d8d261a29f0136204943edb7302886ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 IPv 6 @ Comcast Managing 100+ Million IP Addresses 2006 -02 -06 Alain Durand Advanced Engineering Director – IPv 6 Architect Alain_Durand@cable. comcast. com
IPv 6 @ Comcast Managing 100+ Million IP Addresses 2006 -02 -06 Alain Durand Advanced Engineering Director – IPv 6 Architect Alain_Durand@cable. comcast. com
 Agenda • Comcast needs for IPv 6 • Comcast plans for IPv 6 • The IPv 6 (Cable) Network at Home 2
Agenda • Comcast needs for IPv 6 • Comcast plans for IPv 6 • The IPv 6 (Cable) Network at Home 2
 Comcast needs for IPv 6 3
Comcast needs for IPv 6 3
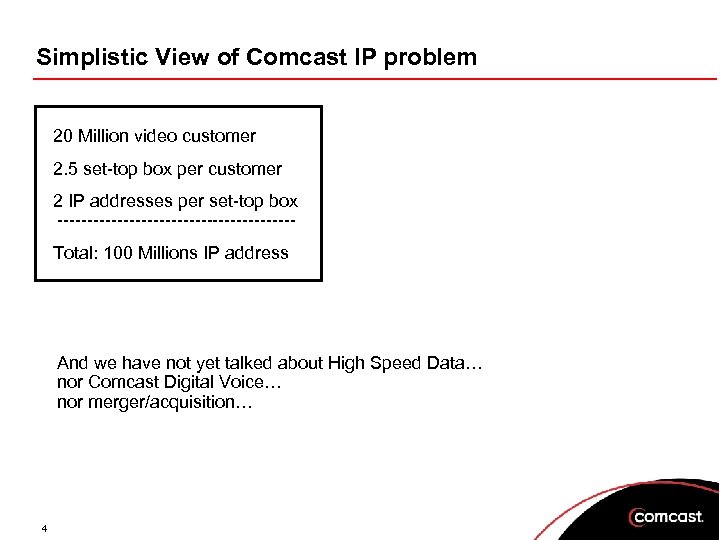 Simplistic View of Comcast IP problem 20 Million video customer 2. 5 set-top box per customer 2 IP addresses per set-top box --------------------Total: 100 Millions IP address And we have not yet talked about High Speed Data… nor Comcast Digital Voice… nor merger/acquisition… 4
Simplistic View of Comcast IP problem 20 Million video customer 2. 5 set-top box per customer 2 IP addresses per set-top box --------------------Total: 100 Millions IP address And we have not yet talked about High Speed Data… nor Comcast Digital Voice… nor merger/acquisition… 4
 Comcast Specific Needs • The extra large address space we need is for management (a. k. a. control plane) of Cable Modems, e. MTA and Set-Top boxes. This is not for customer PC-type devices (data plane). This would require a separate allocation. • This address space is for internal consumption only, i. e. it is not seen from outside Comcast. • Until recently, Comcast was using Net 10 (RFC 1918) for managing the modems. That space has been exhausted. • Comcast recently was allocated the largest part of Net 73 and is currently renumbering cable modems in that space. • In the control plane, all devices need to be remotely managed, so NAT isn’t going to help us… • IPv 6 is the clear solution for us • However, even we are starting now, the move to IPv 6 is not going to happen overnight 5
Comcast Specific Needs • The extra large address space we need is for management (a. k. a. control plane) of Cable Modems, e. MTA and Set-Top boxes. This is not for customer PC-type devices (data plane). This would require a separate allocation. • This address space is for internal consumption only, i. e. it is not seen from outside Comcast. • Until recently, Comcast was using Net 10 (RFC 1918) for managing the modems. That space has been exhausted. • Comcast recently was allocated the largest part of Net 73 and is currently renumbering cable modems in that space. • In the control plane, all devices need to be remotely managed, so NAT isn’t going to help us… • IPv 6 is the clear solution for us • However, even we are starting now, the move to IPv 6 is not going to happen overnight 5
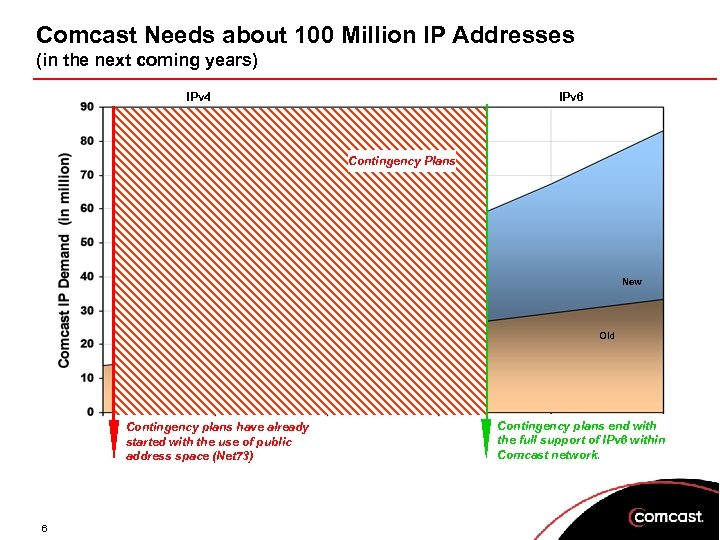 Comcast Needs about 100 Million IP Addresses (in the next coming years) IPv 4 IPv 6 Contingency Plans New Old Contingency plans have already started with the use of public address space (Net 73) 6 Contingency plans end with the full support of IPv 6 within Comcast network.
Comcast Needs about 100 Million IP Addresses (in the next coming years) IPv 4 IPv 6 Contingency Plans New Old Contingency plans have already started with the use of public address space (Net 73) 6 Contingency plans end with the full support of IPv 6 within Comcast network.
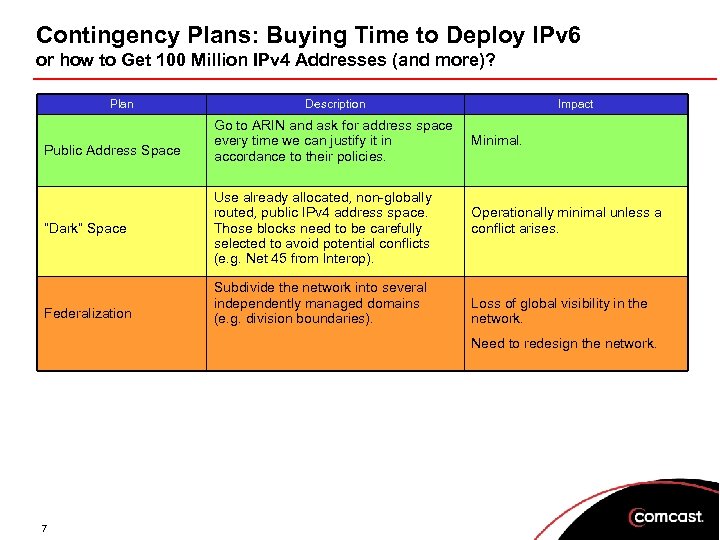 Contingency Plans: Buying Time to Deploy IPv 6 or how to Get 100 Million IPv 4 Addresses (and more)? Plan Public Address Space “Dark” Space Federalization Description Go to ARIN and ask for address space every time we can justify it in accordance to their policies. Use already allocated, non-globally routed, public IPv 4 address space. Those blocks need to be carefully selected to avoid potential conflicts (e. g. Net 45 from Interop). Subdivide the network into several independently managed domains (e. g. division boundaries). Impact Minimal. Operationally minimal unless a conflict arises. Loss of global visibility in the network. Need to redesign the network. 7
Contingency Plans: Buying Time to Deploy IPv 6 or how to Get 100 Million IPv 4 Addresses (and more)? Plan Public Address Space “Dark” Space Federalization Description Go to ARIN and ask for address space every time we can justify it in accordance to their policies. Use already allocated, non-globally routed, public IPv 4 address space. Those blocks need to be carefully selected to avoid potential conflicts (e. g. Net 45 from Interop). Subdivide the network into several independently managed domains (e. g. division boundaries). Impact Minimal. Operationally minimal unless a conflict arises. Loss of global visibility in the network. Need to redesign the network. 7
 Comcast plans for IPv 6 8
Comcast plans for IPv 6 8
 Comcast IPv 6 Strategy 1 - Plan for IPv 6 deployment NOW 2 – Deploy IPv 6 initially for the management and operation of the customer devices we manage: - Docsis CM - Set Top boxes, Packet. Cable MTA, … 3 - Be ready to offer to customers services that take advantage of IPv 6 9
Comcast IPv 6 Strategy 1 - Plan for IPv 6 deployment NOW 2 – Deploy IPv 6 initially for the management and operation of the customer devices we manage: - Docsis CM - Set Top boxes, Packet. Cable MTA, … 3 - Be ready to offer to customers services that take advantage of IPv 6 9
 IPv 6 Migration – Guiding Principles • The migration to IPv 6 project has the following principles: – Deploying IPv 6 must be minimally disruptive to the operations of existing networks and devices – IPv 6 must be included in the roadmap of next generation equipment and devices – Comcast operations, infrastructure and systems must become ready to support IPv 6 -enabled devices – IPv 6 will slowly penetrate Comcast DNA 10
IPv 6 Migration – Guiding Principles • The migration to IPv 6 project has the following principles: – Deploying IPv 6 must be minimally disruptive to the operations of existing networks and devices – IPv 6 must be included in the roadmap of next generation equipment and devices – Comcast operations, infrastructure and systems must become ready to support IPv 6 -enabled devices – IPv 6 will slowly penetrate Comcast DNA 10
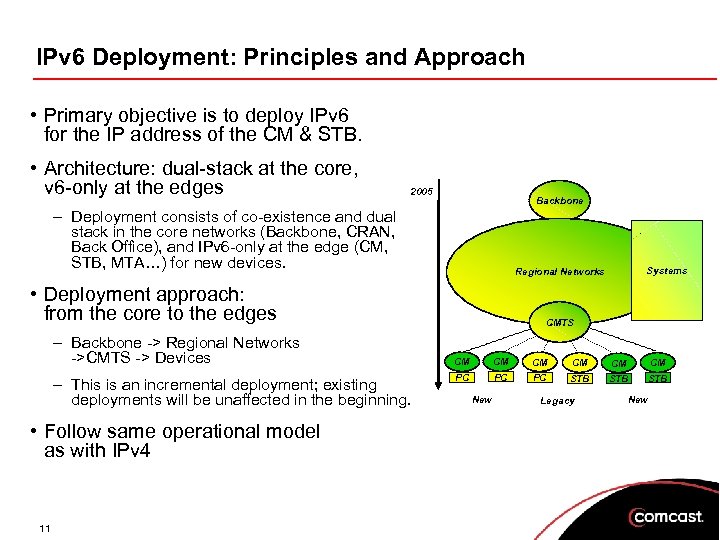 IPv 6 Deployment: Principles and Approach • Primary objective is to deploy IPv 6 for the IP address of the CM & STB. • Architecture: dual-stack at the core, v 6 -only at the edges 2005 Backbone – Deployment consists of co-existence and dual stack in the core networks (Backbone, CRAN, Back Office), and IPv 6 -only at the edge (CM, STB, MTA…) for new devices. • Deployment approach: from the core to the edges – Backbone -> Regional Networks ->CMTS -> Devices – This is an incremental deployment; existing deployments will be unaffected in the beginning. • Follow same operational model as with IPv 4 11 Systems Regional Networks CMTS CM CM CM PC PC PC STB STB New Legacy New
IPv 6 Deployment: Principles and Approach • Primary objective is to deploy IPv 6 for the IP address of the CM & STB. • Architecture: dual-stack at the core, v 6 -only at the edges 2005 Backbone – Deployment consists of co-existence and dual stack in the core networks (Backbone, CRAN, Back Office), and IPv 6 -only at the edge (CM, STB, MTA…) for new devices. • Deployment approach: from the core to the edges – Backbone -> Regional Networks ->CMTS -> Devices – This is an incremental deployment; existing deployments will be unaffected in the beginning. • Follow same operational model as with IPv 4 11 Systems Regional Networks CMTS CM CM CM PC PC PC STB STB New Legacy New
 IPv 6 Certification • Basic IPv 4 –compliance is somehow taken for granted today on most equipment – IP level component testing is thus limited • IPv 6 is still a very new technology • The level of maturity of implementations varies greatly among vendors – Some have had an IPv 6 story for about 10 years • Even those implementations have some features that are not fully baked – Others have still nothing and are going to rush to buy a 3 rd party stack and integrate it on their products • The bar for acceptance of IPv 6 product has to be set higher than for IPv 4 – Formal IPv 6 requirement list at purchase time – IPv 6 conformance certification to accept products 12
IPv 6 Certification • Basic IPv 4 –compliance is somehow taken for granted today on most equipment – IP level component testing is thus limited • IPv 6 is still a very new technology • The level of maturity of implementations varies greatly among vendors – Some have had an IPv 6 story for about 10 years • Even those implementations have some features that are not fully baked – Others have still nothing and are going to rush to buy a 3 rd party stack and integrate it on their products • The bar for acceptance of IPv 6 product has to be set higher than for IPv 4 – Formal IPv 6 requirement list at purchase time – IPv 6 conformance certification to accept products 12
 IPv 6 Training • IPv 6 is still a very new technology • Most engineers have heard about it but don’t know much about it – Fear factor is important to control • We can expect new hires to have 2 -4 years of IPv 4 experience, but can’t expect anything about IPv 6 • Initial and continuous training is critical – Academic style training presentation – Web-based classes – Hands-on exprience 13
IPv 6 Training • IPv 6 is still a very new technology • Most engineers have heard about it but don’t know much about it – Fear factor is important to control • We can expect new hires to have 2 -4 years of IPv 4 experience, but can’t expect anything about IPv 6 • Initial and continuous training is critical – Academic style training presentation – Web-based classes – Hands-on exprience 13
 IPv 6 Challenge: Aligning Several Timelines • IPv 6 cable modem availability • Dual Stack Network • IPv 6 -aware CMTS • Provisioning and monitoring system made IPv 6 aware • Video / Voice systems • Retail Market (Consumer Electronic) – Home Gateways – Video (e. g. TV with embedded cable modem) 14
IPv 6 Challenge: Aligning Several Timelines • IPv 6 cable modem availability • Dual Stack Network • IPv 6 -aware CMTS • Provisioning and monitoring system made IPv 6 aware • Video / Voice systems • Retail Market (Consumer Electronic) – Home Gateways – Video (e. g. TV with embedded cable modem) 14
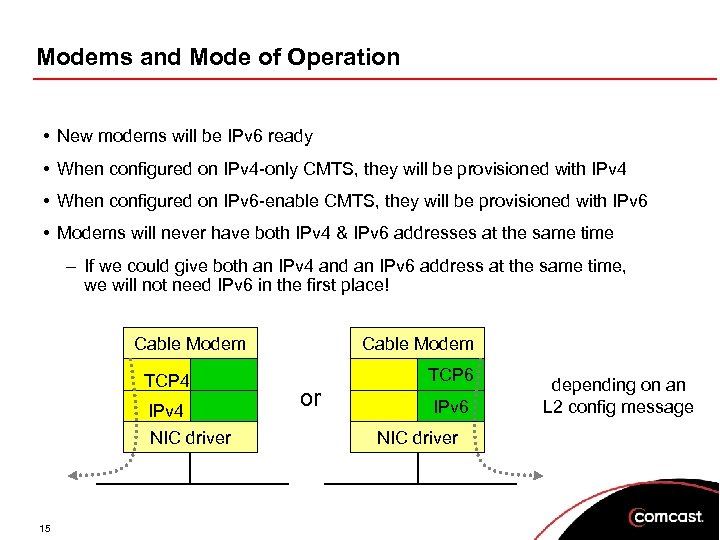 Modems and Mode of Operation • New modems will be IPv 6 ready • When configured on IPv 4 -only CMTS, they will be provisioned with IPv 4 • When configured on IPv 6 -enable CMTS, they will be provisioned with IPv 6 • Modems will never have both IPv 4 & IPv 6 addresses at the same time – If we could give both an IPv 4 and an IPv 6 address at the same time, we will not need IPv 6 in the first place! Cable Modem TCP 4 IPv 4 NIC driver 15 Cable Modem or TCP 6 IPv 6 NIC driver depending on an L 2 config message
Modems and Mode of Operation • New modems will be IPv 6 ready • When configured on IPv 4 -only CMTS, they will be provisioned with IPv 4 • When configured on IPv 6 -enable CMTS, they will be provisioned with IPv 6 • Modems will never have both IPv 4 & IPv 6 addresses at the same time – If we could give both an IPv 4 and an IPv 6 address at the same time, we will not need IPv 6 in the first place! Cable Modem TCP 4 IPv 4 NIC driver 15 Cable Modem or TCP 6 IPv 6 NIC driver depending on an L 2 config message
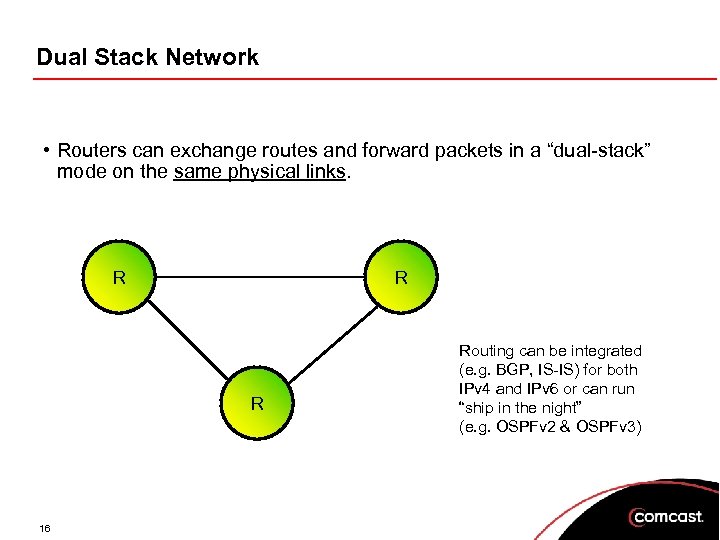 Dual Stack Network • Routers can exchange routes and forward packets in a “dual-stack” mode on the same physical links. R R R 16 Routing can be integrated (e. g. BGP, IS-IS) for both IPv 4 and IPv 6 or can run “ship in the night” (e. g. OSPFv 2 & OSPFv 3)
Dual Stack Network • Routers can exchange routes and forward packets in a “dual-stack” mode on the same physical links. R R R 16 Routing can be integrated (e. g. BGP, IS-IS) for both IPv 4 and IPv 6 or can run “ship in the night” (e. g. OSPFv 2 & OSPFv 3)
 Network Challenges • Monitoring routers – IPv 6 MIBs and software to monitor them • Choice of IGP – Comcast run OSPFv 2 for IPv 4 – Should we run OSPFv 3 for IPv 6 “Ship in the Night” or migrate the whole thing to run “integrated” with IS-IS? – What are the failure mode for end to end dual stack applications when the routing for either IPv 4 or IPv 6 fails? – Impact on MTR – Impact of BFD • Integrating IPv 4 & IPv 6 security • Integrating IPv 4 & IPv 6 Qo. S 17
Network Challenges • Monitoring routers – IPv 6 MIBs and software to monitor them • Choice of IGP – Comcast run OSPFv 2 for IPv 4 – Should we run OSPFv 3 for IPv 6 “Ship in the Night” or migrate the whole thing to run “integrated” with IS-IS? – What are the failure mode for end to end dual stack applications when the routing for either IPv 4 or IPv 6 fails? – Impact on MTR – Impact of BFD • Integrating IPv 4 & IPv 6 security • Integrating IPv 4 & IPv 6 Qo. S 17
 Provisioning, Monitoring, Back-Office • Mostly a software upgrade problem – Not unlike the Y 2 K problem – Fields need to be bigger in database & web scripts • Should system “X” be upgraded for IPv 6? – Transport questions • Does system “X” communicate with devices that are potentially IPv 6 -only (e. g. CM)? – Payload questions • Does system “X” manipulate IP data (store, input or display)? • Could those data be IPv 6? • Comcast case – About 100 “systems” – 10 need major updates for transport – 30 need minor updates for display/storage 18
Provisioning, Monitoring, Back-Office • Mostly a software upgrade problem – Not unlike the Y 2 K problem – Fields need to be bigger in database & web scripts • Should system “X” be upgraded for IPv 6? – Transport questions • Does system “X” communicate with devices that are potentially IPv 6 -only (e. g. CM)? – Payload questions • Does system “X” manipulate IP data (store, input or display)? • Could those data be IPv 6? • Comcast case – About 100 “systems” – 10 need major updates for transport – 30 need minor updates for display/storage 18
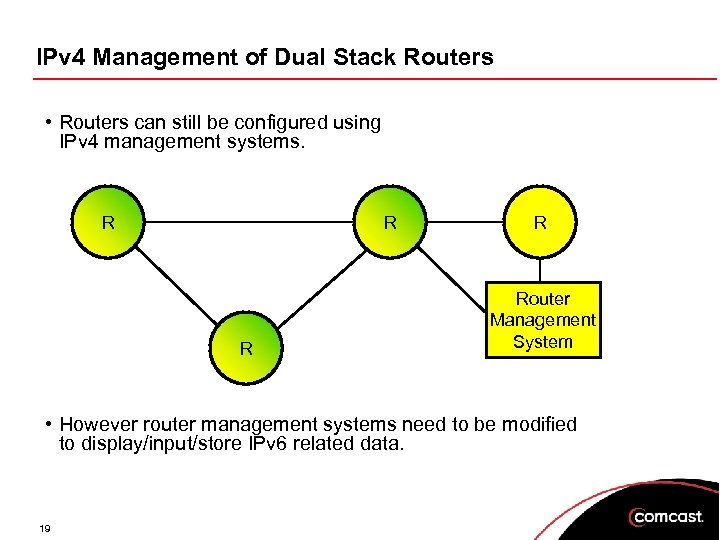 IPv 4 Management of Dual Stack Routers • Routers can still be configured using IPv 4 management systems. R R Router Management System • However router management systems need to be modified to display/input/store IPv 6 related data. 19
IPv 4 Management of Dual Stack Routers • Routers can still be configured using IPv 4 management systems. R R Router Management System • However router management systems need to be modified to display/input/store IPv 6 related data. 19
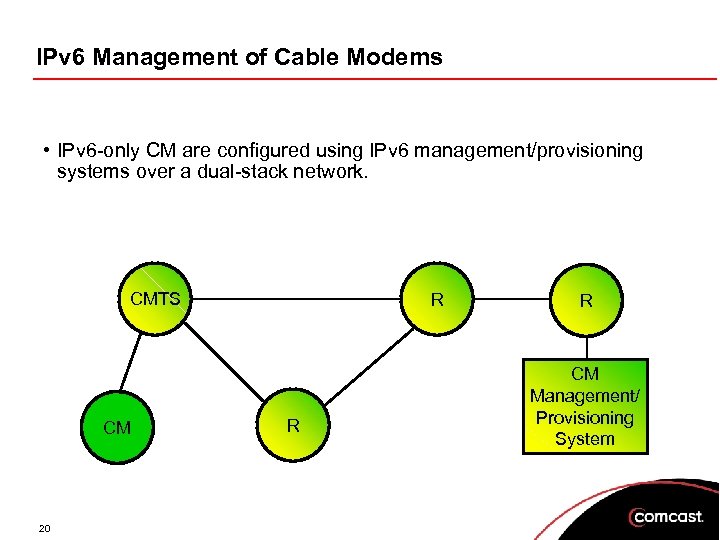 IPv 6 Management of Cable Modems • IPv 6 -only CM are configured using IPv 6 management/provisioning systems over a dual-stack network. CMTS CM 20 R R R CM Management/ Provisioning System
IPv 6 Management of Cable Modems • IPv 6 -only CM are configured using IPv 6 management/provisioning systems over a dual-stack network. CMTS CM 20 R R R CM Management/ Provisioning System
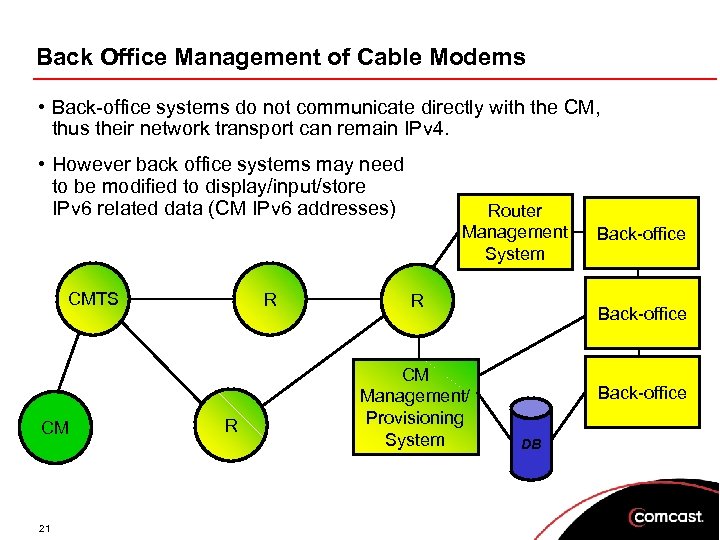 Back Office Management of Cable Modems • Back-office systems do not communicate directly with the CM, thus their network transport can remain IPv 4. • However back office systems may need to be modified to display/input/store IPv 6 related data (CM IPv 6 addresses) CMTS CM 21 R R Router Management System R CM Management/ Provisioning System Back-office DB
Back Office Management of Cable Modems • Back-office systems do not communicate directly with the CM, thus their network transport can remain IPv 4. • However back office systems may need to be modified to display/input/store IPv 6 related data (CM IPv 6 addresses) CMTS CM 21 R R Router Management System R CM Management/ Provisioning System Back-office DB
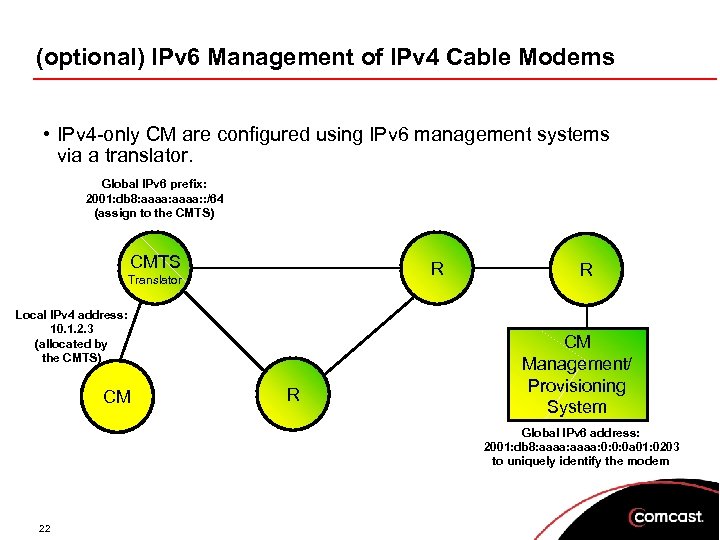 (optional) IPv 6 Management of IPv 4 Cable Modems • IPv 4 -only CM are configured using IPv 6 management systems via a translator. Global IPv 6 prefix: 2001: db 8: aaaa: : /64 (assign to the CMTS) CMTS R Translator Local IPv 4 address: 10. 1. 2. 3 (allocated by the CMTS) CM R R CM Management/ Provisioning System Global IPv 6 address: 2001: db 8: aaaa: 0: 0: 0 a 01: 0203 to uniquely identify the modem 22
(optional) IPv 6 Management of IPv 4 Cable Modems • IPv 4 -only CM are configured using IPv 6 management systems via a translator. Global IPv 6 prefix: 2001: db 8: aaaa: : /64 (assign to the CMTS) CMTS R Translator Local IPv 4 address: 10. 1. 2. 3 (allocated by the CMTS) CM R R CM Management/ Provisioning System Global IPv 6 address: 2001: db 8: aaaa: 0: 0: 0 a 01: 0203 to uniquely identify the modem 22
 The IPv 6 (Cable) Network at Home 23
The IPv 6 (Cable) Network at Home 23
 Key Elements of the Home Network of the Future • Large number of IP devices, not all being computers – Dual stack networks (v 4/v 6) • Multiple links with different characteristics: – Wired/wireless, different speeds, multi-cast support, … • New network layer demand – Mobility, Security, Qo. S • Additional services – Home automation, video communications – Network Storage, … • Very limited management skills • Evolution, not revolution 24
Key Elements of the Home Network of the Future • Large number of IP devices, not all being computers – Dual stack networks (v 4/v 6) • Multiple links with different characteristics: – Wired/wireless, different speeds, multi-cast support, … • New network layer demand – Mobility, Security, Qo. S • Additional services – Home automation, video communications – Network Storage, … • Very limited management skills • Evolution, not revolution 24
 How to Build it? • IPv 6 and Docsis 3. 0 are the basic building blocs – Address space – Bandwidth • DHCPv 6 is the IP configuration method of choice for any device either directly attached to the cable or bridged to it. – Devices behind a home router may use stateless auto-configuration • The home networks of the future require smart gateway – Not just access routers, but include all kinds of features/services 25
How to Build it? • IPv 6 and Docsis 3. 0 are the basic building blocs – Address space – Bandwidth • DHCPv 6 is the IP configuration method of choice for any device either directly attached to the cable or bridged to it. – Devices behind a home router may use stateless auto-configuration • The home networks of the future require smart gateway – Not just access routers, but include all kinds of features/services 25
 Case Studies • The single PC at home • The IP Set Top Box with an embedded CM • The combined MTA + PC modem • The home network with a home gateway 26
Case Studies • The single PC at home • The IP Set Top Box with an embedded CM • The combined MTA + PC modem • The home network with a home gateway 26
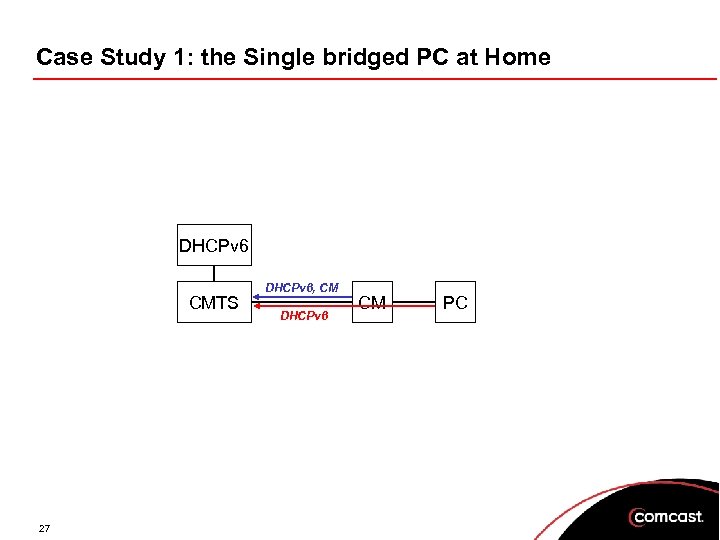 Case Study 1: the Single bridged PC at Home DHCPv 6 CMTS 27 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6 CM PC
Case Study 1: the Single bridged PC at Home DHCPv 6 CMTS 27 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6 CM PC
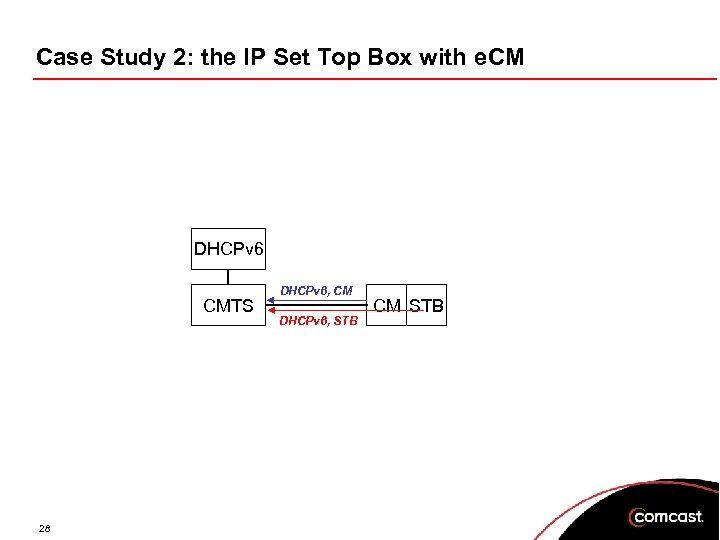 Case Study 2: the IP Set Top Box with e. CM DHCPv 6 CMTS 28 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6, STB CM STB
Case Study 2: the IP Set Top Box with e. CM DHCPv 6 CMTS 28 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6, STB CM STB
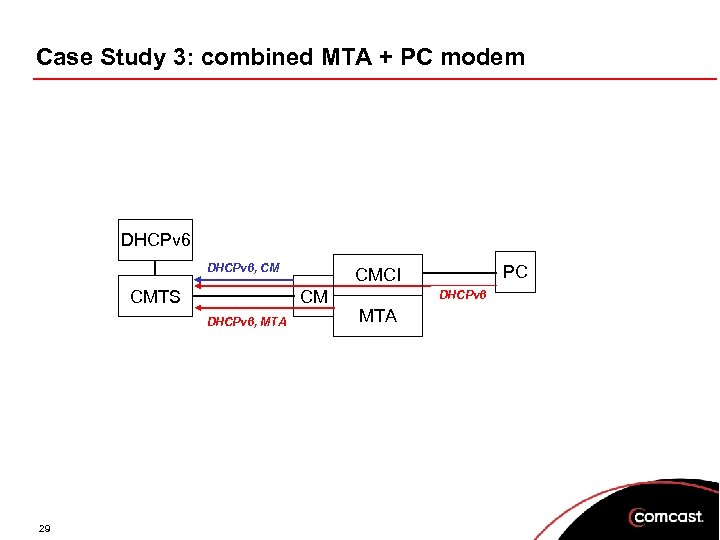 Case Study 3: combined MTA + PC modem DHCPv 6, CM CMTS CM DHCPv 6, MTA 29 PC CMCI DHCPv 6 MTA
Case Study 3: combined MTA + PC modem DHCPv 6, CM CMTS CM DHCPv 6, MTA 29 PC CMCI DHCPv 6 MTA
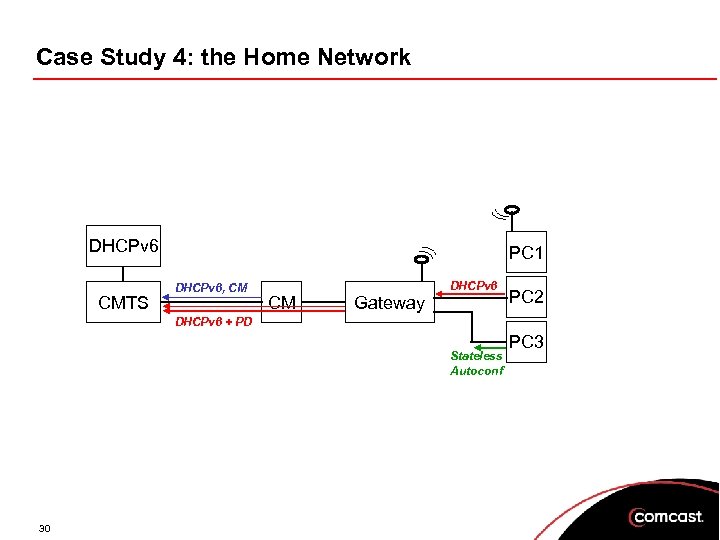 Case Study 4: the Home Network DHCPv 6 CMTS PC 1 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6 CM Gateway PC 2 DHCPv 6 + PD Stateless Autoconf 30 PC 3
Case Study 4: the Home Network DHCPv 6 CMTS PC 1 DHCPv 6, CM DHCPv 6 CM Gateway PC 2 DHCPv 6 + PD Stateless Autoconf 30 PC 3


