db903d17e460d8219b1b14af68bd3046.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 IPSec NS-H 0503 -02/1104 1
IPSec NS-H 0503 -02/1104 1
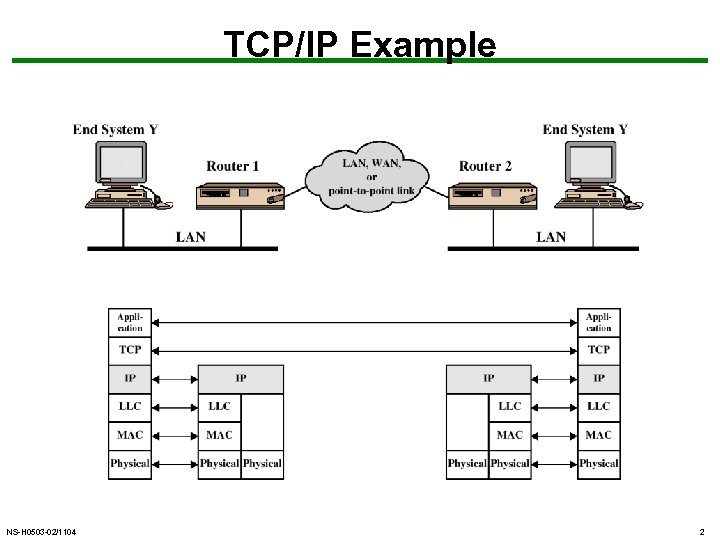 TCP/IP Example NS-H 0503 -02/1104 2
TCP/IP Example NS-H 0503 -02/1104 2
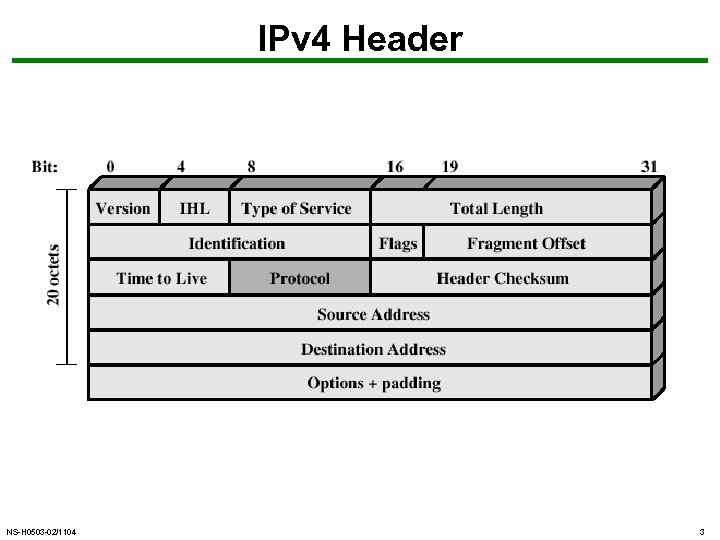 IPv 4 Header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 3
IPv 4 Header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 3
 IPSec • general IP Security mechanisms • provides – authentication – confidentiality – key management • applicable to use over LANs, across public & private WANs, & for the Internet NS-H 0503 -02/1104 4
IPSec • general IP Security mechanisms • provides – authentication – confidentiality – key management • applicable to use over LANs, across public & private WANs, & for the Internet NS-H 0503 -02/1104 4
 IP Security Overview IPSec is not a single protocol. Instead, IPSec provides a set of security algorithms plus a general framework that allows a pair of communicating entities to use whichever algorithms provide security appropriate for the communication. NS-H 0503 -02/1104 5
IP Security Overview IPSec is not a single protocol. Instead, IPSec provides a set of security algorithms plus a general framework that allows a pair of communicating entities to use whichever algorithms provide security appropriate for the communication. NS-H 0503 -02/1104 5
 IP Security Overview • Applications of IPSec – Secure branch office connectivity over the Internet – Secure remote access over the Internet – Establsihing extranet and intranet connectivity with partners – Enhancing electronic commerce security NS-H 0503 -02/1104 6
IP Security Overview • Applications of IPSec – Secure branch office connectivity over the Internet – Secure remote access over the Internet – Establsihing extranet and intranet connectivity with partners – Enhancing electronic commerce security NS-H 0503 -02/1104 6
 IP Security Overview • Benefits of IPSec – Transparent to applications (below transport layer (TCP, UDP) – Provide security for individual users • IPSec can assure that: – A router or neighbor advertisement comes from an authorized router – A redirect message comes from the router to which the initial packet was sent – A routing update is not forged NS-H 0503 -02/1104 7
IP Security Overview • Benefits of IPSec – Transparent to applications (below transport layer (TCP, UDP) – Provide security for individual users • IPSec can assure that: – A router or neighbor advertisement comes from an authorized router – A redirect message comes from the router to which the initial packet was sent – A routing update is not forged NS-H 0503 -02/1104 7
 IP Security Architecture • specification is quite complex • defined in numerous RFC’s – incl. RFC 2401/2402/2406/2408 – many others, grouped by category • mandatory in IPv 6, optional in IPv 4 • IPSec documents: – RFC 2401: An overview of security architecture – RFC 2402: Description of a packet encryption extension to IPv 4 and IPv 6 – RFC 2406: Description of a packet emcryption extension to IPv 4 and IPv 6 – RFC 2408: Specification of key managament capabilities NS-H 0503 -02/1104 8
IP Security Architecture • specification is quite complex • defined in numerous RFC’s – incl. RFC 2401/2402/2406/2408 – many others, grouped by category • mandatory in IPv 6, optional in IPv 4 • IPSec documents: – RFC 2401: An overview of security architecture – RFC 2402: Description of a packet encryption extension to IPv 4 and IPv 6 – RFC 2406: Description of a packet emcryption extension to IPv 4 and IPv 6 – RFC 2408: Specification of key managament capabilities NS-H 0503 -02/1104 8
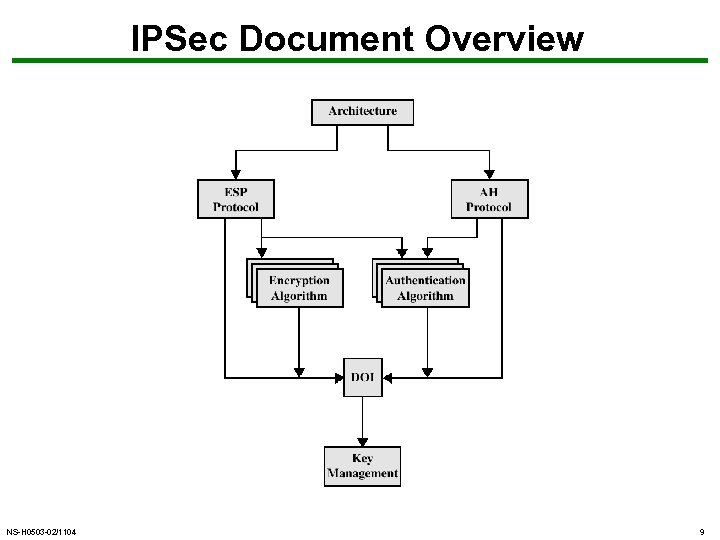 IPSec Document Overview NS-H 0503 -02/1104 9
IPSec Document Overview NS-H 0503 -02/1104 9
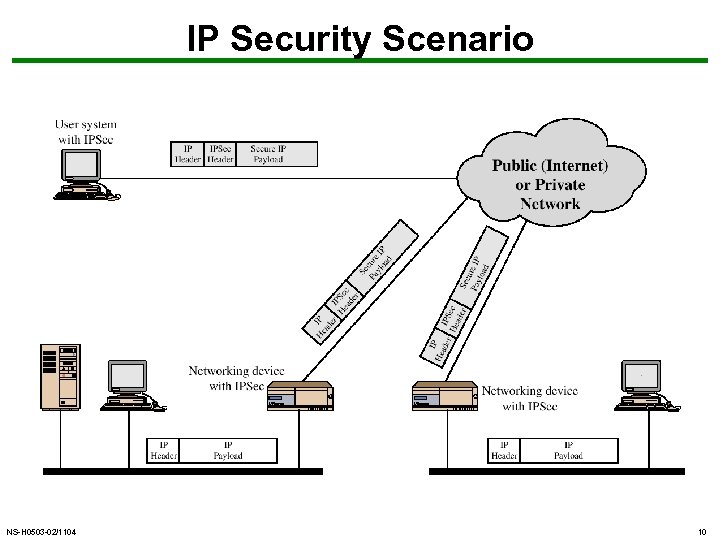 IP Security Scenario NS-H 0503 -02/1104 10
IP Security Scenario NS-H 0503 -02/1104 10
 Benefits of IPSec • in a firewall/router provides strong security to all traffic crossing the perimeter • is resistant to bypass • is below transport layer, hence transparent to applications • can be transparent to end users • can provide security for individual users if desired NS-H 0503 -02/1104 11
Benefits of IPSec • in a firewall/router provides strong security to all traffic crossing the perimeter • is resistant to bypass • is below transport layer, hence transparent to applications • can be transparent to end users • can provide security for individual users if desired NS-H 0503 -02/1104 11
 IPSec Services • • Access control Connectionless integrity Data origin authentication Rejection of replayed packets – a form of partial sequence integrity • Confidentiality (encryption) • Limited traffic flow confidentiality NS-H 0503 -02/1104 12
IPSec Services • • Access control Connectionless integrity Data origin authentication Rejection of replayed packets – a form of partial sequence integrity • Confidentiality (encryption) • Limited traffic flow confidentiality NS-H 0503 -02/1104 12
 Authentication Header (AH) • provides support for data integrity & authentication of IP packets – end system/router can authenticate user/app – prevents address spoofing attacks by tracking sequence numbers • based on use of a MAC – HMAC-MD 5 -96 or HMAC-SHA-1 -96 • parties must share a secret key NS-H 0503 -02/1104 13
Authentication Header (AH) • provides support for data integrity & authentication of IP packets – end system/router can authenticate user/app – prevents address spoofing attacks by tracking sequence numbers • based on use of a MAC – HMAC-MD 5 -96 or HMAC-SHA-1 -96 • parties must share a secret key NS-H 0503 -02/1104 13
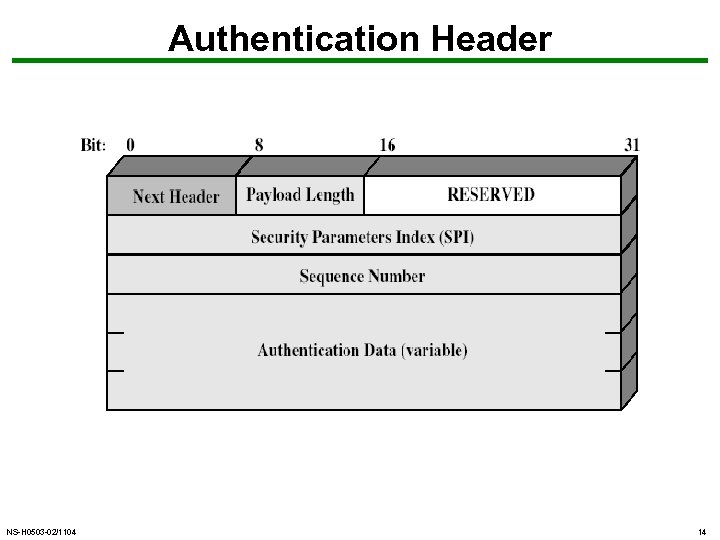 Authentication Header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 14
Authentication Header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 14
 Security Associations • a one-way relationship between sender & receiver that affords security for traffic flow • defined by 3 parameters: – Security Parameters Index (SPI) – IP Destination Address – Security Protocol Identifier • has a number of other parameters – seq no, AH & EH info, lifetime etc • have a database of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 15
Security Associations • a one-way relationship between sender & receiver that affords security for traffic flow • defined by 3 parameters: – Security Parameters Index (SPI) – IP Destination Address – Security Protocol Identifier • has a number of other parameters – seq no, AH & EH info, lifetime etc • have a database of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 15
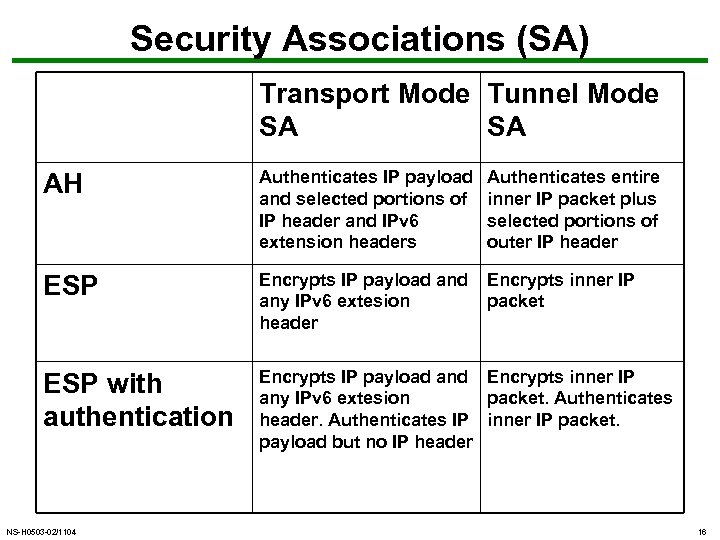 Security Associations (SA) Transport Mode Tunnel Mode SA SA AH Authenticates IP payload and selected portions of IP header and IPv 6 extension headers Authenticates entire inner IP packet plus selected portions of outer IP header ESP Encrypts IP payload any IPv 6 extesion header Encrypts inner IP packet ESP with authentication Encrypts IP payload and Encrypts inner IP any IPv 6 extesion packet. Authenticates header. Authenticates IP inner IP packet. payload but no IP header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 16
Security Associations (SA) Transport Mode Tunnel Mode SA SA AH Authenticates IP payload and selected portions of IP header and IPv 6 extension headers Authenticates entire inner IP packet plus selected portions of outer IP header ESP Encrypts IP payload any IPv 6 extesion header Encrypts inner IP packet ESP with authentication Encrypts IP payload and Encrypts inner IP any IPv 6 extesion packet. Authenticates header. Authenticates IP inner IP packet. payload but no IP header NS-H 0503 -02/1104 16
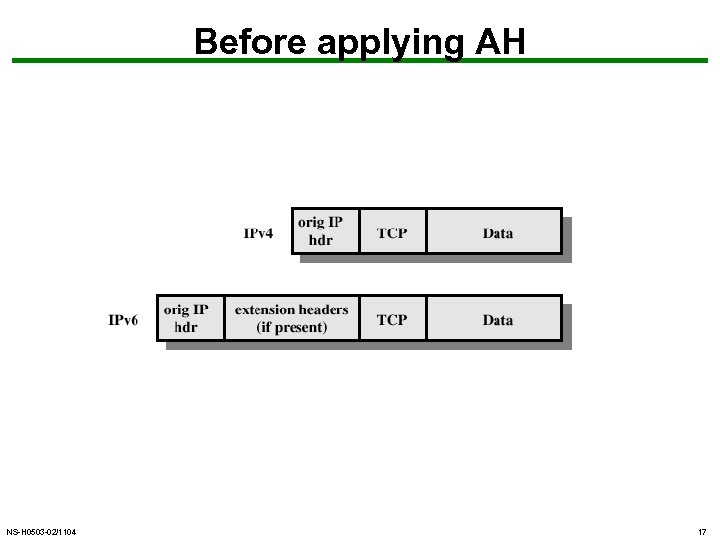 Before applying AH NS-H 0503 -02/1104 17
Before applying AH NS-H 0503 -02/1104 17
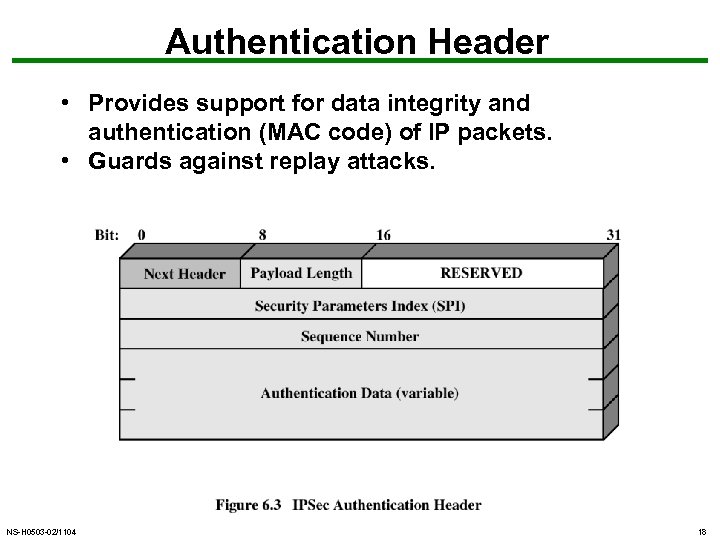 Authentication Header • Provides support for data integrity and authentication (MAC code) of IP packets. • Guards against replay attacks. NS-H 0503 -02/1104 18
Authentication Header • Provides support for data integrity and authentication (MAC code) of IP packets. • Guards against replay attacks. NS-H 0503 -02/1104 18
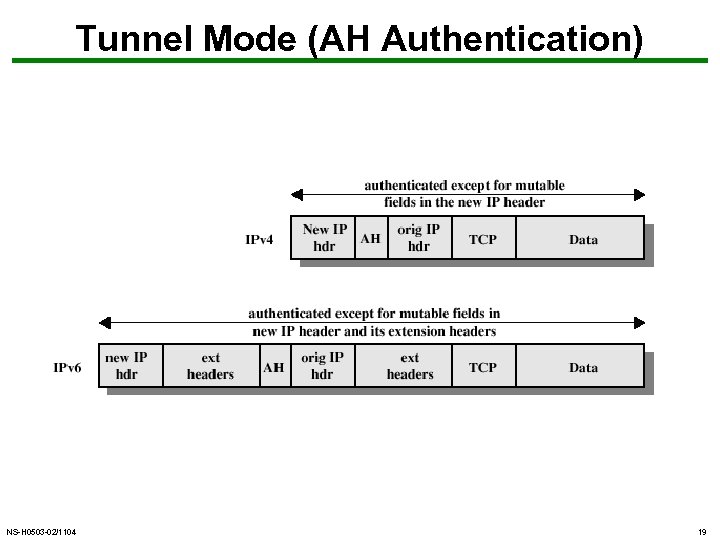 Tunnel Mode (AH Authentication) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 19
Tunnel Mode (AH Authentication) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 19
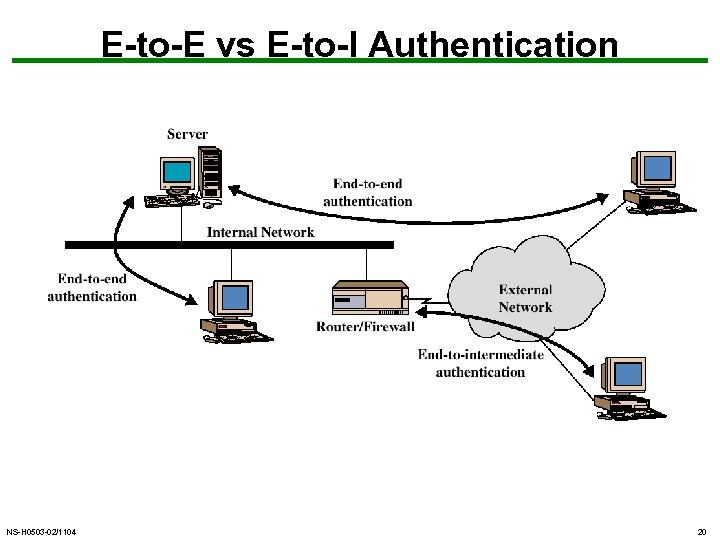 E-to-E vs E-to-I Authentication NS-H 0503 -02/1104 20
E-to-E vs E-to-I Authentication NS-H 0503 -02/1104 20
 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) • provides message content confidentiality & limited traffic flow confidentiality • can optionally provide the same authentication services as AH • supports range of ciphers, modes, padding – incl. DES, Triple-DES, RC 5, IDEA, CAST etc – CBC most common – pad to meet blocksize, for traffic flow NS-H 0503 -02/1104 21
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) • provides message content confidentiality & limited traffic flow confidentiality • can optionally provide the same authentication services as AH • supports range of ciphers, modes, padding – incl. DES, Triple-DES, RC 5, IDEA, CAST etc – CBC most common – pad to meet blocksize, for traffic flow NS-H 0503 -02/1104 21
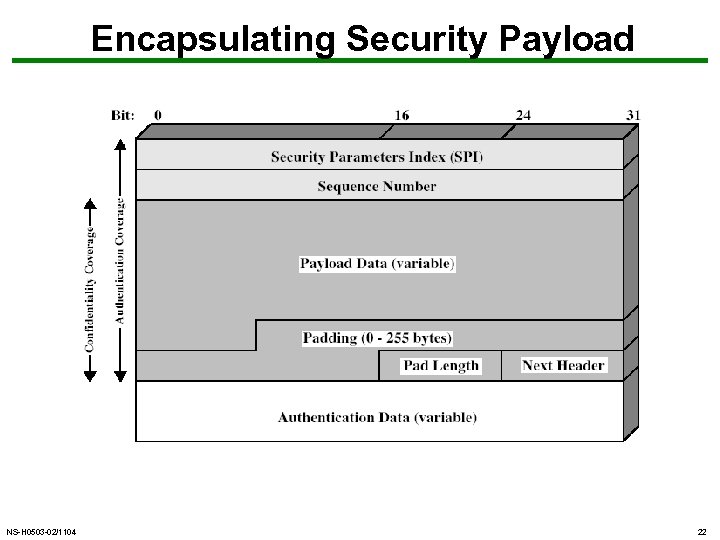 Encapsulating Security Payload NS-H 0503 -02/1104 22
Encapsulating Security Payload NS-H 0503 -02/1104 22
 Encryption&Authentication Algorithms • Encryption: – Three-key triple DES – RC 5 – IDEA – Three-key triple IDEA – CAST – Blowfish • Authentication: – HMAC-MD 5 -96 – HMAC-SHA-1 -96 NS-H 0503 -02/1104 23
Encryption&Authentication Algorithms • Encryption: – Three-key triple DES – RC 5 – IDEA – Three-key triple IDEA – CAST – Blowfish • Authentication: – HMAC-MD 5 -96 – HMAC-SHA-1 -96 NS-H 0503 -02/1104 23
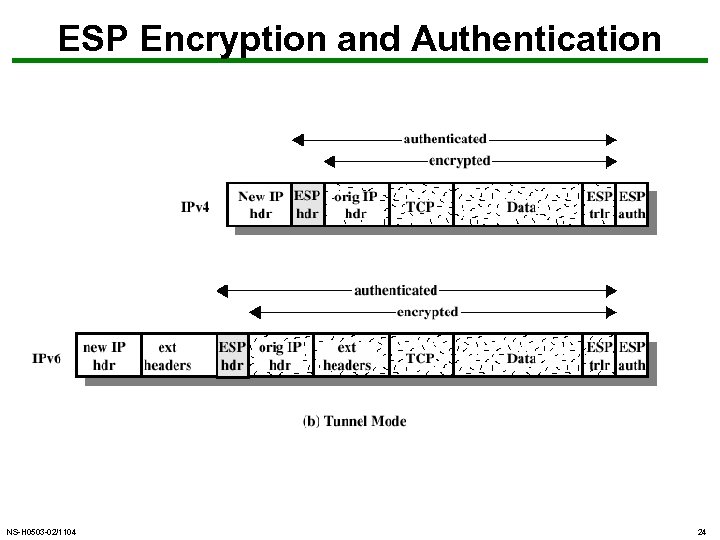 ESP Encryption and Authentication NS-H 0503 -02/1104 24
ESP Encryption and Authentication NS-H 0503 -02/1104 24
 Combining Security Associations • SA’s can implement either AH or ESP • to implement both need to combine SA’s – form a security bundle • have 4 cases (see next) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 25
Combining Security Associations • SA’s can implement either AH or ESP • to implement both need to combine SA’s – form a security bundle • have 4 cases (see next) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 25
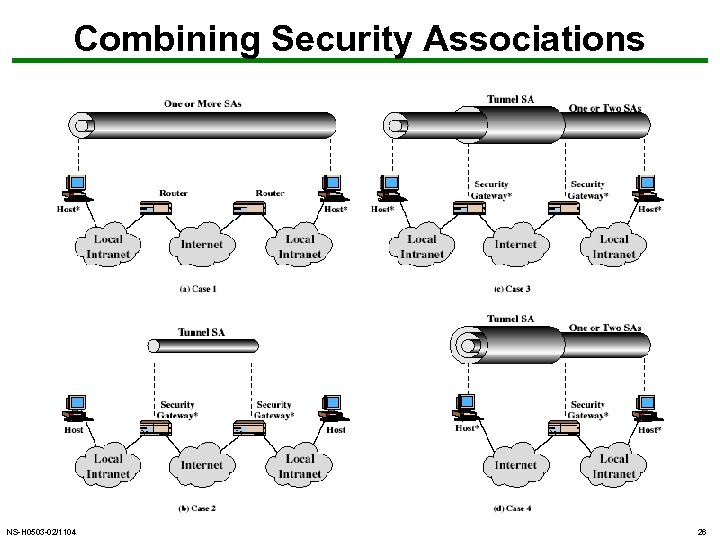 Combining Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 26
Combining Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 26
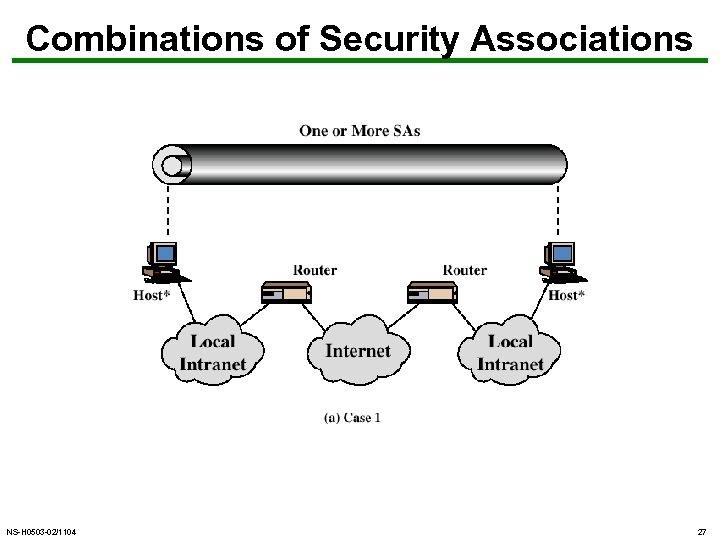 Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 27
Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 27
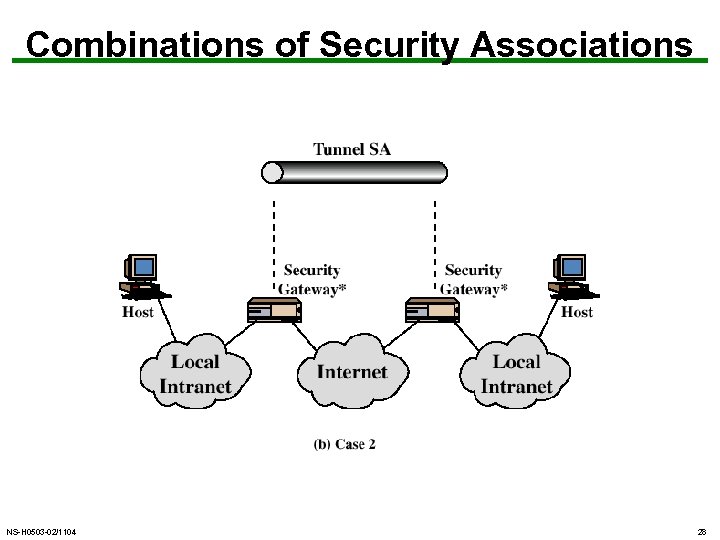 Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 28
Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 28
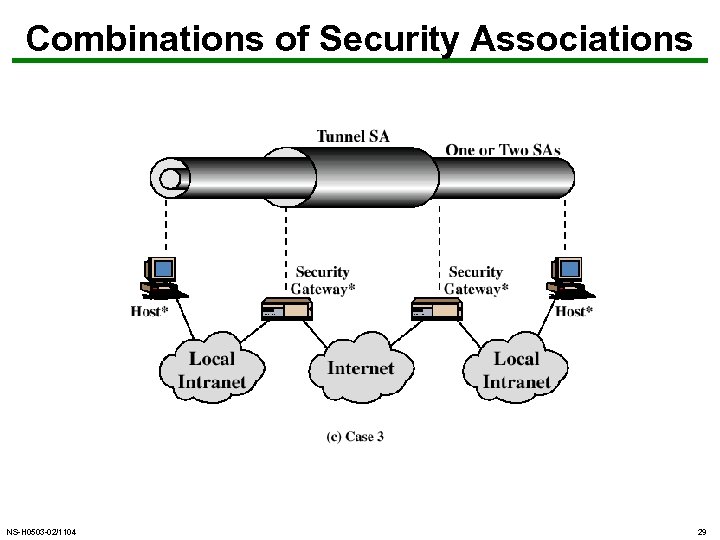 Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 29
Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 29
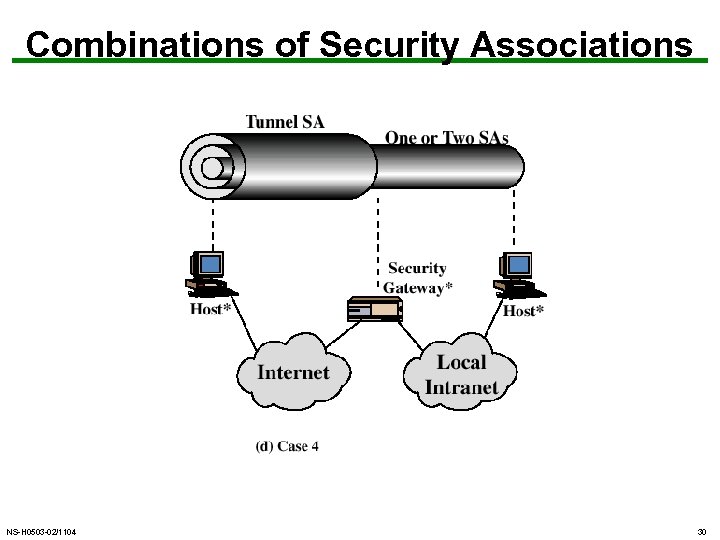 Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 30
Combinations of Security Associations NS-H 0503 -02/1104 30
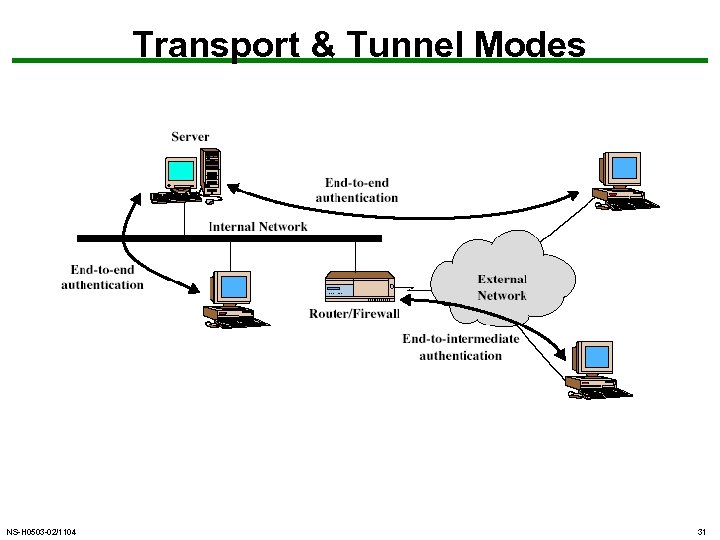 Transport & Tunnel Modes NS-H 0503 -02/1104 31
Transport & Tunnel Modes NS-H 0503 -02/1104 31
 Transport vs Tunnel Mode ESP • transport mode is used to encrypt & optionally authenticate IP data – data protected but header left in clear – can do traffic analysis but is efficient – good for ESP host to host traffic • tunnel mode encrypts entire IP packet – add new header for next hop – good for VPNs, gateway to gateway security NS-H 0503 -02/1104 32
Transport vs Tunnel Mode ESP • transport mode is used to encrypt & optionally authenticate IP data – data protected but header left in clear – can do traffic analysis but is efficient – good for ESP host to host traffic • tunnel mode encrypts entire IP packet – add new header for next hop – good for VPNs, gateway to gateway security NS-H 0503 -02/1104 32
 Key Management • Two types: – Manual – Automated • Oakley Key Determination Protocol • Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 33
Key Management • Two types: – Manual – Automated • Oakley Key Determination Protocol • Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) NS-H 0503 -02/1104 33
 Key Management • handles key generation & distribution • typically need 2 pairs of keys – 2 per direction for AH & ESP • manual key management – sysadmin manually configures every system • automated key management – automated system for on demand creation of keys for SA’s in large systems – has Oakley & ISAKMP elements NS-H 0503 -02/1104 34
Key Management • handles key generation & distribution • typically need 2 pairs of keys – 2 per direction for AH & ESP • manual key management – sysadmin manually configures every system • automated key management – automated system for on demand creation of keys for SA’s in large systems – has Oakley & ISAKMP elements NS-H 0503 -02/1104 34
 Oakley • Three authentication methods: – Digital signatures – Public-key encryption – Symmetric-key encryption NS-H 0503 -02/1104 35
Oakley • Three authentication methods: – Digital signatures – Public-key encryption – Symmetric-key encryption NS-H 0503 -02/1104 35
 Oakley • a key exchange protocol • based on Diffie-Hellman key exchange • adds features to address weaknesses – cookies, groups (global params), nonces, DH key exchange with authentication • can use arithmetic in prime fields or elliptic curve fields NS-H 0503 -02/1104 36
Oakley • a key exchange protocol • based on Diffie-Hellman key exchange • adds features to address weaknesses – cookies, groups (global params), nonces, DH key exchange with authentication • can use arithmetic in prime fields or elliptic curve fields NS-H 0503 -02/1104 36
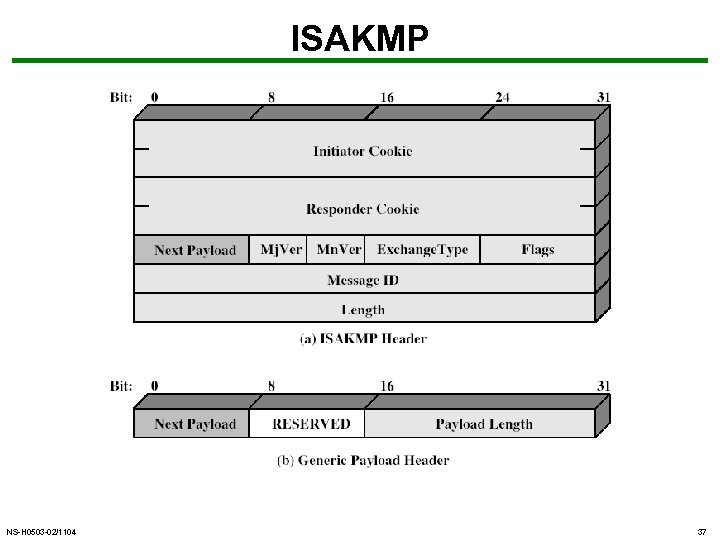 ISAKMP NS-H 0503 -02/1104 37
ISAKMP NS-H 0503 -02/1104 37
 ISAKMP • Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol • provides framework for key management • defines procedures and packet formats to establish, negotiate, modify, & delete SAs • independent of key exchange protocol, encryption alg, & authentication method NS-H 0503 -02/1104 38
ISAKMP • Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol • provides framework for key management • defines procedures and packet formats to establish, negotiate, modify, & delete SAs • independent of key exchange protocol, encryption alg, & authentication method NS-H 0503 -02/1104 38


