cc704a18681e2f992ef5ffb402ca79d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 IPv 6 and IPv 4 Interoperation and Transition Tony Hain co-chair IETF ngtrans WG alh-ietf@tndh. net 1
IPv 6 and IPv 4 Interoperation and Transition Tony Hain co-chair IETF ngtrans WG alh-ietf@tndh. net 1
 Agenda • Transition issues • ngtrans tool set • Environments • Summary 2
Agenda • Transition issues • ngtrans tool set • Environments • Summary 2
 Transition issues • Islands vs. Integrated • Automated vs. Managed • Applications • Long process 3
Transition issues • Islands vs. Integrated • Automated vs. Managed • Applications • Long process 3
 IPv 6 Timeline (A pragmatic projection) 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 • Early adopter • Application porting <= Duration 3+ years => • ISP adoption <= Duration 3+ years => • Consumer adoption <= • Enterprise adoption Duration 5+ years => <= Duration 3+ years => 4
IPv 6 Timeline (A pragmatic projection) 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 • Early adopter • Application porting <= Duration 3+ years => • ISP adoption <= Duration 3+ years => • Consumer adoption <= • Enterprise adoption Duration 5+ years => <= Duration 3+ years => 4
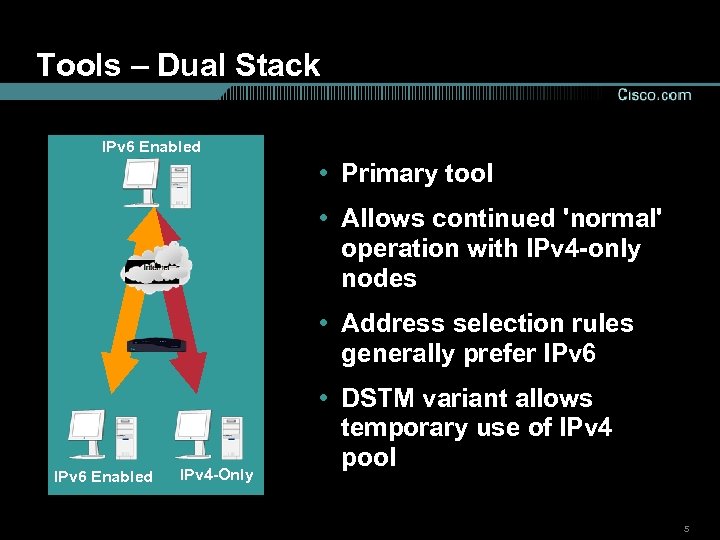 Tools – Dual Stack IPv 6 Enabled • Primary tool • Allows continued 'normal' operation with IPv 4 -only nodes • Address selection rules generally prefer IPv 6 Enabled IPv 4 -Only • DSTM variant allows temporary use of IPv 4 pool 5
Tools – Dual Stack IPv 6 Enabled • Primary tool • Allows continued 'normal' operation with IPv 4 -only nodes • Address selection rules generally prefer IPv 6 Enabled IPv 4 -Only • DSTM variant allows temporary use of IPv 4 pool 5
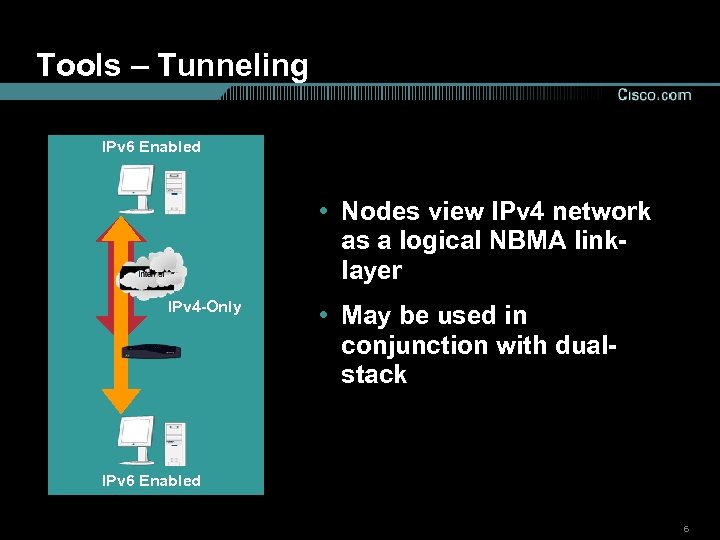 Tools – Tunneling IPv 6 Enabled • Nodes view IPv 4 network as a logical NBMA linklayer IPv 4 -Only • May be used in conjunction with dualstack IPv 6 Enabled 6
Tools – Tunneling IPv 6 Enabled • Nodes view IPv 4 network as a logical NBMA linklayer IPv 4 -Only • May be used in conjunction with dualstack IPv 6 Enabled 6
 Tunneling Mechanisms (operationally challenging) • Configured Prearranged addresses for both IPv 4 & IPv 6, manually configured • Tunnel Broker Builds on configured tunnel via IPv 4 auth scheme to establish mapping ; typically default route • 6 over 4 Any address, but requires IPv 4 multicast for ND • Automatic Host-to-host – IPv 4 address embedded in low 32 bits with prefix : : /96 Requires injecting IPv 4 BGP table into IPv 6 routing 7
Tunneling Mechanisms (operationally challenging) • Configured Prearranged addresses for both IPv 4 & IPv 6, manually configured • Tunnel Broker Builds on configured tunnel via IPv 4 auth scheme to establish mapping ; typically default route • 6 over 4 Any address, but requires IPv 4 multicast for ND • Automatic Host-to-host – IPv 4 address embedded in low 32 bits with prefix : : /96 Requires injecting IPv 4 BGP table into IPv 6 routing 7
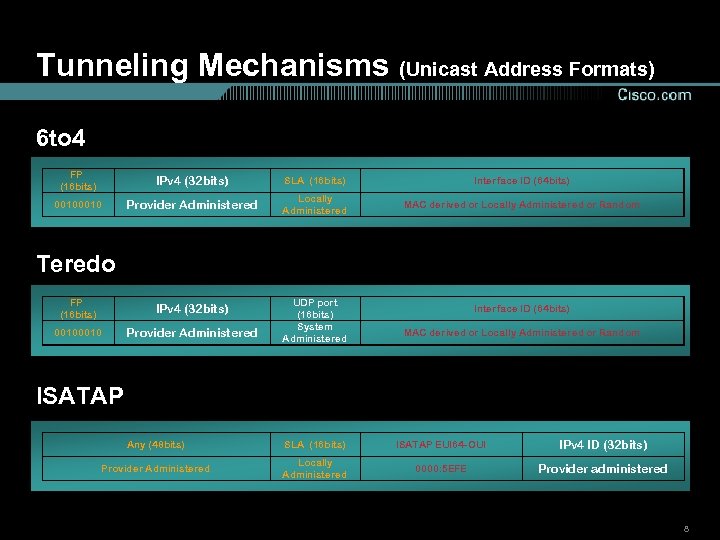 Tunneling Mechanisms (Unicast Address Formats) 6 to 4 FP (16 bits) IPv 4 (32 bits) SLA (16 bits) Interface ID (64 bits) 0010 Provider Administered Locally Administered MAC derived or Locally Administered or Random FP (16 bits) IPv 4 (32 bits) 0010 Provider Administered UDP port (16 bits) System Administered Any (48 bits) SLA (16 bits) ISATAP EUI 64 -OUI IPv 4 ID (32 bits) Provider Administered Locally Administered 0000: 5 EFE Provider administered Teredo Interface ID (64 bits) MAC derived or Locally Administered or Random ISATAP 8
Tunneling Mechanisms (Unicast Address Formats) 6 to 4 FP (16 bits) IPv 4 (32 bits) SLA (16 bits) Interface ID (64 bits) 0010 Provider Administered Locally Administered MAC derived or Locally Administered or Random FP (16 bits) IPv 4 (32 bits) 0010 Provider Administered UDP port (16 bits) System Administered Any (48 bits) SLA (16 bits) ISATAP EUI 64 -OUI IPv 4 ID (32 bits) Provider Administered Locally Administered 0000: 5 EFE Provider administered Teredo Interface ID (64 bits) MAC derived or Locally Administered or Random ISATAP 8
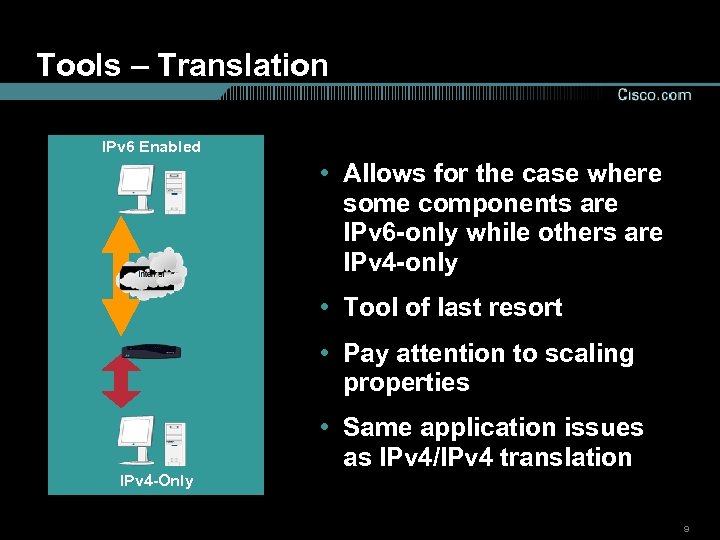 Tools – Translation IPv 6 Enabled • Allows for the case where some components are IPv 6 -only while others are IPv 4 -only • Tool of last resort • Pay attention to scaling properties • Same application issues as IPv 4/IPv 4 translation IPv 4 -Only 9
Tools – Translation IPv 6 Enabled • Allows for the case where some components are IPv 6 -only while others are IPv 4 -only • Tool of last resort • Pay attention to scaling properties • Same application issues as IPv 4/IPv 4 translation IPv 4 -Only 9
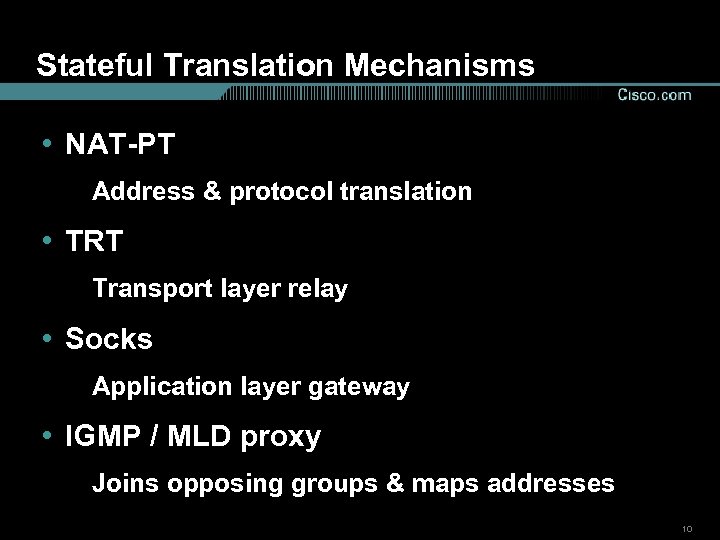 Stateful Translation Mechanisms • NAT-PT Address & protocol translation • TRT Transport layer relay • Socks Application layer gateway • IGMP / MLD proxy Joins opposing groups & maps addresses 10
Stateful Translation Mechanisms • NAT-PT Address & protocol translation • TRT Transport layer relay • Socks Application layer gateway • IGMP / MLD proxy Joins opposing groups & maps addresses 10
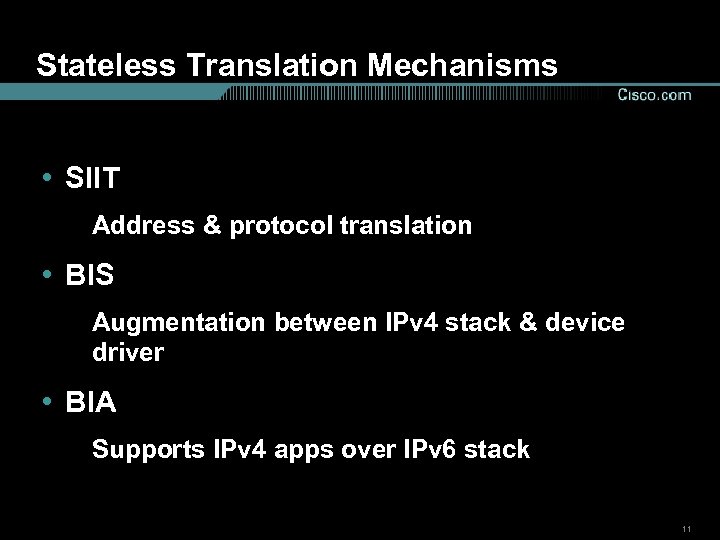 Stateless Translation Mechanisms • SIIT Address & protocol translation • BIS Augmentation between IPv 4 stack & device driver • BIA Supports IPv 4 apps over IPv 6 stack 11
Stateless Translation Mechanisms • SIIT Address & protocol translation • BIS Augmentation between IPv 4 stack & device driver • BIA Supports IPv 4 apps over IPv 6 stack 11
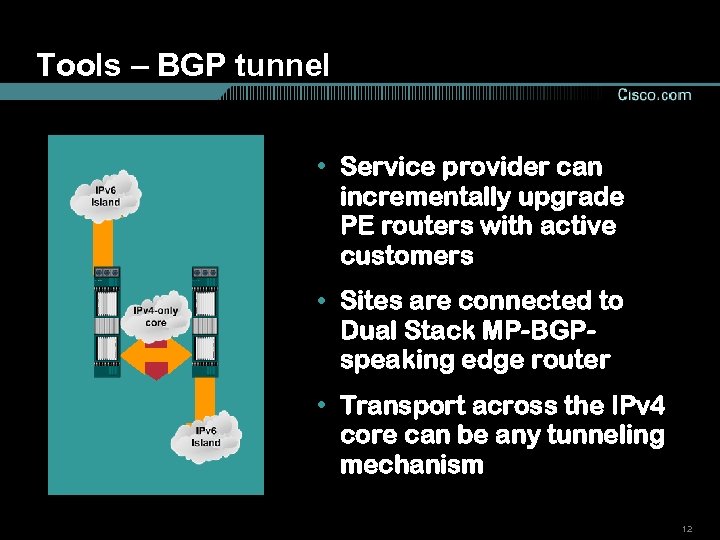 Tools – BGP tunnel • Service provider can incrementally upgrade PE routers with active customers • Sites are connected to Dual Stack MP-BGPspeaking edge router • Transport across the IPv 4 core can be any tunneling mechanism 12
Tools – BGP tunnel • Service provider can incrementally upgrade PE routers with active customers • Sites are connected to Dual Stack MP-BGPspeaking edge router • Transport across the IPv 4 core can be any tunneling mechanism 12
 Tools – Services • DNS-ALG in NAT-PT distorts perception Referral chain consistency with resolver Remember glue & reverse records for IPv 6 • SMTP Create MX records for both IPv 4 & IPv 6 on dual-stack DNS failure on AAAA may cause mail requeue • DHCP Spec about finished; products will follow Prefix allocation current driver 13
Tools – Services • DNS-ALG in NAT-PT distorts perception Referral chain consistency with resolver Remember glue & reverse records for IPv 6 • SMTP Create MX records for both IPv 4 & IPv 6 on dual-stack DNS failure on AAAA may cause mail requeue • DHCP Spec about finished; products will follow Prefix allocation current driver 13
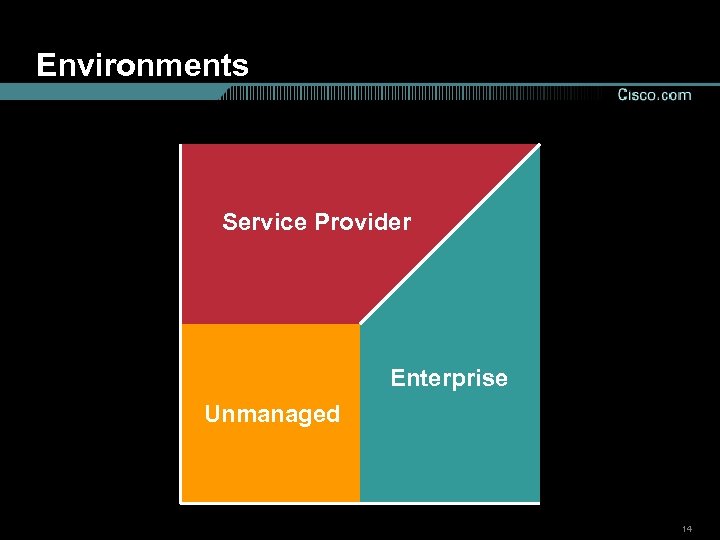 Environments Service Provider Enterprise Unmanaged 14
Environments Service Provider Enterprise Unmanaged 14
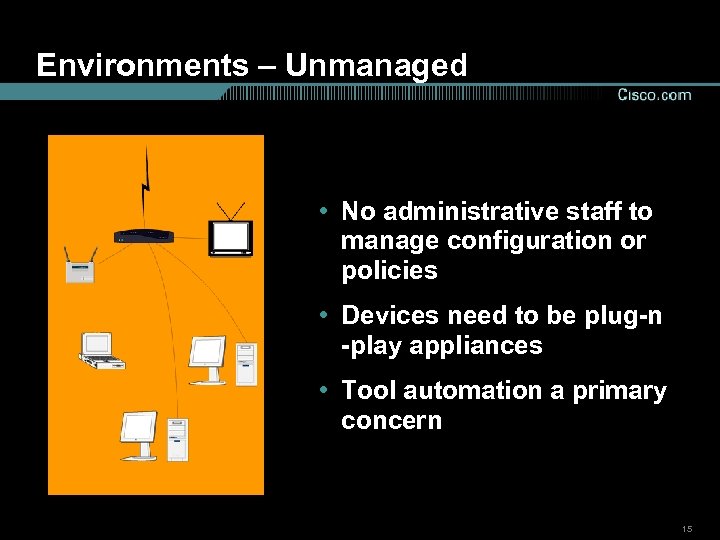 Environments – Unmanaged • No administrative staff to manage configuration or policies • Devices need to be plug-n -play appliances • Tool automation a primary concern 15
Environments – Unmanaged • No administrative staff to manage configuration or policies • Devices need to be plug-n -play appliances • Tool automation a primary concern 15
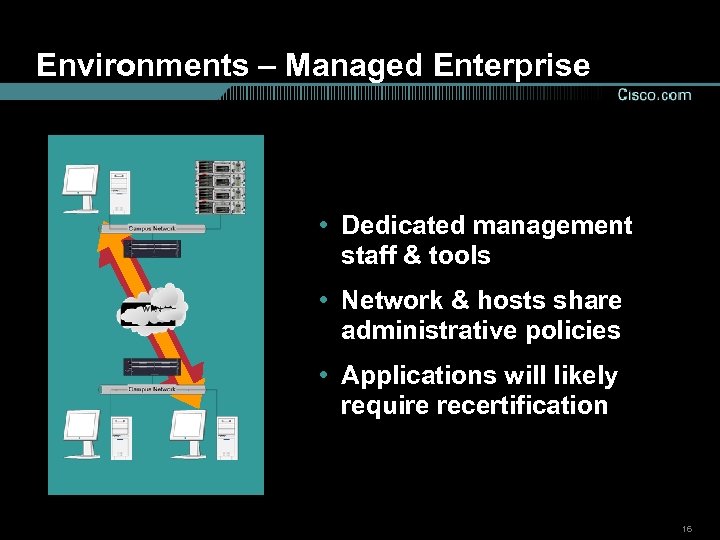 Environments – Managed Enterprise • Dedicated management staff & tools • Network & hosts share administrative policies • Applications will likely require recertification 16
Environments – Managed Enterprise • Dedicated management staff & tools • Network & hosts share administrative policies • Applications will likely require recertification 16
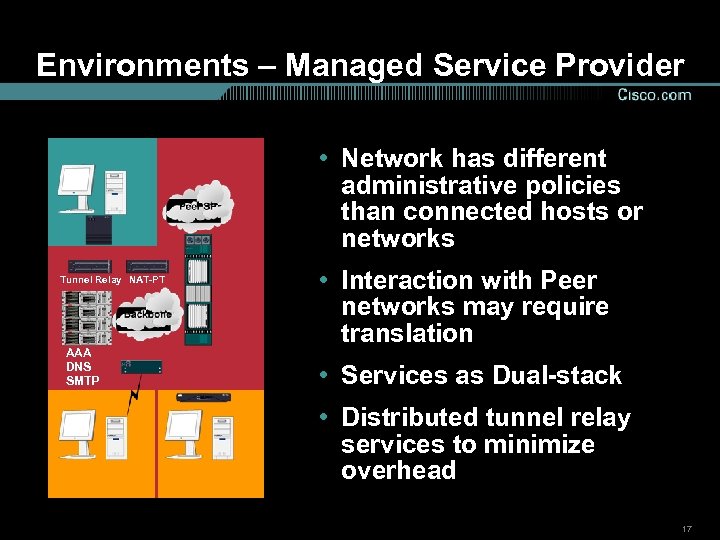 Environments – Managed Service Provider • Network has different administrative policies than connected hosts or networks Tunnel Relay NAT-PT AAA DNS SMTP • Interaction with Peer networks may require translation • Services as Dual-stack • Distributed tunnel relay services to minimize overhead 17
Environments – Managed Service Provider • Network has different administrative policies than connected hosts or networks Tunnel Relay NAT-PT AAA DNS SMTP • Interaction with Peer networks may require translation • Services as Dual-stack • Distributed tunnel relay services to minimize overhead 17
 Summary • Transition will not be a quick process • Tool set goal : minimize interdependence • Dual-stack & Tunneling before Translation • Recognize environment characteristics • Applications will drive deployments 18
Summary • Transition will not be a quick process • Tool set goal : minimize interdependence • Dual-stack & Tunneling before Translation • Recognize environment characteristics • Applications will drive deployments 18
 19
19
 Questions? 20
Questions? 20


