217710dd1207f28b3b22161091d97850.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
IR Cryogenic optomechanics E. Bendek, Dec 2009 V 30

Outline n n n Introduction Example Instrument Description Optical overview Functions overview Vessel, vacuum and cryogenics.
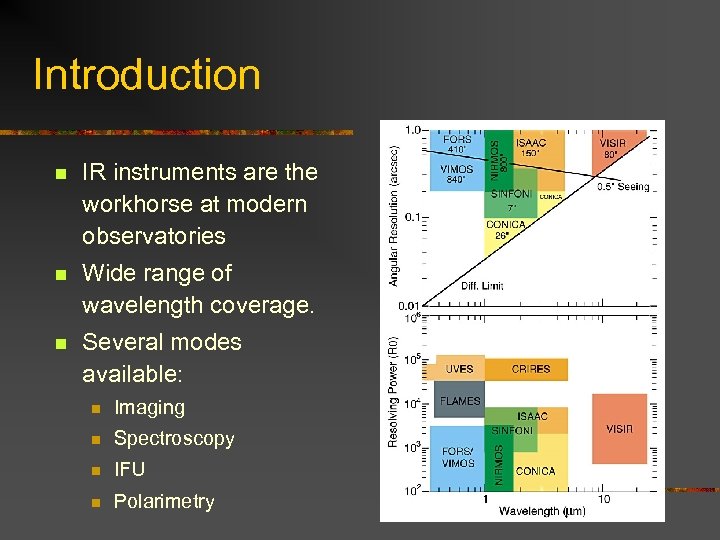
Introduction n IR instruments are the workhorse at modern observatories n Wide range of wavelength coverage. n Several modes available: n Imaging n Spectroscopy n IFU n Polarimetry
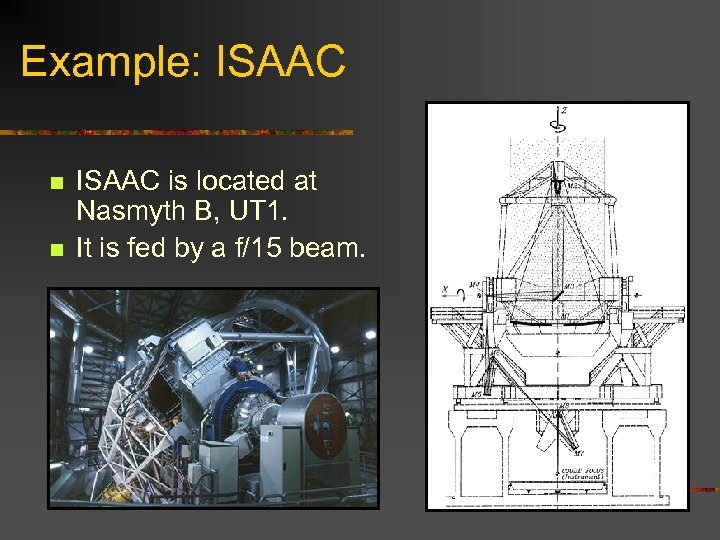
Example: ISAAC n n ISAAC is located at Nasmyth B, UT 1. It is fed by a f/15 beam.
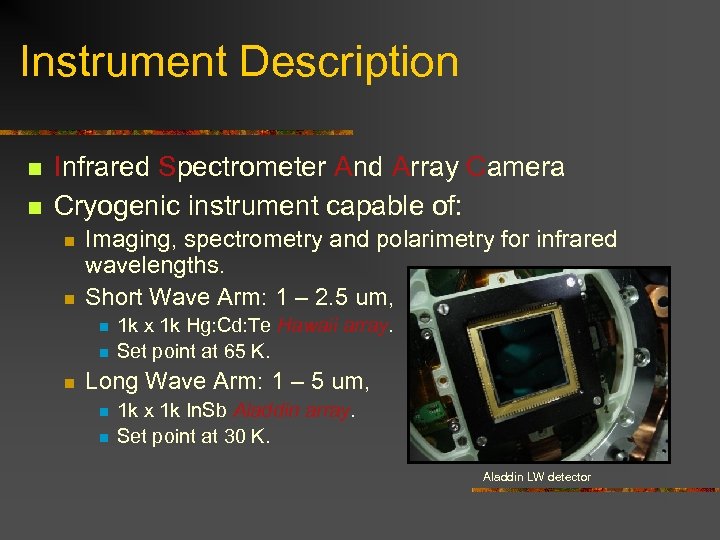
Instrument Description n n Infrared Spectrometer And Array Camera Cryogenic instrument capable of: n n Imaging, spectrometry and polarimetry for infrared wavelengths. Short Wave Arm: 1 – 2. 5 um, n n n 1 k x 1 k Hg: Cd: Te Hawaii array. Set point at 65 K. Long Wave Arm: 1 – 5 um, n n 1 k x 1 k In. Sb Aladdin array. Set point at 30 K. Aladdin LW detector
Instrument Description n Instrument capabilities: n Imaging: Obtain direct images of a field. n Polarimetry: Allows to identify polarization components of polarized light. n Spectroscopy: Obtain the spectral distribution of a target. n In total 10 optical modes or configurations are possible!

Optical Overview n Optics: n Common path: n n Slit/Mask wheel (F 1): Define the field with slits or mask. n Mode selector (F 3): Select Imaging or spectroscopy mode. n Collimator (F 5): Adjust the Collimation of the beam. n n Calibration mirror (F 12): Select the light source. Detector Selector (F 4): Select the SW or LW camera. 2 Cameras, SW and LW each one has: n 2 filters wheels n 1 objective wheel
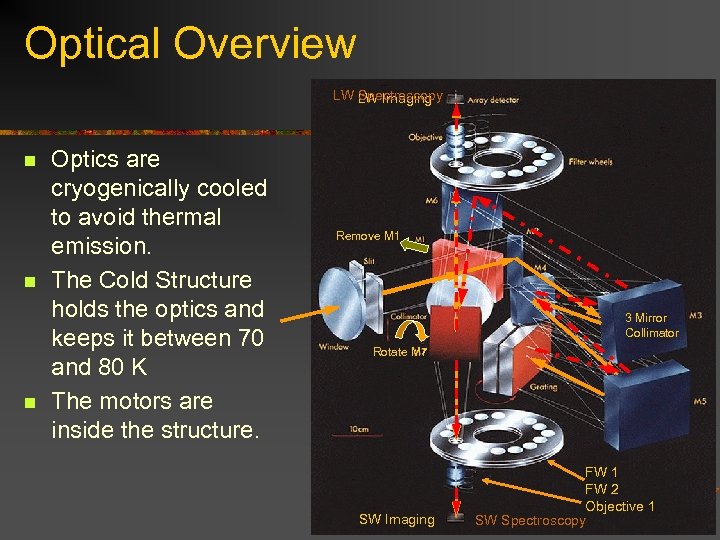
Optical Overview LW LW Imaging Spectroscopy n n n Optics are cryogenically cooled to avoid thermal emission. The Cold Structure holds the optics and keeps it between 70 and 80 K The motors are inside the structure. Remove M 1 3 Mirror Collimator Rotate M 7 SW Imaging FW 1 FW 2 Objective 1 SW Spectroscopy

Optical Overview Sample of Flat field images. Slit mask wheel offset Normal Flat M 1 out of position Filter offset M 7 out of position
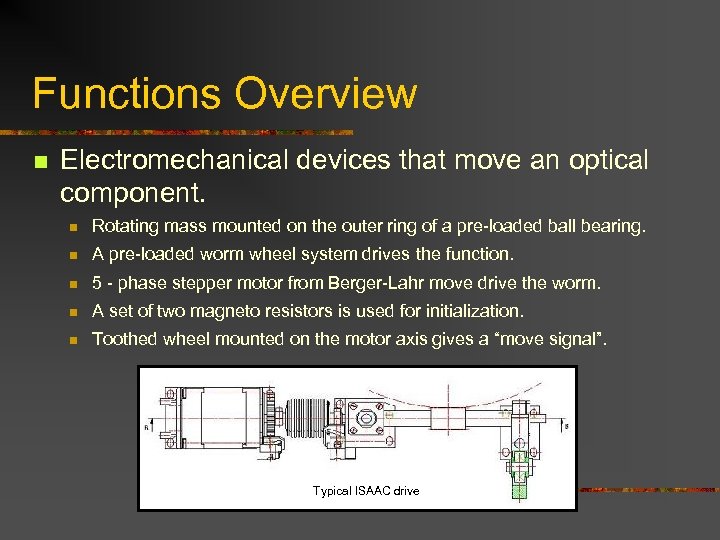
Functions Overview n Electromechanical devices that move an optical component. n Rotating mass mounted on the outer ring of a pre-loaded ball bearing. n A pre-loaded worm wheel system drives the function. n 5 - phase stepper motor from Berger-Lahr move drive the worm. n A set of two magneto resistors is used for initialization. n Toothed wheel mounted on the motor axis gives a “move signal”. Typical ISAAC drive

Functions Overview n Cryogenic motors n n n Specially prepared Berger Lahr 545/100 motors. 5 phases, 1000 half steps/rev. No feed back on function position. (no encoders) Berger Lahr 545 / 100, already prepared for cryogenic operation

Functions Overview n n n Cryogenic motors preparation More than a factor 10 cheaper than a UHV qualified motor like a Phytron VSS! Preparation is done in house. On the left the motor is dismounted, on the right new parts for cryogenic operation are shown
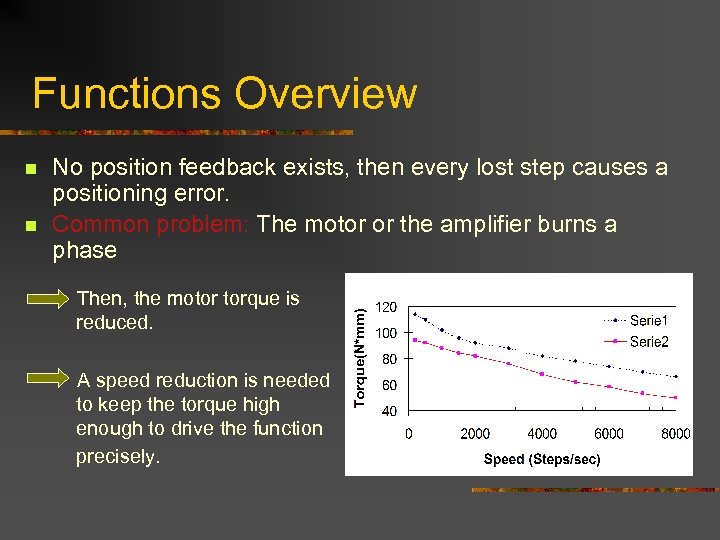
Functions Overview n n No position feedback exists, then every lost step causes a positioning error. Common problem: The motor or the amplifier burns a phase Then, the motor torque is reduced. A speed reduction is needed to keep the torque high enough to drive the function precisely.
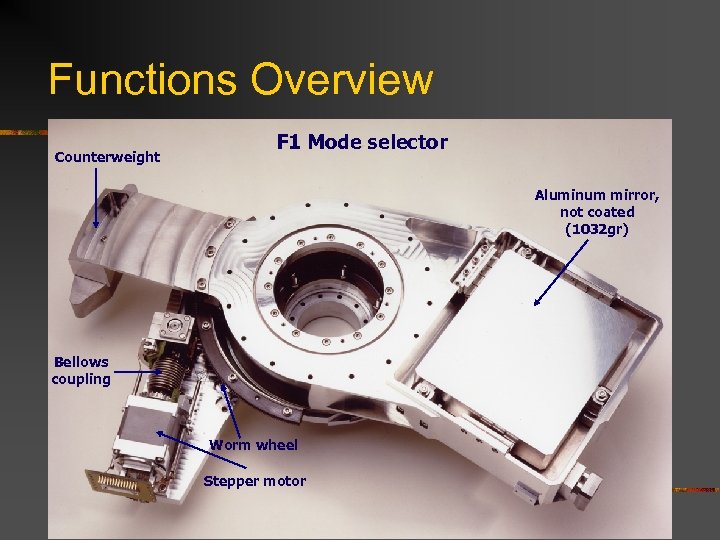
Functions Overview Counterweight F 1 Mode selector Aluminum mirror, not coated (1032 gr) Bellows coupling Worm wheel Stepper motor
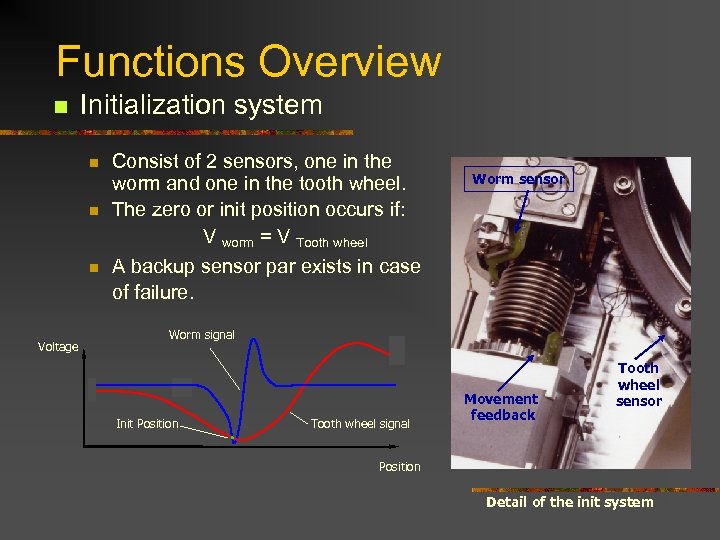
Functions Overview n Initialization system n n n Voltage Consist of 2 sensors, one in the worm and one in the tooth wheel. The zero or init position occurs if: V worm = V Tooth wheel Worm sensor A backup sensor par exists in case of failure. Worm signal Init Position Tooth wheel signal Movement feedback Tooth wheel sensor Position Detail of the init system
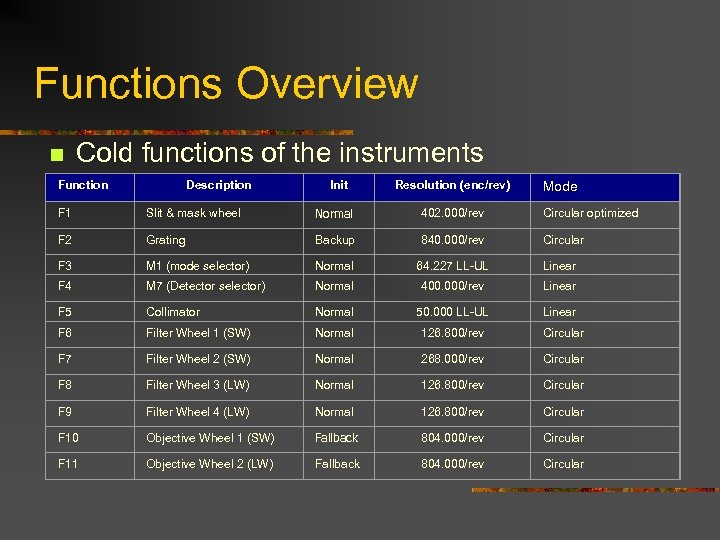
Functions Overview n Cold functions of the instruments Function Description Init Resolution (enc/rev) Mode F 1 Slit & mask wheel Normal 402. 000/rev Circular optimized F 2 Grating Backup 840. 000/rev Circular F 3 M 1 (mode selector) Normal 64. 227 LL-UL Linear F 4 M 7 (Detector selector) Normal 400. 000/rev Linear F 5 Collimator Normal 50. 000 LL-UL Linear F 6 Filter Wheel 1 (SW) Normal 126. 800/rev Circular F 7 Filter Wheel 2 (SW) Normal 268. 000/rev Circular F 8 Filter Wheel 3 (LW) Normal 126. 800/rev Circular F 9 Filter Wheel 4 (LW) Normal 126. 800/rev Circular F 10 Objective Wheel 1 (SW) Fallback 804. 000/rev Circular F 11 Objective Wheel 2 (LW) Fallback 804. 000/rev Circular
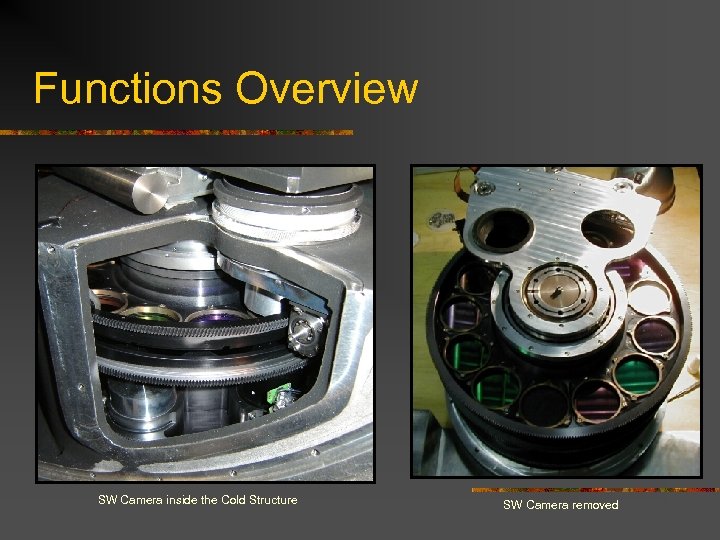
Functions Overview SW Camera inside the Cold Structure SW Camera removed
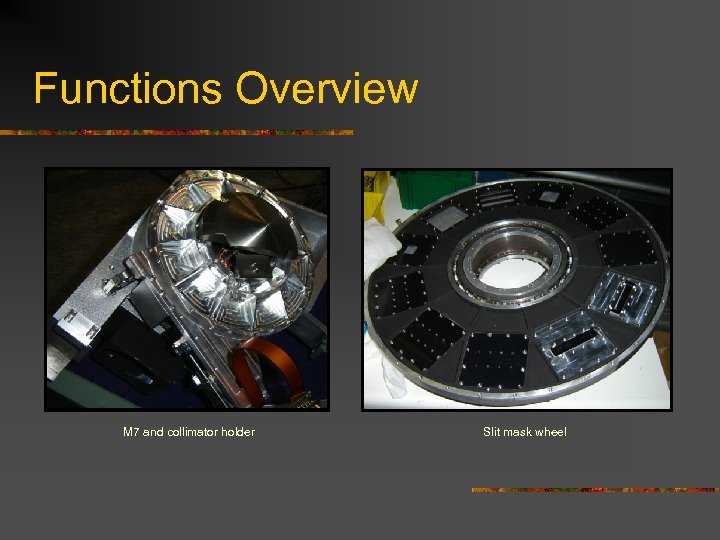
Functions Overview M 7 and collimator holder Slit mask wheel
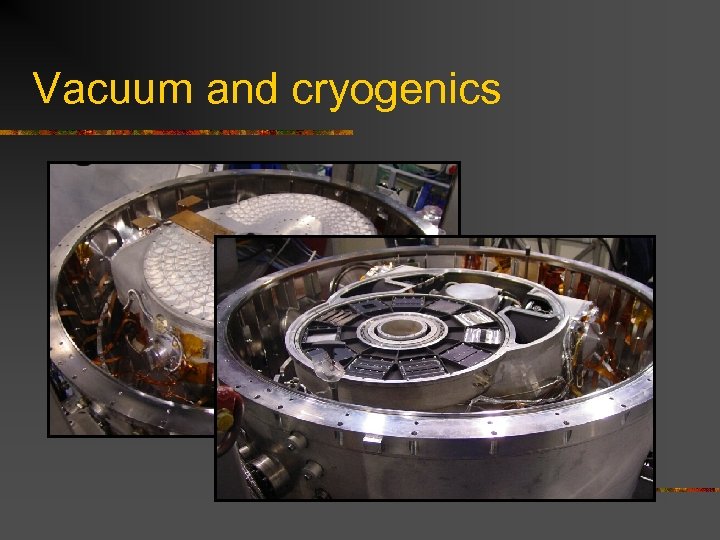
Vacuum and cryogenics

Vacuum and cryogenics n Vessel volume: ~ 3 m 3 n Weight: ~ 2. 500 Kg n Vacuum: Scroll Pump n Turbomolecular: Seiko Seiki Maglev. n Operational vacuum: ~ 5 x 10 -7 mbar n Cold Structure temp: 70 K n Cooling: 2 x Leybold Cold head. n Compressor: 1 Leybold RW 6000
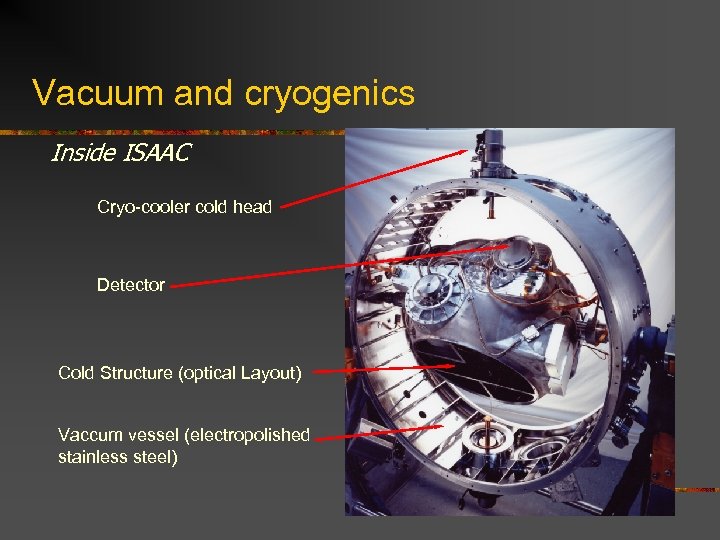
Vacuum and cryogenics Inside ISAAC Cryo-cooler cold head Detector Cold Structure (optical Layout) Vaccum vessel (electropolished stainless steel)

The interventions… ISAAC retrofited super insulation and radiation shield Fixing the Cold Structure
IR Cryogenic optomechanics E. Bendek, Dec 2009 V 30
217710dd1207f28b3b22161091d97850.ppt