01da9215f7c1cc7a64e502311005f2ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 IPSec • Access control • Connectionless integrity • Data origin authentication • Rejection of replayed packets • Confidentiality Sheng-Liang Song ssl@cisco. com
IPSec • Access control • Connectionless integrity • Data origin authentication • Rejection of replayed packets • Confidentiality Sheng-Liang Song ssl@cisco. com
 IPSec • Complexity • Security worst “enemy” • “best practice” Sheng-Liang Song ssl@cisco. com
IPSec • Complexity • Security worst “enemy” • “best practice” Sheng-Liang Song ssl@cisco. com
 Agenda n IPSec Overview n IPSec (Network Layer) n Modes (Tunnel/Transport) n Protocols (ESP/AH) n IKE (Internet Key Exchange) n IPSec Cases n IPSec Discussion n Q&A
Agenda n IPSec Overview n IPSec (Network Layer) n Modes (Tunnel/Transport) n Protocols (ESP/AH) n IKE (Internet Key Exchange) n IPSec Cases n IPSec Discussion n Q&A
 Key Words n ISAKMP (Internet Security Association n and Key Management Protocol) n SA (Security Associations) n SPD (Security Policy Database) n IKE (Internet Key Exchange) n AH (Authentication Header) n ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) n HMAC (Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication) n H(K XOR opad_5 C, H(K XOR ipad_36, text))
Key Words n ISAKMP (Internet Security Association n and Key Management Protocol) n SA (Security Associations) n SPD (Security Policy Database) n IKE (Internet Key Exchange) n AH (Authentication Header) n ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) n HMAC (Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication) n H(K XOR opad_5 C, H(K XOR ipad_36, text))
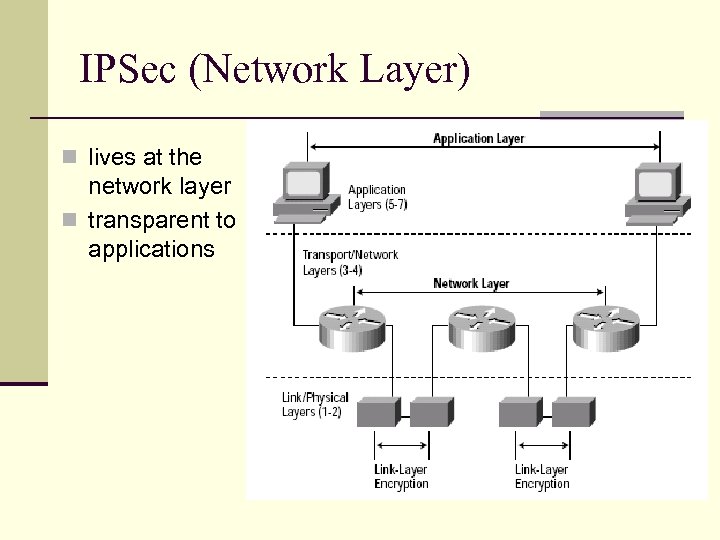 IPSec (Network Layer) n lives at the network layer n transparent to applications IPSec User transport SSL application OS network link physical NIC
IPSec (Network Layer) n lives at the network layer n transparent to applications IPSec User transport SSL application OS network link physical NIC
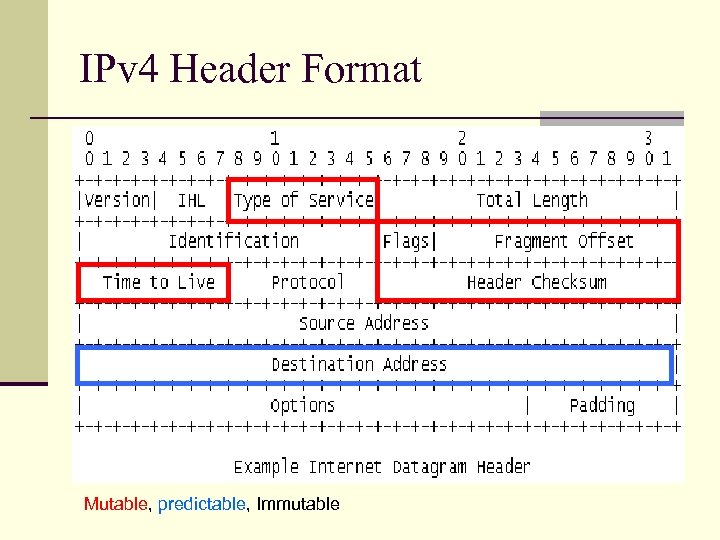 IPv 4 Header Format Mutable, predictable, Immutable
IPv 4 Header Format Mutable, predictable, Immutable
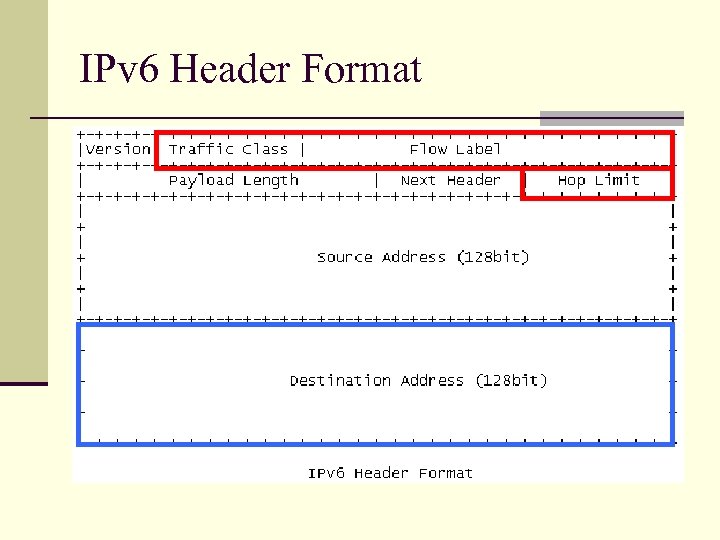 IPv 6 Header Format
IPv 6 Header Format
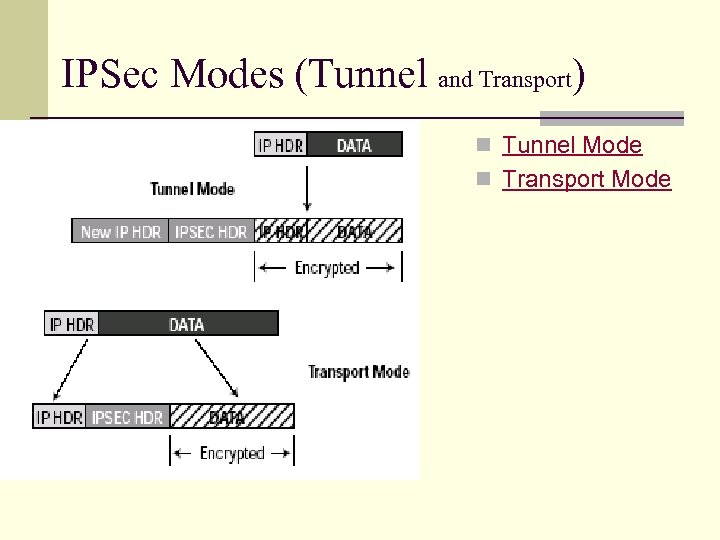 IPSec Modes (Tunnel and Transport) n Transport Mode n Tunnel Mode n Transport Mode IP header data IP header ESP/AH data n Tunnel Mode IP header data new IP hdr ESP/AH IP header data
IPSec Modes (Tunnel and Transport) n Transport Mode n Tunnel Mode n Transport Mode IP header data IP header ESP/AH data n Tunnel Mode IP header data new IP hdr ESP/AH IP header data
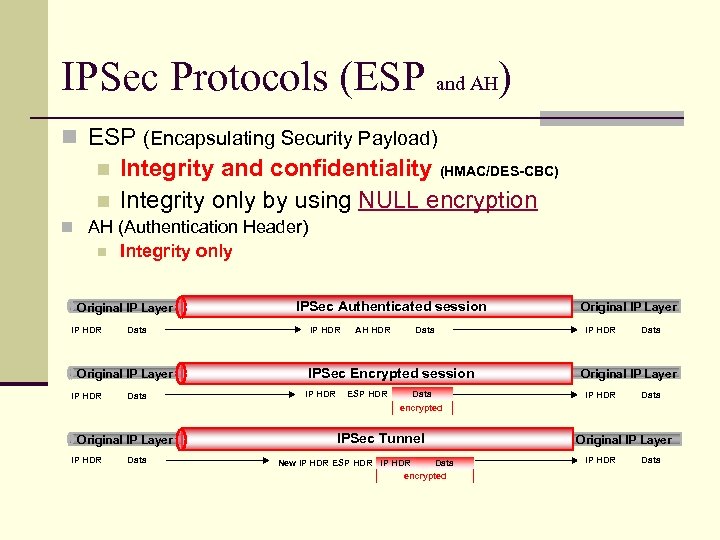 IPSec Protocols (ESP and AH) n ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) n Integrity and confidentiality (HMAC/DES-CBC) Integrity only by using NULL encryption n n AH (Authentication Header) n Integrity only Original IP Layer IP HDR Data IPSec Authenticated session IP HDR AH HDR Data IPSec Encrypted session IP HDR ESP HDR Data Original IP Layer IP HDR Data encrypted Original IP Layer IP HDR Data IPSec Tunnel Data New IP HDR ESP HDR IP HDR encrypted Original IP Layer IP HDR Data
IPSec Protocols (ESP and AH) n ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) n Integrity and confidentiality (HMAC/DES-CBC) Integrity only by using NULL encryption n n AH (Authentication Header) n Integrity only Original IP Layer IP HDR Data IPSec Authenticated session IP HDR AH HDR Data IPSec Encrypted session IP HDR ESP HDR Data Original IP Layer IP HDR Data encrypted Original IP Layer IP HDR Data IPSec Tunnel Data New IP HDR ESP HDR IP HDR encrypted Original IP Layer IP HDR Data
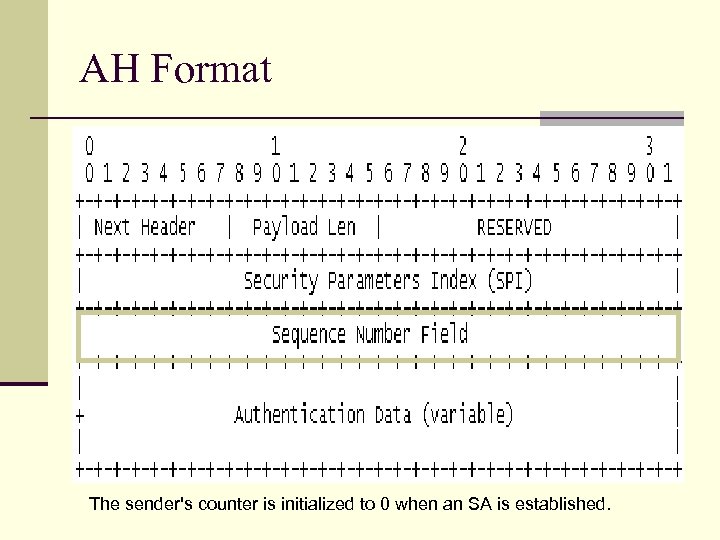 AH Format The sender's counter is initialized to 0 when an SA is established.
AH Format The sender's counter is initialized to 0 when an SA is established.
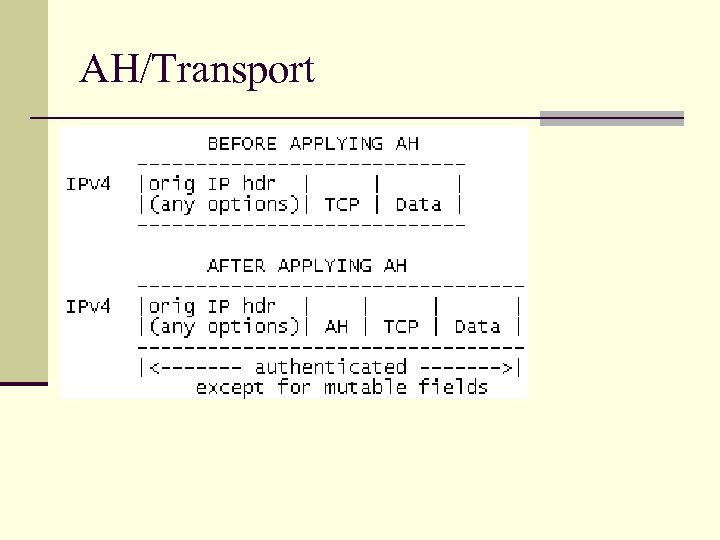 AH/Transport
AH/Transport
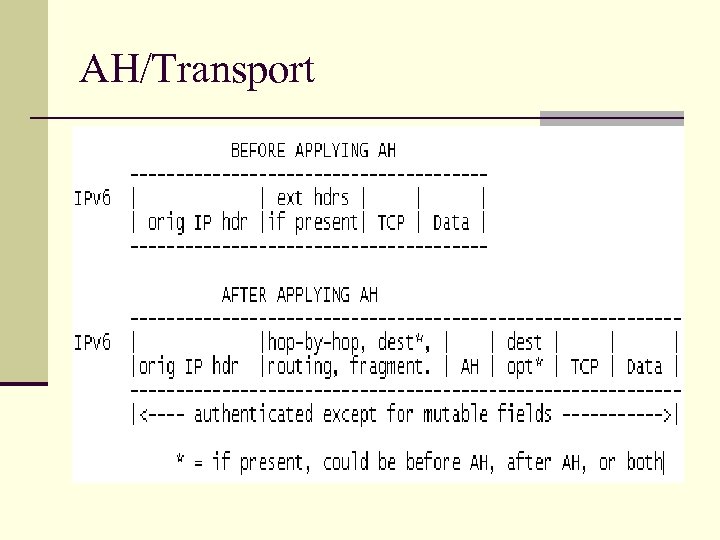 AH/Transport
AH/Transport
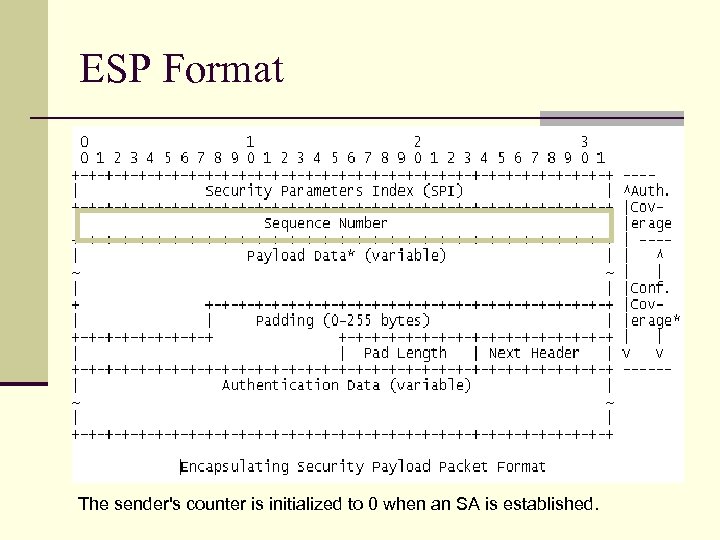 ESP Format The sender's counter is initialized to 0 when an SA is established.
ESP Format The sender's counter is initialized to 0 when an SA is established.
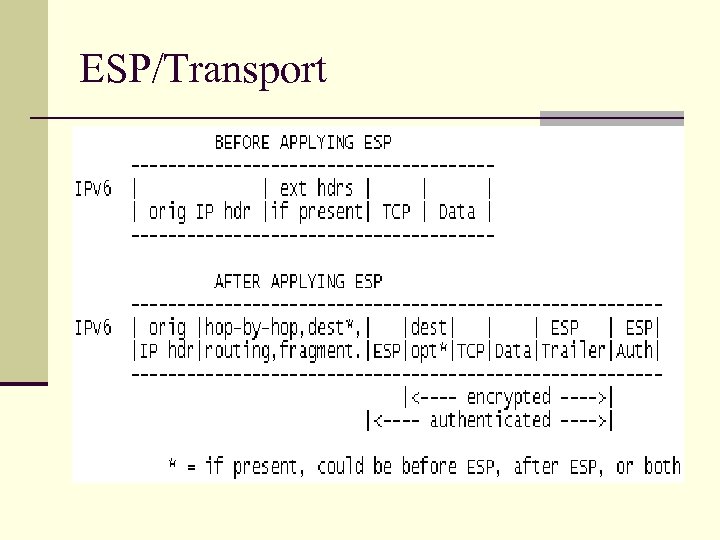 ESP/Transport
ESP/Transport
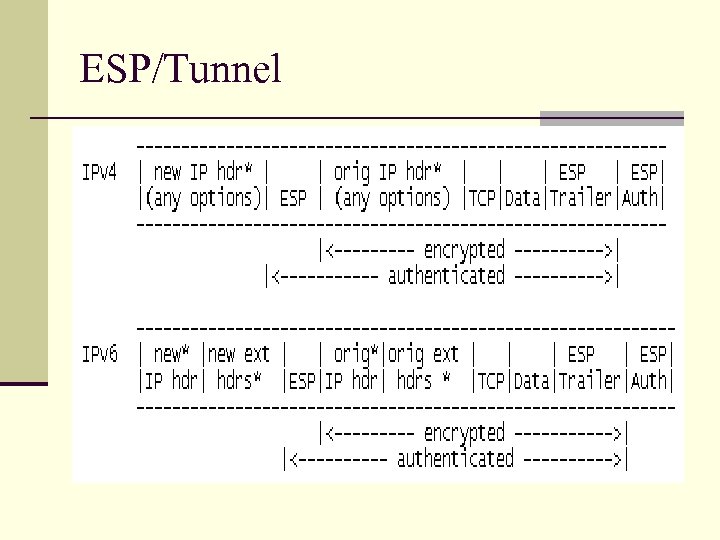 ESP/Tunnel
ESP/Tunnel
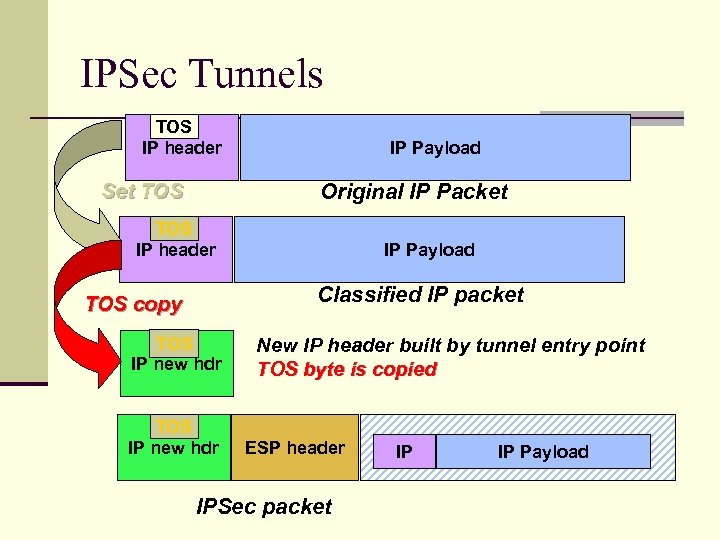 IPSec Tunnels TOS IP header Set TOS IP Payload Original IP Packet TOS IP header IP Payload Classified IP packet TOS copy TOS IP new hdr New IP header built by tunnel entry point TOS byte is copied ESP header IPSec packet IP IP Payload
IPSec Tunnels TOS IP header Set TOS IP Payload Original IP Packet TOS IP header IP Payload Classified IP packet TOS copy TOS IP new hdr New IP header built by tunnel entry point TOS byte is copied ESP header IPSec packet IP IP Payload
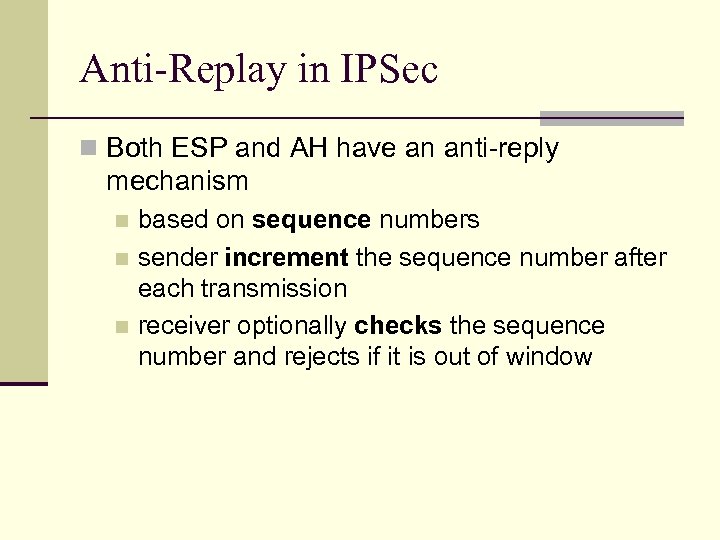 Anti-Replay in IPSec n Both ESP and AH have an anti-reply mechanism based on sequence numbers n sender increment the sequence number after each transmission n receiver optionally checks the sequence number and rejects if it is out of window n
Anti-Replay in IPSec n Both ESP and AH have an anti-reply mechanism based on sequence numbers n sender increment the sequence number after each transmission n receiver optionally checks the sequence number and rejects if it is out of window n
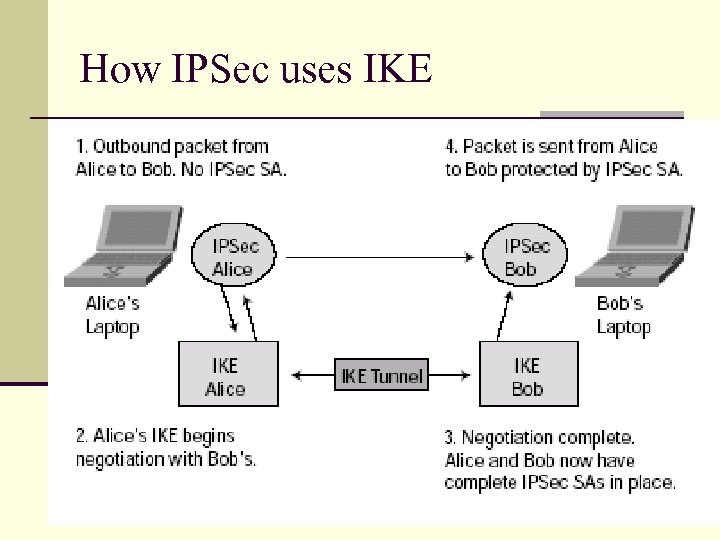 How IPSec uses IKE
How IPSec uses IKE
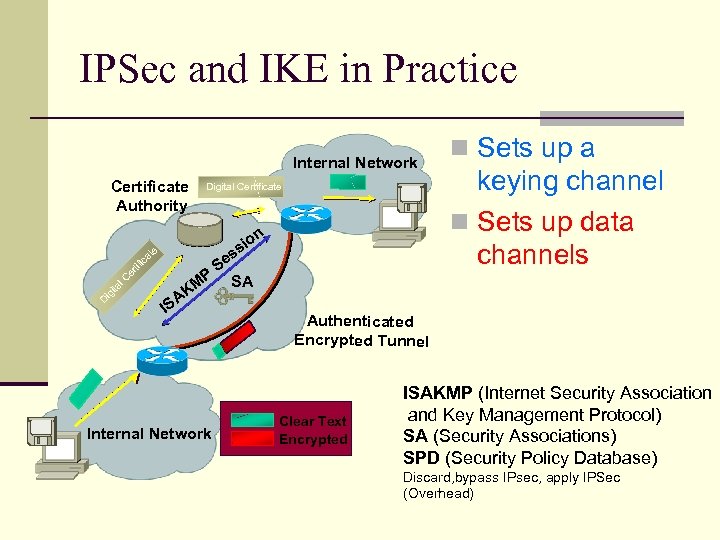 IPSec and IKE in Practice Internal Network Certificate Authority Digital Certificate n io s D ig ita l. C er tif ic at e s Se P SA M n Sets up a keying channel n Sets up data channels K A IS Internal Network Authenticated Encrypted Tunnel Clear Text Encrypted ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol) SA (Security Associations) SPD (Security Policy Database) Discard, bypass IPsec, apply IPSec (Overhead)
IPSec and IKE in Practice Internal Network Certificate Authority Digital Certificate n io s D ig ita l. C er tif ic at e s Se P SA M n Sets up a keying channel n Sets up data channels K A IS Internal Network Authenticated Encrypted Tunnel Clear Text Encrypted ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol) SA (Security Associations) SPD (Security Policy Database) Discard, bypass IPsec, apply IPSec (Overhead)
 IPSec (IKE 1 Phase 1) n Authenticated with Signatures n Authenticated with Shared key n Authenticated with Public Key Encryption (Revised)
IPSec (IKE 1 Phase 1) n Authenticated with Signatures n Authenticated with Shared key n Authenticated with Public Key Encryption (Revised)
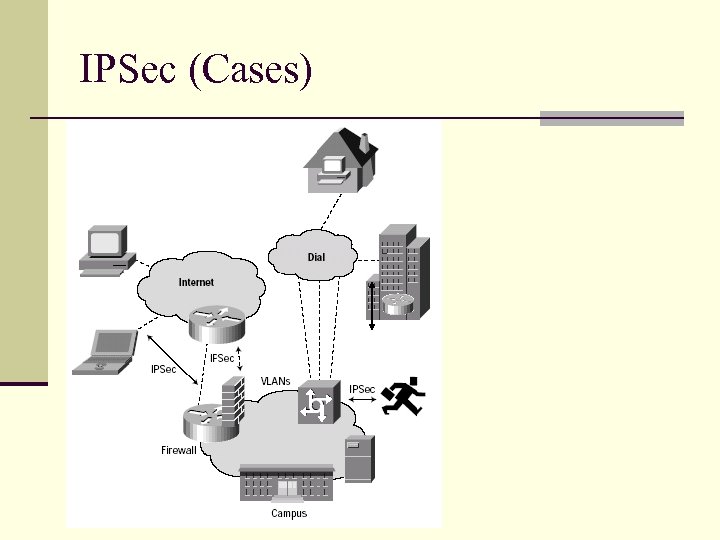 IPSec (Cases)
IPSec (Cases)
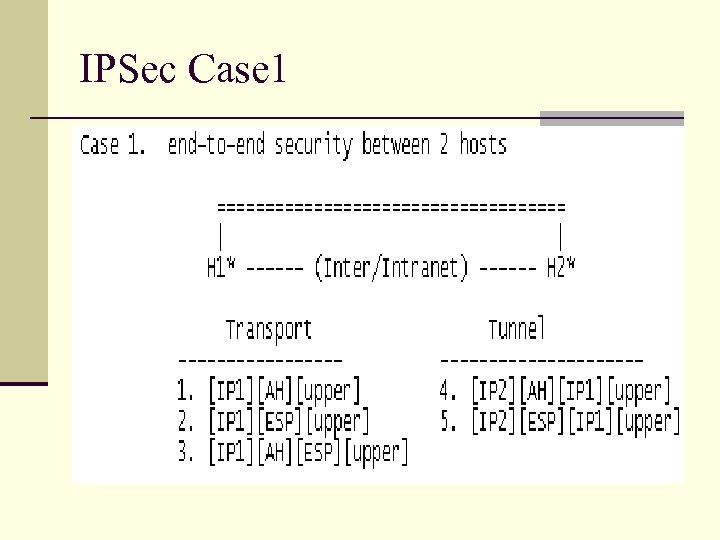 IPSec Case 1
IPSec Case 1
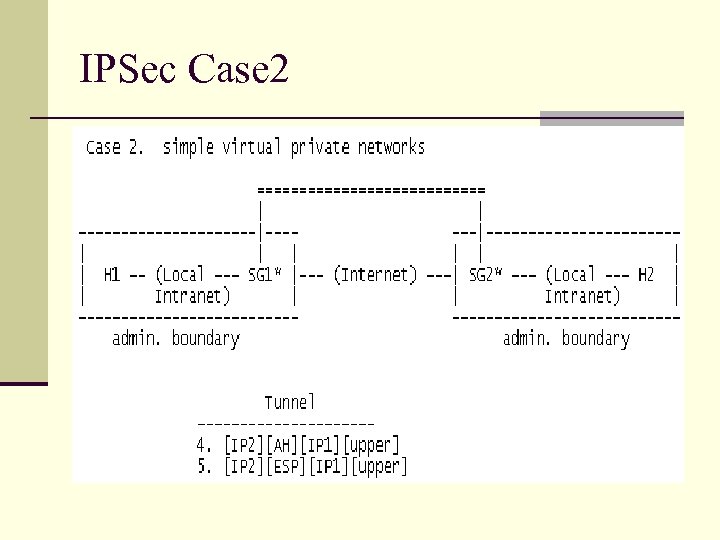 IPSec Case 2
IPSec Case 2
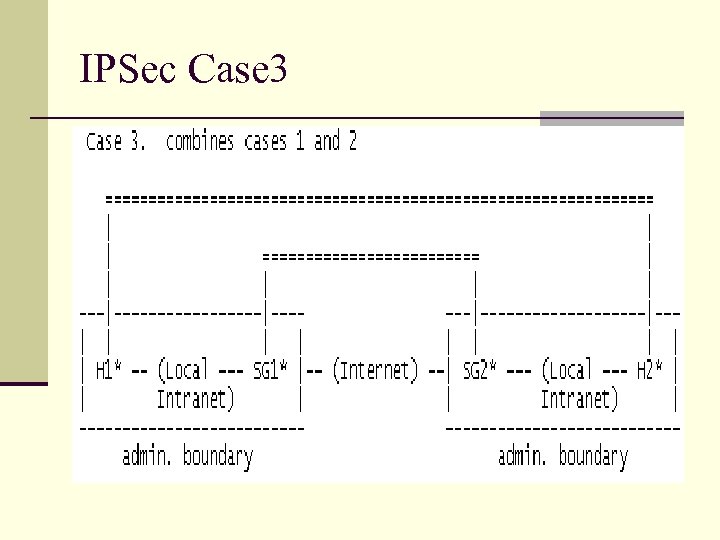 IPSec Case 3
IPSec Case 3
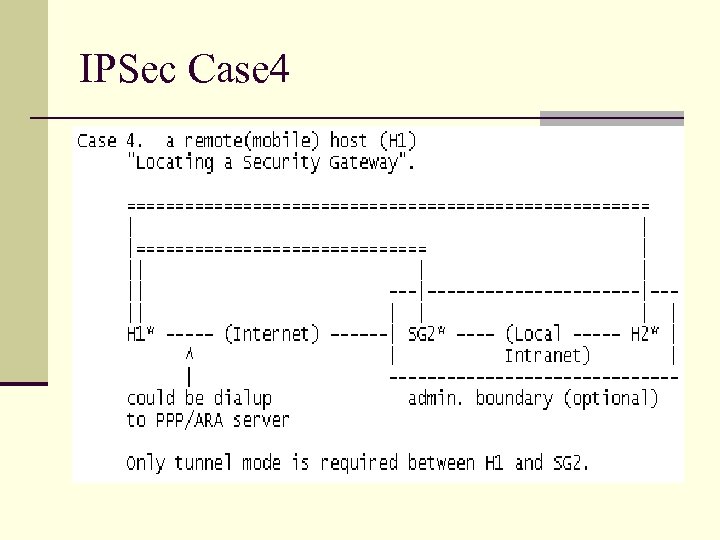 IPSec Case 4
IPSec Case 4
 IPSec Discussion 1. IPSec authenticates machines, not users 2. Does not stop denial of service attacks 1. Easier to do Do. S 3. Order of operations: Encryption/Authentication 4. Q & A
IPSec Discussion 1. IPSec authenticates machines, not users 2. Does not stop denial of service attacks 1. Easier to do Do. S 3. Order of operations: Encryption/Authentication 4. Q & A
 Reference n n n Information Security: Principles and Practice, Mark Stamp, Jan 29, 2005 http: //www. ietf. org/ Cisco IOS IPsec www. cisco. com/go/ipsec/ Cisco White Paper, IPsec, http: //www. cisco. com/warp/public/cc/so/neso/sqso/e qso/ipsec_wp. htm N. Ferguson and B. Schneier, A Cryptographic Evaluation of IPsec, http: //www. schneier. com/paperipsec. html IPsec, Security for the Internet Protocol, http: //www. freeswan. org/freeswan_trees/freeswan 2. 06/doc/intro. html
Reference n n n Information Security: Principles and Practice, Mark Stamp, Jan 29, 2005 http: //www. ietf. org/ Cisco IOS IPsec www. cisco. com/go/ipsec/ Cisco White Paper, IPsec, http: //www. cisco. com/warp/public/cc/so/neso/sqso/e qso/ipsec_wp. htm N. Ferguson and B. Schneier, A Cryptographic Evaluation of IPsec, http: //www. schneier. com/paperipsec. html IPsec, Security for the Internet Protocol, http: //www. freeswan. org/freeswan_trees/freeswan 2. 06/doc/intro. html


