790021fd454a591e7736915d161b7bb0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Is there life after X. 509 ? Security Workshop Globus World 2004 Frank Siebenlist (Ph. D) Argonne National Laboratory The Globus Alliance franks@mcs. anl. gov http: //www. globus. org/
Is there life after X. 509 ? Security Workshop Globus World 2004 Frank Siebenlist (Ph. D) Argonne National Laboratory The Globus Alliance franks@mcs. anl. gov http: //www. globus. org/
 Objective l Provoke discussion u l So boring if we all agree The X 509/PKI dream clearly never came thru… u u l Learn from deployment issues Maybe alternatives would work better X 509 is used in ways it was never intended… u l Our proxy-certs are a good example Some entertainment for the last talk on Friday late afternoon at the end of a looong conference u … plus it’s therapeutic for me rant on about this… franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 2
Objective l Provoke discussion u l So boring if we all agree The X 509/PKI dream clearly never came thru… u u l Learn from deployment issues Maybe alternatives would work better X 509 is used in ways it was never intended… u l Our proxy-certs are a good example Some entertainment for the last talk on Friday late afternoon at the end of a looong conference u … plus it’s therapeutic for me rant on about this… franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 2
 Questions, l l l l l Questions… Why pay $20/EE-cert and 0$ for a Kerberos principal? Why are lawyers involved with CAs, but not with other authentication/assertion services? Why are there no armed guards to protect the attribute/authorization servers? Is the Subject’s DN ever meant to be readable? Who are the poor people that use DNs? Why do username/password systems work? Why doesn’t everyone check revocation in real-time? How many more RFCs is PKIX going to produce? What is that “pixie-dust” on those X. 509 certs? Will my children in 20 years still suffer from X. 509? franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 3
Questions, l l l l l Questions… Why pay $20/EE-cert and 0$ for a Kerberos principal? Why are lawyers involved with CAs, but not with other authentication/assertion services? Why are there no armed guards to protect the attribute/authorization servers? Is the Subject’s DN ever meant to be readable? Who are the poor people that use DNs? Why do username/password systems work? Why doesn’t everyone check revocation in real-time? How many more RFCs is PKIX going to produce? What is that “pixie-dust” on those X. 509 certs? Will my children in 20 years still suffer from X. 509? franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 3
 X. 509 Certificate l Trusted third party (CA) vouches that combination of a public key and some (identity) information applies to the subject that can prove the possession of the associated private key. u u l l “Vouching” through signing Implicit trust of CA CA signature “binds” identity information to public key CA responsible for revocation/renewal franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security Certificate Identity Info (DN & other stuff) Public Key CA Identifier CA Signature 4
X. 509 Certificate l Trusted third party (CA) vouches that combination of a public key and some (identity) information applies to the subject that can prove the possession of the associated private key. u u l l “Vouching” through signing Implicit trust of CA CA signature “binds” identity information to public key CA responsible for revocation/renewal franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security Certificate Identity Info (DN & other stuff) Public Key CA Identifier CA Signature 4
 X. 509 Identity Certificate l l Vetting of the “real” identity by a RA Binding of the public key to the subject name by CA u l Guarantees about uniqueness of name u l CRLs, OCSP, ? ? ? After path validation, relying party can use subject name in place of key u l CAs somehow have to agree on part of name space CA also responsible for certificate revocation u l Plus some other stuff Issuer becomes “X. 509” Expensive to do all of this correctly franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 5
X. 509 Identity Certificate l l Vetting of the “real” identity by a RA Binding of the public key to the subject name by CA u l Guarantees about uniqueness of name u l CRLs, OCSP, ? ? ? After path validation, relying party can use subject name in place of key u l CAs somehow have to agree on part of name space CA also responsible for certificate revocation u l Plus some other stuff Issuer becomes “X. 509” Expensive to do all of this correctly franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 5
 Need for On-line Certificate Revocation Checking l “Real” deployments need real-time, on-line certificate revocation checking Business needs to know if a key is compromised u Issuance of CRLs not frequent enough u Off-line PKI turns out to be just a dream… u Deployment no different from Kerberos-like system u l Any real-time, mission critical, on-line system is expensive franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 6
Need for On-line Certificate Revocation Checking l “Real” deployments need real-time, on-line certificate revocation checking Business needs to know if a key is compromised u Issuance of CRLs not frequent enough u Off-line PKI turns out to be just a dream… u Deployment no different from Kerberos-like system u l Any real-time, mission critical, on-line system is expensive franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 6
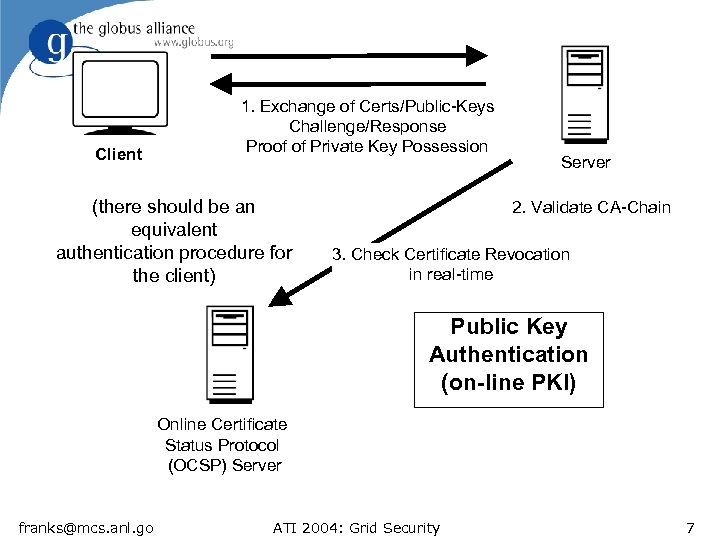 Client 1. Exchange of Certs/Public-Keys Challenge/Response Proof of Private Key Possession (there should be an equivalent authentication procedure for the client) Server 2. Validate CA-Chain 3. Check Certificate Revocation in real-time Public Key Authentication (on-line PKI) Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Server franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 7
Client 1. Exchange of Certs/Public-Keys Challenge/Response Proof of Private Key Possession (there should be an equivalent authentication procedure for the client) Server 2. Validate CA-Chain 3. Check Certificate Revocation in real-time Public Key Authentication (on-line PKI) Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Server franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 7
 Key => Subject => user. Id + Attributes l (almost) nobody uses DN u u l Plus… any serious application needs user attributes u l l Not a very friendly format Already other identifiers in place customer. Id, SS#, drivers-license, ? ? ? Privacy considerations Etc. , etc. Group membership, roles, clearance levels, credit card numbers/limits, address, etc. Real-time, on-line lookup of user. Id + attributes Equivalent “vetting” or RA-procedure to map subject to user. Id+attributes u Differentiate the Bills from the Williams from the William III…. franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 8
Key => Subject => user. Id + Attributes l (almost) nobody uses DN u u l Plus… any serious application needs user attributes u l l Not a very friendly format Already other identifiers in place customer. Id, SS#, drivers-license, ? ? ? Privacy considerations Etc. , etc. Group membership, roles, clearance levels, credit card numbers/limits, address, etc. Real-time, on-line lookup of user. Id + attributes Equivalent “vetting” or RA-procedure to map subject to user. Id+attributes u Differentiate the Bills from the Williams from the William III…. franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 8
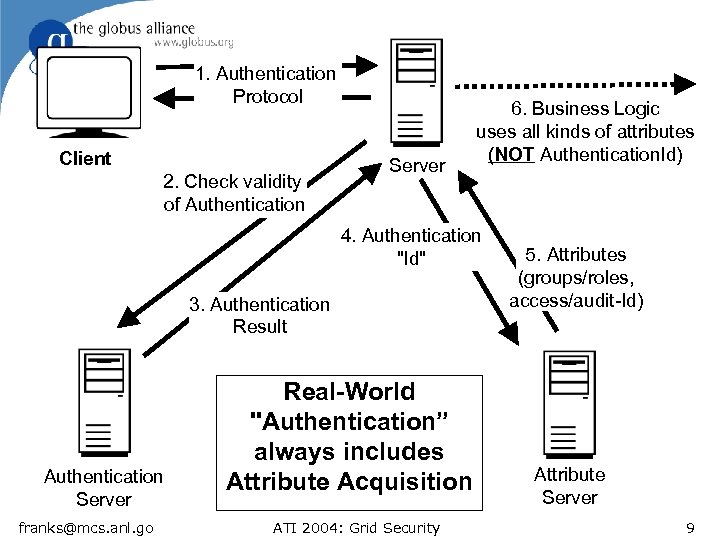 1. Authentication Protocol Client 2. Check validity of Authentication Server 6. Business Logic uses all kinds of attributes (NOT Authentication. Id) 4. Authentication "Id" 3. Authentication Result Authentication Server franks@mcs. anl. go Real-World "Authentication” always includes Attribute Acquisition ATI 2004: Grid Security 5. Attributes (groups/roles, access/audit-Id) Attribute Server 9
1. Authentication Protocol Client 2. Check validity of Authentication Server 6. Business Logic uses all kinds of attributes (NOT Authentication. Id) 4. Authentication "Id" 3. Authentication Result Authentication Server franks@mcs. anl. go Real-World "Authentication” always includes Attribute Acquisition ATI 2004: Grid Security 5. Attributes (groups/roles, access/audit-Id) Attribute Server 9
 Central Path Validation Service (CPVS) l l l Path validation is complicated, error-prone, expensive, black magic, … Centralize its function as a “CPVS” Service Maybe require registration first u u u l All other services do “key-only” authentication u u l Users authenticate with certificate Service performs path validation Registers/caches results Query CPVS for validation (+ user. Id/attributes) (Redirection protocol for those that forgot to register first…) (XKMS protocol could be used for this…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 10
Central Path Validation Service (CPVS) l l l Path validation is complicated, error-prone, expensive, black magic, … Centralize its function as a “CPVS” Service Maybe require registration first u u u l All other services do “key-only” authentication u u l Users authenticate with certificate Service performs path validation Registers/caches results Query CPVS for validation (+ user. Id/attributes) (Redirection protocol for those that forgot to register first…) (XKMS protocol could be used for this…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 10
 1. Exchange of Public-Keys Challenge/Response Proof of Private Key Possession Client 0. Register certificates Server 2. Check key validity 3. Return relevant attributes Online Central Path Validation Service Check certificate revocations/validity franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 11
1. Exchange of Public-Keys Challenge/Response Proof of Private Key Possession Client 0. Register certificates Server 2. Check key validity 3. Return relevant attributes Online Central Path Validation Service Check certificate revocations/validity franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 11
 Key => user. Id + Attributes l We have to make real-time, online lookups anyway… u u l Why do we need the x. 509/subject name? u u l Similar to X. 509 -RA procedure Key revocation/renewal is simple u l Key => user. Id + attributes Elimination of extra indirection Human Resource can “bind” key to user. Id record u l Revocation check user. Id + attributes Update of database record (XKMS could be used for this…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 12
Key => user. Id + Attributes l We have to make real-time, online lookups anyway… u u l Why do we need the x. 509/subject name? u u l Similar to X. 509 -RA procedure Key revocation/renewal is simple u l Key => user. Id + attributes Elimination of extra indirection Human Resource can “bind” key to user. Id record u l Revocation check user. Id + attributes Update of database record (XKMS could be used for this…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 12
 1. Authentication Protocol based on key only Client Server 2. Key Direct mapping of Key=> Attributes in Corporate Attribute Svc franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 4. Business Logic uses all kinds of attributes (NOT Authentication. Id) 3. Attributes (groups/roles, access/audit-Id) Attribute Server 13
1. Authentication Protocol based on key only Client Server 2. Key Direct mapping of Key=> Attributes in Corporate Attribute Svc franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 4. Business Logic uses all kinds of attributes (NOT Authentication. Id) 3. Attributes (groups/roles, access/audit-Id) Attribute Server 13
 Key Revocation/Renewal… l l Lost or compromised key – who to tell? Revocation: removal of “key => user. Id/attributes” mapping Renewal: new “key => user. Id/attribute” mapping Have to go through (alternative) authentication/registration procedure u l Every registry that maintains mapping must be updated! u u l Not different from x. 509… One registry => no issue Many registries => big issue May not work well for “very” distributed Grid applications franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 14
Key Revocation/Renewal… l l Lost or compromised key – who to tell? Revocation: removal of “key => user. Id/attributes” mapping Renewal: new “key => user. Id/attribute” mapping Have to go through (alternative) authentication/registration procedure u l Every registry that maintains mapping must be updated! u u l Not different from x. 509… One registry => no issue Many registries => big issue May not work well for “very” distributed Grid applications franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 14
 Key Revocation & Many Registries l Use a trusted third party as revocation service l Only revocation, not key renewal… u Less trust involved l Register both key and revocation service with RAs l Key mapping service should check with revocation svc u l PGP-like… Doesn’t solve renewal… u Still has to be done “in person” franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 15
Key Revocation & Many Registries l Use a trusted third party as revocation service l Only revocation, not key renewal… u Less trust involved l Register both key and revocation service with RAs l Key mapping service should check with revocation svc u l PGP-like… Doesn’t solve renewal… u Still has to be done “in person” franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 15
 Master Key & Proxy Key l Master Key will be ultimate “authority” u u To To To All empower proxy key revoke proxy key “renew” by empowering new proxy key through assertions l Central revocation service still useful Similar to PGP without email “identity” Similar to proxy-cert without subject l But … user has to store/maintain/manage extra key l l u Arguably incapable to manage any long term key… franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 16
Master Key & Proxy Key l Master Key will be ultimate “authority” u u To To To All empower proxy key revoke proxy key “renew” by empowering new proxy key through assertions l Central revocation service still useful Similar to PGP without email “identity” Similar to proxy-cert without subject l But … user has to store/maintain/manage extra key l l u Arguably incapable to manage any long term key… franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 16
 Non-Identity X. 509 Certificate l Use X. 509 certificate for that one extra level of indirection… u l l Subject name just some meaningless unique number “identity vetting” will be left to key => user. Id/attribute registration Use X. 509 standard certificate revocation/renewal methods Registration/revocation/renewal still requires (alternative) authentication with RA/CA u u l l But not for “identity”! Password/mother’s maiden name/? ? ? Or … drivers license, passport, finger print, ? ? ? not for identity vetting but to ensure that the person who registers/revokes/renews is the same person Non-Identity CA much cheaper to operate ESNet opportunity (getting close already…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 17
Non-Identity X. 509 Certificate l Use X. 509 certificate for that one extra level of indirection… u l l Subject name just some meaningless unique number “identity vetting” will be left to key => user. Id/attribute registration Use X. 509 standard certificate revocation/renewal methods Registration/revocation/renewal still requires (alternative) authentication with RA/CA u u l l But not for “identity”! Password/mother’s maiden name/? ? ? Or … drivers license, passport, finger print, ? ? ? not for identity vetting but to ensure that the person who registers/revokes/renews is the same person Non-Identity CA much cheaper to operate ESNet opportunity (getting close already…) franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 17
 “Public-Key=Identity” X. 509 Certificate l Existing SSL runtime spoils the fun… u u u l We could use public key as subject name u l (base 64 of sha 1 digest of key) Need a real CA to vouch for that binding u u u l Requires exchange of real certs Baked-in path validation process Pre-configured list of “trusted” CAs Must be “trusted” to bind the right thing No vetting of identity, though! Much cheaper to deploy. Maybe a nice ESNet service… the PK-CA franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 18
“Public-Key=Identity” X. 509 Certificate l Existing SSL runtime spoils the fun… u u u l We could use public key as subject name u l (base 64 of sha 1 digest of key) Need a real CA to vouch for that binding u u u l Requires exchange of real certs Baked-in path validation process Pre-configured list of “trusted” CAs Must be “trusted” to bind the right thing No vetting of identity, though! Much cheaper to deploy. Maybe a nice ESNet service… the PK-CA franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 18
 Conclusion l Alternative “CAs” are moving in u u u l How to establish the “trust” in these heretic-CAs? u l l Equivalent of same-sex marriage, gay Bishops, … Alternative identity assertions u l Absolutely unthinkable five years ago! Use of X. 509 because of revocation not identity… Slowly the X. 509 religion is eroding/enriched… u l Need “language” to express deployment trust levels PKIX standardization of proxy-certs… u l My. Proxy as a “CA”? That stores private keys… KX 509 ESNet’s use of DNs is “interesting”… SAML, LA/WS-Federation… There alternatives to X. 509 deployment… u u Some cheaper, easier to deploy – depends on application XKMS-like tools allow for migration & enables alternatives franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 19
Conclusion l Alternative “CAs” are moving in u u u l How to establish the “trust” in these heretic-CAs? u l l Equivalent of same-sex marriage, gay Bishops, … Alternative identity assertions u l Absolutely unthinkable five years ago! Use of X. 509 because of revocation not identity… Slowly the X. 509 religion is eroding/enriched… u l Need “language” to express deployment trust levels PKIX standardization of proxy-certs… u l My. Proxy as a “CA”? That stores private keys… KX 509 ESNet’s use of DNs is “interesting”… SAML, LA/WS-Federation… There alternatives to X. 509 deployment… u u Some cheaper, easier to deploy – depends on application XKMS-like tools allow for migration & enables alternatives franks@mcs. anl. go ATI 2004: Grid Security 19


