cost: culture of exceptions, Shariah credibility, competitive disadvantages i To build an enabling framework requires concerted efforts – Collaboration between IFIs, endowed industry institutions and regulators – Exploration of narrow banking principles i We must preserve what is distinctive about Islamic finance – Industry regulations and governance heading towards mainstream globalization – Balancing different elements of Shariah credibility

Overview of Kuwait Finance House • • Key Kuwait Finance House K. S. C. (KFH) was established in the State of Kuwait in 1977, as the first bank operating in accordance with the Islamic Banking principles. KFH is listed with the Kuwait Stock Exchange (KSE), with a market capitalization of US$ 9. 55 Billion as of 22 June 2009. Assets total US$ 37 Billion and deposits amount to US$ 24 Billion as at Q 1 2009. • In the global Islamic arena, KFH is in the forefront of the industry in terms of international presence, spectrum of activities, strategic alliances, networking and innovation. • KFH has been awarded by the Banker Magazine as the World’s Best Islamic Financial Institution, and for third successive year it has been awarded by Euromoney magazine as the best Islamic Bank in the Middle East. • KFH is engaged in providing Islamic banking services, and its spectrum includes consumer banking, corporate finance, Islamic capital markets, real estate finance, structured finance, investment portfolios, and other products and services. Facts
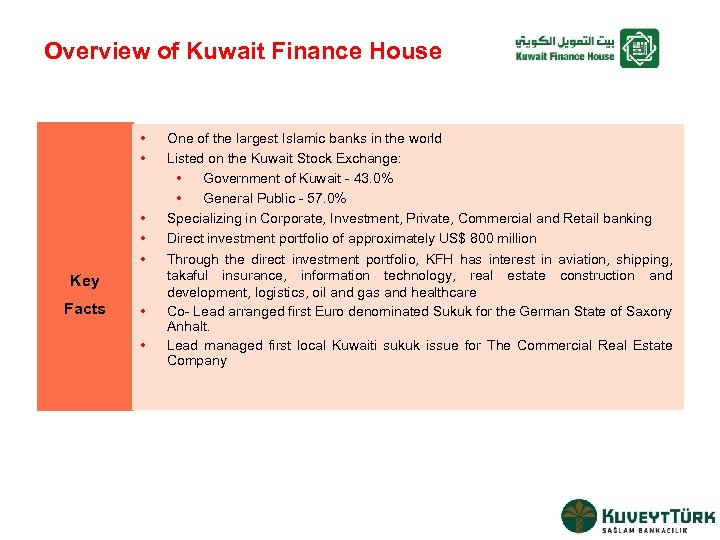
Overview of Kuwait Finance House • • • Key Facts • • One of the largest Islamic banks in the world Listed on the Kuwait Stock Exchange: • Government of Kuwait - 43. 0% • General Public - 57. 0% Specializing in Corporate, Investment, Private, Commercial and Retail banking Direct investment portfolio of approximately US$ 800 million Through the direct investment portfolio, KFH has interest in aviation, shipping, takaful insurance, information technology, real estate construction and development, logistics, oil and gas and healthcare Co- Lead arranged first Euro denominated Sukuk for the German State of Saxony Anhalt. Lead managed first local Kuwaiti sukuk issue for The Commercial Real Estate Company
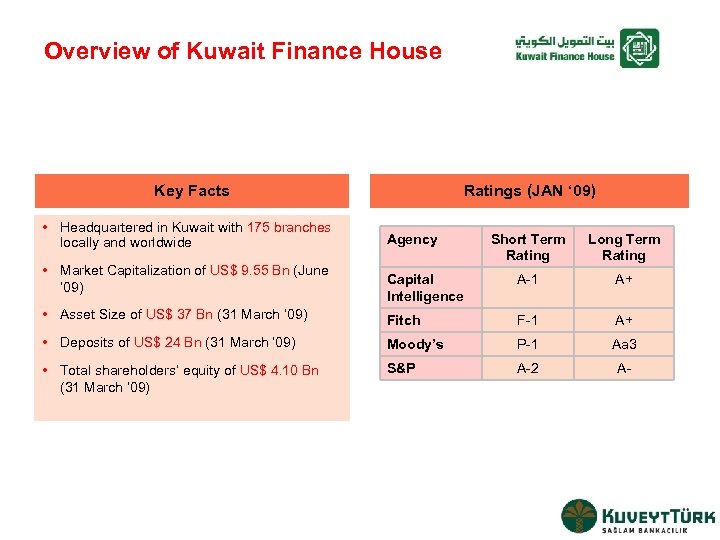
Overview of Kuwait Finance House Key Facts • Headquartered in Kuwait with 175 branches locally and worldwide Ratings (JAN ‘ 09) Short Term Rating Long Term Rating Capital Intelligence A-1 A+ • Asset Size of US$ 37 Bn (31 March ‘ 09) Fitch F-1 A+ • Deposits of US$ 24 Bn (31 March ‘ 09) Moody’s P-1 Aa 3 • Total shareholders’ equity of US$ 4. 10 Bn (31 March ’ 09) S&P A-2 A- • Market Capitalization of US$ 9. 55 Bn (June ‘ 09) Agency

Overview of Kuwait Finance House • Ability to structure and close transactions rapidly due to bank’s seasoned expertise, network, strategic partnerships, financial strength and sound liquidity position. • A deeply entrenched brand franchise with subsidiaries in Bahrain, Turkey, Malaysia, Singapore, Australia, Jordan and Saudi Arabia and affiliates in UAE and Oman Competitive • Strengths Strong underwriting ability: unrivalled access to Islamic deposits in the domestic & regional market. • Formation of Liquidity House as an investment house fully dedicated to Sukuk issuances. • Strong links with regional and international financial institutions • presence in the domestic and regional real estate market and proven transactional expertise in the international arena. • Recognized and respectable Advisory Board and structuring expertise; KFH Advisory Board clearances and approvals on structures are in most, if not all, cases taken for granted by other fellow participants in deals and transactions.
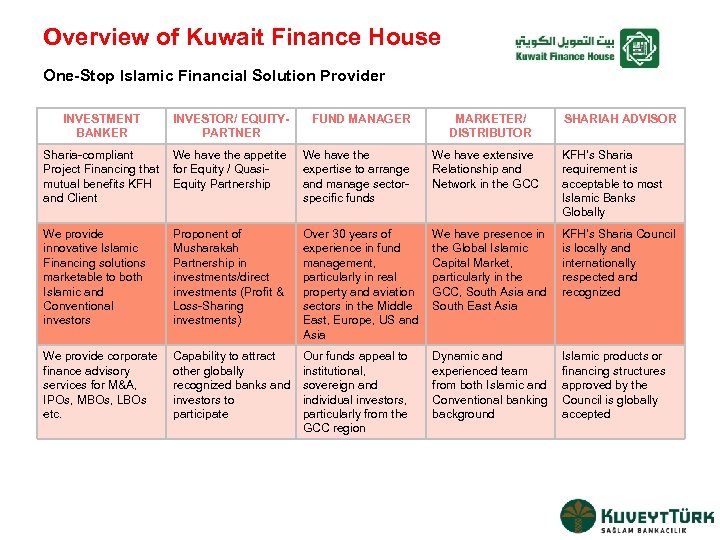
Overview of Kuwait Finance House One-Stop Islamic Financial Solution Provider INVESTMENT BANKER INVESTOR/ EQUITYPARTNER FUND MANAGER MARKETER/ DISTRIBUTOR SHARIAH ADVISOR Sharia-compliant Project Financing that mutual benefits KFH and Client We have the appetite for Equity / Quasi. Equity Partnership We have the expertise to arrange and manage sectorspecific funds We have extensive Relationship and Network in the GCC KFH’s Sharia requirement is acceptable to most Islamic Banks Globally We provide innovative Islamic Financing solutions marketable to both Islamic and Conventional investors Proponent of Musharakah Partnership in investments/direct investments (Profit & Loss-Sharing investments) Over 30 years of experience in fund management, particularly in real property and aviation sectors in the Middle East, Europe, US and Asia We have presence in the Global Islamic Capital Market, particularly in the GCC, South Asia and South East Asia KFH’s Sharia Council is locally and internationally respected and recognized We provide corporate finance advisory services for M&A, IPOs, MBOs, LBOs etc. Capability to attract other globally recognized banks and investors to participate Our funds appeal to institutional, sovereign and individual investors, particularly from the GCC region Dynamic and experienced team from both Islamic and Conventional banking background Islamic products or financing structures approved by the Council is globally accepted
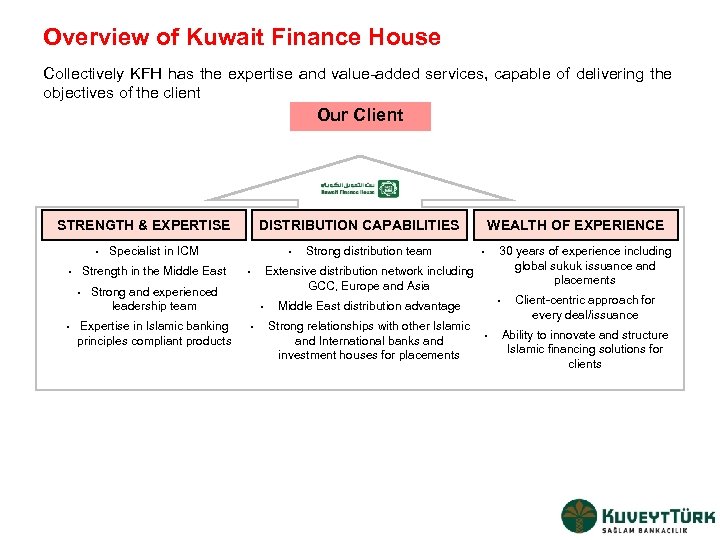
Overview of Kuwait Finance House Collectively KFH has the expertise and value-added services, capable of delivering the objectives of the client Our Client STRENGTH & EXPERTISE • • • Specialist in ICM Strength in the Middle East • DISTRIBUTION CAPABILITIES • • Extensive distribution network including GCC, Europe and Asia • Strong and experienced leadership team Expertise in Islamic banking principles compliant products Strong distribution team WEALTH OF EXPERIENCE • • • Middle East distribution advantage Strong relationships with other Islamic and International banks and investment houses for placements 30 years of experience including global sukuk issuance and placements • Client-centric approach for every deal/issuance Ability to innovate and structure Islamic financing solutions for clients

KFH RESEARCH LIMITED KFH Research Ltd is the world's first Islamic investment research arm to be established by an Islamic Bank. A direct subsidiary of Kuwait Finance House, KFH Research was established in 2007, comprising industry professionals and 'star' research analysts with broad experience in Islamic finance & global markets. Below is a sample of their reports:

KFH GROUP: A SAMPLE Next Steps
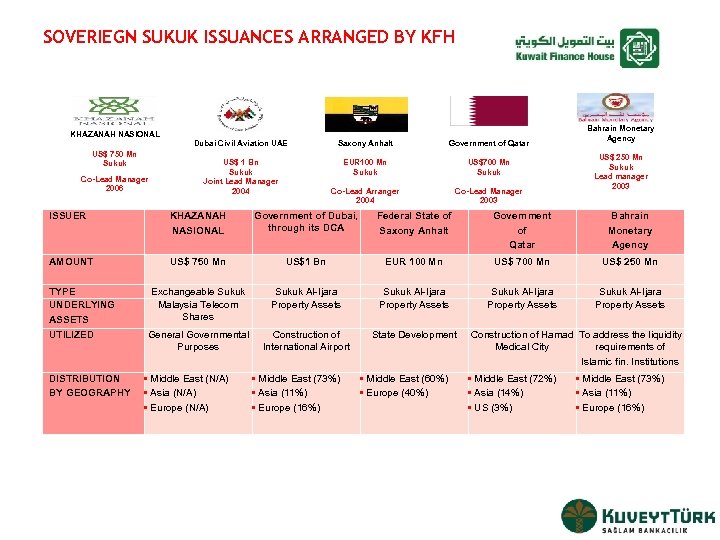
SOVERIEGN SUKUK ISSUANCES ARRANGED BY KFH KHAZANAH NASIONAL US$ 750 Mn Sukuk Co-Lead Manager 2006 Dubai Civil Aviation UAE Saxony Anhalt Government of Qatar US$ 1 Bn Sukuk Joint Lead Manager 2004 EUR 100 Mn Sukuk US$700 Mn Sukuk Co-Lead Arranger 2004 Co-Lead Manager 2003 Bahrain Monetary Agency US$ 250 Mn Sukuk Lead manager 2003 ISSUER KHAZANAH NASIONAL Government of Dubai, through its DCA Federal State of Saxony Anhalt Government of Qatar Bahrain Monetary Agency AMOUNT US$ 750 Mn US$1 Bn EUR 100 Mn US$ 700 Mn US$ 250 Mn Exchangeable Sukuk Malaysia Telecom Shares Sukuk Al-Ijara Property Assets General Governmental Purposes Construction of International Airport State Development TYPE UNDERLYING ASSETS UTILIZED DISTRIBUTION BY GEOGRAPHY • Middle East (N/A) • Asia (N/A) • Europe (N/A) • Middle East (73%) • Asia (11%) • Europe (16%) • Middle East (60%) • Europe (40%) Construction of Hamad To address the liquidity Medical City requirements of Islamic fin. Institutions • Middle East (72%) • Asia (14%) • US (3%) • Middle East (73%) • Asia (11%) • Europe (16%)
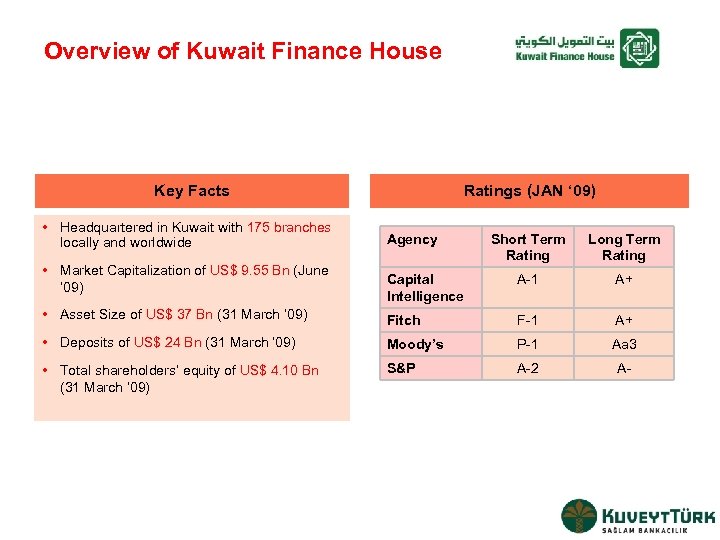
Overview of Kuwait Finance House Key Facts • Headquartered in Kuwait with 175 branches locally and worldwide Ratings (JAN ‘ 09) Short Term Rating Long Term Rating Capital Intelligence A-1 A+ • Asset Size of US$ 37 Bn (31 March ‘ 09) Fitch F-1 A+ • Deposits of US$ 24 Bn (31 March ‘ 09) Moody’s P-1 Aa 3 • Total shareholders’ equity of US$ 4. 10 Bn (31 March ’ 09) S&P A-2 A- • Market Capitalization of US$ 9. 55 Bn (June ‘ 09) Agency
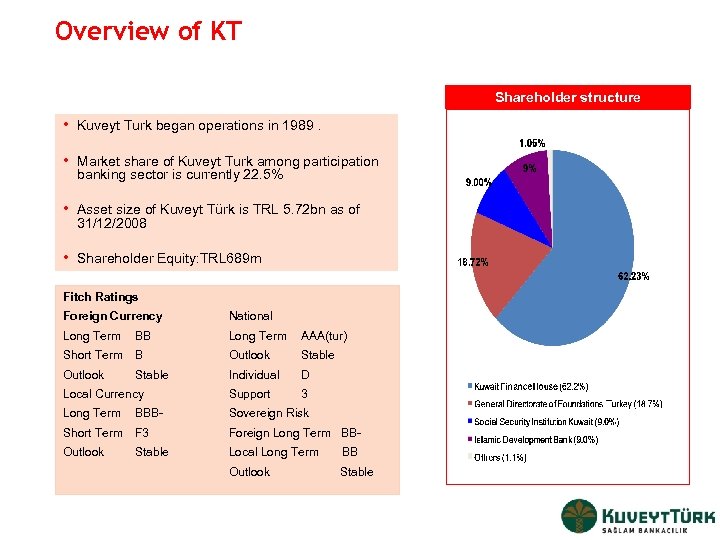
Overview of KT Shareholder structure • Kuveyt Turk began operations in 1989. • Market share of Kuveyt Turk among participation banking sector is currently 22. 5% • Asset size of Kuveyt Türk is TRL 5. 72 bn as of 31/12/2008 • Shareholder Equity: TRL 689 m Fitch Ratings Foreign Currency National Long Term BB Long Term AAA(tur) Short Term B Outlook Stable Individual D Local Currency Support 3 Long Term BBB- Sovereign Risk Short Term F 3 Foreign Long Term BB- Outlook Stable Local Long Term BB Outlook Stable
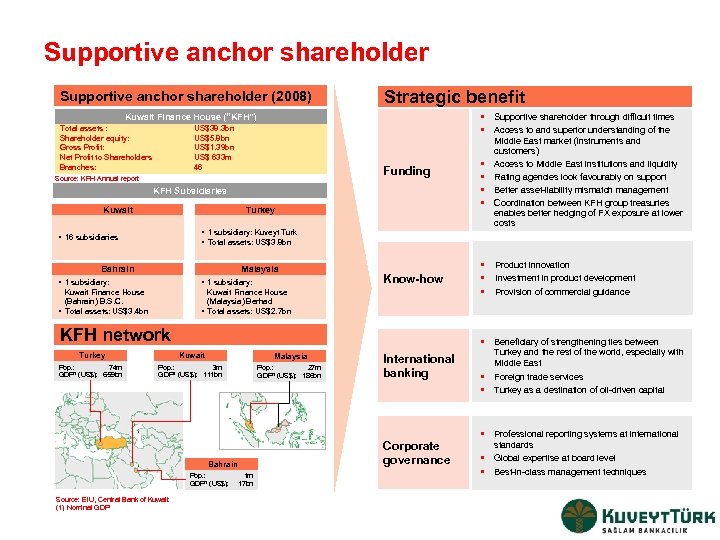
Supportive anchor shareholder (2008) Strategic benefit • Supportive shareholder through difficult times • Access to and superior understanding of the Kuwait Finance House (“KFH”) Total assets : Shareholder equity: Gross Profit: Net Profit to Shareholders Branches: US$38. 3 bn US$5. 8 bn US$1. 39 bn US$ 633 m 46 Funding Source: KFH Annual report KFH Subsidiaries Kuwait Turkey • 1 subsidiary: Kuveyt Turk • Total assets: US$3. 8 bn • 16 subsidiaries Bahrain Malaysia • 1 subsidiary: Kuwait Finance House (Bahrain) B. S. C. • Total assets: US$3. 4 bn Know-how Kuwait Finance House (Malaysia) Berhad • Total assets: US$2. 7 bn KFH network • Product innovation • Investment in product development • Provision of commercial guidance • Beneficiary of strengthening ties between Turkey Kuwait Malaysia Pop. : 74 m GDP 1 (US$): 659 bn Pop. : 3 m GDP 1 (US$): 111 bn Pop. : 27 m GDP 1 (US$): 186 bn Bahrain Pop. : GDP 1 (US$): Source: EIU, Central Bank of Kuwait (1) Nominal GDP • • Middle East market (instruments and customers) Access to Middle East institutions and liquidity Rating agencies look favourably on support Better asset-liability mismatch management Coordination between KFH group treasuries enables better hedging of FX exposure at lower costs 1 m 17 bn International banking Corporate governance Turkey and the rest of the world, especially with Middle East • Foreign trade services • Turkey as a destination of oil-driven capital • Professional reporting systems at international standards Global expertise at board level • • Best-in-class management techniques
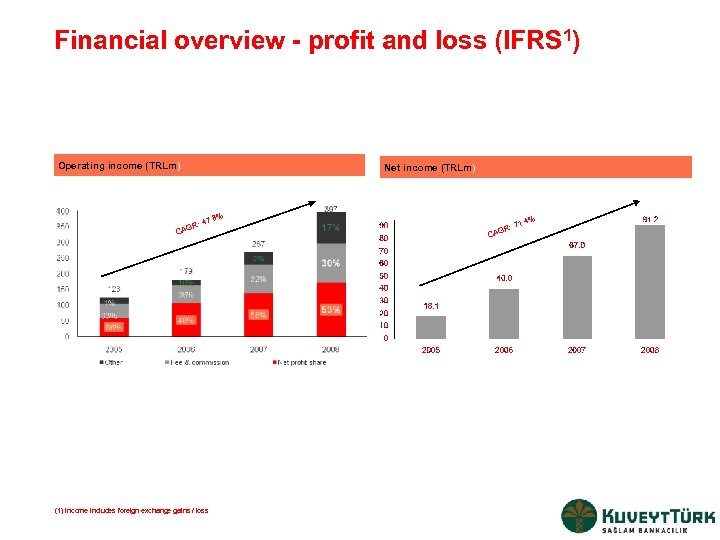
Financial overview - profit and loss (IFRS 1) Operating income (TRLm) Net income (TRLm) 7. 8% R: 4 CAG (1) Income includes foreign exchange gains / loss . 4% : 71 R CAG
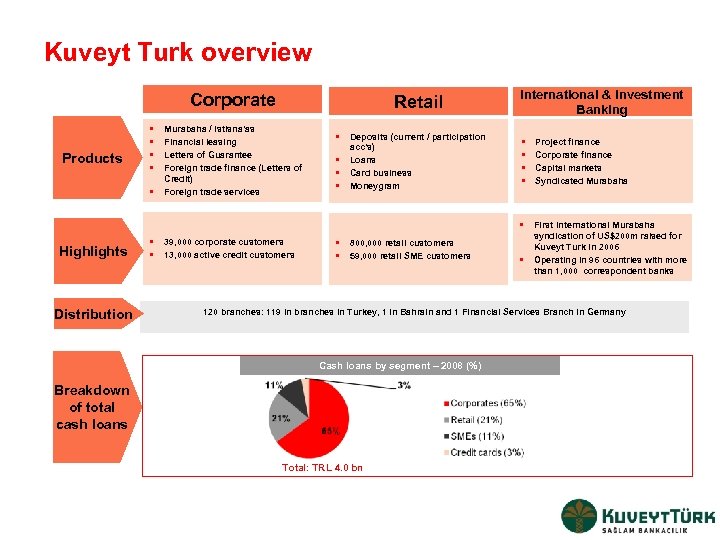
Kuveyt Turk overview Corporate Products • • • Retail Murabaha / Istisna’as Financial leasing Letters of Guarantee Foreign trade finance (Letters of Credit) Foreign trade services • Deposits (current / participation • • • acc’s) Loans Card business Moneygram International & Investment Banking • • Project finance Corporate finance Capital markets Syndicated Murabaha • First international Murabaha Highlights Distribution • 39, 000 corporate customers • 13, 000 active credit customers • 800, 000 retail customers • 59, 000 retail SME customers • syndication of US$200 m raised for Kuveyt Turk in 2006 Operating in 96 countries with more than 1, 000 correspondent banks 120 branches: 119 in branches in Turkey, 1 in Bahrain and 1 Financial Services Branch in Germany Cash loans by segment – 2008 (%) Breakdown of total cash loans Total: TRL 4. 0 bn
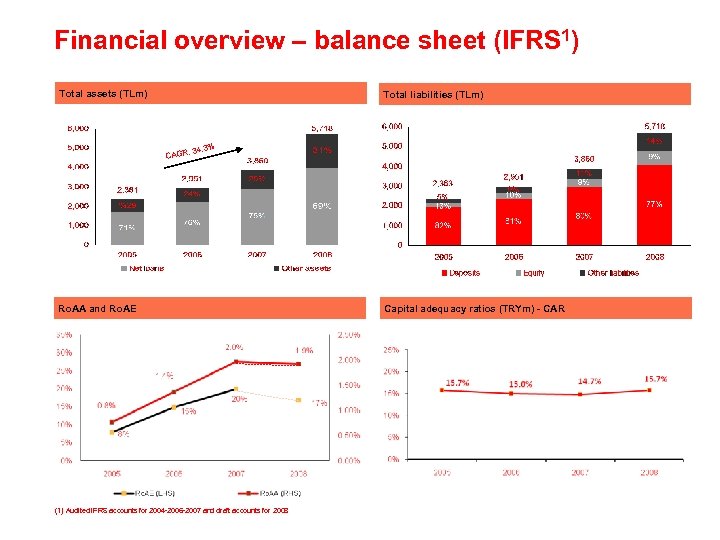
Financial overview – balance sheet (IFRS 1) Total assets (TLm) Total liabilities (TLm) : CAGR 34. 3% Ro. AA and Ro. AE (1) Audited IFRS accounts for 2004 -2006 -2007 and draft accounts for 2008 Capital adequacy ratios (TRYm) - CAR
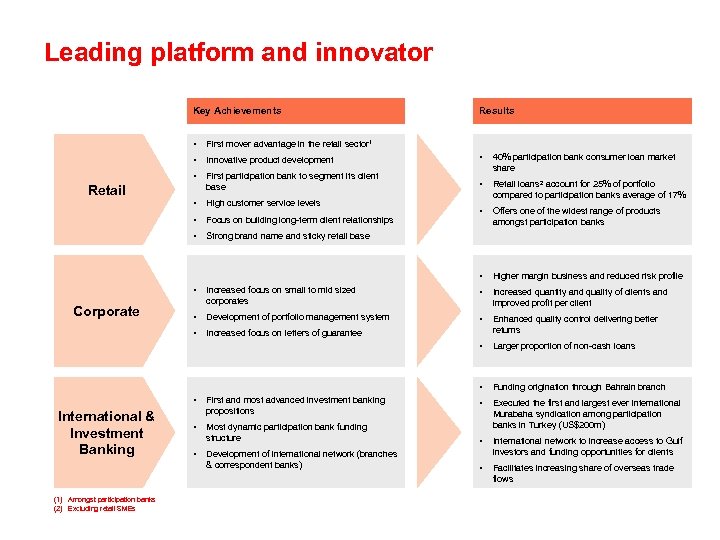
Leading platform and innovator Key Achievements Results • First mover advantage in the retail sector 1 • Innovative product development • • First participation bank to segment its client base 40% participation bank consumer loan market share • • High customer service levels Retail loans 2 account for 25% of portfolio compared to participation banks average of 17% • Focus on building long-term client relationships • Offers one of the widest range of products amongst participation banks • Strong brand name and sticky retail base • Higher margin business and reduced risk profile Retail • • Increased quantity and quality of clients and improved profit per client • Development of portfolio management system • • Increased focus on letters of guarantee Enhanced quality control delivering better returns • Larger proportion of non-cash loans • Corporate Increased focus on small to mid sized corporates Funding origination through Bahrain branch • Executed the first and largest ever international Murabaha syndication among participation banks in Turkey (US$200 m) • International & Investment Banking (1) Amongst participation banks (2) Excluding retail SMEs First and most advanced investment banking propositions • Most dynamic participation bank funding structure • Development of international network (branches & correspondent banks) International network to increase access to Gulf investors and funding opportunities for clients • Facilitates increasing share of overseas trade flows •
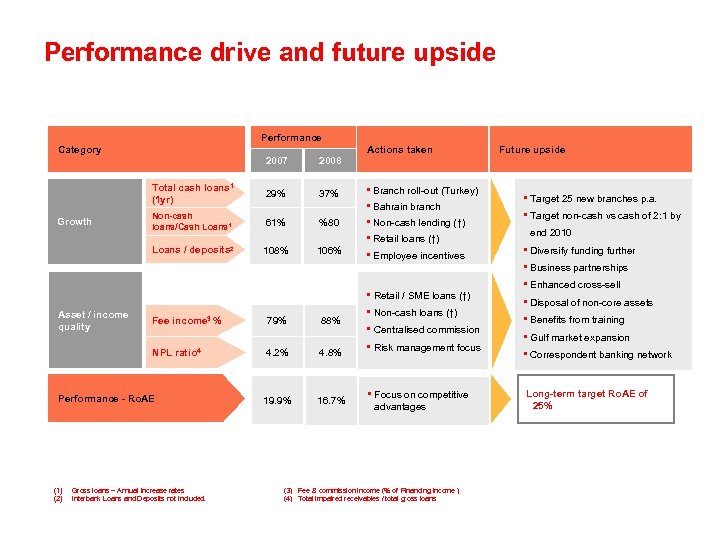
Performance drive and future upside Performance Category Actions taken 2007 Total cash loans 1 (1 yr) 37% Non-cash loans/Cash Loans 1 61% %80 Loans / deposits Growth 29% 108% 106% 2 • Branch roll-out (Turkey) • Bahrain branch • Non-cash lending (↑) • Retail loans (↑) • Employee incentives • Retail / SME loans (↑) Asset / income quality Fee income 3 % NPL ratio 4 Performance - Ro. AE (1) (2) Future upside 2008 Gross loans – Annual increase rates Interbank Loans and Deposits not included. 79% 88% 4. 2% 4. 8% 19. 9% 16. 7% • Non-cash loans (↑) • Centralised commission • Risk management focus • Focus on competitive advantages (3) Fee & commission income (% of Financing income ) (4) Total impaired receivables / total gross loans • Target 25 new branches p. a. • Target non-cash vs cash of 2: 1 by end 2010 • Diversify funding further • Business partnerships • Enhanced cross-sell • Disposal of non-core assets • Benefits from training • Gulf market expansion • Correspondent banking network Long-term target Ro. AE of 25%
Strategy Capitalise on advanced retail / SME franchise Capture trade flows from overseas locations Grow local customer base through branch roll-out Leverage existing customer base through enhanced product range / offering Enhance non-cash business Improve operational efficiency through cost control initiatives Become Turkey’s leading participation bank and one of Turkey’s top 10 banks

Strategy in International Banking Key highlights • Raised US$200 m through a syndicated commodity Murabaha transaction for Kuveyt Turk in 2006 • Arranged US$240 m of international syndications since 2006 • Correspondent banking relationship with around 1, 000 financial institutions in 96 countries Key strategic goal • Increase market share in international syndicated facilities • Leverage off KFH relationship and Bahrain branch to drive growth through increased access to Gulf investors • Expand German representative office into full branch operation Products Means of achieving strategic goals • Focus on increasing quality and size of international syndications • Expand treasury function • Increase international services to retail and corporate customers International expansion • Dubai branch expected to be operational • Germany representative office awarded Financial Services branch license in 2009 • Expected to add value on fund mobilisation from Turkish and Muslim population. • Further expand correspondent bank network in line with demand for trade finance activities International expansion and access to Gulf investors key to growing ahead of the market

Let’s move together further ahead to explore new peaks and horizons of Islamic banking Thank you Murat Çetinkaya EVP, Kuwait Turkish Participation Bank
2076b9be382e1e0ea539832b8cd961e7.ppt