68c92d1077aa95e763eb6e22cb309285.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 IPv 6 Prospects TERENA – Rhodes – June 9 th, 2004 Patrick Grossetete Cisco IOS IPv 6 Product Manager Cisco Systems pgrosset@cisco. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1
IPv 6 Prospects TERENA – Rhodes – June 9 th, 2004 Patrick Grossetete Cisco IOS IPv 6 Product Manager Cisco Systems pgrosset@cisco. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1
 Agenda • Building the “IPv 6 House” • IPv 6 Prospects Innovation and new Business Models © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
Agenda • Building the “IPv 6 House” • IPv 6 Prospects Innovation and new Business Models © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
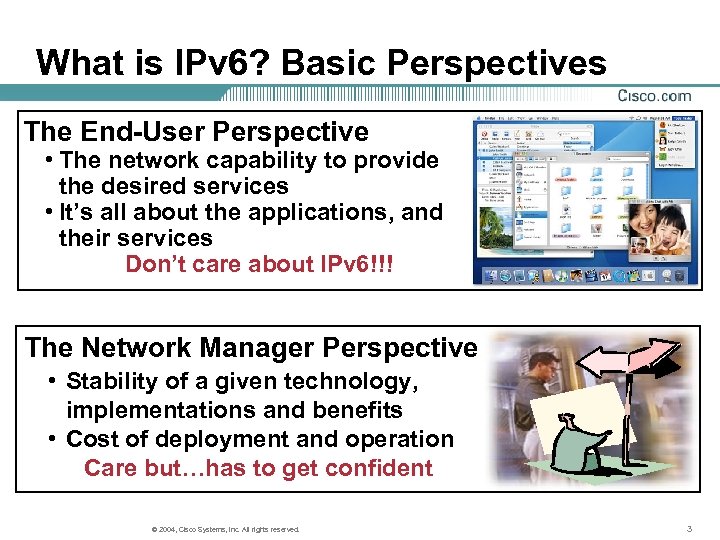 What is IPv 6? Basic Perspectives The End-User Perspective • The network capability to provide the desired services • It’s all about the applications, and their services Don’t care about IPv 6!!! The Network Manager Perspective • Stability of a given technology, implementations and benefits • Cost of deployment and operation Care but…has to get confident © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 3
What is IPv 6? Basic Perspectives The End-User Perspective • The network capability to provide the desired services • It’s all about the applications, and their services Don’t care about IPv 6!!! The Network Manager Perspective • Stability of a given technology, implementations and benefits • Cost of deployment and operation Care but…has to get confident © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 3
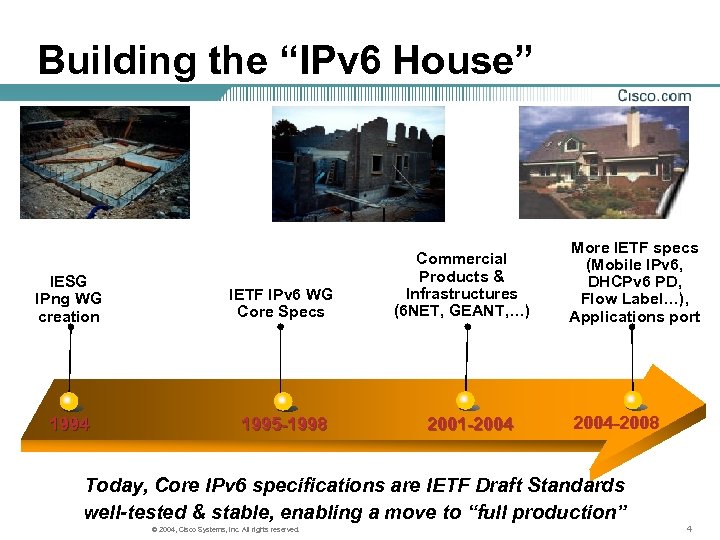 Building the “IPv 6 House” IESG IPng WG creation IETF IPv 6 WG Core Specs 1994 1995 -1998 Commercial Products & Infrastructures (6 NET, GEANT, …) 2001 -2004 More IETF specs (Mobile IPv 6, DHCPv 6 PD, Flow Label…), Applications port 2004 -2008 Today, Core IPv 6 specifications are IETF Draft Standards well-tested & stable, enabling a move to “full production” © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 4
Building the “IPv 6 House” IESG IPng WG creation IETF IPv 6 WG Core Specs 1994 1995 -1998 Commercial Products & Infrastructures (6 NET, GEANT, …) 2001 -2004 More IETF specs (Mobile IPv 6, DHCPv 6 PD, Flow Label…), Applications port 2004 -2008 Today, Core IPv 6 specifications are IETF Draft Standards well-tested & stable, enabling a move to “full production” © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 4
 Networking Trends Ubiquity of the Internet Security and Privacy of a Network • Mobility through a Wireless Network Next Generation Networks Simplicity of Ethernet IPv 6 Ready Capacity of an Optical Network © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Content Richness of Television 5
Networking Trends Ubiquity of the Internet Security and Privacy of a Network • Mobility through a Wireless Network Next Generation Networks Simplicity of Ethernet IPv 6 Ready Capacity of an Optical Network © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Content Richness of Television 5
 Broadband Home – A necessity for IPv 6 ! Home Networking • • Internet access Multiple voice lines Wireless printing Wireless IP Phone • At the heart of the digital home sits the Broadband access point distributing a host of enhanced content and services throughout the home IP Phone Printer Wireless Laptop • Distance learning • Video calls • MP 3 downloads PDA Wired PC Broadband Internet Access • Streaming Video • Print/file sharing Tivo Services • Commercial download • TV guide Broadband Access Point Wireless Gaming © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. • • Multiplayer gaming Video on demand Home security Digital audio 6
Broadband Home – A necessity for IPv 6 ! Home Networking • • Internet access Multiple voice lines Wireless printing Wireless IP Phone • At the heart of the digital home sits the Broadband access point distributing a host of enhanced content and services throughout the home IP Phone Printer Wireless Laptop • Distance learning • Video calls • MP 3 downloads PDA Wired PC Broadband Internet Access • Streaming Video • Print/file sharing Tivo Services • Commercial download • TV guide Broadband Access Point Wireless Gaming © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. • • Multiplayer gaming Video on demand Home security Digital audio 6
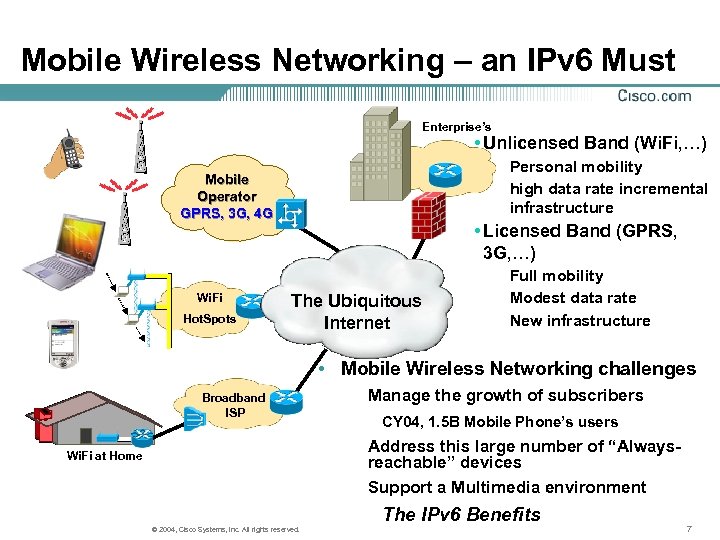 Mobile Wireless Networking – an IPv 6 Must Enterprise’s • Unlicensed Band (Wi. Fi, …) Personal mobility high data rate incremental infrastructure Mobile Operator GPRS, 3 G, 4 G Wi. Fi Hot. Spots • Licensed Band (GPRS, 3 G, …) The Ubiquitous Internet Full mobility Modest data rate New infrastructure • Mobile Wireless Networking challenges Broadband ISP Manage the growth of subscribers CY 04, 1. 5 B Mobile Phone’s users Address this large number of “Alwaysreachable” devices Support a Multimedia environment Wi. Fi at Home The IPv 6 Benefits © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 7
Mobile Wireless Networking – an IPv 6 Must Enterprise’s • Unlicensed Band (Wi. Fi, …) Personal mobility high data rate incremental infrastructure Mobile Operator GPRS, 3 G, 4 G Wi. Fi Hot. Spots • Licensed Band (GPRS, 3 G, …) The Ubiquitous Internet Full mobility Modest data rate New infrastructure • Mobile Wireless Networking challenges Broadband ISP Manage the growth of subscribers CY 04, 1. 5 B Mobile Phone’s users Address this large number of “Alwaysreachable” devices Support a Multimedia environment Wi. Fi at Home The IPv 6 Benefits © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 7
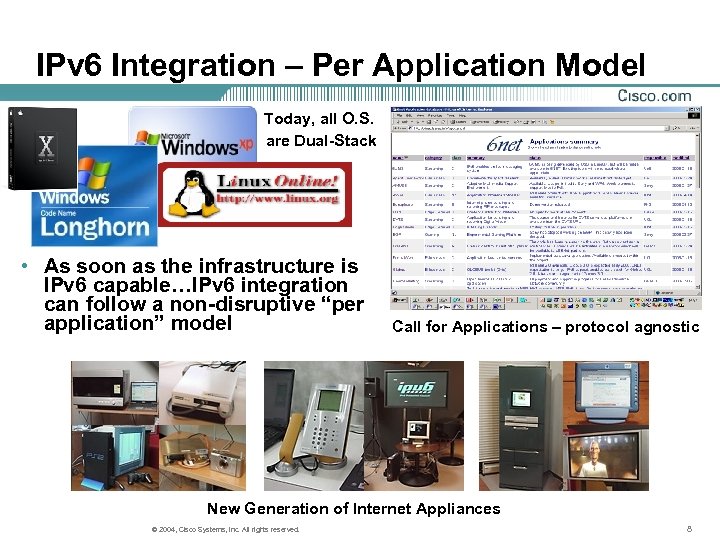 IPv 6 Integration – Per Application Model Today, all O. S. are Dual-Stack • As soon as the infrastructure is IPv 6 capable…IPv 6 integration can follow a non-disruptive “per application” model Call for Applications – protocol agnostic New Generation of Internet Appliances © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 8
IPv 6 Integration – Per Application Model Today, all O. S. are Dual-Stack • As soon as the infrastructure is IPv 6 capable…IPv 6 integration can follow a non-disruptive “per application” model Call for Applications – protocol agnostic New Generation of Internet Appliances © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 8
 Some non-Technical Challenges • The Internet is “highly decentralized” – Regional modes of adoption IPv 6 impacts the overall infrastructure Must avoid an Internet balkanization Status Quo (no change) versus Co-Existence (Niche) versus Full Integration • Education Next generation’s graduates are key for IPv 6 deployment • Social impacts of this new Internet environment Privacy, Usage, … • Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Not related to IPv 6 but may be highlighted by usage © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 9
Some non-Technical Challenges • The Internet is “highly decentralized” – Regional modes of adoption IPv 6 impacts the overall infrastructure Must avoid an Internet balkanization Status Quo (no change) versus Co-Existence (Niche) versus Full Integration • Education Next generation’s graduates are key for IPv 6 deployment • Social impacts of this new Internet environment Privacy, Usage, … • Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Not related to IPv 6 but may be highlighted by usage © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 9
 Agenda • Building the “IPv 6 House” • IPv 6 Prospects Innovation and new Business Models © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 10
Agenda • Building the “IPv 6 House” • IPv 6 Prospects Innovation and new Business Models © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 10
 Business Model – Basic Perspectives • A need for different address allocation and charging model IPv 6 prefix (/48 to /64) versus a single dynamic or static IPv 4 address Provisioning for always-on technologies does not really allow over-subscription • ISP added values need to shift to End-Points and associated services Ie: NTT-Comms m 2 m-x www. ipv 6 style. jp/en/apps/20040224/index. shtml © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
Business Model – Basic Perspectives • A need for different address allocation and charging model IPv 6 prefix (/48 to /64) versus a single dynamic or static IPv 4 address Provisioning for always-on technologies does not really allow over-subscription • ISP added values need to shift to End-Points and associated services Ie: NTT-Comms m 2 m-x www. ipv 6 style. jp/en/apps/20040224/index. shtml © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
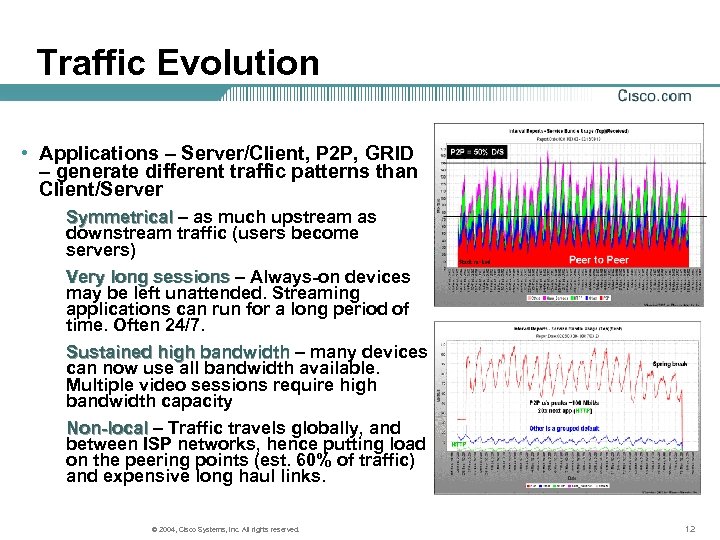 Traffic Evolution • Applications – Server/Client, P 2 P, GRID – generate different traffic patterns than Client/Server Symmetrical – as much upstream as downstream traffic (users become servers) Very long sessions – Always-on devices may be left unattended. Streaming applications can run for a long period of time. Often 24/7. Sustained high bandwidth – many devices can now use all bandwidth available. Multiple video sessions require high bandwidth capacity Non-local – Traffic travels globally, and between ISP networks, hence putting load on the peering points (est. 60% of traffic) and expensive long haul links. © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 12
Traffic Evolution • Applications – Server/Client, P 2 P, GRID – generate different traffic patterns than Client/Server Symmetrical – as much upstream as downstream traffic (users become servers) Very long sessions – Always-on devices may be left unattended. Streaming applications can run for a long period of time. Often 24/7. Sustained high bandwidth – many devices can now use all bandwidth available. Multiple video sessions require high bandwidth capacity Non-local – Traffic travels globally, and between ISP networks, hence putting load on the peering points (est. 60% of traffic) and expensive long haul links. © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 12
 Some Technical Challenges • Multi-Homing From IETF Multi 6 WG charter The multihoming approaches currently used in IPv 4 can of course be used in IPv 6, but IPv 6 represents an opportunity for more scalable approaches. • Security Though IPsec is mandatory in IPv 6, Security is a much broader topic than just IPsec as same issues remain from IPv 4: Configuration complexity, Key management… Centralized (Firewall) – Distributed (IPsec on hosts) co-existence • Dual Stack Network Management MIB’s dependencies - www. ietf. org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-v 6 ops-ipv 4 surveyops-05. txt Network Management Applications – provisioning, monitoring, billing, … Plug & Play/Renumbering on large scale Internet population An opportunity for Research © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
Some Technical Challenges • Multi-Homing From IETF Multi 6 WG charter The multihoming approaches currently used in IPv 4 can of course be used in IPv 6, but IPv 6 represents an opportunity for more scalable approaches. • Security Though IPsec is mandatory in IPv 6, Security is a much broader topic than just IPsec as same issues remain from IPv 4: Configuration complexity, Key management… Centralized (Firewall) – Distributed (IPsec on hosts) co-existence • Dual Stack Network Management MIB’s dependencies - www. ietf. org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-v 6 ops-ipv 4 surveyops-05. txt Network Management Applications – provisioning, monitoring, billing, … Plug & Play/Renumbering on large scale Internet population An opportunity for Research © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
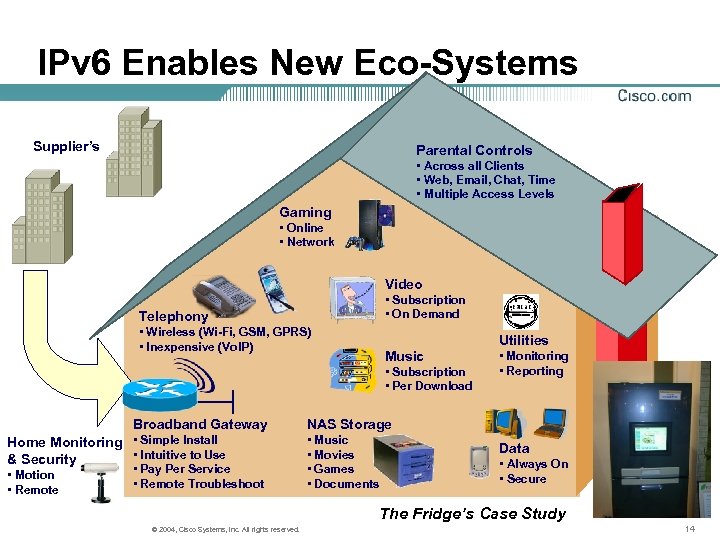 IPv 6 Enables New Eco-Systems Supplier’s Parental Controls • Across all Clients • Web, Email, Chat, Time • Multiple Access Levels Gaming • Online • Network Video • Subscription • On Demand Telephony • Wireless (Wi-Fi, GSM, GPRS) • Inexpensive (Vo. IP) Utilities Music • Subscription • Per Download Broadband Gateway Home Monitoring • Simple Install • Intuitive to Use & Security • Motion • Remote • Pay Per Service • Remote Troubleshoot • Monitoring • Reporting NAS Storage • Music • Movies • Games • Documents Data • Always On • Secure The Fridge’s Case Study © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 14
IPv 6 Enables New Eco-Systems Supplier’s Parental Controls • Across all Clients • Web, Email, Chat, Time • Multiple Access Levels Gaming • Online • Network Video • Subscription • On Demand Telephony • Wireless (Wi-Fi, GSM, GPRS) • Inexpensive (Vo. IP) Utilities Music • Subscription • Per Download Broadband Gateway Home Monitoring • Simple Install • Intuitive to Use & Security • Motion • Remote • Pay Per Service • Remote Troubleshoot • Monitoring • Reporting NAS Storage • Music • Movies • Games • Documents Data • Always On • Secure The Fridge’s Case Study © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 14
 Expanding the Market Place Internet Cafe Digital Theater Hot Spot Shop, Museum Photo Service Digital Studio Cafeteria/Meeting Rm. © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 15
Expanding the Market Place Internet Cafe Digital Theater Hot Spot Shop, Museum Photo Service Digital Studio Cafeteria/Meeting Rm. © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 15
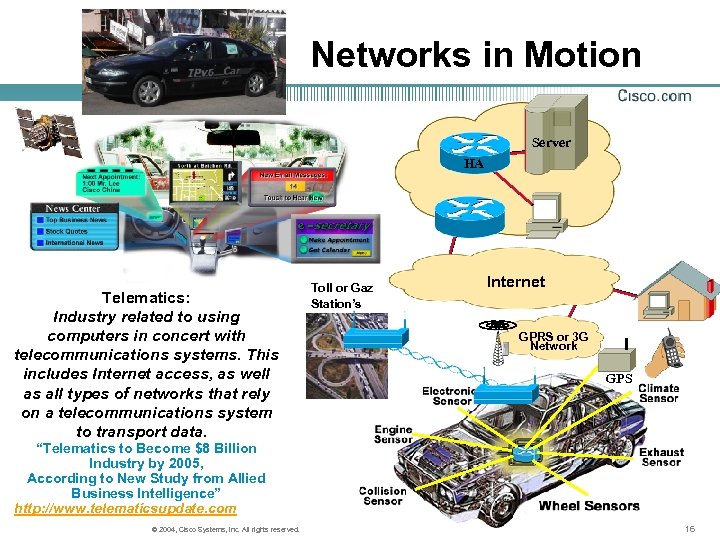 Networks in Motion Server HA Telematics: Industry related to using computers in concert with telecommunications systems. This includes Internet access, as well as all types of networks that rely on a telecommunications system to transport data. Toll or Gaz Station’s Internet GPRS or 3 G Network GPS “Telematics to Become $8 Billion Industry by 2005, According to New Study from Allied Business Intelligence” http: //www. telematicsupdate. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
Networks in Motion Server HA Telematics: Industry related to using computers in concert with telecommunications systems. This includes Internet access, as well as all types of networks that rely on a telecommunications system to transport data. Toll or Gaz Station’s Internet GPRS or 3 G Network GPS “Telematics to Become $8 Billion Industry by 2005, According to New Study from Allied Business Intelligence” http: //www. telematicsupdate. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
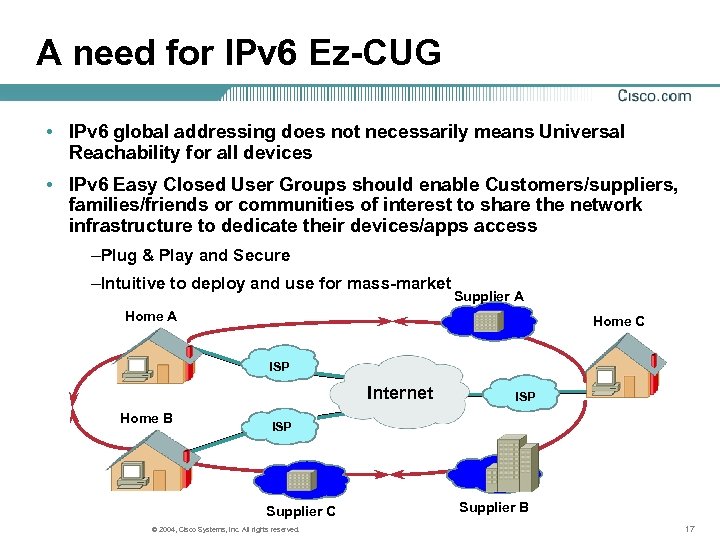 A need for IPv 6 Ez-CUG • IPv 6 global addressing does not necessarily means Universal Reachability for all devices • IPv 6 Easy Closed User Groups should enable Customers/suppliers, families/friends or communities of interest to share the network infrastructure to dedicate their devices/apps access –Plug & Play and Secure –Intuitive to deploy and use for mass-market Supplier A Home C ISP Internet Home B ISP Supplier C © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Supplier B 17
A need for IPv 6 Ez-CUG • IPv 6 global addressing does not necessarily means Universal Reachability for all devices • IPv 6 Easy Closed User Groups should enable Customers/suppliers, families/friends or communities of interest to share the network infrastructure to dedicate their devices/apps access –Plug & Play and Secure –Intuitive to deploy and use for mass-market Supplier A Home C ISP Internet Home B ISP Supplier C © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Supplier B 17
 A Case Study – IPv 6 in Schools (1) • School’s business is Education Read, Write, Maths, Foreign Languages as foundations to Knowledge The above are minimum end-users requirements to access the Internet Analytic mind is key to value the data retrieved from the Internet • Schools are part of the Information Society Today, more and more schools get an Internet connection – a Must Lease lines, Broadband Access, … Linked to NRN or local government • Today, Applications and Services Client-Server: e-mails, web browsing Servers generally hosted externally Most of the time using PAT (a single global IPv 4 address) © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 18
A Case Study – IPv 6 in Schools (1) • School’s business is Education Read, Write, Maths, Foreign Languages as foundations to Knowledge The above are minimum end-users requirements to access the Internet Analytic mind is key to value the data retrieved from the Internet • Schools are part of the Information Society Today, more and more schools get an Internet connection – a Must Lease lines, Broadband Access, … Linked to NRN or local government • Today, Applications and Services Client-Server: e-mails, web browsing Servers generally hosted externally Most of the time using PAT (a single global IPv 4 address) © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 18
 A Case Study – IPv 6 in Schools (2) • Developing new Class of Applications and Services Class to Class collaboration – internal to the school, between schools (national & international) Sharing Database, creating server’s, … Teachers-Students collaboration “After-time” support, digital pupil desk, foreign languages class, … Content delivery between schools or Information Providers – Multimedia streaming IP Telephony between schools Tele-surveillance – Physical security Secure Information – Transfer between schools-academy, teachers-school • Integrating those services over IPv 6 could easily be configured on (Cisco ) routers connecting the schools NRN or Local Government can delegate production IPv 6 prefixes to the schools. • It can be done Today IPv 4 applications must not get disturbed Keep IPv 4 as it is, even using PAT © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 19
A Case Study – IPv 6 in Schools (2) • Developing new Class of Applications and Services Class to Class collaboration – internal to the school, between schools (national & international) Sharing Database, creating server’s, … Teachers-Students collaboration “After-time” support, digital pupil desk, foreign languages class, … Content delivery between schools or Information Providers – Multimedia streaming IP Telephony between schools Tele-surveillance – Physical security Secure Information – Transfer between schools-academy, teachers-school • Integrating those services over IPv 6 could easily be configured on (Cisco ) routers connecting the schools NRN or Local Government can delegate production IPv 6 prefixes to the schools. • It can be done Today IPv 4 applications must not get disturbed Keep IPv 4 as it is, even using PAT © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 19
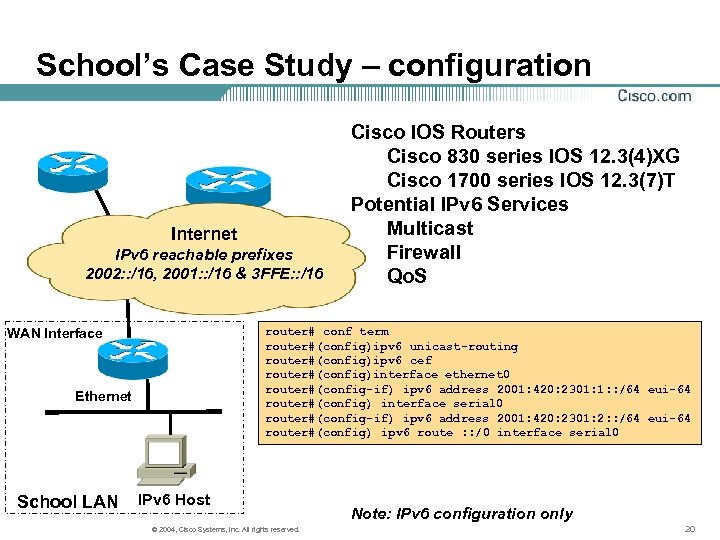 School’s Case Study – configuration Internet IPv 6 reachable prefixes 2002: : /16, 2001: : /16 & 3 FFE: : /16 router# conf term router#(config)ipv 6 unicast-routing router#(config)ipv 6 cef router#(config)interface ethernet 0 router#(config-if) ipv 6 address 2001: 420: 2301: 1: : /64 eui-64 router#(config) interface serial 0 router#(config-if) ipv 6 address 2001: 420: 2301: 2: : /64 eui-64 router#(config) ipv 6 route : : /0 interface serial 0 WAN Interface Ethernet School LAN Cisco IOS Routers Cisco 830 series IOS 12. 3(4)XG Cisco 1700 series IOS 12. 3(7)T Potential IPv 6 Services Multicast Firewall Qo. S IPv 6 Host © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Note: IPv 6 configuration only 20
School’s Case Study – configuration Internet IPv 6 reachable prefixes 2002: : /16, 2001: : /16 & 3 FFE: : /16 router# conf term router#(config)ipv 6 unicast-routing router#(config)ipv 6 cef router#(config)interface ethernet 0 router#(config-if) ipv 6 address 2001: 420: 2301: 1: : /64 eui-64 router#(config) interface serial 0 router#(config-if) ipv 6 address 2001: 420: 2301: 2: : /64 eui-64 router#(config) ipv 6 route : : /0 interface serial 0 WAN Interface Ethernet School LAN Cisco IOS Routers Cisco 830 series IOS 12. 3(4)XG Cisco 1700 series IOS 12. 3(7)T Potential IPv 6 Services Multicast Firewall Qo. S IPv 6 Host © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Note: IPv 6 configuration only 20
 IPv 6 – A Key Driver for the e-Economy O. S. & Applications Mobile Networking Restoring an environment for Innovation The Ubiquitous Internet Agriculture/Wildlife Consumer & Services Manufacturing Services on the edge of the Network Higher Ed. /Research © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Transportation Medical e-Nations Government 21 (Federal/Public Sector)
IPv 6 – A Key Driver for the e-Economy O. S. & Applications Mobile Networking Restoring an environment for Innovation The Ubiquitous Internet Agriculture/Wildlife Consumer & Services Manufacturing Services on the edge of the Network Higher Ed. /Research © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Transportation Medical e-Nations Government 21 (Federal/Public Sector)
 Presentation_ID © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 22
Presentation_ID © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 22
 More Information • CCO IPv 6 - http: //www. cisco. com/ipv 6 • The ABC of IPv 6 http: //www. cisco. com/en/US/products/sw/iosswr el/ios_abcs_ios_the_abcs_ip_version_6_listing. html • IPv 6 Application Notes http: //www. cisco. com/warp/public/732/Tech/ipv 6_techdoc. shtml • Cisco IOS IPv 6 manuals http: //www. cisco. com/univercd/cc/td/doc/produ ct/software/ios 123/123 cgcr/ipv 6_vcg. htm © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 23
More Information • CCO IPv 6 - http: //www. cisco. com/ipv 6 • The ABC of IPv 6 http: //www. cisco. com/en/US/products/sw/iosswr el/ios_abcs_ios_the_abcs_ip_version_6_listing. html • IPv 6 Application Notes http: //www. cisco. com/warp/public/732/Tech/ipv 6_techdoc. shtml • Cisco IOS IPv 6 manuals http: //www. cisco. com/univercd/cc/td/doc/produ ct/software/ios 123/123 cgcr/ipv 6_vcg. htm © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 23
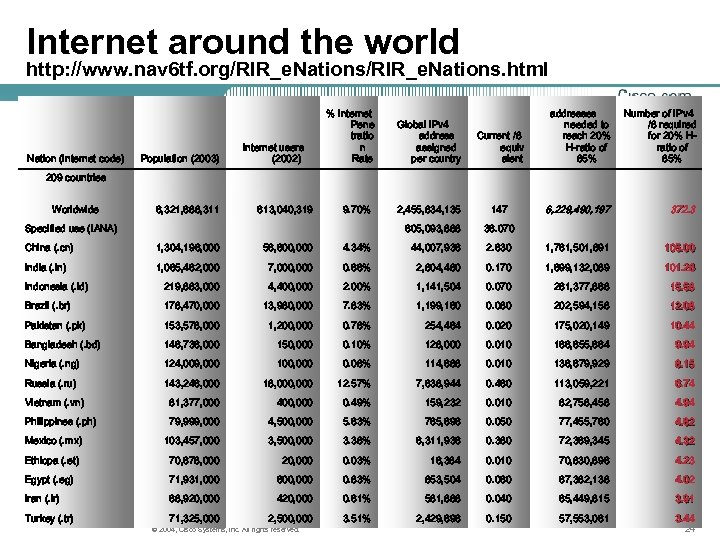 Internet around the world http: //www. nav 6 tf. org/RIR_e. Nations. html Nation (Internet code) Population (2003) Internet users (2002) % Internet Pene tratio n Rate Global IPv 4 address assigned per country 2, 455, 834, 135 Current /8 equiv alent addresses needed to reach 20% H-ratio of 85% Number of IPv 4 /8 required for 20% Hratio of 85% 147 6, 229, 490, 197 372. 3 209 countries Worldwide 6, 321, 688, 311 613, 040, 319 9. 70% Specified use (IANA) 605, 093, 888 36. 070 China (. cn) 1, 304, 196, 000 56, 600, 000 4. 34% 44, 007, 936 2. 630 1, 761, 501, 891 105. 00 India (. in) 1, 065, 462, 000 7, 000 0. 66% 2, 804, 480 0. 170 1, 699, 132, 089 101. 28 Indonesia (. id) 219, 883, 000 4, 400, 000 2. 00% 1, 141, 504 0. 070 261, 377, 868 15. 58 Brazil (. br) 178, 470, 000 13, 980, 000 7. 83% 1, 199, 160 0. 080 202, 594, 158 12. 08 Pakistan (. pk) 153, 578, 000 1, 200, 000 0. 78% 254, 464 0. 020 175, 020, 149 10. 44 Bangladesh (. bd) 146, 736, 000 150, 000 0. 10% 128, 000 0. 010 166, 655, 664 9. 94 Nigeria (. ng) 124, 009, 000 100, 000 0. 08% 114, 688 0. 010 136, 679, 929 8. 15 Russia (. ru) 143, 246, 000 18, 000 12. 57% 7, 638, 944 0. 460 113, 059, 221 6. 74 Vietnam (. vn) 81, 377, 000 400, 000 0. 49% 159, 232 0. 010 82, 758, 458 4. 94 Philippines (. ph) 79, 999, 000 4, 500, 000 5. 63% 765, 696 0. 050 77, 455, 760 4. 62 Mexico (. mx) 103, 457, 000 3, 500, 000 3. 38% 6, 311, 936 0. 380 72, 369, 345 4. 32 Ethiopa (. et) 70, 678, 000 20, 000 0. 03% 16, 384 0. 010 70, 830, 896 4. 23 Egypt (. eg) 71, 931, 000 600, 000 0. 83% 853, 504 0. 060 67, 382, 138 4. 02 Iran (. ir) 68, 920, 000 420, 000 0. 61% 581, 888 0. 040 65, 449, 815 3. 91 71, 325, 000 2, 500, 000 3. 51% 2, 429, 696 0. 150 57, 553, 061 3. 44 Turkey (. tr) © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 24
Internet around the world http: //www. nav 6 tf. org/RIR_e. Nations. html Nation (Internet code) Population (2003) Internet users (2002) % Internet Pene tratio n Rate Global IPv 4 address assigned per country 2, 455, 834, 135 Current /8 equiv alent addresses needed to reach 20% H-ratio of 85% Number of IPv 4 /8 required for 20% Hratio of 85% 147 6, 229, 490, 197 372. 3 209 countries Worldwide 6, 321, 688, 311 613, 040, 319 9. 70% Specified use (IANA) 605, 093, 888 36. 070 China (. cn) 1, 304, 196, 000 56, 600, 000 4. 34% 44, 007, 936 2. 630 1, 761, 501, 891 105. 00 India (. in) 1, 065, 462, 000 7, 000 0. 66% 2, 804, 480 0. 170 1, 699, 132, 089 101. 28 Indonesia (. id) 219, 883, 000 4, 400, 000 2. 00% 1, 141, 504 0. 070 261, 377, 868 15. 58 Brazil (. br) 178, 470, 000 13, 980, 000 7. 83% 1, 199, 160 0. 080 202, 594, 158 12. 08 Pakistan (. pk) 153, 578, 000 1, 200, 000 0. 78% 254, 464 0. 020 175, 020, 149 10. 44 Bangladesh (. bd) 146, 736, 000 150, 000 0. 10% 128, 000 0. 010 166, 655, 664 9. 94 Nigeria (. ng) 124, 009, 000 100, 000 0. 08% 114, 688 0. 010 136, 679, 929 8. 15 Russia (. ru) 143, 246, 000 18, 000 12. 57% 7, 638, 944 0. 460 113, 059, 221 6. 74 Vietnam (. vn) 81, 377, 000 400, 000 0. 49% 159, 232 0. 010 82, 758, 458 4. 94 Philippines (. ph) 79, 999, 000 4, 500, 000 5. 63% 765, 696 0. 050 77, 455, 760 4. 62 Mexico (. mx) 103, 457, 000 3, 500, 000 3. 38% 6, 311, 936 0. 380 72, 369, 345 4. 32 Ethiopa (. et) 70, 678, 000 20, 000 0. 03% 16, 384 0. 010 70, 830, 896 4. 23 Egypt (. eg) 71, 931, 000 600, 000 0. 83% 853, 504 0. 060 67, 382, 138 4. 02 Iran (. ir) 68, 920, 000 420, 000 0. 61% 581, 888 0. 040 65, 449, 815 3. 91 71, 325, 000 2, 500, 000 3. 51% 2, 429, 696 0. 150 57, 553, 061 3. 44 Turkey (. tr) © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 24


