8c8459b1d6a9a7cefba3b104c4eab24d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Is your patient fit for work? Part 1 Stakeholders and standards Grant Mc. Millan Hon Senior Clinical Lecturer Institute of Occupational and Environmental Health University of Birmingham Number 9 of a series of lectures and tutorials for medical undergraduates
Is your patient fit for work? Part 1 Stakeholders and standards Grant Mc. Millan Hon Senior Clinical Lecturer Institute of Occupational and Environmental Health University of Birmingham Number 9 of a series of lectures and tutorials for medical undergraduates
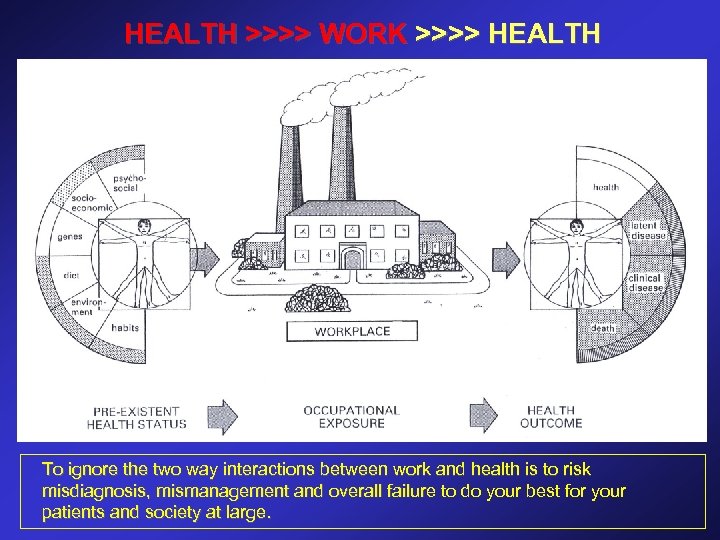 HEALTH >>>> WORK >>>> HEALTH To ignore the two way interactions between work and health is to risk misdiagnosis, mismanagement and overall failure to do your best for your patients and society at large.
HEALTH >>>> WORK >>>> HEALTH To ignore the two way interactions between work and health is to risk misdiagnosis, mismanagement and overall failure to do your best for your patients and society at large.
 Learning points • Stakeholders, assumptions and expectations • Complexity of absence – role of health professional • Usefulness of task-related health and fitness standards in matching people to employment • Importance of ensuring that the patient and you agree that return to work is a planned outcome of treatment
Learning points • Stakeholders, assumptions and expectations • Complexity of absence – role of health professional • Usefulness of task-related health and fitness standards in matching people to employment • Importance of ensuring that the patient and you agree that return to work is a planned outcome of treatment
 Stakeholders in workers’ health • Individual workers • Community of workers • Workers’ families • Employers and shareholders • Government and “society” • Health professionals
Stakeholders in workers’ health • Individual workers • Community of workers • Workers’ families • Employers and shareholders • Government and “society” • Health professionals
 Ground rules All stakeholders benefit from employees being fit and healthy. Employees need not be entirely fit and healthy for all stakeholders to benefit. Employees who are not entirely fit and healthy may still be employable. Employability may be enhanced by altering the work and/or workplace.
Ground rules All stakeholders benefit from employees being fit and healthy. Employees need not be entirely fit and healthy for all stakeholders to benefit. Employees who are not entirely fit and healthy may still be employable. Employability may be enhanced by altering the work and/or workplace.
 Absence is complex - not just about a health problem It is vital to have the right people dealing with the right issues • Health related - assessment of fitness for role • Social/domestic such as debt, childcare, divorce • Work-related manager/employee relationships • Reasonable adjustment of work and rehabilitation
Absence is complex - not just about a health problem It is vital to have the right people dealing with the right issues • Health related - assessment of fitness for role • Social/domestic such as debt, childcare, divorce • Work-related manager/employee relationships • Reasonable adjustment of work and rehabilitation
 Stakeholders in workers’ health • Individual workers • Community of workers • Workers’ families • Employers and shareholders • Government and “society” • Health professionals
Stakeholders in workers’ health • Individual workers • Community of workers • Workers’ families • Employers and shareholders • Government and “society” • Health professionals
 Absence is complex - not just about a health problem Health Professionals should focus on health issues and liaise with fellow stakeholders on other matters • Health related - assessment of fitness for role • Social/domestic such as debt, childcare, divorce • Work-related manager/employee relationships • Reasonable adjustment of work and rehabilitation
Absence is complex - not just about a health problem Health Professionals should focus on health issues and liaise with fellow stakeholders on other matters • Health related - assessment of fitness for role • Social/domestic such as debt, childcare, divorce • Work-related manager/employee relationships • Reasonable adjustment of work and rehabilitation
 Learning point 1 It is vital to have the right people dealing with the right issues
Learning point 1 It is vital to have the right people dealing with the right issues
 Matching people to employment – Assessment of fitness to work The purpose of a medical assessment for fitness to work is to determine that an individual is fit or unfit to perform the tasks involved effectively and without risk to their own health and safety and that of others. If found unfit, the assessment should define the limiting parameters so that a solution may be sought.
Matching people to employment – Assessment of fitness to work The purpose of a medical assessment for fitness to work is to determine that an individual is fit or unfit to perform the tasks involved effectively and without risk to their own health and safety and that of others. If found unfit, the assessment should define the limiting parameters so that a solution may be sought.
 Medical certification of unfitness for work A “sick certificate” is a frequent routine request by patients to doctors. Doctors often see it as a worthless, time - wasting chore, yet offer little resistance lest they upset their relationship with the patient. Do they issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought?
Medical certification of unfitness for work A “sick certificate” is a frequent routine request by patients to doctors. Doctors often see it as a worthless, time - wasting chore, yet offer little resistance lest they upset their relationship with the patient. Do they issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought?
 Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought? If so, why?
Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought? If so, why?
 Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought? Don’t they care?
Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought? Don’t they care?
 Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought. Perhaps, they don’t know what the patient does nor the demands that job imposes?
Do some issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought. Perhaps, they don’t know what the patient does nor the demands that job imposes?
 They issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought. Probably, they don’t know the employer’s attitudes to and arrangements for reduced health and fitness employees?
They issue the certificate with little or no constructive thought. Probably, they don’t know the employer’s attitudes to and arrangements for reduced health and fitness employees?
 Hurdles faced by GPs and Secondary Care doctors They may not know: • what the patient does, • the demands of that work, • the employer’s attitudes to and arrangements for reduced health and fitness employees?
Hurdles faced by GPs and Secondary Care doctors They may not know: • what the patient does, • the demands of that work, • the employer’s attitudes to and arrangements for reduced health and fitness employees?
 Solutions? • Employers should examine each job: • define the demands, hazards and risks • effect changes to maximise safety and minimise exclusion • derive, publish and apply evidence – based standards of health and fitness
Solutions? • Employers should examine each job: • define the demands, hazards and risks • effect changes to maximise safety and minimise exclusion • derive, publish and apply evidence – based standards of health and fitness
 Learning point 2 Published task-related health and fitness standards set by employers can be useful in matching people to jobs and determining whether workers are fit for work.
Learning point 2 Published task-related health and fitness standards set by employers can be useful in matching people to jobs and determining whether workers are fit for work.
 Fit for what? Three aspects of standards • Safety • Health • Functionality
Fit for what? Three aspects of standards • Safety • Health • Functionality
 Safety-critical jobs • • • road vehicle drivers pilots seafarers train drivers air traffic controllers
Safety-critical jobs • • • road vehicle drivers pilots seafarers train drivers air traffic controllers
 Driving as a safety-critical task • vocational, non-vocational • • perceptual requirements cognitive requirements motor requirements stability, sudden change – epilepsy, hypoglycaemia,
Driving as a safety-critical task • vocational, non-vocational • • perceptual requirements cognitive requirements motor requirements stability, sudden change – epilepsy, hypoglycaemia,
 Driving impairment • medical condition • • • treatment of condition fatigue – hours of work, time of day alcohol – limits and tolerability illicit and recreational drugs age – young: zest + inexperience – age: information processing impaired
Driving impairment • medical condition • • • treatment of condition fatigue – hours of work, time of day alcohol – limits and tolerability illicit and recreational drugs age – young: zest + inexperience – age: information processing impaired
 Other safety-critical jobs • • • Commercial diving Control room operators Emergency services Armed forces User of hazardous materials and equipment • Food preparation • Steel erector • Medical personnel
Other safety-critical jobs • • • Commercial diving Control room operators Emergency services Armed forces User of hazardous materials and equipment • Food preparation • Steel erector • Medical personnel
 Health-critical aspects of jobs Diabetes Epilepsy Back pain Skin disease Mental health Cardiac surgery
Health-critical aspects of jobs Diabetes Epilepsy Back pain Skin disease Mental health Cardiac surgery
 Function-critical • General - fit to be present in the workplace do the job effectively and safely, without excess risk of harm to self or other. • Specific - fit for special aspects of tasks eg printers, fabric matchers, fruit selectors having normal colour vision
Function-critical • General - fit to be present in the workplace do the job effectively and safely, without excess risk of harm to self or other. • Specific - fit for special aspects of tasks eg printers, fabric matchers, fruit selectors having normal colour vision
 Fit for what? Appreciation of Safety + Health + Function = Ability to decide on fitness for work, if you know the demands of the job
Fit for what? Appreciation of Safety + Health + Function = Ability to decide on fitness for work, if you know the demands of the job
 Fit for what? Appreciation of Safety + Health + Function = Ability to decide on fitness for work, if you know the standards for the job
Fit for what? Appreciation of Safety + Health + Function = Ability to decide on fitness for work, if you know the standards for the job
 Disability Discrimination Act Does the individual’s disability fall within the definition of the Act? What adjustments may be needed to accommodate the disabled individual in the workplace?
Disability Discrimination Act Does the individual’s disability fall within the definition of the Act? What adjustments may be needed to accommodate the disabled individual in the workplace?
 Learning point 3 Employers should examine each job: • define physical and mental demands • define hazards and risks • maximise safety and minimise risk and exclusion of “disabled” • derive, publish and apply evidence – based standards of health and fitness
Learning point 3 Employers should examine each job: • define physical and mental demands • define hazards and risks • maximise safety and minimise risk and exclusion of “disabled” • derive, publish and apply evidence – based standards of health and fitness
 Learning point 4 Importance of you and the patient agreeing that return to work is a planned outcome of treatment and agreeing on a plan to achieve that aim
Learning point 4 Importance of you and the patient agreeing that return to work is a planned outcome of treatment and agreeing on a plan to achieve that aim
 Forecast when will patient be sufficiently Safe + Healthy + Functional to agreed standards?
Forecast when will patient be sufficiently Safe + Healthy + Functional to agreed standards?
 Consider and act on the most important psycho-social predictors for risk of long term incapacity
Consider and act on the most important psycho-social predictors for risk of long term incapacity
 Low back pain • • • Age Pain intensity/functional disability Poor perception of general health Psychological distress, depression Fear avoidance Catastrophising Pain behaviour Job satisfaction and worker disaffection Duration of absence/incapacity Whether or not still employed Expectation about return to work
Low back pain • • • Age Pain intensity/functional disability Poor perception of general health Psychological distress, depression Fear avoidance Catastrophising Pain behaviour Job satisfaction and worker disaffection Duration of absence/incapacity Whether or not still employed Expectation about return to work
 Is your patient fit for work? Grant Mc. Millan Hon Senior Clinical Lecturer Thank you for your attention
Is your patient fit for work? Grant Mc. Millan Hon Senior Clinical Lecturer Thank you for your attention


