fa34473ebb2b486aa242250305a724b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Islam Theme: Religion’s impact on society Lesson 15
Islam Theme: Religion’s impact on society Lesson 15
 Islam and Muslim • Islam means “submission” – Signifies obedience to the rule and will of Allah • A Muslim is one who accepts the Islamic faith – Means “one who has submitted”
Islam and Muslim • Islam means “submission” – Signifies obedience to the rule and will of Allah • A Muslim is one who accepts the Islamic faith – Means “one who has submitted”
 Muhammad • Born in 570 into a reputable family of merchants in Mecca • Lost both of his parents by the time he was 6 years old • As a young man, Muhammad worked for Khadija, a wealthy widow who he married around 595 – This marriage gained him a position of some prominence in Meccan society – By the age of 30 Muhammad had established himself as a merchant
Muhammad • Born in 570 into a reputable family of merchants in Mecca • Lost both of his parents by the time he was 6 years old • As a young man, Muhammad worked for Khadija, a wealthy widow who he married around 595 – This marriage gained him a position of some prominence in Meccan society – By the age of 30 Muhammad had established himself as a merchant
 Muhammad • Muhammad’s status as a merchant undoubtedly brought him in contact with both Jews and Christians and he would have had a basic knowledge of both faiths • About 610, when he was about 40, Muhammad had a spiritual experience that convinced him that there was only one true deity, Allah (“God”)
Muhammad • Muhammad’s status as a merchant undoubtedly brought him in contact with both Jews and Christians and he would have had a basic knowledge of both faiths • About 610, when he was about 40, Muhammad had a spiritual experience that convinced him that there was only one true deity, Allah (“God”)
 Allah • Elements of Muhammad’s spiritual transformation – Allah rules the universe – Idolatry and the recognition of other gods amounts to wickedness – Allah would soon bring his judgment on the world • Muhammad received messages or revelations from Gabriel, the archangel, instructing him to explain his faith to others
Allah • Elements of Muhammad’s spiritual transformation – Allah rules the universe – Idolatry and the recognition of other gods amounts to wickedness – Allah would soon bring his judgment on the world • Muhammad received messages or revelations from Gabriel, the archangel, instructing him to explain his faith to others
 Quran (Koran) • Muhammad originally just shared the message with his family and close friends, but gradually others became interested • By about 620, a zealous and expanding minority in Mecca had joined Muhammad’s circle • As the Muslim community grew, Muhammad’s followers began writing down his oral recitations into written texts – During the 650 s these writings were issued as the Quran (“recitation”)
Quran (Koran) • Muhammad originally just shared the message with his family and close friends, but gradually others became interested • By about 620, a zealous and expanding minority in Mecca had joined Muhammad’s circle • As the Muslim community grew, Muhammad’s followers began writing down his oral recitations into written texts – During the 650 s these writings were issued as the Quran (“recitation”)
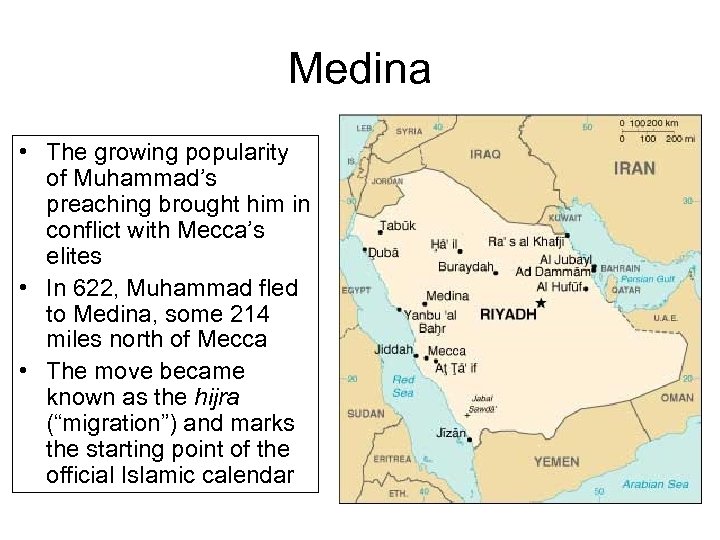 Medina • The growing popularity of Muhammad’s preaching brought him in conflict with Mecca’s elites • In 622, Muhammad fled to Medina, some 214 miles north of Mecca • The move became known as the hijra (“migration”) and marks the starting point of the official Islamic calendar
Medina • The growing popularity of Muhammad’s preaching brought him in conflict with Mecca’s elites • In 622, Muhammad fled to Medina, some 214 miles north of Mecca • The move became known as the hijra (“migration”) and marks the starting point of the official Islamic calendar
 Reasons for Muhammad’s Conflict in Mecca • Insistence that Allah was the only true god clashed with many polytheistic Arabs • Muhammad’s denunciation of greed as a moral weakness that Allah would punish threatened Mecca’s wealthy merchants • Muhammad’s attack on idolatry represented an economic threat to those who profited from the many shrines to the various deities – Ka’ba was one such shrine
Reasons for Muhammad’s Conflict in Mecca • Insistence that Allah was the only true god clashed with many polytheistic Arabs • Muhammad’s denunciation of greed as a moral weakness that Allah would punish threatened Mecca’s wealthy merchants • Muhammad’s attack on idolatry represented an economic threat to those who profited from the many shrines to the various deities – Ka’ba was one such shrine
 Umma • In Mecca, Muhammad had lived within an established political framework and therefore concentrated on moral and religious dimensions • In Medina, the society in exile needed guidance in more than just spiritual matters – Muhammad organizes his followers into a cohesive community called the umma (“community of the faithful”)
Umma • In Mecca, Muhammad had lived within an established political framework and therefore concentrated on moral and religious dimensions • In Medina, the society in exile needed guidance in more than just spiritual matters – Muhammad organizes his followers into a cohesive community called the umma (“community of the faithful”)
 Umma • Muhammad provided a comprehensive legal and social code • He led the community in prayer and in battle • He provided economic support both by organizing commercial ventures and by raiding caravans from Mecca • He provided for the relief of orphans and widows and made almsgiving a prime moral value
Umma • Muhammad provided a comprehensive legal and social code • He led the community in prayer and in battle • He provided economic support both by organizing commercial ventures and by raiding caravans from Mecca • He provided for the relief of orphans and widows and made almsgiving a prime moral value
 Umma • Individuals belong to a community • The positive benefits of all who embrace Islam (social justice, solidarity and purpose, and political stability) are enjoyed by all in areas guided by Islamic law (dar al-Islam means the “house of Islam” and refers to lands under Islamic rule) Mecca Detroit East London
Umma • Individuals belong to a community • The positive benefits of all who embrace Islam (social justice, solidarity and purpose, and political stability) are enjoyed by all in areas guided by Islamic law (dar al-Islam means the “house of Islam” and refers to lands under Islamic rule) Mecca Detroit East London
 Return to Mecca • In 630, Muhammad attacked Mecca, conquered it, and forced the elites to adopt the faith • Destroyed pagan shrines and replaced them with mosques • Imposed a government dedicated to Allah • Building on the conquest of Mecca, Muhammad launched other military campaigns and by the time of his death in 632, most of Arabia was under his control
Return to Mecca • In 630, Muhammad attacked Mecca, conquered it, and forced the elites to adopt the faith • Destroyed pagan shrines and replaced them with mosques • Imposed a government dedicated to Allah • Building on the conquest of Mecca, Muhammad launched other military campaigns and by the time of his death in 632, most of Arabia was under his control
 Ka’ba • Muhammad spared the Ka’ba from destruction and preserved it as a symbol of Mecca’s greatness • In 632, Muhammad led the first pilgrimage to the Ka’ba – Establishes the hajj as an example for all devout Muslims
Ka’ba • Muhammad spared the Ka’ba from destruction and preserved it as a symbol of Mecca’s greatness • In 632, Muhammad led the first pilgrimage to the Ka’ba – Establishes the hajj as an example for all devout Muslims
 Five Pillars of Islam • Acknowledge Allah as the only god and Muhammad as his prophet (iman) • Pray to Allah daily while facing Mecca (salah) • Observe a fast during daylight hours of the month of Ramadan (sawm) • Contribute alms to the relief of the weak and poor (zakah) • Those who are physically and financially able must make at least one pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj)
Five Pillars of Islam • Acknowledge Allah as the only god and Muhammad as his prophet (iman) • Pray to Allah daily while facing Mecca (salah) • Observe a fast during daylight hours of the month of Ramadan (sawm) • Contribute alms to the relief of the weak and poor (zakah) • Those who are physically and financially able must make at least one pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj)
 Translation of the Adan (Call to Prayer) God is Great. I testify that there is none worthy of worship except God. I testify that Muhammad is the messenger of God. Come to prayer! Come to success! God is Great! There is none worthy of worship except God.
Translation of the Adan (Call to Prayer) God is Great. I testify that there is none worthy of worship except God. I testify that Muhammad is the messenger of God. Come to prayer! Come to success! God is Great! There is none worthy of worship except God.
 Ramadan • Ninth month of the Islamic calendar – A time for inner reflection, devotion to God, and self-control • Daily period of fasting from dawn to dusk – Observers totally abstain from food, drink, smoking, and sex • Ramadan ends with a joyous celebration called 'Eid-ul-Fitr (the Festival of Fast. Breaking)
Ramadan • Ninth month of the Islamic calendar – A time for inner reflection, devotion to God, and self-control • Daily period of fasting from dawn to dusk – Observers totally abstain from food, drink, smoking, and sex • Ramadan ends with a joyous celebration called 'Eid-ul-Fitr (the Festival of Fast. Breaking)
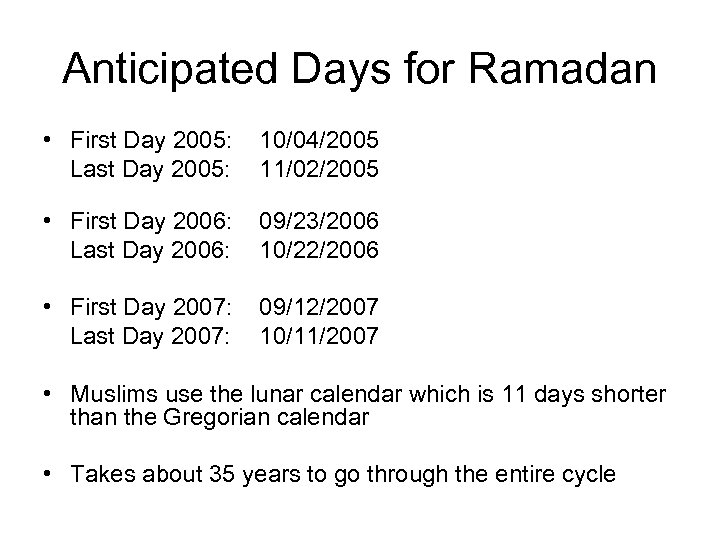 Anticipated Days for Ramadan • First Day 2005: 10/04/2005 Last Day 2005: 11/02/2005 • First Day 2006: 09/23/2006 Last Day 2006: 10/22/2006 • First Day 2007: 09/12/2007 Last Day 2007: 10/11/2007 • Muslims use the lunar calendar which is 11 days shorter than the Gregorian calendar • Takes about 35 years to go through the entire cycle
Anticipated Days for Ramadan • First Day 2005: 10/04/2005 Last Day 2005: 11/02/2005 • First Day 2006: 09/23/2006 Last Day 2006: 10/22/2006 • First Day 2007: 09/12/2007 Last Day 2007: 10/11/2007 • Muslims use the lunar calendar which is 11 days shorter than the Gregorian calendar • Takes about 35 years to go through the entire cycle
 Jihad • Sometimes called the sixth pillar • Jihad is more than a “holy war” – It is an exertion or struggle in achieving the ways of Allah – It requires a vigilance “against all that distracts us from God and exertion to do His will within ourselves as well as preserving and reestablishing the order and harmony that He has willed for Islamic society and the world about us. ” • Seyyed Nasr in Our Religions, ed. Arvind Sharma, 475
Jihad • Sometimes called the sixth pillar • Jihad is more than a “holy war” – It is an exertion or struggle in achieving the ways of Allah – It requires a vigilance “against all that distracts us from God and exertion to do His will within ourselves as well as preserving and reestablishing the order and harmony that He has willed for Islamic society and the world about us. ” • Seyyed Nasr in Our Religions, ed. Arvind Sharma, 475
 Jihad • In the late 20 th and early 21 st Centuries, extremists began using the concept of jihad to rationalize and legitimize terrorism and revolution • “… in compliance with Allah's order, we issue the following fatwa [a legal pronouncement issued by a religious law specialist on a specific issue] to all Muslims: – The ruling to kill the Americans and their allies -- civilians and military -- is an individual duty for every Muslim who can do it in any country in which it is possible to do it, in order to liberate the al-Aqsa Mosque and the holy mosque [Mecca] from their grip, and in order for their armies to move out of all the lands of Islam, defeated and unable to threaten any Muslim. This is in accordance with the words of Almighty Allah, ‘and fight the pagans all together as they fight you all together, ’ and ‘fight them until there is no more tumult or oppression, and there prevail justice and faith in Allah. ’” • World Islamic Front Statement, 23 February 1998
Jihad • In the late 20 th and early 21 st Centuries, extremists began using the concept of jihad to rationalize and legitimize terrorism and revolution • “… in compliance with Allah's order, we issue the following fatwa [a legal pronouncement issued by a religious law specialist on a specific issue] to all Muslims: – The ruling to kill the Americans and their allies -- civilians and military -- is an individual duty for every Muslim who can do it in any country in which it is possible to do it, in order to liberate the al-Aqsa Mosque and the holy mosque [Mecca] from their grip, and in order for their armies to move out of all the lands of Islam, defeated and unable to threaten any Muslim. This is in accordance with the words of Almighty Allah, ‘and fight the pagans all together as they fight you all together, ’ and ‘fight them until there is no more tumult or oppression, and there prevail justice and faith in Allah. ’” • World Islamic Front Statement, 23 February 1998
 Islamic Ethics • Islam values practice over belief • Of the Five Pillars, four concern practice (acts, deeds or endeavors) that adherents must fulfill – – Prayer Fasting Almsgiving Pilgrimage • Living correctly takes precedence over creeds and doctrines
Islamic Ethics • Islam values practice over belief • Of the Five Pillars, four concern practice (acts, deeds or endeavors) that adherents must fulfill – – Prayer Fasting Almsgiving Pilgrimage • Living correctly takes precedence over creeds and doctrines
 Sharia • After the death of Muhammad, the sharia, Islamic holy law, emerged to give detailed guidance on proper behavior in almost every aspect of daily life • Drew its inspiration from the Quran and historical accounts of Muhammad’s life and teachings • Through the sharia, Islam became more than a religious doctrine – It developed into a way of life complete with social and ethical values derived from Islamic religious doctrine.
Sharia • After the death of Muhammad, the sharia, Islamic holy law, emerged to give detailed guidance on proper behavior in almost every aspect of daily life • Drew its inspiration from the Quran and historical accounts of Muhammad’s life and teachings • Through the sharia, Islam became more than a religious doctrine – It developed into a way of life complete with social and ethical values derived from Islamic religious doctrine.
 Expansion of Islam • Muhammad made no provisions for a successor after his death – Serious divisions arose • Within a short time however, the Islamic community launched a series of military campaigns that extended its influence far beyond the boundaries of Arabia
Expansion of Islam • Muhammad made no provisions for a successor after his death – Serious divisions arose • Within a short time however, the Islamic community launched a series of military campaigns that extended its influence far beyond the boundaries of Arabia
 Caliphs • Since Muhammad was “the seal of the prophets, ” no one could succeed him as another prophet • Abu Bakr, one of Muhammad’s closest friend’s and disciples followed him as caliph (“deputy”) • Caliphs would lead the umma as lieutenants or substitutes for Muhammad, rather than as prophets
Caliphs • Since Muhammad was “the seal of the prophets, ” no one could succeed him as another prophet • Abu Bakr, one of Muhammad’s closest friend’s and disciples followed him as caliph (“deputy”) • Caliphs would lead the umma as lieutenants or substitutes for Muhammad, rather than as prophets
 Expansion and Problems • Islamic warriors gained remarkable victories over the Byzantine and Sasanid empires which were exhausted from fighting each other and besieged by internal problems
Expansion and Problems • Islamic warriors gained remarkable victories over the Byzantine and Sasanid empires which were exhausted from fighting each other and besieged by internal problems
 Expansion and Problems • As Islam expanded, it was faced with problems of governance and administration • One problem was selecting the caliphs – Political ambitions, personal differences, and clan loyalties complicated the process • Disagreements over succession led to the emergence of the Shia sect
Expansion and Problems • As Islam expanded, it was faced with problems of governance and administration • One problem was selecting the caliphs – Political ambitions, personal differences, and clan loyalties complicated the process • Disagreements over succession led to the emergence of the Shia sect
 Shia • Shia (“party”) are the most important alternative to the majority Muslim group, the Sunni (“traditionalists”) • Shiites favored Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son in law, as caliph instead of Abu Bakr • Ali did become the fourth caliph (656 -661) but was assassinated and his killers imposed their own caliph • Shiites vigorously resisted and struggled to return the caliphate to the line of Ali
Shia • Shia (“party”) are the most important alternative to the majority Muslim group, the Sunni (“traditionalists”) • Shiites favored Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son in law, as caliph instead of Abu Bakr • Ali did become the fourth caliph (656 -661) but was assassinated and his killers imposed their own caliph • Shiites vigorously resisted and struggled to return the caliphate to the line of Ali
 Shia • Shiites strengthened their identity by adopting doctrines and rituals distinct from the Sunnis – Observed holy days in honor of their leaders and martyrs – Taught that the descendants of Ali were infallible, sinless, and divinely appointed to rule
Shia • Shiites strengthened their identity by adopting doctrines and rituals distinct from the Sunnis – Observed holy days in honor of their leaders and martyrs – Taught that the descendants of Ali were infallible, sinless, and divinely appointed to rule
 Differences Between Shia and Sunni • Shiites – About 15% of all Muslims – Islam’s leader should be a descendant of Mohammad – Qualified religious leaders have the authority to interpret the sharia (Islamic law) • Sunnis – About 85% of all Muslims – Leaders should be chosen through ijma, or consensus – The sharia was codified and closed by the 10 th century
Differences Between Shia and Sunni • Shiites – About 15% of all Muslims – Islam’s leader should be a descendant of Mohammad – Qualified religious leaders have the authority to interpret the sharia (Islamic law) • Sunnis – About 85% of all Muslims – Leaders should be chosen through ijma, or consensus – The sharia was codified and closed by the 10 th century
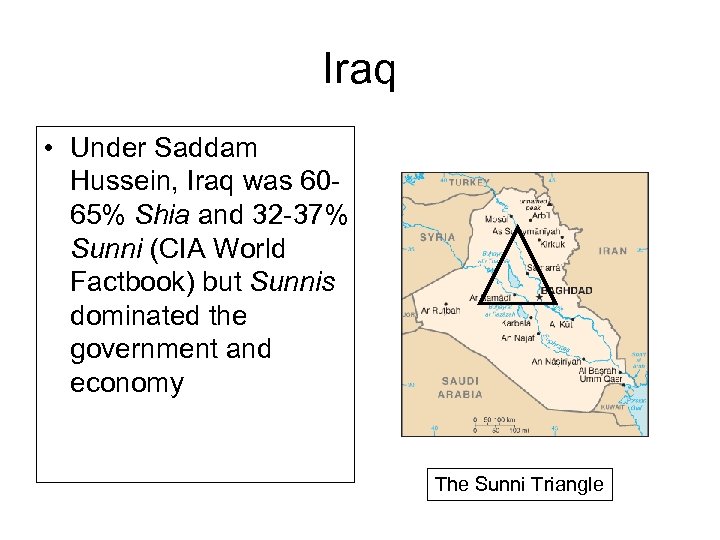 Iraq • Under Saddam Hussein, Iraq was 6065% Shia and 32 -37% Sunni (CIA World Factbook) but Sunnis dominated the government and economy The Sunni Triangle
Iraq • Under Saddam Hussein, Iraq was 6065% Shia and 32 -37% Sunni (CIA World Factbook) but Sunnis dominated the government and economy The Sunni Triangle
 Sufi • Sufi is a third Muslim group – Encourages a personal, emotional, devotional approach to Islam; has a very mystical and spiritual component – Do not insist on fine points of doctrine or formal religious teachings; instead work to deepen spiritual awareness – Most lead pious and ascetic lives – Very effective as missionaries, brought Islam to India Representation of Sufi theologian al-Ghazali (1058 -1111)
Sufi • Sufi is a third Muslim group – Encourages a personal, emotional, devotional approach to Islam; has a very mystical and spiritual component – Do not insist on fine points of doctrine or formal religious teachings; instead work to deepen spiritual awareness – Most lead pious and ascetic lives – Very effective as missionaries, brought Islam to India Representation of Sufi theologian al-Ghazali (1058 -1111)
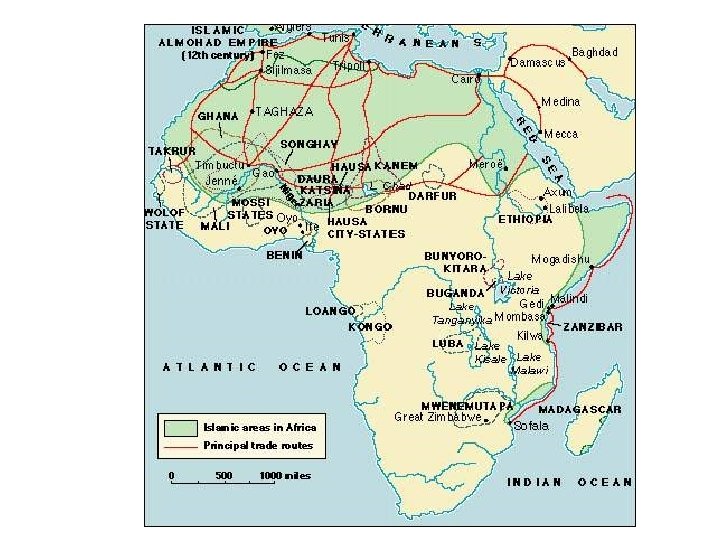
 Islam in Africa (Review from Lesson 9) • Contact with Muslim merchants encouraged sub-Sahara west Africans and coastal east Africans to adopt Islam • It served as a cultural foundation for business relationships – Yet African ruling elites and merchants did not convert for purely mercenary reasons; they took their new faith seriously
Islam in Africa (Review from Lesson 9) • Contact with Muslim merchants encouraged sub-Sahara west Africans and coastal east Africans to adopt Islam • It served as a cultural foundation for business relationships – Yet African ruling elites and merchants did not convert for purely mercenary reasons; they took their new faith seriously
 Major World Religions Source: About, Inc http: //christianity. about. com/library/weekly/blreligiontop. htm Religion Members Christianity Islam Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Sikhism Baha‘i Confucianism Jainism Shintoism Wicca Zoroastrianism 2 Billion 1. 2 Billion 785 Million 360 Million 17 Million 16 Million 5 Million 4 Million 3 Million. 7 Million. 2 Million
Major World Religions Source: About, Inc http: //christianity. about. com/library/weekly/blreligiontop. htm Religion Members Christianity Islam Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Sikhism Baha‘i Confucianism Jainism Shintoism Wicca Zoroastrianism 2 Billion 1. 2 Billion 785 Million 360 Million 17 Million 16 Million 5 Million 4 Million 3 Million. 7 Million. 2 Million
 Religions Compared
Religions Compared
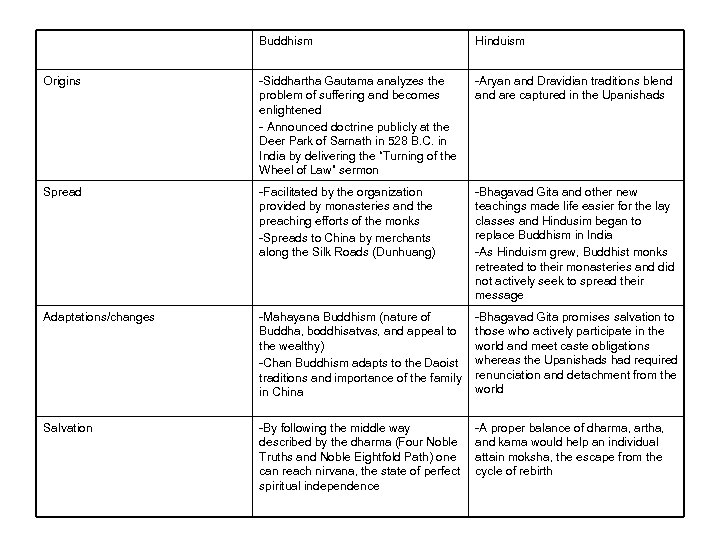 Buddhism Hinduism Origins -Siddhartha Gautama analyzes the problem of suffering and becomes enlightened - Announced doctrine publicly at the Deer Park of Sarnath in 528 B. C. in India by delivering the “Turning of the Wheel of Law” sermon -Aryan and Dravidian traditions blend are captured in the Upanishads Spread -Facilitated by the organization provided by monasteries and the preaching efforts of the monks -Spreads to China by merchants along the Silk Roads (Dunhuang) -Bhagavad Gita and other new teachings made life easier for the lay classes and Hindusim began to replace Buddhism in India -As Hinduism grew, Buddhist monks retreated to their monasteries and did not actively seek to spread their message Adaptations/changes -Mahayana Buddhism (nature of Buddha, boddhisatvas, and appeal to the wealthy) -Chan Buddhism adapts to the Daoist traditions and importance of the family in China -Bhagavad Gita promises salvation to those who actively participate in the world and meet caste obligations whereas the Upanishads had required renunciation and detachment from the world Salvation -By following the middle way described by the dharma (Four Noble Truths and Noble Eightfold Path) one can reach nirvana, the state of perfect spiritual independence -A proper balance of dharma, artha, and kama would help an individual attain moksha, the escape from the cycle of rebirth
Buddhism Hinduism Origins -Siddhartha Gautama analyzes the problem of suffering and becomes enlightened - Announced doctrine publicly at the Deer Park of Sarnath in 528 B. C. in India by delivering the “Turning of the Wheel of Law” sermon -Aryan and Dravidian traditions blend are captured in the Upanishads Spread -Facilitated by the organization provided by monasteries and the preaching efforts of the monks -Spreads to China by merchants along the Silk Roads (Dunhuang) -Bhagavad Gita and other new teachings made life easier for the lay classes and Hindusim began to replace Buddhism in India -As Hinduism grew, Buddhist monks retreated to their monasteries and did not actively seek to spread their message Adaptations/changes -Mahayana Buddhism (nature of Buddha, boddhisatvas, and appeal to the wealthy) -Chan Buddhism adapts to the Daoist traditions and importance of the family in China -Bhagavad Gita promises salvation to those who actively participate in the world and meet caste obligations whereas the Upanishads had required renunciation and detachment from the world Salvation -By following the middle way described by the dharma (Four Noble Truths and Noble Eightfold Path) one can reach nirvana, the state of perfect spiritual independence -A proper balance of dharma, artha, and kama would help an individual attain moksha, the escape from the cycle of rebirth
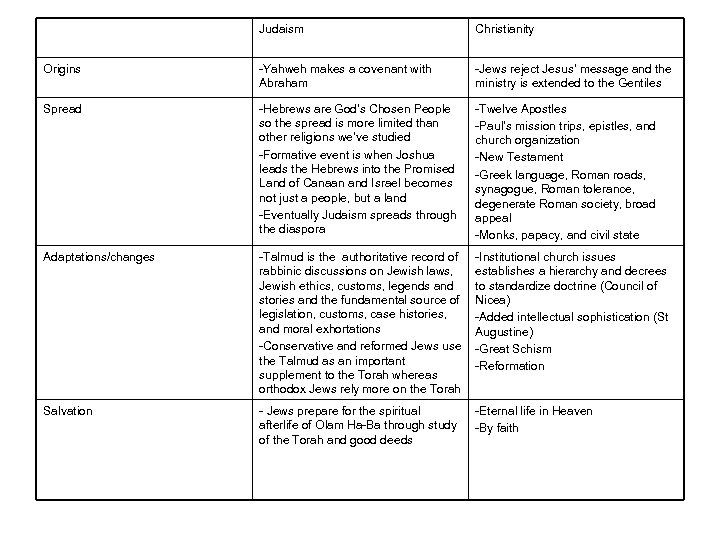 Judaism Christianity Origins -Yahweh makes a covenant with Abraham -Jews reject Jesus’ message and the ministry is extended to the Gentiles Spread -Hebrews are God’s Chosen People so the spread is more limited than other religions we’ve studied -Formative event is when Joshua leads the Hebrews into the Promised Land of Canaan and Israel becomes not just a people, but a land -Eventually Judaism spreads through the diaspora -Twelve Apostles -Paul’s mission trips, epistles, and church organization -New Testament -Greek language, Roman roads, synagogue, Roman tolerance, degenerate Roman society, broad appeal -Monks, papacy, and civil state Adaptations/changes -Talmud is the authoritative record of rabbinic discussions on Jewish laws, Jewish ethics, customs, legends and stories and the fundamental source of legislation, customs, case histories, and moral exhortations -Conservative and reformed Jews use the Talmud as an important supplement to the Torah whereas orthodox Jews rely more on the Torah -Institutional church issues establishes a hierarchy and decrees to standardize doctrine (Council of Nicea) -Added intellectual sophistication (St Augustine) -Great Schism -Reformation Salvation - Jews prepare for the spiritual afterlife of Olam Ha-Ba through study of the Torah and good deeds -Eternal life in Heaven -By faith
Judaism Christianity Origins -Yahweh makes a covenant with Abraham -Jews reject Jesus’ message and the ministry is extended to the Gentiles Spread -Hebrews are God’s Chosen People so the spread is more limited than other religions we’ve studied -Formative event is when Joshua leads the Hebrews into the Promised Land of Canaan and Israel becomes not just a people, but a land -Eventually Judaism spreads through the diaspora -Twelve Apostles -Paul’s mission trips, epistles, and church organization -New Testament -Greek language, Roman roads, synagogue, Roman tolerance, degenerate Roman society, broad appeal -Monks, papacy, and civil state Adaptations/changes -Talmud is the authoritative record of rabbinic discussions on Jewish laws, Jewish ethics, customs, legends and stories and the fundamental source of legislation, customs, case histories, and moral exhortations -Conservative and reformed Jews use the Talmud as an important supplement to the Torah whereas orthodox Jews rely more on the Torah -Institutional church issues establishes a hierarchy and decrees to standardize doctrine (Council of Nicea) -Added intellectual sophistication (St Augustine) -Great Schism -Reformation Salvation - Jews prepare for the spiritual afterlife of Olam Ha-Ba through study of the Torah and good deeds -Eternal life in Heaven -By faith
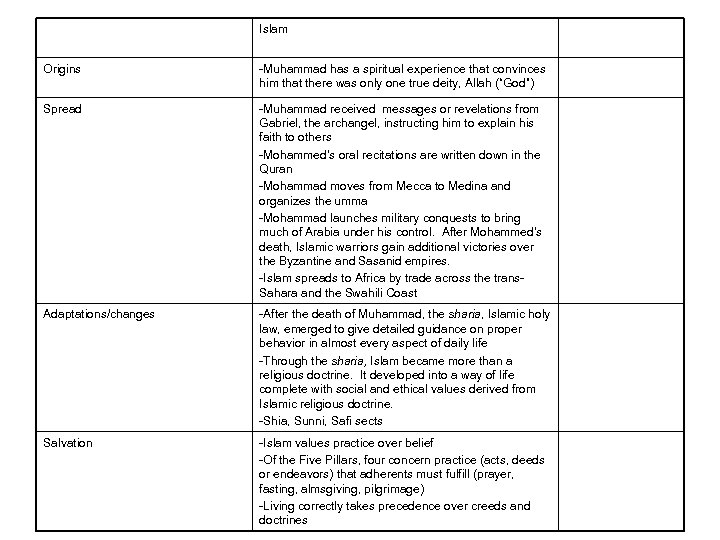 Islam Origins -Muhammad has a spiritual experience that convinces him that there was only one true deity, Allah (“God”) Spread -Muhammad received messages or revelations from Gabriel, the archangel, instructing him to explain his faith to others -Mohammed’s oral recitations are written down in the Quran -Mohammad moves from Mecca to Medina and organizes the umma -Mohammad launches military conquests to bring much of Arabia under his control. After Mohammed’s death, Islamic warriors gain additional victories over the Byzantine and Sasanid empires. -Islam spreads to Africa by trade across the trans. Sahara and the Swahili Coast Adaptations/changes -After the death of Muhammad, the sharia, Islamic holy law, emerged to give detailed guidance on proper behavior in almost every aspect of daily life -Through the sharia, Islam became more than a religious doctrine. It developed into a way of life complete with social and ethical values derived from Islamic religious doctrine. -Shia, Sunni, Safi sects Salvation -Islam values practice over belief -Of the Five Pillars, four concern practice (acts, deeds or endeavors) that adherents must fulfill (prayer, fasting, almsgiving, pilgrimage) -Living correctly takes precedence over creeds and doctrines
Islam Origins -Muhammad has a spiritual experience that convinces him that there was only one true deity, Allah (“God”) Spread -Muhammad received messages or revelations from Gabriel, the archangel, instructing him to explain his faith to others -Mohammed’s oral recitations are written down in the Quran -Mohammad moves from Mecca to Medina and organizes the umma -Mohammad launches military conquests to bring much of Arabia under his control. After Mohammed’s death, Islamic warriors gain additional victories over the Byzantine and Sasanid empires. -Islam spreads to Africa by trade across the trans. Sahara and the Swahili Coast Adaptations/changes -After the death of Muhammad, the sharia, Islamic holy law, emerged to give detailed guidance on proper behavior in almost every aspect of daily life -Through the sharia, Islam became more than a religious doctrine. It developed into a way of life complete with social and ethical values derived from Islamic religious doctrine. -Shia, Sunni, Safi sects Salvation -Islam values practice over belief -Of the Five Pillars, four concern practice (acts, deeds or endeavors) that adherents must fulfill (prayer, fasting, almsgiving, pilgrimage) -Living correctly takes precedence over creeds and doctrines
 Next • Maintaining Order: Persia, India, and China
Next • Maintaining Order: Persia, India, and China


