78a92606193a569255990b66ea7965ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
Is My Method Fit For Purpose ? Rebecca Moffat Marine Institute 27 th Oct 2016

Determining if validation data meets acceptance criteria For Commission Decision 2002/657/EC

Contents n Marine Institute Documents of Reference n Validation under 2002/657/EC n q q q n Parameters Commonly Evaluated in Validation Confirming Positive Sample Criteria Validation Data For Dyes Analysis by LC-MS/MS Conclusion

Marine Institute
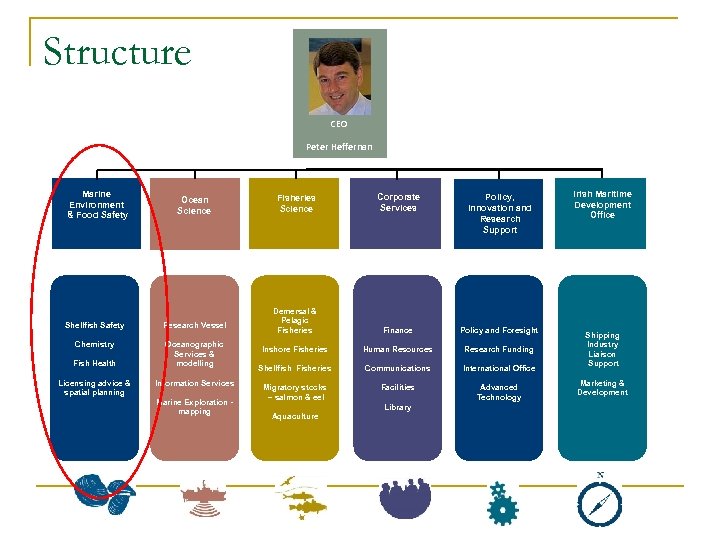
Structure CEO Peter Heffernan Marine Environment & Food Safety Ocean Science Shellfish Safety Research Vessel Chemistry Oceanographic Services & modelling Fish Health Licensing advice & spatial planning Information Services Marine Exploration mapping Fisheries Science Corporate Services Policy, Innovation and Research Support Demersal & Pelagic Fisheries Finance Policy and Foresight Inshore Fisheries Human Resources Research Funding Shellfish Fisheries Communications International Office Migratory stocks – salmon & eel Facilities Advanced Technology Library Aquaculture Irish Maritime Development Office Shipping Industry Liaison Support Marketing & Development

Marine Environment and Food Safety n n n Monitoring Research Advice q q Sampling Analysis Data management Quality – ISO 17025

Marine Environment and Food Safety n n n Seafood Safety – underpin consumer protection and support market Science of marine environmental management Services for management and regulation of aquacluture

Quality System n n Marine Institute Accredited to ISO 17025 since 2002. 35 Accredited methods – 4 ext to scope in 2017. Methods Accredited in multidisciplinary areas Chemistry, (residues, metals, organics), biotoxins, fish diseases, microbiology, phytoplankton, molecular. MI also holds ISO 9001 Certification in the Fish Health Competent Authority Unit.

Residues Programme for Aquaculture n n MI carries out sampling and analysis in accordance with NRCP 3 categories of Residues q Banned – Group A compounds n q Authorized – Group B compounds n q A 3 Steroids: Methlytestosterone B 2(c) Carbamates/Pyrethroids: Cypermethrin Unauthorized – Group B compounds n B 3(e) Dyes: Malachite Green

Documents of Reference n Commission Decision 2002/657/EC q q Eurachem: Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods INAB PS 15 – Guide to Method validation for Quantitative Analysis in Chemical Testing Laboratories (ISO 17025)
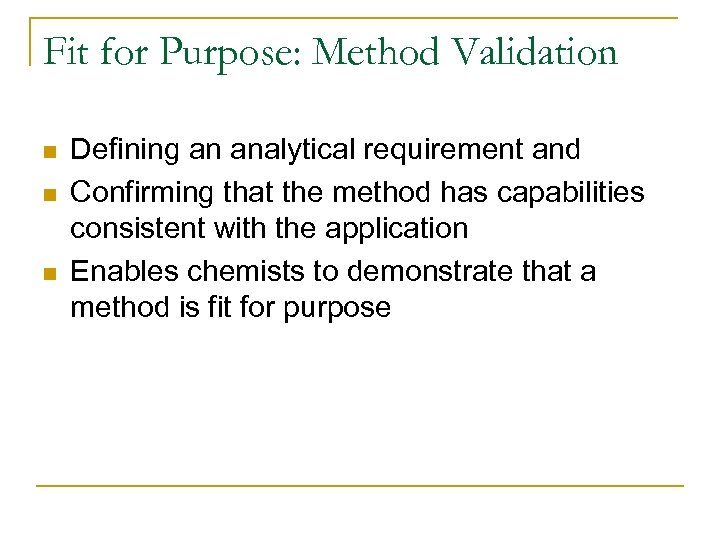
Fit for Purpose: Method Validation n Defining an analytical requirement and Confirming that the method has capabilities consistent with the application Enables chemists to demonstrate that a method is fit for purpose
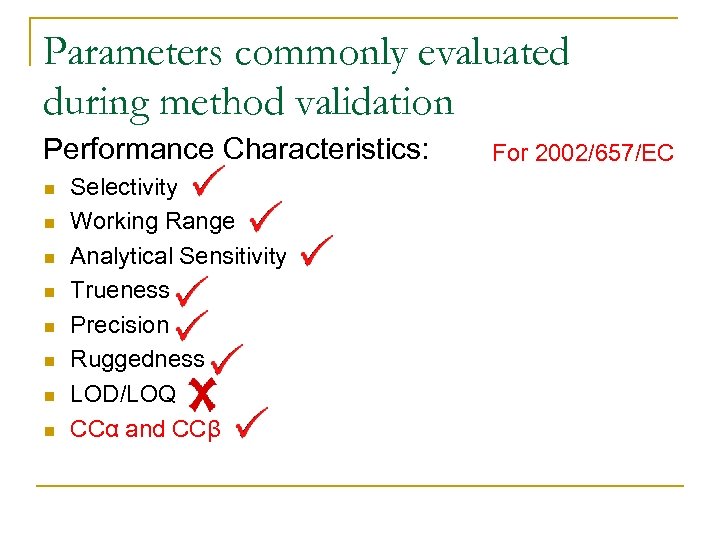
Parameters commonly evaluated during method validation Performance Characteristics: n n n n Selectivity Working Range Analytical Sensitivity Trueness Precision Ruggedness LOD/LOQ CCα and CCβ For 2002/657/EC
Analysis of Dyes by LCMSMS n n n Confirmatory method Based on EU-RL method for Dyes analysed include: q n BG, CV, LMG, MG and VB Awarded INAB accreditation in 2014

Validation under 2002/657/EC n Residues Directive Commission Decision 2002/657/EC states: q Confirmatory methods shall provide information in the chemical structure of the analyte and consequently methods based only on chromatographic analysis without the use of spectrometric detection are not suitable on their own for use as a confirmatory method
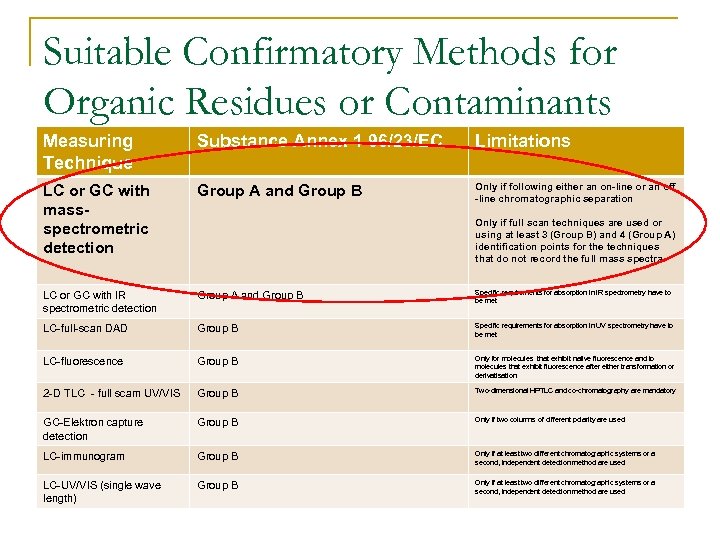
Suitable Confirmatory Methods for Organic Residues or Contaminants Measuring Technique Substance Annex 1 96/23/EC Limitations LC or GC with massspectrometric detection Group A and Group B Only if following either an on-line or an off -line chromatographic separation LC or GC with IR spectrometric detection Group A and Group B Specific requirements for absorption in IR spectrometry have to be met LC-full-scan DAD Group B Specific requirements for absorption in UV spectrometry have to be met LC-fluorescence Group B Only for molecules that exhibit native fluorescence and to molecules that exhibit fluorescence after either transformation or derivatisation 2 -D TLC - full scam UV/VIS Group B Two-dimensional HPTLC and co-chromatography are mandatory GC-Elektron capture detection Group B Only if two columns of different polarity are used LC-immunogram Group B Only if at least two different chromatographic systems or a second, independent detection method are used LC-UV/VIS (single wave length) Group B Only if at least two different chromatographic systems or a second, independent detection method are used Only if full scan techniques are used or using at least 3 (Group B) and 4 (Group A) identification points for the techniques that do not record the full mass spectra
Common Performance Criteria and Requirements n Internal Standards: q q Where used in the method, a suitable internal standard shall be added to the test portion at the beginning of the extraction procedure. Depending of availability, either stable isotopelabelled forms of the analyte, or compounds that are structurally related to the analyte shall be used. n Deuterated Dyes

Confirming Positive sample acceptance criteria: MS/MS tolerance n Criteria for confirming: MS/MS tolerance ion ratio: q Relative intensities of the detected ions, shall correspond to those of the calibration standard, at comparable concentrations, measured under the same conditions within the following tolerances:
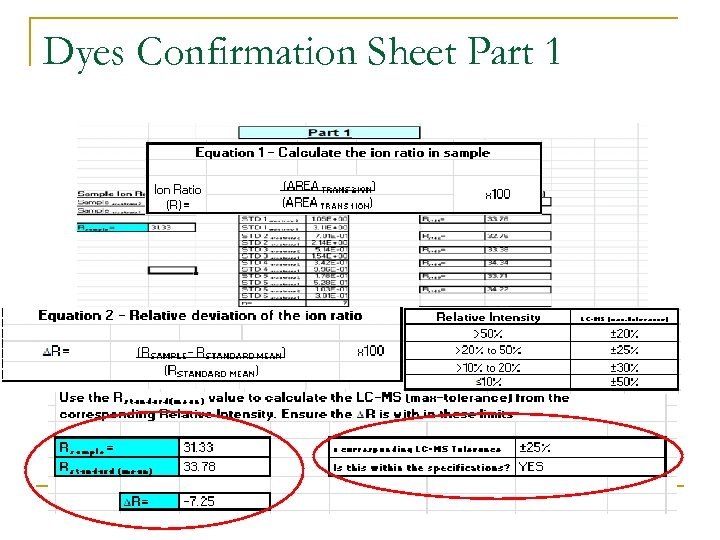
Dyes Confirmation Sheet Part 1
Confirming Positive Sample Criteria: RRT n Criteria for confirming: Relative Retention Time: q q The retention time (or relative retention time) of the analyte in the test portion shall match that of the calibration standard within a specified retention window The ratio of the chromatographic RT of the analyte to the Internal Standard, shall correspond to that of the calibration solution at a tolerance of ± 0. 5% for GC and ± 2. 5% for LC
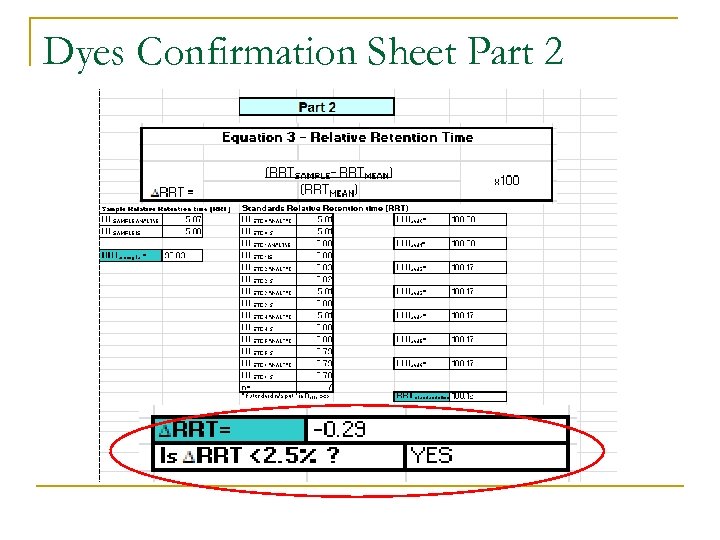
Dyes Confirmation Sheet Part 2
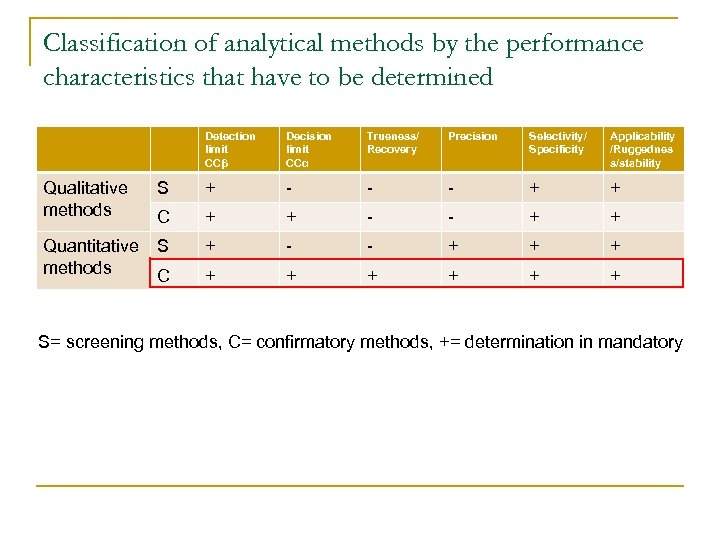
Classification of analytical methods by the performance characteristics that have to be determined Detection limit CCβ Decision limit CCα Trueness/ Recovery Precision Selectivity/ Specificity Applicability /Ruggednes s/stability Qualitative methods S + - - - + + C + + - - + + Quantitative methods S + - - + + + C + + + S= screening methods, C= confirmatory methods, += determination in mandatory
Specificity n Specificity: q n Ability of a method to distinguish between the analyte being measured and other substances Determined by q q Analysing blank representative samples and showing no interfering peaks in mass range window Analysing each standard individually
Specificity n n LC-MS/MS offers high degree of selectivity and specificity Small interfering peaks were observed at RT for some analytes in chromatograms of nonfortified samples q n Areas so low to be of little consequence Quantification of each analyte not influeneced notably by levels detected in negative controls
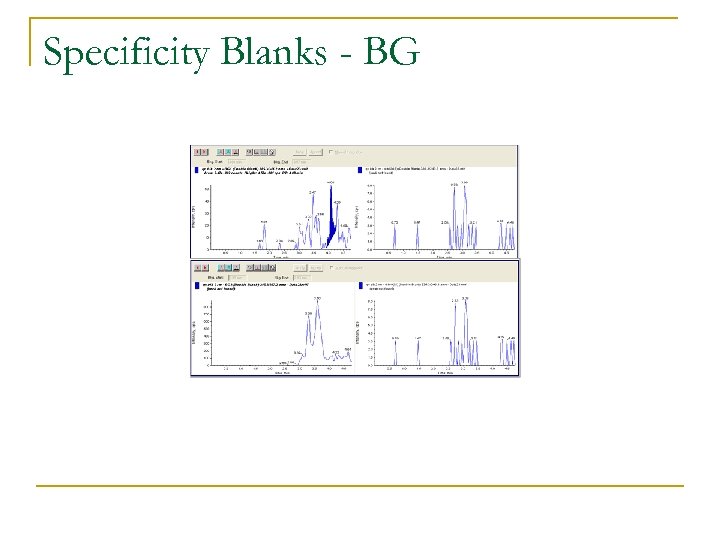
Specificity Blanks - BG
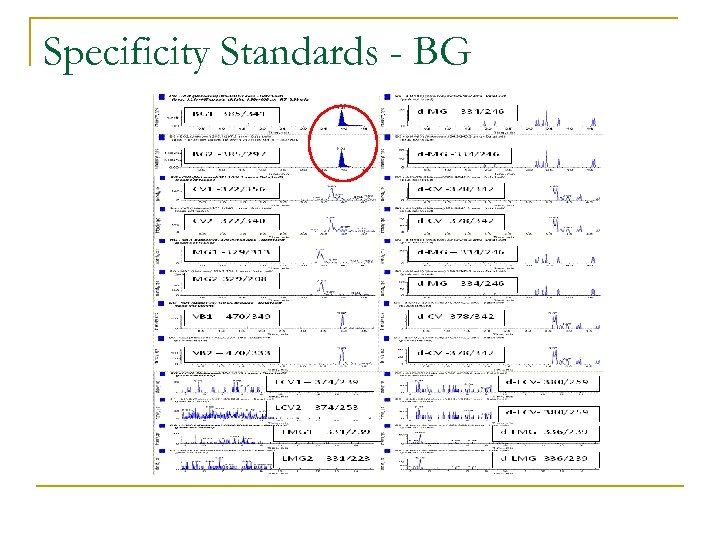
Specificity Standards - BG
Working Range n n n Linearity of matrix matched calibration curve Upper Linear Range Saturation Point and method range
Matrix matched curve n n Fortify negative control salmon tissue across range of concentrations and bring through extraction procedure Matrix can have effect on the signal produced (suppression or enhancement) q MM calibration curve used to ensure these effects are accounted for in quantification of unknowns
Calibration Standard Levels Level ~ Amount (ng analyte/g tissue) ~MRPL level 7 0 0 6 0. 5 0. 25 5 1 0. 5 4 2 1 3 3. 5 1. 75 2 5 2. 5 1 7. 5 3. 75 0 10 5
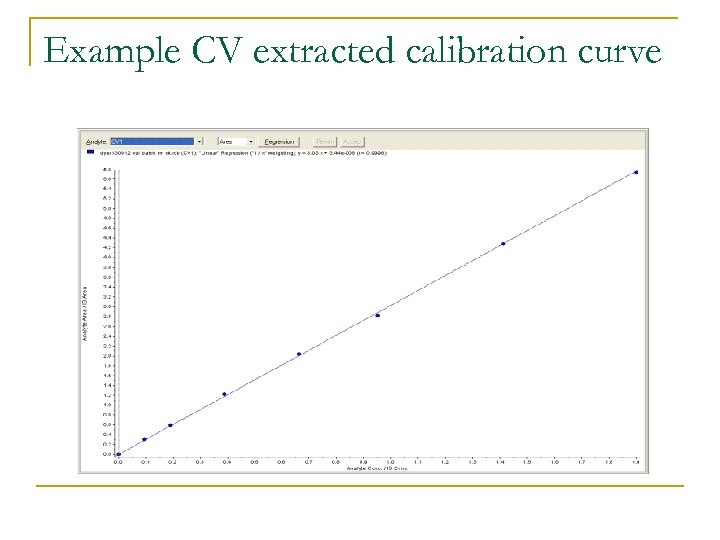
Example CV extracted calibration curve
Upper Linear Range n n Matrix matched Calibration Curves Calibration standards concentrations range: q n 0µg/kg – 15µg/kg Most suitable range for all analyes: q q 0µg/kg – 10µg/kg Lowest standard with analyte present 0. 5µg/kg n 0. 25*MRPL
Saturation point and method range n Saturation point examined in triplicate at 5 and 7. 5 * MRPL for all dyes q n n n Equivalent to 10µg/kg and 15µg/kg Acceptable recoveries achievable for 4/6 CV, MG, LCV, LMG analytes at 15µg/kg Acceptable recoveries achievable for 6/6 analytes at 10µg/kg BG, CV, MG, VB, LCV, LMG Method range: 0. 5µg/kg – 10µg/kg (15µg/kg)
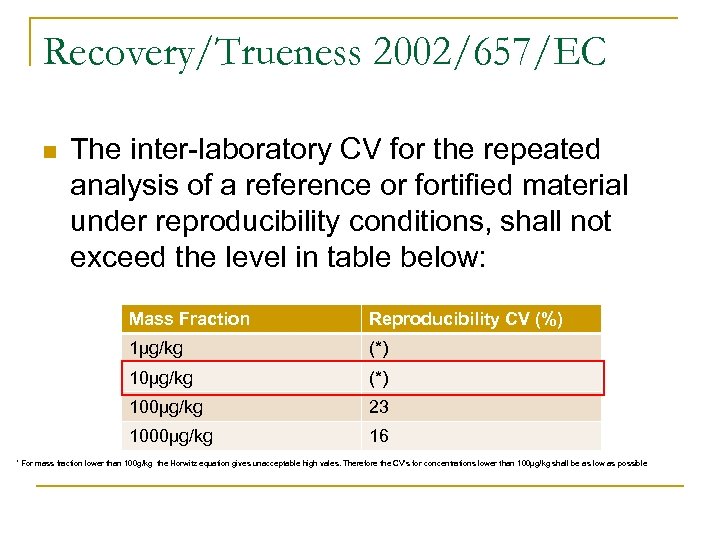
Recovery/Trueness 2002/657/EC n The inter-laboratory CV for the repeated analysis of a reference or fortified material under reproducibility conditions, shall not exceed the level in table below: Mass Fraction Reproducibility CV (%) 1µg/kg (*) 100µg/kg 23 1000µg/kg 16 * For mass fraction lower than 100 g/kg the Horwitz equation gives unacceptable high vales. Therefore the CV’s for concentrations lower than 100µg/kg shall be as low as possible
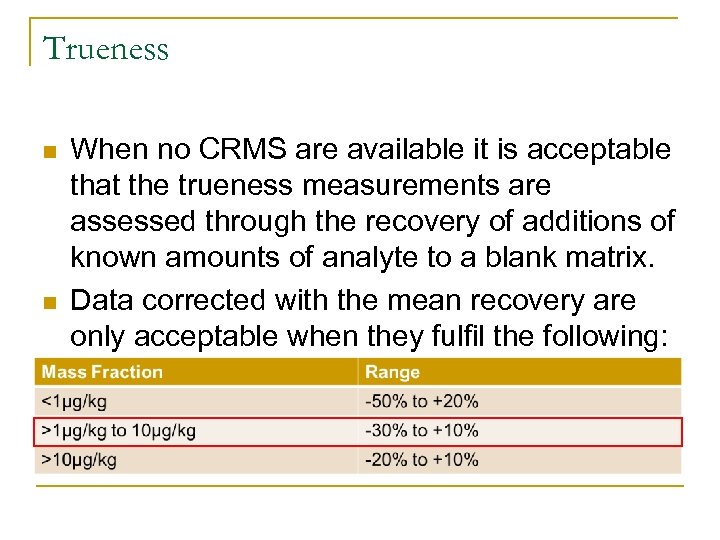
Trueness n n When no CRMS are available it is acceptable that the trueness measurements are assessed through the recovery of additions of known amounts of analyte to a blank matrix. Data corrected with the mean recovery are only acceptable when they fulfil the following:
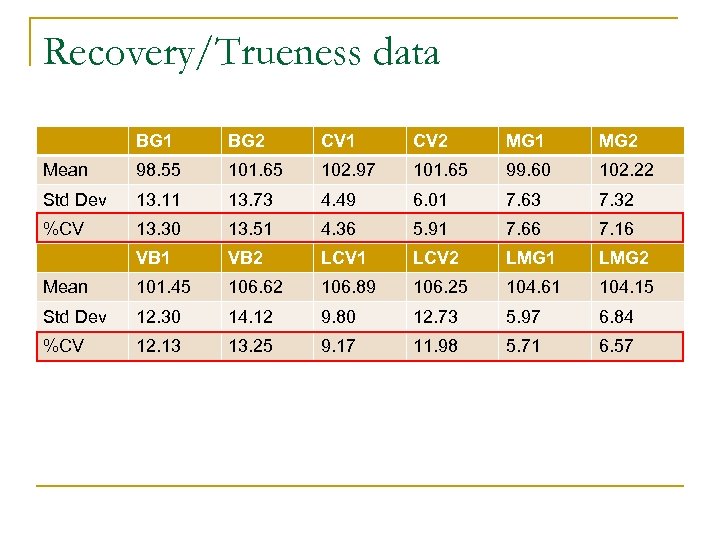
Recovery/Trueness data BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 98. 55 101. 65 102. 97 101. 65 99. 60 102. 22 Std Dev 13. 11 13. 73 4. 49 6. 01 7. 63 7. 32 %CV 13. 30 13. 51 4. 36 5. 91 7. 66 7. 16 VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 101. 45 106. 62 106. 89 106. 25 104. 61 104. 15 Std Dev 12. 30 14. 12 9. 80 12. 73 5. 97 6. 84 %CV 12. 13 13. 25 9. 17 11. 98 5. 71 6. 57
Precision n Falls under 2 categories q q Within Batch Repeatability Within Lab Reproducability
Within Batch Repeatability n n Prepare a set f samples of identical matrices, fortified with the analyte to yield concentrations equivalent to 1, 1. 5 and 2 times MRPL Each level analysed with 7 replicates
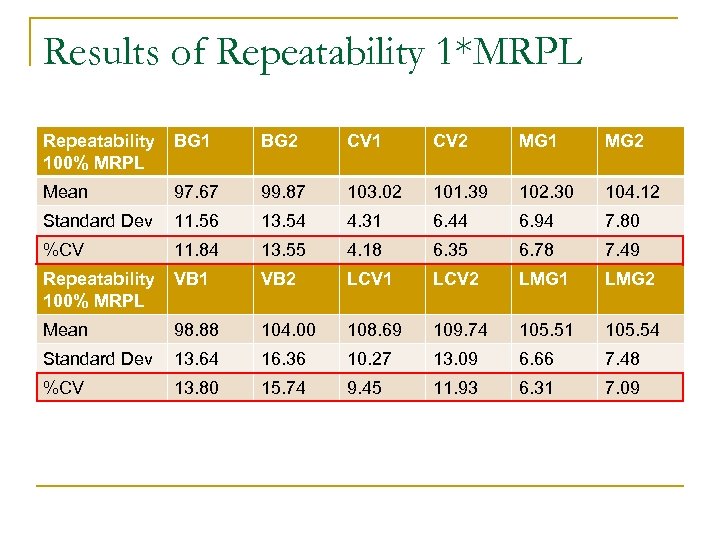
Results of Repeatability 1*MRPL Repeatability 100% MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 97. 67 99. 87 103. 02 101. 39 102. 30 104. 12 Standard Dev 11. 56 13. 54 4. 31 6. 44 6. 94 7. 80 %CV 11. 84 13. 55 4. 18 6. 35 6. 78 7. 49 Repeatability 100% MRPL VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 98. 88 104. 00 108. 69 109. 74 105. 51 105. 54 Standard Dev 13. 64 16. 36 10. 27 13. 09 6. 66 7. 48 %CV 13. 80 15. 74 9. 45 11. 93 6. 31 7. 09
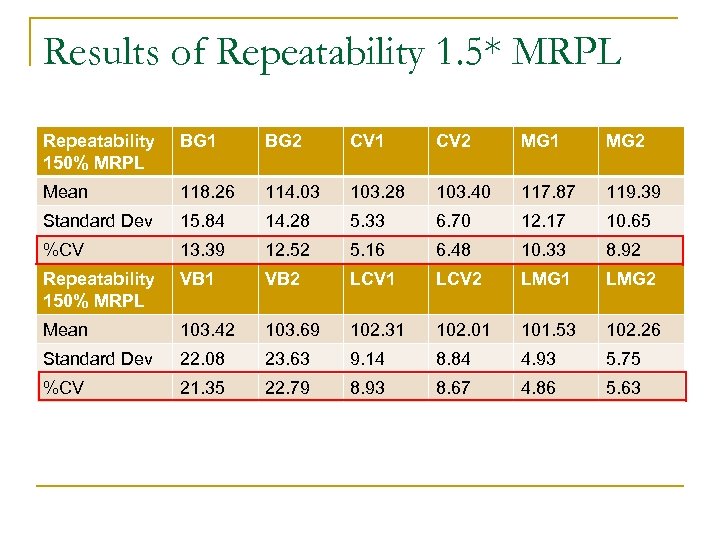
Results of Repeatability 1. 5* MRPL Repeatability 150% MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 118. 26 114. 03 103. 28 103. 40 117. 87 119. 39 Standard Dev 15. 84 14. 28 5. 33 6. 70 12. 17 10. 65 %CV 13. 39 12. 52 5. 16 6. 48 10. 33 8. 92 Repeatability 150% MRPL VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 103. 42 103. 69 102. 31 102. 01 101. 53 102. 26 Standard Dev 22. 08 23. 63 9. 14 8. 84 4. 93 5. 75 %CV 21. 35 22. 79 8. 93 8. 67 4. 86 5. 63
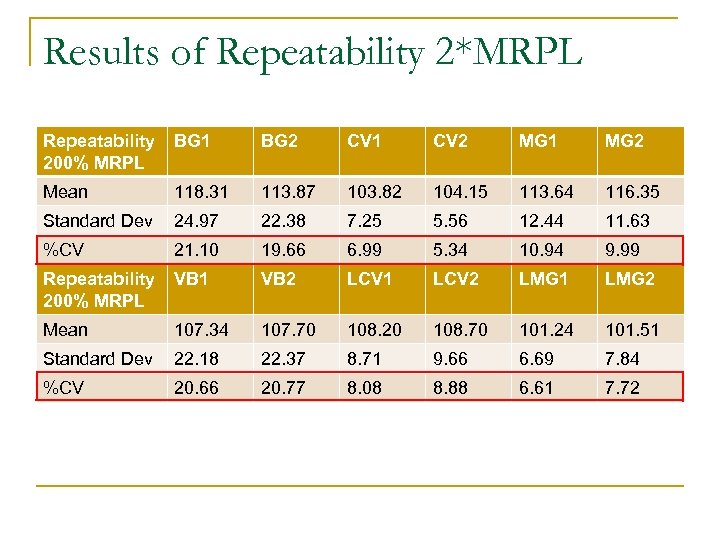
Results of Repeatability 2*MRPL Repeatability 200% MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 118. 31 113. 87 103. 82 104. 15 113. 64 116. 35 Standard Dev 24. 97 22. 38 7. 25 5. 56 12. 44 11. 63 %CV 21. 10 19. 66 6. 99 5. 34 10. 94 9. 99 Repeatability 200% MRPL VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 107. 34 107. 70 108. 20 108. 70 101. 24 101. 51 Standard Dev 22. 18 22. 37 8. 71 9. 66 6. 69 7. 84 %CV 20. 66 20. 77 8. 08 8. 88 6. 61 7. 72
Within Lab Reproducability n Samples spiked at approx 1, 1. 5 and 2*MRPL were analysed on 3 occasions by 2 analysts q q Analyst A – twice using different batches of reagents and solvents Analyst B
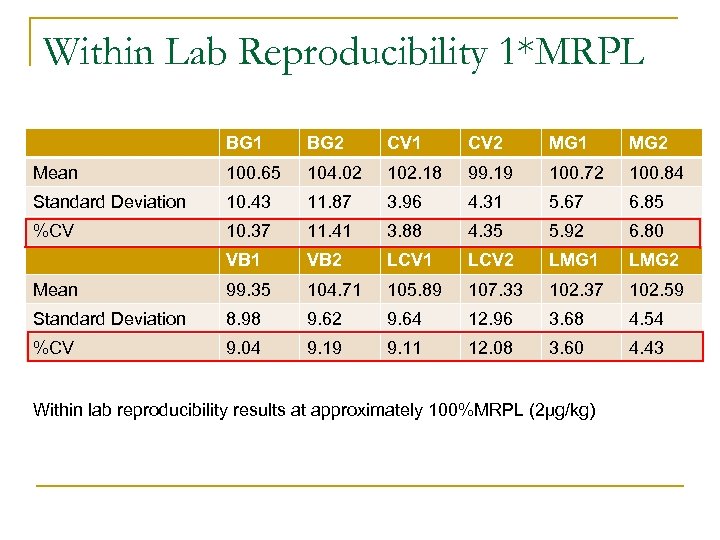
Within Lab Reproducibility 1*MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 100. 65 104. 02 102. 18 99. 19 100. 72 100. 84 Standard Deviation 10. 43 11. 87 3. 96 4. 31 5. 67 6. 85 %CV 10. 37 11. 41 3. 88 4. 35 5. 92 6. 80 VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 99. 35 104. 71 105. 89 107. 33 102. 37 102. 59 Standard Deviation 8. 98 9. 62 9. 64 12. 96 3. 68 4. 54 %CV 9. 04 9. 19 9. 11 12. 08 3. 60 4. 43 Within lab reproducibility results at approximately 100%MRPL (2µg/kg)
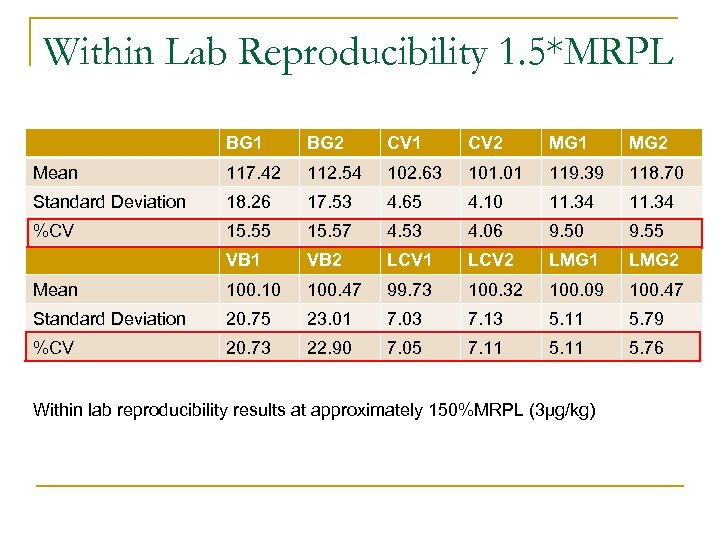
Within Lab Reproducibility 1. 5*MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 117. 42 112. 54 102. 63 101. 01 119. 39 118. 70 Standard Deviation 18. 26 17. 53 4. 65 4. 10 11. 34 %CV 15. 55 15. 57 4. 53 4. 06 9. 50 9. 55 VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 100. 10 100. 47 99. 73 100. 32 100. 09 100. 47 Standard Deviation 20. 75 23. 01 7. 03 7. 13 5. 11 5. 79 %CV 20. 73 22. 90 7. 05 7. 11 5. 76 Within lab reproducibility results at approximately 150%MRPL (3µg/kg)
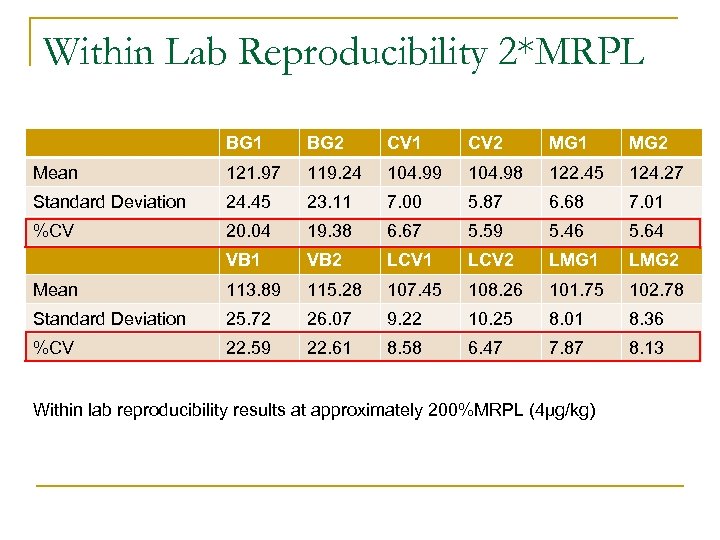
Within Lab Reproducibility 2*MRPL BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Mean 121. 97 119. 24 104. 99 104. 98 122. 45 124. 27 Standard Deviation 24. 45 23. 11 7. 00 5. 87 6. 68 7. 01 %CV 20. 04 19. 38 6. 67 5. 59 5. 46 5. 64 VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Mean 113. 89 115. 28 107. 45 108. 26 101. 75 102. 78 Standard Deviation 25. 72 26. 07 9. 22 10. 25 8. 01 8. 36 %CV 22. 59 22. 61 8. 58 6. 47 7. 87 8. 13 Within lab reproducibility results at approximately 200%MRPL (4µg/kg)

Ruggedness n Examined using the Youden approach q q Choose a subset of 8 combinations that have a balance between capital and small letters 8 determinations are made which will use a combination of the chosen factors A-G
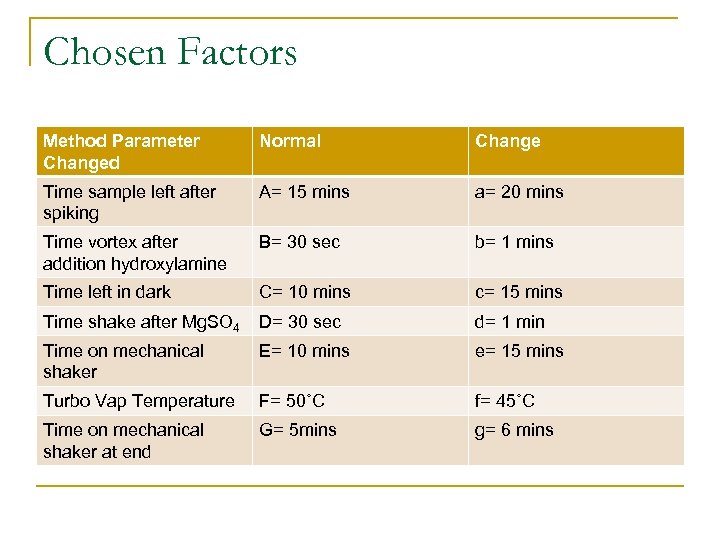
Chosen Factors Method Parameter Changed Normal Change Time sample left after spiking A= 15 mins a= 20 mins Time vortex after addition hydroxylamine B= 30 sec b= 1 mins Time left in dark C= 10 mins c= 15 mins Time shake after Mg. SO 4 D= 30 sec d= 1 min Time on mechanical shaker E= 10 mins e= 15 mins Turbo Vap Temperature F= 50˚C f= 45˚C Time on mechanical shaker at end G= 5 mins g= 6 mins
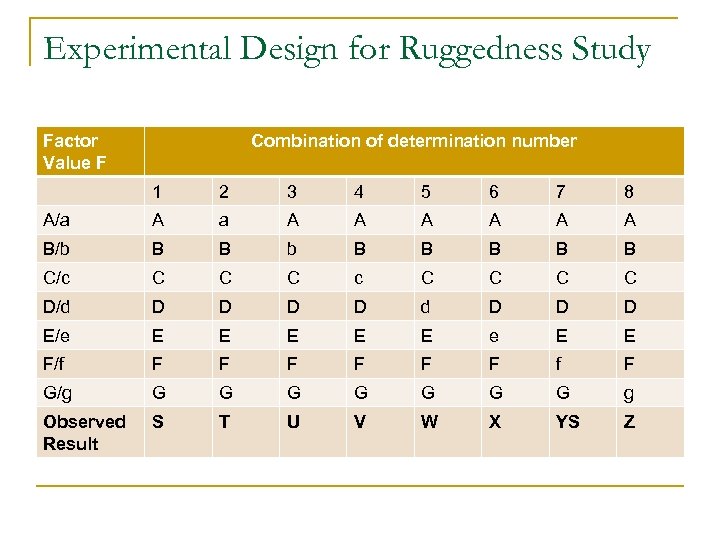
Experimental Design for Ruggedness Study Factor Value F Combination of determination number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 A/a A A A A B/b B B B B B C/c C C C C D/d D D D E/e E E E e E E F/f F F F f F G/g G G G G g Observed Result S T U V W X YS Z
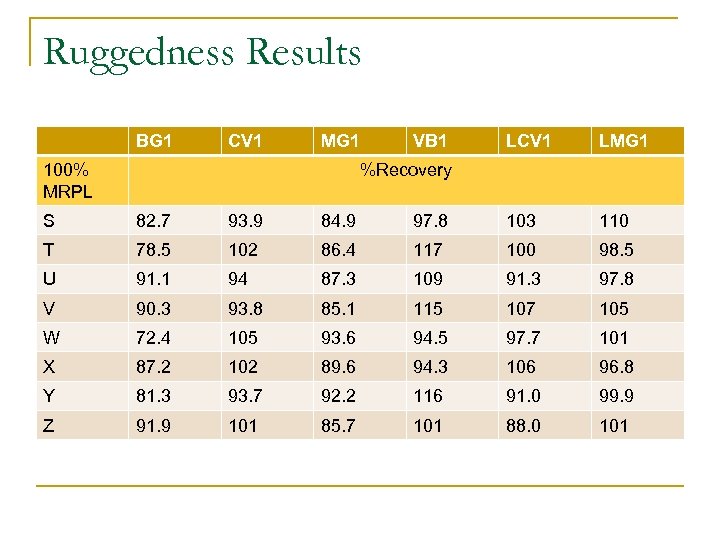
Ruggedness Results BG 1 CV 1 MG 1 100% MRPL VB 1 LCV 1 LMG 1 %Recovery S 82. 7 93. 9 84. 9 97. 8 103 110 T 78. 5 102 86. 4 117 100 98. 5 U 91. 1 94 87. 3 109 91. 3 97. 8 V 90. 3 93. 8 85. 1 115 107 105 W 72. 4 105 93. 6 94. 5 97. 7 101 X 87. 2 102 89. 6 94. 3 106 96. 8 Y 81. 3 93. 7 92. 2 116 91. 0 99. 9 Z 91. 9 101 85. 7 101 88. 0 101
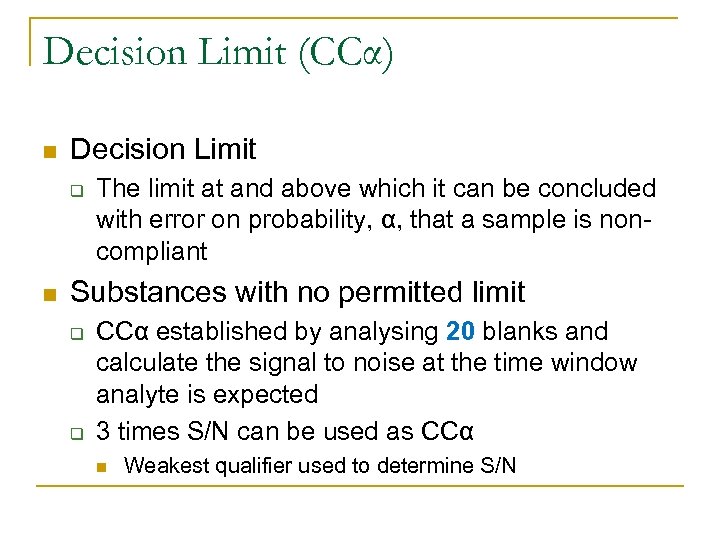
Decision Limit (CCα) n Decision Limit q n The limit at and above which it can be concluded with error on probability, α, that a sample is noncompliant Substances with no permitted limit q q CCα established by analysing 20 blanks and calculate the signal to noise at the time window analyte is expected 3 times S/N can be used as CCα n Weakest qualifier used to determine S/N
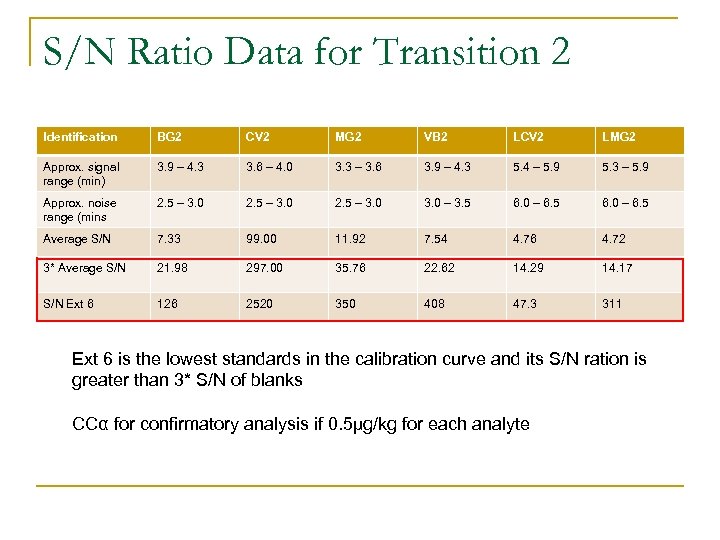
S/N Ratio Data for Transition 2 Identification BG 2 CV 2 MG 2 VB 2 LCV 2 LMG 2 Approx. signal range (min) 3. 9 – 4. 3 3. 6 – 4. 0 3. 3 – 3. 6 3. 9 – 4. 3 5. 4 – 5. 9 5. 3 – 5. 9 Approx. noise range (mins 2. 5 – 3. 0 – 3. 5 6. 0 – 6. 5 Average S/N 7. 33 99. 00 11. 92 7. 54 4. 76 4. 72 3* Average S/N 21. 98 297. 00 35. 76 22. 62 14. 29 14. 17 S/N Ext 6 126 2520 350 408 47. 3 311 Ext 6 is the lowest standards in the calibration curve and its S/N ration is greater than 3* S/N of blanks CCα for confirmatory analysis if 0. 5µg/kg for each analyte
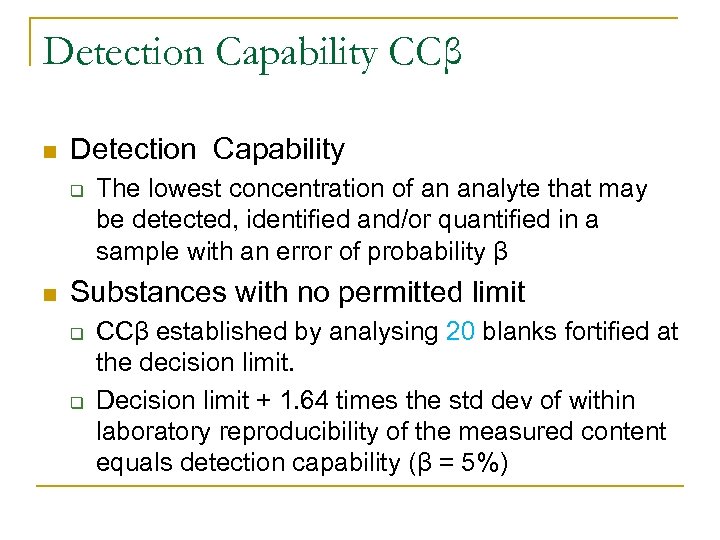
Detection Capability CCβ n Detection Capability q n The lowest concentration of an analyte that may be detected, identified and/or quantified in a sample with an error of probability β Substances with no permitted limit q q CCβ established by analysing 20 blanks fortified at the decision limit. Decision limit + 1. 64 times the std dev of within laboratory reproducibility of the measured content equals detection capability (β = 5%)
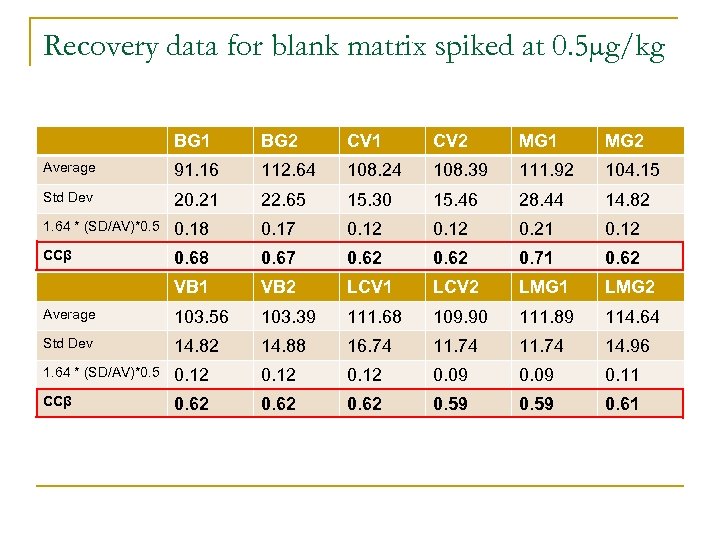
Recovery data for blank matrix spiked at 0. 5µg/kg BG 1 BG 2 CV 1 CV 2 MG 1 MG 2 Average 91. 16 112. 64 108. 24 108. 39 111. 92 104. 15 Std Dev 20. 21 22. 65 15. 30 15. 46 28. 44 14. 82 1. 64 * (SD/AV)*0. 5 0. 18 0. 17 0. 12 0. 21 0. 12 CCβ 0. 68 0. 67 0. 62 0. 71 0. 62 VB 1 VB 2 LCV 1 LCV 2 LMG 1 LMG 2 Average 103. 56 103. 39 111. 68 109. 90 111. 89 114. 64 Std Dev 14. 82 14. 88 16. 74 11. 74 14. 96 1. 64 * (SD/AV)*0. 5 0. 12 0. 09 0. 11 CCβ 0. 62 0. 59 0. 61
Conclusion n n Method for analysis of Dyes by LCMSMS was validated. Validation data shows the performance of analytical method is Fit For Purpose and acceptable within acceptance criteria as stated in Commission 2002/657/EC
78a92606193a569255990b66ea7965ec.ppt