5babcf0788bdad8f8994c9b1397d98de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 IS 553 Advanced Systems Development Practices James Nowotarski 27 April 2004
IS 553 Advanced Systems Development Practices James Nowotarski 27 April 2004
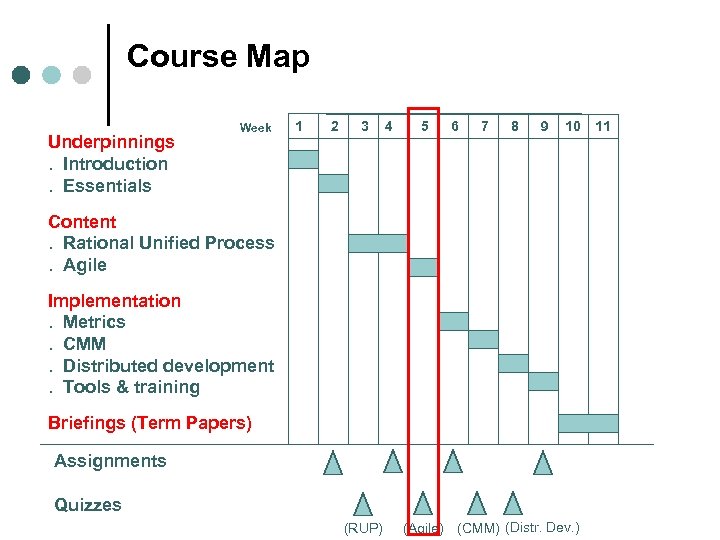 Course Map Underpinnings. Introduction. Essentials Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Content. Rational Unified Process. Agile Implementation. Metrics. CMM. Distributed development. Tools & training Briefings (Term Papers) Assignments Quizzes (RUP) (Agile) (CMM) (Distr. Dev. ) 11
Course Map Underpinnings. Introduction. Essentials Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Content. Rational Unified Process. Agile Implementation. Metrics. CMM. Distributed development. Tools & training Briefings (Term Papers) Assignments Quizzes (RUP) (Agile) (CMM) (Distr. Dev. ) 11
 Today’s Objectives Background on Agile Methods ¢ Understand basics of Extreme Programming ¢ Guiding Principles l Benefits l What’s Different l Applicability l Track Record l Key Players & Products l References l
Today’s Objectives Background on Agile Methods ¢ Understand basics of Extreme Programming ¢ Guiding Principles l Benefits l What’s Different l Applicability l Track Record l Key Players & Products l References l
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
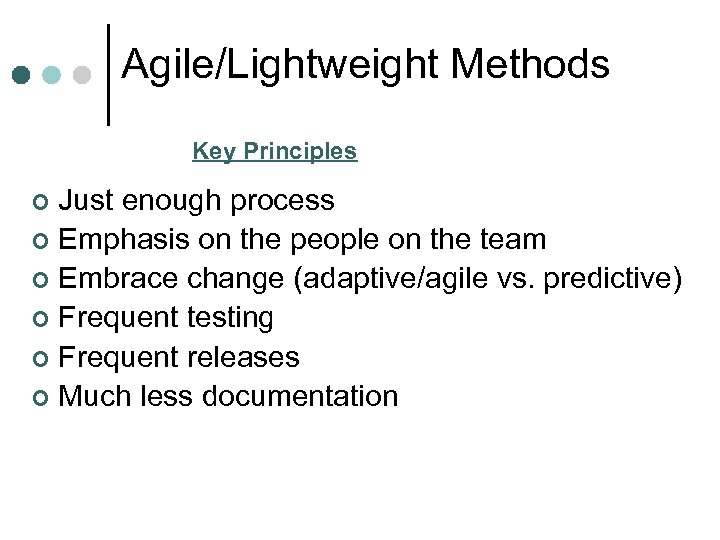 Agile/Lightweight Methods Key Principles Just enough process ¢ Emphasis on the people on the team ¢ Embrace change (adaptive/agile vs. predictive) ¢ Frequent testing ¢ Frequent releases ¢ Much less documentation ¢
Agile/Lightweight Methods Key Principles Just enough process ¢ Emphasis on the people on the team ¢ Embrace change (adaptive/agile vs. predictive) ¢ Frequent testing ¢ Frequent releases ¢ Much less documentation ¢
 Agile/Lightweight Methods Several methodologies fit under this lightweight banner Extreme Programming (XP) (Kent Beck) ¢ Crystal (Alistair Cockburn) ¢ Adaptive Software Development (Jim Highsmith) ¢ SCRUM (Ken Schwaber) ¢ Feature Driven Development (Peter Coad, Ken De. Luca, Steve Palmer) ¢
Agile/Lightweight Methods Several methodologies fit under this lightweight banner Extreme Programming (XP) (Kent Beck) ¢ Crystal (Alistair Cockburn) ¢ Adaptive Software Development (Jim Highsmith) ¢ SCRUM (Ken Schwaber) ¢ Feature Driven Development (Peter Coad, Ken De. Luca, Steve Palmer) ¢
 Agile/Lightweight Methods ¢ On February 11 -12, 2001 seventeen proponents met at Snowbird ski resort and what emerged was the: Agile “Software Development” Alliance ¢ “We have come to value: l l Individuals and interactions Working software over Customer collaboration over Responding to change over processes and tools comprehensive documentation contract negotiation following a plan”
Agile/Lightweight Methods ¢ On February 11 -12, 2001 seventeen proponents met at Snowbird ski resort and what emerged was the: Agile “Software Development” Alliance ¢ “We have come to value: l l Individuals and interactions Working software over Customer collaboration over Responding to change over processes and tools comprehensive documentation contract negotiation following a plan”
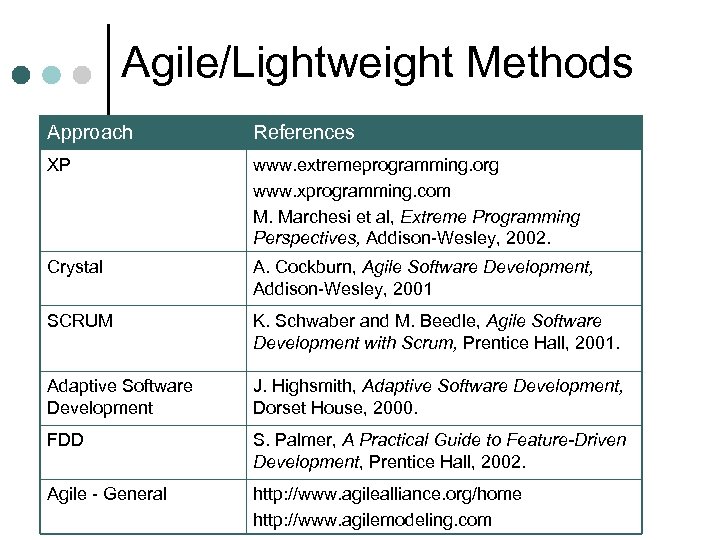 Agile/Lightweight Methods Approach References XP www. extremeprogramming. org www. xprogramming. com M. Marchesi et al, Extreme Programming Perspectives, Addison-Wesley, 2002. Crystal A. Cockburn, Agile Software Development, Addison-Wesley, 2001 SCRUM K. Schwaber and M. Beedle, Agile Software Development with Scrum, Prentice Hall, 2001. Adaptive Software Development J. Highsmith, Adaptive Software Development, Dorset House, 2000. FDD S. Palmer, A Practical Guide to Feature-Driven Development, Prentice Hall, 2002. Agile - General http: //www. agilealliance. org/home http: //www. agilemodeling. com
Agile/Lightweight Methods Approach References XP www. extremeprogramming. org www. xprogramming. com M. Marchesi et al, Extreme Programming Perspectives, Addison-Wesley, 2002. Crystal A. Cockburn, Agile Software Development, Addison-Wesley, 2001 SCRUM K. Schwaber and M. Beedle, Agile Software Development with Scrum, Prentice Hall, 2001. Adaptive Software Development J. Highsmith, Adaptive Software Development, Dorset House, 2000. FDD S. Palmer, A Practical Guide to Feature-Driven Development, Prentice Hall, 2002. Agile - General http: //www. agilealliance. org/home http: //www. agilemodeling. com
 XP Background ¢ ¢ ¢ Developed by Kent Beck and Ward Cunningham Based on Beck and Ward’s experiences developing Smalltalk software at Tektronix First large project was the C 3 Payroll Project at Chrysler l l 1993 project started with Business Modeling 1994 development begun with a small 40 person consulting firm & Smalltalk 1995 performance problems - Kent Beck brought in to improve quality 1996 Kent Beck took over project and began implementing project in a new method that we now call Extreme Programming
XP Background ¢ ¢ ¢ Developed by Kent Beck and Ward Cunningham Based on Beck and Ward’s experiences developing Smalltalk software at Tektronix First large project was the C 3 Payroll Project at Chrysler l l 1993 project started with Business Modeling 1994 development begun with a small 40 person consulting firm & Smalltalk 1995 performance problems - Kent Beck brought in to improve quality 1996 Kent Beck took over project and began implementing project in a new method that we now call Extreme Programming
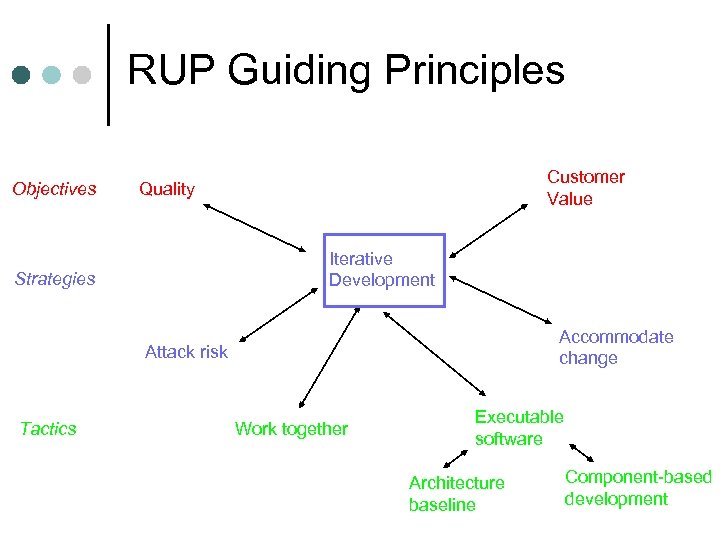 RUP Guiding Principles Objectives Customer Value Quality Iterative Development Strategies Accommodate change Attack risk Tactics Work together Executable software Architecture baseline Component-based development
RUP Guiding Principles Objectives Customer Value Quality Iterative Development Strategies Accommodate change Attack risk Tactics Work together Executable software Architecture baseline Component-based development
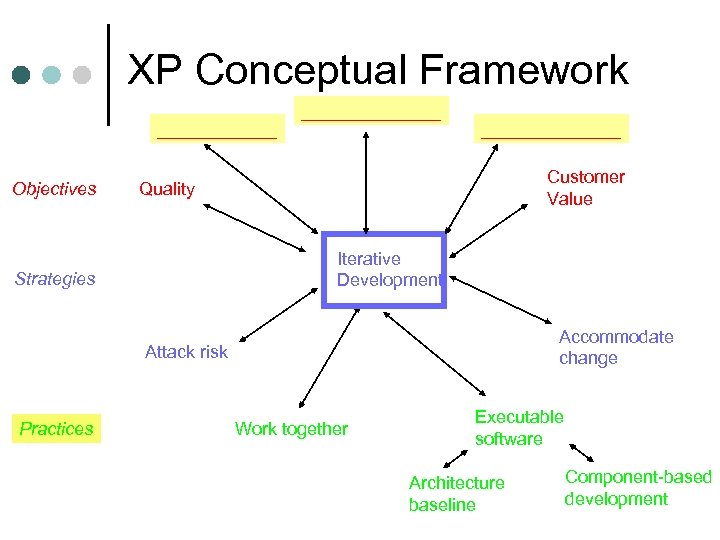 XP Conceptual Framework ______ Objectives ______________ Customer Value Quality Iterative Development Strategies Accommodate change Attack risk Practices Work together Executable software Architecture baseline Component-based development
XP Conceptual Framework ______ Objectives ______________ Customer Value Quality Iterative Development Strategies Accommodate change Attack risk Practices Work together Executable software Architecture baseline Component-based development
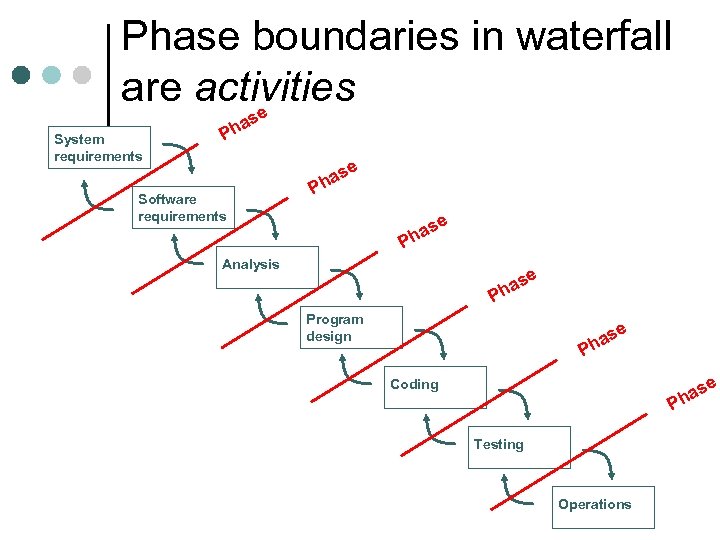 Phase boundaries in waterfall are activities e s System requirements a Ph e Software requirements s ha P se a Ph Analysis e as h P Program design se ha P e as h Coding P Testing Operations
Phase boundaries in waterfall are activities e s System requirements a Ph e Software requirements s ha P se a Ph Analysis e as h P Program design se ha P e as h Coding P Testing Operations
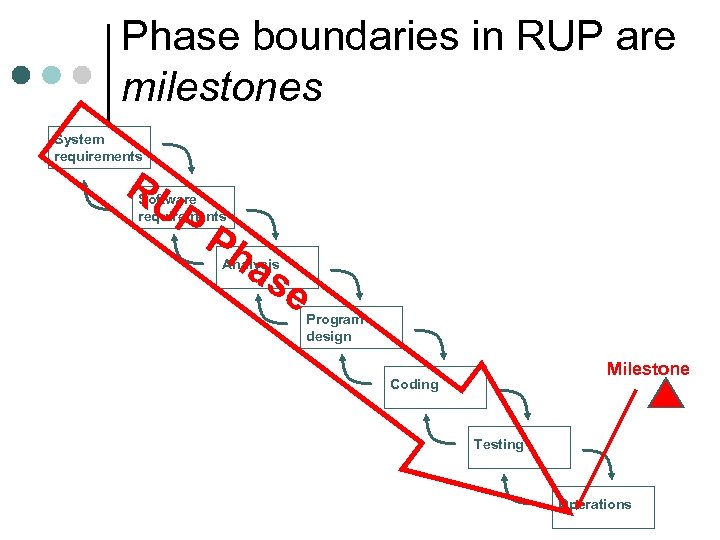 Phase boundaries in RUP are milestones System requirements RU P Software requirements Ph as Analysis e Program design Milestone Coding Testing Operations
Phase boundaries in RUP are milestones System requirements RU P Software requirements Ph as Analysis e Program design Milestone Coding Testing Operations
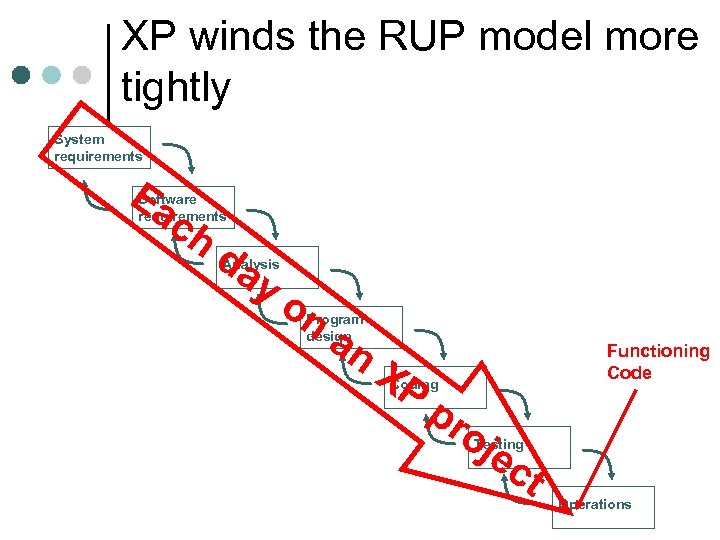 XP winds the RUP model more tightly System requirements Ea c Software requirements h da Analysis yo n Program design an XP Functioning Code Coding pr oj ec t Testing Operations
XP winds the RUP model more tightly System requirements Ea c Software requirements h da Analysis yo n Program design an XP Functioning Code Coding pr oj ec t Testing Operations
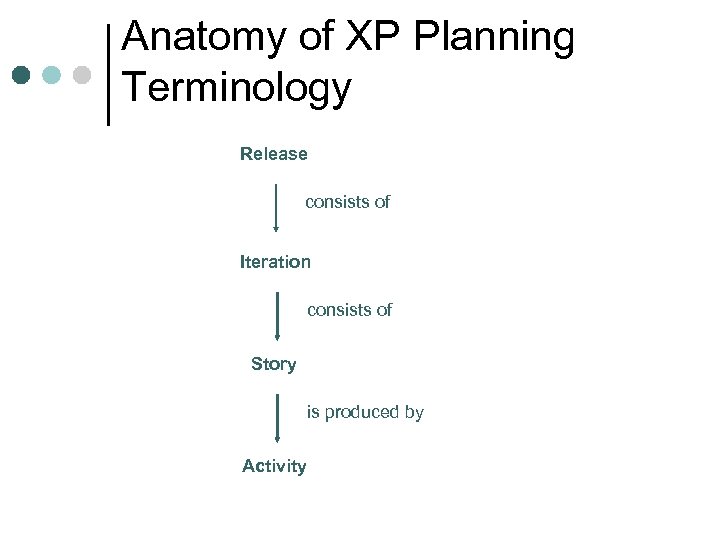 Anatomy of XP Planning Terminology Release consists of Iteration consists of Story is produced by Activity
Anatomy of XP Planning Terminology Release consists of Iteration consists of Story is produced by Activity
 What is XP First Principles ¢ ¢ ¢
What is XP First Principles ¢ ¢ ¢
 What is XP Rapid Feedback ¢ ¢ “Don’t ask me, ask the system” “Have you written a test case for that yet” Put in production as soon as possible l i. e. , don’t “shelter” your code “Without this first pass, the project manager is at the mercy of human judgment. With this first-pass ‘simulation, ’ he can at least perform experimental tests of some key hypotheses and scope down what remains for human judgment, which in the case of computer program design. . . is invariably and seriously optimistic” – Royce, 1970
What is XP Rapid Feedback ¢ ¢ “Don’t ask me, ask the system” “Have you written a test case for that yet” Put in production as soon as possible l i. e. , don’t “shelter” your code “Without this first pass, the project manager is at the mercy of human judgment. With this first-pass ‘simulation, ’ he can at least perform experimental tests of some key hypotheses and scope down what remains for human judgment, which in the case of computer program design. . . is invariably and seriously optimistic” – Royce, 1970
 What is XP Assume Simplicity Embrace Change “What is the simplest thing that could possibly work? ” ¢ Flattened change curve ¢
What is XP Assume Simplicity Embrace Change “What is the simplest thing that could possibly work? ” ¢ Flattened change curve ¢
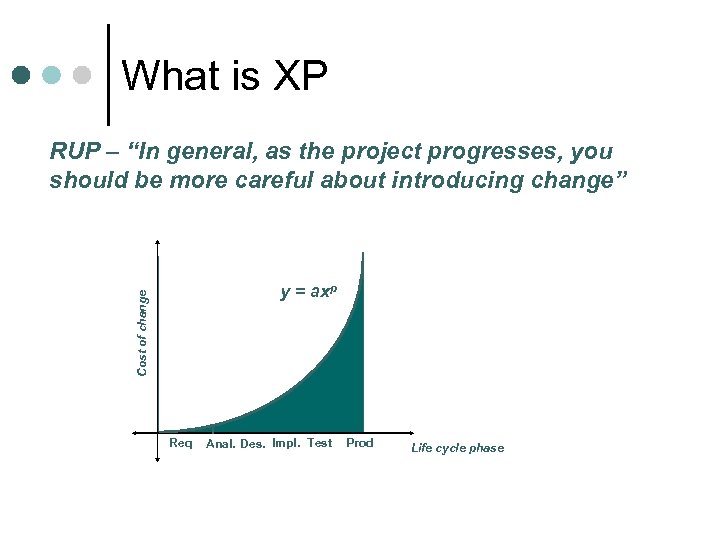 What is XP RUP – “In general, as the project progresses, you should be more careful about introducing change” Cost of change y = axp Req Anal. Des. Impl. Test Prod Life cycle phase
What is XP RUP – “In general, as the project progresses, you should be more careful about introducing change” Cost of change y = axp Req Anal. Des. Impl. Test Prod Life cycle phase
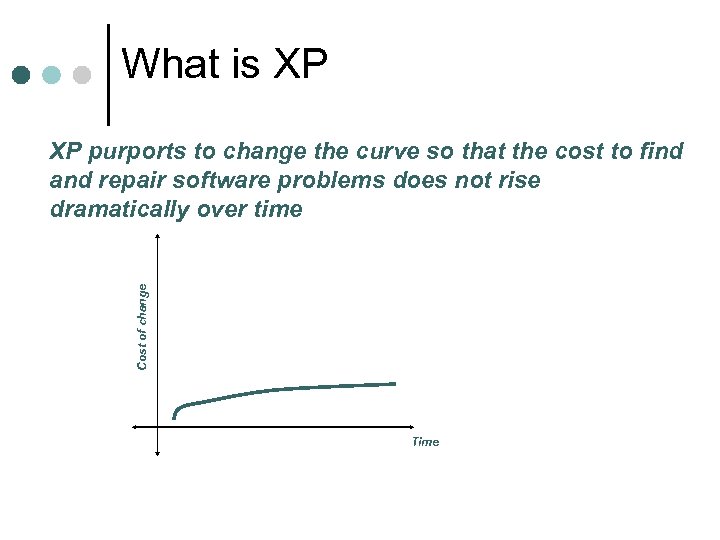 What is XP Cost of change XP purports to change the curve so that the cost to find and repair software problems does not rise dramatically over time Time
What is XP Cost of change XP purports to change the curve so that the cost to find and repair software problems does not rise dramatically over time Time
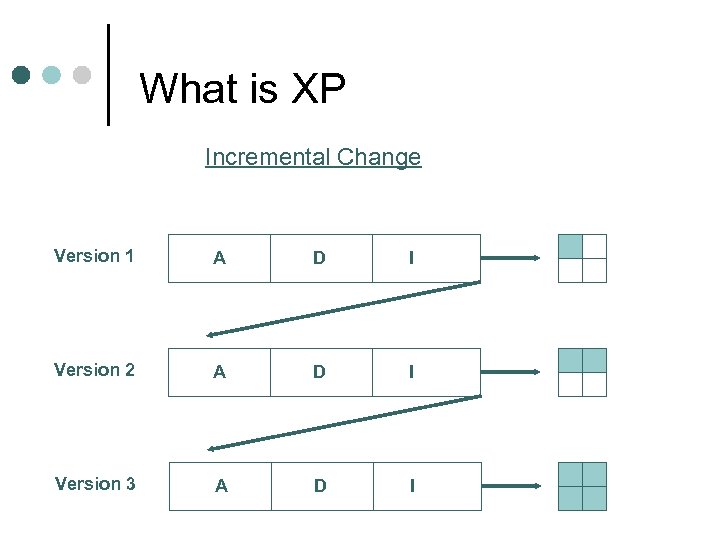 What is XP Incremental Change Version 1 A D I Version 2 A D I Version 3 A D I
What is XP Incremental Change Version 1 A D I Version 2 A D I Version 3 A D I
 What is XP Quality Work ¢ Quality is assumed Excellent, or l Insanely excellent l
What is XP Quality Work ¢ Quality is assumed Excellent, or l Insanely excellent l
 What is XP Key Practices/Features ¢ ¢ ¢ Test all the time Continuous integration Pair programming Coding standards Collective ownership Do simplest thing that will work today l ¢ ¢ “design tomorrow for tomorrow’s problems” Metaphor to aid in understanding the architecture Refactoring and evolutionary design
What is XP Key Practices/Features ¢ ¢ ¢ Test all the time Continuous integration Pair programming Coding standards Collective ownership Do simplest thing that will work today l ¢ ¢ “design tomorrow for tomorrow’s problems” Metaphor to aid in understanding the architecture Refactoring and evolutionary design
 What is XP Key Practices/Features (cont. ) Customer on-site as integral part of team ¢ Incremental planning ¢ learning to drive l programmers provide estimates l ¢ Short iterations, small releases l ¢ 2 month releases, 2 week iterations 40 -hour week
What is XP Key Practices/Features (cont. ) Customer on-site as integral part of team ¢ Incremental planning ¢ learning to drive l programmers provide estimates l ¢ Short iterations, small releases l ¢ 2 month releases, 2 week iterations 40 -hour week
 What is XP Begin with the end in mind. . . Start design with a test ¢ Start coding with a test ¢ Test things that might break ¢ Testing is isolated ¢ Testing is integrated ¢ Testing is automated ¢ At least one dedicated tester ¢
What is XP Begin with the end in mind. . . Start design with a test ¢ Start coding with a test ¢ Test things that might break ¢ Testing is isolated ¢ Testing is integrated ¢ Testing is automated ¢ At least one dedicated tester ¢
 “Cruft is not allowed to accumulate” ¢ Definition An unpleasant substance, e. g. , the dust that accumulates under your bed l Results of shoddy construction l Excess, superfluous junk, e. g. , redundant or superseded code l ¢ Which XP practice(s) does this pertain to?
“Cruft is not allowed to accumulate” ¢ Definition An unpleasant substance, e. g. , the dust that accumulates under your bed l Results of shoddy construction l Excess, superfluous junk, e. g. , redundant or superseded code l ¢ Which XP practice(s) does this pertain to?
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
 What is XP Benefits Faster ¢ Better quality ¢ Cheaper ¢ Reduced risk ¢ More likely to be followed than a heavyweight methodology ¢ More fun ¢
What is XP Benefits Faster ¢ Better quality ¢ Cheaper ¢ Reduced risk ¢ More likely to be followed than a heavyweight methodology ¢ More fun ¢
 XP vs. Heavyweight: What’s the Same ¢
XP vs. Heavyweight: What’s the Same ¢
 XP vs. Heavyweight: What’s Different ¢
XP vs. Heavyweight: What’s Different ¢
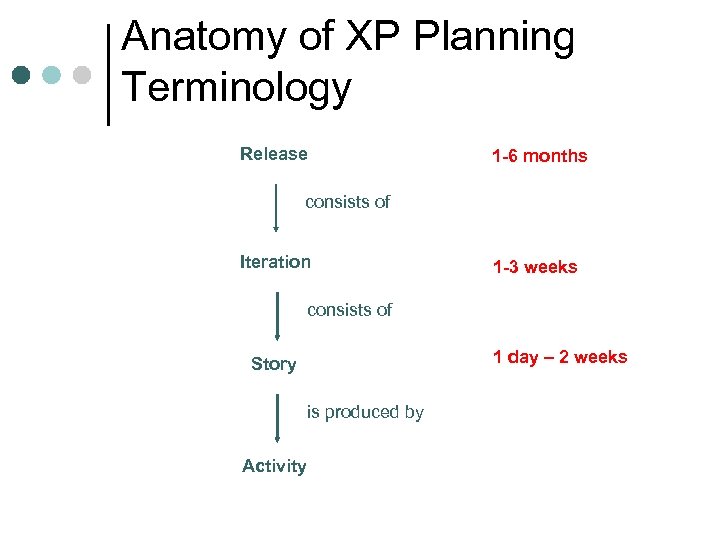 Anatomy of XP Planning Terminology Release 1 -6 months consists of Iteration 1 -3 weeks consists of 1 day – 2 weeks Story is produced by Activity
Anatomy of XP Planning Terminology Release 1 -6 months consists of Iteration 1 -3 weeks consists of 1 day – 2 weeks Story is produced by Activity
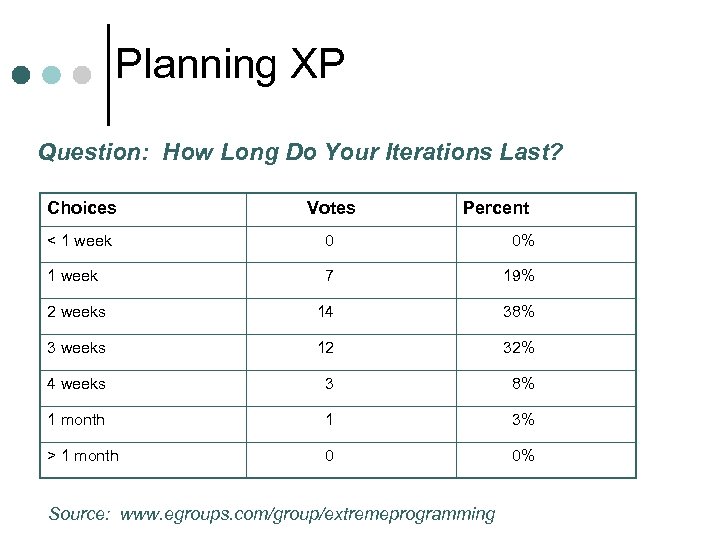 Planning XP Question: How Long Do Your Iterations Last? Choices Votes Percent < 1 week 0 0% 1 week 7 19% 2 weeks 14 38% 3 weeks 12 32% 4 weeks 3 8% 1 month 1 3% > 1 month 0 0% Source: www. egroups. com/group/extremeprogramming
Planning XP Question: How Long Do Your Iterations Last? Choices Votes Percent < 1 week 0 0% 1 week 7 19% 2 weeks 14 38% 3 weeks 12 32% 4 weeks 3 8% 1 month 1 3% > 1 month 0 0% Source: www. egroups. com/group/extremeprogramming
 When to Use XP ¢
When to Use XP ¢
 When Not to Use XP ¢
When Not to Use XP ¢
 Quiz 2 Recap
Quiz 2 Recap
 Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
Today’s Agenda Topic Duration ¢ Assignment 2 Recap ¢ Agile/XP *** Break 15 minutes 45 minutes 15 minutes ¢ Current Event Reports 15 minutes ¢ Agile/XP (cont. ) 60 minutes ¢ Term Paper 15 minutes
 Term Paper Summary: A briefing on a significant, currently relevant software development methodology, process-related framework, or business/technology trend and its impact on systems development Deliverables: Assignment 3 (due May 4) Title Abstract Reference Presentation and Discussion (20 minutes max) Pick date: June 1 or June 8 DL Students: Use Impatica Term Paper (due June 8) Development Process: Individual OR in pairs
Term Paper Summary: A briefing on a significant, currently relevant software development methodology, process-related framework, or business/technology trend and its impact on systems development Deliverables: Assignment 3 (due May 4) Title Abstract Reference Presentation and Discussion (20 minutes max) Pick date: June 1 or June 8 DL Students: Use Impatica Term Paper (due June 8) Development Process: Individual OR in pairs
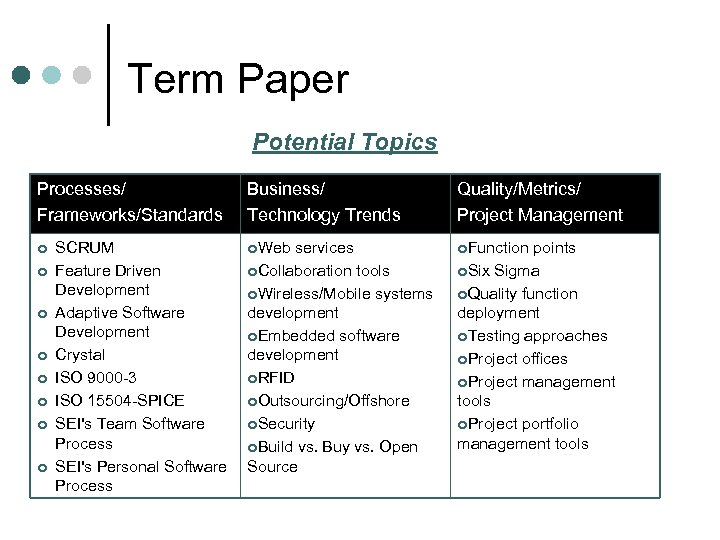 Term Paper Potential Topics Processes/ Frameworks/Standards ¢ ¢ ¢ ¢ SCRUM Feature Driven Development Adaptive Software Development Crystal ISO 9000 -3 ISO 15504 -SPICE SEI's Team Software Process SEI's Personal Software Process Business/ Technology Trends Quality/Metrics/ Project Management ¢Web ¢Function services ¢Collaboration tools ¢Wireless/Mobile systems development ¢Embedded software development ¢RFID ¢Outsourcing/Offshore ¢Security ¢Build vs. Buy vs. Open Source points ¢Six Sigma ¢Quality function deployment ¢Testing approaches ¢Project offices ¢Project management tools ¢Project portfolio management tools
Term Paper Potential Topics Processes/ Frameworks/Standards ¢ ¢ ¢ ¢ SCRUM Feature Driven Development Adaptive Software Development Crystal ISO 9000 -3 ISO 15504 -SPICE SEI's Team Software Process SEI's Personal Software Process Business/ Technology Trends Quality/Metrics/ Project Management ¢Web ¢Function services ¢Collaboration tools ¢Wireless/Mobile systems development ¢Embedded software development ¢RFID ¢Outsourcing/Offshore ¢Security ¢Build vs. Buy vs. Open Source points ¢Six Sigma ¢Quality function deployment ¢Testing approaches ¢Project offices ¢Project management tools ¢Project portfolio management tools
 Term Paper Outline: 1. Abstract 2. Historical Background 3. Description • Philosophy/Principles • Components • Benefits 4. Usage Guidelines • When to use/avoid • Success factors/Challenges 5. Marketplace Analysis • Key Players/Products/Gurus • Market data/forecasts 6. References • Books, articles, web sites • Extra credit: Interview a practitioner and/or faculty member
Term Paper Outline: 1. Abstract 2. Historical Background 3. Description • Philosophy/Principles • Components • Benefits 4. Usage Guidelines • When to use/avoid • Success factors/Challenges 5. Marketplace Analysis • Key Players/Products/Gurus • Market data/forecasts 6. References • Books, articles, web sites • Extra credit: Interview a practitioner and/or faculty member
 Topics for May 4
Topics for May 4


